Theorems (Carnegie Learning M2T2)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
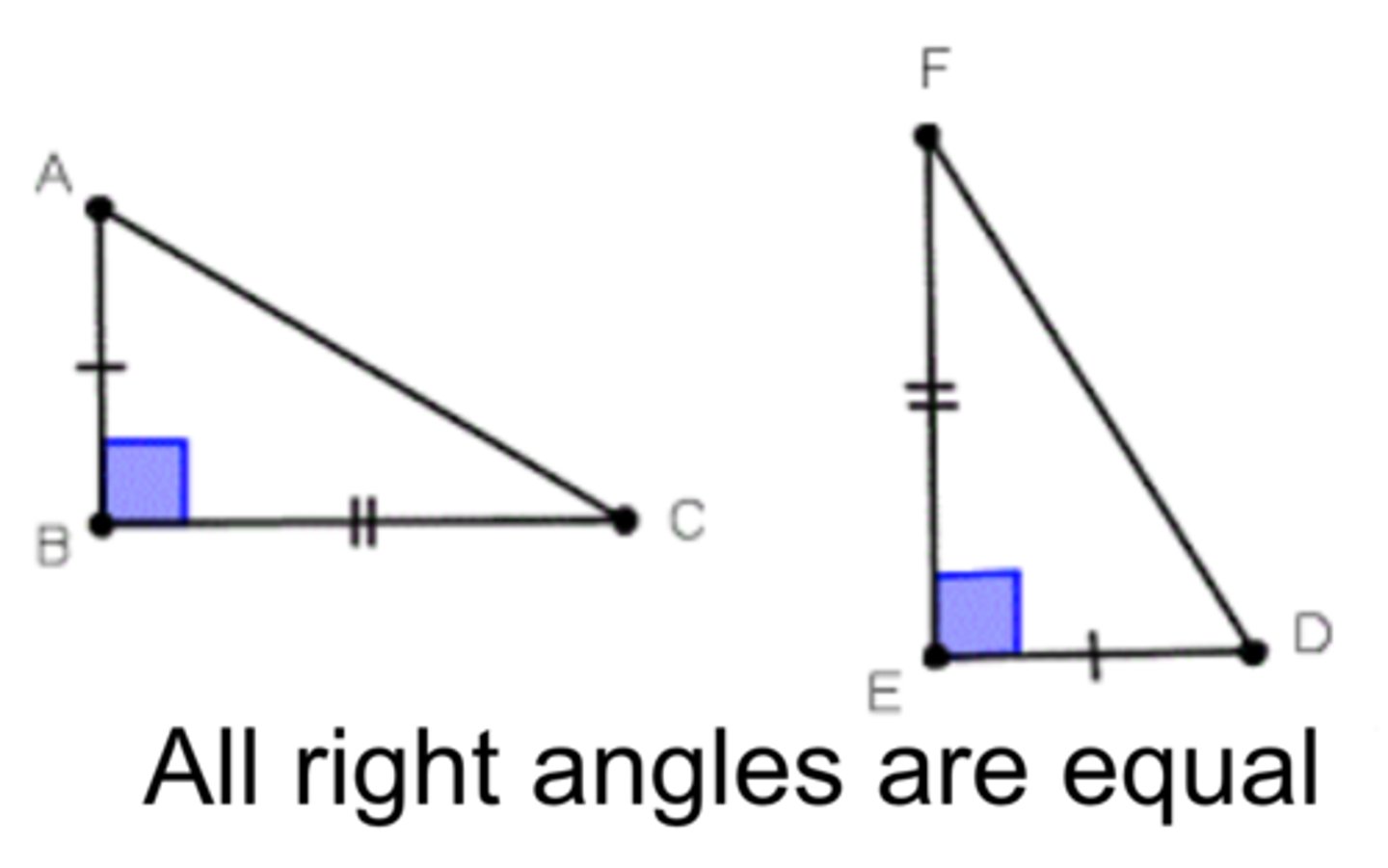
Right Angle Congruence Postulate
All right angles are congruent
Addition POE
If a=b, then a+c=b+c
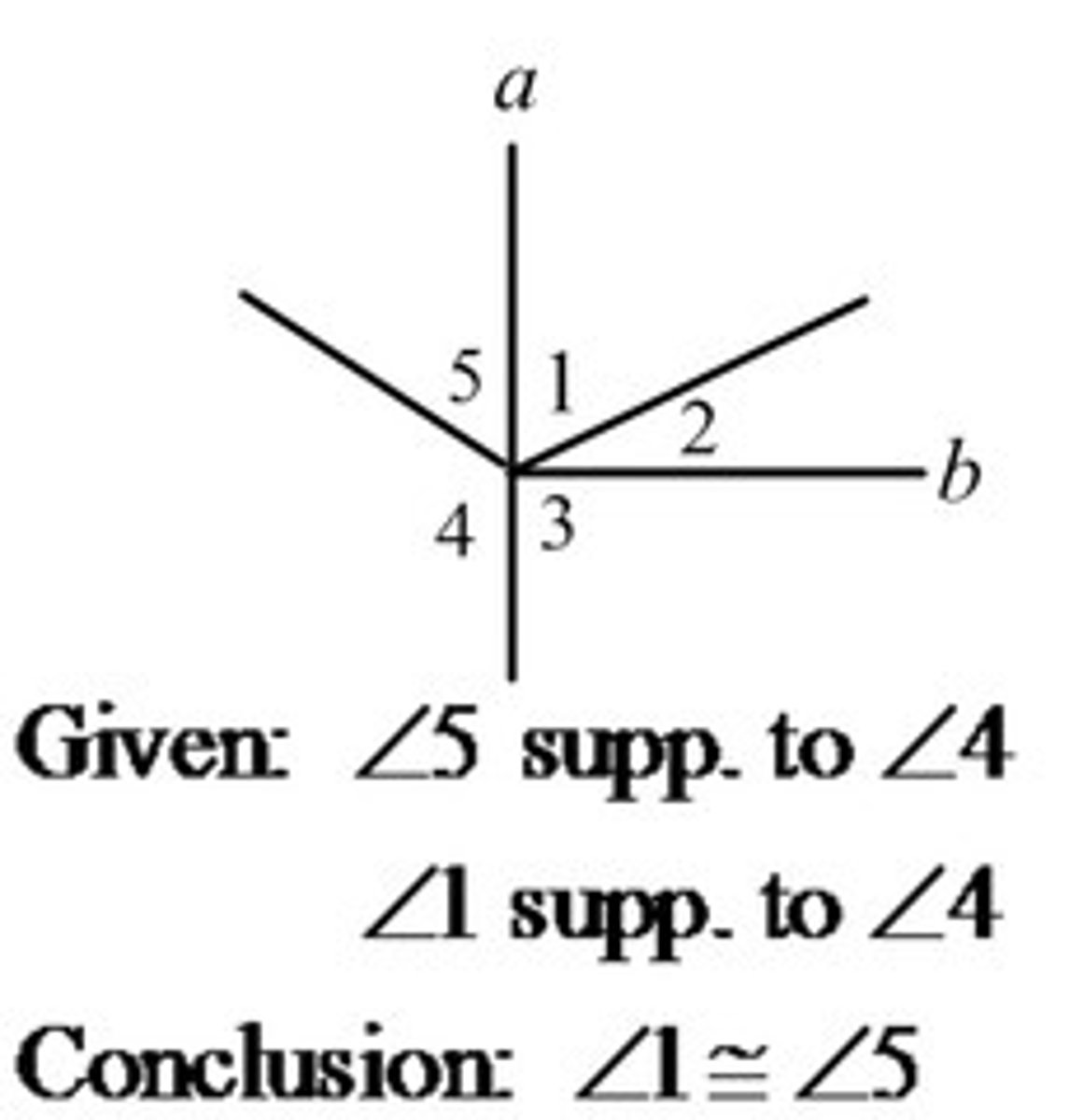
Congruent Supplement Theorem
If two angles are supplements of the same angle or of congruent angles, then the angles are congruent
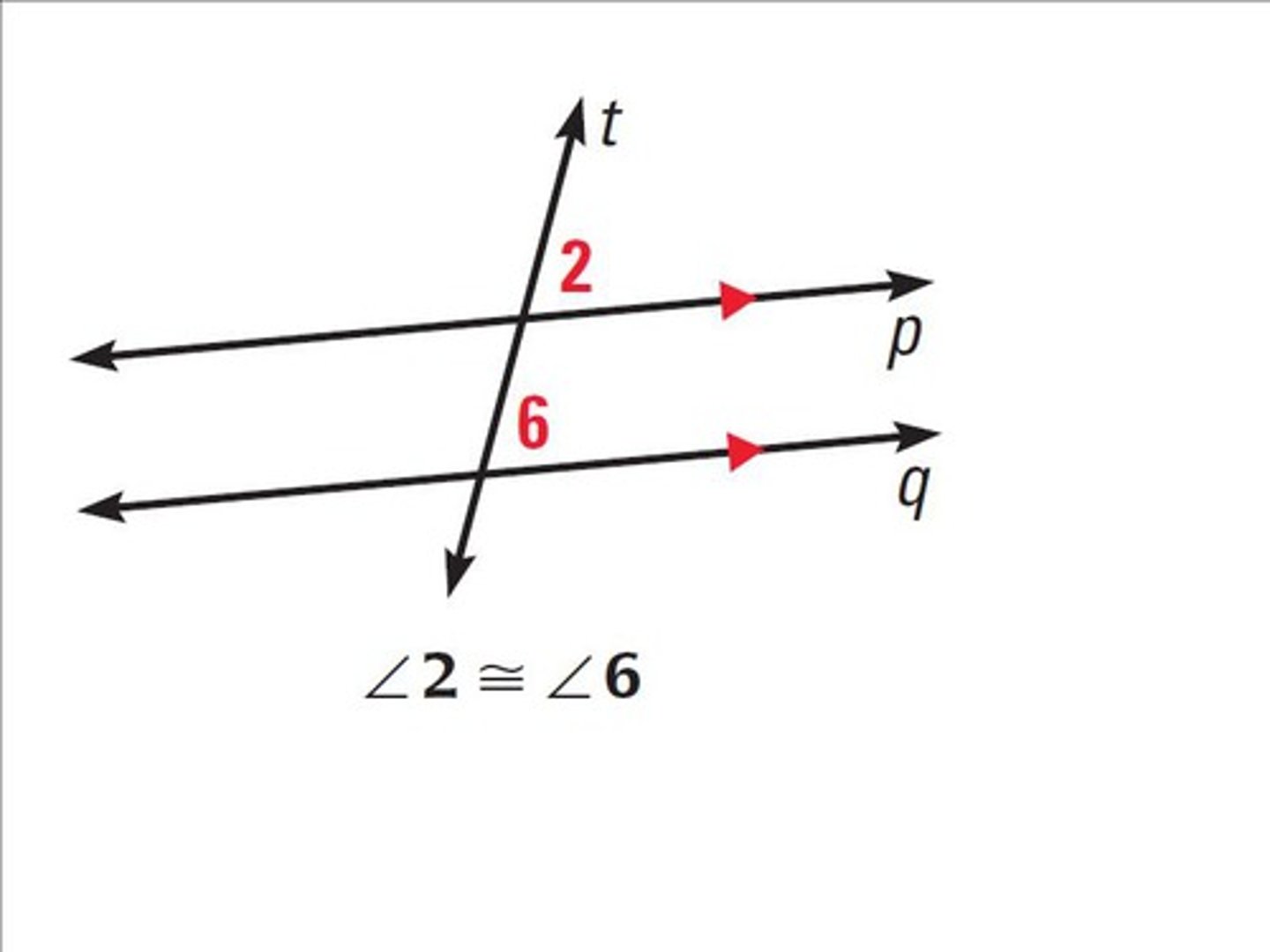
Corresponding Angles Theorem
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then corresponding angles are congruent.
Corresponding Angles Converse Theorem
If two lines are cut by a transversal so the corresponding angles are congruent, then the lines are parallel.
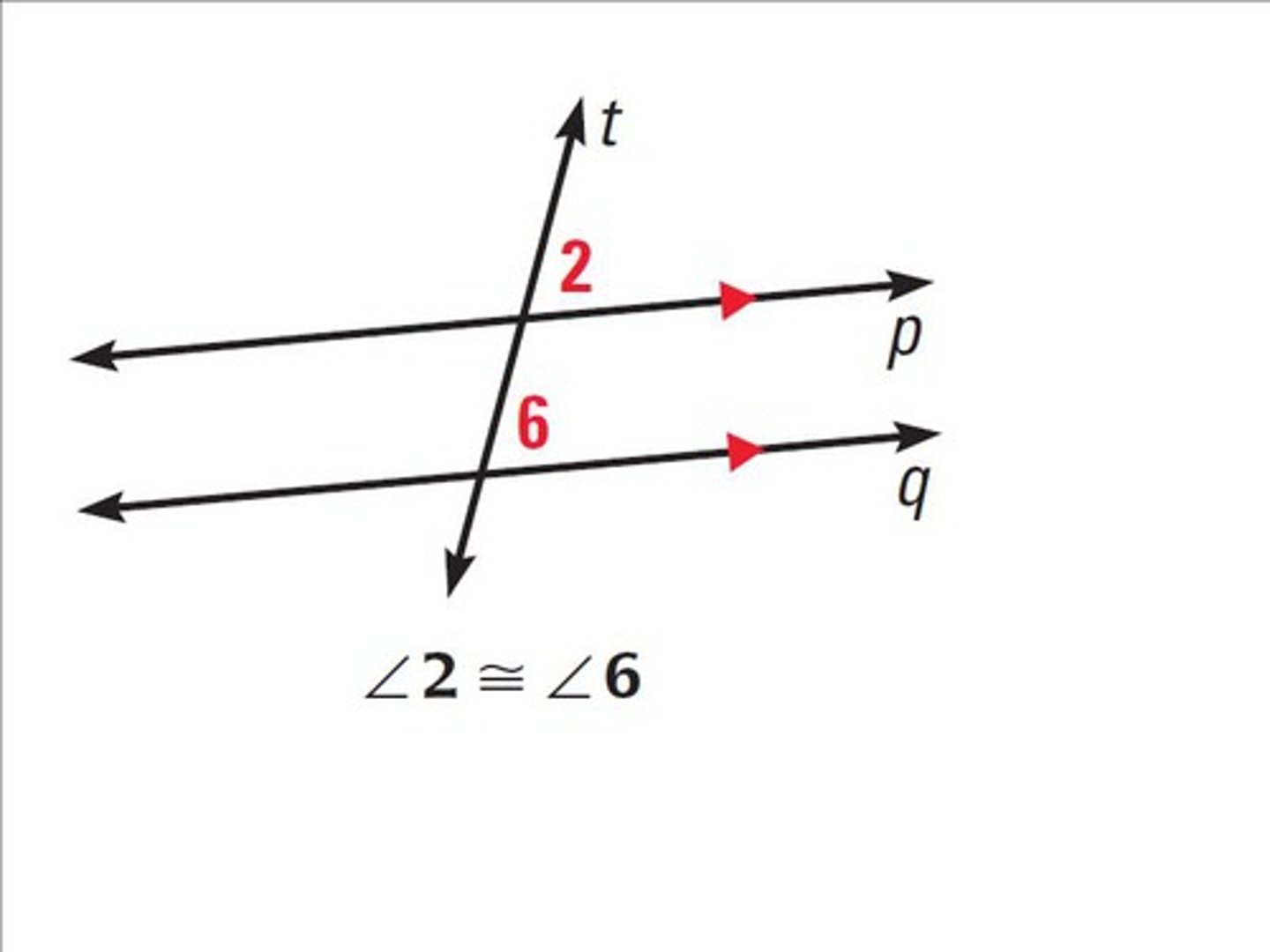
Same-Side Interior Angles Theorem
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then same-side interior angles are supplementary.
Alternate Interior Angles Theorem
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the pairs of alternate interior angles are congruent.
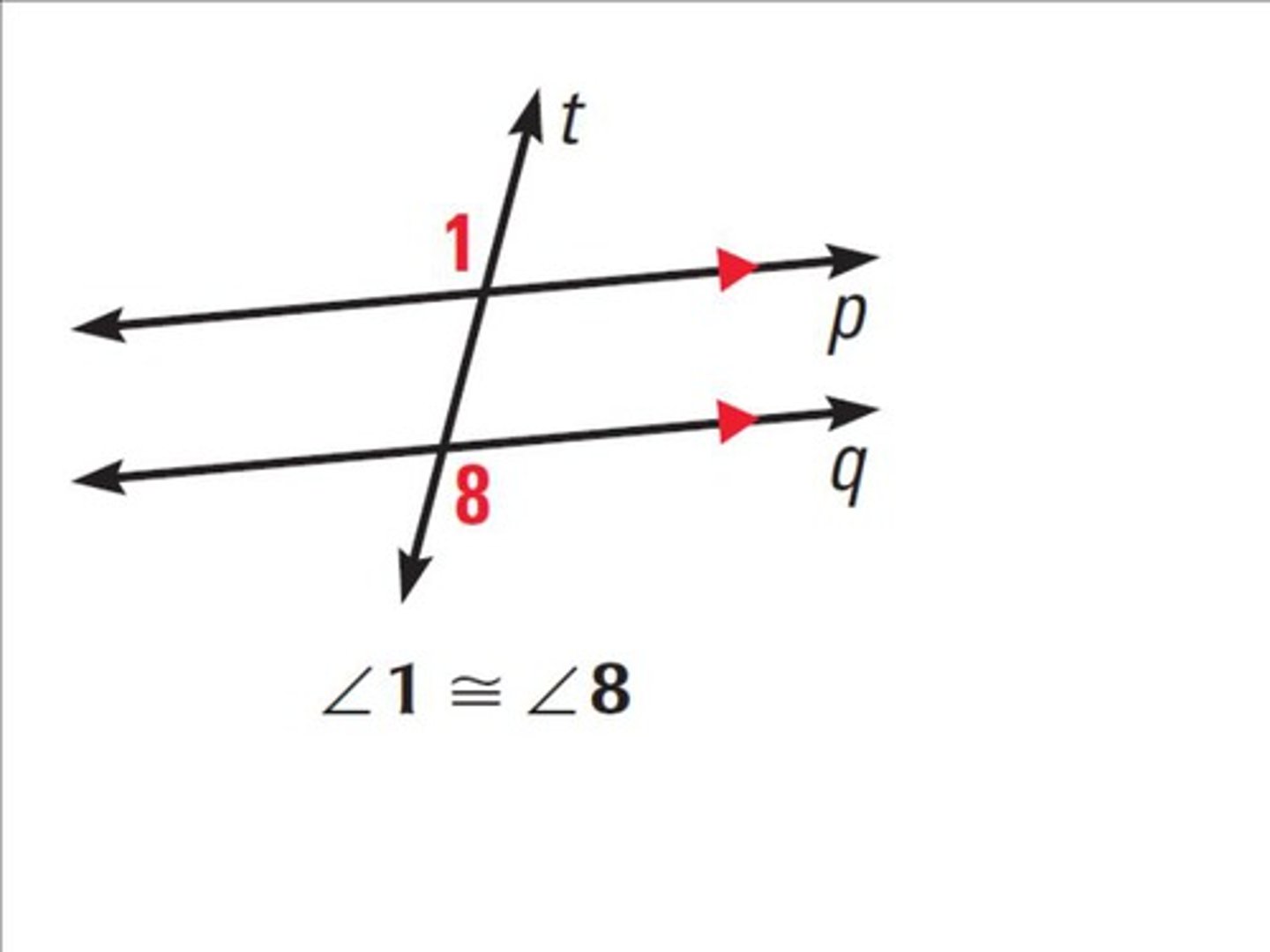
Alternate Exterior Angles Theorem
If two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the pairs of alternate exterior angles are congruent
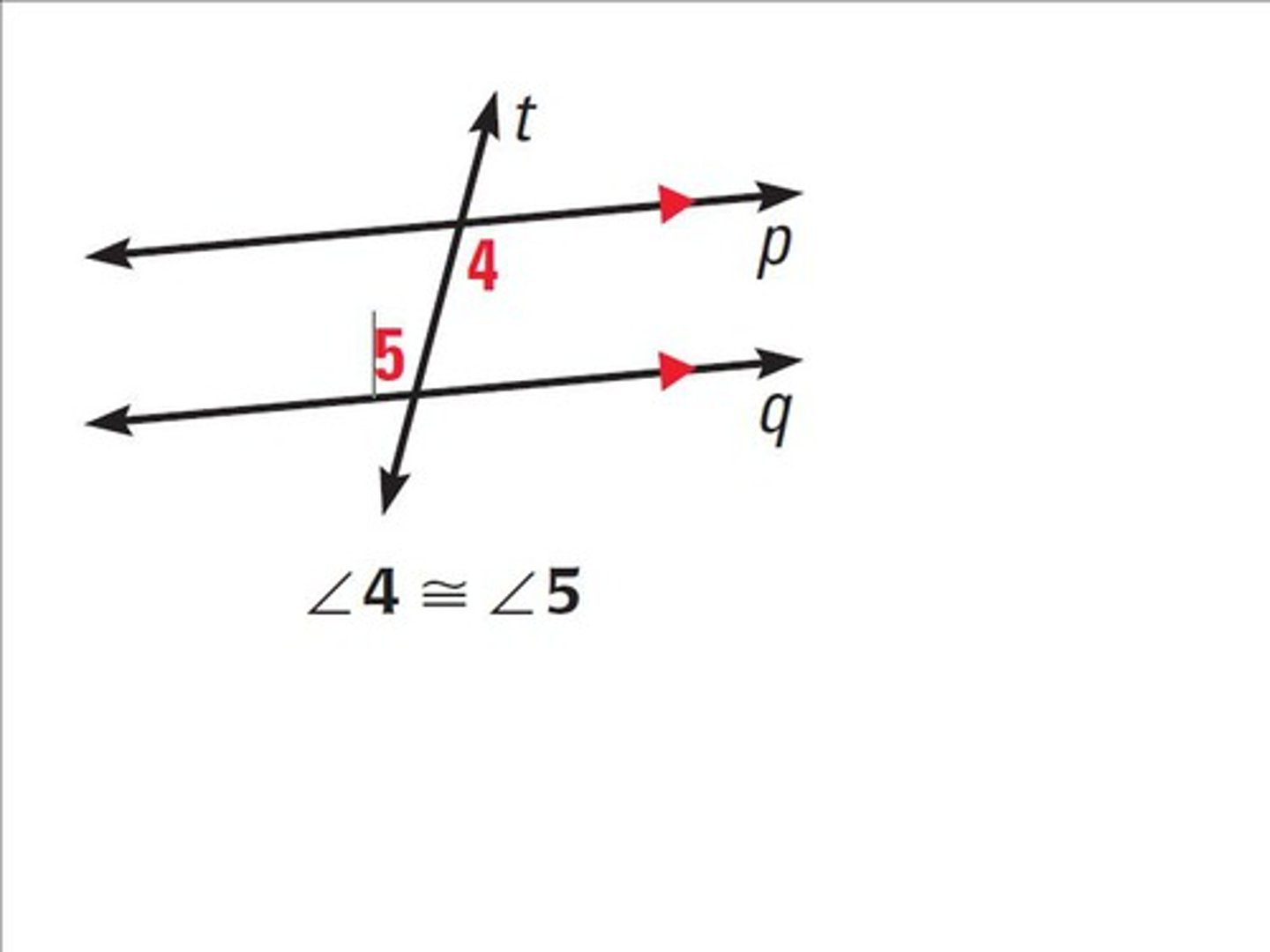
Same-Side Exterior Angles Theorem
If a transversal intersects two parallel lines, then same-side exterior angles are supplementary.
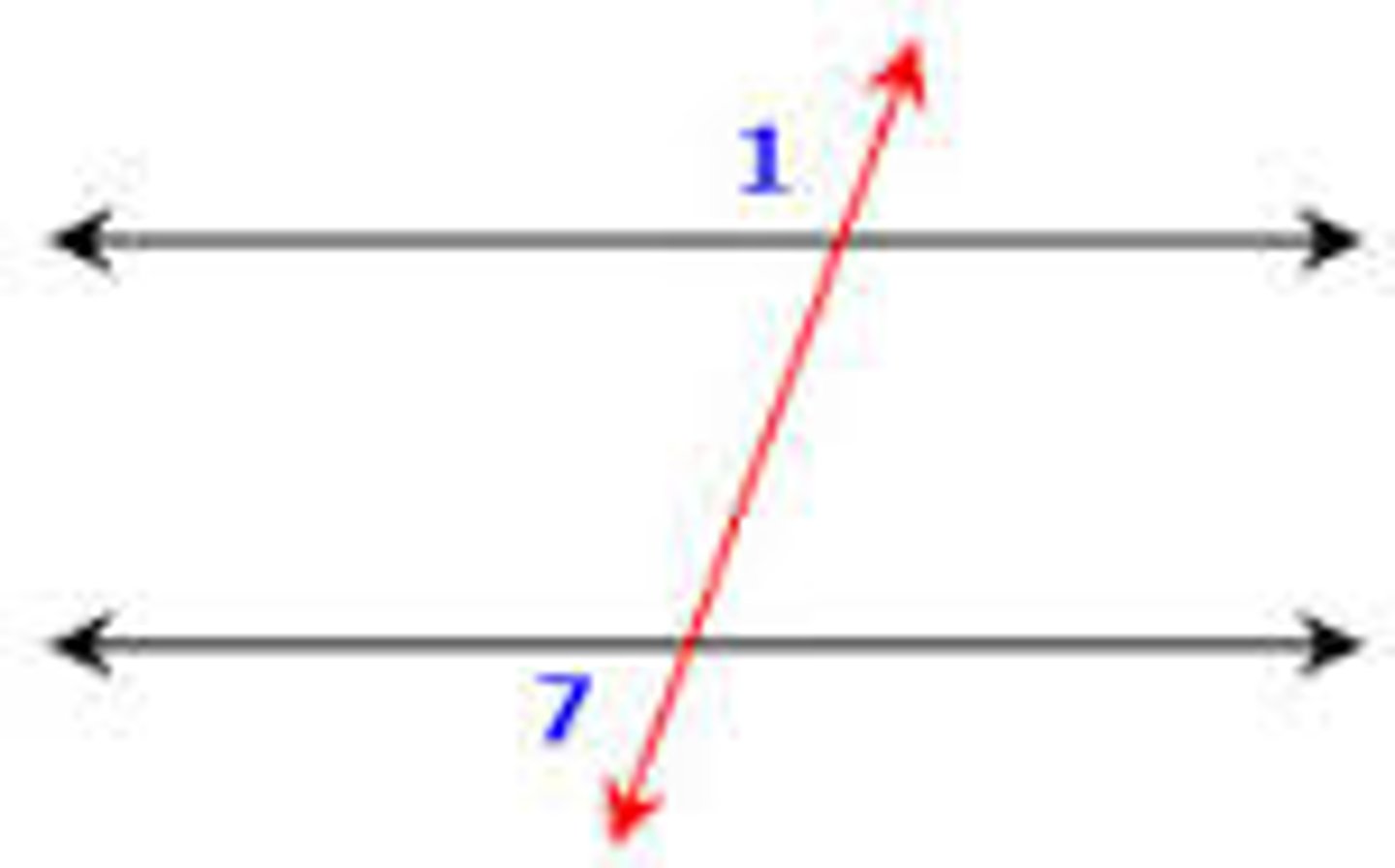
Alternate Interior Angles Converse Theorem
If two lines are cut by a transversal so that alternate interior angles are congruent, then the lines are parallel
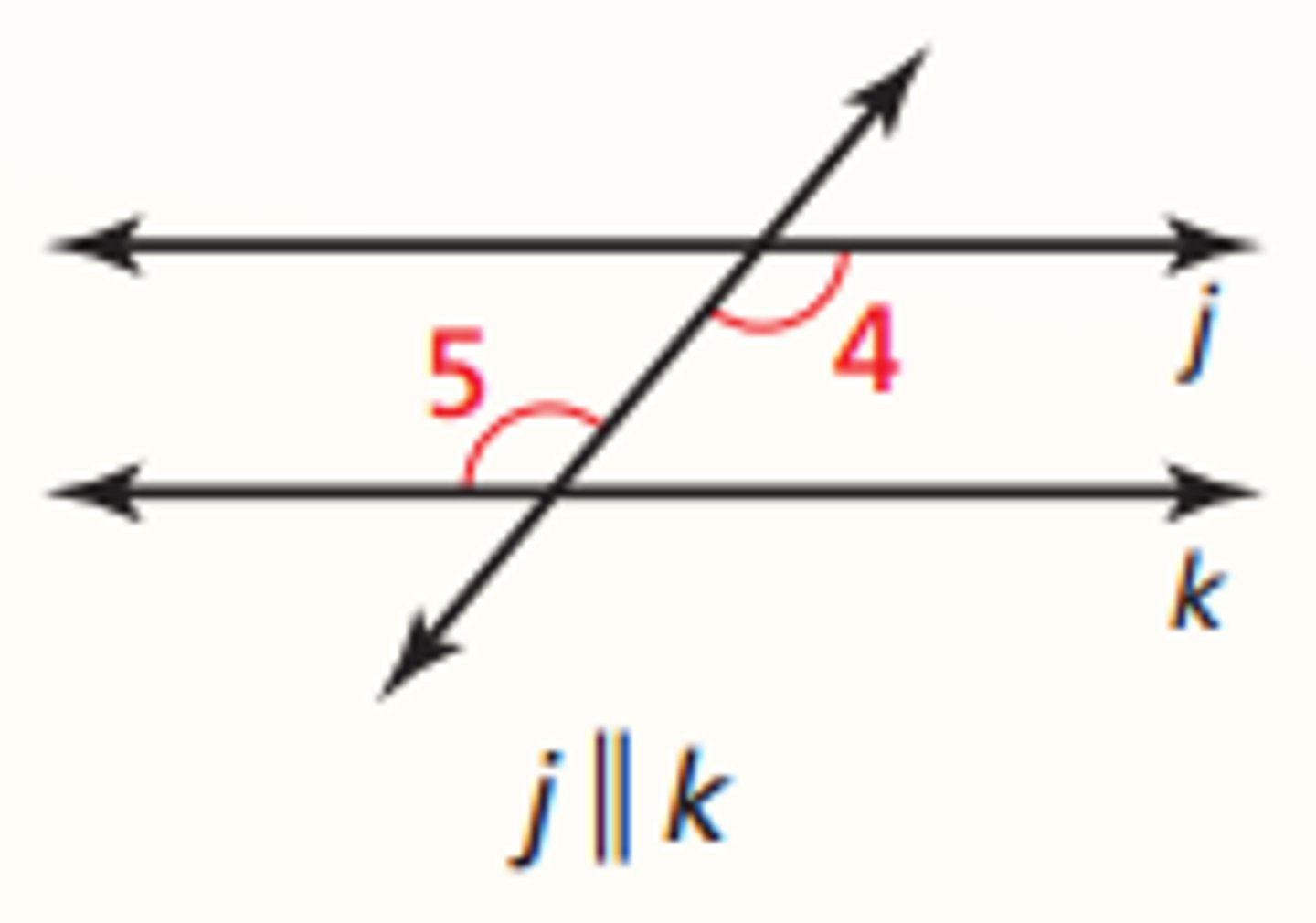
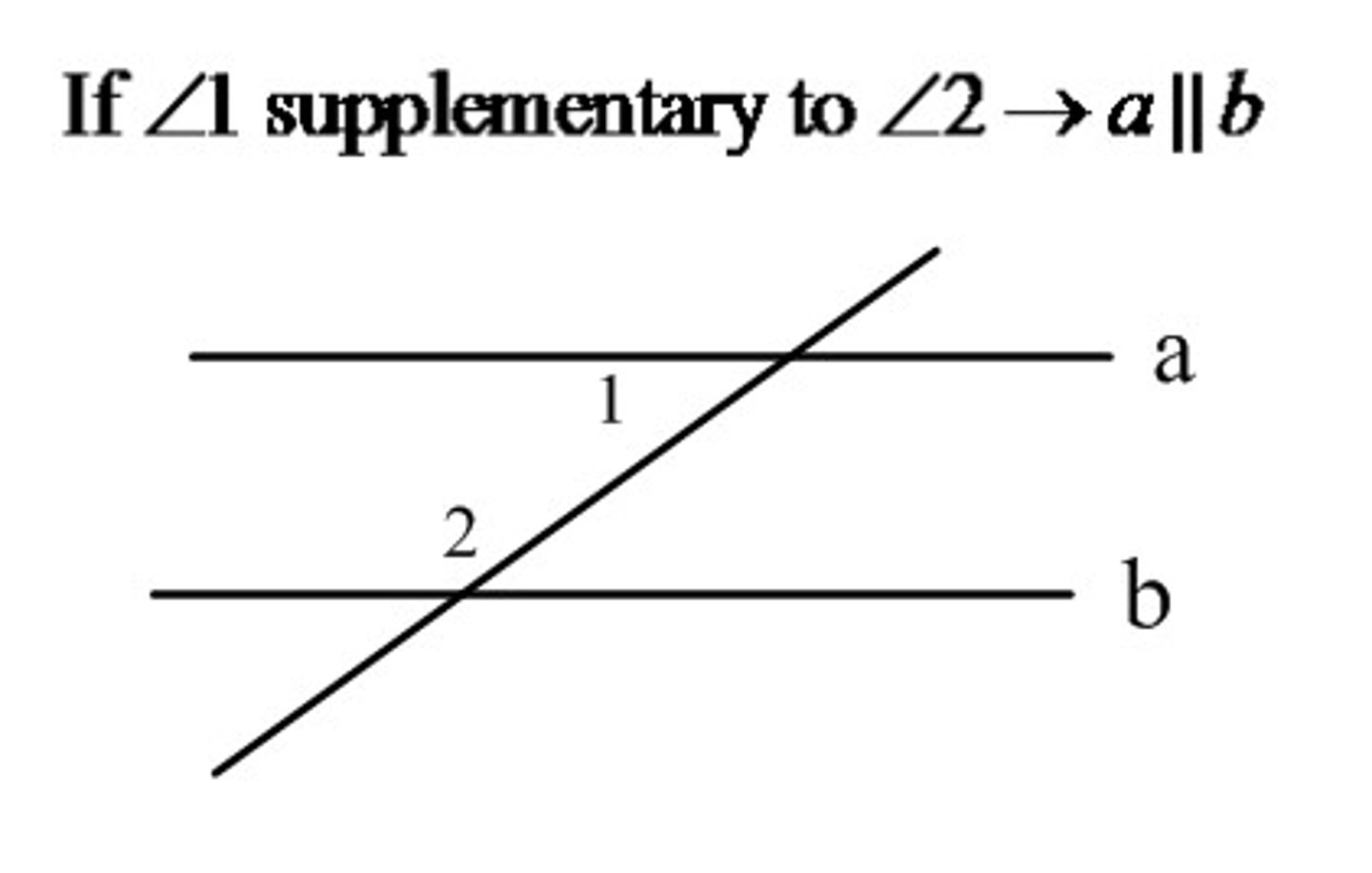
Same-Side Interior Angles Converse Theorem
If two lines are cut by a transversal and same-side interior angles are supplementary, then the lines are parallel.
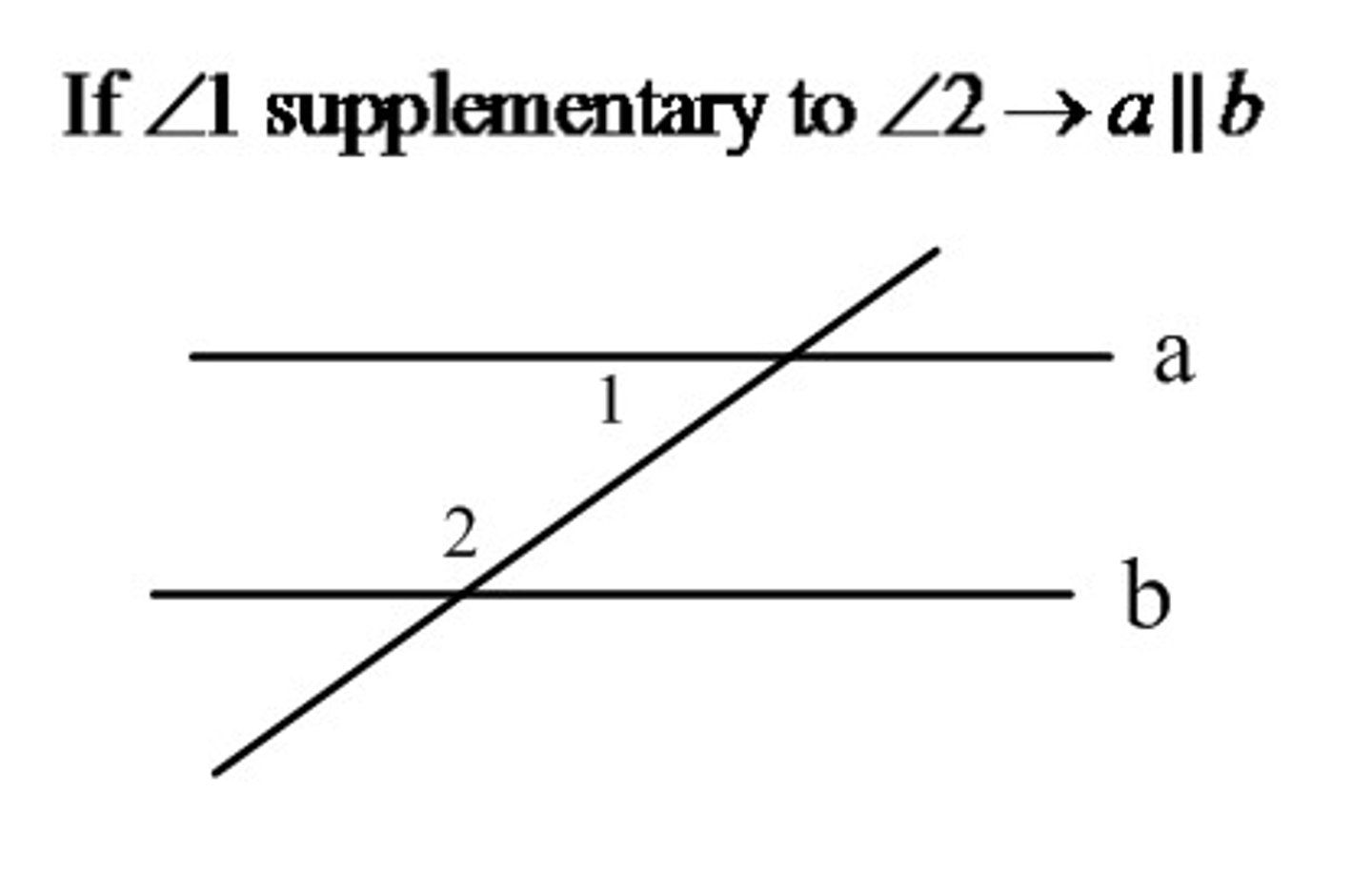
Alternate Exterior Angles Converse Theorem
If two lines are cut by a transversal so that alternate exterior angles are congruent, then the lines are parallel.
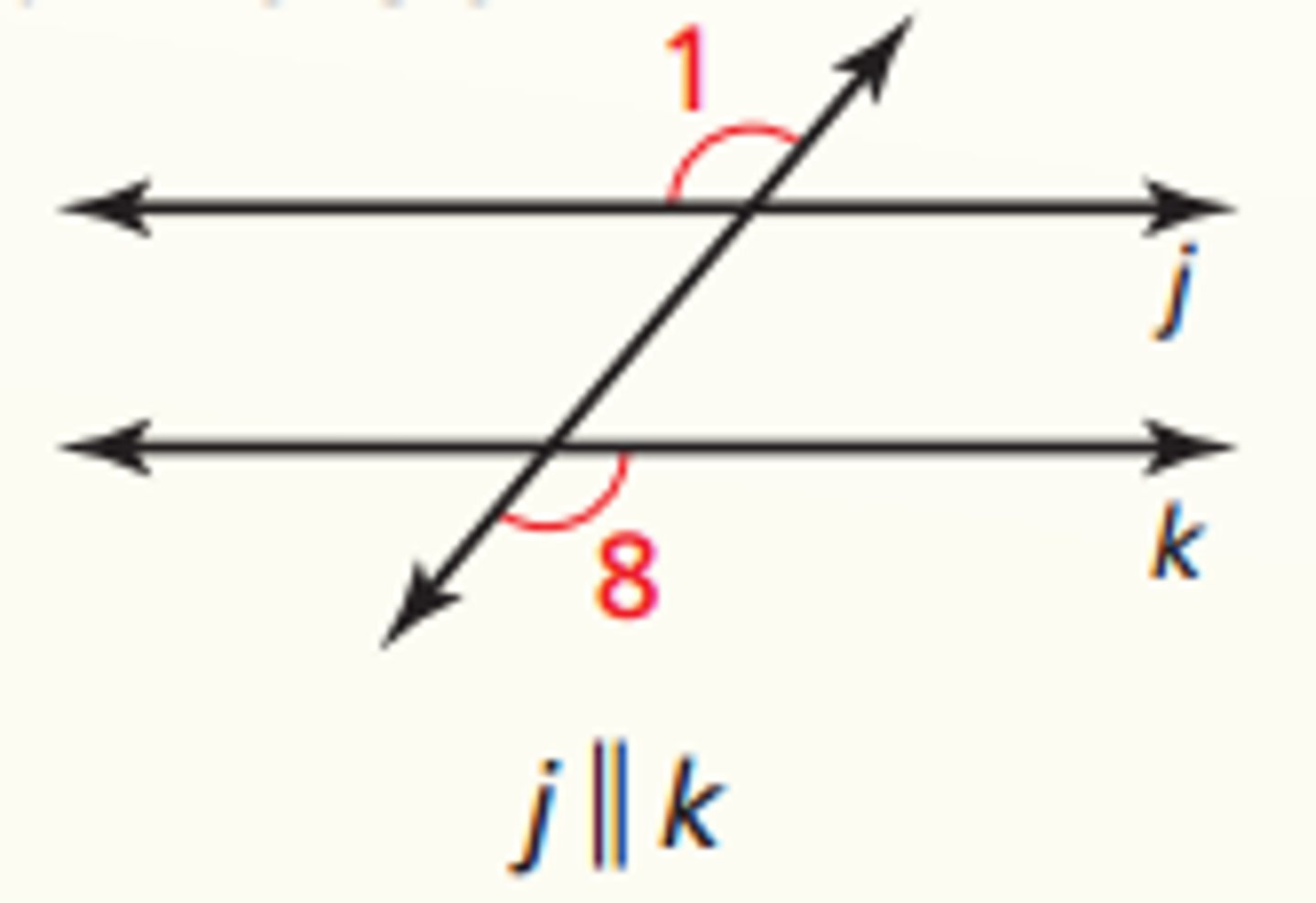
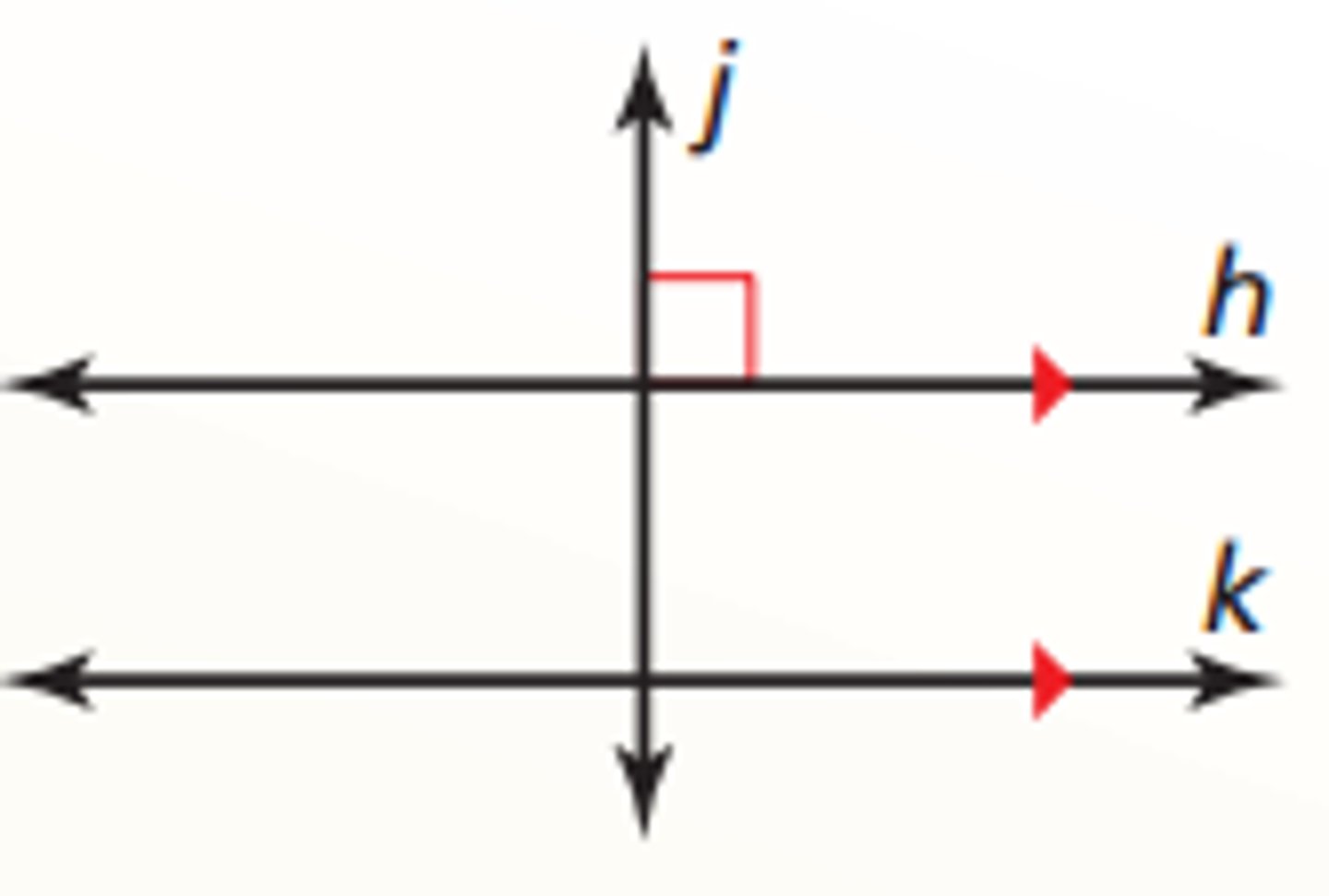
Perpendicular/Parallel Line Theorem
If two lines are perpendicular to the same line, then the two lines are parallel to each other.
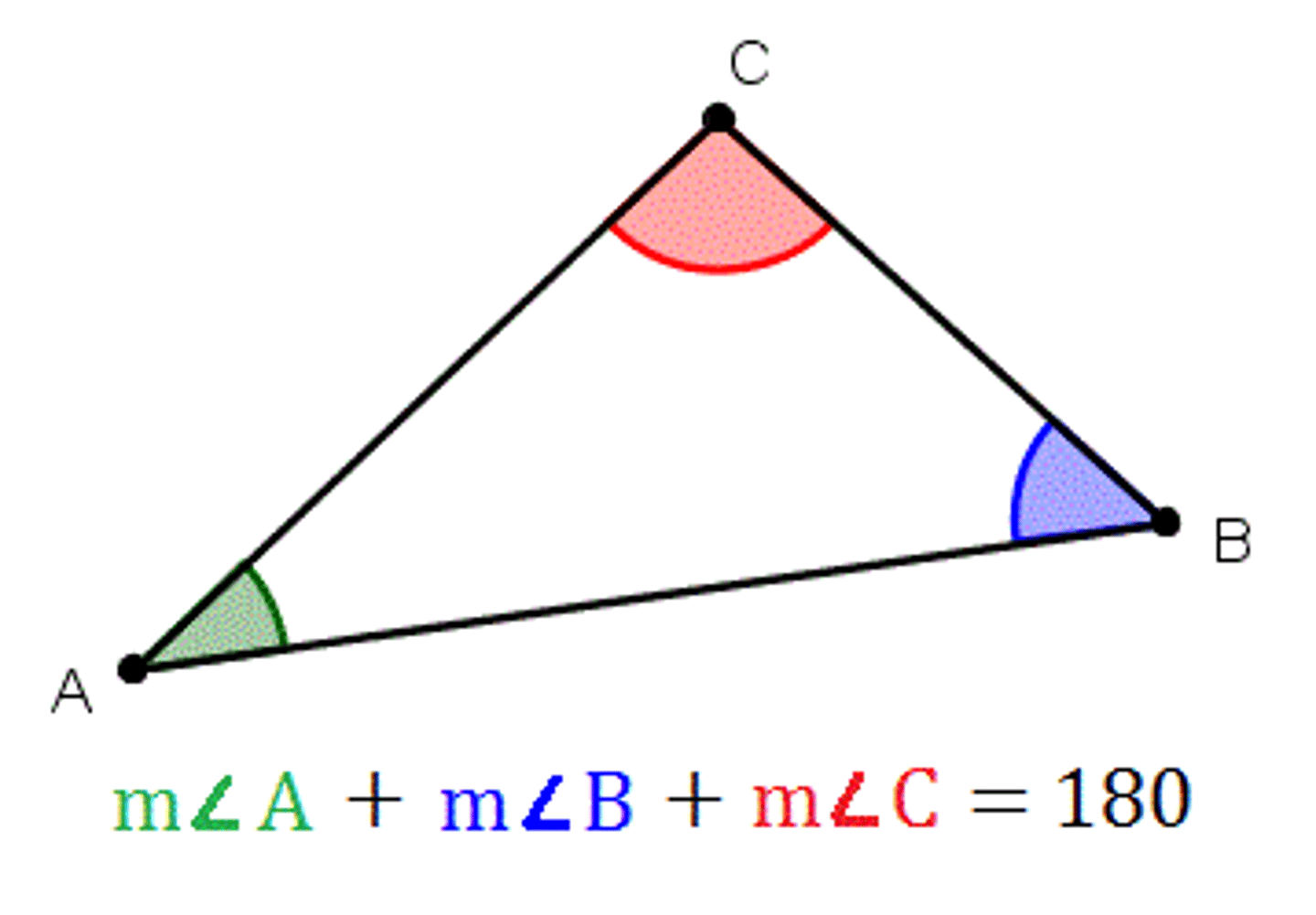
Triangle Sum Theorem
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees
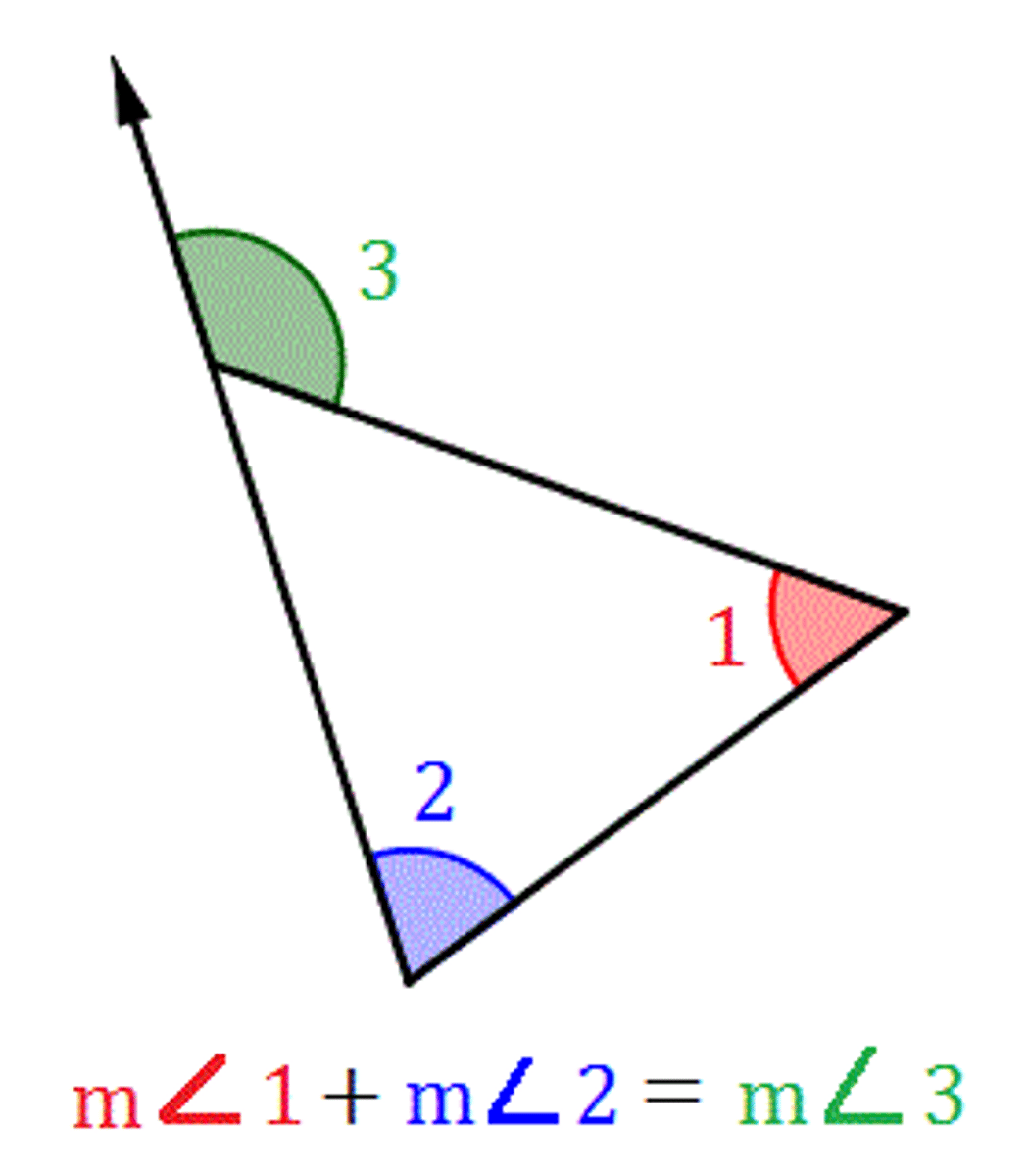
Exterior Angle Theorem
The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles.
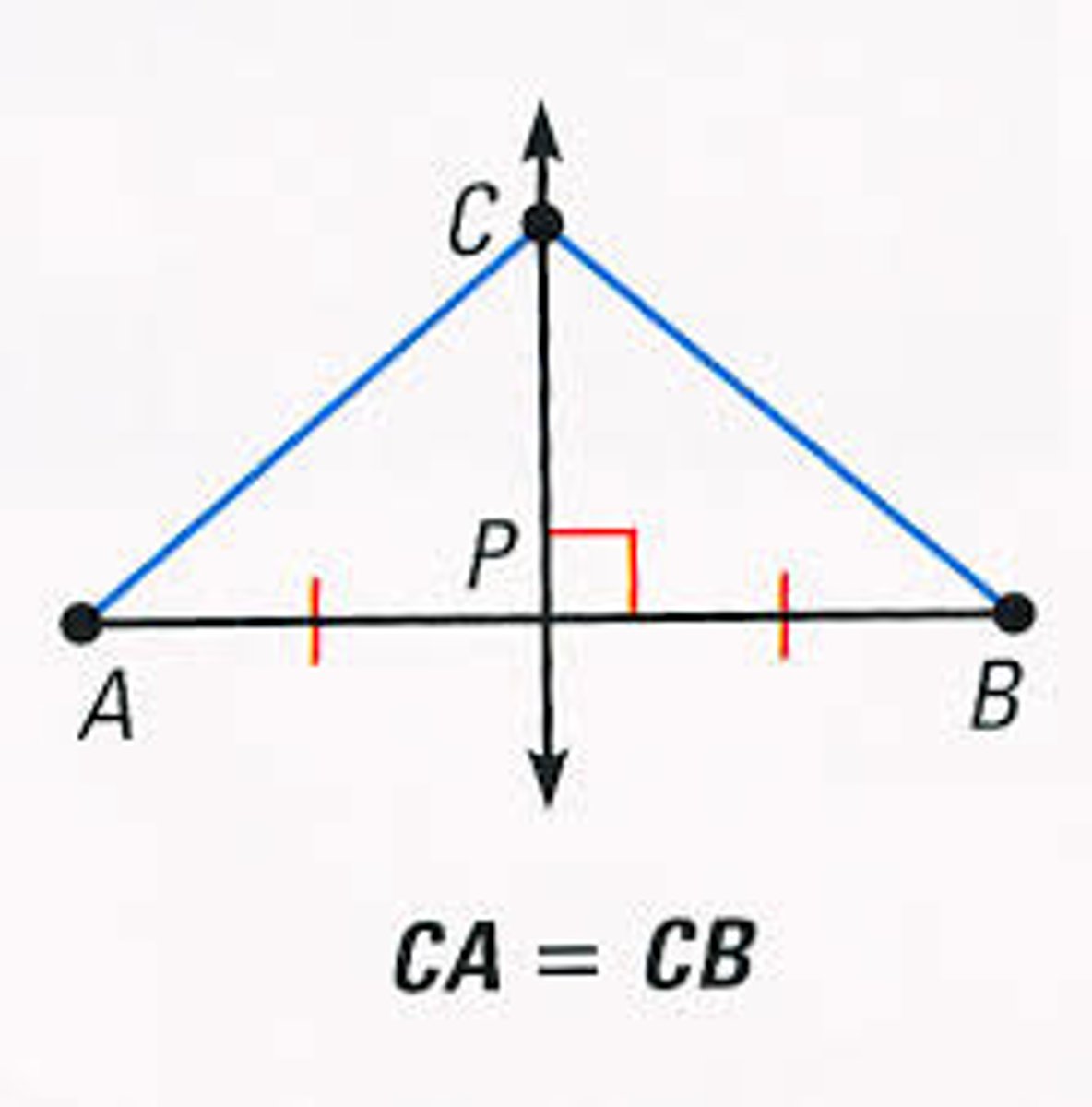
Perpendicular Bisector Converse Theorem
If a point is equidistant from the endpoints of a segment, then it lies on the perpendicular bisector of the segment.
Isosceles Triangle Base Angles Theorem
If two sides of a triangle are congruent, the angles opposite those sides are congruent.
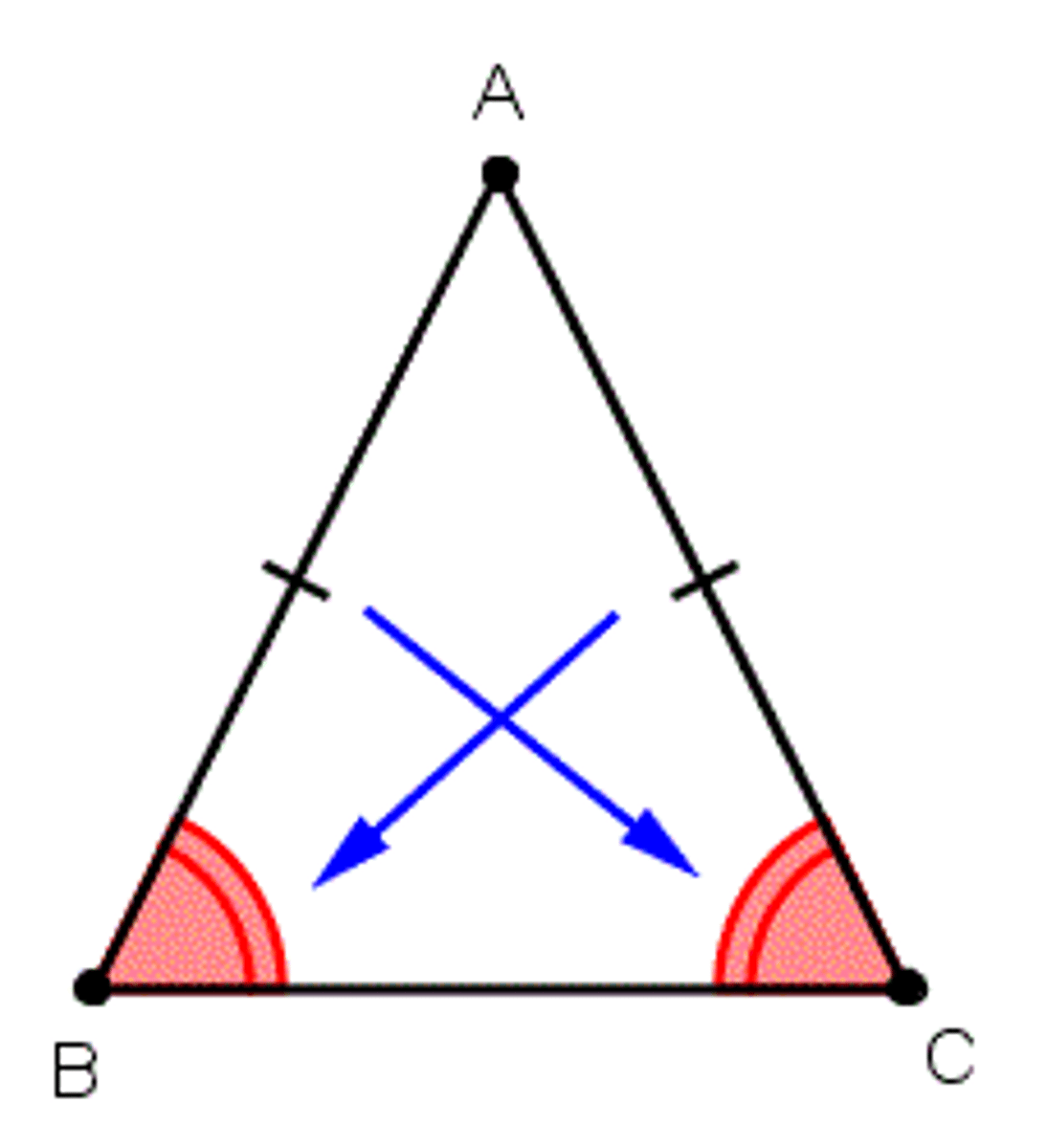
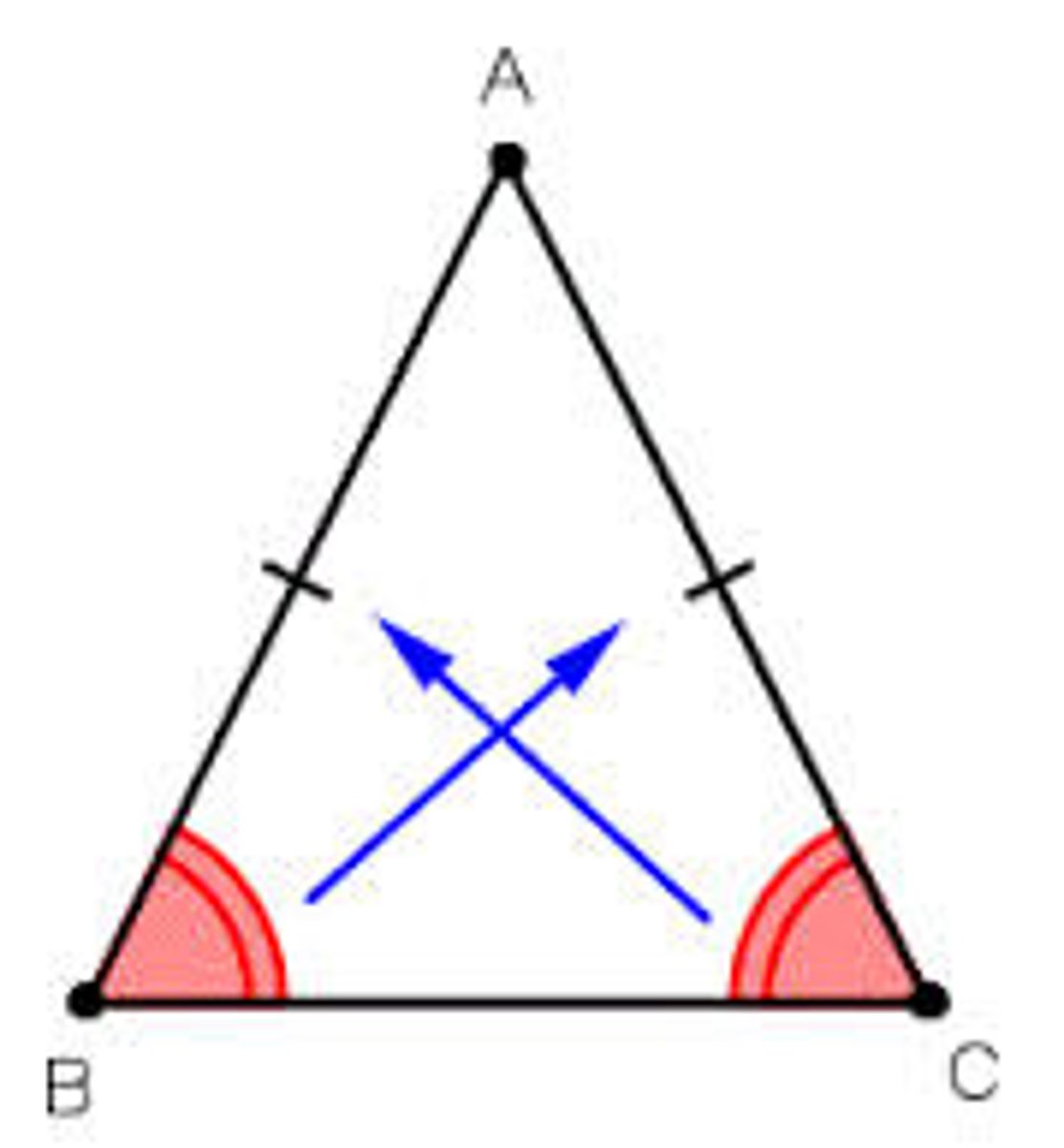
Isosceles Triangle Base Angles Converse Theorem
If two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite them are congruent.
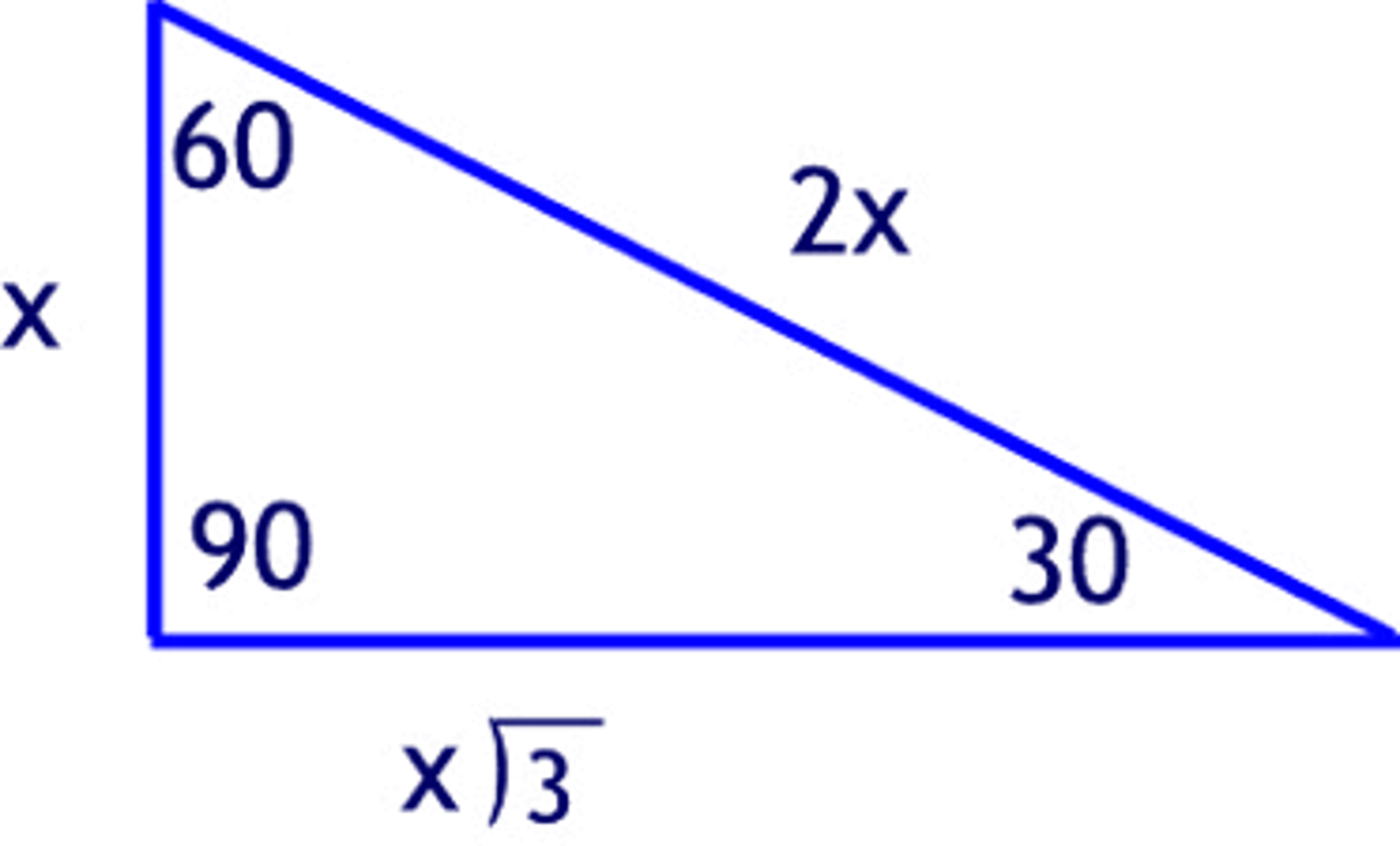
30°- 60°- 90° Triangle Theorem
x, x√3, 2x
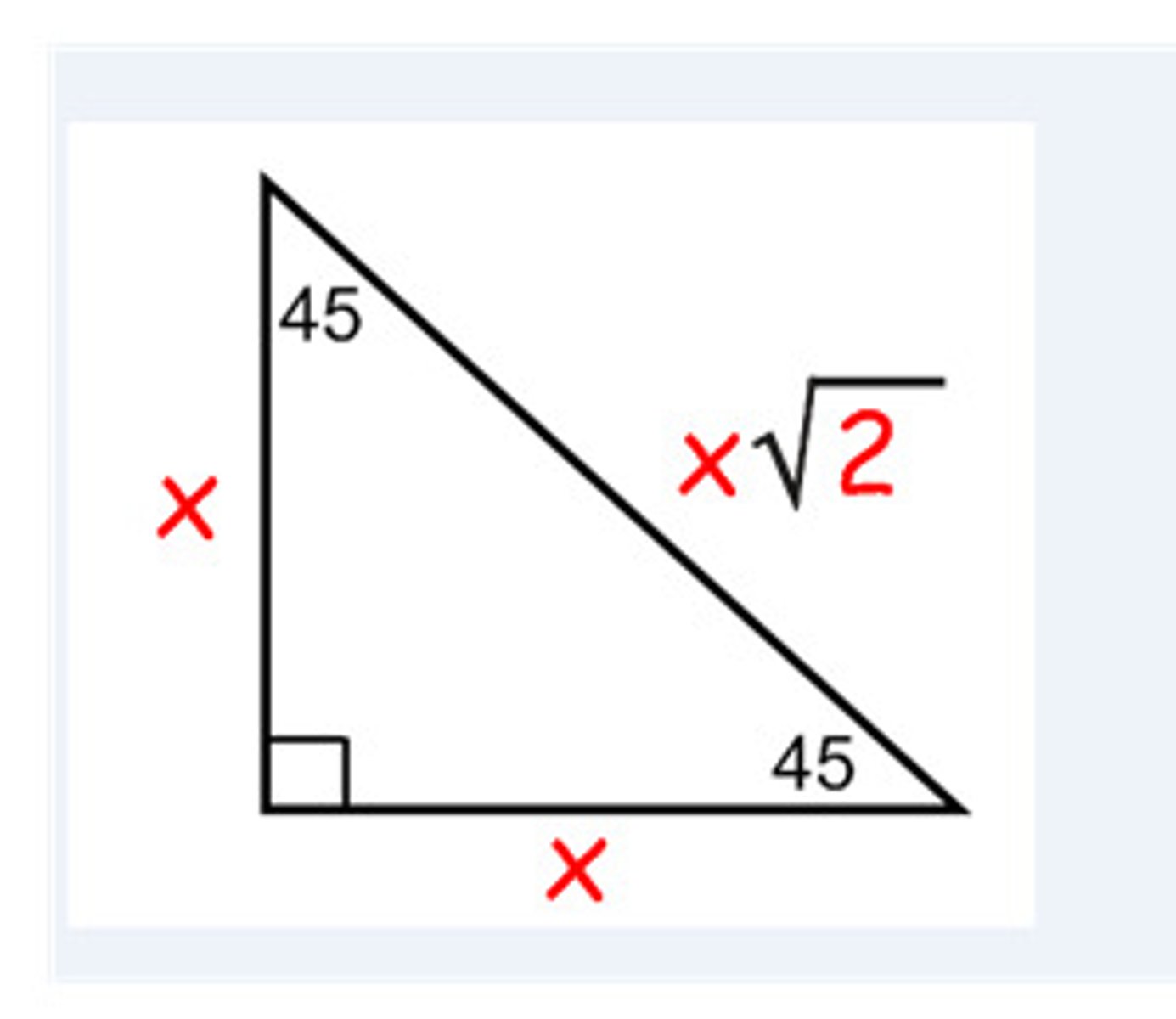
45°- 45°- 90° Triangle Theorem
x, x, x√2
Product Property of Radicals
√ab = √a * √b
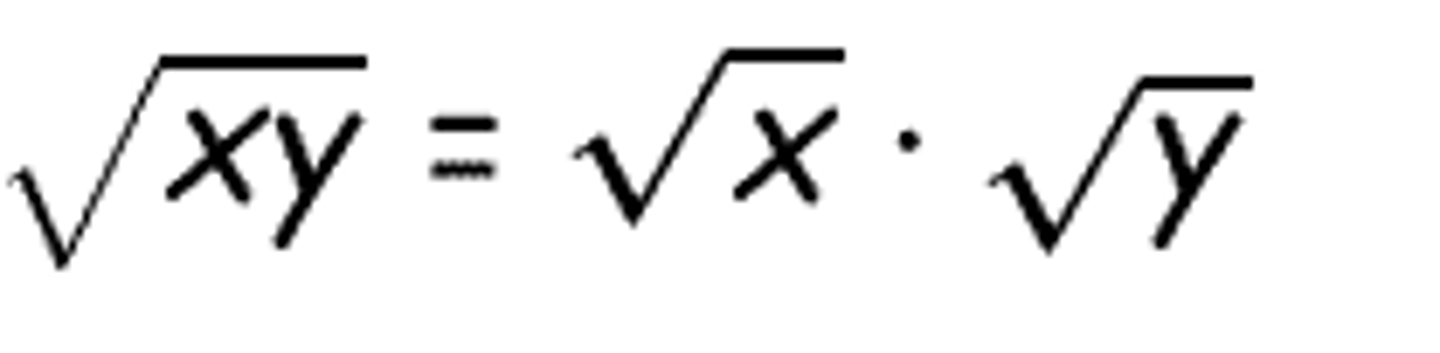
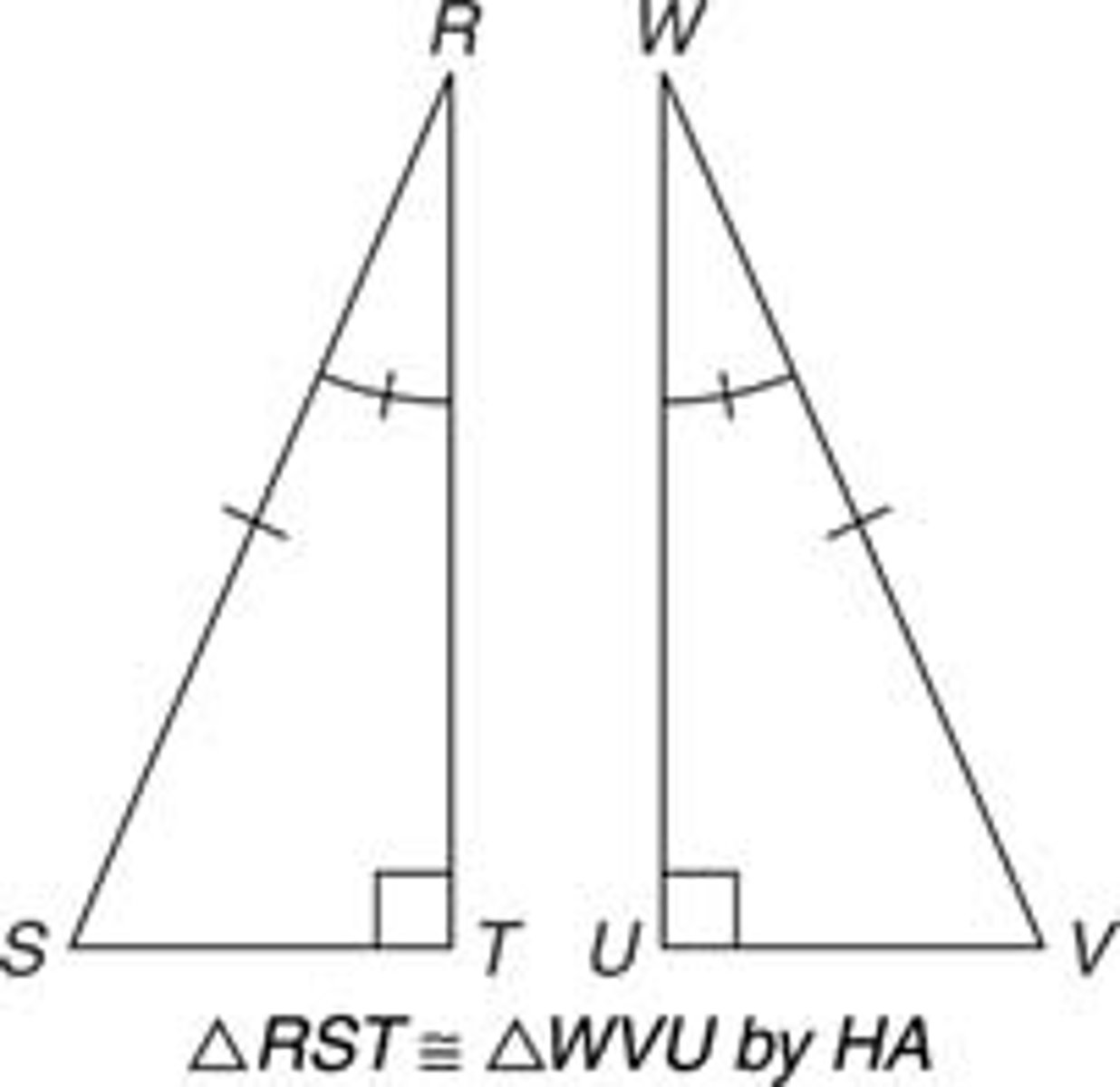
Hypotenuse-Angle (HA) Congruence Theorem
If the hypotenuse and an acute angle of one right triangle are congruent to the hypotenuse and acute angle of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent
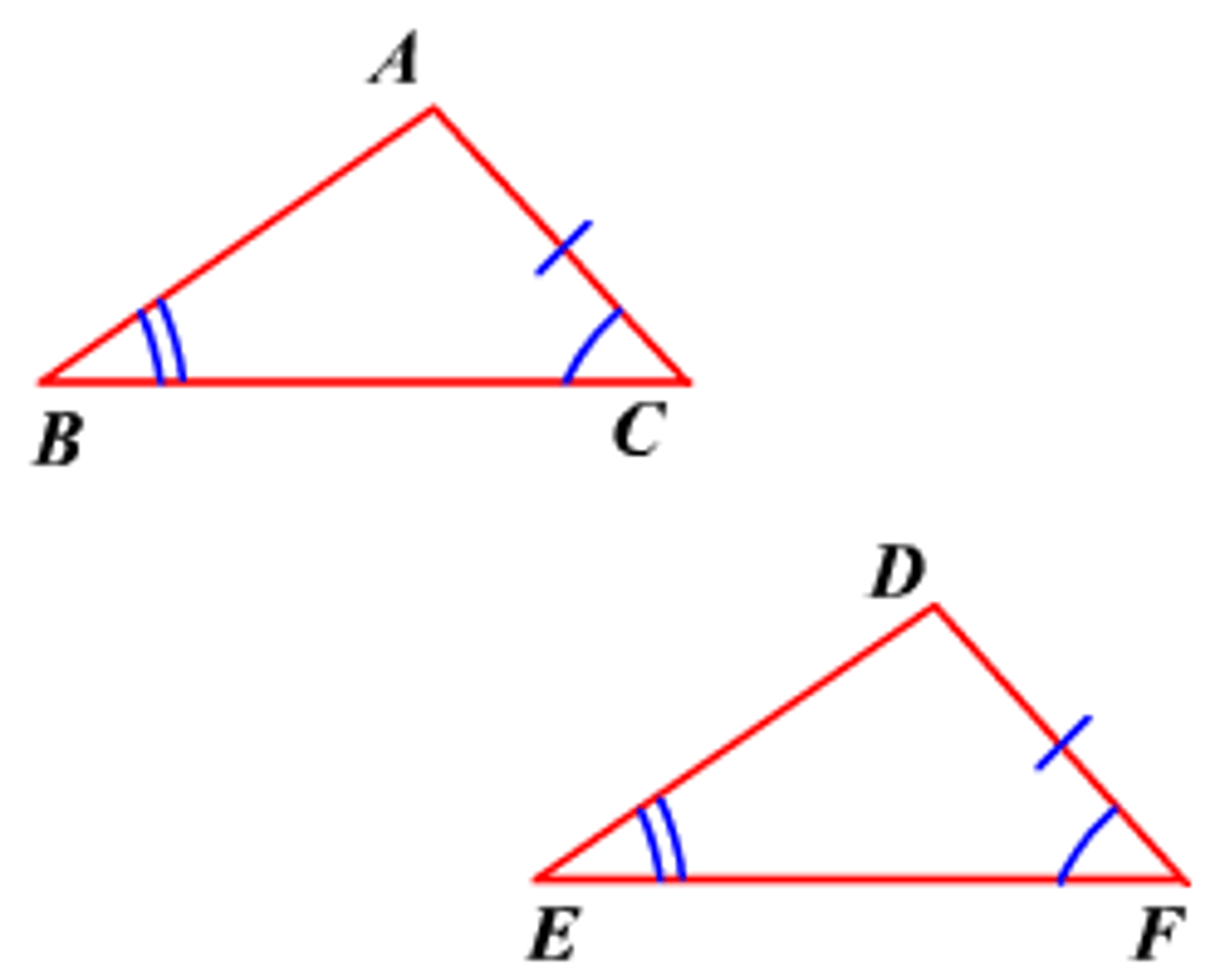
Angle-Angle-Side (AAS) Congruence Theorem
If two angles and a non-included side of one triangle are congruent to two angles and the corresponding non-included side of a second triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
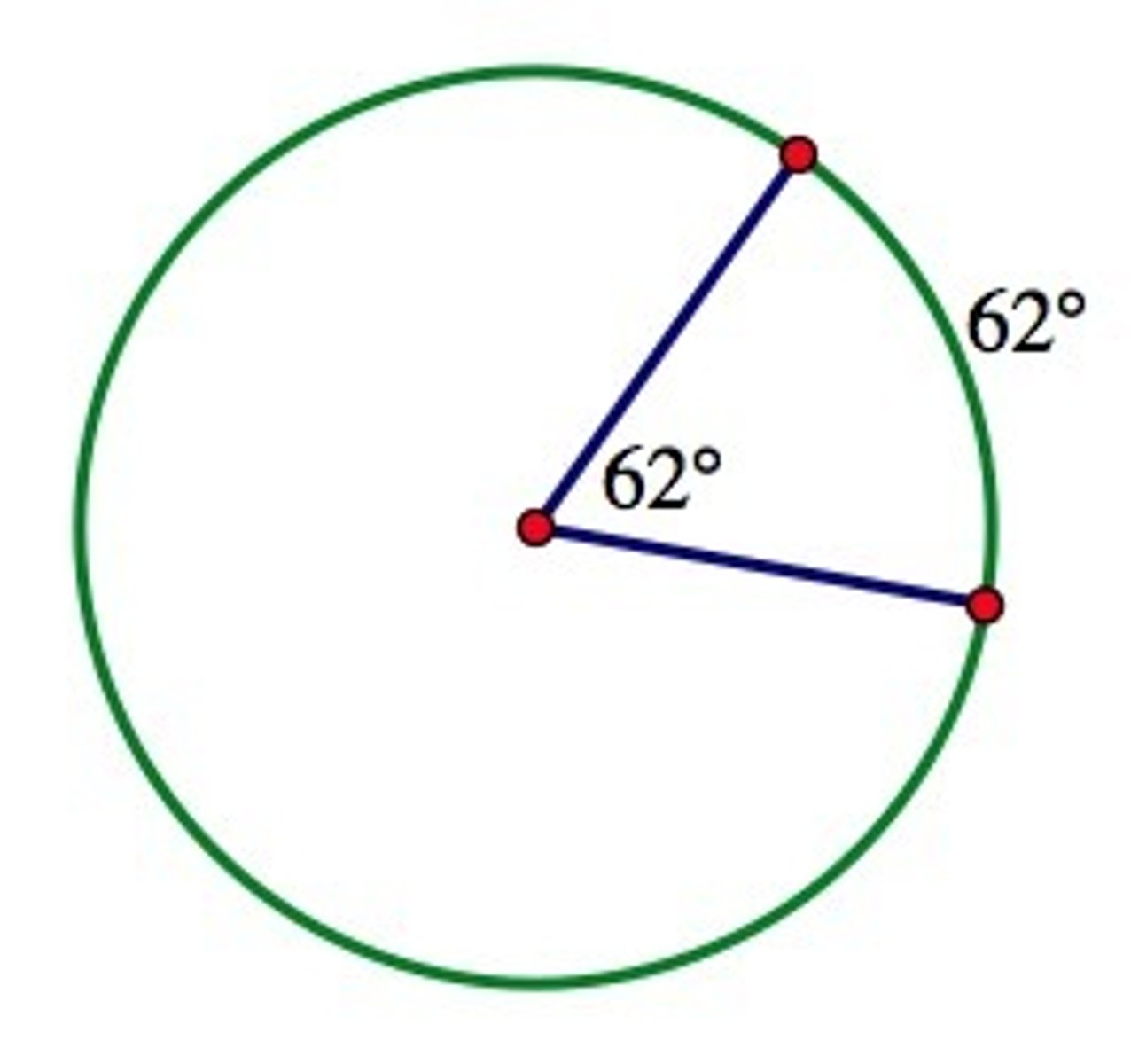
degree measure of an arc is...
equal to the measure of the central angle
adjacent arcs
arcs of the same circle that have exactly one point in common
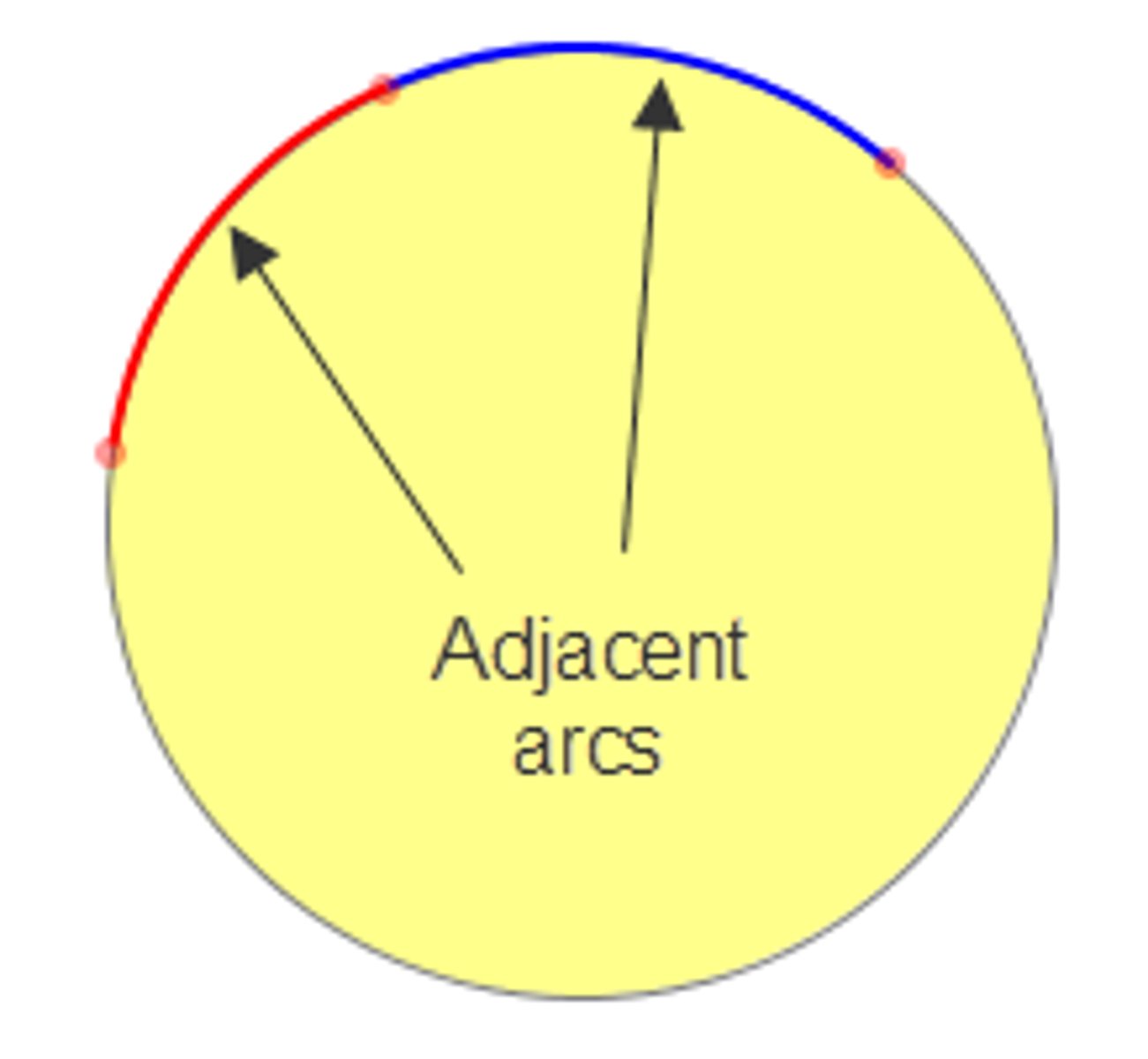
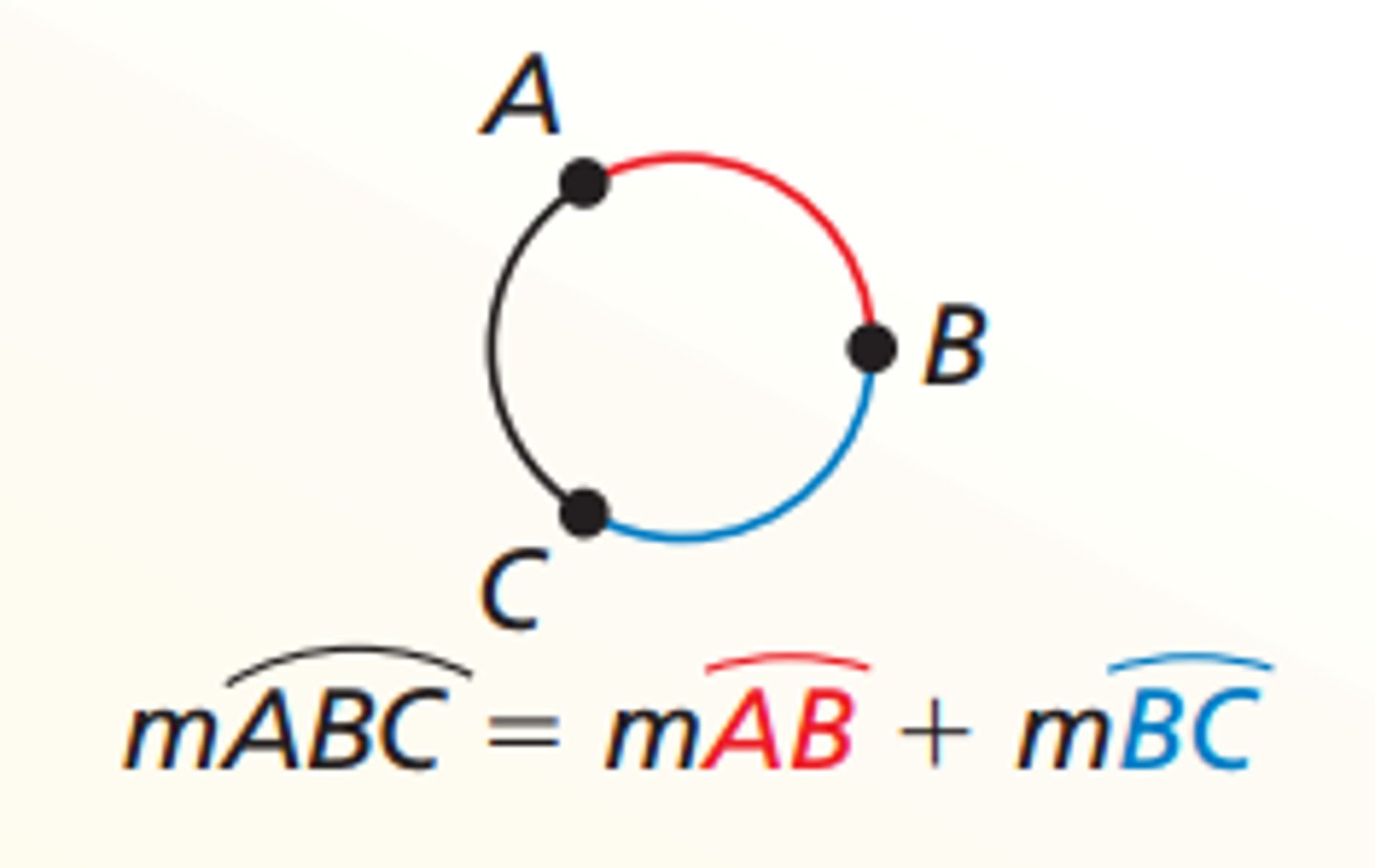
Arc Addition Postulate
The measure of an arc formed by two adjacent arcs is the sum of the measures of the two arcs
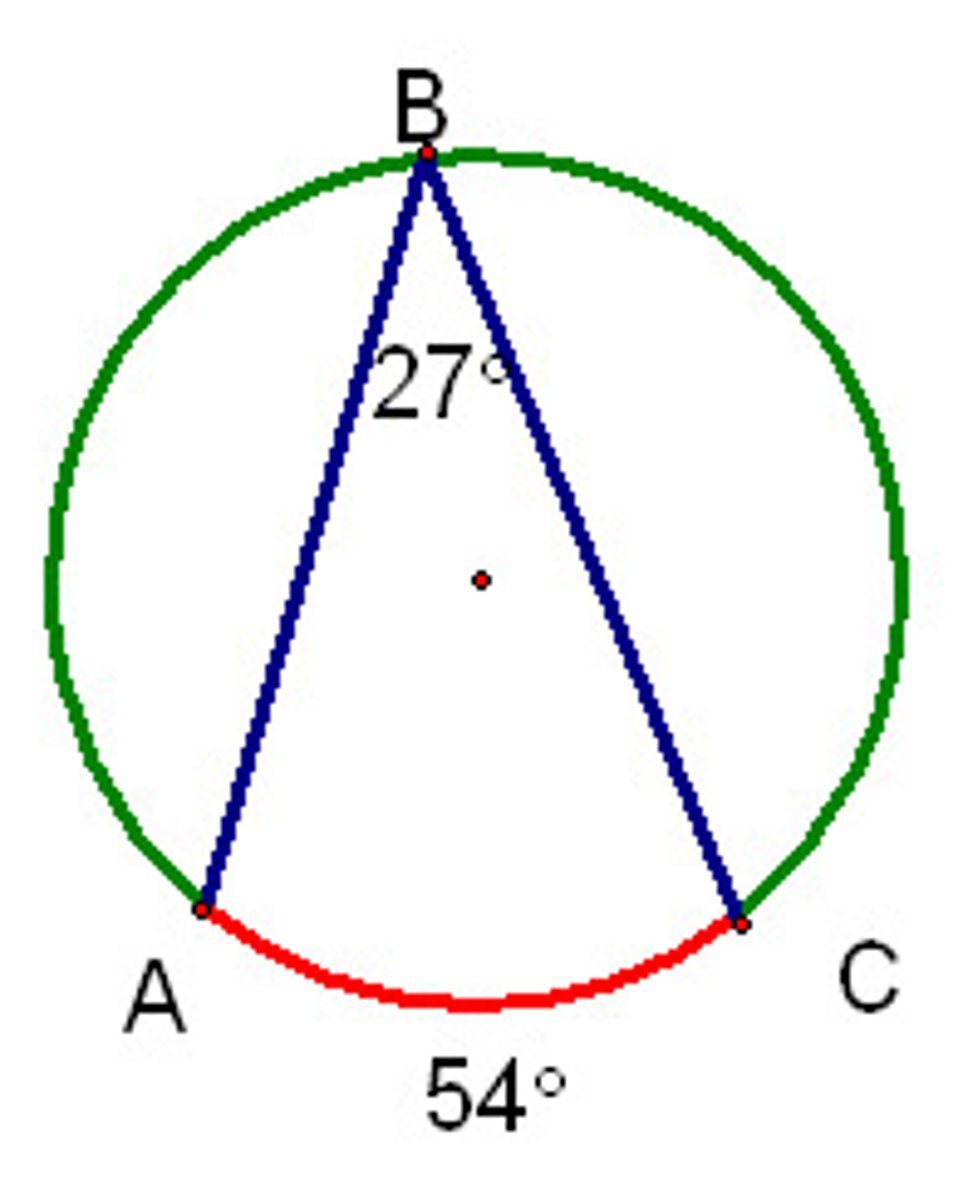
Inscribed Angle Theorem
If an angle is inscribed in a circle, then the measure of the angle equals one half the measure of its intercepted arc.
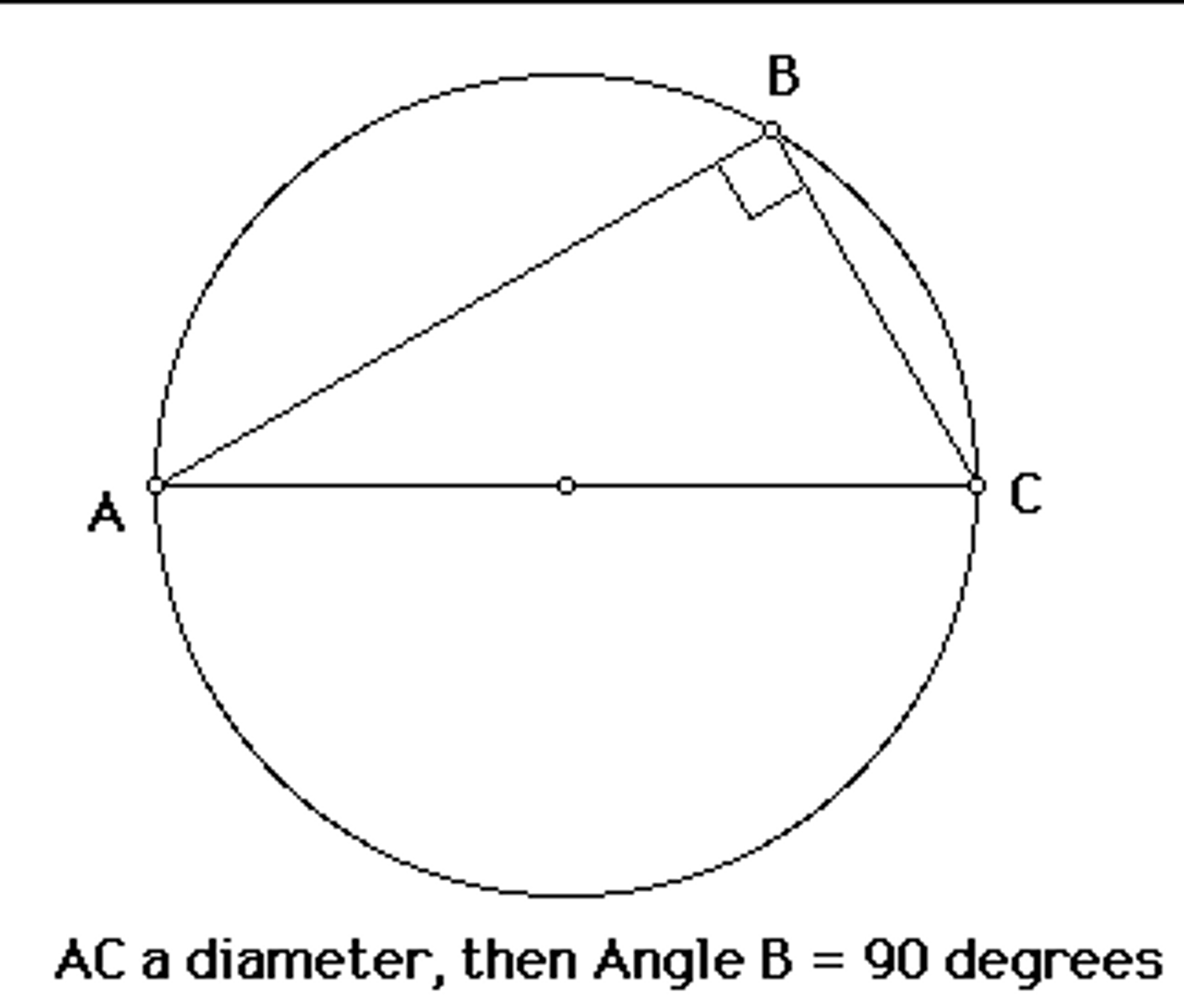
Inscribed Right Triangle Theorem
If a right triangle is inscribed in a circle, then the hypotenuse is a diameter of the circle.
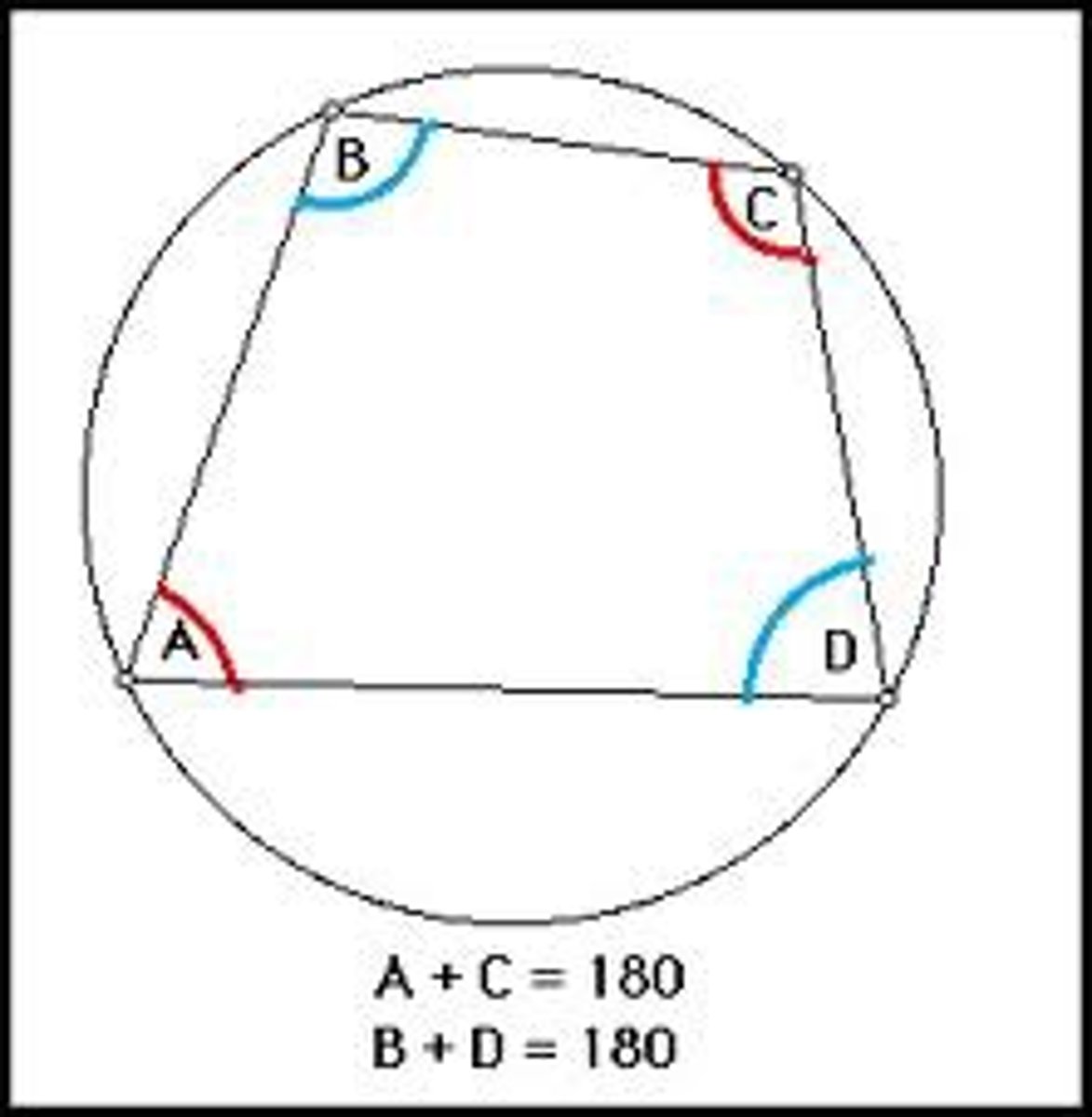
Inscribed Quadrilateral Theorem
A quadrilateral can be inscribed in a circle if and only if its opposite angles are supplementary.
Interior Angles of a Circle Theorem
If an angle is formed by two intersecting chords or secants of a circle such that the vertex of the angle is in the interior of the circle, then the measure of the angle is half of the sum of the measures of the arcs intercepted by the angle and its vertical angle.
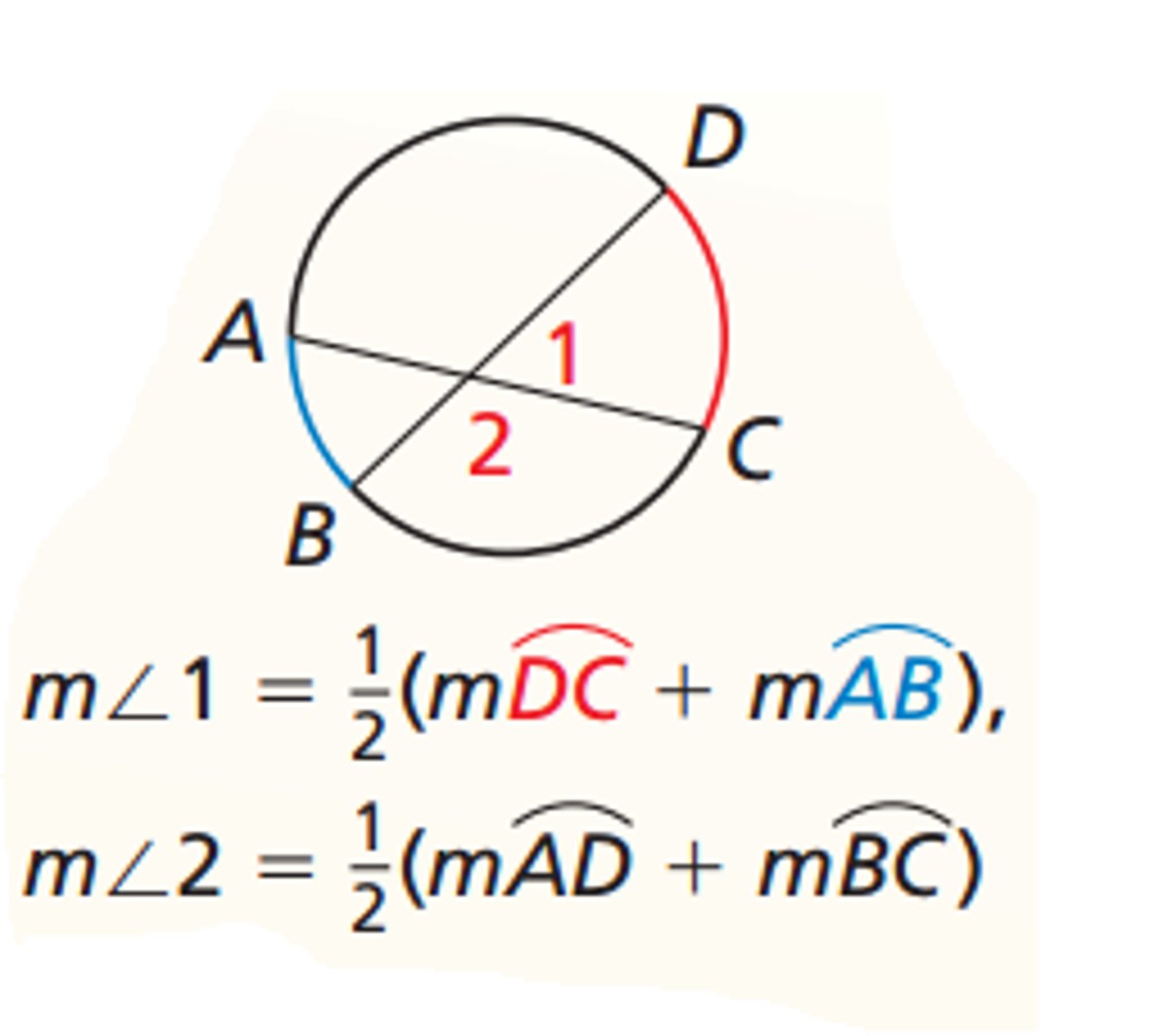
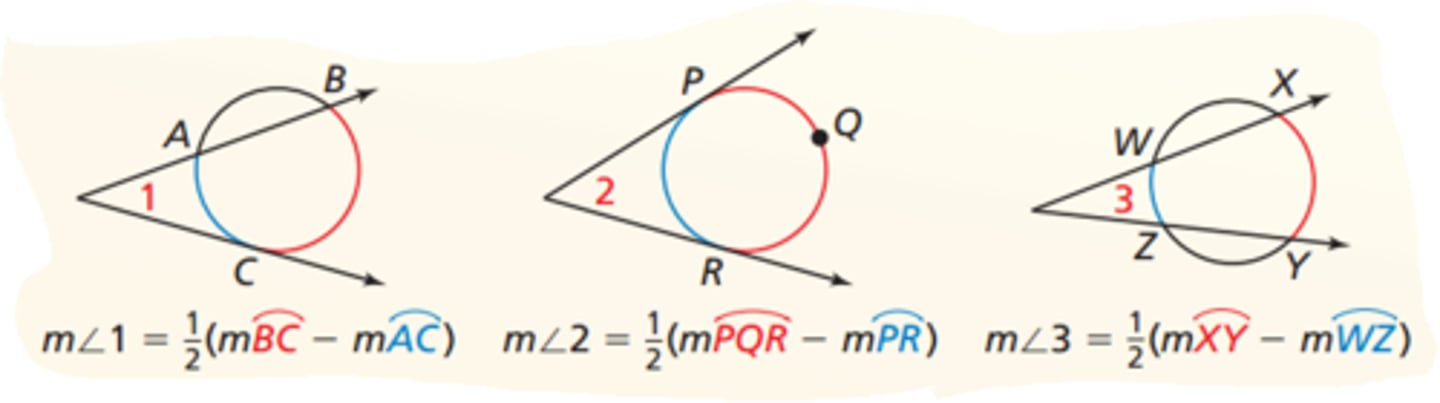
Exterior Angles of a Circle Theorem
If an angle is formed by two intersecting chords or secants of a circle such that the vertex of the angle is in the exterior of the circle, then the measure of the angle is half of the difference of the measures of the arcs intercepted by the angle.
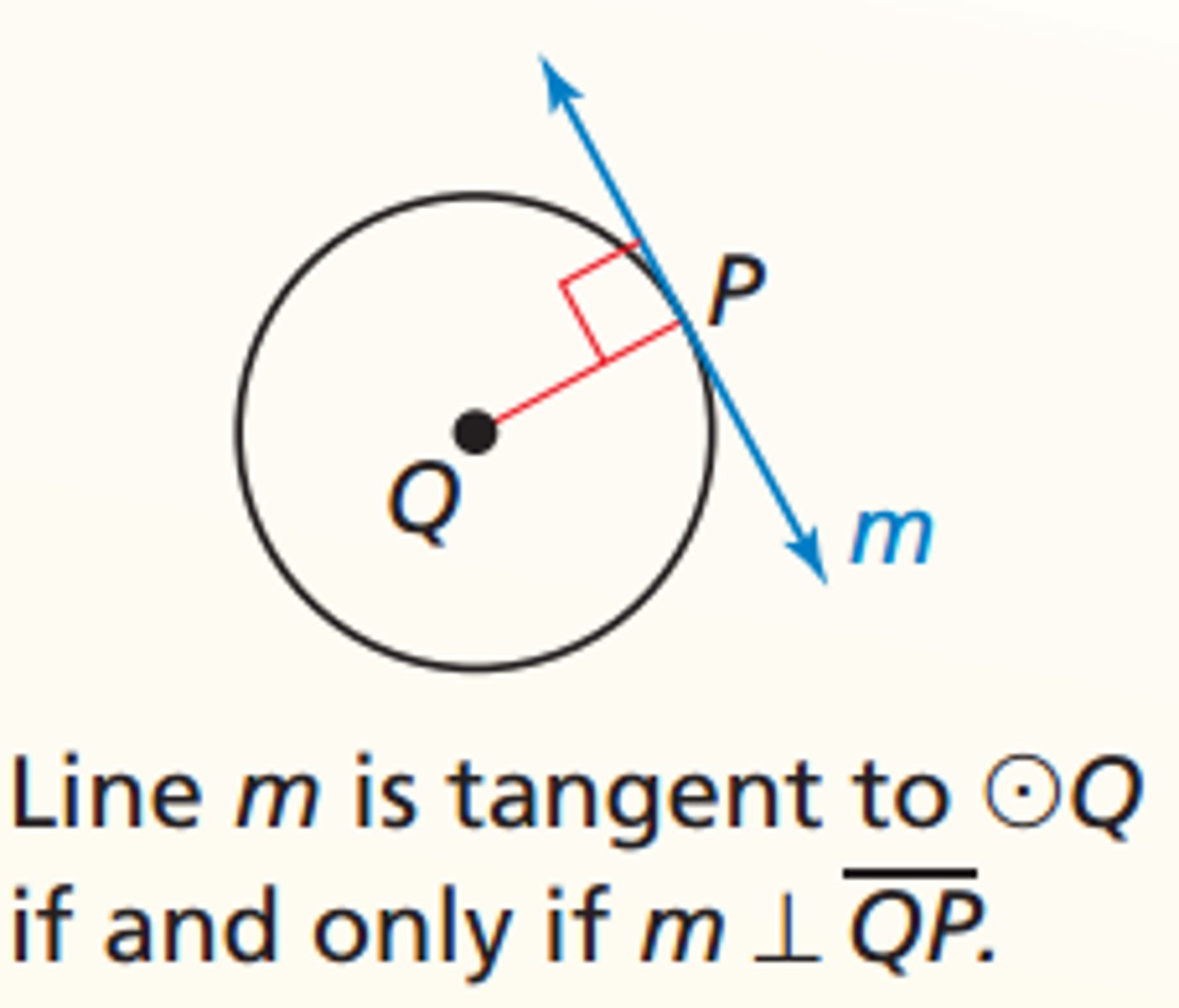
Tangent to a Circle Theorem
A line drawn tangent to a circle is perpendicular to a radius of the circle drawn to the point of tangency.
rationalize the denominator
rewrite it so there are no radicals in any denominator and no denominators in any radical
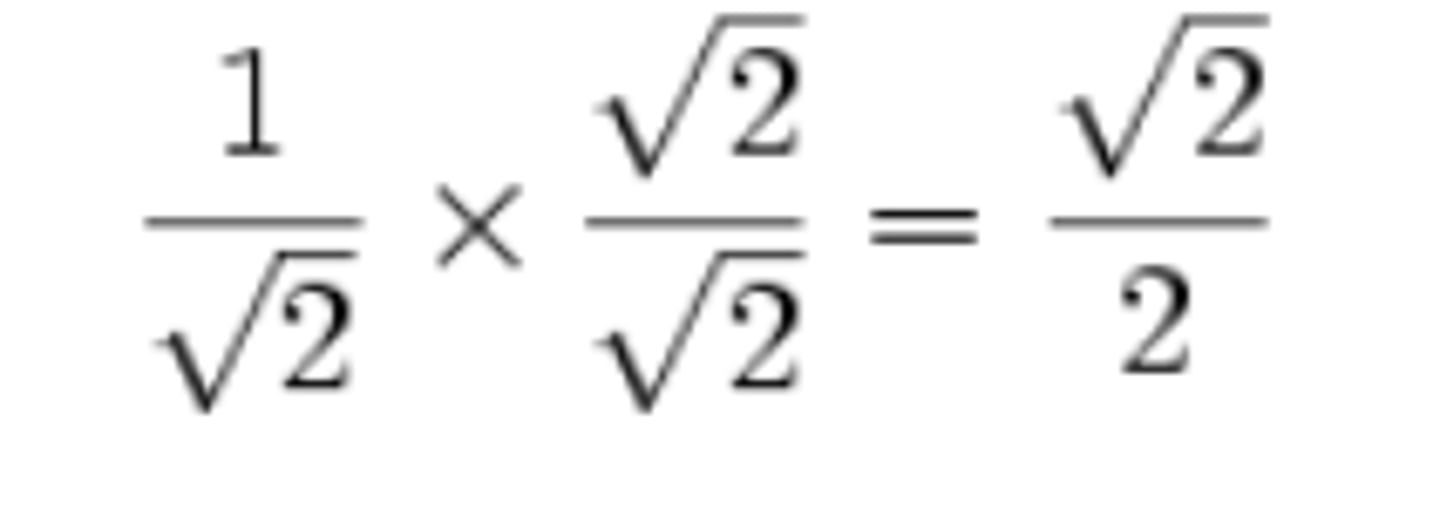
extract the roots
The process of removing all perfect square numbers from under the radical symbol.

Tangent-Chord Angle Theorem
The measure of an angle formed by a tangent and a chord is equal to one half the intercepted arc
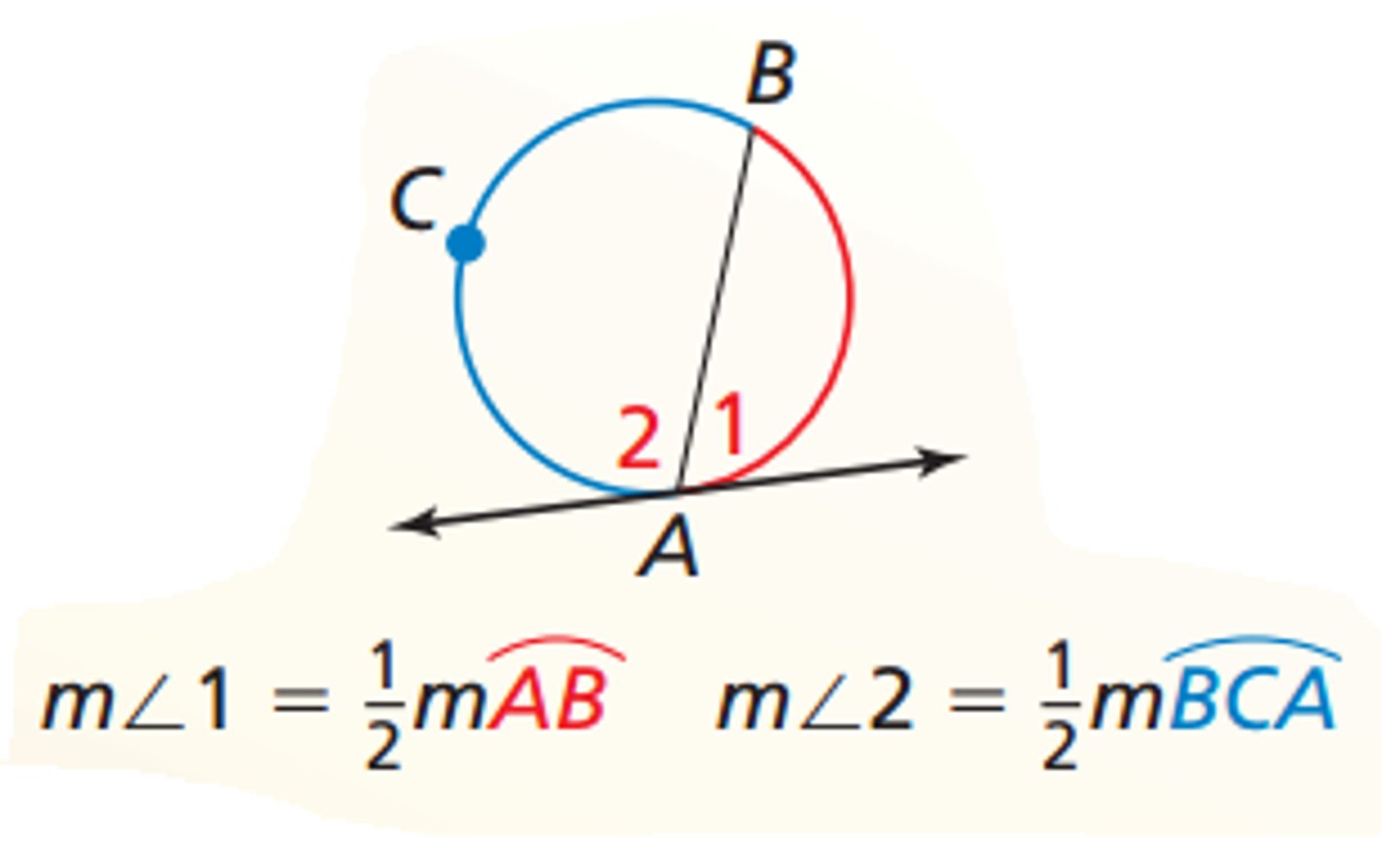
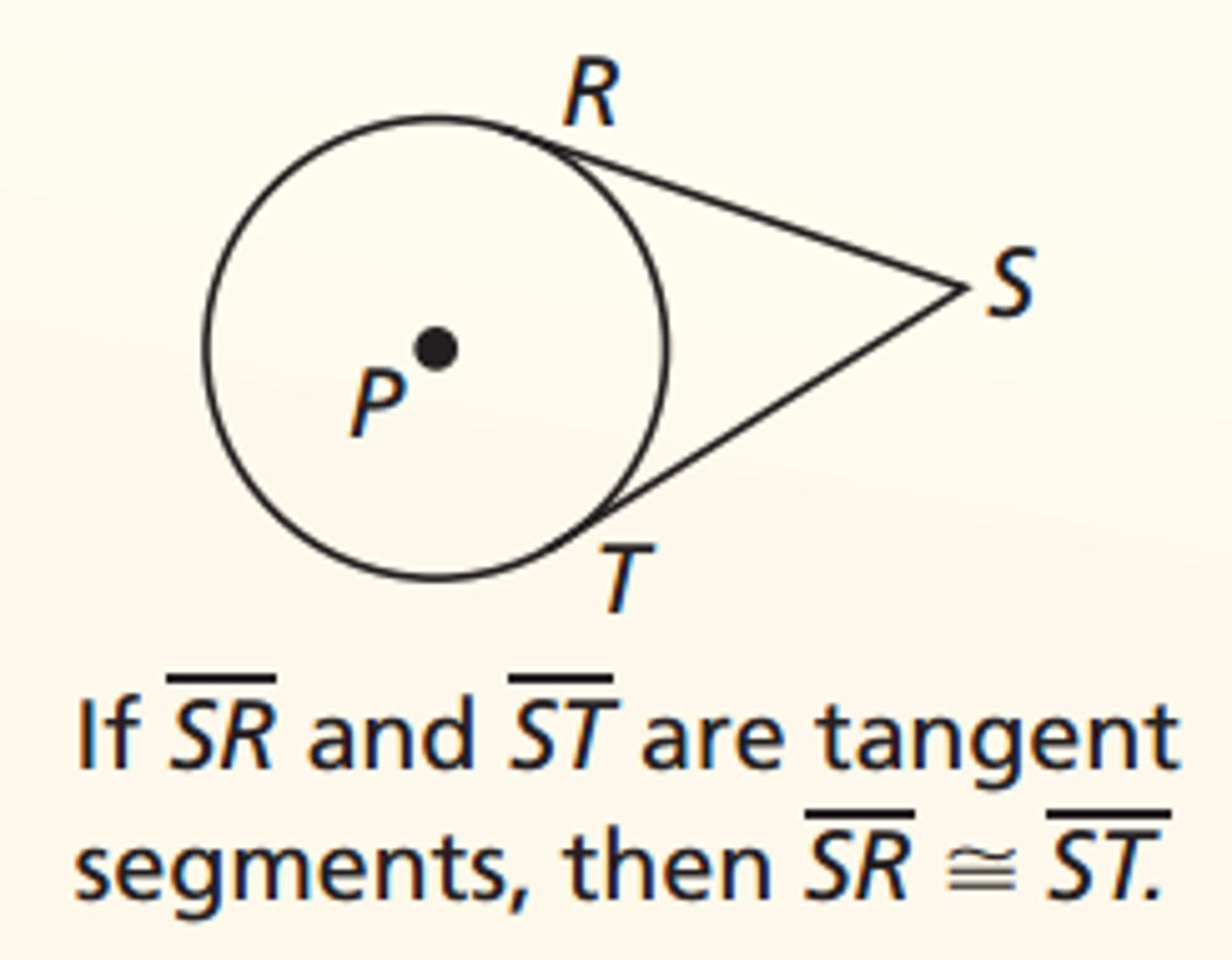
Tangent at an External Point Theorem
If two tangents are drawn from the same external point, then the segments are equal.