X-ray Interactions: Photoelectric Effect and Compton Scatter
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
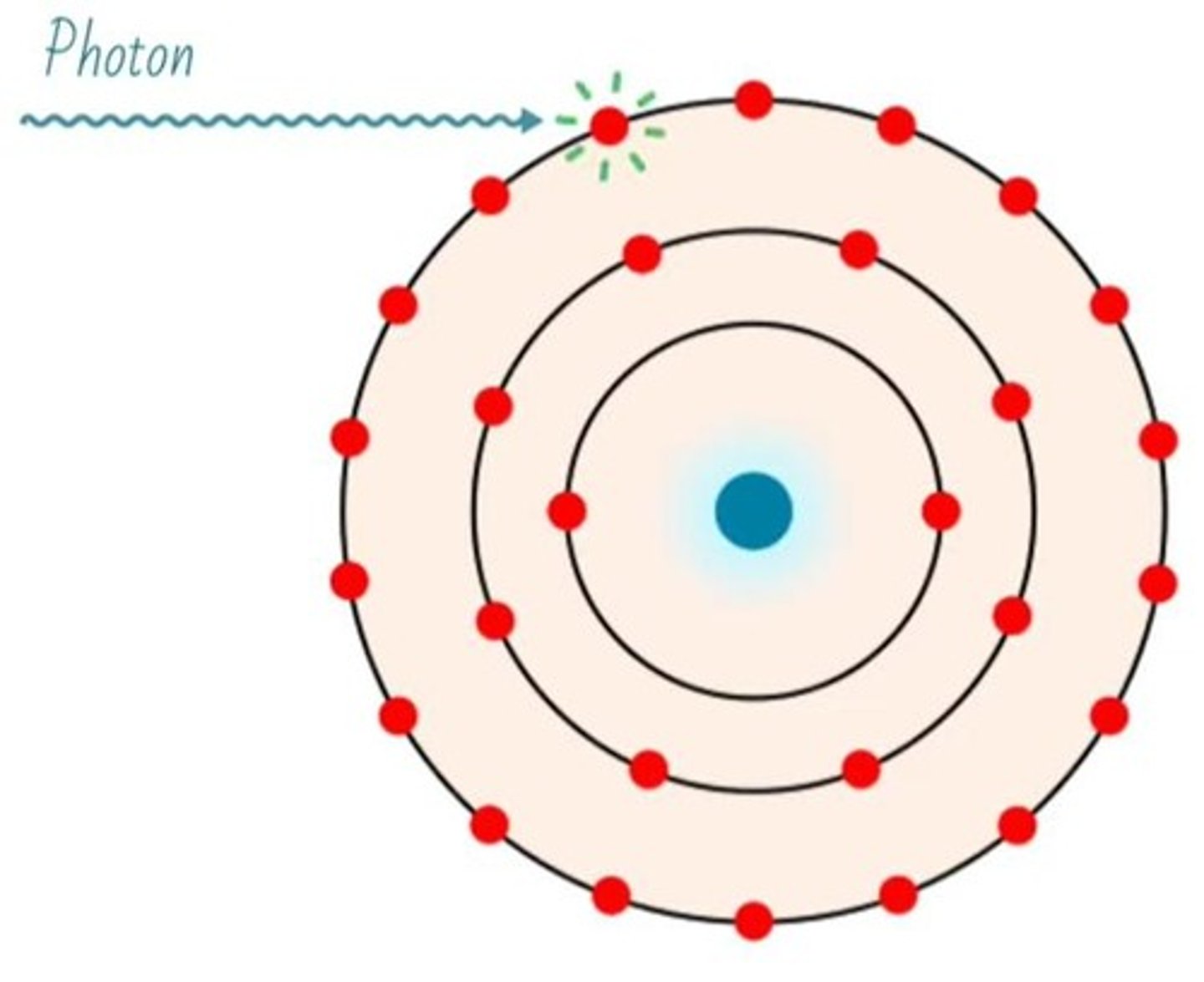
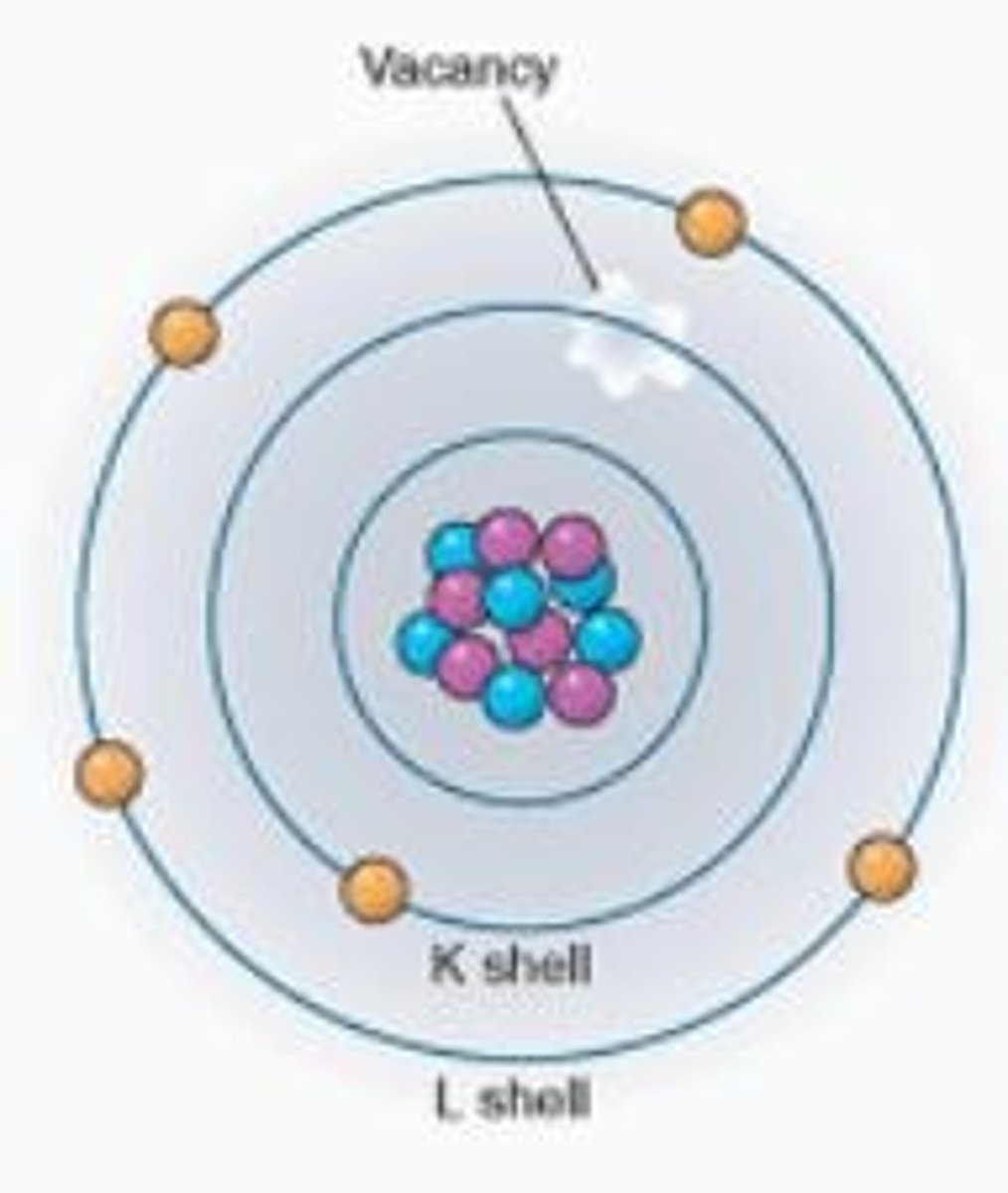
Photoelectric Effect
Photon energy transfers to eject inner shell electron.
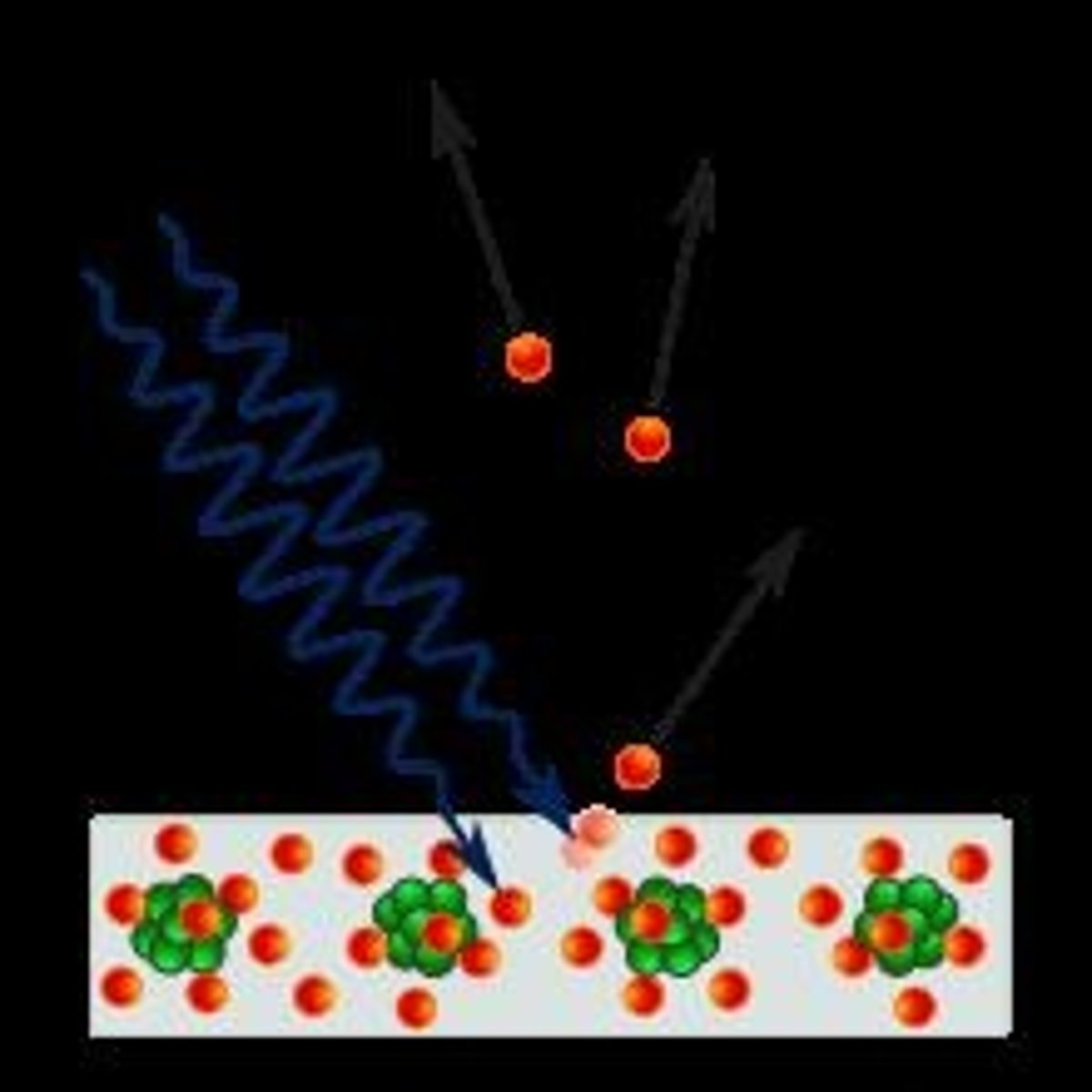
Compton Scatter
results in the removal of an outer shell electron leading to the photon becoming scattered.
this electron with move in a different direction than the beam
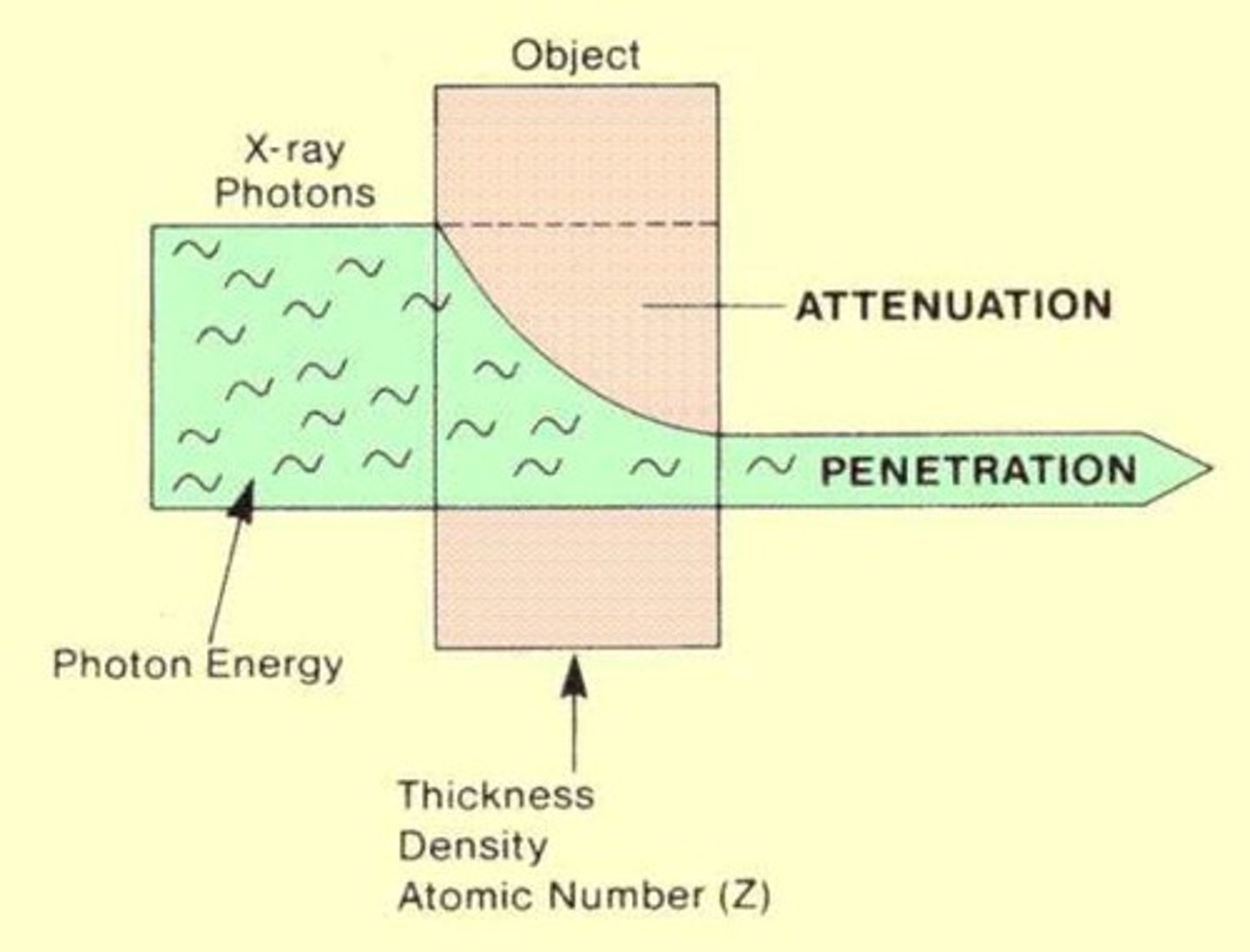
Attenuation
in relation to x-rays it reduces x-ray beam intensity.
affected by absorption and scatter
X-ray Absorption
Process where X-rays are absorbed by tissue.

Inverse Square Law
Intensity decreases with distance squared from source.
Electron Binding Energy
Minimum energy to remove an electron from atom.
Atomic Number (Z)
Number of protons in an atom's nucleus.
High Atomic Number
Higher Z leads to greater photoelectric absorption.
Soft Tissue Absorption
Soft tissue has average atomic number of 7.4.
Bone Absorption
Bone has average atomic number of 13.8.
Radiation Dose
Amount of radiation energy absorbed by tissue.
photoelectron effect increases skin exposure
Compton scatter increases patient exposure
Image Quality
Clarity and detail of X-ray images.
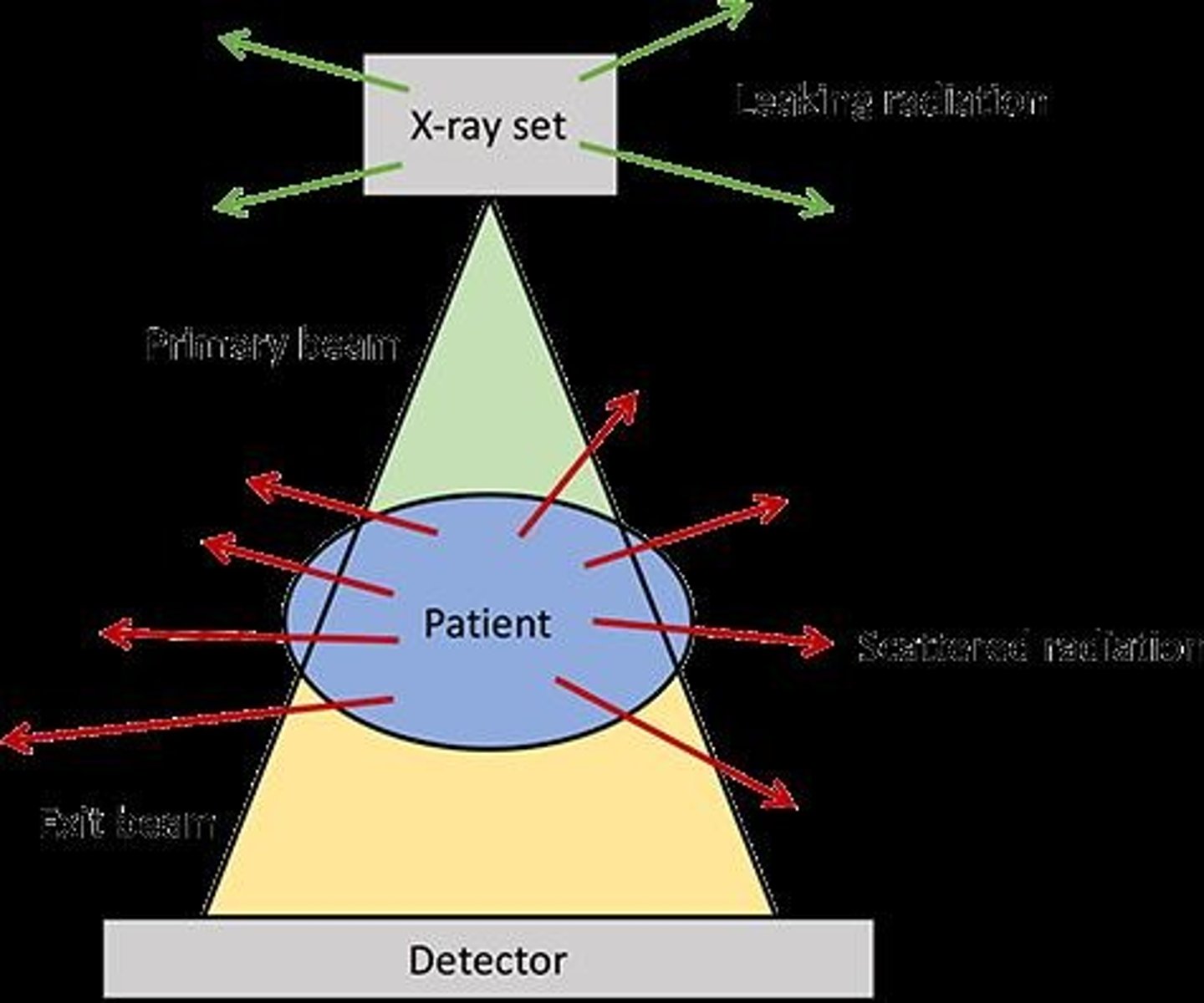
Scattered Photon
Photon that changes direction after interaction.
Forward Scatter
Higher energy scatter that may reach receptor, this will lead reduced image quality
Side Scatter
has lower energy levels but can create a dose for anyone else in the room
Air Gap Technique
Space between patient and receptor to reduce scatter.
Grids
used to stop scattered x-rays from reaching receptor.
made of lead strips with gaps between.
placed between patient and receptor.
scattered x-rays are absorbed by the lead
Radiation Protection
Measures to safeguard against excessive radiation exposure.

Occupational Dose
Radiation exposure to healthcare workers.
Image Contrast
Difference in brightness between areas in an image.
Tissue Thickness
Greater thickness increases likelihood of scatter.
Density of Matter
Higher density leads to increased attenuation.
Vacuum Attenuation
Attenuation is zero in a vacuum.
K-shell Electron
Inner shell electron with high binding energy.
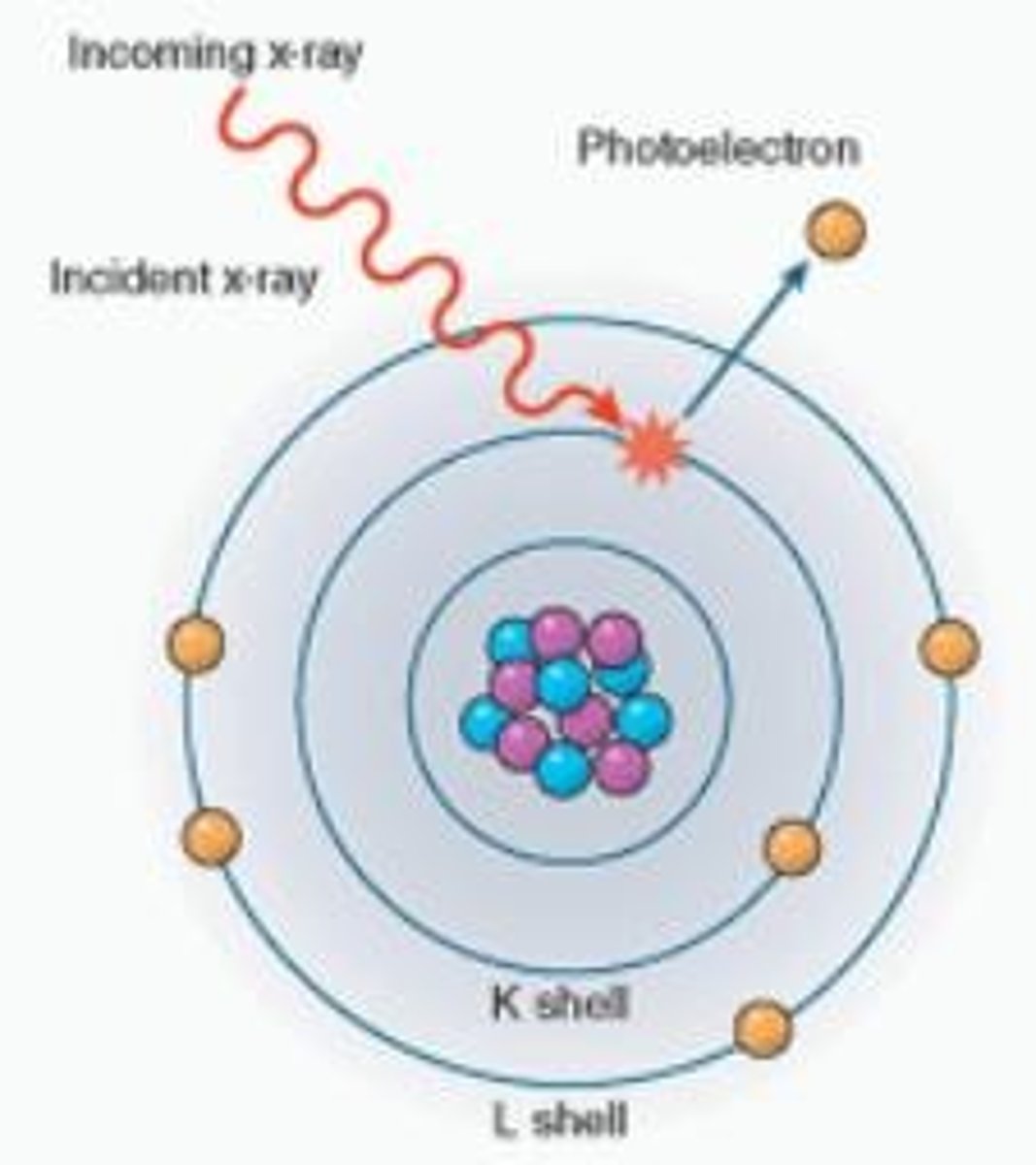
L-shell Electron
Outer shell electron with lower binding energy.
Mathematical Algorithms
Technology to reduce scatter post-exposure.
can remove scatter post procedure and improve contrast.
Radiographic Techniques
Methods to optimize X-ray imaging quality.