Orgo Mini Exam 1
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
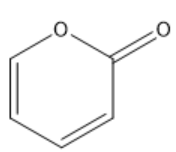
How many sigma bonds are there in the molecule below? Do not forget those atoms skipped when drawing bond-line structures.
11
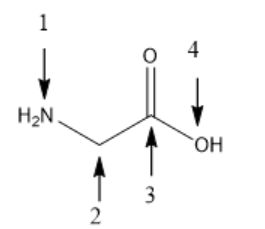
Glycine (NH2-CH2-COOH), one of 20 basic amino acids. What is the geometry (or molecular shape) of N atom in glycine?
Trigonal pyramidal
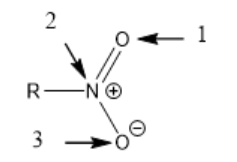
Below shows one of two equivalent resonance structures of nitro group (with lone pairs skipped), which is an electron withdrawing group. R is an alkyl group. What are the hybridizations of those 3 atoms in nitro group?
sp2 for all of them
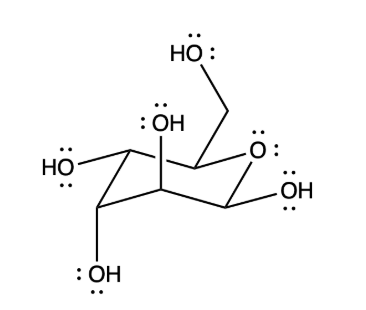
Which statement best describes the physical properties of the following sugar?
-low solubility in water and large dipole moment
- high boiling point and hydrophobic
-large dipole moment and no hydrogen bonding
-low melting point and large dipole moment
-high melting point and high solubility in water
-high melting point and high solubility in water
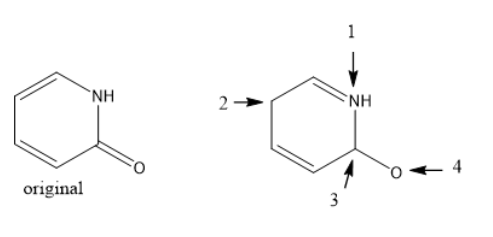
A student tried to draw resonance structure from the original molecule (both shown below; the second is one of the resonance structures of the original molecule, which may or may not necessarily be the best). However, the student forgot to label formal charges. What is the formal charge on atom #1 on the resonance structure? (hint: the student tried to use two resonance patterns at once, which is never a good idea).
+1
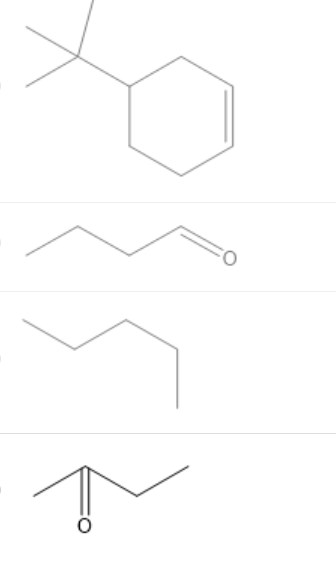
Which of the following is not a proper bond-line structure? Select the best answer
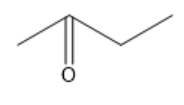
What functional groups are there in the molecule? Select one best answer.
Alkyl halide
Alkene
Ether
Ketone
Ester
1, 2 and 5
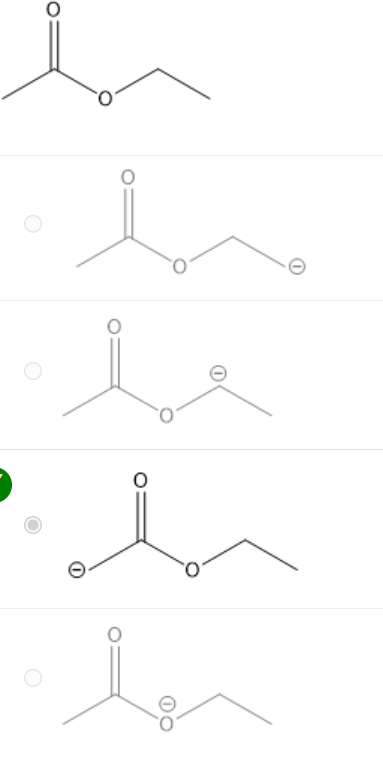
Think about the most acidic H of ethyl acetate (shown below). What is its most stable conjugate base?
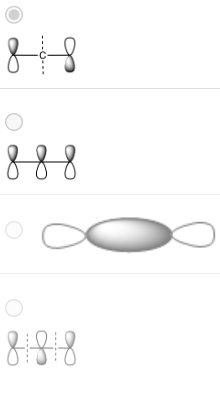
Which picture corresponds to the HOMO of the following molecule?
Select the strongest acid.
2&4
First consider the number of atoms and orbitals that participated in delocalization in the molecule below. If we use MO theory to study the delocalization, how many MO orbitals should we have?
5
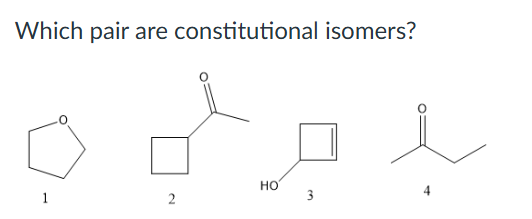
What is the relationship between the following structures?
Resonance structures
In uracil, one of 4 most common RNA bases, how many delocalized lone pairs are there? How many delocalized electrons total in uracil, including but not limited to those delocalized lone pairs?
-There are 2 delocalized lone pairs and total of 10 delocalized electrons.
-There are 2 delocalized lone pairs and total of 8 delocalized electrons.
-There are 2 delocalized lone pairs and total of 6 delocalized electrons.
-There is just 1 delocalized lone pairs and total of 4 delocalized electrons.
There are 2 delocalized lone pairs and total of 10 delocalized electrons.
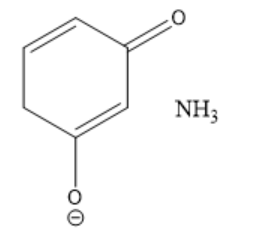
What is the product of the acid-base reaction based on the curved arrow drawn?
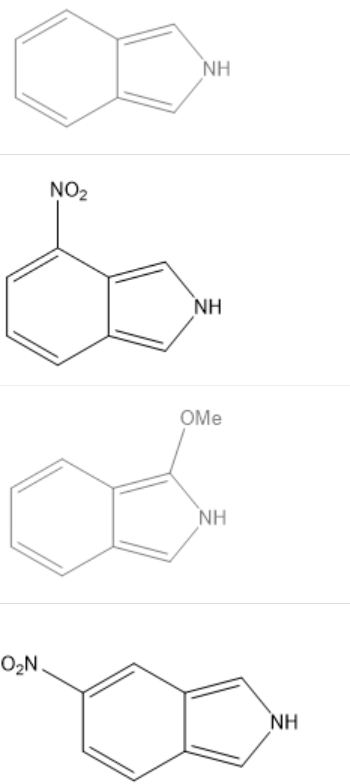
All of the following are common organic solvents. Identify the polar molecules from the list below.
Acetone (CH3COCH3)
Ethanol (CH3CH2OH)
Methylene chloride (CH2Cl2)
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
Toluene (C6H5CH3)
1, 2 and 3 only
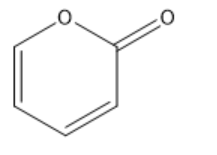
Consider all resonance patterns and all delocalized electrons in the molecule, which one is the best resonance hybrid of this molecule?
If HA has a pKa of 5 and HB has a pKa of 10, what is correct about the equilibrium and equilibrium constant about the following acid-base reaction?
HA + B- <-> A- + HB
-The equilibrium will favor the reactant side because the reactants are weaker acids/bases.
-The equilibrium will favor the products side because the products are weaker acids/bases.
-The equilibrium will favor the reactant side because the reactants are stronger acids/bases.
-The equilibrium will favor the products side because the products are stronger acids/bases.
The equilibrium will favor the products side because the products are weaker acids/bases.
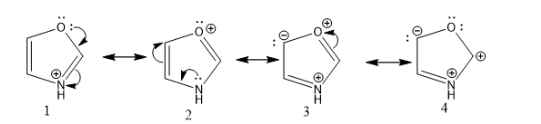
What is the proper ranking of significance of those 4 resonance structures (from most to least significant)?
1 > 2 > 3 > 4
Identify the structure that shows the correct placement of all lone pairs for the compound illustrated below.
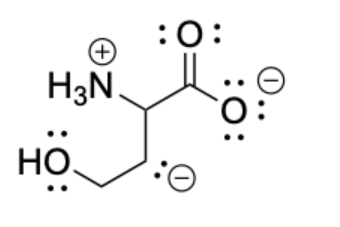
1&4