Micro Problems I got wrong on exam
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
3) Rebecca likes to read in her spare time. If not reading, Rebecca also likes to do yoga, take walks on the beach, go wine tasting, and text with friends. Suppose that today she only has time for one of those activities, and suppose that if she reads, Rebecca will get 50 units of satisfaction ("utils"). She will get 30 utils from doing yoga, 40 utils walking on the beach, 25 utils wine tasting, and 35 utils texting with friend:
Based on this information, today we expect that Rebecca will
A) walk on the beach.
B) text with friends.
C) do yoga.
D) read.
D) read.
5) Which of the following is a microeconomic statement?
A) The real domestic output increased by 1.6 percent last year.
B) Unemployment was 5.2 percent of the labor force last year.
C) The price of smartphones declined 2.8 percent last year.
D) The general price level increased by 1.1 percent last year.
C) The price of smartphones declined 2.8 percent last year.
6) Matt observes that "there is a high correlation between educational attainment and the level of income." Jean concurs and adds that "high school graduates should all proceed to college."
A) Both Matt's and Jean's statements are positive. -
B) Both Mat's and Jean's statements are normative.
C) Matt's statement is normative, while Jean's statement is positive,
D) Matt's statement is positive, while Jean's statement is normative.
D) Matt's statement is positive, while Jean's statement is normative.
8) Assume the price of product Y (the quantity of which is on the vertical axis) is $15 and the price of product X (the quantity of which is on the horizontal axis) is $3. Also assume that money income is $60. The absolute value of the slope of the resulting budget line is
A) 5.
B) 1/5.
C) 4.
D) 20.
B) 1/5.
20) Which of the following statements is an example of the post hoe fallacy?
A) "It's raining today because I just washed my car."
B) “If it’s good for an individual to save more, it’s therefore good if we all save more.”
C) "Anyone advocating for more government regulation is a socialist."
D) 'Daily temperatures and ice cream purchases are positively related."
A) "It's raining today because I just washed my car."
23) Human specialization- the division of labor - enhances productivity and efficiency by
A) allowing workers to take advantage of existing differences in their abilities and skills.
B) avoiding the time loss involved in shifting from one production task to another.
C) allowing workers to develop skills by working on one, or a limited number, of tasks.
D) all of the means identified in the other answers.
D) all of the means identified in the other answers.
24) If competitive industry A is is experiencing substantial economic losses, output will
A) fall in industry A as new firms enter the industry.
B) fall in industry A as firms exit the industry.
C) expand in industry A as more resources flow into the industry.
D) expand in industry A, but no new firms will enter the industry.
B) fall in industry A as firms exit the industry.
28) In a competitive market economy, firms select the least-cost production technique because
(A) such choices will result in full employment of available resources.
B) to do so will maximize the firms' profits.
C) this will prevent new firms from entering the industry.
D) "dollar voting" by consumers mandates such a choice.
B) to do so will maximize the firms' profits.
30) In the product market,
A) the price of land is determined.
B) resources flow to households.
C) businesses earn revenue from selling goods and services.
D) resources flow to businesses.
C) businesses earn revenue from selling goods and services.
***41) A demand curve
A) it promotes an efficient allocation of resources.
B) it leads to equality in the distribution of income.
C) it provides incentives for greater production and higher incomes.
D) it emphasizes the freedom to pursue self-interest.
A) it promotes an efficient allocation of resources.
42) Which of the following statements is correct?
A) An increase in the price of C will decrease the demand for complementary product D.
B) A decrease in income will decrease the demand for an inferior good.
C) An increase in income will reduce the demand for a normal good.
D) decline in the price of X will increase the demand for substitute product Y.
A) An increase in the price of C will decrease the demand for complementary product D.
53) The idea of the Law of Demand, as applied to electric cars, assumes which of the following to be constant?
A) price of electric cars
B) price of gasoline cars
C) quantity of electric cars demanded by buyers
D) how much sellers are charging customers for electric cars
B) price of gasoline cars
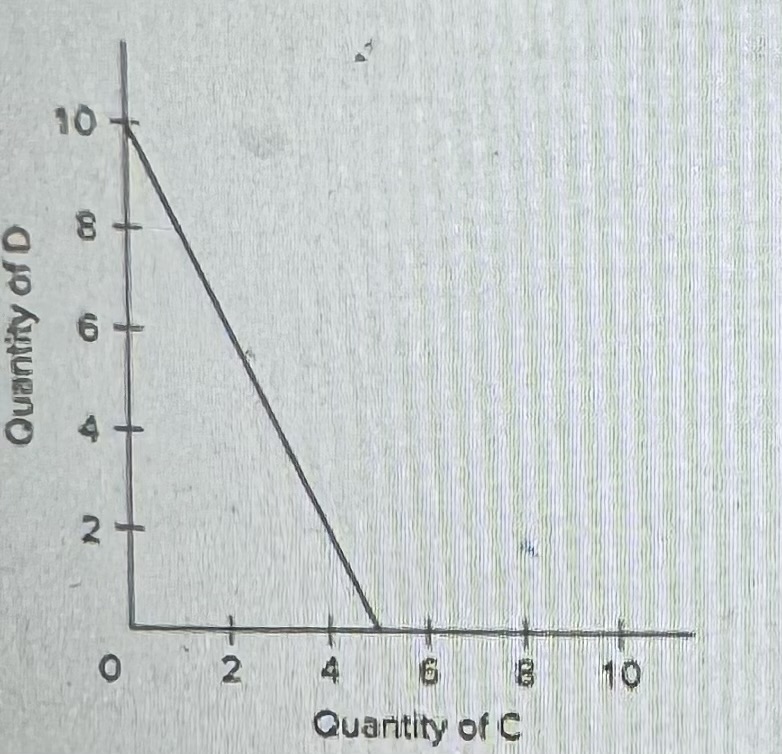
Refer to the diagram. Technological advance that improves the ability to produce capital goods but not consumer goods is shown by the shift of the production possibilities curve from AB to
A) CD.
B) ВЕ.
C) AF.
D) GH.
B) BE.
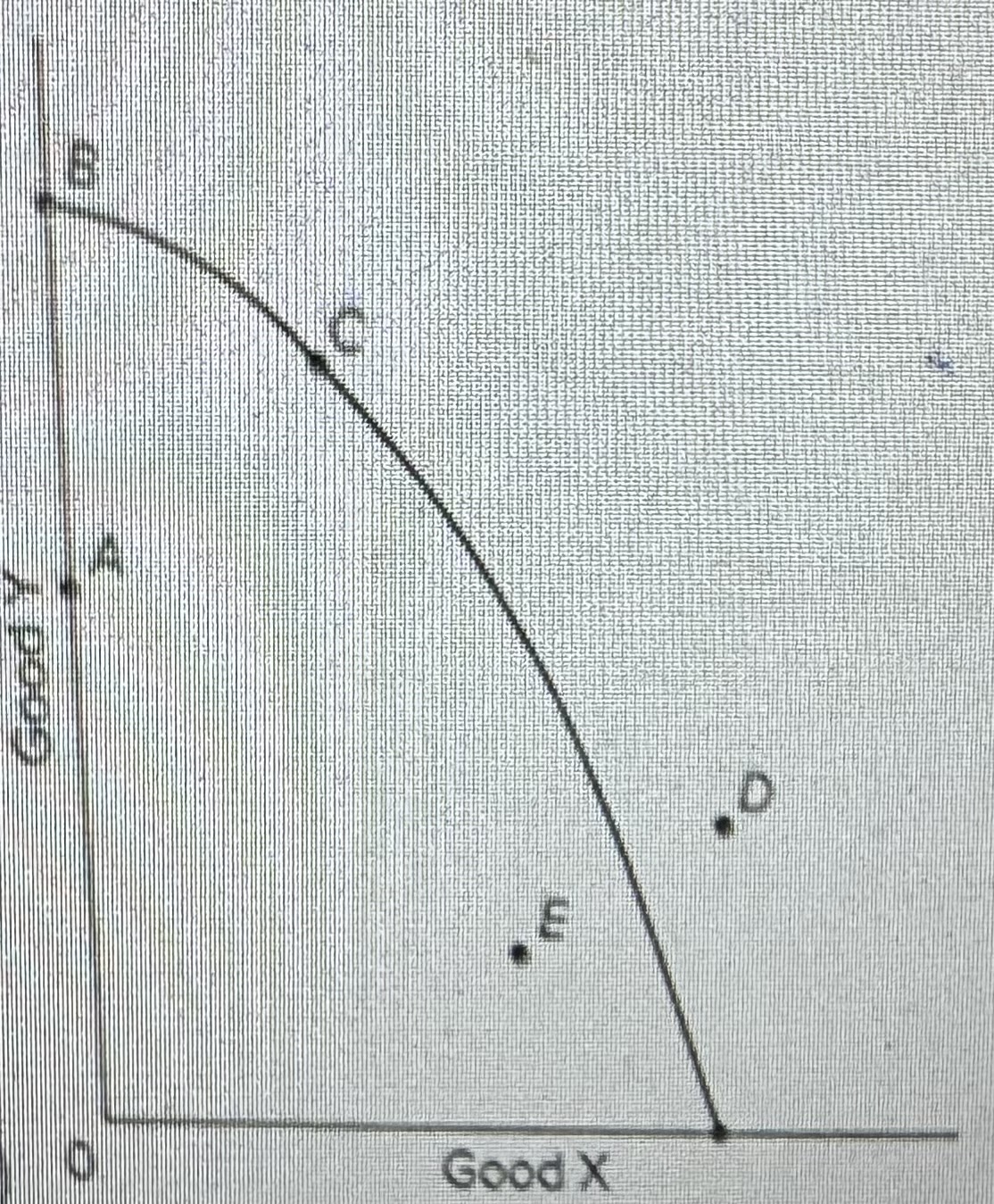
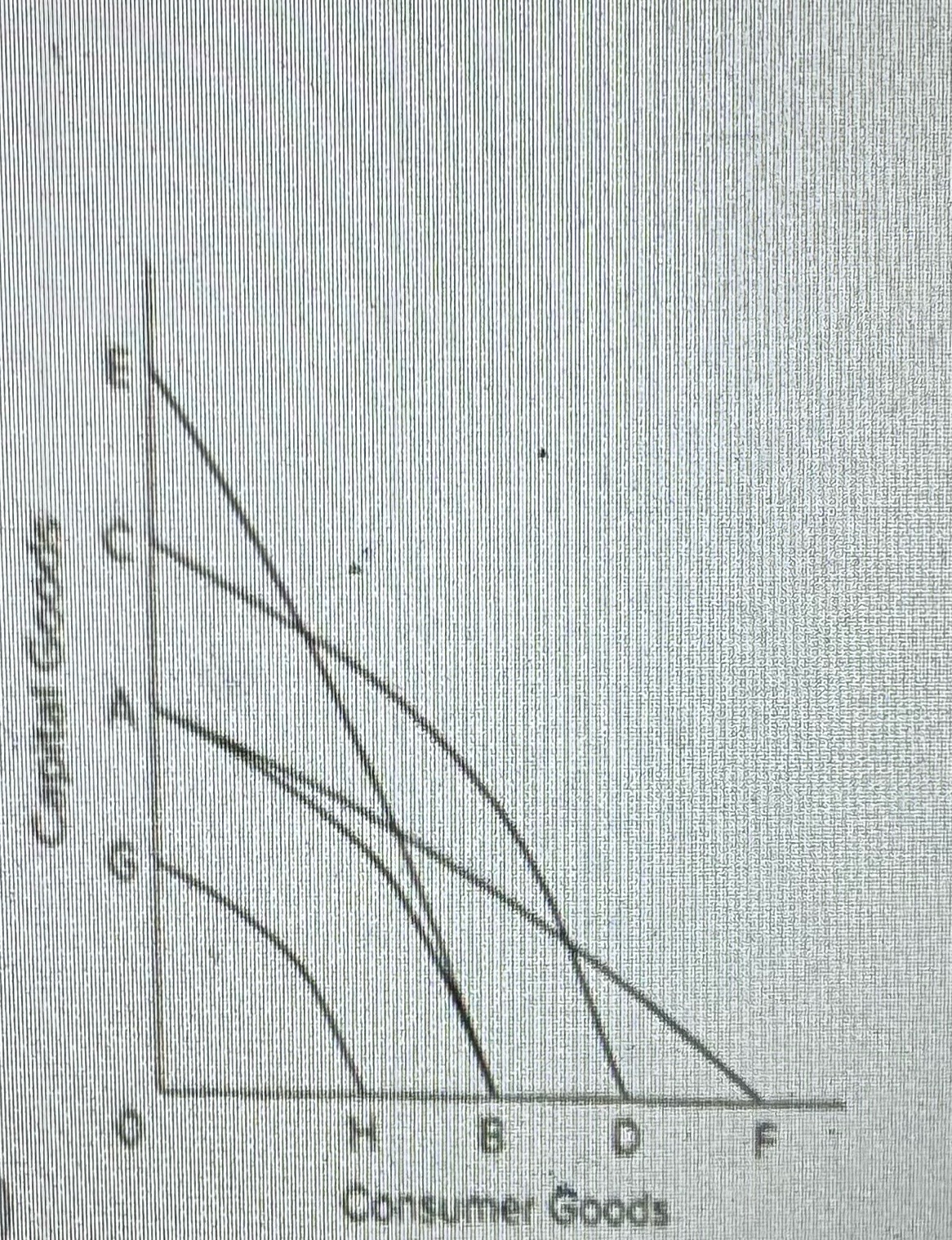
Refer to the provided graph. Which of the following movements wendid indicate economic growth?
A) from point A to point C
B) from point B to point C
C)from point A to point E
D)from point C to point D
D)from point C to point D
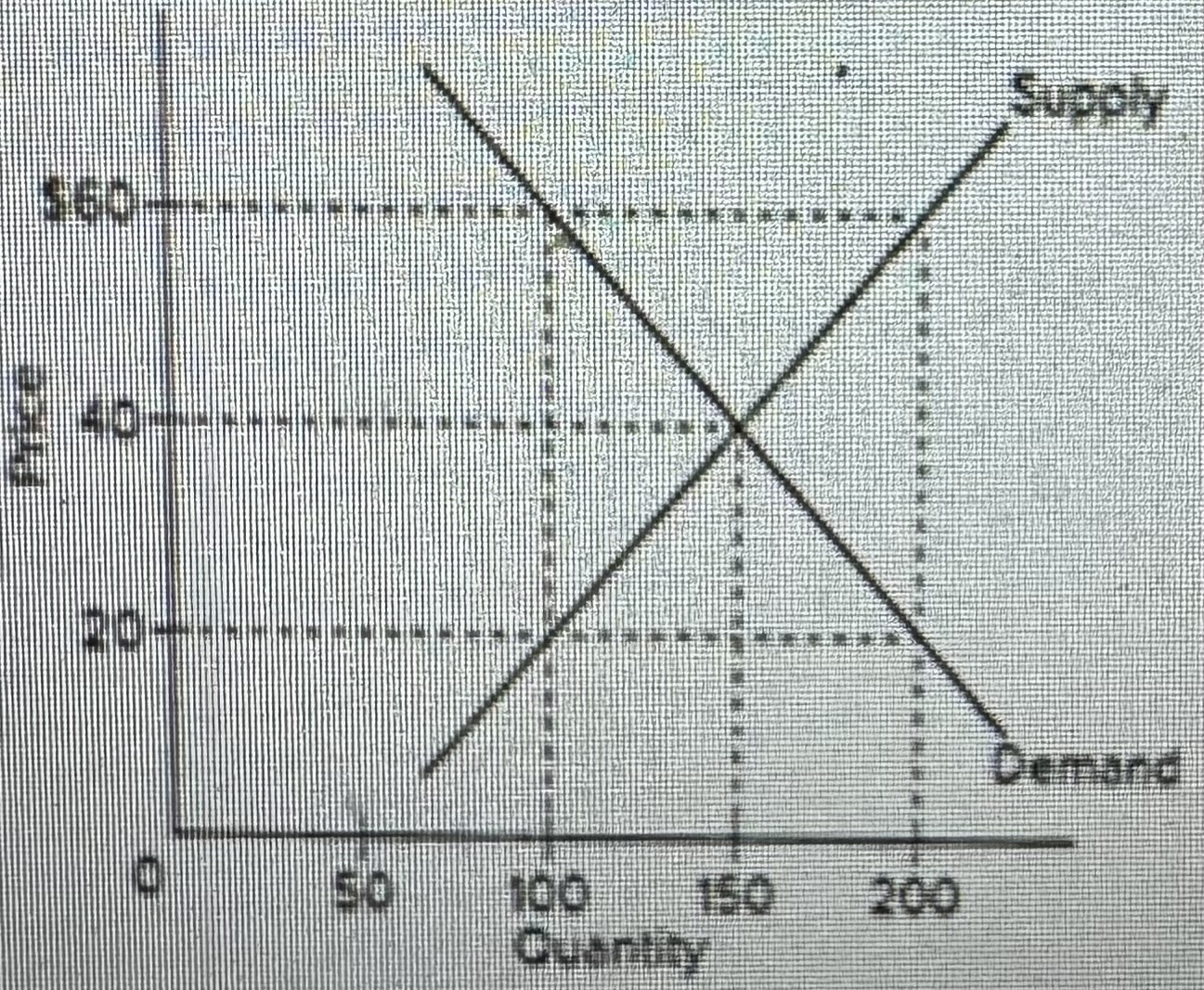
Refer to the diagram. The highest price that buyers will be willing and able to pay for 100 units of this product is
A) $30.
B) $60.
C) $40.
D) $20.
B) $60.
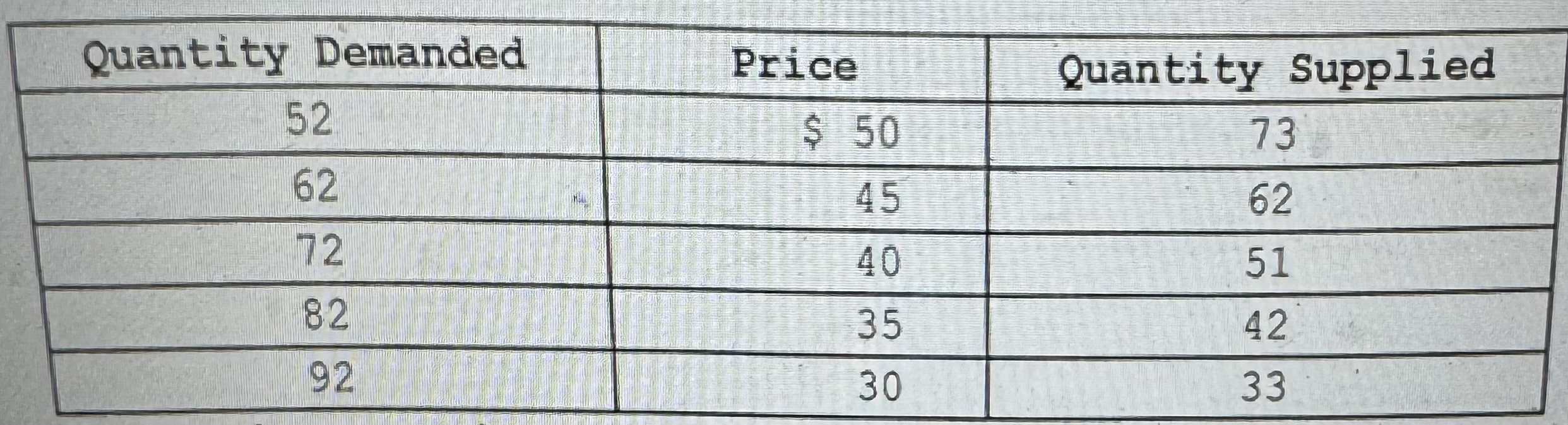
In this market, economists would call a goverment-set minimum price of $50 a(n)
A)price ceiling.
B)price floor.
C)equilibrium price.
D)fair price.
B)price floor.
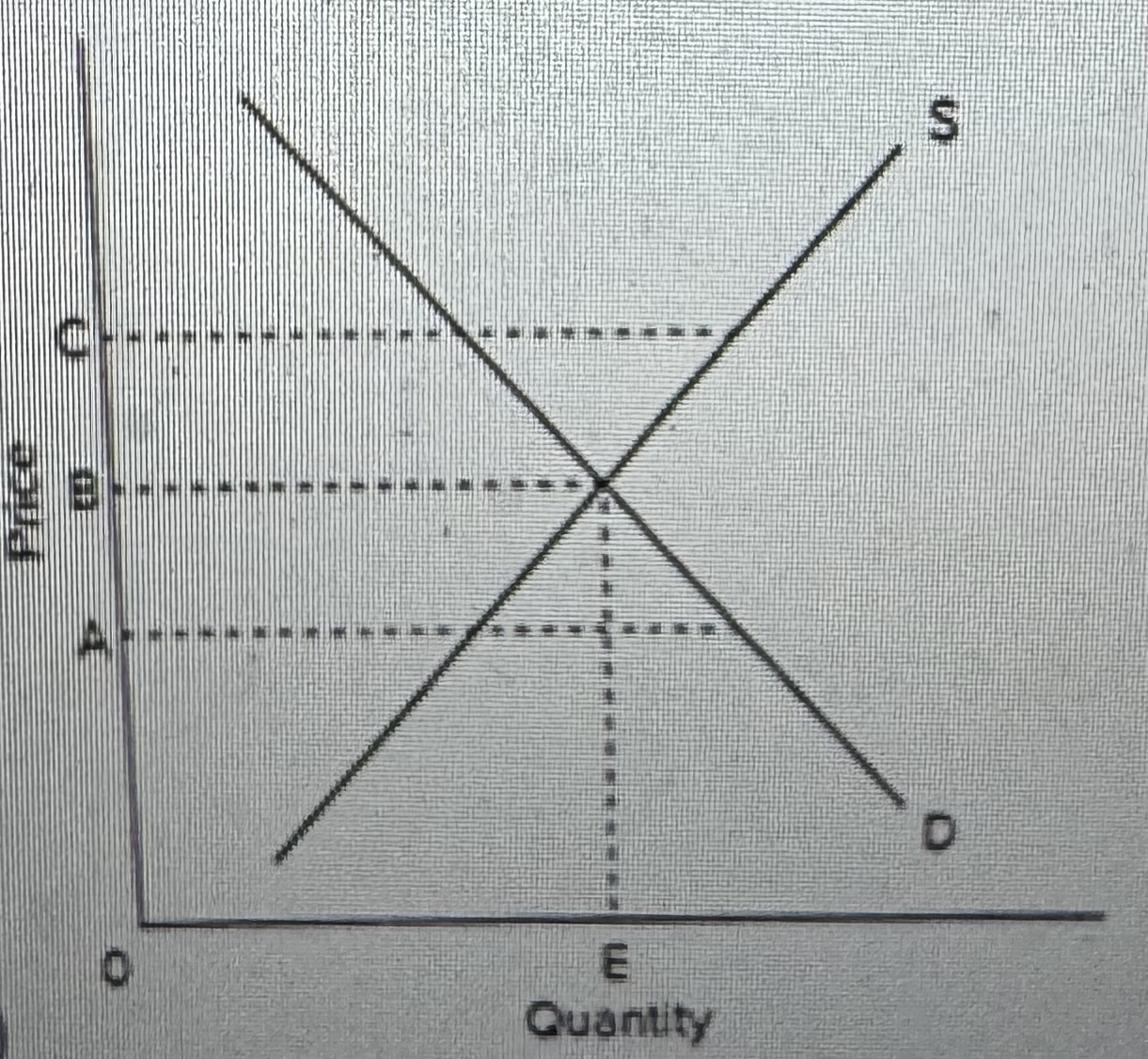
Refer to the diagram. A goyernment price support program to aid farmers is best illustrated by
A) quantity E.
B) price C.
C) price A.
D) price B.
D) price B.
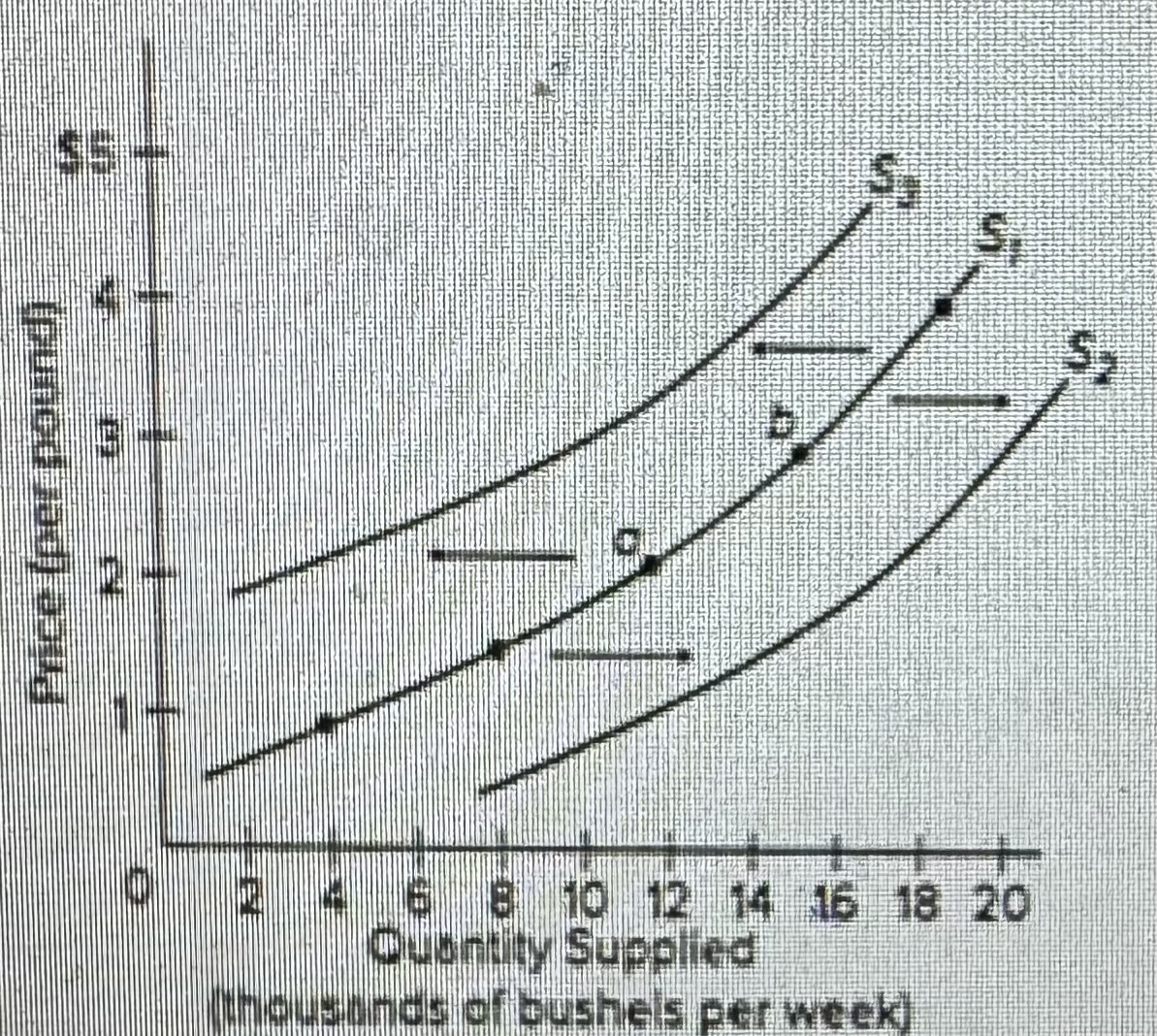
Refer to the diagram above, which shows three supply curves for corn. Which of the following would cause the supply of corn to shift from S1 to S3?
a decrease in the cost of equipment used in corn farming
B) an increase in the price of soybeans
C) a decrease in the price of corn
D) an increase in the number of acres of farmland allocated to corn
B) an increase in the price of soybeans
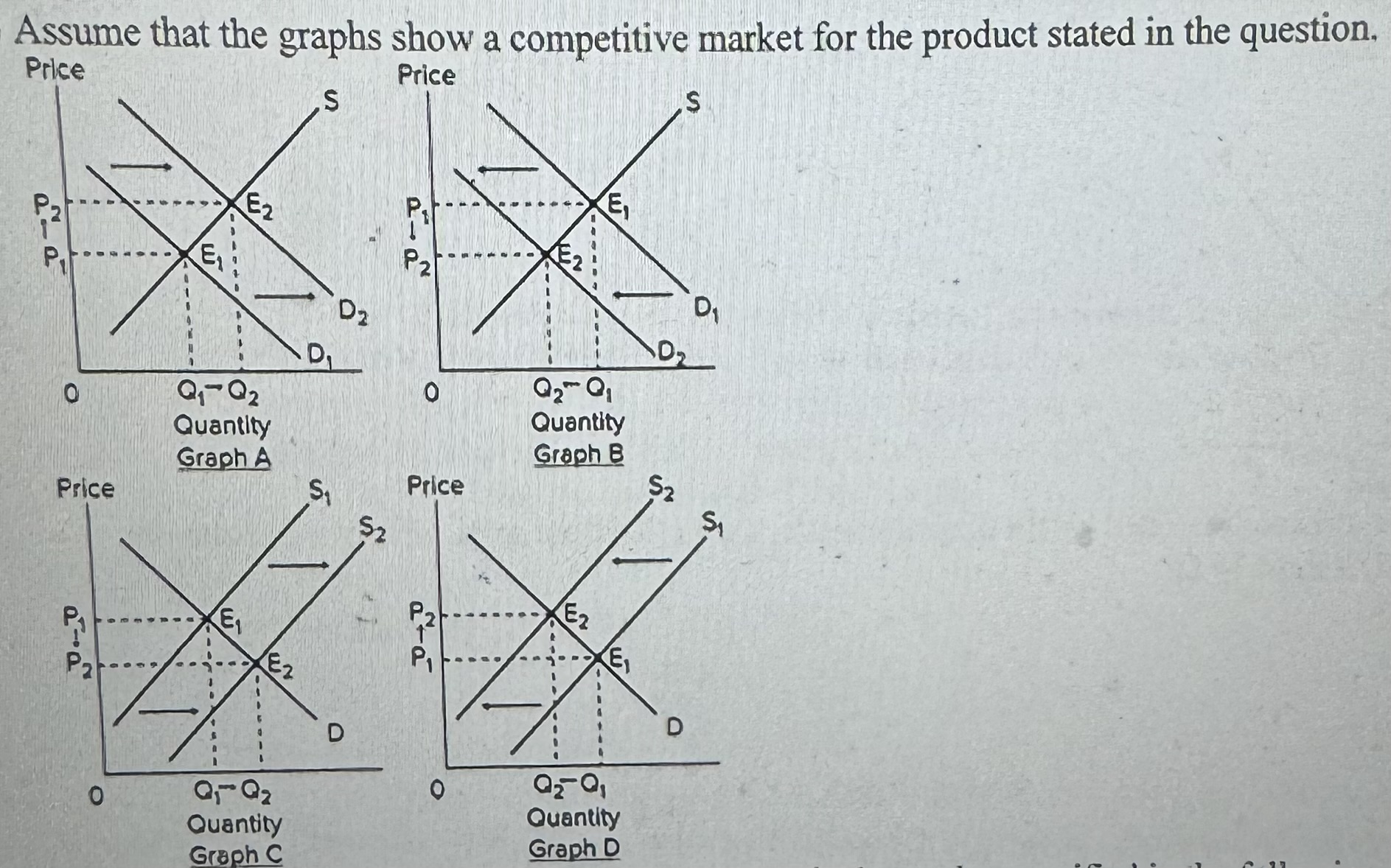
Select the graph above that best shows the change in the market specified in the following situation: the market for leather coats, when leather coats become less fashionable among young consumers.
A) Graph A
B) Graph B
C) Graph C
D) Graph D
B) Graph B
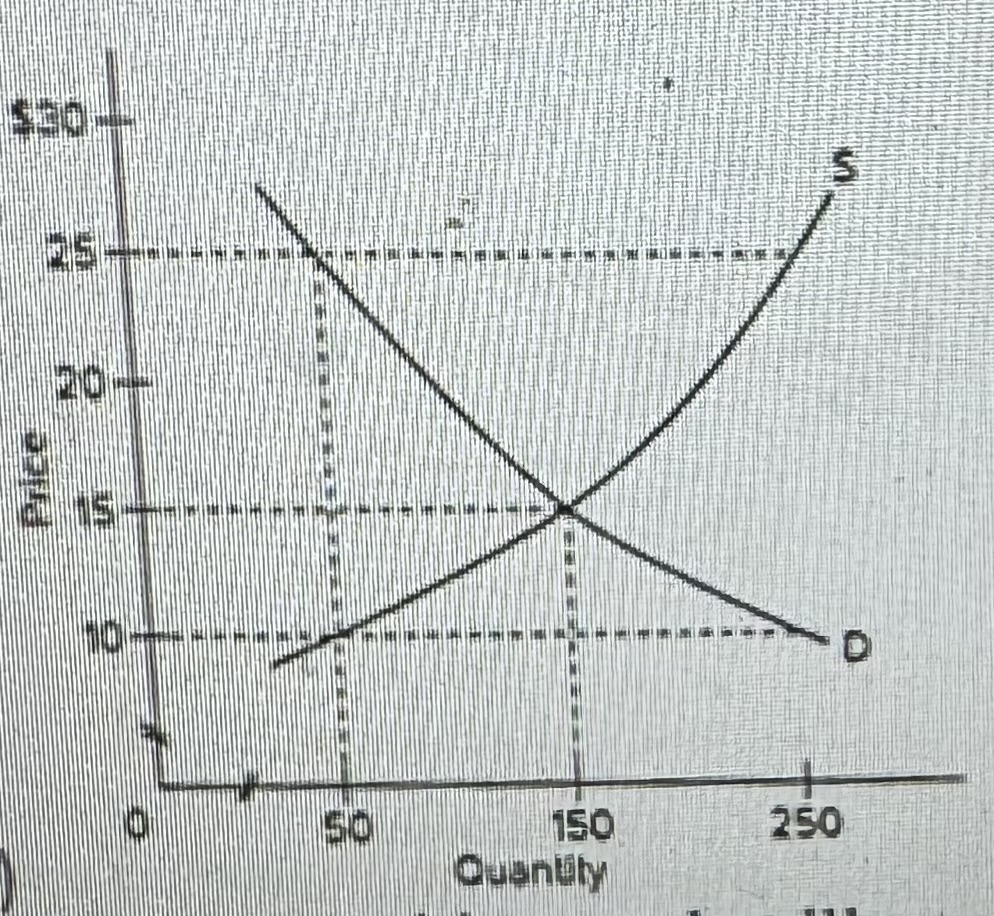
In a competitive market illustrated by the diagram above, for a price floor to be eflective and alter the market situation, it must be set
A) at $15.
B) below $15.
C) above $15.
D) at $10.
C) above $15.
2) True or False: The private information held by buyers may put them in a position to take advantage of the sellers.
True
7) True or False: With diminishing marginal utility, if a consumer reduces her consumption of a good, then her marginal utility from that good would increase.
True
3) True or False: When the government bails out failing banks, it creates a moral hazard problem; but it bails out homeowners who are defaulting on their mortgages, there is no moral hazard.
False
13) Economic efficiency
A) consists of productive efficiency and allocative efficiency.
B) is where the lowest-cost production occurs but not necessarily where MB = МС.
C) is where MB = MC but not necessarily where the lowest-cost production occurs.
D) is never found in competitive markets.
A) consists of productive efficiency and allocative efficiency.
14) (Consider This) According to the Coase theorem,
A) government should levy excise taxes on firms that generate spillover or external costs.
B) taxes should be levied such that they change private behavior as little as possible.
C) private individuals can often negotiate their own resolution of externality problems, without the need for government intervention.
D) private firms should not provide public goods
C) private individuals can often negotiate their own resolution of externality problems, without the need for government intervention.
If a good that generates positive externalities was produced and priced to take into account these spillover benefits, then its
A) price and output would increase.
B) output would increase, but price would remain constant.
C) price would increase and output would decrease.
D) price would increase, but output would remain constant.
A) price and output would increase.
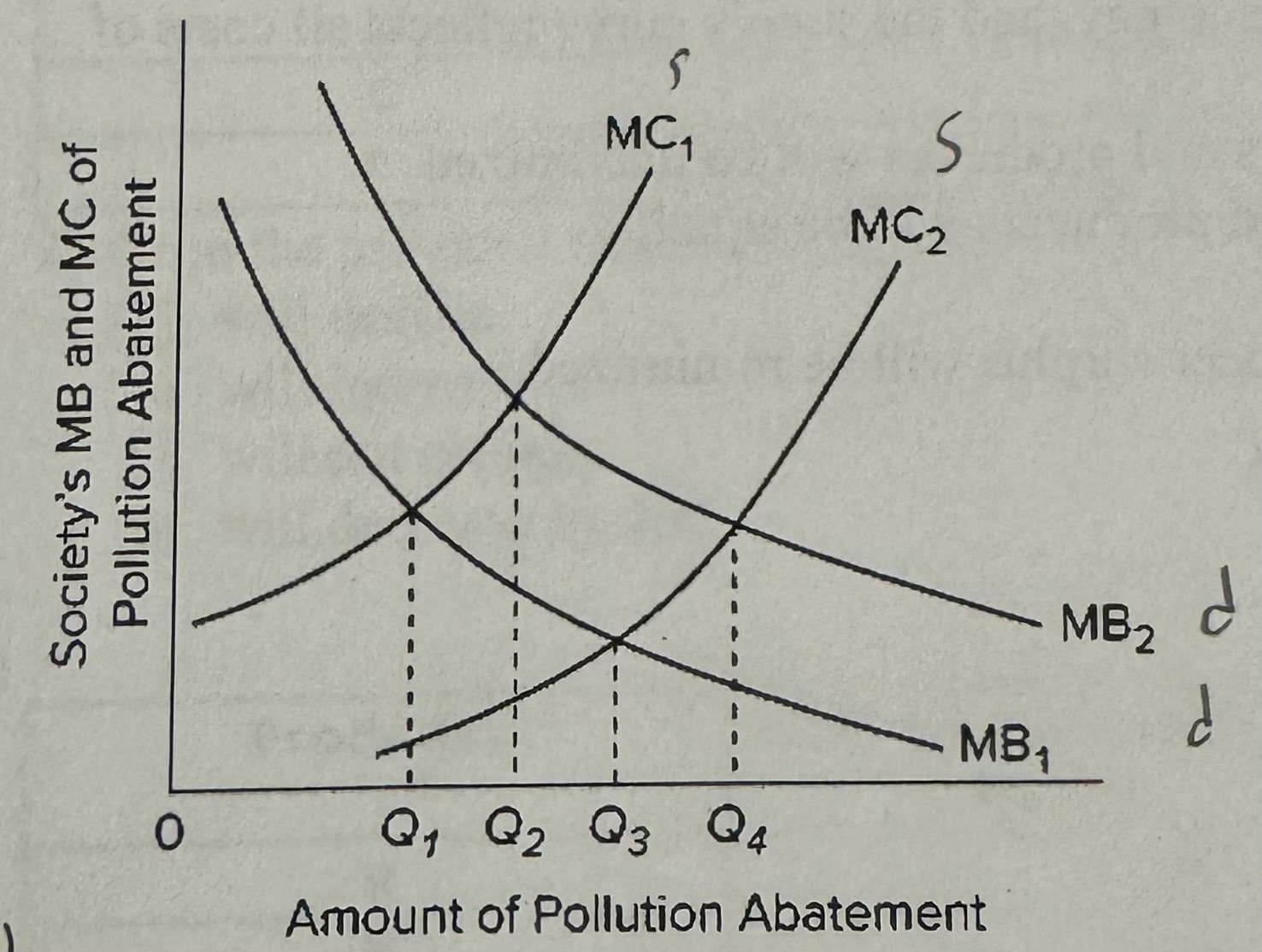
The MC curves in the diagram slope upward because of the law of
A) demand.
B) conservation of matter and energy.
C) diminishing marginal utility.
D) increasing opportunity costs.
D) increasing opportunity costs.
21) Some sellers of used cars provide warranties to buyers, with the aim of reassuring buyers that the car is of good quality. These warranties help reduce the chance of what occurring?
A) negative externalities
B) adverse selection
C) spillover benefits
D) moral hazard
B) adverse selection
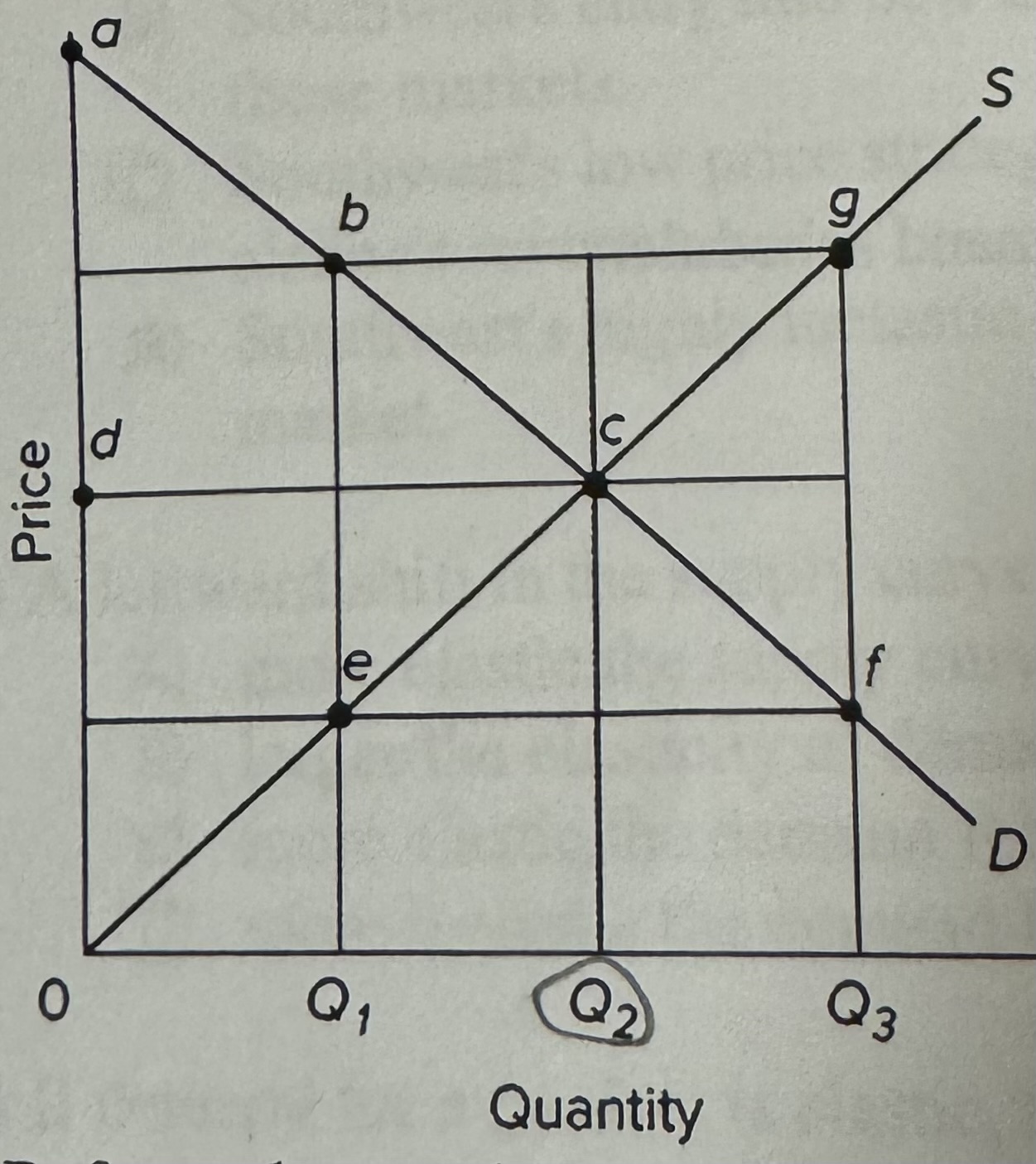
Refer to the provided graph of a competitive market. If the output level is 2, then there will be
A) greater marginal benefits than marginal costs of the product.
B) allocative efficiency but not productive efficiency.
C) an overallocation of resources to the production of the product.
D) maximum combined consumer and producer surplus.
D) maximum combined consumer and producer surplus.
25) It has been proposed that a government agency be charged with the task of determining the amount of pollution that the atmosphere (or a body of water) can safely absorb, establish "permits" to this limited amount of pollution, and sell those limited amount of permits to firms. The firms can then buy and sell these permits among themselves later. This approach is known as the
A) taxes and subsidies system.
B) cap-and-trade system.
C) property rights system
D) market and command system
B) cap-and-trade system.
29) What is the most likely effect of the development of rental movies and online movie streaming on the movie theater (or cinema) industry?
A)decreased costs of producing movies
B) increased demand for movie theater tickets
C) movie theater tickets become an inferior good
D) increased price elasticity of demand for movie tickets
D) increased price elasticity of demand for movie tickets
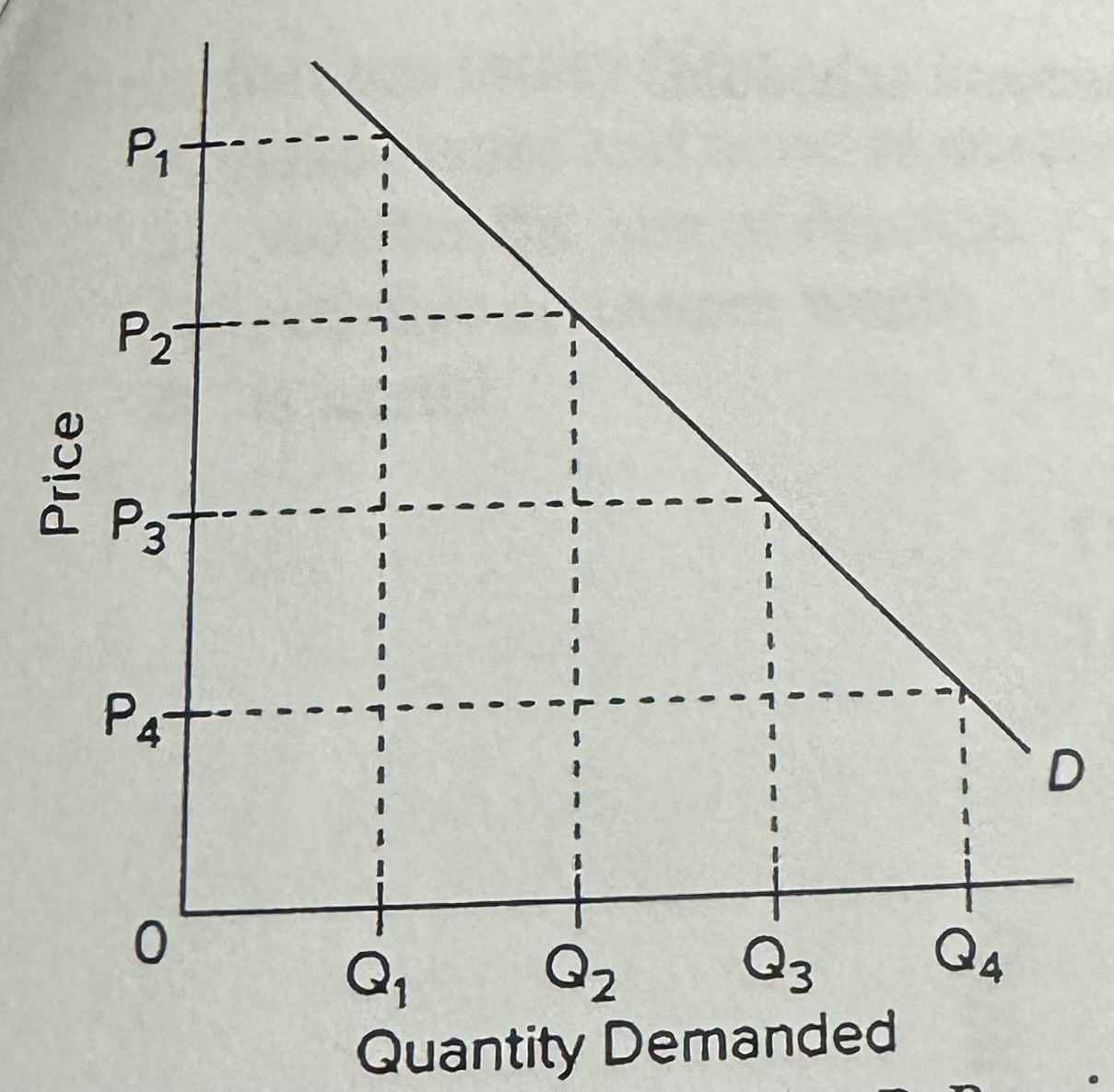
Refer to the diagram. In the P3P4 price range, demand is
A) of unit elasticity.
B) relatively inelastic.
C)relatively elastic.
D) perfectly elastic.
B) relatively inelastic.
40) The supply of product X is elastic if the price of X rises by
A) 8 percent and quantity supplied rises by 8 percent.
B) 10 percent and quantity supplied remains the same.
C) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
D) 7 percent and quantity supplied rises by 5 percent.
C) 5 percent and quantity supplied rises by 7 percent.
53) If total utility has reached a maximum level, and assuming that diminishing marginal utility already applies, then what will happen as the consumer consumes additional units of the product?
A) Marginal utility of the additional units will be greater than zero.
B) Total utility will turn negative.
C) Marginal utility of the additional units will turn negative.
D) Total utility will increase at a diminishing rate.
C) Marginal utility of the additional units will turn negative.
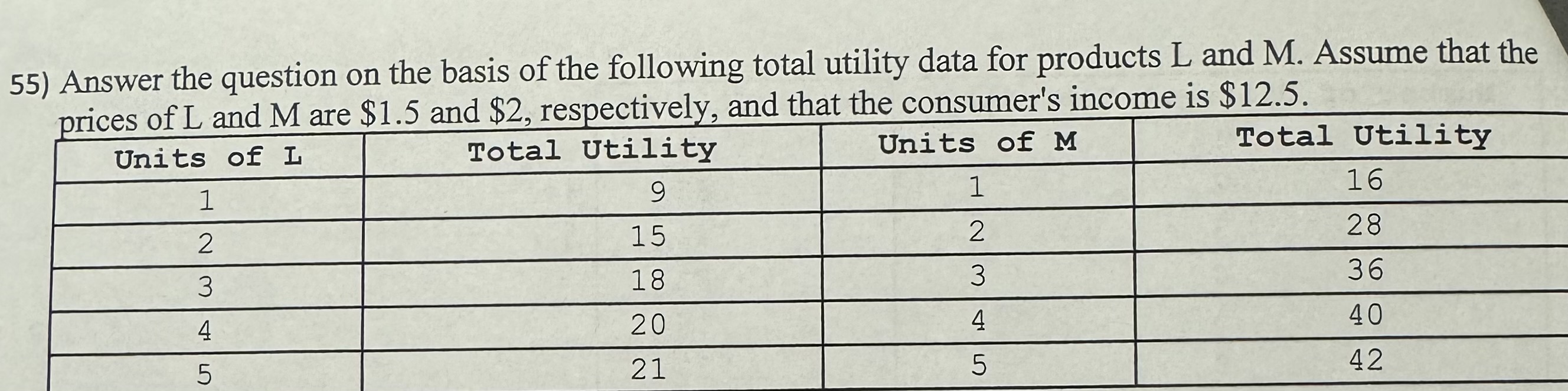
What level of total utility does the rational consumer realize in equilibrium?
A) 49 utils
B) 162 utils
C) 46 utils
D) 58 utils
D) 58 utils
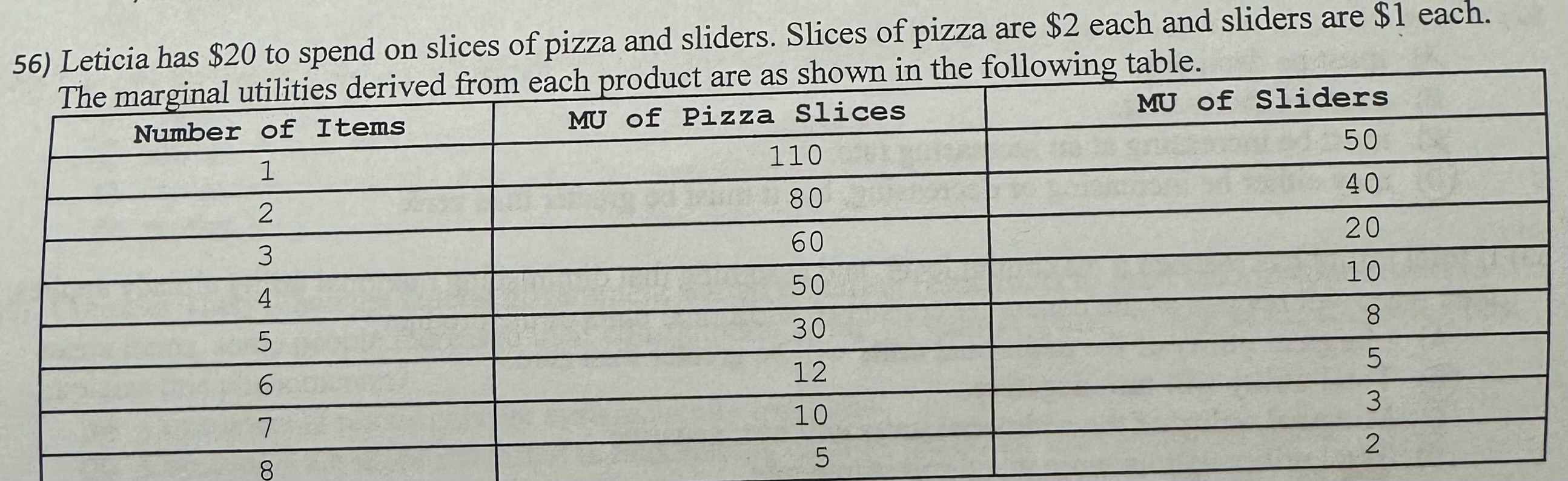
Which combination would give Leticia the maximum utility out of spending $20?
A) 7 pizza slices and 8 sliders
B) 6 pizza slices and 8 sliders
C) 7 pizza slices and 6 sliders
D) 8 pizza slices and 4 sliders
C) 7 pizza slices and 6 sliders
True or False: Competitive firms are price takers largely because of intensive advertising by their competitors.
False
True or False: if a purely competitive firm is producing a level of output greater than its profit maximizing output, then its profits must be negative.
False.
12) If economic profits in an industry are zero and implicit costs are greater than zero, then
A) resources will move out of the industry.
B) there will be no production in the short run.
C)accounting profits are greater than zero.
D) new firms will enter the industry.
C)accounting profits are greater than zero.
Marginal product is
A) the change in total output attributable to the employment of one more worker.
B)the change in total revenue attributable to the employment of one more worker.
C)the change in total cost attributable to the employment of one more worker.
D) total product divided by the number of workers employed.
A) the change in total output attributable to the employment of one more worker.
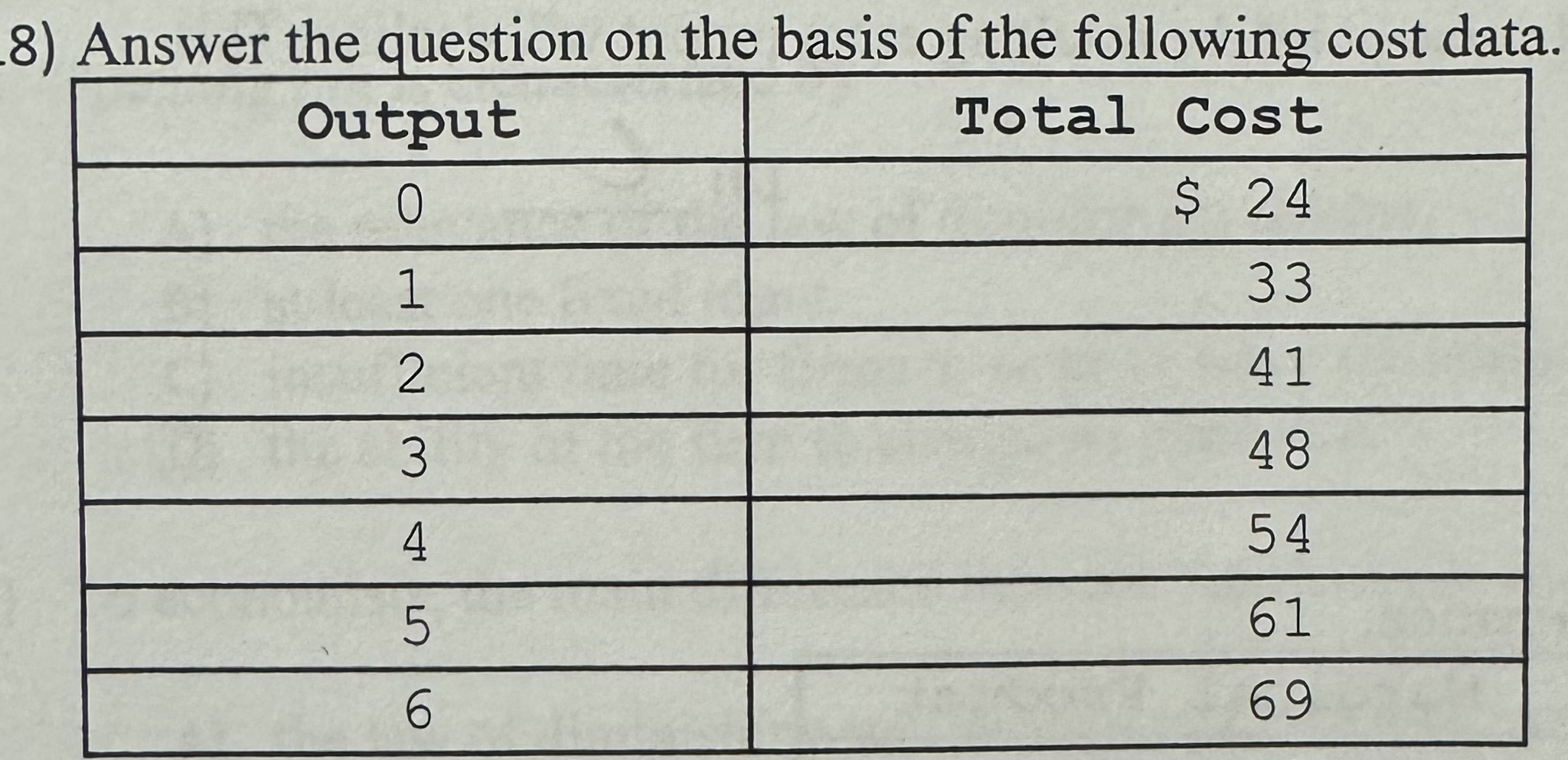
The average variable cost of producing 3 units of output is:
A) $8.
B) $24.
C) $16.
D) $12.
A) $8.
19) Answer the question on the basis of the following information.
TFC = Total Fixed Cost Q = Quantity of Output
MC = Marginal Cost P = Product Price
TVC = Total Variable Cost AVC = Average Variable Cost
AFC = Average Fixed Cost ATC = Average Total Cost
Total variable cost is
A) ATC × Q
B) (ATC - AFC) × Q
C) MC x Q
D) P x AVC
B) (ATC - AFC) × Q
20) Average fixed costs for a given level of output can be determined graphically by
A) summing the marginal costs of any number of units of output and dividing the sum by that output.
B) the vertical distance between TC and TVC.
C) the vertical distance between AVC and MC.
D) the vertical distance between ATC and AVC.
D) the vertical distance between ATC and AVC.
22) When producing 8 units of output, average fixed cost is $12.50 and average variable cost is $81.25. Total cost at thi output level is
A) $93.75.
B) $97.78.
C) $750.
D) $880.
C) $750.
(Last Word) While the restaurant, hotel, and rental ear industries all struggled as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic which was best able to avoid firms shutting down?
A) The restaurant industry.
B) The hotel industry.
C) The rental car industry.
D) All three industries suffered similar rates of permanent closure.
C) The rental car industry.
28) (Last Word) Which of the following is most accurate about the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the restaurant, hotel, and rental car industries?
A) Variable costs dropped to zero as firms shut down and laid off most of their workforce
B) Fixed costs dropped significantly as firms stopped producing during lockdowns.
C) Revenue remained relatively stable during the pandemic.
D All three industries saw numerous firms leave the market, each seeing a reduction of about 20 percent of the number of firms from pre-pandemic levels.
A) Variable costs dropped to zero as firms shut down and laid off most of their workforce
35) The short-run supply curve of a purely competitive producer is based primarily on its
A) AVC curve.
B) ATC curve.
C) AFC curve.
D) MC curve.
B) ATC curve.
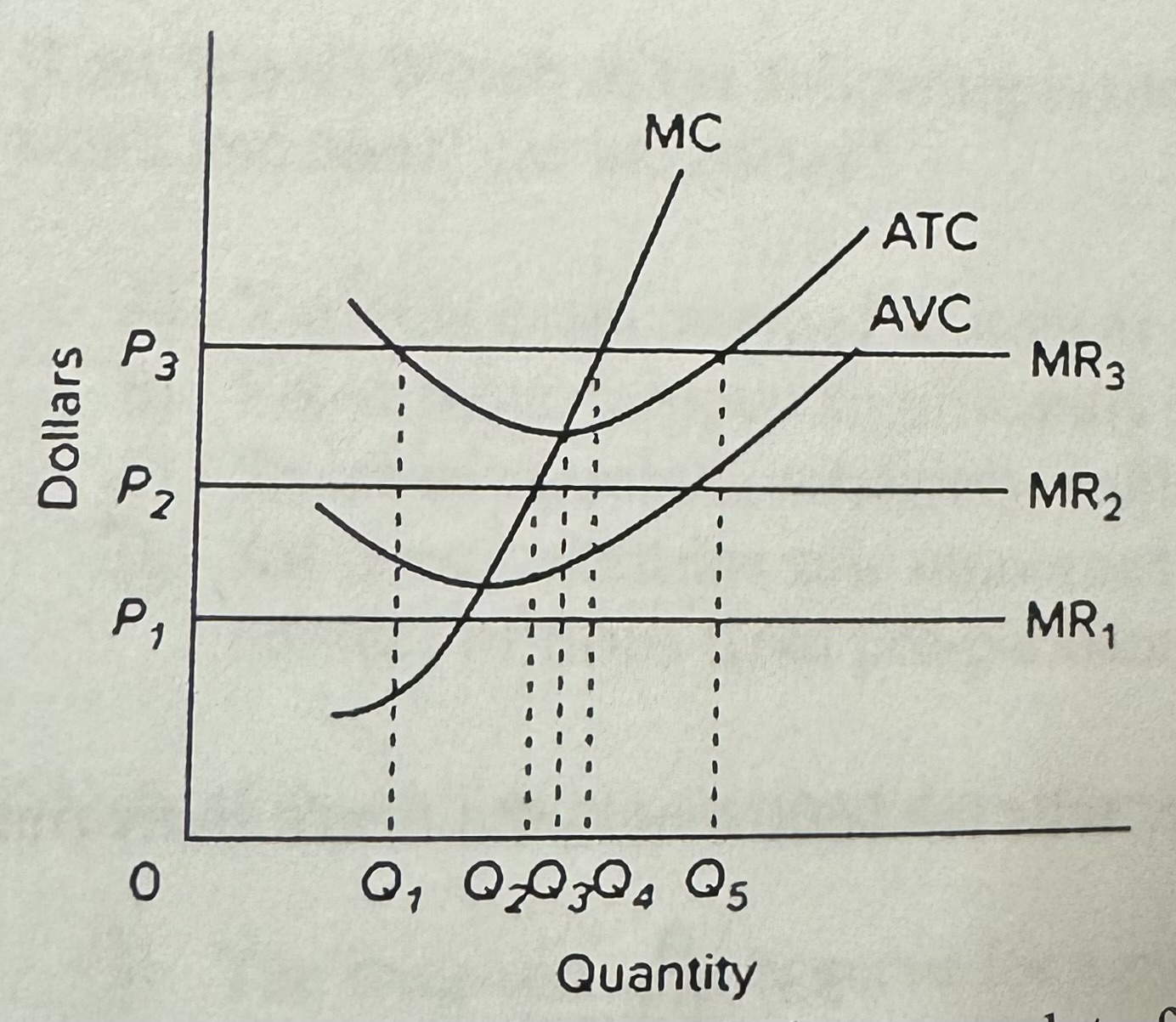
The provided graph gives short-run data for a firm. If the product price is P2, the firm will
A) close down to avoid a loss.
B) produce Q2 units and make an economic profit.
C) produce Q5 units and break even.
D) produce Q2 units and suffer a loss.
D) produce Q2 units and suffer a loss.
39) Long-run adjustments in purely competitive markets primarily take the form of
A) variations in the cost curves of different firms in the market.
B) entry or exit of firms in the market.
C) evolution of the market from a constant-cost to an increasing-cost industry.
D) product differentiation.
B) entry or exit of firms in the market.
40) Suppose losses cause industry X to contract and, as a result, the prices of relevant inputs decline. Industry X is
A) a constant-cost industry.
B) a decreasing-cost industry.
C) an increasing-cost industry.
D) encountering X-inefficiency.
C) an increasing-cost industry.
41) A long-run supply curve that is downward-sloping indicates that the firms' ATC curves
A) shift up when the industry expands.
B) shift down when the industry contracts.
C) shift down when the industry expands.
D) do not shift when the industry contracts.
C) shift down when the industry expands.
Barriers to entering an industry
A) encourage allocative efficiency.
B) encourage productive efficiency.
C) are the basis for monopoly.
D) apply only to purely monopolistic industries.
C) are the basis for monopoly.
51) A pure monopolist is selling 32 units at a price of $220. If the marginal revenue of the 3rd unit is $47, then the price of the 33rd unit
A) cannot be determined with the information given.
B) is less than $200.
C) is $200.
D) is $215.
D) is $215.
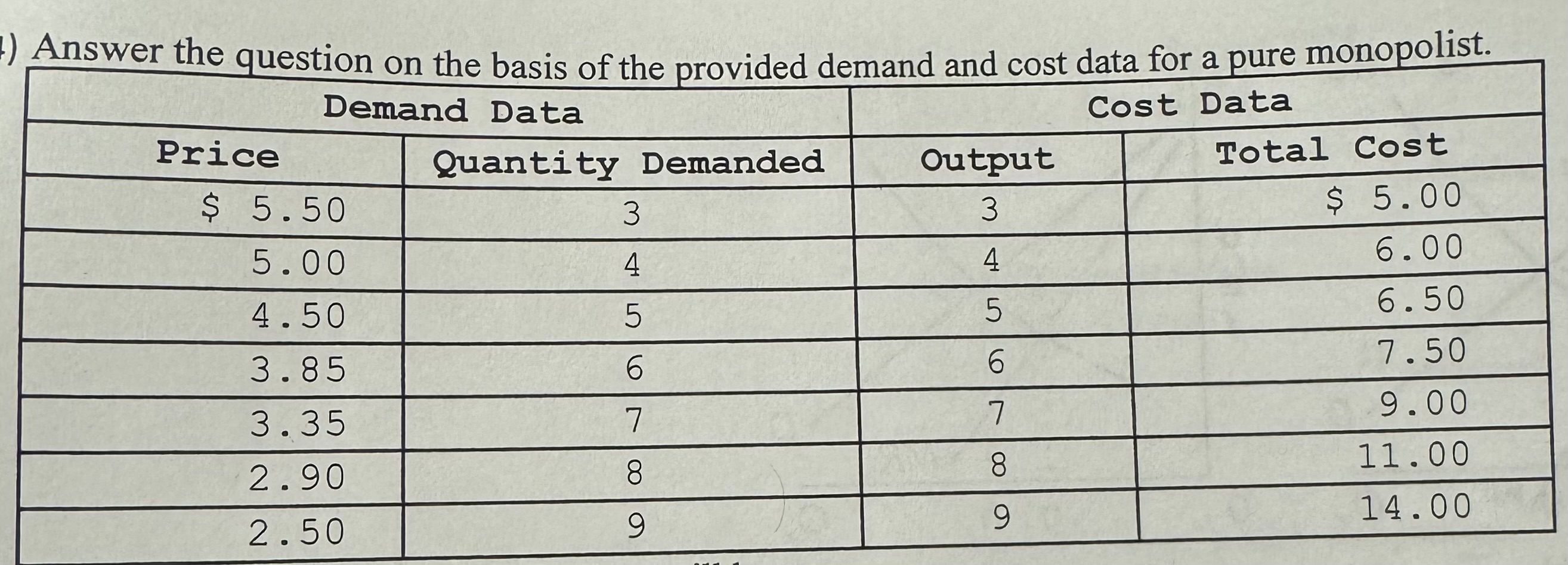
The profit maximizing level of output is
A) 4 units.
B) 7 units.
C) 6 units.
D) 5 units.
D) 5 units.
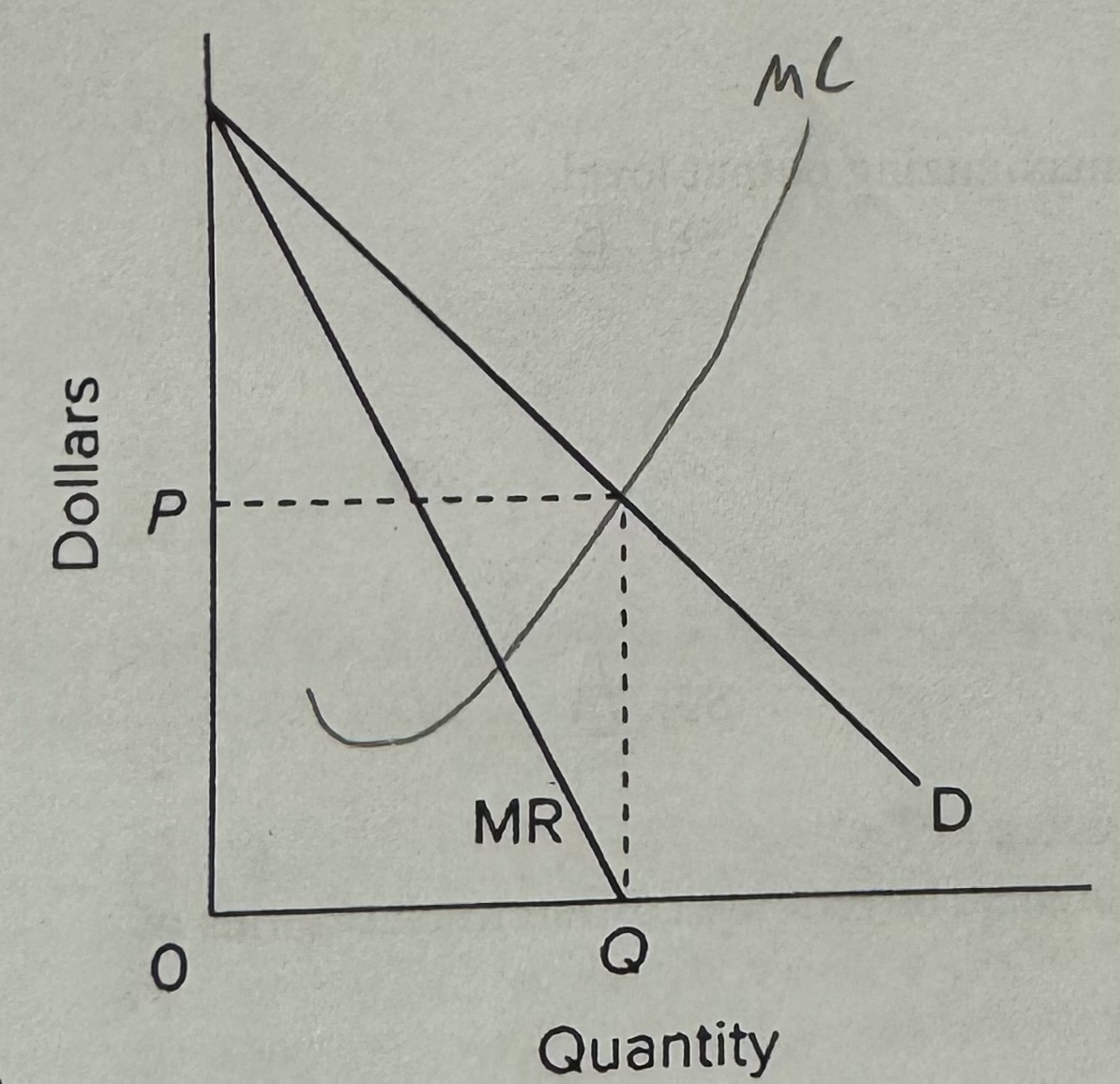
Assume a pure monopolist is charging price P and selling output Q, as shown on the diagram. On the basis of this information, we can say that
A) if marginal costs were somehow zero, the firm would be maximizing its profits.
B) if marginal costs were positive, the firm would increase profits by reducing price and selling more output.
C) the firm is producing where the price elasticity coefficient is less than one.
D) the firm is a " price taker."
A) if marginal costs were somehow zero, the firm would be maximizing its profits.
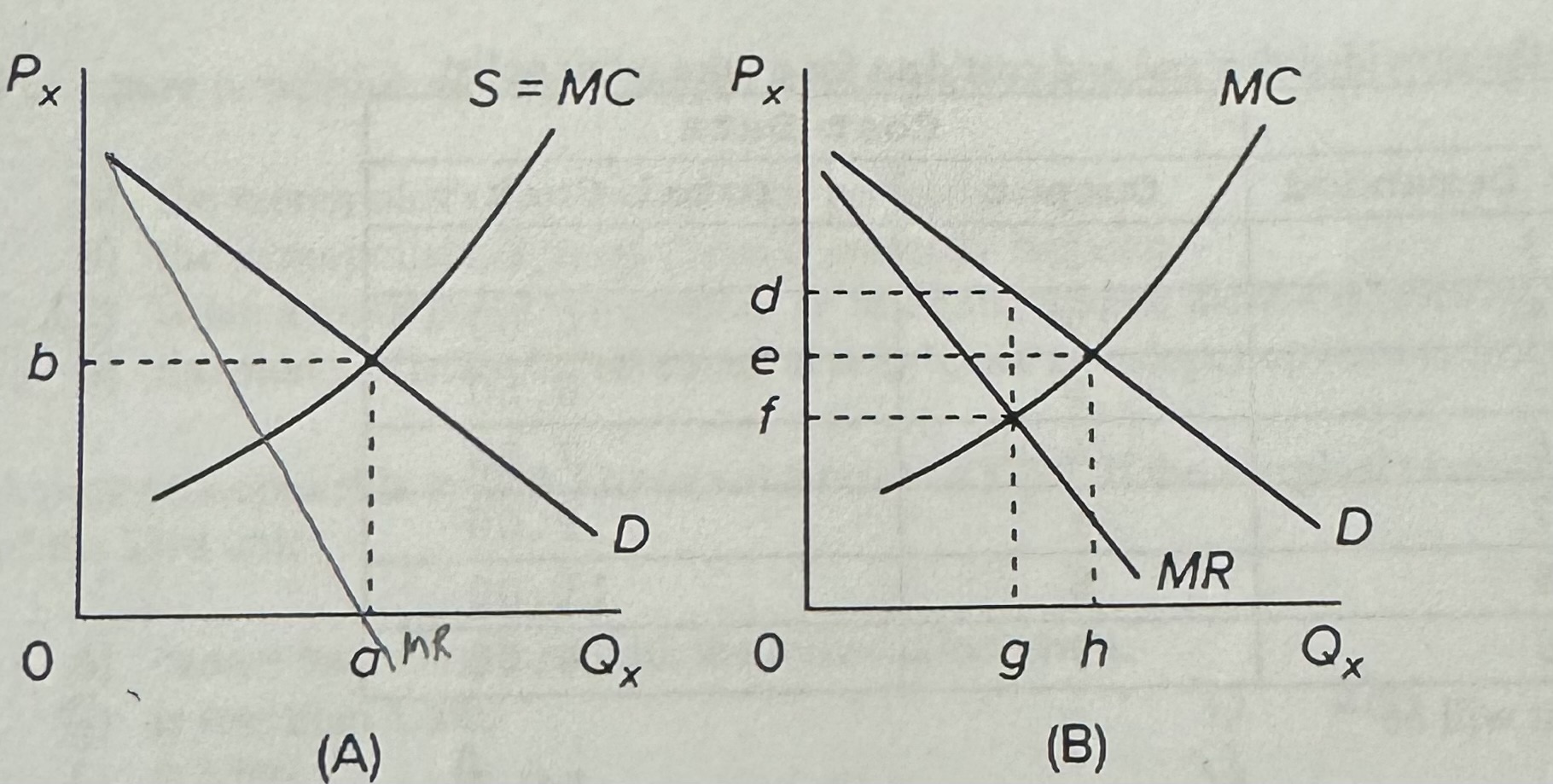
Refer to the diagrams, In which of the cases would we expect individual firms to achieve allocative efficieney?
A) both diagram A and B
B) neither diagram A nor B
C) diagram A only
D) diagram B only
C) diagram A only
58) Allocative inefficiency happens in a monopoly because at the profit-maximizing output level,
A) P > ATC.
B) P> MR.
C) Р > МС.
D) P> AVC.
C) Р > МС.
True or False: Of all U.S. firms, Disney spent the most on advertising in 2021.
False
True or False: The adoption of a limit-pricing strategy by oligopolists would tend to make the price of the product closer to marginal cost.
True
True or False: If an oligopolist's competitors follow its price cuts but ignore its price increases, the oligopolist would end up holding its price constant even if its marginal cost changes.
True
True or False: If an oligopolist's several rivals exactly match any price changes it initiates, the demand curve will be less elastic than if its price changes are ignored by its rivals.
True
True or False: The Celler-Kefauver Act made vertical mergers legal, provided each firm does not have more than 30 percent its relevant market.
False
9) Under monopolistic competition, entry to the industry is
A) completely free of barriers.
B) more difficult than under pure competition but not nearly as difficult as under pure monopoly.
C) more difficult than under pure monopoly.
D) blocked.
B) more difficult than under pure competition but not nearly as difficult as under pure monopoly.
18) Which industry would be best characterized as monopolistically competitive?
A) smartphone manufacturing
B) Internet-search sites
C) web design consulting
D) business cloud-computing services
C) web design consulting
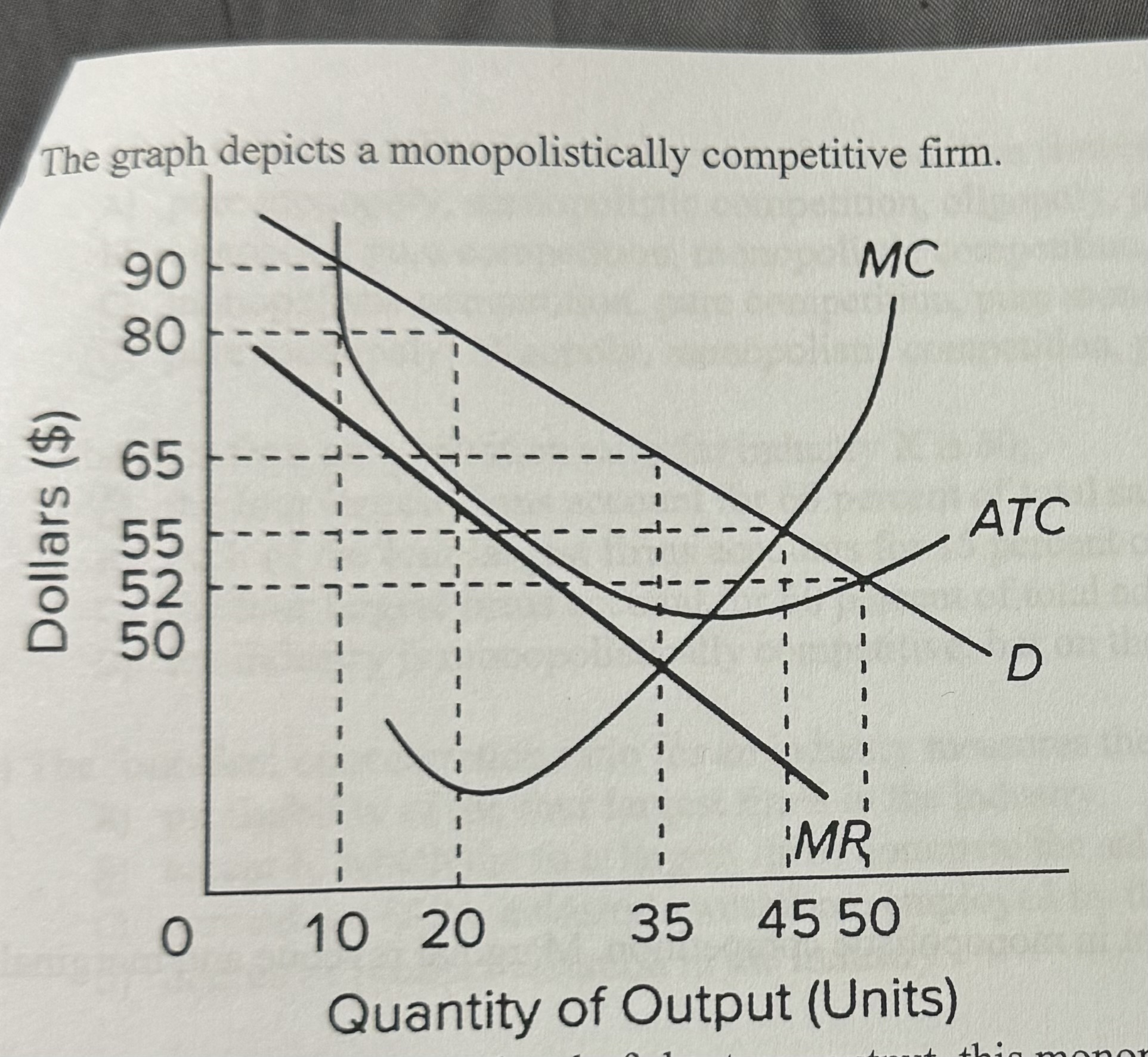
At the profit-maximizing level of short-run output, this monopolistically competitive firm will be making a profit of
A) $275.
B) $350.
C) $500.
D) $525.
D) $525.
37) Which statement about oligopoly is false?
A) Oligopolistic firms recognize their interdependence.
B) Prices in an oligopoly are predicted to fluctuate widely and
C) A few firms play an important role in the sale of a product.
D) One firm's behavior is a function of what its rivals do.
B) Prices in an oligopoly are predicted to fluctuate widely and
44) Which of the following terms would economists define as "government regulation of the conditions under which goods are produced, the physical characteristics of the goods that are produced, and the impact of production consumption on society?"
A) Antitrust policy.
B) Industrial regulation.
C) Social regulation.
D) Federal consumer policy.
C) Social regulation.
46) Situations where a director of one firm is also a board member of a competing firm is an example of
A) a tying contract.
B) an interlocking directorate.
C) a corporate merger.
D) a violation of the Wheeler-Lea Act.
B) an interlocking directorate.
A) Dell and Gateway (personal computer makers)
B) Boeing and Airbus (aircraft manufacturers)
C Heinz and Del Monte (food product firms)
D) Apple, Harper Collins, and Penguin (e-books)
D) Apple, Harper Collins, and Penguin (e-books)
48) The situation where a single firm can supply the product to an entire market at a lower unit cost than if the market were split among a number of competing firms, is called a
A) dominant firm oligopoly.
B) structured market.
C)natural monopoly.
D) trust.
C)natural monopoly.
50) What is most likely to happen as the output of a natural monopoly increases over the range of market dem
A) There is a small decrease in average total cost and then it increases as output increases.
B) There is an increase in average total cost and then it decreases as output increases.
C) Average total cost increases as output increases.
D) Average total cost decreases as output increases.
D) Average total cost decreases as output increases.
53) Suppose that two firms in an industry with a Herfindahl index of 5,000 announce a merger. The U.S. Just Department concludes the merger will boost the index to 5,500. The antitrust authorities will most likely
A) allow the merger but watch the new firm
B) carefully for future violations of the antitrust laws.
C) allow the merger if foreign entry to the industry is possible.
D) prevent the merger, contending that it violates the Clayton Act.
D) prevent the merger, contending that it violates the Clayton Act.
57) Differences in the interpretation and the enforcement of antitrust laws are in part rooted on the issue of focus. On such issue pertains to the question of whether the policy focus should be on
A) domestic firms versus multinationals.
B) intrastate trade versus interstate trade.
C) monopoly output versus monopoly pricing
D) monopoly behavior versus monopoly structure.
D) monopoly behavior versus monopoly structure.
60) (Last Word) Using the Internet, some firms are now employing software that uses pricing algorithms to constantly adjust their online prices in response to what rivals are charging for similar products. This is making it easier for
A) firms to collude tacitly in their pricing schemes.
B) government to prove price-fixing.
C) firms to gain monopoly power over their rivals.
D) government to enforce industrial regulation.
A) firms to collude tacitly in their pricing schemes.