Lecture 10- Temporary direct restorations materials
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Materials for temporary direct restorations: protective restorations (4)
zinc- oxide eugenol
calcium- sulfate
light cured resin
gic
(intermediate restorative material = IRM aka temp)
1) zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE)
Z O E (reinforced with PMMA)
self cured
base protective restoration
eugenol inhibits polymerization
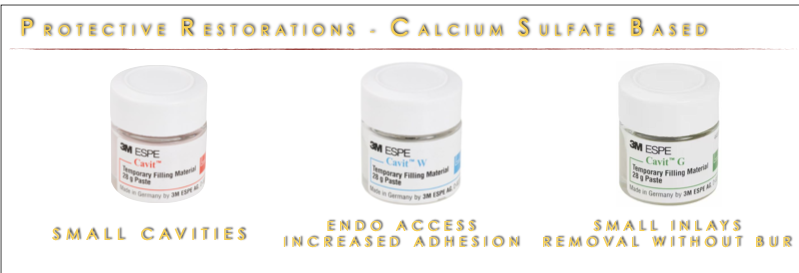
2) Calcium sulfate based
calcium sulfate zinc oxide sulfate
hygroscopic setting
high expansion
setting time 2 hrs
ex: Cavit
harden through hydration, not polymerization (water like saliva)
used for small cavities (use spoon exavator or carbide bur or cavitron to remove to avoid touching tooth structure), endo access and small inlays (no need for bur to remove)
3) resin base materials
light cured polymerization reaction
contains flouride
uses: inlays/ onlays/ impant screw sealing
cure the resin base temp filling for 20 seconds

4) glass ionomer cements (GIC)
used in conjunction with protective coatings or sealants to improve its wear resistance and durability
temp cement: glass (base) mixed with acid reaction
calcium aluminosilicate with polyacrylic acid
bonds to tooth
uses: protective restoration, endo access, class v
GIC indications
luting cements
ortho cements
fissure sealants
direct restorations
core build up
base/ restorative foundations
liners
cavity liner
It is in the coating, varnish, or other protective material to cover the dental cavity wall and protect dentin and pulp from sensitivity
Usually a resinous film-forming agent in a volatile solvent, or a suspension of hydroxide in a solution of a synthetic resin.

base/ restorative foundation
Substance placed under a restoration that blocks out undercuts in the preparation, acts as a thermal or chemical barrier to the pulp, and/or controls the thickness of the overlying restoration.

core build up
Foundation restoration which restores sufficient coronal anatomy of a vital or endodontically treated tooth
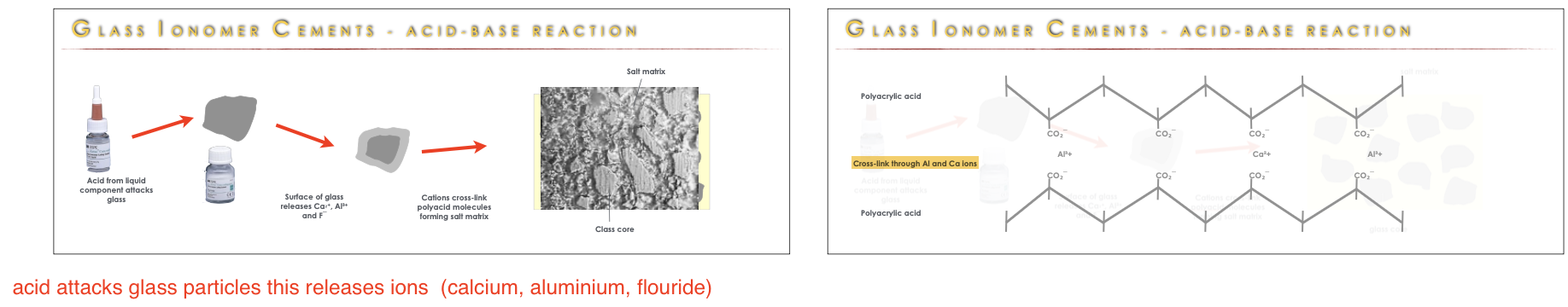
The setting reaction of glass-ionomer cement is characterized by an ______.
This involves the reaction between the polyacrylic acid (an acid) and the calcium-fluoro-aluminosilicate glass powder (a base), acid attacks glass particles which releases ions (calcium, aluminium, flouride), leads to the formation of a salt matrix and the setting of the cement.
acid-base reaction
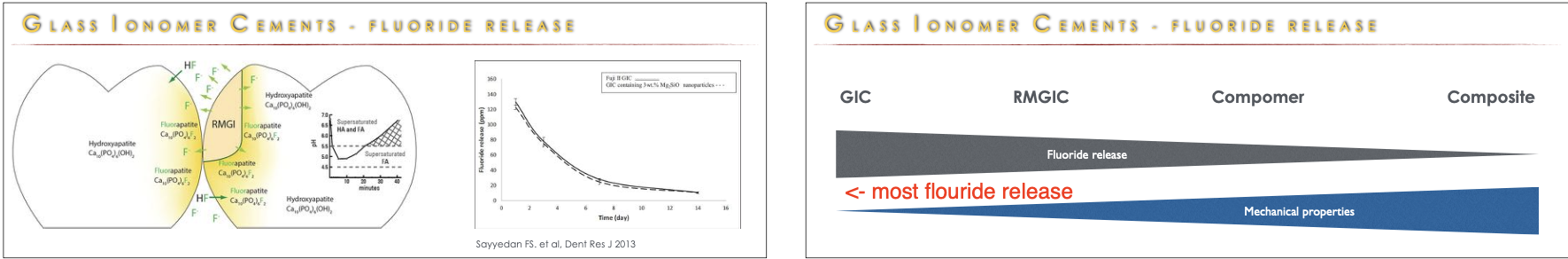
Gic flouride release
fluorapatite is less soluble to acid than hydroxyapatite so more resistant to acid attack
flouride release decreases overtime
applying temporary protective varnish (glycerin gel) over gic:
bec moisture sensitive
do not have too much water or too dry while setting
light cure after last increment before polishing
cure for 40 seconds
GIC: fuji ix (will use this)
self cured
for protective restorations, endo access, base/ build up
mixing time: 10 sec
working time: 2 min
setting time: 6 min

Resin Modified Glass Ionomer Cements - composition
GIC are tooth colored but not strong enough → RMGIC introduced
resin composition: Methacrylate polyacid Hydroxyethylmethacrylate (HEMA) Activator/Initiators/Stabilizers

Resin Modified Glass Ionomer Cements- setting reactions
3-step reaction
1) acid base reaction
2) polymerization (combines many small molecules (monomers) into long chains (polymers))
3) Esterification
RMGIC - Fuji 2 LC
dual cured
resin modified
used for: protective restoration, class iii/ v base
mixing time: 10 sec
working time: 3 min 15 sec
depth of cure: 1.8 mm

RMGIC- Fuji triage
acid base reaction
pink
used for: protective restoration, sealant
mixing time: 10 sec
working time: 1 min 40 sec
setting time: 2 min 30 sec
shortest working time

cavity conditioner
consists of 20% polyacrylic acid
apply for 10 sec BEFORE GIC
rinse, dry, but do not desicate
application of GIC:
cavity cleaning
activate (Unpack, shake, push button, Activate capsule in dispensing gun)
mix (7 sec)
dispense
Rank the fluoride release of GIC, RMGIC, and composite from most fluoride release to least
GIC
RMGIC
resin composite