Lesson 5
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards provide key vocabulary and definitions essential for understanding audit evidence and documentation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Sufficiency
The measure of the quantity of audit evidence.
Appropriateness
The measure of the quality of audit evidence.
Relevance
Reliability
Independent source outside the entity
Effectiveness of internal control
Auditor’s direct personal knowledge
Documentary evidence
Original documents
Audit documentation
Relevant audit evidence obtained, and conclusions the auditor reached. Audit documentation is also referred to as working papers or the audit file. You can think of audit documentation as the “story” of the audit.
(1) to provide principal support for the representation in the auditor’s report that the audit was conducted in accordance with GAAS
(2) to aid in the planning, performance, and supervision of the audit
(3) to provide the basis for the review of the quality of the work by providing a written documentation of the evidence supporting the auditor’s significant conclusions. The form and content of the audit documentation are functions of the circumstances of the specific engagement
Management assertions
Representations made by management regarding recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure of items in financial statements and disclosures. These assertions are categorized based on the type of information they relate to:
classes of transactions and events and account balances
Existence (audit program)
We want to test the accounts/receivables that exist
Confirm Accounts Recievable
Completeness (audit program)
Agree total of accounts receivable subsidiary ledger to accounts receivable control account.
Accuracy, valuation, or allocation (audit program)
Test the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts.
Cutoff
Transactions and events have been recorded in the correct accounting period.
Classification
Transactions and events have been recorded in the proper accounts.
Presentation
Transactions are appropriately aggregated or disaggregated, and disclosures are clear.
Physical examination
Inspection of tangible assets to confirm their existence.
Analytical procedures
Evaluations of financial information made by a study of plausible relationships among both financial and nonfinancial data.
we are evaluating the information that has been reported and comparing that with an expectation, it could be comparing what we see then we can expect to see.
Recalculation
Checking the mathematical accuracy of documents or records.
if the auditor recalculates the schedule that they get from the client and the flip it to make sure it adds up or they recalculate deprecation, then that’s the highest form of evidence we can get
Reperformance
The auditor’s independent execution of procedures or controls that were originally performed by company personnel.
Relates specifically to internal controls
Confirmation
Evidence obtained as a direct written response from a third party.
The way it should work it should be a direct response to the auditor
For example, if we are trying to test accounts receivable and we want a confirmation we want the customer to send it to us (the auditor) directly not the company first
Inspection
• Examining records, documents, or tangible assets. Evidence obtained from external documents is more reliable than evidence obtained from internal documents.
We might look at accounting records or contracts, and typically we argue that anything we get from an external source is more reliable
Example: let’s say we’re looking at the sales journal and the sales transaction recorded actually occurred, we want to vouch for the source documents
Have the goods been shipped is there a shipping document
Inquiry
In conducting inquiry, the auditor should:
• Consider the knowledge, objectivity, experience, responsibility, and qualifications of the individual to be questioned.
• Ask clear, concise, and relevant questions.
• Use open or closed questions appropriately.
• Listen actively and effectively.
• Consider the reactions and responses and ask follow-up questions.
• Evaluate the response.
Tolerable difference
The acceptable variance between expected and recorded amounts during analytical procedures.
Quantification
Determining whether an explanation accounts for an observed difference.
Substantive procedures
Audit procedures designed to detect material misstatements.
Audit program
A set of audit procedures prepared to test assertions for financial statements.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act
requires audit documentation to be retained for a number of years from the completion date of the engagement. (ADDMORE)
requires audit documentation to be retained for a number of years from the completion date of the engagement
Audit documentation should be organized so that audit team members and others can find evidence supporting financial statement accounts
Financial statement assertions
Claims made by management about the financial position and operations.
Budgeting expectations
Predicted financial outcomes based on planned budgets.
Statement of cash flows
A financial report summarizing cash inflows and outflows.
Working papers
Documents that record the audit process, evidence gathered, and conclusions drawn.
Account balances
Total amounts presented on the balance sheet at period end.
Existence assurance
The auditor's confirmation that reported amounts exist.
Board minutes
Official records of decisions made during board meetings.
Higher
Greater risk of misstatement requires a _____ quantity of audit evidence.
Lower
Higher quality audit evidence results in a ______ quantity of audit evidence (inverse relationship between the sufficiency and appropriateness).
Refers to the form or type of information
Accounting Records
Records of initial entries and supporting records
General and subsidiary ledgers, journal entries, and other adjustments to financials not reflected in journal entries.
Work sheets and spreadsheets supporting cost allocations, computations, reconciliations, and disclosures
Contracts
Other Information
Minutes of meetings
Confirmations from third parties
Industry analysts’ reports
Comparable data about competitors
Control Manuals
Information obtained by the auditor from inquiry, observation and inspection
6 categories of assertion concern items on the balance sheet
Assertions about account balances, and related disclosures, at the period end
Existence
Rights and obligations
Completeness
Accuracy, valuation, and allocation
Classification
Presentation
Relationship of audit evidence and audit report
Financial statements, about which management makes assertions, which assertions are tested by audit procedures, which provide evidence on the fairness of the statements, which evidence allows the auditor to reach a conclusion, and this conclusion is given as an opinion in the audit report, which in turn accompanies the financial statements.
7 assertions concern the income statement and statement of cash flows
Transactions and Events
Occurrence: Transactions and events that have been recorded have occurred and pertain to the entity.
Completeness: All transactions and events that should have been recorded have been recorded.
Authorization: All transactions and events have been properly authorized.
Accuracy: Amounts and other data relating to recorded transactions and events have been recorded appropriately.
Cutoff: Transactions and events have been recorded in the correct accounting period.
Classification: Transactions and events have been recorded in the proper accounts.
Presentation: Transactions and events are appropriately aggregated or disaggregated and clearly described, and related disclosures are relevant and understandable in the context of the applicable financial reporting framework.
Audit Evidence
Proper evaluation of evidence requires an understanding of the:
• Types of evidence available.
• Relative reliability of available evidence.
An auditor should be thorough in searching for evidence and unbiased in its evaluation.
audit procedures
are specific acts performed by the auditor to gather evidence about whether specific assertions are being met.
These include:
• Risk assessment procedures
• Tests of controls
• Substantive procedures
Rights and obligation (audit program)
Inquire of management whether receivables have been sold.
Observation
The process of watching a process or procedure being performed by others.
Watching the asset or procedure being performed
Higher Reliability Relationship
Inspection of an asset, reperformance, recalculation
Lower Reliability Relationship
Inspection observation, inquiry
permanent FIles
• Corporate charter
• Important contracts
• Chart of accounts
• Internal control documentation
• Organization chart
• Terms of stock and bond issues
• Prior years’ analytical procedures
• Prior years’ analytical procedure results
Current Files
• Adjusting journal entries
• Audit plan and programs
• Reclassification journal entries
• Working trial balance
• Current financial statements and auditor’s report
• Minutes of meetings
• Working papers supporting accounts
audit documentation should include
Include a written audit program detailing auditing procedures necessary to accomplish audit objectives.
Enable a knowledgeable and experienced reviewer to:
Understand the nature, timing, extent, and results of audit procedures, evidence obtained, and conclusions reached.
Determine who performed and reviewed the work, as well as the dates of the work and reviews.
Format
Enittiy name
title of the working paper
Entitys year-end date
Indexing and cross-referencing
Notations that provide a trail from financial statements to audit documents that a reviewer can easily follow.
Tick Marks
Notations made next to work paper items indicating auditor actions
Risk assessment Procedures
To assist the auditor to better understand the business and to plan the nature, timing, and extent of audit procedures. (ADDMORE)
Substantive Analytical Procedures:
To obtain evidential matter about particular assertions related to account balances or classes of transactions. (ADDMORE)
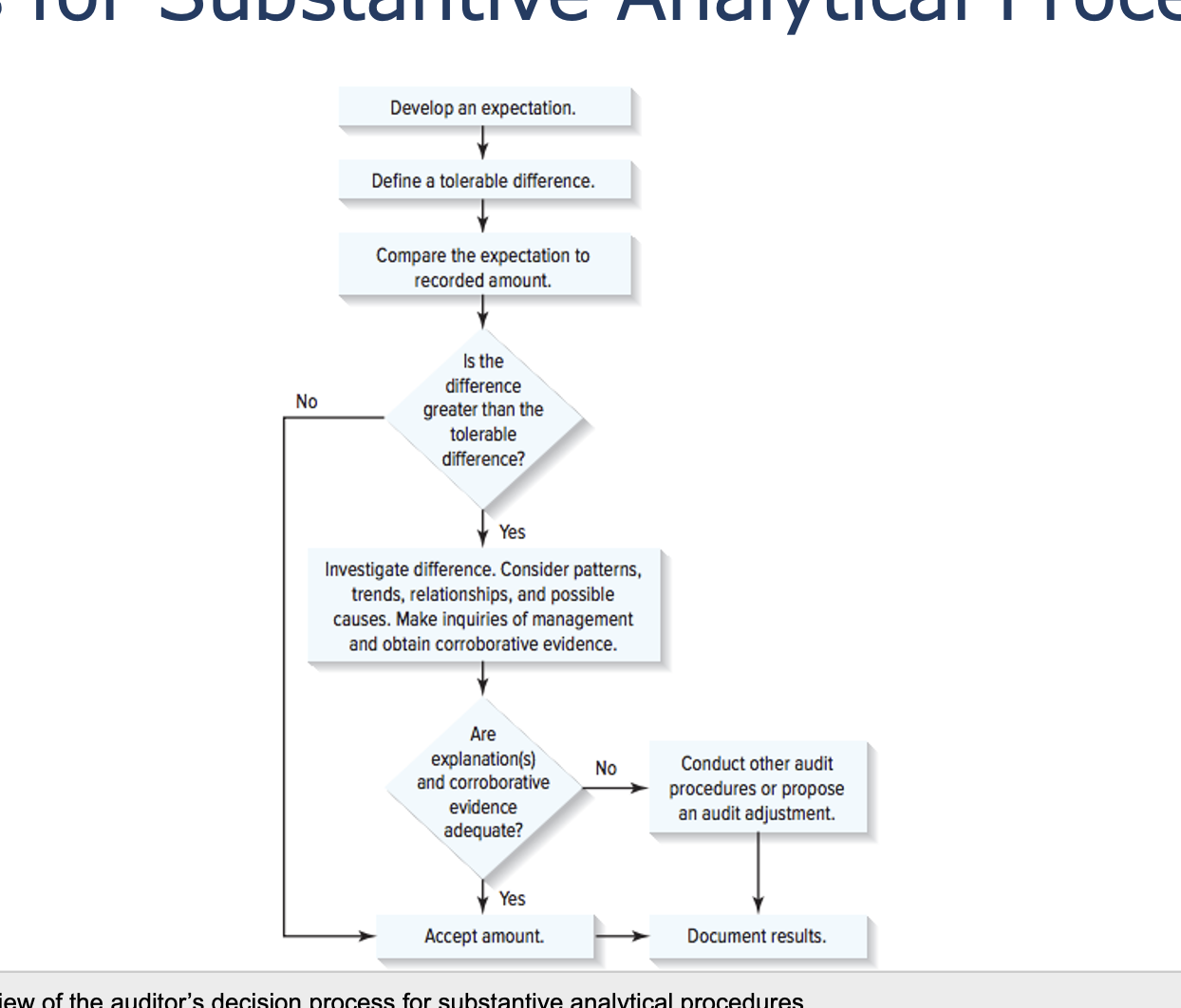
Types of analytical procedures
Trend Analysis
Ratio Analysis
Reasonableness Analysis
precision
the potential effectiveness of an analytical procedure
the degree of reliance that can be placed on the procedure
how closely the expectation approximates the “correct” but unknown amount.
When it comes to expectations, we have to consider the precision. The quality of an expectation
4 factors that affect precision in analytical processes
Disaggregation
The Plausibility and Predictability of the Relationship Being Studied
Data Reliability
Type of Analytical Procedure Used to Form an Expectation
Tolerable Difference
the significance of the account;
the desired degree of reliance on the substantive analytical procedures;
the level of disaggregation in the amount being tested; and
the precision of the expectation.
The tolerable difference will usually be equal to the account’s tolerable misstatement