KNES 348 Chapter #1 (Cellular Reactions)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Kinesiology What is this?
The scientific study of human movement
Kinesis: To move
Logy: science or study of
What does the term Exercise Physiology mean?
The study of how the body physiologically responds, adjust, and adapt to exercise or the lack of exercise.
What is Metabolism?
Sum of all chemical reactions that occur in the body-two general categories of chemical reactions
Anabolic reactions are?
Synthesis of molecules
Catabolic reactions are?
The breakdown of molecules
What are Bioenergetics?
The process of converting foodstuffs (fats proteins, carbohydrates) into usable energy for cell work
What are Endergonic reactions?
Require energy to be added
What are Exergonic reactions?
Releases energy
What are coupled reactions?
Liberation of energy in an exergonic reaction drives an endergonic reaction
Classification of enzymes
Almost every enzyme names end with an (ase)
What does Kinases do?
Adds a phosphate group
What does Dehydrogenases (ases) do?
Removes hydrogen atoms
What are Oxidases?
Catalyze oxidation-reactions involving oxygen
What is Bioenergetics?
The process of converting foodstuffs (fats, proteins, carbohydrates) into usable energy for cell work
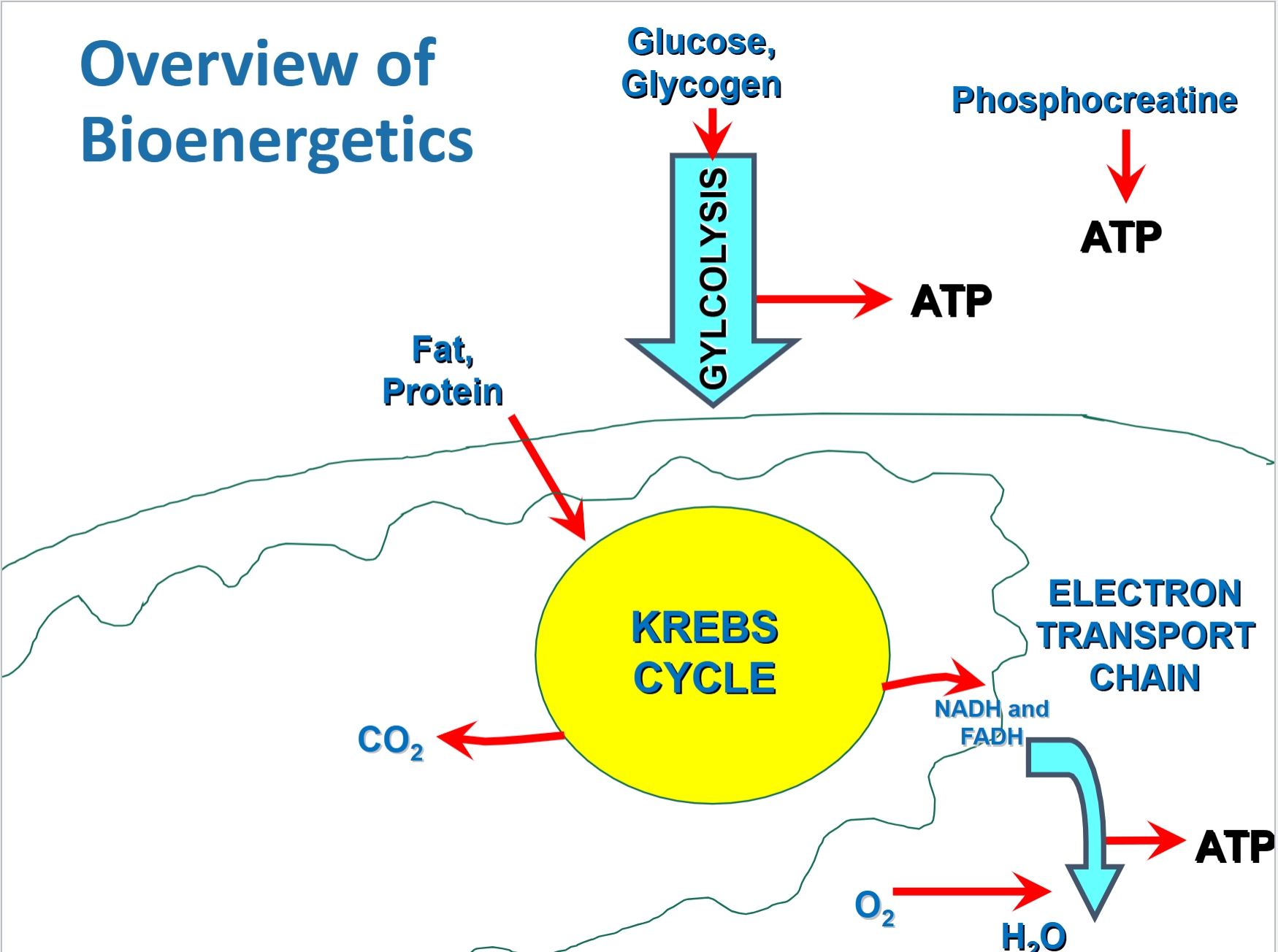
What is the formation of ATP?
Phosphocreatine (PC) breakdown
Degradation of glucose and glycogen (glycolysis)
What are Anaerobic pathways?
Does not involve O2
PC breakdown and glycolysis
What are Aerobic pathways
Requires O2
Oxidative phosphorylation, substrates utilized could be carbohydrate, fats, and protein
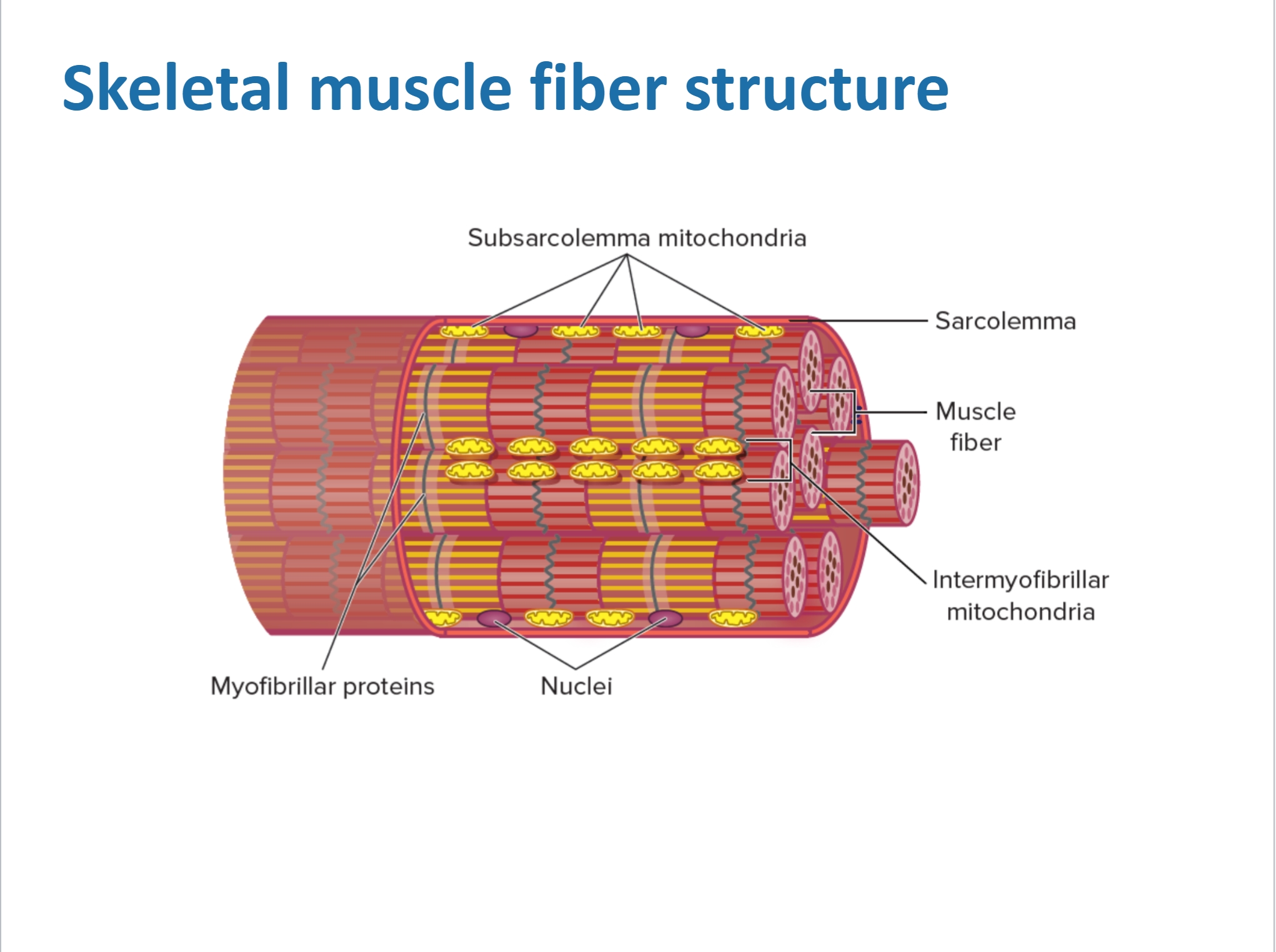
What is the Cell membrane? (Sarcolemma in skeletal muscle) Cell structure
Semipermeable membrane that separates the cell from the extracellular environment
Cell structure (Nucleus)
contains genes that regulate protein synthesis
cell structure (Cytoplasm) (sarcoplasm in muscle)
Fluid portion of cell
Contains organelles
Mitochondria
Skeletal muscle fiber structure
Overview of Bioenergetics
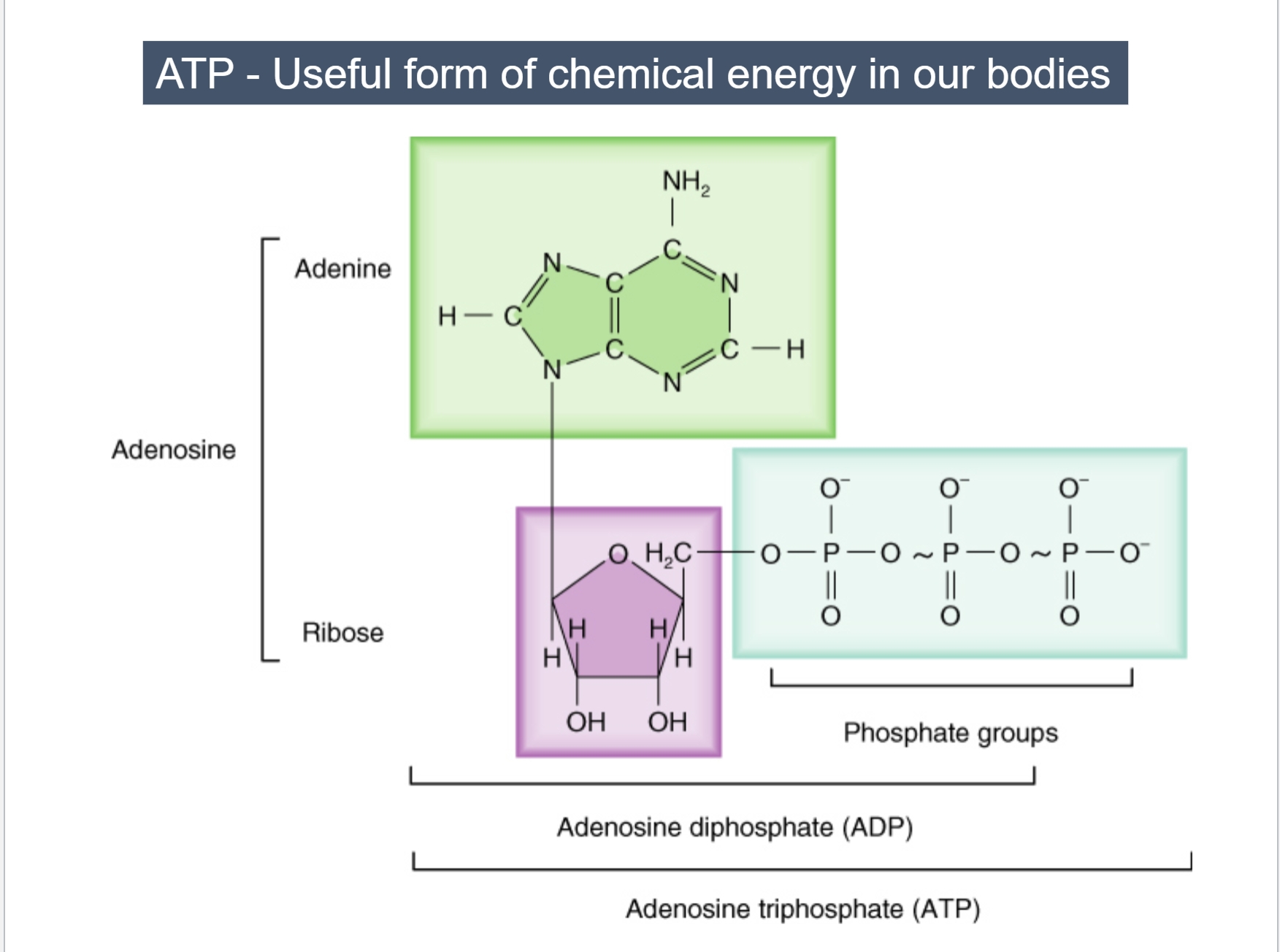
What is Adenosine Triphosphate? (ATP)
Energy from food that is not directly used to perform work
Chemical energy stored in ATP comes from the food we ingest
Immediately usable form of chemcial energy —→ emergency currency
(Food Chemical Energy —> Converted inside body —> ATP Chemical Energy)
ATP - A Useful form of chemical energy in our bodies
The bond between each phosphate is termed a “high-energy” bond
ATP is formed through the process of metabolism (metabolism)
Sums of all chemical reactions
ATP is formed through the process of metabolism (catabolism)
breakdown of molecules
ATP is formed through the process of metabolism (anabolism)
synthesis or building of molecules
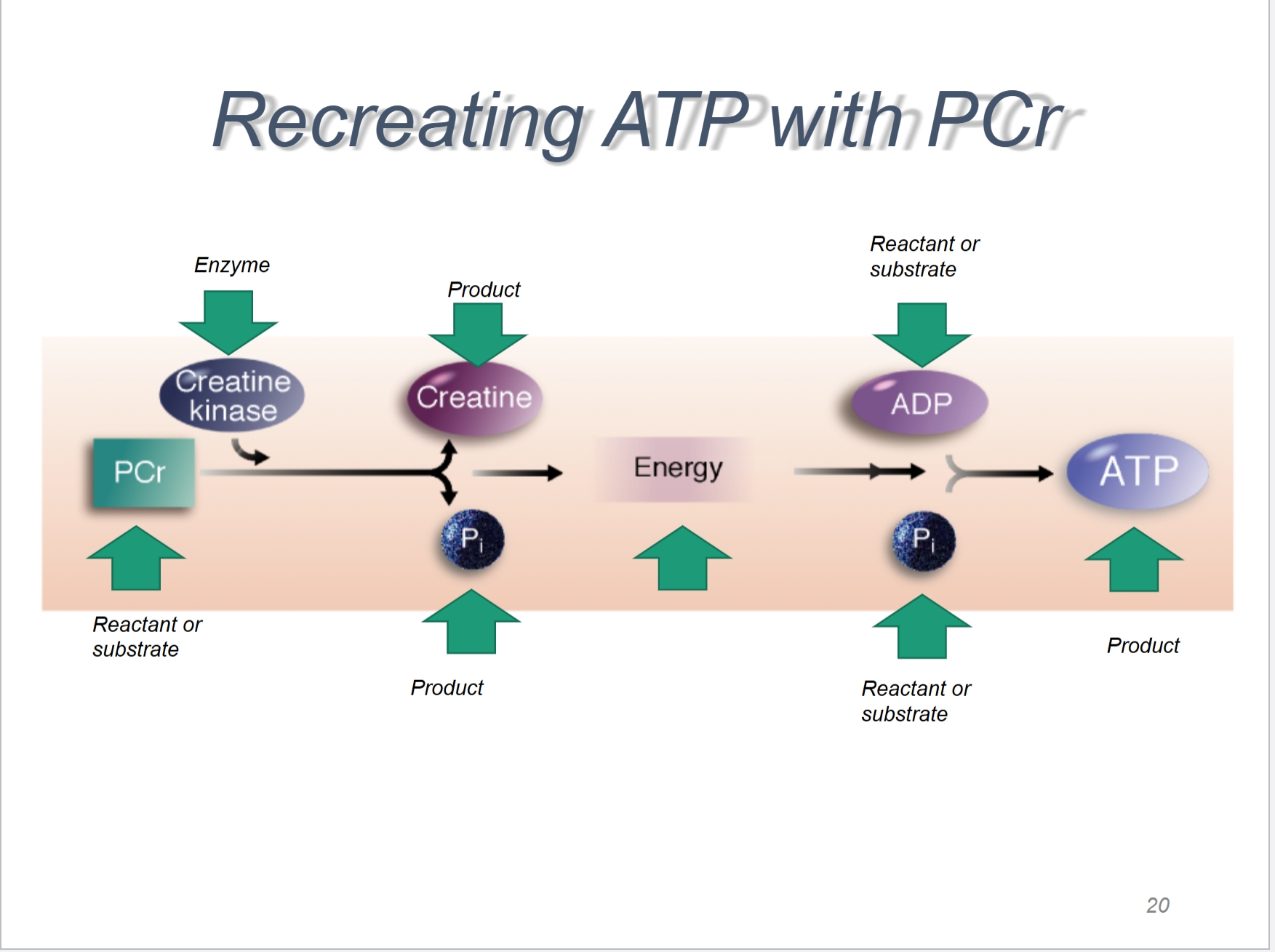
ATP-PC System: What is it?
High-intensity —> exercise utilizes ATP much faster than it can be produced aerobically
Phosphocreatine (PC) is similar to what?
Similar to ATP: high-energy phosphate bonds
stored in small amounts in the cytoplasm of muscle
ATP Molecule
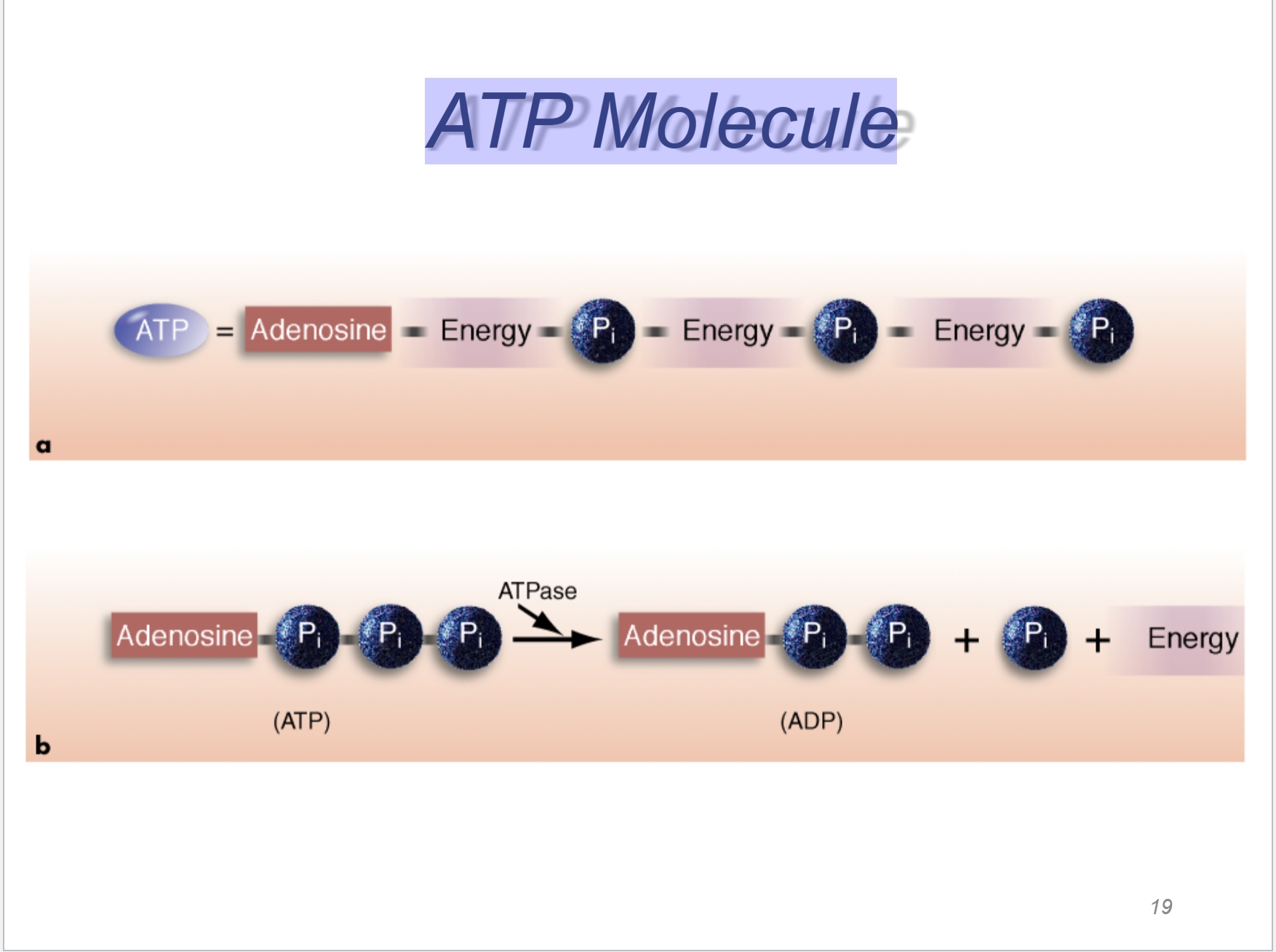
Recreating ATP with PCr
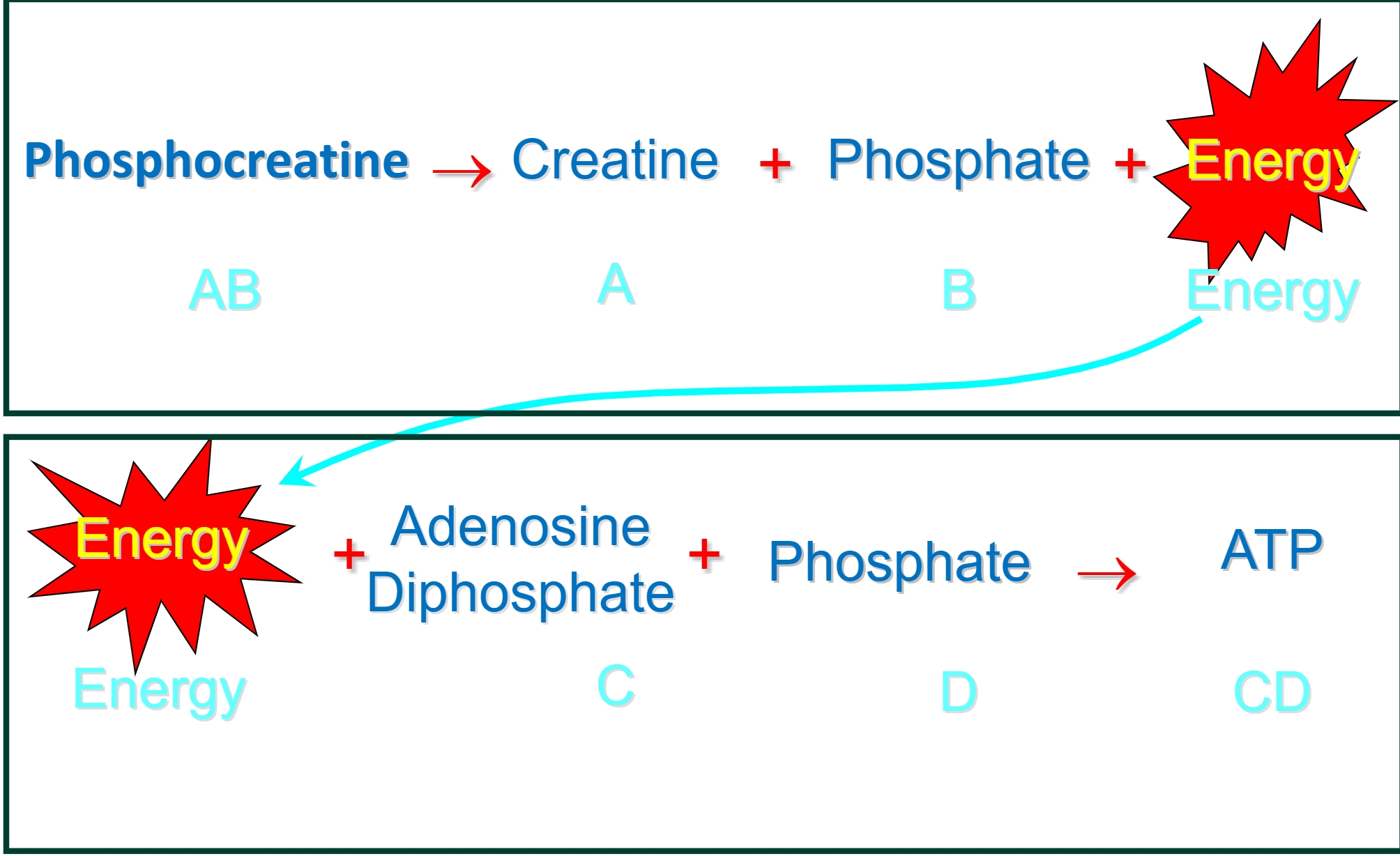
Summary of Phosphagen System
Provides energy for maximal activities lasting up to
10 to 15 seconds (main system)It is somewhat important for activities lasting 30 to
90 secondsIt does not contribute heavily to activities lasting
more than 90 seconds
Issues with the consumption of
nutritional supplements (Creatine)
The US Federal Trade Commission regulates advertising
and labelingThe Food and Drug Administration does not analyze the
content of the supplementsThe label may include the “other ingredients” statement
The product may have other ingredients not disclosed
No standard dose or serving size
information Creatine
Creatine naturally occurs in the body and can
be synthesized in the body (liver and kidneys)Healthy people gain and break down 2g/day
Fish and red meat are the main sources in our diet
Muscles store: creatine (70%) and PCr (30%)
Creatine loading effects for
performance summary
Effective for short-duration events (seconds)
Detrimental for endurance events (gains in body mass)
Creatine monohydrate
30 % of people are non-responders
(Means you take the supplement, but do not see
gains in PCr stores or creatine in the muscle)Gains in PCr stores can be about 40%
How does it work?
Proposed mechanisms of action
Increased PCr availability, which means greater ability to make ATP from this system (longer or more)
Increased rate of PCr resynthesis, which means
increased ability to recover and use the PCr system
intermittently. This is important for high intensityIt does not stimulate protein synthesis; what leads to protein synthesis or muscle building is the training itself, which can be improved by supplementing with creatine
intermittent activities