Muscle Length Testing
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
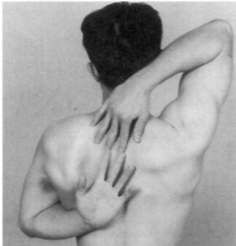
Apley’s scratch test
Apley’s Scratch
Position: Seated or standing
Instruction: Place the palm of the hand on your back, bending your elbow and reaching behind the back as far as possible. Place the other hand behind your back with the palm facing forward, reaching up as far as possible.
Measure the distance between the middle fingertips.
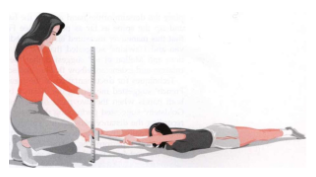
Shoulder and wrist elevation test
Position: Prone-lying, arms extended and holding a stick.
Instruction: Lift the stick as much as possible, keep your head down and keep your wrists straight (neutral).
Measure the distance from the stick to the floor.
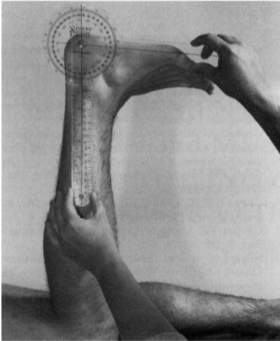
MLT for latissimus dorsi - goniometer
Position: Supine
Examiner: Flex the arm through the available ROM.
Axis: Shoulder, lateral to acromion
Stationary arm: Midaxillary line
Movable arm: Lateral epicondyle of humerus
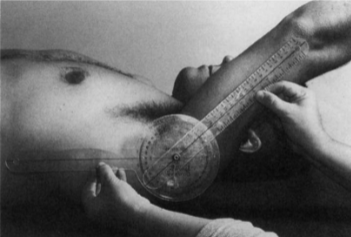
MLT for latissimus dorsi - tape
Position: Supine
Examiner: Flex the arm through the available ROM.
Measure the distance from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus to the support surface.
Pectoralis major - tape measure
Patient: Supine, hands clasped together behind the head (no lumbar or cervical flexion)
Measure the distance between the olecranon process and the support surface.
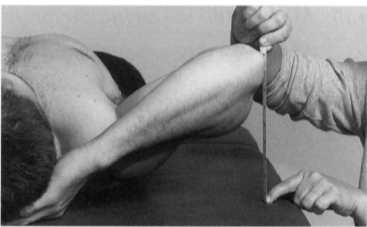
Pectoralis major (clavicular) - tape
Position: Supine, shoulder abducted to 90° and externally rotated (thumb out)
Measure the distance between the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the support surface.
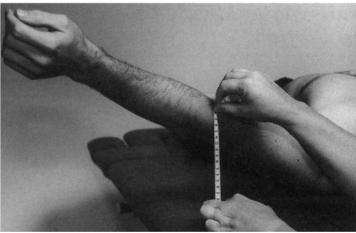
Pectoralis major (sternal) - tape
Position: Supine, shoulder abducted to 135° and externally rotated (thumb out)
Measure the distance between the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and the support surface.
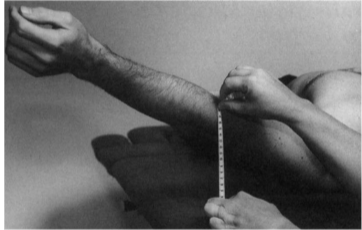
Pectoralis major (sternal) - goniometer
Pectoralis major (clavicular) - goniometer
Position: Both fibers are measured in the same position as with tape, but the difference is the angle of abduction (sternal 135° & clavicular 90°)
Axis: Lateral tip of acromion
Stationary arm: Parallel to support surface
Movable arm: Midline of humerus towards the lateral epicondyle
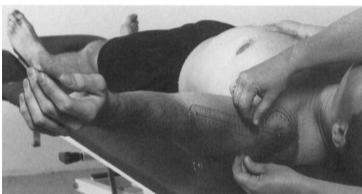
Pectoralis minor - tape
Position: Supine, arms at the side and external rotated, forearm supinated
Measure the distance between posterior border of acromion and the support surface.
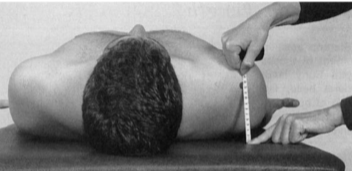
Triceps - goniometer
Position: Seated, shoulder flexed and elbow extended, forearm supinated
Examiner: Flex the elbow
Axis: Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Stationary arm: Lateral midline of humerus towards the humeral head
Movable arm: Lateral midline of radius towards the radial styloid
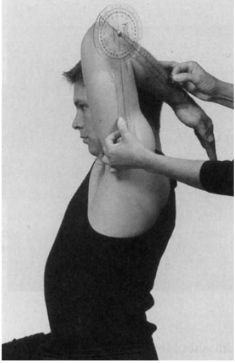
Biceps - goniometer
Position: Supine, shoulder at the edge of the bed, elbow extended, forearm pronated
Examiner: Extend the shoulder
Axis: Lateral midline of humerus towards the lateral aspect of the acromion process
Stationary arm: Lateral midline of thorax
Movable arm: Lateral epicondyle of humerus
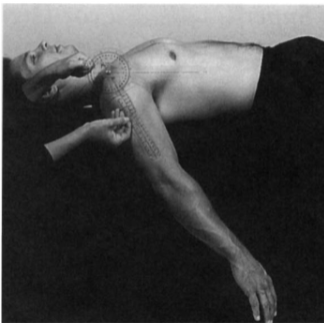
Forearm flexors - goniometer
Position: Supine, shoulder abducted to 70-90°, elbow extended, forearm supinated, fingers extended
Examiner: Extend the wrist
Axis: Lunate
Stationary arm: Insertion of the biceps (radial tuberosity)
Movable arm: Anterior midline of the 3rd metacarpal
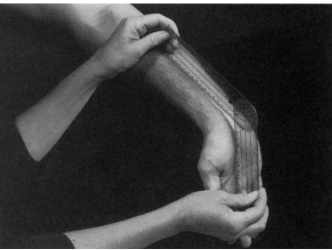
Forearm extensors - goniometer
Position: Supine, shoulder abducted to 70-90°, elbow extended, forearm pronated, fingers extended
Examiner: Flex the wrist
Axis: Lunate
Stationary arm: Lateral epicondyle of humerus
Movable arm: Posterior midline of the 3rd metacarpal
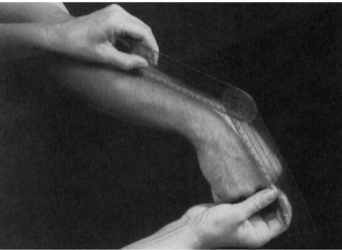
Test to measure hamstring flexibility
Sit and reach test
Position: Long sitting
Instruction: Reach forward with both hands as far as possible, without flexing your knees.
Record the distance.
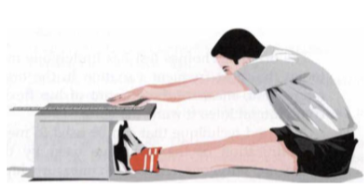
Iliopsoas (Thomas test) - goniometer
Position: Supine, hip of testing side extended, flex contralateral hip by grasping knee to chest. If the muscle length is normal, the thigh of the testing side will remain on the table.
With tightness, the thigh will rise off the table - measure the hip flexion.
Axis: Greater trochanter of femur
Stationary arm: Midaxillary line
Movable arm: Lateral epicondyle of femur
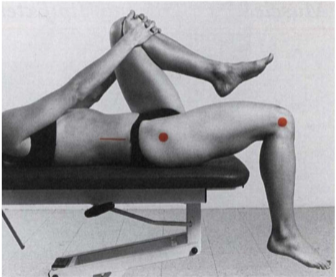
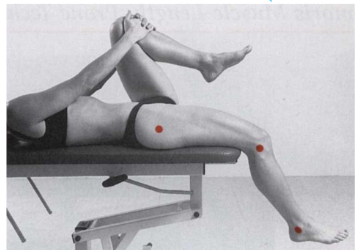
Rectus femoris (Thomas test) - goniometer
Position: Supine, hip of testing side extended, flex contralateral hip by grasping knee to chest. If the muscle length is normal, the knee of the testing side will have an angle of 90°.
With tightness, the knee will extend slightly - measure the knee flexion.
Axis: Lateral epicondyle
Stationary arm: Greater trochanter of femur
Movable arm: Lateral malleolus
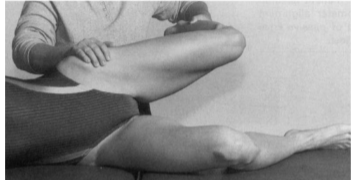
Iliotibial band and TFL (Ober test)
Position: Side-lying, lowermost leg flexed to 45°
Examiner: One hand on ipsilateral pelvis and the other hand is used to extend and abduct the hip by the ankle while maintaining knee in 90° flexion.
The patient is asked to relax while allowing the limb to drop into adduction towards the table. As limb drops, examiner prevents hip flexion and internal rotation.
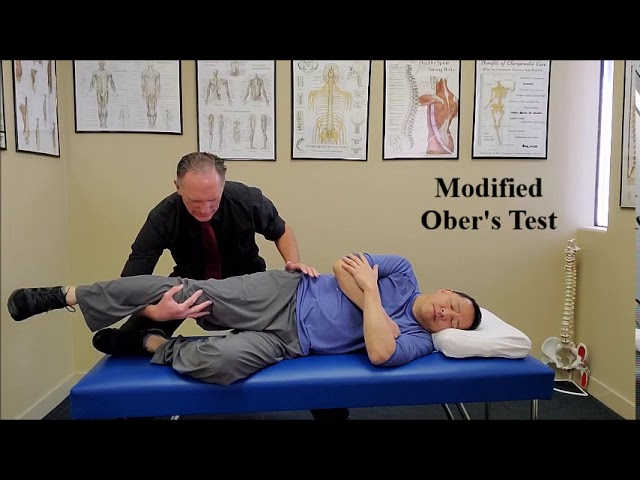
Iliotibial band and TFL (modified Ober test)
Position: Side-lying, lowermost leg flexed to 45°
Examiner: One hand on ipsilateral pelvis and the other hand is used to extend and abduct the hip by cradling the limb while maintaining knee in full extension.
The patient is asked to relax while allowing the limb to drop into adduction towards the table. As limb drops, examiner prevents hip flexion and internal rotation.
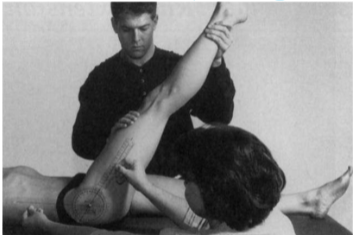
Hamstrings (SLR test) - goniometer
Position: Supine, hip and knee extended
Examiner: Flex hip through full available ROM with full knee extension by placing hand over anterior thigh.
An assistant is needed to measure the hip flexion.
Axis: Greater trochanter of femur
Stationary arm: Midaxillary line
Movable arm: Lateral epicondyle of femur
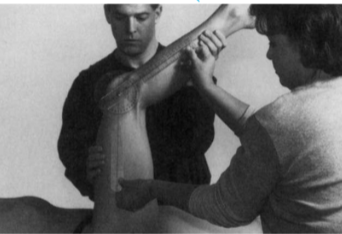
Hamstrings (Knee extension test) - goniometer
Position: Supine, hip flexed to 90°
Examiner: Extend the knee through full available ROM while maintaining hip flexion.
An assistant is needed to measure the amount of knee extension.
Axis: Lateral epicondyle of femur
Stationary arm: Greater trochanter of femur
Movable arm: Lateral malleolus
Gastrocnemius - goniometer
Position: Supine, hip and knee extended
Examiner: Dorsiflex the ankle while maintaining the extended knee
Axis: Lateral to the lateral malleolus
Stationary arm: Head of fibula
Movable arm: Parallel to fifth metatarsal
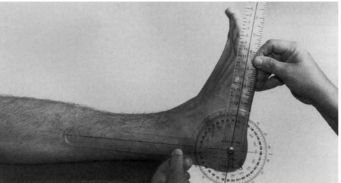
Soleus - goniometer
Position: Prone, knee flexed to 90°
Examiner: Dorsiflex the ankle while maintaining the 90° of the knee
Axis: Lateral to the lateral malleolus
Stationary arm: Head of fibula
Movable arm: Parallel to fifth metatarsal