Macroeconomics Chapter 13
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
The Federal Reserve System is the
A.
federal government agency that collects taxes and spends these receipts on tanks, bridges, government employees' salaries, etc.
B.
company that delivers packages to your front door.
C.
central bank of the United States.
D.
federal government agency that collects and disseminates all the economic data that economists are interested in.
C.
central bank of the United States.
The Federal Reserve System began operations in
A.
1834.
B.
1896.
C.
1914.
D.
1935.
C.
1914.
The United States is divided into __________ Federal Reserve districts, each with a district bank.
A.
three
B.
eight
C.
twelve
D.
twenty E. fifty
C.
twelve
The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve is part of a larger policy-making group called the
A.
Senate Banking Committee.
B.
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
C.
American Banking Association.
D.
Federal Open Market Committee.
D.
Federal Open Market Committee.
Which of the following is not a major responsibility of the Fed?
A.
controlling the money supply
B.
serving as the federal government's banker
C.
determining tax rates
D.
acting as a lender of last resort
C.
determining tax rates
Which of the following statements is false?
A.
The Fed serves as the lender of last resort for banks.
B.
The Fed serves as a fiscal agent for the U.S. Treasury.
C.
A major responsibility of the Fed is to control the nation's money supply.
D.
The federal government is the Fed's banker.
D.
The federal government is the Fed's banker.
When commercial banks need more Federal Reserve Notes,
A.
they call the Bureau of Engraving and Printing, which delivers the requested amount.
B.
they call the Board of Governors of the Fed, which delivers the requested amount.
C.
they ask their customers to exchange their Federal Reserve Notes for U.S. Treasury securities.
D.
they call the Treasury, which delivers the requested amount.
E.
they call their Federal Reserve District Bank, which delivers the requested amount
E.
they call their Federal Reserve District Bank, which delivers the requested amount
When a check is written on an account at Bank A and deposited in Bank B, the reserve account of __________ will rise and reserves of the entire banking system will __________.
A.
Bank A; rise
B.
Bank A; remain constant
C.
Bank B; rise
D.
Bank B; remain constant
D.
Bank B; remain constant
When we speak of the Fed's responsibility to supervise member banks, we are saying that the
A.
Fed's advisory board will help member banks manage their assets and liabilities.
B.
Fed's Open Market Committee will advise member banks regarding the purchase and sale of government securities.
C.
Fed's Board of Governors will advise member banks regarding the appropriate interest rates to be charged on various loans.
D.
Fed will advise member banks regarding the nature of loans and compliance with regulations.
E.
Fed will advise member banks about the proper control of each individual bank's money supply.
D.
Fed will advise member banks regarding the nature of loans and compliance with regulations.
Open Market Operations are conducted by
A.
the main Fed office in Washington, D.C.
B.
the U.S. Treasury on behalf of the Fed.
C.
the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
D.
a consortium of private banks contracted by the Fed.
C.
the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
Open market operations are the
A.
buying and selling of Federal Reserve Notes in the open market.
B.
means by which the Fed supplies the economy with currency.
C.
means by which the Fed acts as the government's banker.
D.
buying and selling of government securities by the Fed.
E.
buying and selling of government securities by the Treasury.
D.
buying and selling of government securities by the Fed.
When the Fed is acting as fiscal agent for the Treasury, it will
A.
buy securities from the Treasury, thereby providing the Treasury with money to pay the government's bills.
B.
receive and process bids for Treasury securities in preparation for the Treasury's auction of securities.
C.
serve as a lender of last resort.
D.
supply the Treasury with paper money whenever the Treasury does not have enough funds to meet its bills.
E.
supervise the Treasury by examining its books.
B.
receive and process bids for Treasury securities in preparation for the Treasury's auction of securities.
When the federal government incurs a budget deficit, it will
A.
mint more coins and spend them.
B.
create money out of thin air.
C.
impose a special tax on all income earners.
D.
borrow money from the Federal Reserve System by issuing securities.
E.
borrow money from the public by issuing government securities.
E.
borrow money from the public by issuing government securities.
If the Fed purchases government securities from a commercial bank, which of the following will happen?
A.
The Fed will increase the bank's reserves on deposit at the Fed.
B.
The Fed will decrease the bank's reserves on deposit at the Fed.
C.
The assets (government securities) of the Fed will decrease.
D.
The assets (government securities) of the Fed will increase.
E.
a and d
E.
a and d
If the Fed wants to increase the money supply through an open market operation, it will
A.
purchase government securities.
B.
sell government securities.
C.
first purchase, then sell, government securities.
D.
lend more reserves to commercial banks.
A.
purchase government securities.
Suppose the Fed sells a $50,000 U.S. Treasury security to Martha, a member of the public. If Martha writes a check to the Fed in order to buy this security, the money in her checking account will be transferred to
A.
the Fed, and now the Fed will have $50,000 more in reserves than it had before.
B.
her bank, and now her bank will have $50,000 more in reserves than it had before.
C.
the Fed, and now it is as if the money doesn't exist.
D.
the Treasury, and now the Treasury will have $50,000 more in reserves than it had before.
C.
the Fed, and now it is as if the money doesn't exist.
The sale of a government security by the Fed
A.
decreases the supply of money.
B.
increases the supply of money.
C.
decreases the demand for money.
D.
increases the demand for money.
A.
decreases the supply of money.
An open market purchase by the Fed
A.
decreases the supply of money.
B.
increases the supply of money.
C.
decreases the demand for money.
D.
increases the demand for money.
B.
increases the supply of money.
Suppose the Fed forecasts a reduction in cash leakages. It might offset the effect of this on the money supply by
A.
buying government securities.
B.
selling government securities.
C.
lowering the required reserve ratio.
D.
lowering the discount rate.
B.
selling government securities.
Suppose the Fed forecasts a reduction in excess reserve holdings by banks. It might offset the effect of this on the money supply by
A.
buying government securities.
B.
lowering the required reserve ratio.
C.
lowering the discount rate.
D.
selling government securities.
E.
a, b, and c
D.
selling government securities.
The Fed can change the money supply by changing
A.
the required reserve ratio.
B.
marginal income tax rates.
C.
federal excise taxes.
D.
unemployment benefits.
A.
the required reserve ratio.
If banks are currently holding zero excess reserves and the Fed lowers the required reserve ratio, which of the following will happen? A.
Banks will have a reserve deficiency.
B.
Banks will have positive excess reserves.
C.
Banks will extend fewer loans.
D.
Banks will call in some of their loans to meet the reserve deficiency.
B.
Banks will have positive excess reserves.
The larger the simple deposit multiplier,
A.
the higher the required reserve ratio.
B.
the higher the discount rate.
C.
the larger the change in the money supply for a given change in deposits.
D.
the less likely the Fed will be to use its monetary policy tools.
C.
the larger the change in the money supply for a given change in deposits.
The word that best describes the relationship between the required reserve ratio and the money supply is
A.
direct.
B.
constant.
C.
inverse.
D.
roundabout.
C.
inverse.
A commercial bank can receive a loan from another commercial bank in the
A.
federal funds market.
B.
bank loan market.
C.
Fed market.
D.
discount market.
A.
federal funds market.
When one commercial bank borrows from another commercial bank, it pays the __________ rate.
A.
discount
B.
bank interest
C.
federal funds
D.
prime
E.
none of the above
C.
federal funds
The interest rate that a commercial bank pays when it borrows from the Fed is the __________ rate.
A.
discount
B.
exchange
C.
federal
D.
bank
A.
discount
The lower the discount rate relative to the federal funds rate, the more likely a commercial bank will borrow from
A.
another commercial bank instead of the Fed.
B.
the Fed instead of another commercial bank.
C.
the U.S. Treasury instead of either the Fed or another commercial bank.
D.
the public.
B.
the Fed instead of another commercial bank.
When a commercial bank borrows from the Fed,
A.
the reserves of the bank fall.
B.
the bank can make more loans.
C.
it must be because the bank is not meeting its reserve requirements. D.
the money supply falls.
B.
the bank can make more loans.
Which of the following will decrease the money supply?
A.
an increase in the discount rate (relative to the federal funds rate)
B.
an increase in the required reserve ratio
C.
an open market purchase by the Fed
D.
a and b
E.
a, b, and c
D.
a and b
The Federal Reserve System
A.
is the central bank of the United States.
B.
controls the money supply.
C.
is the lender of last resort.
D.
is the fiscal agent for the Treasury.
E.
all of the above
E.
all of the above
The Fed
A.
clears checks.
B.
holds depository institutions' reserves.
C.
is the government's banker.
D.
supplies Federal Reserve Notes.
E.
all of the above
E.
all of the above
13-33. When the Fed purchases securities from a bank, it __________ reserves and ____________ the money supply.
A.
decreases; decreases
B.
increases; increases
C.
decreases; increases
D.
increases; decreases
E.
has no impact on; has no impact on
B.
increases; increases
When the Fed sells government securities to a bank, the securities will be
A.
an asset for the bank.
B.
a liability for the bank.
C.
both an asset and a liability for the bank.
D.
neither an asset nor a liability for the bank.
A.
an asset for the bank.
When Bank A obtains a loan from the Fed, the
A.
discount rate is probably higher than the federal funds rate.
B.
bank’s reserves increase.
C.
simple deposit multiplier decreases.
D.
b and c
E.
none of the above
B.
bank’s reserves increase.
When the Fed increases the required reserve ratio, a bank's
A.
required reserves are unaffected.
B.
required reserves are increased.
C.
required reserves are decreased.
D.
excess reserves are decreased.
E.
b and d
E.
b and d
Which of the following is not a monetary policy tool of the Fed?
A.
changing the required reserve ratio
B.
changing the discount rate
C.
setting the price level and the market rate of interest
D.
conducting open market operations
C.
setting the price level and the market rate of interest
The required reserve ratio is set by the
A.
U.S. Congress.
B.
President of the United States.
C.
Secretary of the Treasury.
D.
Federal Reserve.
E.
Director of Monetary Affairs.
D.
Federal Reserve.
A bank is less likely to borrow from the central bank when the __________ falls relative to the __________.
A.
discount rate; required reserve ratio
B.
excess reserve; required reserves
C.
discount rate; federal funds rate
D.
federal funds rate; discount rate
D.
federal funds rate; discount rate
Which of the following will not increase the money supply in the United States?
A.
lowering the required reserve ratio
B.
Fed purchases of government securities on the open market
C.
lowering the discount rate relative to the federal funds rate
D.
Fed sales of government securities on the open market
E.
none of the above
D.
Fed sales of government securities on the open market
The Fed has been called "the lender of last resort" because it
A.
is the biggest bank in the country.
B.
is the only lender to the federal government.
C.
serves as the last place to acquire loans for banks suffering cash management, or liquidity, problems.
D.
a and b
E.
all of the above
C.
serves as the last place to acquire loans for banks suffering cash management, or liquidity, problems.
The banking system currently holds $20 billion in required reserves and zero excess reserves. The Fed lowers the required reserve ratio from 15 percent to 12.5 percent. Assuming that there are no cash leakages, the resulting change in checkable deposits (or the money supply) is approximately
A.
$2.7 billion.
B.
$1.5 billion.
C.
$2.0 billion.
D.
$12.5 billion.
E.
$26.6 billion.
E.
$26.6 billion.
If a bank has zero excess reserves and one of its creditworthy customers applies for a loan, the bank may be able to grant the loan if it can
A.
apply some of its loan repayments to obtain the funds for the new loan.
B.
obtain extra funds in the federal funds market.
C.
obtain extra funds by borrowing from the Fed.
D.
any of the above
E.
b or c
D.
any of the above
One of the Fed's functions is to be the government's banker. This means that the
A.
Fed issues government securities.
B.
Fed extends loans to the government whenever it spends more than it collects in tax revenues.
C.
government's checking account is at the Fed.
D.
all of the above
C.
government's checking account is at the Fed.
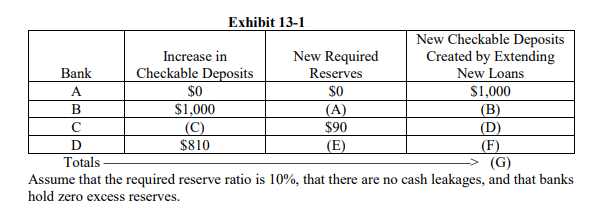
Refer to Exhibit 13-1. Suppose that the Federal Reserve conducts open market operations by purchasing $1,000 worth of government securities from Bank A. As a result, Bank A finds itself with $1,000 in excess reserves that it lends out and those funds end up in Bank B. What dollar value goes in blanks (A) and (B), respectively?.
A.
$100; $90
B.
$10; $90
C.
$10; $990
D.
$100; $900
D.
$100; $900
Suppose that the Fed undertakes an open market sale, selling $1 million worth of securities to a bank. If the required reserve ratio is 8%, checkable deposits (or the money supply), would _______________ by ________________ million, assuming that there are no cash leakages and that banks hold zero excess reserves.
A.
rise; $12.5
B.
decline; $8
C.
decline; $12.5
D.
rise; $8
C.
decline; $12.5