CompTIA A+ Essentials – Lecture Review
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards summarizing key hardware, networking, printer, and cloud concepts from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Fuser Printer
Component that melts and bonds toner to paper; failure causes loose or unfused toner.
802.11a
Wi-Fi standard that operates exclusively in the 5 GHz band.
DDR (Double Data Rate) RAM
Memory type required for dual-channel operation on modern motherboards.
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol)
E-mail protocol that keeps messages on the server, enabling access and sync from multiple devices.
Intrusion Prevention (IPS)
Security function not listed by NIST as a core characteristic of cloud computing.
Magnetic Tape Backup
Removable media best suited for very large, long-term data backups and archiving.
Switch MAC Learning
A switch builds its MAC address table by examining the source MAC of incoming frames.
Laser Printer
Type of printer that requires toner replacement during routine maintenance.
Tracert / Traceroute
Network utility that shows each hop to a destination to locate communication breakdowns.
Firewall Port 80 (Outbound)
Exception that must be open for a client to initiate HTTP requests to a web server.
Inkjet Printer Voltage Control
Technique that regulates ink usage by varying print-head voltage.
DVI-D Cable
Digital Visual Interface connector that carries video signals only (no audio).
ECC (Error-Correcting Code) Memory
RAM feature that detects and corrects single-bit data errors for improved reliability.
MAM (Mobile Application Management)
Software solution that controls which apps users can install or run on corporate devices.
Server‐Grade System
Computer category most likely to employ ECC RAM for high reliability.
255 in Subnet Mask
Indicates the corresponding IP octet is part of the network portion.
Rapid Elasticity
Cloud trait allowing resources to be provisioned or released quickly in response to demand.
MAC Address Length
Hardware address made up of 48 bits (6 bytes).
Network Hub
Legacy device that repeats incoming frames out all other ports (layer-1).
Laptop Display Bezel
Plastic frame around the screen that must be removed to access and replace a Wi-Fi antenna.
Inkjet Nozzle Cleaning
First troubleshooting step for vertical color stripes—run the printer’s built-in nozzle-clean utility.
Wireless Mesh Networks
Generally suited for small or ad-hoc deployments; not ideal for large enterprise networks.
RAID 0 Drive Failure
Loss of a single disk results in loss of the entire striped volume with no data redundancy.
FTP Ports
Passive mode uses port 21; active mode uses ports 21 and 20.
RJ-45 Connector
8-position plug commonly crimped onto UTP Ethernet cables.
S.M.A.R.T. Alert
Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology warning indicating impending hard-drive failure.
SMB (Server Message Block)
File-sharing protocol that listens on TCP port 445.
VM Anti-Malware
Each virtual machine should have its own anti-malware software installed for protection.
IPv6 Address Length
Consists of 128 bits, written as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits.
Scanner Lock Switch
Mechanical latch that must be unlocked on a multifunction printer’s flatbed scanner before use.
2.5-Inch HDD
Standard platter diameter for hard drives installed in most laptops.
Dial-Up Speed Limitation
Dial-up connections do not meet broadband definitions (max ~56 Kbps, far below 1.5 Mbps).
LC Connector
Small form-factor fiber-optic connector used with multimode or single-mode cabling.
Broken Cooling Fan
Likely cause of a PC shutting down after ~15 minutes due to overheating.
OLED Display
Thin-panel technology that uses organic compounds which emit light when current is applied.
Restarting the Print Spooler
Follow-up action when cancel/restart attempts fail—stop and start the Windows Print Spooler service.
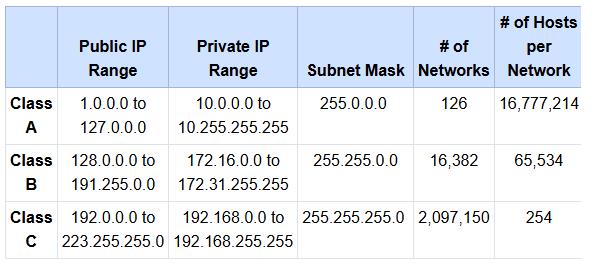
Class A, B, and C network IPv4