histo final nmu
1/234
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
235 Terms
cytoplasmic organelles are
membranous
mitochondria endoplasmic reteculum
golgi apparatus
lysosomes
non membranous
ribosomes
membranous cytoplasmic organelles are 4
▪ Mitochondria.
▪ Endoplasmic reticulum.
▪ Golgi apparatus.
▪ Lysosomes.
non membranous cytoplasmic organelles are 1?
ribosomes
cell membrane is ?
other name is ?
thickness ?
visible by ?
outer limiting membrane that surrounds the cell
also called plasma membrane or plasmalemma
thickness is 7.5-10 nm
visible by EM only
cell membrane appearance under EM is
trilaminar appearance
two E dense lines (black) separated by an electro lucent one (white)
cell membrane is formed of 3
lipid moelcules
proteins
carbohydrates
lipid molecules of cell mebrane are 2
phospholipids and cholesterol
about phospholipid molecule
consists of ?
organization way ?
head hydrophilic
tail hydrophobic
organized into a double layer (bilayer)
the hydrophobic tails are directed towards the middle away from water & the hydrophilic heads are facing the water
cholesterol in cell membrane place and function
between the phospholipid molecules
they regulate the fluidity of the phospholipid bilayer & stabilise it
protein molecules in cell membrane types ? 2
integral proteins and pperipheral proteins
intergral proteins are ?
firmly embedded in the lipid bilayer and not easily extracted
transmembrane proteins are ?
properties ?
attachment ?
act as ?
they are a type of integral proteins
they are large and completely span the lipid bilayer
usually attached to microfilaments in the cytoplasmic side for fixation
they act as channels
peripheral proteins are? (properties)
they are loosely attached to the outer or inner membrane surfaces and they can be easily extracted
carbohydrate molecules of cell membrane are ?
properties ?
glycolipids and glycoproteins
they are projecting from the external surface of the membrane forming the cell coat or glycocalyx
4 functions of cell membrane
exchange of materials
endocytosis
exocytosis
and functions of cell coat
what are types of exchange of materials (one of cell membrane functions)
passive diffusion
active transport
selective transport
passive diffusion occurs for what ? and needs what to occur
it occurs for gases and ions and it doesnt need anything as it occurs according to concentration gradiant
active transport occurs for ? needs ?
for amino acids glucose and fatty acids
needs enzymes and energy
واخد بالك انهم كلهم صور للتغذيه ؟
سكر وبروتين ودهون ;)
selective transport occurs for ? needs what ?
occurs for hormones drugs and bacteria
needs receptors and energy
endocytosis is classified into 3 and explain each
phagocytosis (cell eating) for solid particles
pinocytosis (cell drinkin) for fluids
receptor mediated endocytosis
needs receptor (integral proteins)
for large molecules like protein hormones and some drugs
نفس ال selective transport
exocytosis is (explain briefly)
opposite to phagocytosis as the cell expels any waste product
3 functions of cell coat
adhesive function for adjacent cells
plays a role in immunity (cell recognitions as it recognize cells of its own type and the foreign cells)
participate in the formation of basement membrane
mitochondria is ?
size and shape variety ? examples ?
number ?
site ? example ?
membranous organelle containing enzymes specialized for production of energy (atp)
mitochondria vary in size and shape
may be elongated, rod shaped, or spherical
number is highly variable depending on the activity of the cell (liver cells) contain numerous mitochondria while (lymphocytes) contain very few as the number of mitochondria is modified by mitochondrial division
mitochondria site is very mobile as they localise at sites of maximum energy requirement e.g between myofibrils in cardiac muscle cells
routine stain for LM
hematoxylin and eosin
hematoxylin
nature ?
color?
reacts with ?
basic
blue
reacts with acidic structures inside the cell
DNA (INSIDE THE NUCLEUS)
RNA (IN RIBOSOMES & RER) outside the nucleus !!!
eosin
nature ?
color?
reacts with ?
acidic
red
reacts with basic structures inside the cell usually the cytoplasm which is rich in mitochondria
plasma cells rich in ?
so it appears ?
اوعي تفوتك دي
ribosomes and RER so it appears blue with routine stain
renal tubules rich in ?
so it appears ?
mitochondria
it appears red with the routine stain
presence of succinic dehydrogenase enzyme is an indecation of ?
mitochondria as its an enzyme of krebs citric acid cycle and its exclusive to the mitochondria
mitochondria consists of 4 compartments and describe the one with details from them
1-outer membrane (smooth no folds)
2-inner membrane (forms complex folds called cristae and their number is increased in more active cells )
3-intermembranous space
4-mitochondrial matrix
contains mitochondrial DNA and ribosomes
cristae are ?
its relation to cell activity?
the complex folds formed in the inner membrane of the mitochondria
their number increase in more active cells
mitochondria have 3 functions
1. Provide the cell with ATP: Aerobic respiration takes place within the matrix & on the inner membrane to produce energy.
2. The mitochondrial matrix contains one or more circular strands of DNA & Thus can divide and increase their number according to energy need of the cell.
3. The matrix also contains ribosomes & thus the Mitochondria can synthesise most of its own proteins.
ribosomes are ?
size ?
ribosomes are non-membranous organelles they are the protein factory of the cell
very small (20-30 nm) in diameter
ribosome structure under L.M
The individual ribosome is too small to be seen by L.M. Aggregation of ribosomes leads to basophilia of the cytoplasm due to rRNA.
ribosomes appearance under E.M
▪ Ribosomes are small electron-dense particles.
▪ Composed of two subunits; small & large subunits.
▪ The two subunits are formed of rRNA and about 80 different protein molecules.
what are the 2 types of ribosomes and describe them briefly
free ribosomes (many ribosomes bound to a single mRNA molecule)
attached ribosomes (the single ribosome or polysomes are attached to the surface of endoplasmic reticulum forming the RER)
function of the free ribosomes
function of the attached ribosomes
synthesize protein for the use of the cell : cytoplasmic and cytoskeletal proteins
.
synthesize proteins to be secreted outside the cell as secretory proteins or remain in the cytoplasm as primary lysosomes
chipi chipi
chapa chapa
endoplasmic reteculum is ?
formed from ?
types ?
.
membranous organelle formed of a network (reticulum) that extends from the nuclear membrane to the cell membrane and also intercommunicating channels called cisternae (reservoirs)
RER: the cisternae are covered by ribosomes and polysomes
SER: no attached ribosomes
relation between RER and SER
both are continuous with each other
RER is ?
prominant in ? 2 ex ?
L.M appearence?
E.M appearence ?
functions ? 2?
membranous organelle concerned with synthesis of protein mostly to be secreted outside the cell
.
prominent in cells specialized for protein secretion like fibroblasts (synthesize collagen) and plasma cells (synthesize antibodies)
.
L.M
.
basophilic due to the attached ribosomes
.
parallel cisternae
flartened in shape
have attached ribosomes & polysomes
.
1-segregation of protein synthesized by the attached ribosomes
2-initial glycosylation of protein
Proteins synthesized in the RER have several destinations: 3?
1-transported to the golgi apparatus for secretion outside the cell
2- form primary lysosomes
3-form the integral proteins of cell membrane
SER is ?
prominant in ?
E.M?
endoplasmic reticulum (cisternae with no attached ribosomes) NOT BASOPHILIC
.
liver cells
cells specialized for lipid biosynthesis like adrenal glands testis and ovary
muscle cells
.
cisternae are tubular or vascular in shape (NOOOOT FLATTENED)
smooth surface with no attached ribosomes
functions of SER 5
1-synthesize phospholipids of the cell membrane
in liver cells :
2-glycogen metabolism
3-detoxification of certain drugs and toxic substance like alcohol
in the adrenal gland testis and ovary :
4-lipid biosynthesis (steroid hormones)
in muscles :
5-sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions during contraction and reuptakes it during relaxation.
golgi apparatus is ?
appearence L.M ?
L.M special stain ?
a membranous organelle concerned with secretion of protein which is synthesized by RER
.
H&E unstained area near the nucleus (negative golgi image)
using a special stain (silver stain) and it appears dark brown
.
golgi apparatus E.M we see?
1-golgi saccules
4-10 saccules forming a stack each stack has 2 surfaces
a) cis face (immature) convex which receives transfer vesicle carrying proteins from RER
b) trans face (mature) concave releases secretory vesicles outside the cell
transfer vesicle is ?
small carry ptotein from the RER to the immature face of golgi
secretory vesicle is ?
large arise from the mature face and its either secreted outside the cell (exocytosis)
or remain in the cytoplasm as primary lysosomes
functions of golgi apparatsus 4
1-conc. packaging and storage of proteins to be secreted
2-glycosylation of proteins (begins in the RER and is completed here)
3-forms primary lysosomes
4-synthesis of many glycosaminoglycans that form the extracellular matrix of connective tissue
lysosomes are ?
other name ?
site ?
optimal ph ? examples 2?
its formation ?
membranous organelles which contains about 40 hydrolytic enzymes
they are called suicide bags
.
present in the cytoplasm of all cells but more abundant in cells with great phagocytic activity (macrophages)
.
optimal activity is at ph (5) proteases & phosphatases
.
synthesized & segregated in the RER and became primary lysosomes after transference to golgi apparatus
the marker of lysosomes is ? and present where ?
acid phosphotase and its present in renal tubules
(UNDER LIGHT MICROSCOPE)
primary lysosomes properties ?
secondary lysosomes properties ?
primary :
freshly synthesized, spherical, small, homogenous moderate E dense granular core
secondary : they start intracytoplasmic digestion
irregular, larger, heterogenous because of the digested materials
types of 2ndry lysosomes 3?
and explain composition of each ?
1- heterolysosomes
primary lysosome + solid particle
2- multivesicular body
primary lysosome + fluid particle
3- autophagic vacuole
primary lysosomes + dead or non functional cell organelles
functions of lysosomes ? and what about undigested parts ?
lysosomal enzymes digest the phagocytosed particles to simple molecules .
the remaining undigested portion are called residual bodies and they are usually expelled outside of the cell by exocytosis but in some long lived cells (neurons and cardiac muscles) residual bodies can accumulate over time as !!!LIPOFUSCIN!!! pigments
chippi chippi
chappa chappa
general characters of cytoskeleton 4
Non-membranous structures.
Determine the shapes of the cell.
Allow movement of the entire cell.
Play an important role in movements of cell organelles.
cytoskeleton is composed of 3 and diameter of each
microfilaments (5-9nm)
intermediate filamemnts (10nm)
microtubules (25nm)
microfilaments structure (actin filaments)
fine strands of actin protein
each filament (F-actin) consists of 2 protofilaments twisted to form a double helix and each protofilament is made of multiple globular actin molecules (G-actin) and they are associated with ATP to provide energy for contraction
actin is present in 4
1-skeletal muscles (actin is associated with thick myosin filaments)
2-cell cortex under the plasma membrane
3-in the core of microvilli
4-contractile rings formed during cell division
actin filaments functions 4?
1-cell shape (by actin in the cell cortex)
it also plays a role in cell movement, pino and phago cytosis
2-muscle contraction
3-contraction of contractile rings during cell division
4-increase the surface of microvilli
what are intermediate filaments
▪ Intermediate in size (10 nm) between microfilaments & microtubules.
▪ Identified by immuno-cytochemical techniques.
▪ They are not capable of producing contraction.
types of intermediate filaments 6?
1-keratin filaments (epithelial cells and epidermis)
2-vimentin filaments (found in connective tissue)
3-desmin filaments (in muscle cells)
4-neurofilaments (in neurons)
5-glial fibrillary acidic protein (in glial cells oof nervous tissue)
6-lamin (inner side of nuclear membrane)
importance of intermediate filaments 3
1-supporting the shape of the cell
2-keratin : Protection of the epidermis of skin and reduces dehydration.
Bundles of keratin called tonofilaments form the intercellular junctions between epithelial cells.
3-diagnostic pathology to identify different types of tumor
microtubules are ?
formed of ?
the wall consists of ?
hollow tubules their diameter is 25nm and length is variable
formed of α and β tubulin protein which form protofilaments
their wall consists of 13 protofilaments
what are MTOCs
3 places that are MTOCs
Microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs): Centers in the cytoplasm that direct the formation of protofilaments from tubulin protein.
.
Include:
1. Centrosome (the area of cytoplasm around the Centrioles).
2. Basal bodies of cilia.
3. Centromeres of the chromosomes.
4 functions of microtubules
1. Supporting the shape of the cells.
2. Transporting materials and organelles in the cytoplasm.
3. Play a major role in cell division (formation of mitotic spindle).
4. They are the main structural component of:
▪ Centrioles.
▪ Cilia and flagella.
centrioles are ?
place ?
appearance and structure ?
non membranous structure important for cell division
.
present in the centrosome : a specialized area of the cytoplasm which contains a pair of centrioles oriented at the right angle to each other
.
▪ Each centriole appears as a short cylinder.
▪ The wall of each cylinder is composed of 27 microtubules longitudinally arranged in 9 bundles.
▪ Each bundle consists of three micro-tubules (Triplets).
functions of centrioles 2
1. Play an important role in cell division:
The area of the cytoplasm around the centrioles is one of the microtubular organizing centers (MTOCs).
It is the site of formation of the microtubules of the mitotic spindle.
2. In ciliated cells they form the basal bodies of cilia.
cilia are ?
sites ?
number ?
size ?
hair like processes projecting from the free surface of certain epithelial cells
.
in the respiratory system (trachea and bronchi)
in female genital system (uterus and fallopian tube)
.
maybe several hundreds / cell
.
10-15 um in length and 0.2 um in diameter
E.M of cilia ?
in other words its composition
Shaft (axoneme) :
Surrounded by the cell membrane. Contains 9 peripheral doublets of microtubules & 2 central microtubules (Singlets).
.
Basal body :
Short cylinder, similar to centriole: 9 triplets of microtubules.
.
Rootlets :
Striated fibers, which anchor the basal body to the surrounding cytoplasm.
functions of cilia 2
1-Cilia are beating rapidly in one direction to move fluid or secretion which is present on the surface of the cell. Energy for movement is released from ATP
2-cilic may be modified to receive light stimuli (rods and cones in the retina)
flagella site ?
number ?
structure ?
differ from cilia in ?
tail of spermatozoon
.
one flagellum/cell
.
similar to the shaft of cilia 9 peripheral doublets and 2 central singlets .
.
they are much longer than cilia and make a whip like swimming movement
chippi chippi
chappa chappa
what are cell inclusions ?
what are there types ? 3
stored metabolites or other substances iinside the cytoplasm
1-glycogen granules
2-lipid inclusions
3-pigments
glycogen granules are ?
high amount of them present in?
L.M ?
special stain ?
types under E.M and explain their appearence ?
stored form of carbohydrates liver and muscle fibers contain large amounts of glycogen
L.M
H&E : glycogen dissolves during preparation leaving empty vacuoles
special stain is Bests carmine and glycogen granules are stained red
.
types under E.M are 2
1-alpha glycogen granules
found in liver cells appear as aggregated electron dense particles forming rosettes
2- beta glycogen particles
found in the muscle fibers
they appear as single electron dense particles
lipid droplets
prominent in ?
L.M appearance mention routine and special stains
fat cells, adrenal cortex, and liver
.
1. H & E dissolve during preparation leaving empty vacuoles.
2. Frozen sections are stained with:
▪ Sudan Black: black colour of lipid droplets.
▪ Osmic acid: black colour of lipid droplets.
pigments are ?
types ?
Definition:
Naturally coloured substances that can be seen in the cell without staining.
.
1. Exogenous pigments.
2. Endogenous pigments.
exogenous pigments 3 types and explain each if needed
1. Dust particles: from air pollution; black pigments in the lungs and air passages.
2. Lipochrome pigments: e.g. carotene : yellow colouration of skin.
3. Tattoo marks.
endogenous pigments are 3
1-lipofuscin pigments details in another card
2-melanin present in the cells of skin, hair, and eyes
3-hemoglobin&myoglobin
lipofuscin pigments are ?
they are an endogenous pigment
▪ Yellowish brown pigment seen in cardiac muscle fibres, nerve cells and sympathetic ganglia.
▪ Called wear and tear pigments; derived from residual bodies after lysosomal digestion.
▪ They increase with age (age pigments).
melanin pigments are present in the cells of ?
skin, hair and eyes
nucleus is ?
found in ? except ?
number ? and examples pls pleeeeeeease
size and size range ? what about abnormal ?
shape ? 4
the nucleus is the command center of the cell
.
found in all cells except mature erythrocytes (R.B.Cs.) and blood platelets
.
cells are usually mononucleated (No need for example)
binucleated : some liver cells
multinucleated : osteoclasts
.
nucleus is the largest structure in the cell its size ranges from 3-14 um
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!it may reach 25um or more in the ovum !!!!!!!!!!!
▪ Rounded.
▪ Oval.
▪ Kidney-shaped.
▪ Multilobed.
nucleus staining and appearance and it also has 2 looks
the nucleus is basophilic due to its content of nucleic acids : DNA and RNA
.
vesicular (open face) and condensed nucleus
vesicular (open face) nucleus properties ? found in ?
lightly stained , details of the nucleus could be seen , nucleolus appears clearly , and its found in active cells
condensed nucleus properties ? found in ?
deep basophilic
no apparent details
nucleolus doesn’t appear
found in less active cells (lymphocytes)
the nucleus is composed of 4
1. Nuclear membrane
2. Chromatin
3. Nucleolus
-+4. Nuclear sap (karyoplasm)
nuclear membrane structure and function
its Made up of two thin membranes separated by a perinuclear space.
The outer nuclear membrane has many ribosomes on its surface and is continuous with the membranes of the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
The nuclear membrane is interrupted by many nuclear pores.
Functions :
▪ It separates the nucleus from the surrounding cytoplasm.
▪ It allows exchange of material between nucleus & cytoplasm through nuclear pores.
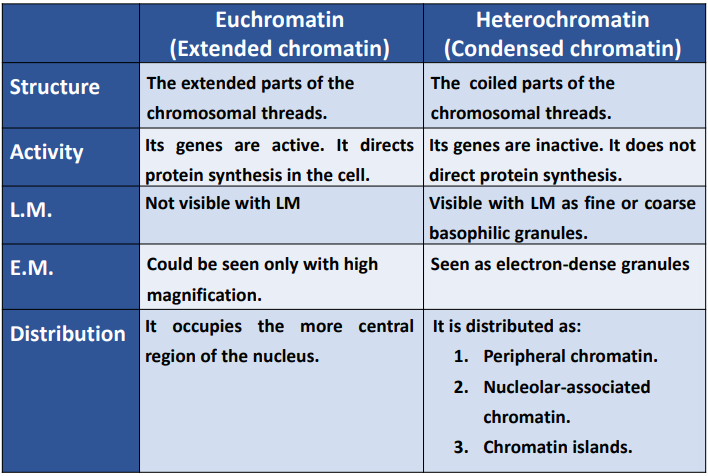
chromatin is ?
appearance in L.M ?
appearance in E.M ?
its a nucleoprotein it consists of DNA conjugated with histone protein
.
it appears in L.M as basophilic granules which represent the coiled parts of the chromosomes
.
two types
1-euchromatin (extended chromatin)
2-heterochromatin (condensed chromatin)
compare between euchromatin and heterochromatin
nucleolus appearence
seen when ? or present when ?
what does it do (functions) 2?
one or more basophilic bodies (due to RNA content)
present in inter phase
.
1-synthesis of rRNA
2-rRNA is conjugated with protein and migrates through nuclear pores to reach the cytoplasm as ribosomes
nucleolar genes are ?
their numbers ?
the genes that code for rRNA and they are present on five pairs of chromosomes 13,14,15,21,22
what is nuclear sap ?
its other name ?
content ?
its a clear solution in which chromatin and nucleoli are suspended .
.
karyoplasm.
.
proteins and nucleoproteins
enzymes catalyzing the synthesis of DNA and RNA
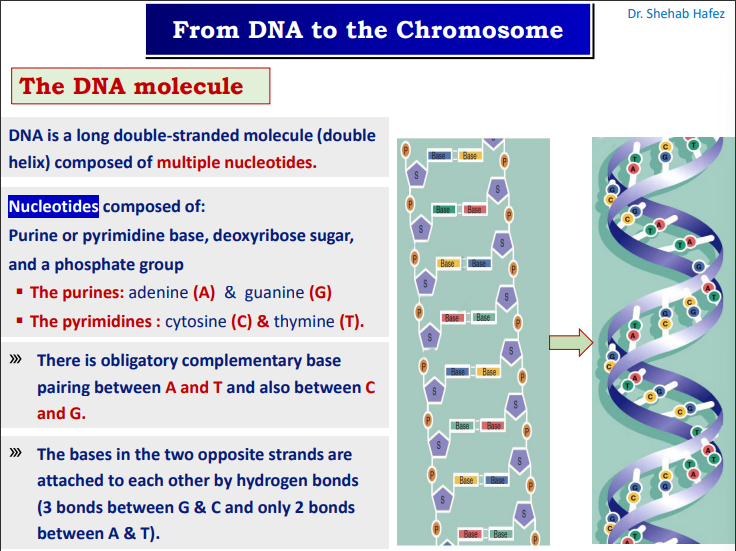
dna is ?
a long double stranded molecule (double helix) composed of multible nuceotides
بص الصراحه اول سلايد تافه اوي يعني فا لو محتاج فيه كروت ربنا يعينك الصراحه السلايد ورا اهو بردو
dna folding and packing stages
nucleosomes (6nm)
filaments (11 nm)
chromatin fibers (30 nm)
chromatin loops (300-700 nm)
metaphase chromosome (1400 nm)
OFC IAM TALKING ABOUT THE DIAMETER
how are nucleosomes formed
the dna double helix winds about 2 turns around a histone core (formed of 8 molecules of histone protein)
the chromosomal number of a typical somatic cell is
46 (diploid)
the chromosomal number of a germ cell is
23 (haploid)
female chromosomal number is (karyotype)
46,xx
male chromosomal number is (karyotype)
46,xy