Patho Unit 2
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
Hereditary
involves chromosomnl or DNA mutation, is passed down
2
New cards
Congenital
deficiency or injury during gestation/ present at birth
3
New cards
Infectious
exposure to pathogenic organisms
4
New cards
Metabolic
disruption of normal chemical reactions
5
New cards
Nutritional deficiency
insufficient quantities of nutrients such as essential amino avids, minerals or vitamins
6
New cards
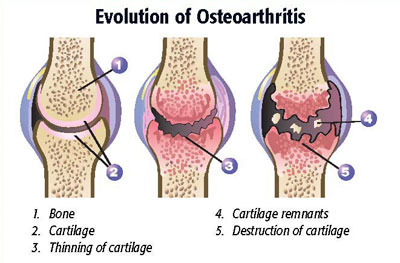
Degenerative
progressive deterioration of a tissue
7
New cards
Neoplastic
involves abnormal cell growth
8
New cards
Immunologic
dysfunction of normal immune responses
9
New cards
Iatrogenic
resulting as a complication of medical treatment

10
New cards
Psychogenic
influenced by psychological factors
11
New cards
Idiopathic
pertaining to disease of unknown origin

12
New cards
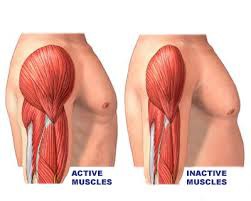
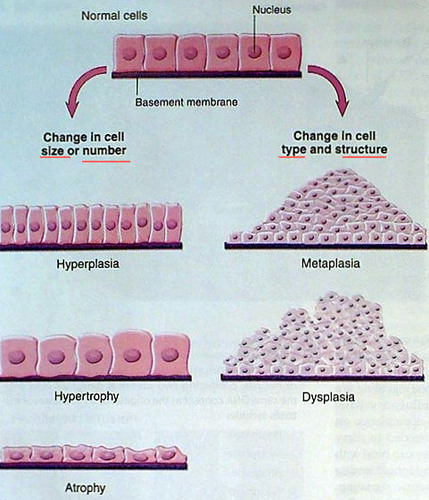
Atrophy
decrease in cell size
13
New cards
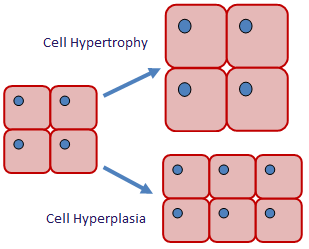
Hypertrophy
increase in cell size
14
New cards
Hyperplasia
increase in number of cells
15
New cards
Dysplasia
deranged cellular growth, not a true admptive state, is atypical hyperplasia
16
New cards
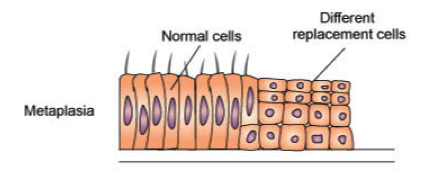
Metaplasia
replacement of one type of cell with another
(change in cell type)
(change in cell type)
17
New cards
Hypoxia
lack at oxygen due to ischemia (low blood supply)
18
New cards
Necrosis
Cell death due to disease or chemical injury (dense dumping of DNA and disruption of plasma and organelle membranes)
19
New cards
Autolysis
cellular self - digestion
20
New cards
Coagulative
due to hypoxin; protein denaturation (Albumin hardens); occurs in kidneys, heart, and adrenal glands
21
New cards
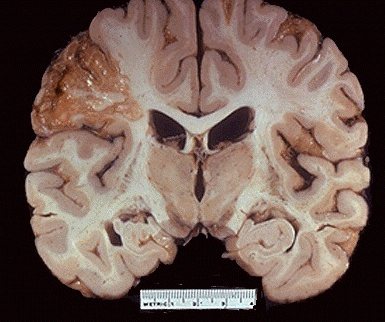
Liquefactive
ischemic injury to brain neurons; cells become digested by their own enzymes
22
New cards
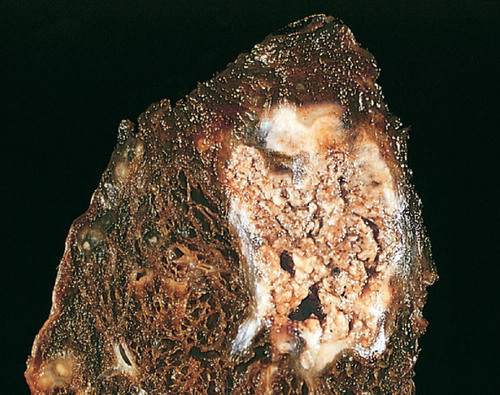
Caseous
pulmonary infection (usually tuberculosis ); dead cells disintegrate but leave cellular debris
(clumped cheese)
(clumped cheese)
23
New cards
Fat
lipases destroy cells; breast, pancreas, abdomen
24
New cards
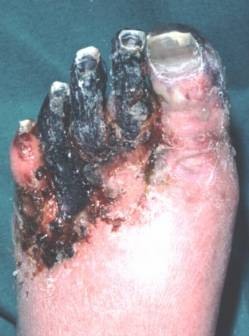
Gangrenous
severe hypoxin and bacterial infection lex. gas gangrene cauved by clostridium)
25
New cards
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
26
New cards
Systemic Disease
disease affecting the whole body system
27
New cards
Incidence
occurrence or influence
28
New cards
Prevelance
The percentage of a population that exhibits a disorder during a specified time period.
29
New cards
Pandemic
Disease that occurs over a wide geographic area and affects a very high proportion of the population.

30
New cards
Epidemic
a widespread occurrence of an infectious disease in a community at a particular time.
31
New cards
Pathogenesis
the origination and development of a disease
32
New cards
Prognosis
the foretelling of a course of a disease
33
New cards
Etiology
cause of disease
34
New cards
Complication
A secondary disease/condition that develops in the course of a primary disease/condition.

35
New cards
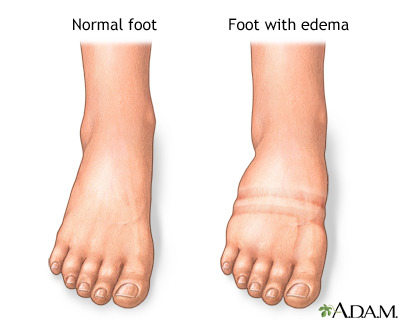
Edema
Abnormal accumulation of serous fluid in connective tissues.
36
New cards
Exacerbations
flaring of symptoms (becoming more severe)
37
New cards
Remission
improvement or absence of signs of disease

38
New cards
Sequela
the negative aftermath of a disease
39
New cards
Benign
a mild type that does not threaten the health or life of a patient
40
New cards
Karyolysis
dissolution of nucleus
41
New cards
Oncosis
Cell death with swelling (occurs before necrosis)
42
New cards
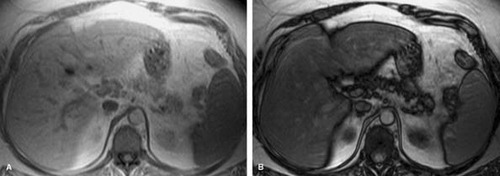
Fatty infiltration
infiltration of the tissue of an organ with excess amounts of fat
43
New cards
Relapse
recurrence of an illness/disease/condition

44
New cards
Nosocomial
acquired or occurring in a hospital
45
New cards
Acute
Sudden/onset/short duration
46
New cards
Chronic
suffering from a disease for a long period of time
47
New cards
Free radicals
they are electrically uncharged atoms w/ and unpaired electron.