Dental Hygiene Diagnosis CH22
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
4 basic steps to considered when planning patient care are
1. Collect & analyze assessment information
2. Establish the diagnosis
3. Select treatment & education interventions based on diagnostic findings
4. Develop a formal care plan
Dental hygiene diagnosis (DHD) is the result of
analysis & synthesis of assessment data and the application of clinical judgment and critical thinking skills.
A dental hygiene care plan is developed and an appointment sequence is formalized using an ___ ___ approach
evidence-based approach
Assessment findings Basics
-Chief compliant
-Risk factors
-Patient’s overall health status
-Oral healthcare literacy level of patient
-Oral self-care ability
Periodontal Risk and Diagnosis Basics
-Current periodontal status
-Classification of periodontal disease
Chief compliant
patient’s reason for seeking dental and dental hygiene care
significant concern (pain) is ALWAYS addressed before initial dental hygiene treatment
Risk factors
• Increase the patient’s potential for disease (dental caries & periodontal)
• Modifiable risk factors identified + controlled to reduce probability or progression of disease
• Goal: To REDUCE risk by intervention (patient education and counseling); use anticipatory guidance when a patient has risk factors
Anticipatory guidance
preventative education and counseling for patients exhibiting risk factors
Risk factors for periodontal disease
poorly controlled diabetes
smoking
Age as related to radiographic bone loss (RBL)
Inflammatory diseases (Ex: systemic like heart disease) measured by C-reactive protein (CRP)
Emerging risk factors for PD disease include
obesity
specific genetic factors
nutrition
physical activity
Periodontal disease association with systemic conditions
cardiovascular disease
diabetes
metabolic syndrome (increase risk for heart disease)
obesity
respiratory disease (asthma, pneumonia, COPD)
adverse pregnancy outcome
osteoporosis
Assessment findings used to help with DHD
Medical, dental, social history review
vitals
IO/EO
comprehensive periodontal exam
radiographs
dental caries/risk for caries
biofilm, calculus, stain
patient’s overall health status
Risk factors for oral cancer
tobacco
betel quid and gutka
heavy alcohol use
sun exposure (lips and face)
male
older than 55 yrs
genetic susceptibility
Patient’s overall health status
Physical:
-medical physical, psychological risk determines modifications
-can use ASA physical status classification system
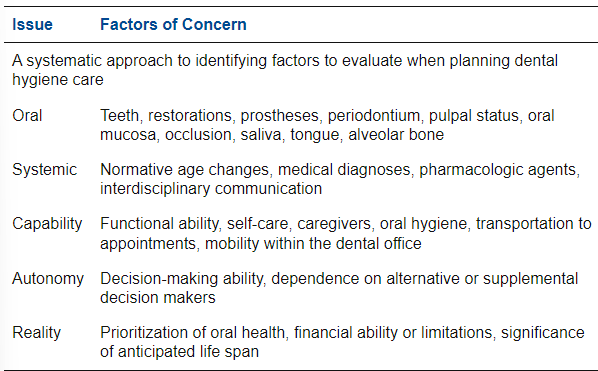
-can use Oral, Systemic, Capability, Autonomy, Reality planning guide
Tobacco
ASA Classification Chart
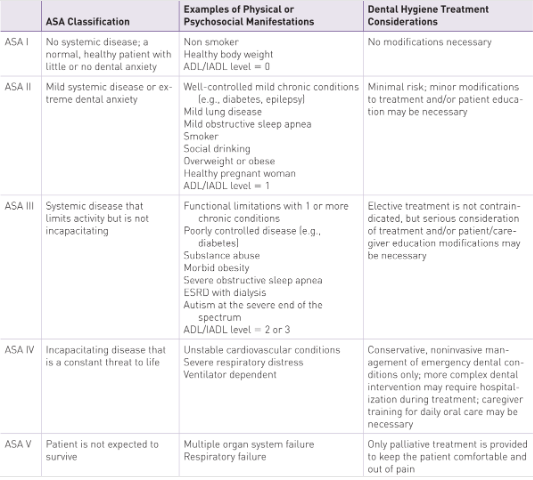
ASA I

ASA II

ASA III

ASA IV

ASA V

Oral, Systemic, Capability, Autonomy, Reality Planning guide chart
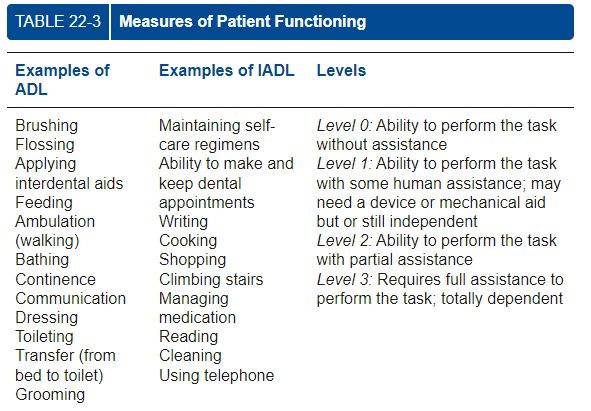
Oral Self-care ability
determines success of planned interventions
modifications for disabilities or physical limitations
can use activities of daily living (ADL/IADL) to determine if aids or caregiver training is needed
Periodontal Risk and Diagnosis (Descriptive)
Current PD status: past and current conditions and risk factors affecting progression
Classification of periodontal disease: gingivitis, periodontitis
Parameters of care:
-clinical diagnosis, therapeutic goals, treatment considerations, outcome assessment
-planning considerations determined by infection severity
Dental caries risk level
-restorative treatment provides by dentist or dental therapist, but dental hygiene care plan includes interventions of risk factors
Dental hygiene diagnosis
Basis: 1) patient interview data (CC, oral problem identification, comprehensive patient histories) 2) physical assessment data (vitals, EO/IO, dental + periodontal charts) 3) radiographs
Diagnostic statements: diagnosis and risk factors contributing to the condition diagnosed; Ex) xerostomia due to medication side effect
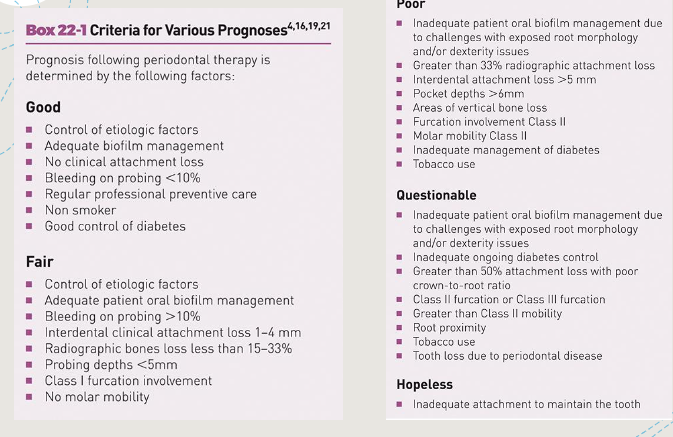
Dental hygiene prognosis
future/anticipated outcome of a disease or condition
describes individual tooth or overall prognosis of patient teeth
overall prognosis determined by dentist
based on treatment and self-care behavior goals agreed by patient and clinician during planning phase of care

Prognosis criteria chart

Factors in assigning a prognosis
Individual:
-% bone loss
-CAL
-extent and type of bone loss
-presence + severity of furcation involvement
-mobility
-caries
-tooth position
-occlusal trauma
-crown to root ratio
-root form (Ex: fused)
Overall:
-age
-medical status
-rate of disease progression
-patient cooperation and compliance
-oral habits and behaviors
-oral health literacy
Prognosis factors (individual tooth)
-% bone loss
-CAL
-extent and type of bone loss
-presence + severity of furcation involvement
-mobility
-caries
-tooth position
-occlusal trauma
-crown to root ratio
-root form (Ex: fused)
Prognosis factors (overall)
-age
-medical status
-rate of disease progression
-patient cooperation and compliance
-oral habits and behaviors
-oral health literacy
Putting it all together
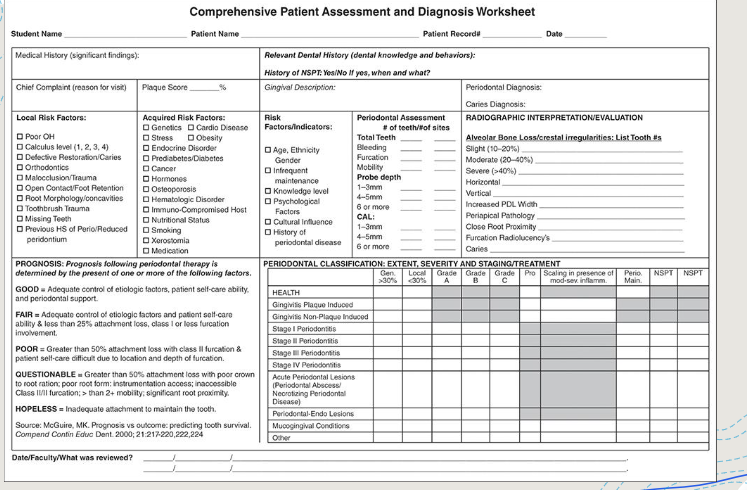
evaluation of assessment data: can use comprehensive patient assessment diagnosis worksheet to gather info together to help in diagnosis, prognosis, care, treatment plan
selection of dental hygiene interventions: evaluation of patient needs to develop personal goals + interventions to improve oral health, clinical findings, evidence based interventions to prevent or manage oral disease (professional literature; must be able to access and evaluate to benefit patient!)
dental hygiene care plan:
Evaluation of assessment data includes the following
summary of histories
chief complaint
summary of PD examination findings
summary of radiographic interpretation
PD classification
diagnosis
prognosis
Documentation
all assessment findings in prep for dental hygiene care plan development
written in ink if not computerized
entries dated and signs
standardized abbreviations only for legal reasons

Step 1
Identify patient’s overall health status:
Extent of patient’s medical, physical, and psychological risk determines modifications necessary during treatment.
Use ASA Classifications
Identify tobacco use:
Tobacco in all forms affect oral status and dental hygiene treatment outcome
Step 2
Determine health literacy of patient
Step 3
-Determine patient’s oral self-care ability
-Activities of daily living (ADL/IADL): classification level to summarize an individual’s ability to carry out/perform basic tasks.
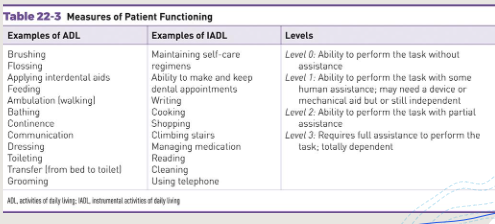
Step 4
determine periodontal risk and diagnosis
planning for number and length of appointments in a treatment sequence influenced by classification of periodontal disease
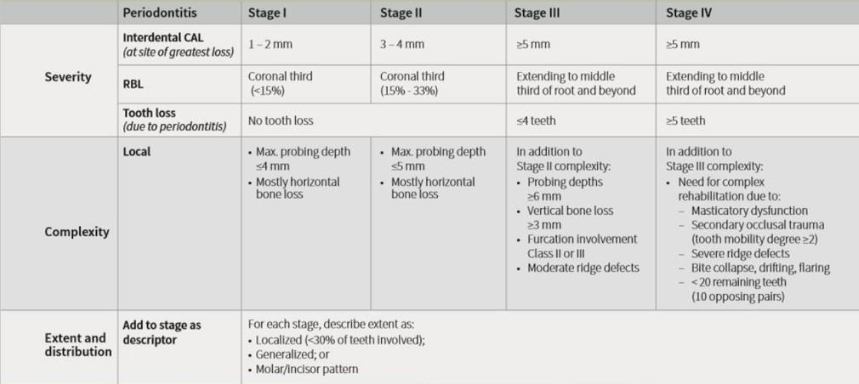
Periodontitis Staging
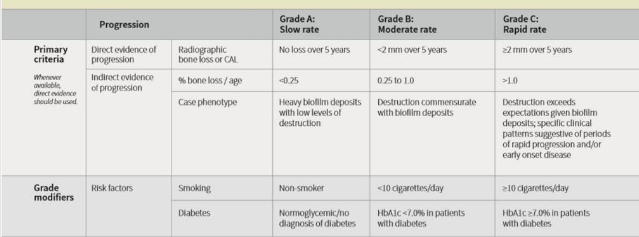
Periodontitis Grading
Gingivitis
Inflammation of gingiva is characterized by changes in color, shape, form, size, and position of margin, with bleeding on probing.
No attachment loss
Does NOT receive a periodontal stage or grade
Why?
Stage I periodontitis
mild
progression of inflammation into the deeper periodontal structures
slight bone loss and connective tissue attachment
Stage II periodontitis
moderate
Increased destruction of the periodontal structures
Increased probing depths, noticeable loss of interdental bony support
Early to moderate furcation, mobility, fremitus
Stage III and IV periodontitis
Major loss of bony support
Increased probing depths
Furcations
Increased tooth mobility and fremitus
Other signs and symptoms
IUSB Degree of difficulty (is/isn’t) a diagnosis
isn’t
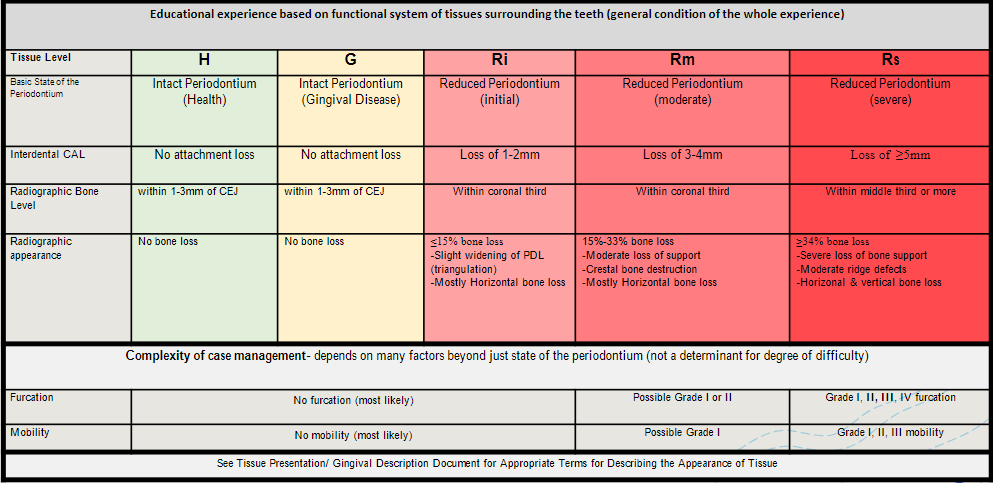
IUSB Calculus level
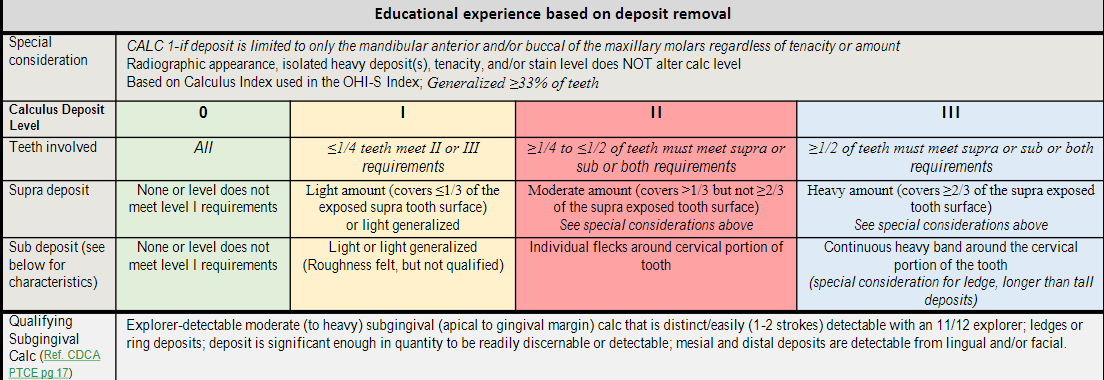
Step 5
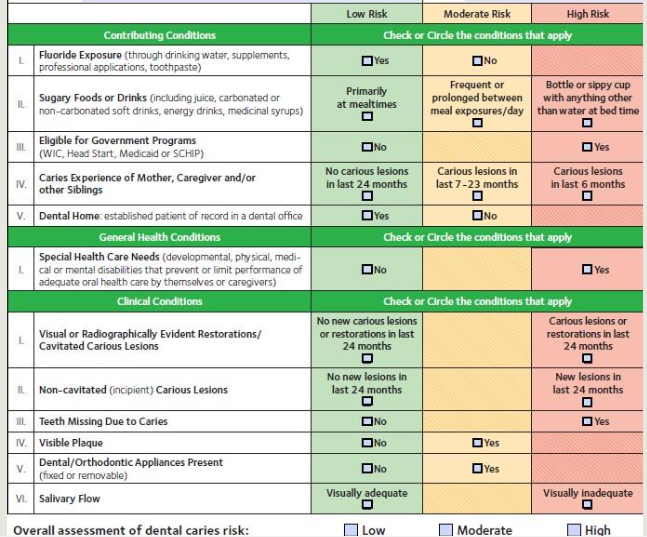
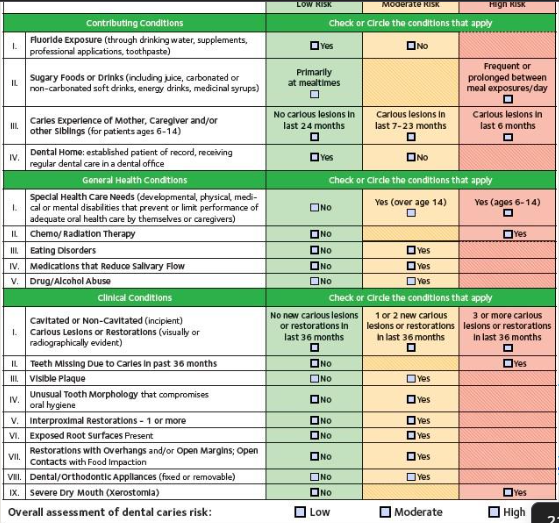
determine caries risk level
managing risk factors
Child less than 6 yrs Caries risk level assessment (0-6 yes)
Caries risk assessment more than 6 yrs
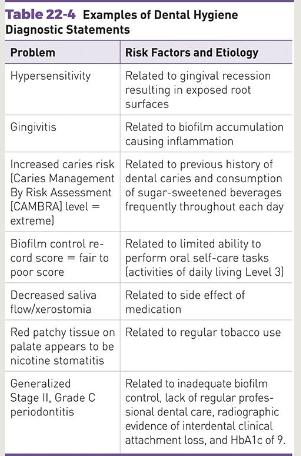
Develop the DHD
1) Use of evidence-based analysis of the assessment findings to determine the patient’s or community’s dental hygiene needs
2) Diagnostic Statements: Include the diagnosis and risk factors contributing to the condition diagnosed + Provide the basis for developing the care plan focusing on:
+ Education
+ Oral self-care
+ Prevention
+ Dental hygiene treatment
(all within scope of dental hygiene practice and referral)
Dental hygiene prognosis
forecast of the anticipated outcome
how’s the patient going to respond to treatment?
based on treatment and self care behavior goals set by clinician with the patient during the planning phase
Factors for individual tooth prognosis: Individual tooth prognosis, percentage of bone loss, clinical attachment loss, Extent and type of bone loss, presence & severity of furcation involvement, Mobility, Caries, Tooth position, Occlusal trauma
Factors for overall prognosis: Age, Medical status, rate of disease progression, patient cooperation and compliance with recommendations, Compliance with recommendations, oral habits and behaviors, Oral health literacy
Putting it all together
Evaluation of Assessment Data:
+Significance of medical & dental history
+Chief complaint
+Risk factors
+Summary of periodontal examination findings
+Summary of radiographic interpretation
+Periodontal classification
+Diagnosis
+Prognosis
Selection of dental hygiene interventions:
+Evidence-based interventions to prevent or manage oral disease
Develop a care plan
Document!! Where in IUSB?
Under DHD in clinical notes
Comprehensive patient assessment and diagnosis worksheet