Cells and Genomes: Universal Features and Diversity
1/440
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
441 Terms
Cells
Basic units of life, containing hereditary information.
Genomes
Complete set of genetic material in an organism.
Heredity
Transmission of traits from parents to offspring.
Species
Group of organisms capable of interbreeding.
Multicellular Organisms
Organisms composed of multiple specialized cells.
Single Cells
Independent living units, often microscopic.
Free Energy
Energy available to do work in biological systems.
Chemical Processes
Reactions that occur within cells to sustain life.
Cell Division
Process by which a single cell replicates.
Living Organisms
Entities that exhibit characteristics of life.
Diversity of Life
Variety of species and forms of life on Earth.
Universal Features
Common characteristics shared by all living cells.
Progeny
Offspring produced by reproduction.
Cell Machinery
Components within cells that perform essential functions.
Organism
Any living entity, from single cells to complex forms.
Biological Functions
Processes that sustain life, like metabolism and reproduction.
Tree of Life
Diagram showing evolutionary relationships among species.
Genetic Information
Instructions encoded in DNA for organism development.
Chemical Factories
Cells that convert raw materials into energy and matter.
Intricate Systems
Complex networks facilitating communication among cells.
Fertilized Egg Cell
Initial cell formed from the fusion of sperm and egg.
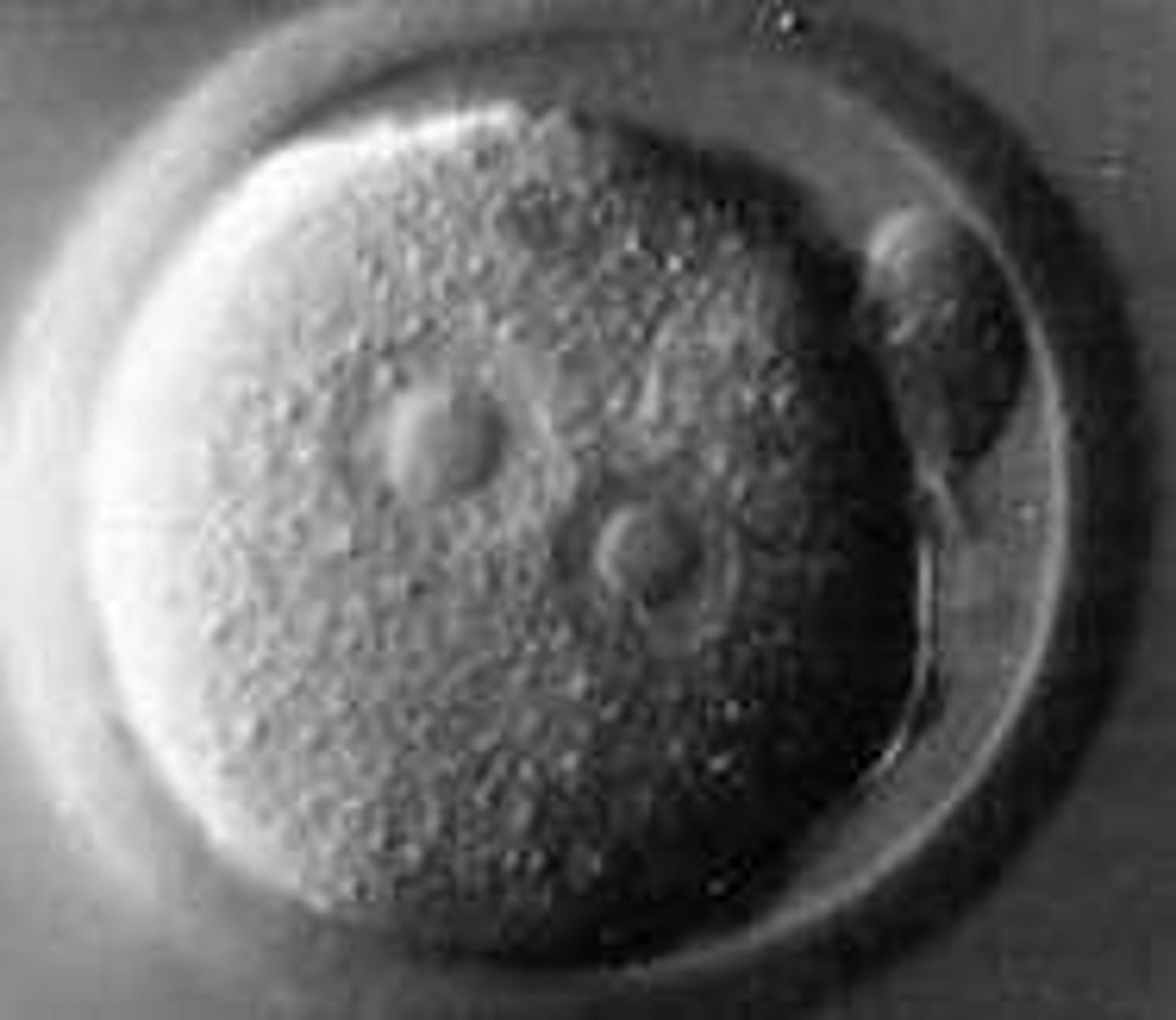
Sea Urchin
Example of a multicellular organism used in studies.
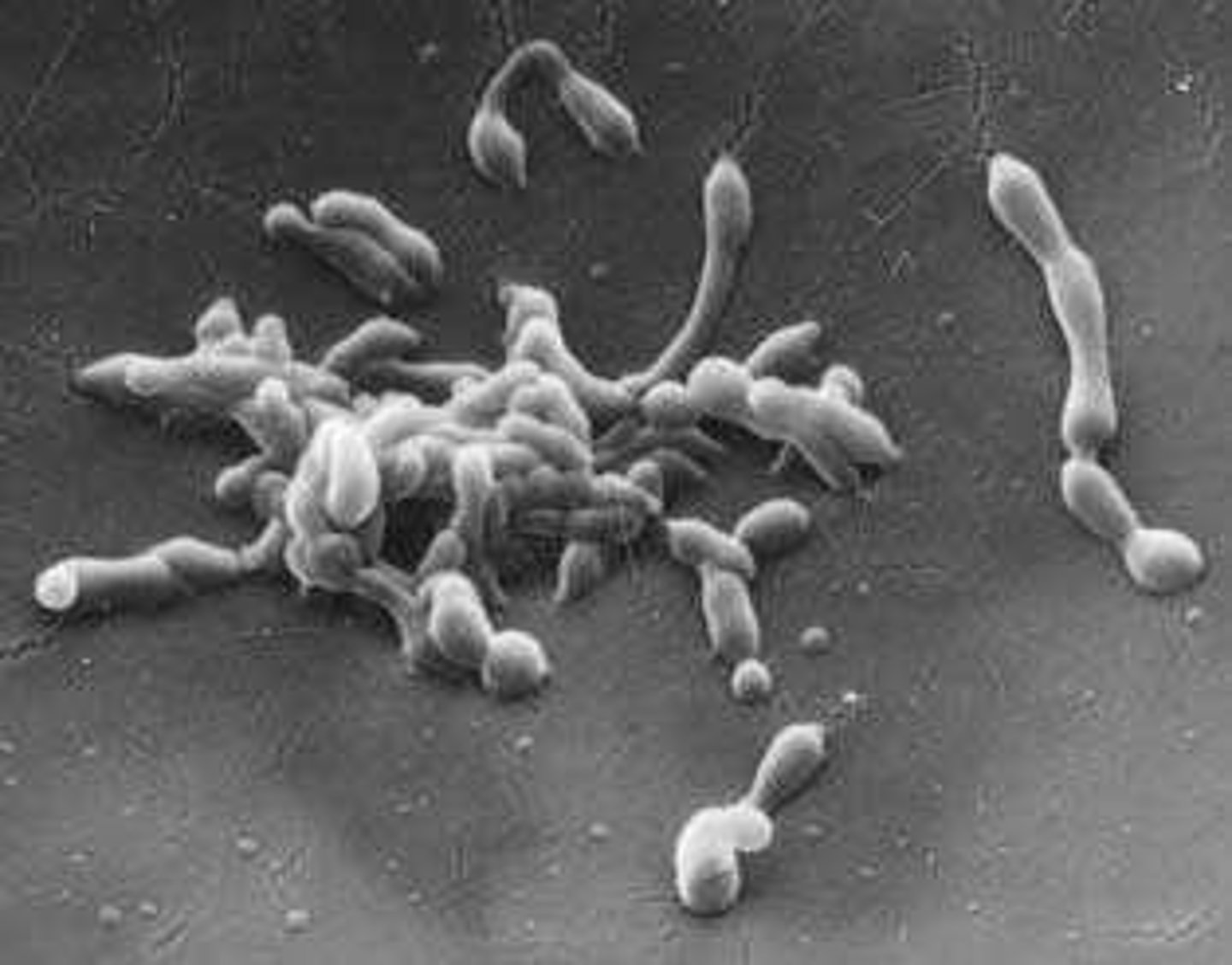
Fucus Seaweed
Example of a simple multicellular organism.
DNA
Double-stranded molecule storing hereditary information.
Nucleotide
Building block of DNA, consisting of sugar, phosphate, base.
Monomer
Single unit that forms a polymer chain.
Adenine (A)
One of four nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Thymine (T)
One of four nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Cytosine (C)
One of four nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Guanine (G)
One of four nitrogenous bases in DNA.
Sugar-phosphate backbone
Structural framework of DNA, linking nucleotides.
Double helix
Twisted structure formed by two DNA strands.
Base pairing
A pairs with T; C pairs with G.
Templated polymerization
DNA synthesis using a preexisting strand as template.
Deoxyribose
Sugar component of DNA nucleotides.
Hydrogen bonds
Weak bonds holding base pairs together in DNA.
Polymer chain
Long sequence of repeating monomer units.
Complementary sequences
Matching nucleotide sequences in DNA strands.
Replication
Process of copying DNA for cell division.
Nucleotide sequence
Order of nucleotides in a DNA strand.
Evolution of cells
Cells have diversified over 3.5 billion years.
Information storage
Cells store hereditary data in DNA format.
Chemical methods
Techniques used to read DNA sequences.
DNA extraction
Process of isolating DNA from cells.
Hereditary information
Genetic data passed from parent to offspring.
Sugar-phosphate linkage
Covalent bond connecting nucleotides in DNA.
Directionality
Orientation of DNA strand; guides molecular processes.
Complementary strands
Two DNA strands with matching nucleotide sequences.
Covalent bonds
Strong bonds linking nucleotides within a DNA strand.
DNA replication
Process of copying DNA to create new strands.
Template strand
Original DNA strand serving as a guide for replication.
New strand
Complementary DNA strand synthesized during replication.
RNA synthesis
Transcription process producing RNA from DNA template.
Transcription
First step in gene expression, forming RNA from DNA.
Translation
Process of synthesizing proteins from RNA templates.
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Single-stranded polymer crucial for protein synthesis.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Double-stranded polymer storing genetic information.
Uracil (U)
RNA base replacing thymine (T) found in DNA.
Ribose
Sugar in RNA backbone, differs from DNA's deoxyribose.
Amino acids
Building blocks of proteins synthesized during translation.
Polymers
Large molecules made of repeating structural units.
DNA strands separation
Process allowing replication by pulling apart double helix.
Polymer molecule
A large molecule made of repeating subunits.
RNA monomers
Building blocks of RNA, differing from DNA.
RNA transcripts
Copies of RNA synthesized from DNA segments.
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
RNA that conveys genetic information for protein synthesis.
Single-stranded RNA
RNA consisting of a single chain of nucleotides.
RNA backbone
Flexible structure formed by sugar-phosphate links.
Internal associations
Interactions within RNA that stabilize its structure.
Complementary segments
Nucleotide sequences that can base pair with each other.
RNA folding
Process where RNA adopts a specific three-dimensional shape.
Catalyze chemical changes
Facilitate reactions involving other molecules.
Polypeptides
Chains of amino acids forming proteins.
Protein synthesis
Process of creating proteins based on mRNA instructions.
20 types of amino acids
Standard set of building blocks for proteins.
Core structure of amino acids
Common framework for all amino acids.
Distinctive chemical character
Unique properties of each amino acid due to side groups.
Three-dimensional form
Specific shape proteins adopt based on amino acid sequence.
Reactive sites
Areas on proteins that interact with other molecules.
RNA catalysis
RNA's ability to accelerate chemical reactions.
Evolution of life
Development of living organisms from simpler forms.
Cell mass composition
Majority of cell's mass consists of proteins.
Polysaccharide
A polymer chain of sugar monomers.
Lysozyme
An enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of polysaccharides.
Catalytic site
Region on an enzyme where substrate binds.
Enzyme
Protein that catalyzes biochemical reactions.
Covalent bond-breaking reaction
Reaction that breaks covalent bonds between molecules.
Polynucleotides
Nucleotide polymers that encode genetic information.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid, involved in protein synthesis.
mRNA
Messenger RNA, carries genetic information from DNA.
Codon
Triplet of nucleotides that codes for an amino acid.
tRNA
Transfer RNA, brings amino acids to ribosomes.
Anticodon
Sequence of three nucleotides on tRNA complementary to mRNA.
Ribosome
Molecular machine that synthesizes proteins from mRNA.
Feedback loop
Cycle where products influence their own production.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
RNA component of ribosomes essential for protein synthesis.
Amino acid sequence
Order of amino acids in a protein determined by mRNA.
Self-reproducing behavior
Characteristic of living organisms to replicate themselves.
Structure maintenance
Function of proteins to maintain cellular integrity.
Signal sensing
Ability of proteins to detect and respond to signals.