Forensic Biology Exam 1
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Stimulus
a detectable change in an organism's internal or external environment that triggers a physical or behavioral response
Chemotaxis
the directed movement of a cell or organism in response to a chemical signal. This fundamental process allows organisms like bacteria to move toward nutrients and away from toxins, while in multicellular organisms, it guides cells such as immune cells to sites of infection or injury.
Phototaxis
the bodily movement of a motile organism in response to light, either toward the source of light ( positive phototaxis ) or away from it ( negative phototaxis ).
External Stimuli
sensory inputs from the external environment, such as sights, sounds, temperature changes, and touch, that trigger a physical or behavioral response in an organism
Internal stimuli
changes, feelings, or conditions originating within an organism's body that prompt a response, often to maintain homeostasis, the body's stable internal environment
Phospholipid Bilayer
Keeps whats inside the cell inside and to regulate the what goes in and out
Homeostasis
the automatic process by which a living organism maintains a stable internal environment necessary for its survival, adjusting to external changes. this includes self regulating process that involves keeping internal factors like body temp. blood glucose levels and hydration. includes the nervous system and endocrine system.
Importance of Reproduction
vital for the continuation and survival of species by creating new individuals to replace dying ones, ensuring genetic diversity through sexual reproduction for adaptation and evolution, and driving population growth and the spread of species into new habitats
Adaptation
all living orgs exhibit a fit to their environment. fit = adaptation consequence of evolution via natural sleection
Structural Adaptation
a physical feature or body part of an organism, such as fur, claws, or webbed feet, that enhances its survival and ability to reproduce in its specific environment
Behavioral Adaptation and example
an action or behavior an organism performs to increase its chances of survival and reproduction in its environment
Are genes the only thing that impacts the growth and development of an organism?
No things like environment and nature/nurture have an effect as well.
Biological Hierarchy
Atom--> Macromolecule--> Organelle-->Tissue--> Organ Systems
Biological Evidence
any biological material from a crime scene or person, such as blood, saliva, semen, hair, and skin cells, that contains genetic material like DNA
Toxicology
scientific discipline that studies the adverse effects of chemical, physical, and biological agents on living organisms, particularly humans. Variety of branches such as analytical, applied, clinical, forensic, environment, reproductive and developmental and immuno
Goal of toxicology, what was taken, when was it taken, how much was taken and did this substance contribute to cause of death.
The above things work together to determine 1) manner of death and 2) mechanism of death
Post Mortem Toxicology
analysis of biological samples, ie blood and tissue for drugs poisons and metabolites.
Seized Drugs Analysis
physical evidence collection and characterization such as pills and powders/
Questions Answered by PostMortem Toxicology
1. Manner of death
2. Mechanism of death
Questions Answered by Seized Drug Analysis
1. What was taken?
2. When was it taken?
3. How much was taken?
4. Did this substance contribute to the cause of death?
Xenobiotic
substances that are foreign to the body
Drug
compound that caused a physiological effect
Poison
a substance that when ingested results in a toxic or damaging physiological response aka toxins
Mary Anne Cotton
England’s first serial killer. only proved to have killed 1 person but a lot of people (20
) around her died from eating poisoned porridge
Inheritance Powder
a historical nickname, particularly in 17th-century French society, for arsenic, a tasteless and easily administered poison used to murder wealthy relatives for their inheritance
Arsenic + name of dye
can bond with hydrogen, oxygen or carbon as well as other elements covalently. can also form alloys with metals. Can be used in industry, cancer treatments (arsenic trioxide) and pesticides as well as to create the dye arsenic green, scheeles and paris green
Matthew Orflia
father of toxicology, dean of medical faculty university that in Paris. cowrote he first paper on poison s in 1814 and studied many poisons especially arsenic.
Isotope, how many does arsenic have.
a variation of a chemical element where atoms have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons, giving them different atomic masses. 33 known isotopes only one stable one.
Covalent Bond
strong bond between 2 or more atoms. It forms when an electron is shared btwn 2 elements
Polar Bond
electrons are shared unequally between two atoms in a molecule,
Non Polar Bond
a covalent bond where two atoms share electrons equally
List 3 things that can affect a drug's ability to be toxic.
Body Weight, Fat %, and individual metabolism
List 3 modes of entry for a drug.
inhalation. oral, IM Injection, IV injection or Dermal Entry
First Pass Effect
all drugs first delivered to liver from gastrointestinal tract to the liver via a portal vein fraction of drug is metabolized in the liver before reaching systemic circulation. therefore bioavailability of the drug is reduced. greater the first pass effect the lower bioavailability of the drug and extent of drug reaching systemic circulation.
2 contributing factors to toxicity in poisoning.
Mode of ingestion
-Identification, measurement &
location of metabolites
-Body weight
-Fat %
Individual metabolism

Levels of toxicity for opiates and opioids. most toxicity given the displayed dose.
carfentanyl
Opiates
derived from poppy seed pods of the opium plant, Heroin ex
Opioid
Can be synthetic which was developed after WW2 and has extreme toxicity. Street heroin can be cut with these synthetic drugs and can be extremely deadly. Increase feelings and high but with more risk.
Opioid and naloxone
When administered intravenously, naloxone completely reverses the effects of opioids within a few minutes
ADME
Administration, Distribution, Metabolism and Excretion
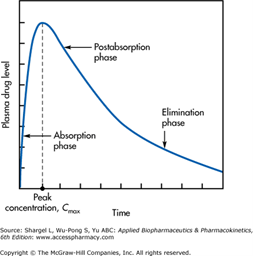
Drug level in body
A)enters via inhalation, oral, injections or dermal entries.
D) may distrubute via plasma (4), interstital fluid (10) and intracellular fluid (28). Total body fluid is 42 L
M) Mode of entry can directly affect metabolism of a drug
Also, the size of the molecule, charge and solubility in water
or fats can affect metabolism
then its broken down vis the liver primarily, kidneys filter out the drugs from blood, into urine, brain , hair and nails.
E) lungs, milk, sweat, saliva, kidneys to liver is lipophillic drugs, urine. Liver to kidneys is hydrophillic drugs. liver to small intestine is bile, feces
arrows mean absorption, peak conc, post absorp and elimination
Metabolite, what can it tell us about drugs and where is the primary loc it can be found
a small molecule, such as glucose or an amino acid, that is either a product or an intermediate in the chemical reactions of metabolism
liver primary location and location as well as amount is important.
The presence and type determine time since ingestion and whether the person died from an overdose or from delayed toxic effects.
Some drugs are metabolized very quickly, so identifying may be the only way to confirm drug use before death.
Metabolites tell investigators that a drug was used and give clues about when, how much, and how recently it was taken, helping confirm whether the drug caused or contributed to death.
Metabolism of drugs
Mode of entry can directly affect drug
Also, the size of the molecule, charge and solubility in water
or fats can affect metabolism
then its broken down vis the liver primarily, kidneys filter out the drugs from blood, into urine, brain , hair and nails.
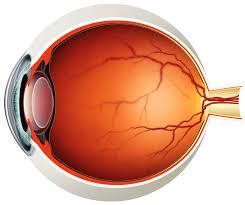
vitreous humor, what is the key advantage when testing for metabolites
clear gel like substance that fills eye, blood alc concentration, moto vehicle trauma, work place accidents, suicides and homicides. can be a reliable sample when other tissues have begun decomposition
Resistant to contamination: provides accurate drug levels long after death.
Phospholipid Bilayer --When the phospholipid bilayer is described as "fluid" this implies that the bilayer is________________________.
Depending on the temperature the two fats move. When its cold they move closer together when its hot they move farther apart. Cholesterol also facilitates movement by keeping the phospholipids from pulling part or clustering too close together and becoming rigid. Lastly, the two different types of fat ,saturated and unsaturated fats, facilitate space for movement.
Cell Membrane
critical to the functioning of a cell, fluid mosaic. the protective outer boundary of all cells, controlling what enters and leaves the cell through a selectively permeable phospholipid bilayer
Cell Membrane - -2 key properties of a cell membrane are that they can function as a __________________ and a _____________________ barrier for the cell.
Physical and Chemical
Saturated Fats morphology
straight and linear
Unsaturated Fats Morphology
bent, or kinked
Fluid Mosaic
Large pieces of artwork made of many tiny pieces."Fluid" refers to the ability of membrane components, including lipids and proteins, to move laterally and maintain the membrane's dynamic nature. "Mosaic" describes the varied proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates embedded within or attached to the phospholipid bilayer, creating a complex and diverse surface
Cholesterol and Lipid Bilayer
Facilitates the movement, and also keeps the phospholipids from pulling apart or from clustering too closely together and becoming rigid
Cell Communication Importance
allows organisms to grow, develop, function, and maintain homeostasis by coordinating actions, responding to stimuli, and regulating internal processes
Integral Membrane Proteins
exposed to aqueous environment on both sides of the membrane and is used to transport molecules across membrane.
Peripheral Membrane Proteins
Located on surface of membrane
Passive Transport
Does not require energy, molecules move through membrane based on Osmosis ( movement from high to low concentration) or diffusion which is not dependent on concentration.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high to low,
Osmosis
water moving across a semipermeable membrane from a higher concentration to a lower concentration, type of diffusion
Active Transport
Cells use energy to move molecules across the cellular membrane. Utilize specific proteins and sometimes have to work against concentration gradient.
Bulk Transport
Endo and Exocytosis, energy requiring process for moving large particles or molecules across cell membranes using membrane bound vesicles
Exocytosis
Moving something out of the cell, the cell forms a vesicle around a material, the vesicle then moves through cell until it fuses with the cell membrane and releases the material out of the cell.
Endocytosis
Taking something into the cell, Pinocytosis takes in fluids and solute. Phagocytosis takes in larger substances such as bacteria.
Phagocytosis
a form of endocytosis where the cell takes in large substances such as bacteria
Bulk transport of Dopamine occurs due to hijacking of endocytosis into the neuronal synapse. What drug does this?
An inhibitor such as Cocaine
What is a thermophile (archaea) and what type of environment do these types of bacteria live in?
Thrive at high temperatures and produces methane. Thrive in hot temperatures.
Specialized small organs within a cell are called___________________________________.
Organelles
Cytoskeleton
Contains an elaborate array of protein fibers that serve functions such as establishing cell shape, mechanical strength, locomotion (cilia and flagella), chromosome seperation during mitosis and meiosis. Intracellular transport of organelles.
Nucleus
contains the cells genetic material and this material exits as chromosomes. Includes the nuclear envelope, nuclear pore, nucleoplasm, chromatin, nucleolus and ER on outside.
ribosome
A small dense organelle mostly made of rRNA (ribosomal RNA) , its attached to the ER or free in the cytoplasmic liquid. Makes proteins . Contains a small and large subunit.
Smooth ER
lacks ribosomes and makes proteins used in the cell
Rough ER
has ribosomes on its surface and makes proteins to expert
Lumen
where synthesized proteins are released after they are completed. they may get sugars and undergo folding modifications
Lysosome
break down unwanted macromolecules.
Plant Cell
Rigid cell wall made of cellulose which gives the cell support, contains a vacuole which contains cell sap that is a weak solution of sugar and salt. green chloroplasts which contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
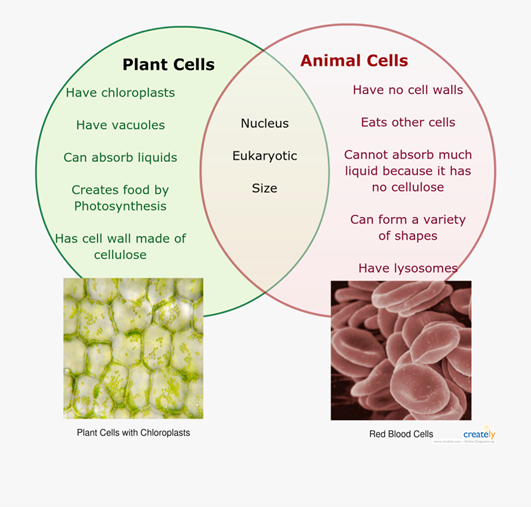
Vacuoles
store water, waste and or food. helps plant cells maintain shape and there is only one large one in plant cells.
Animal cell
Shares a nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane and mitochondria with the plant cell.
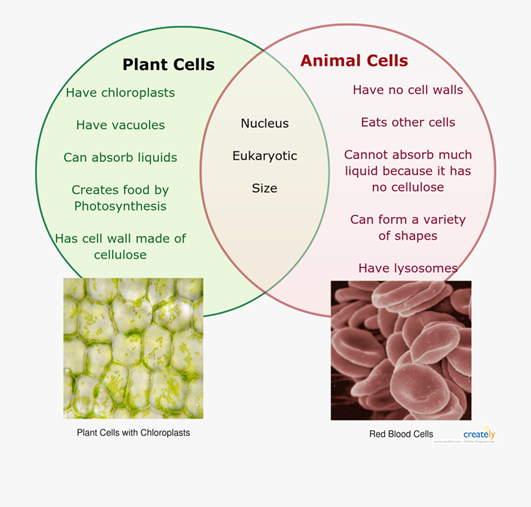
Chloroplasts contain a green pigment called ________________________________.
Chlorophyll
Mitochondria
*Critical player in cellular respiration
*Free floating organelles
*Distribution in the body is not equal. It’s based on energy needs
* have less genes than nuclear DNA
*Forensic scientists can extract and analyze more of this than nuclear DNA. This is an advantage.
*used to analyze old bones, teeth, hair shafts, and other biological samples where nuclear DNA content is low.
-Mitochondria produce ________________________ which is a key molecule in cellular respiration that provides energy.
ATP
-Mitochondrial DNA is ___________________________- (matrilineal, patrilineal)
matrilineal
Probative Value
Evidence which is sufficiently useful to prove something important in a trial. Prove an issue. Make something more or less probable
Mitochondria and Probative Value
Unlike nuclear DNA, which is completely unique to an individual (outside of identical siblings), mtDNA sequences are frequently identical between different people. The occurrence of a match between a person’s mtDNA and mtDNA found at a crime scene only implies their presence there, rather than confirming it.
Because jurors may not understand these properties of MtDNA they may make decisions based on bad assumptions.
difference between internal and external stimuli and examples.
external comes from environment such as temperature, light or sound and internal is from within like hunger thirst pain or emotions
marsh test and the lafarge case
24 to Marie Lafarge accused of killing her husband Charles by putting white powder in his food but preliminary test showed no trace of arsenic. Orfila was called in and found evidence of arsenic using the marsh test which can detect small amounts in food, tissue or stomach contents.
1)Sample placed in flask with arsenic free zinc (metal) and sulfuric gas
2) arsine gas is produced and some hydrogen
3) these products go through a thin drying tube into a hard glass tube/container in which its heated
4) arsenic deposited as a black “mirror” on any part of tube just beyond the area being heated.
key indicator and product is a silvery-black deposit of arsenic
opioid v opiate and example of each
opiates are naturally derived from the opium poppy plant, while opioids are a broader category that includes all natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic substances that act on the body's opioid receptors
morphine v fentanyl
Concisely explain the difference between Integral membrane proteins and peripheral membrane proteins.
and are embedded in the bilayer and facilitate the passage of molecules into and out of the cell.