Exam 2 SMT 444 Q&A
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are 2 of the 4 strategies for Strengthening?
reduce grain size
Form solid solutions
Precipitate strnegthening
Cold work
A ductile metal becomes softer and weaker as it is plastically deformed.
False
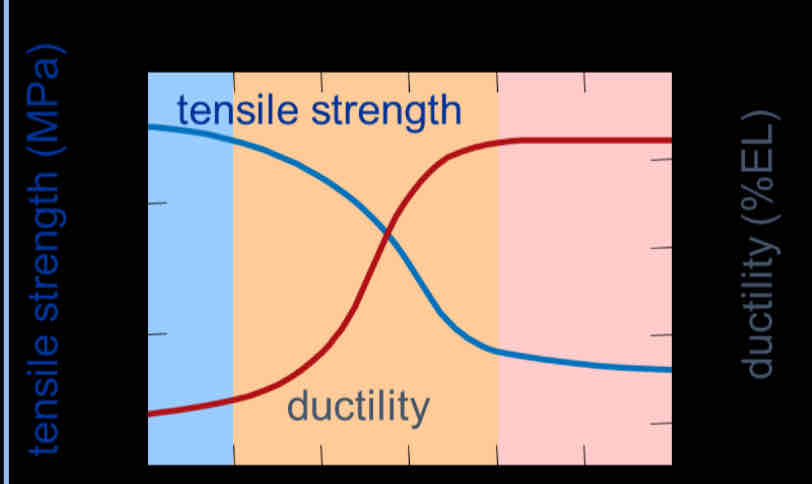
What are the 3 Annealing stages and what order do they go in?
Recovery
Recrystallization
Grain growth
How can anisotropy be induced in the σy direction?
rolling
What gets annihilated in the heat treatment recovery stage?
Dislocation
Give an example for each structure type (AX, AX2, ABX3, AB2X4)
Ax: NaCl, MgO,FeO,CsCl,ZnS,SiC
AX2: CaF2, UO2, ThO2
ABX3: BaTiO3, SrZrO3,SrSnO3
AB2X4: MgAl2O4, FeAlO4
Give an example of an AX crystal structure that has an equal number of cations and anions.
NaCl, CsCl, and zinc blende (ZnS)
What 2 factors determine the structure of crystals?
Relative sizes of ions and maintenance of charge neutrality
What type of material is made from the two most common elements on earth?
Silicates
How can a periodic table be used to predict the degree of ionic character displayed in bonding in ceramics?
The larger the electronegativity difference between two atoms, the greater ionic character will be displayed. Therefore, the farther two elements are from one another on the periodic table, the greater the resulting ionic character will be.
Differentiate between a Frenkel Defect and a Shottky defect
Shottky has a paired set of cation and anion vacancies. Frenkel has an interstitial pair of vacancies. (Shottky is top)
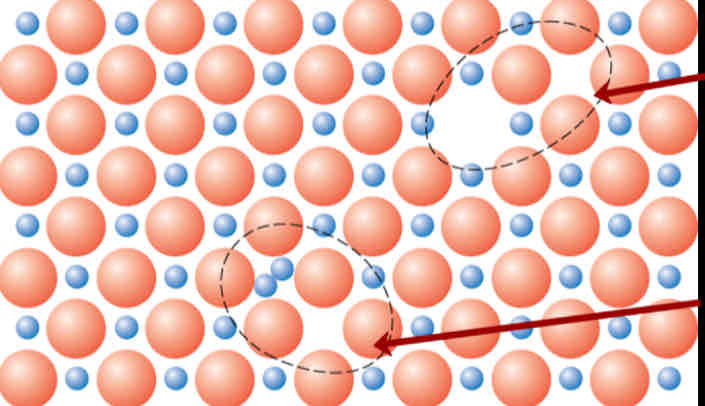
The ___ must be maintained when impurities are present.
Electroneutrality
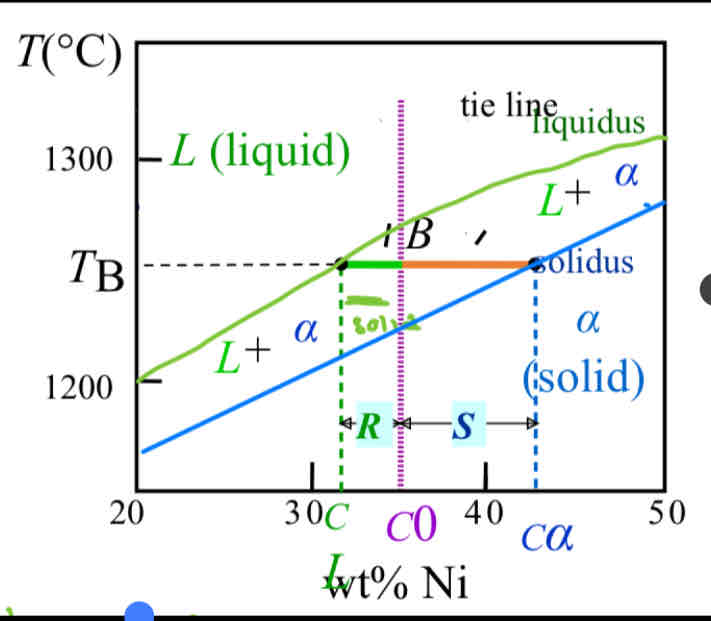
How do you use the tie line to find the composition?
The closer C0 is to the liquidus line, the more liquid there is, so you measure the opposite side of the tie line and label it as the liquid concentration (ie. 8/11)
There are 2 ways to use a tie line
Second way is using it to find how much wt% there is in the liquid or solid phase by following it to the liquid/solid phase and following down to to the wt%
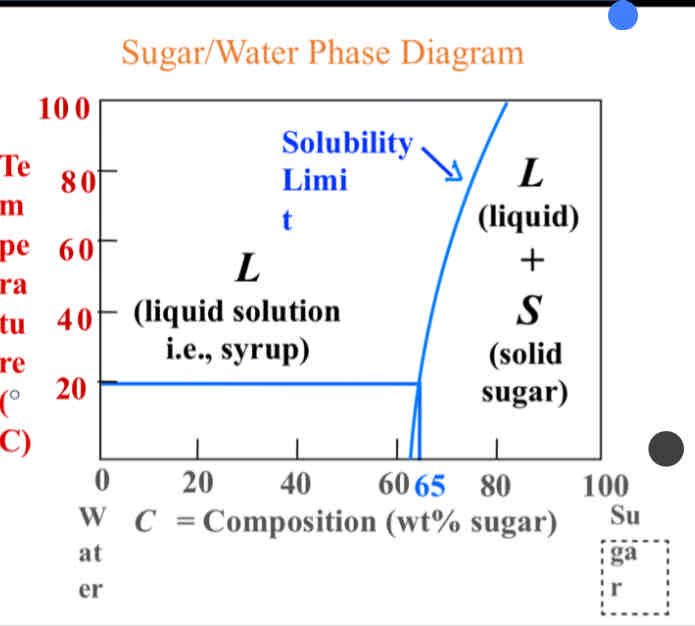
What is the Solubility Limit?
Maximum concentration when only one single phase solution exists.
What are the bonds in ceramics ?
Ionic and covalent
Glass Ceramics - Transform inorganic glasses from a _____ to _____ state by high temperature heat treatment ; process called crystallization
Non crystalline to crystalline
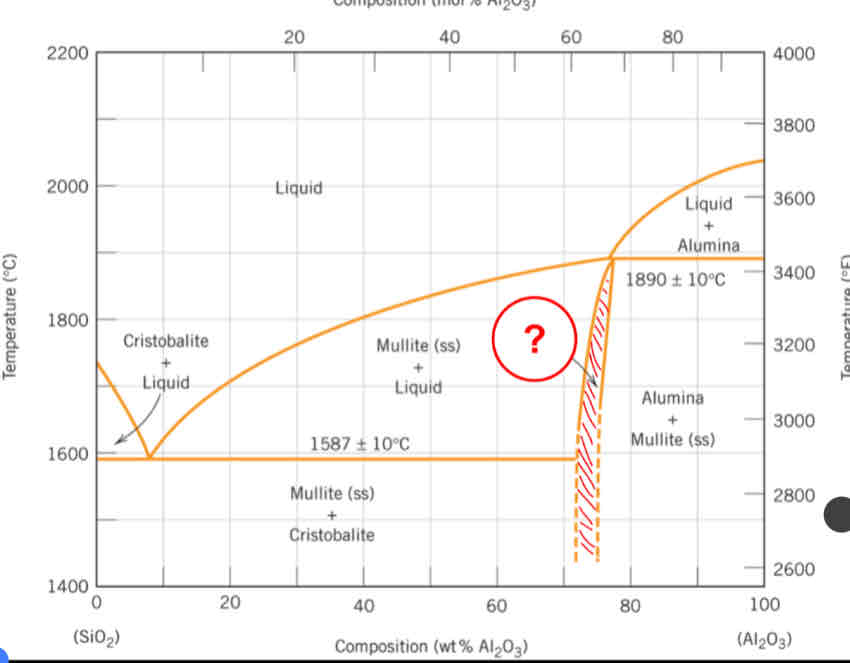
What is the name of the mineral referred to on this silica-alumina system phase diagram?
Mullite
What are the main properties of refractories?
Capacity to withstand high temperatures without melting or decomposing, capacity to remain unreactive and inert when exposed to severe environments; ability to provide thermal insulation.
Why are tensile tests difficult to be performed on brittle materials? What test is done instead?
Tensile tests are difficult due to the inability of gripping the material. A 3-Point bending test is performed instead.
What are the 6 classifications of ceramics? Provide an example for each.
Glasses - optical, composite reinforcement, containers/household
Clay Products - whiteware
Refractories - furnaces
Abrasives - sandpaper
Cements - composites
Advanced Ceramics - engine rotors, valves, bearings, sensors
Glass is a noncrystalline silicate containing other oxides. What are some of these oxides?
CaO, Na2O, K2O, Al2O3
True or false: The presence of silica is beneficial to the high-temperature performance of basic refractories.
False
True or false: Fireclay refractories are a load-bearing material.
false
Describe some of the pros and cons of using advanced ceramics for parts in automobile engines.
Pros: Advanced ceramic parts are able to operate at high temperatures, they have low frictional loss, they are able to operate without a cooling system, and they are lighter than current engines.
Cons: Advanced ceramic parts can be brittle, it’s difficult to remove internal voids, and they can be difficult to form and machine.
What are the two types of heat treatments of glass and what is the process?
Annealing - removes internal stress caused by uneven cooling
Tempering - uneven cooling of the outer layers of glass with hot innards that causes the outer faces to be compressed and the inside to have tension; suppresses surface scratches and cracks
What are the ceramic fabrication methods?
Slip casting - grind and screen constituents to desired particle size, mix it with water and other constituents to form slip, pour the slip into the castings (hollow or solid component), then dry and fire the casted piece.
Hydrocasting forming - mill and grind screen constituents to desired particle size, then extrude the mass into desired shape, then dry and fire the formed piece (a brick).
T-F: If you’re drying a ceramic piece after fabrication and it dries too fast, it’ll be stronger and stay in form better than even and full drying.
False, it will cause the sample to warp and crack due to non-uniform shrinkage
T-F: Viscosity decreases as temperature increases.
True, as temperature increases, the molding and deforming ability increases simultaneously.
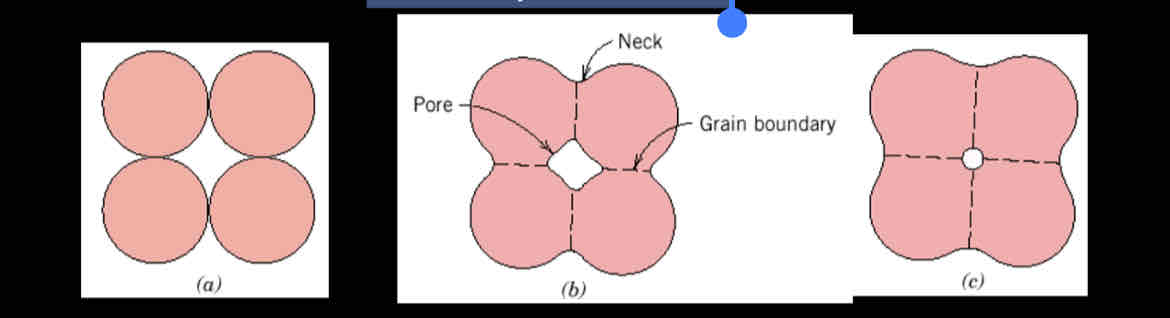
What is sintering?
It occurs during firing of a piece that has been powder pressed - the powder particles coalesce and reduce pore size.
Why are copolymers a large focus for modern-day material scientists?
Copolymers allow for the discovery and development of new materials through improved properties by varying polymerization.
What makes working on polymers with double bonds and bulky side groups difficult?
It is difficult to rotate and change the shape of the polymer.
What are the four types of polymer structures?
Linear, branched, crosslinked, and network polymers