Modern Array Techniques to Improve Beam Profile
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What are the three methods for improving beam profile?
Dynamic aperture
Dynamic apodization
Sub-dicing the elements
Dynamic aperture, dynamic apodization, and sub-dicing the elements are all possible or not possible with a single crystal transducer?
Not possible.
Dynamic aperture, dynamic apodization, and sub-dicing the elements are all automatic or sonographer controlled?
Automatic.
What is an aperture?
The diameter of crystal(s) used to transmit the pulse and/or receive the echoes.
Aperture affects what?
The beam profile.
Old single crystal transducers have what type of aperture?
Fixed.
Array transducers have what type of aperture?
A variable, dynamic aperture.
What is dynamic aperture?
Where the system can set the optimum aperture for the scan. (Electronically Forming DA beam!)
What does a dynamic aperture do?
It varies the size of the transmitting or the receiving aperture.
Dynamic aperture does what to beam geometry?
Improves beam geometry.D
Dynamic aperture improves what type of resolution?
Lateral resolution.
What does dynamic indicate in dynamic aperture?
That it is continuously changing.
Where is dynamic aperture applied?
In the background (not sonographer control).
What type of aperture is used for deep structures?
Wide (Deep and wide, shallow and narrow).
What type of aperture is used for superfical (shallow) structures?
Narrow (Deep and wide, shallow and narrow).
What are side lobes and grating lobes?
Weak intensity peripheral beams.
Side lobes are produced by what type of transducers?
All transducers.
Gating lobes are produced by what type of transducers?
Array transducers.
What are side lobes and grating lobes caused by?
Width and length mode vibration in crystals.
Side lobes and grating incidence can be reduced by what?
Apodization.
What is apodization?
The variation in amplitude of driving voltages to the elements in an array transducer.
Apodization is applied in what type of transducer to suppress side lobes?
Array.
Apodization is what type of process?
A dynamic one, meaning it occurs automatically and is done in the background.
What does apodization do?
It combats side lobes and grating lobes by reducing the
Where are the strongest amplitudes when there is apodization?
To the center elements.
What are grating lobes?
Peripheral weak beams surrounding the main beam.
Grating lobes are produced by what types of transducers?
Linear and phased array transducers.
Grating lobes are caused by what?
Element spacing.
Grating lobes can produce what type of artifact?
Grating lobe artifact.
At what type of reflector (strong or weak) can grating lobe artifact appear?
Strong reflectors.
Grating lobes can be reduced with what?
Apodization and sub-dicing.
Grating lobes are worse with what type of beam steering?
Electronic beam steering.
What is sub-dicing?
An array transducer construction technique where elements are cut into small units with small spaces in between them.
What does sub-dicing do to geometry?
It changes the array geometry.
Sub-dicing reduces what?
Grating lobes.
Phased arrays typically have more or less side and grating lobes than linear arrays?
More.
What does beamformer mean?
A term used to describe all the circuits used in modern equipment to produce the beam and receive the echoes.
What circuits are used in modern equipment that fall under beamformer? (6)
Beam steering
Transmit focus
Receive focus
Dynamic focus
Dynamic apodization
Coded excitation
The beamformer techniques uses what in the transducer to create the beam?
A digital chip.
What is the frequency of endovaginal transducers?
5-10 MHz
What is the frequency of endorectal transducers?
5 MHz
What is the frequency of transesophageal transducers?
3 MHz
What is the frequency of endoscopic transducers?
12-20 MHz
What is the frequency of intraluminal transducers?
30 MHz
How are the crystals in biplane endorectal transducers situation?
One row of elements for longitudinal imaging and one row for transverse imaging.
And endoscopic transducer (phased array) has how many elements integrated into a 10 Fr catheter?
64.
What is Fr?
A unit for the French catheter scale, which measures the external diameter. 3 Fr = 1 mm, 10 Fr = 3.3 mm.
What are intraoperative transducers?
Those that are used in the operation room and used directly ontop of the region of interest. (ie. liver).
What are the four different display formats for ultrasound?
Sector
Rectangular
Trapezoid
Parallelogram
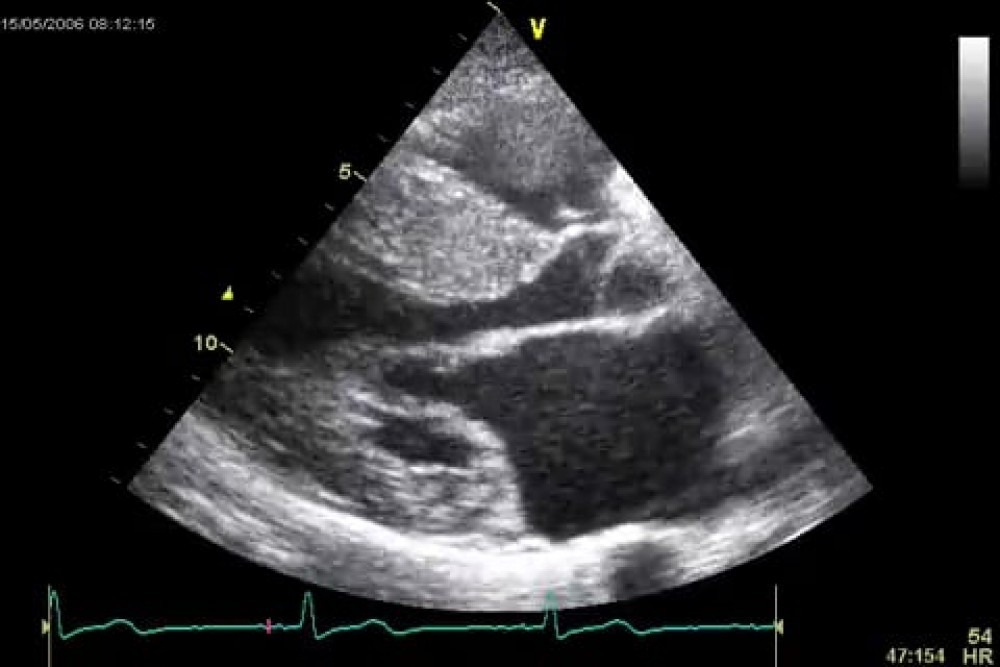
What does a sector display format look like?
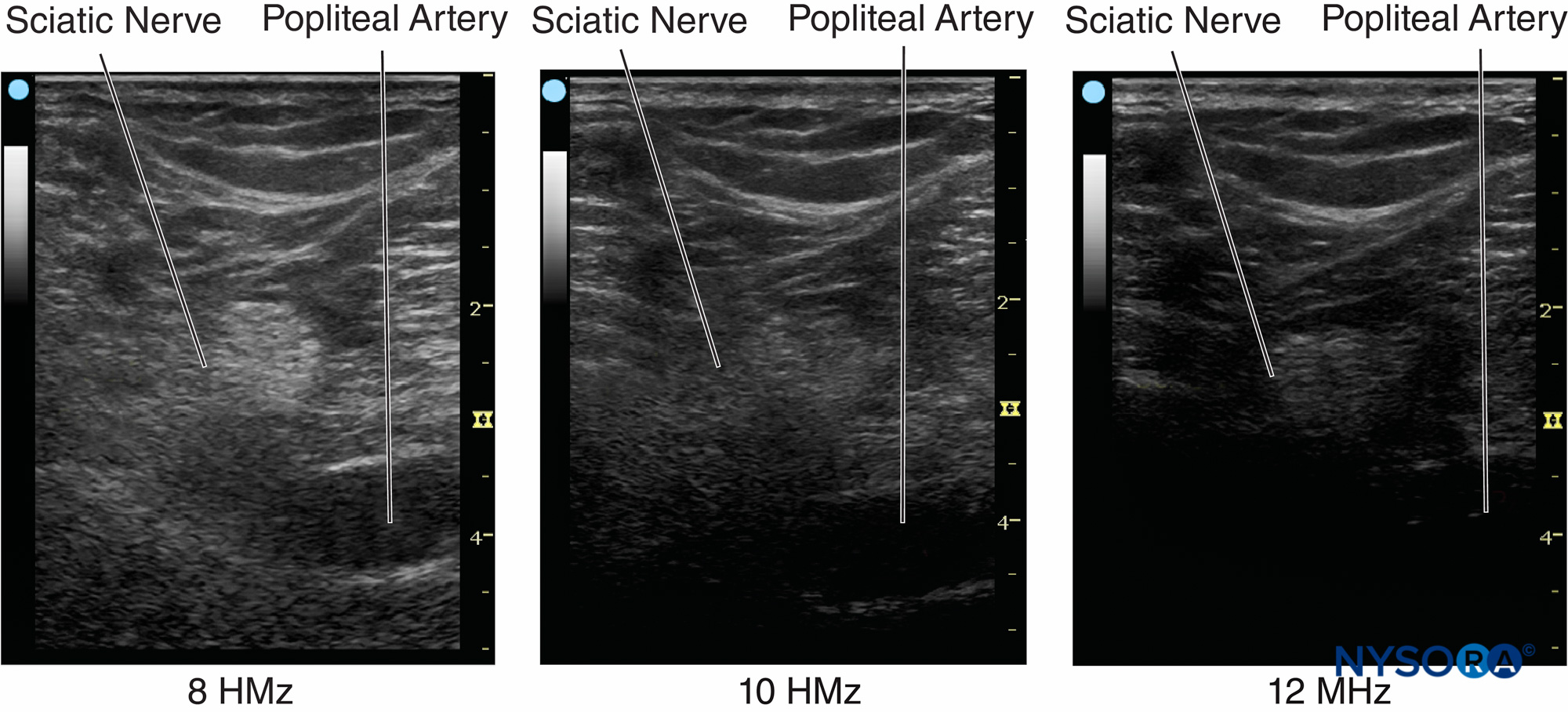
What does a rectangular display format look like?
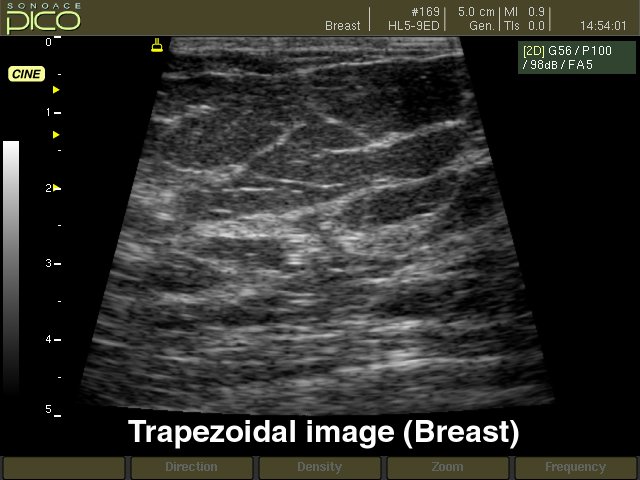
What does a trapezoid display format look like?
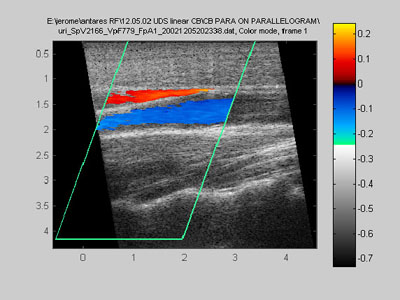
What does a parallelogram display format look like?
What is interpolation?
The filling in of the pixels between adjacent scan lines with averaged data.