ANTH 1001 Final
1/469
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
470 Terms
Lake
How is lacustrine sediment deposited?
Landslide
How is colluvial sediment deposited?
Wind
How is eolian sediment deposited?
River
How is alluvial sediment deposited?
Lacustrine
Which sediment is deposited by a lake?
Colluvial
Which sediment is deposited by a landslide?
Eolian
Which sediment is deposited by the wind?
Alluvial
Which sediment is deposited by a river?
The fossil animal you found was deposited in a lake and buried by lake sediments
Let’s say you found a fossil in some lacustrine sediments. Which conclusion can you reasonably draw from this? (The fossil animal you found was killed by a crocodile and ate fish, The fossil animal you found lived on land, The fossil animal you found lived in a lake, The fossil animal you found was deposited in a lake and buried by lake sediments)
Paleomagnetism
Which method can date when the earth’s magnetic polarity flipped?
OSL
Which method can date when sediments were buried and no longer exposed to light?
Carbon-14
Which method can date when a living organism died?
Argon-Argon
Which method can date volcanic eruptions?
context
The ___ of a fossil is extremely important in understanding the extinct organism’s behaviors when it was alive.
Cranially oriented glenoid fossa on the scapula
Which trait is not a postcranial adaptation seen in humans? (Tibial plateau large and robust, Shorter arms than legs, Very robust femur, Cranially oriented glenoid fossa on the scapula, Valgus knee)
Shallow bicipital groove
Which trait is not a postcranial adaptation seen in chimpanzees? (Shallow bicipital groove, Tall and narrow pelvis, Long and curved metacarpals and phalanges, Robust arms, More asymmetric femoral condyles)
double, single
Bipeds have a ___ arch in the foot, while suspensory apes, like the chimpanzee, have a ___ arch.
True
True or false? The humero-femoral index is used to quantify the length difference between the entire arm and the entire leg of an individual.
Humerus
1
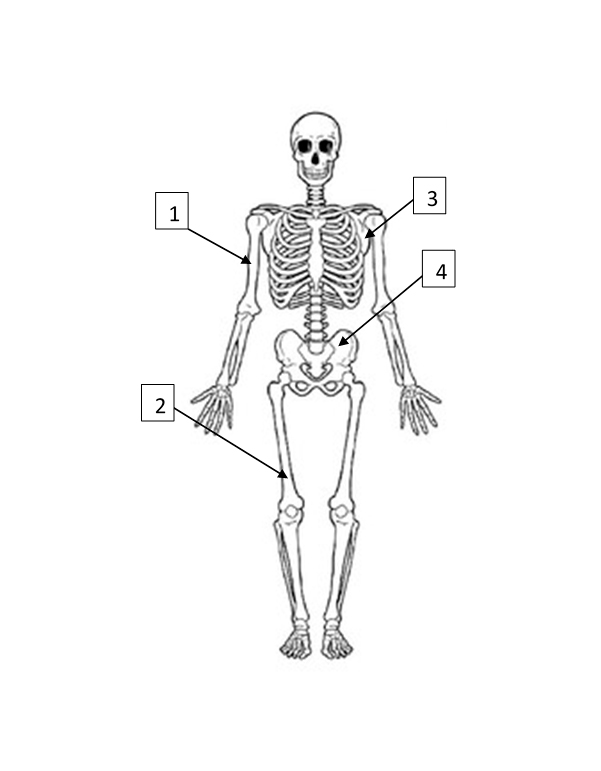
Femur
2
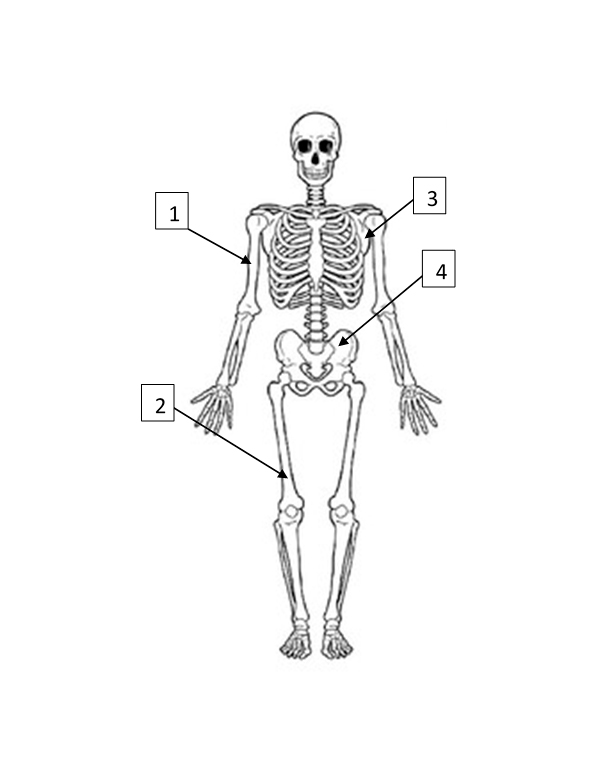
Scapula
3
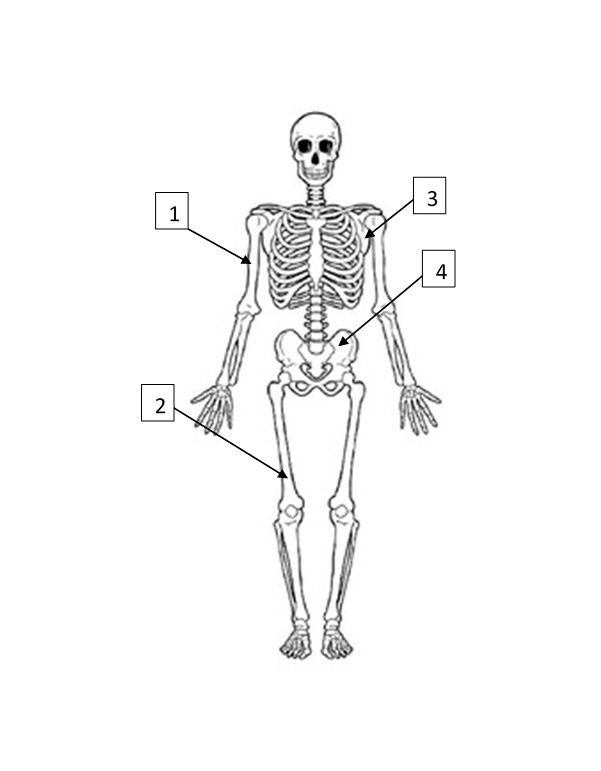
Pelvis
4
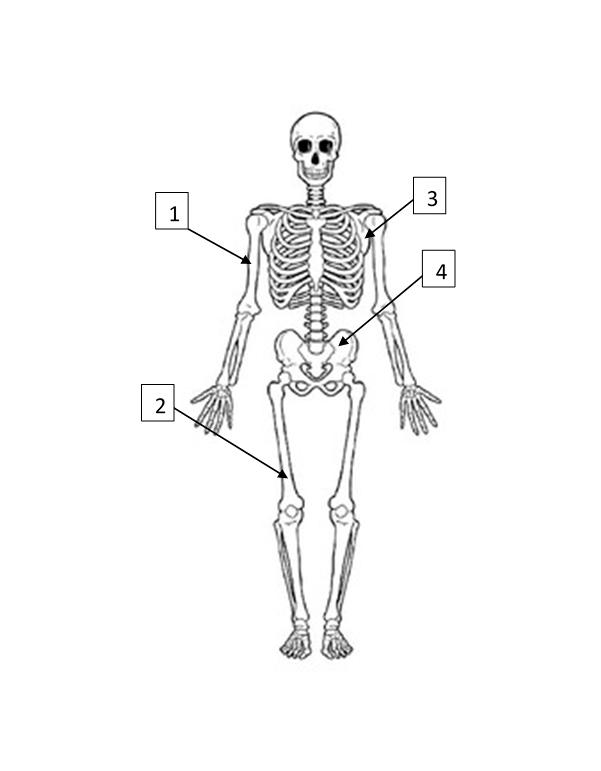
Ripe fruits
Chimpanzee diet
Insects
Tarsier diet
Cooked and/or processed foods
Human diet
Leaves and herbaceous plants
Gorilla diet
Strong and robust masticatory apparatus, Low and rounded cusped molars
Which morphological traits are adaptations for hard object feeding (seeds, nuts, hard fruit, etc.) in primates? (Strong and robust masticatory apparatus, Low and rounded cusped molars, Procumbent incisors, Prognathic face, Pointy premolars)
Thick enamel, Procumbent incisors
Which morphological traits are adaptations for frugivory (eating fruit) in primates? (Pointy and robust masticatory apparatus, Thick enamel, Pointy premolars, Procumbent incisors, High and sharp cusped molars)
High and sharp cusped molars, Pointy premolars
What morphological traits are adaptations for folivory (leaf eating) in primates? (High and sharp cusped molars, Pointy premolars, Thick enamel, Procumbent incisors, Weak and gracile masticatory apparatus)
masseter
The ___ muscle originates on the zygomatic arch and inserts on the lower part of the ascending ramus of the mandible.
diastema
The ___ is a gap next to the canine that leaves space for the corresponding upper or lower canine when the mouth is closed.
mean
The standard deviation is a measure of how much a measurement differs from the ___.
Size of the orbits
Which of the following is not a cranial feature that provides information about sexual dimorphism in primate species? (Size of the brow ridge, Size of the temporalis muscle, Degree of prognathism, Size of the orbits)
size
The coefficient of variation is the standard deviation divided by the mean. This removes differences due to ___.
10
If your coefficient of variation measurement is greater than ___%, you likely have multiple species in your sample.
habilis, rudolfensis
KNM-ER 1813 is attributed to Homo ___ while KNM-ER 1470 is attributed to Homo ___.
Platform
Flat area containing the point where the hammerstone struck
Point of percussion
Exact point where the hammerstone struck the core
Bulb of percussion
Bulge resulting from the percussion
Cortex
Outside rind of the nodule
Temporal variation, Age variation, Sexual dimorphism, Geographic variation
Variation between individuals within a species can occur due to what factors? (Temporal variation, Age variation, Sexual dimorphism, Geographic variation)
flake
A small, sharp piece of stone that is removed from a larger stone is called a ___.
Homo erectus/ergaster
Which hominin is the first (but not only) species associated with the Acheulean technology?
core
A stone nodule that has had one or more flakes removed from it is called a ___.
Beyond the Movius Line to the NE, there are few Acheulean tools found in the archaeological record, The Movius Line marks where bamboo grows in abundance (NE of the line) and H. erectus in this area might have preferred bamboo tools to complex stone tools
Which statement(s) is/are true about the Movius Line? (Hominins below the Movius Line are capable of more complex culture because they have abundant evidence of stone tools, Beyond the Movius Line to the NE, there are few Acheulean tools found in the archaeological record, The Movius Line marks the geographical division of early Homo and Homo erectus, The Movius Line marks where bamboo grows in abundance (NE of the line) and H. erectus in this area might have preferred bamboo tools to complex stone tools)
grammatical, semantic, phonemic, symbolic
Language is unique from other forms of communication observed in organisms other than humans because it is ___, ___, ___, and ___.
Icon
Connects the reference to the sign by physical similarity
Index
Connects the reference to the sign by a preexisting association
Symbol
Connects the reference to the sign by mutual agreement and convention alone
False
True or false? Allen’s rule indicates that limbs will be shorter and thicker relative to body size in warmer climates compared to colder climates.
True
True or false? Bergmann’s rule indicates that individuals in colder regions should be larger, and individuals in warmer regions should be smaller.
Australopithecus, Homo naledi, Paranthropus, Homo rudolfensis, Homo habilis
Which of the following hominins are only found in Africa? (Australopithecus, Homo heidelbergensis, Homo sapiens, Homo naledi, Paranthropus, Homo erectus, Homo rudolfensis, Homo habilis, Homo floresiensis)
adaptive process, event
Speciation is a(n) ___, not a(n) ___.
front teeth
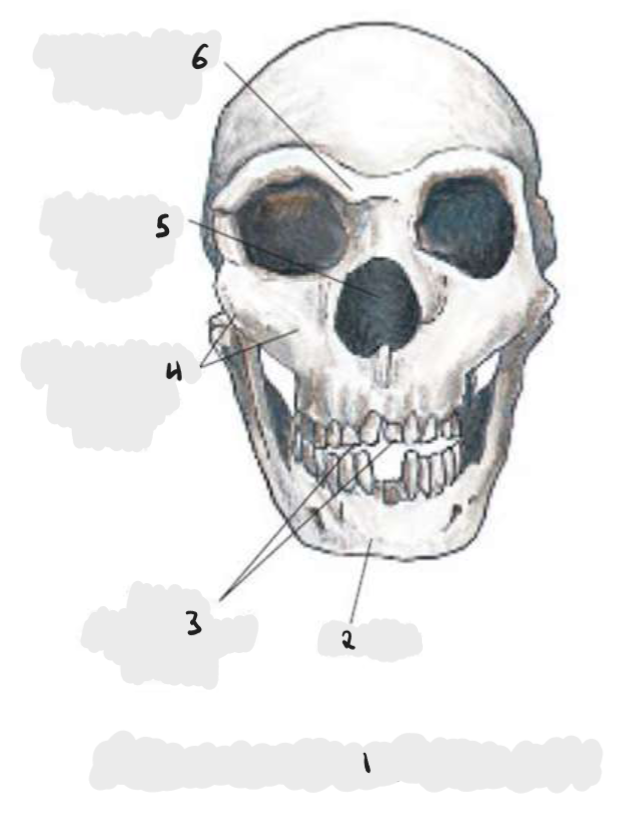
In the jaw, the greatest amount of force is placed on the ___ in a prognathic face.
Homo neanderthalensis
Which hominin has mid-facial prognathism, an occipital bun, a robust skeleton, and a retromolar gap?
Australopithecus, Paranthropus, and Homo habilis/rudolfensis are all associated with the Oldowan, Homo erectus is associated with both the Oldowan and the Acheulean traditions, Australopithecus afarensis was extant in East Africa when stone tools (even simpler than the Oldowan) were made at Lomekwi 3, Kenya
Which hominins are associated with particular types of stone tools? (Australopithecus, Paranthropus, and Homo habilis/rudolfensis are all associated with the Oldowan, Only Paranthropus, Homo habilis/rudolfensis, and Homo erectus are associated with the Oldowan, Only Early Homo and Homo erectus are associated with the Oldowan, Homo erectus is only associated with the Acheulean tradition, Homo erectus is associated with both the Oldowan and the Acheulean traditions, Australopithecus afarensis was extant in East Africa when stone tools (even simpler than the Oldowan) were made at Lomekwi 3, Kenya)
Paranthropus
While doing field work in Africa, you discover a skull with the following traits: a sagittal crest, flared zygomatic arches, strong postorbital constriction, molariform premolars, thick enamel, and an orthognathic face. Which genus of primate have you discovered?
Australopithecus had a more gracile cranial morphology and likely fed on less tough foods than Paranthropus
The main difference between Paranthropus and Australopithecus is… (Australopithecus had a significantly larger brain size when compared to Paranthropus; Paranthropus was a habitual biped while Australopithecus was an arboreal climber; Paranthropus was primarily a fruit-eater, while Australopithecus ate primarily nuts; Australopithecus had a more gracile cranial morphology and likely fed on less tough foods than Paranthropus; Paranthropus is more closely related to Ardipithecus than Australopithecus)
Homo erectus
Which hominin species first settled in East Asia (e.g., China, Indonesia, etc.)?
Social behaviors changed allowing for longevity as seen by old individuals at Dmanisi
Which of the following hypotheses for why Homo erectus was able to disperse out of Africa is supported by the fossil record at Dmanisi? (Climate change allowed African fauna in general to disperse out of Africa into Eurasia, and H. erectus followed these animals; H. erectus developed new stone tool technologies (found at Dmanisi) allowing them to inhabit a greater range of habitats; Social behaviors changed allowing for longevity as seen by old individuals at Dmanisi; H. erectus has a significantly larger brain than early Homo, which can be seen in the Dmanisi specimens; H. erectus had a monogamous mating system as indicated by reduced sexual dimorphism seen in the fossils at Dmanisi)
A fully opposable thumb, Complex tool use, A large brain
Which of the following features have been used to put species in the genus Homo? (A fully opposable thumb, Complex tool use, Pronounced sexual dimorphism, A large brain)
2-1.9 mya
You discover hominin skeletal remains at a site in East Africa. The hominin remains are found between two volcanic layers - the bottom layer dates to 2.5 million years while the top layer dates to 1.9 million years. The sediments exhibit normal magnetic polarity, indicating they were deposited during the Olduvai subchron, which dates to 2-1.78 million years. Using all lines of evidence, what is the best date estimate for this site?
A spine with a single curve (C-shaped)
Which of the following is not an anatomical feature associated with bipedalism? (A humero-femoral index of 70, Vertebrae increase in size from neck to pelvis, Short and straight toe bones, Valgus knee, A spine with a single curve (C-shaped))
A laterally-oriented glenoid fossa
Which of the following is not an anatomical feature associated with arboreality? (A humero-femoral index over 100, A pronounced bicipital groove, Curved metatarsals and phalanges, A laterally-oriented glenoid fossa, Divergent big toe)
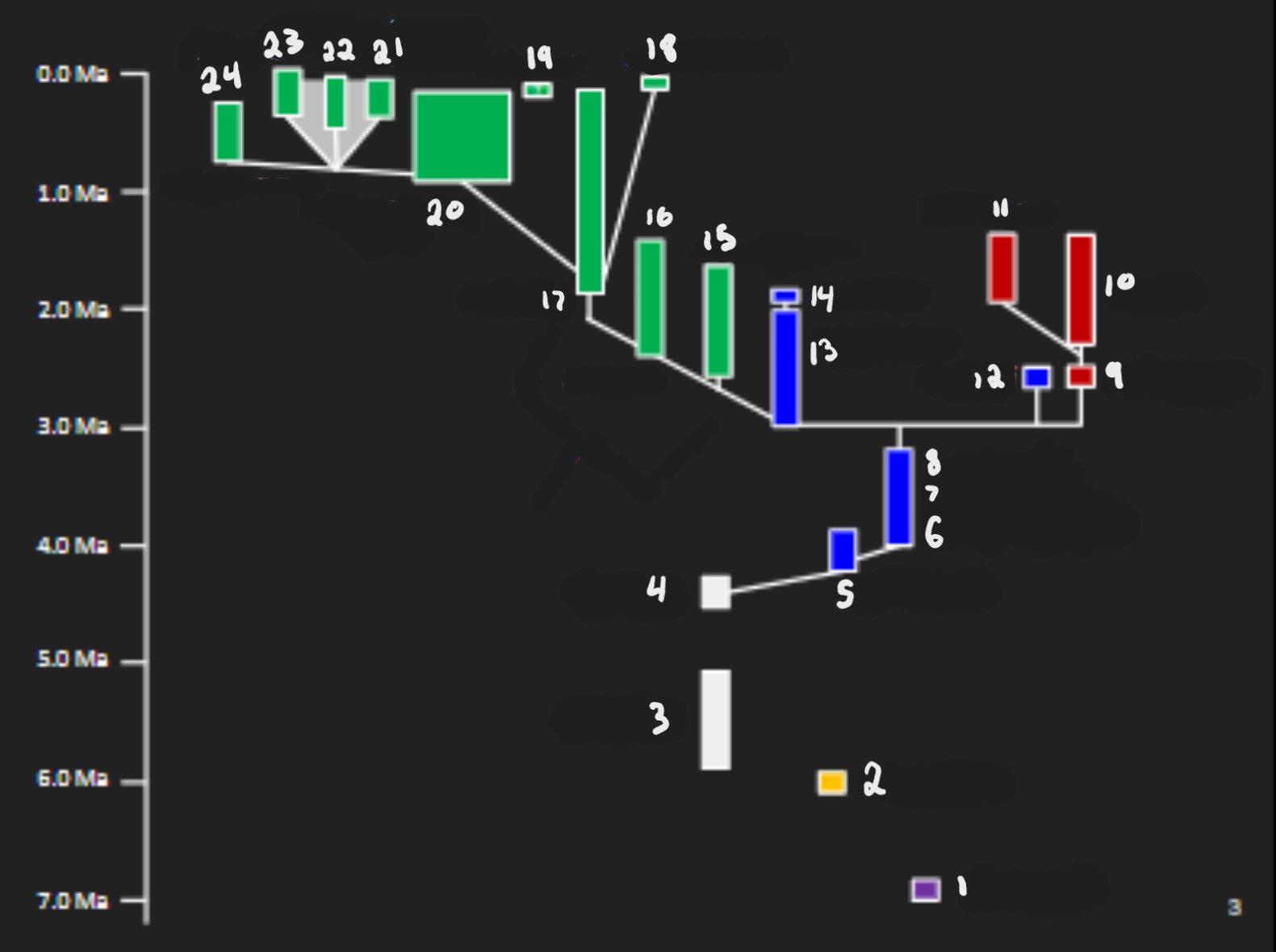
S. tchadensis, O. tugenensis, Ar. kadabba, Ar. ramidus, Au. amanensis, Au. “bahrelghazali,” Au. deyiremeda, Au. afarensis, P. aethiopicus, P. boisei, P. robustus, Au. garhi, Au. africanus, Au. sediba, H. rudolfensis, H. habilis, H. erectus, H. floresiensis, H. naledi, Mid. Pleistocene Homo, Denisovans, H. neanderthalensis, H. sapiens, H. antecessor
Label
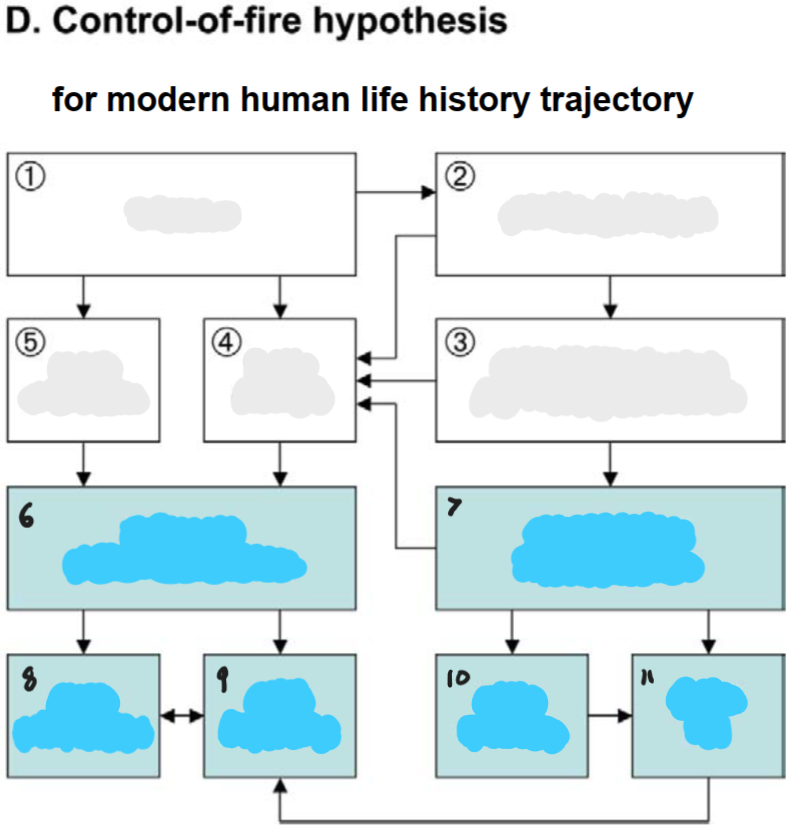
fire use; cooking of food; enhanced energy, digestibility, softness; less disease; less predation; reduced extrinsic mortality; provisioning of younger kin; slow maturation; high longevity; early weaning; short inter-birth interval
Label
Bergmann’s rule
In colder regions, body size will be larger because the volume of the organism increases faster than does its surface area.
Allen’s rule
In colder climates, shorter appendages are better at preventing heat loss due to an increased mass-to-surface ratio. In warmer climates, longer appendages are better at promoting heat loss due to a lower mass-to-surface ratio.
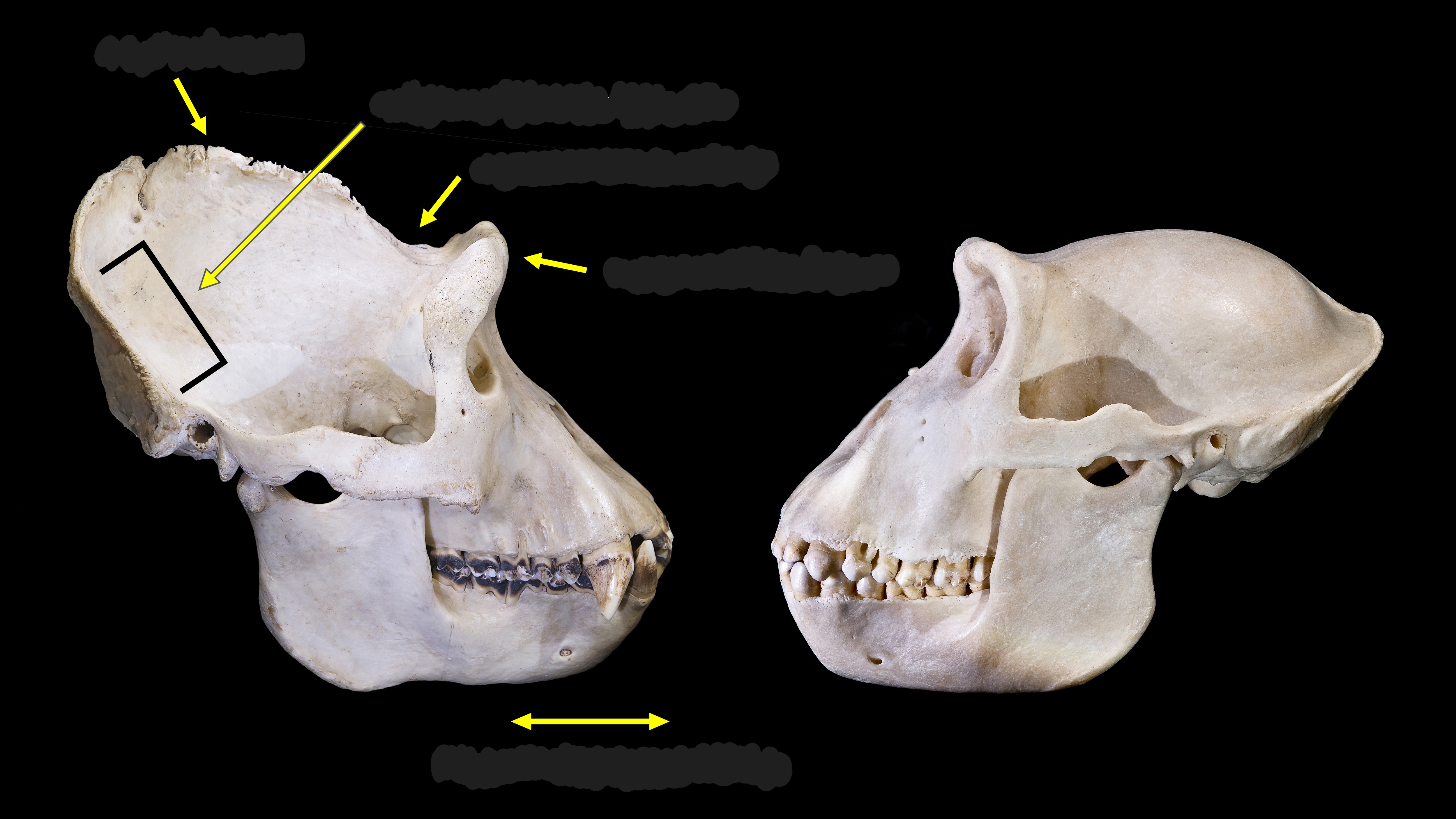
degree of prognathism, supraorbital torus, supraorbital sulcus, origin of temporalis, sagittal crest
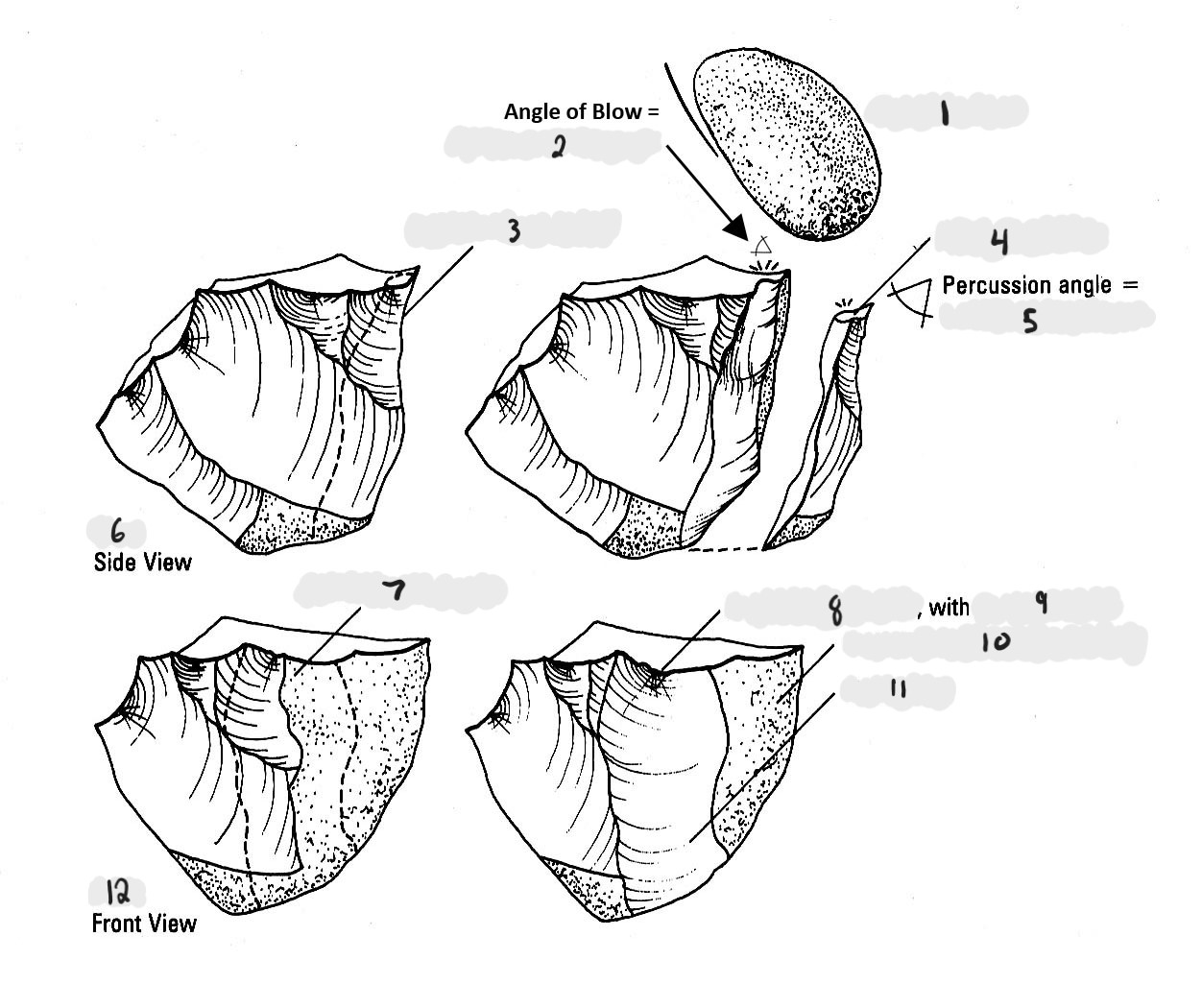
Label (bottom to top)
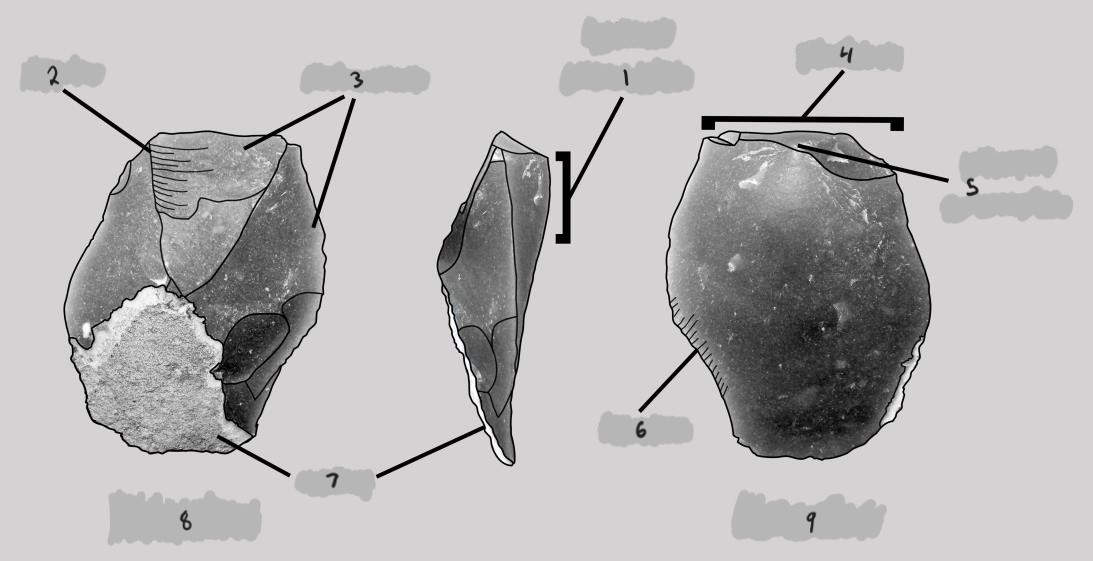
hammer stone, less than 90 degrees, flake to be removed, platform of flake, less than 90 degrees, core, flake to be removed, point of percussion, negative bulb, cortex (natural stone surface), flake scar, core
Label
bulb of percussion, ripples, flake scars, platform, point of percussion, fissures, cortex, exterior, interior
Label
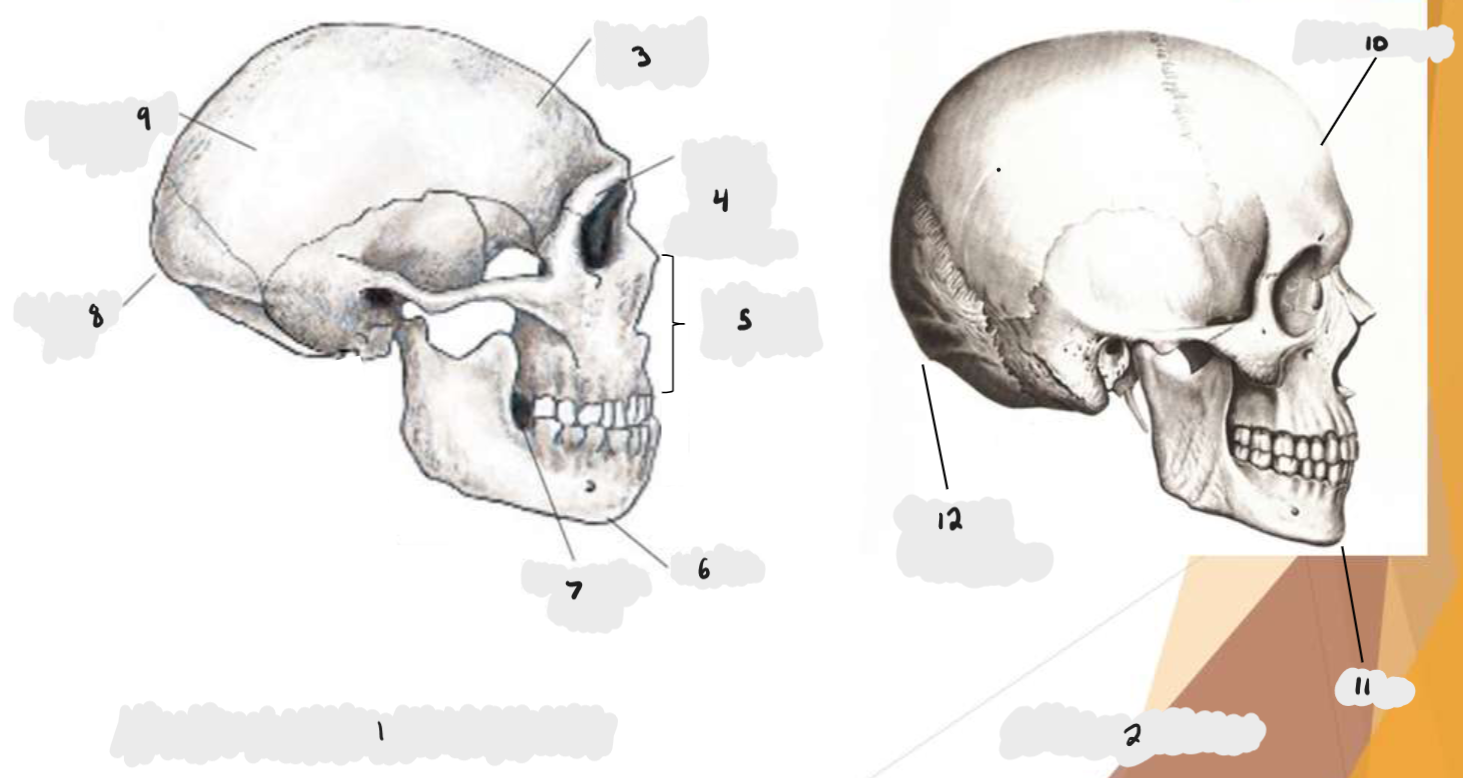
Homo erectus, Homo sapiens, sagittal keel, thick supraorbital torus, thin supraorbital torus
Label
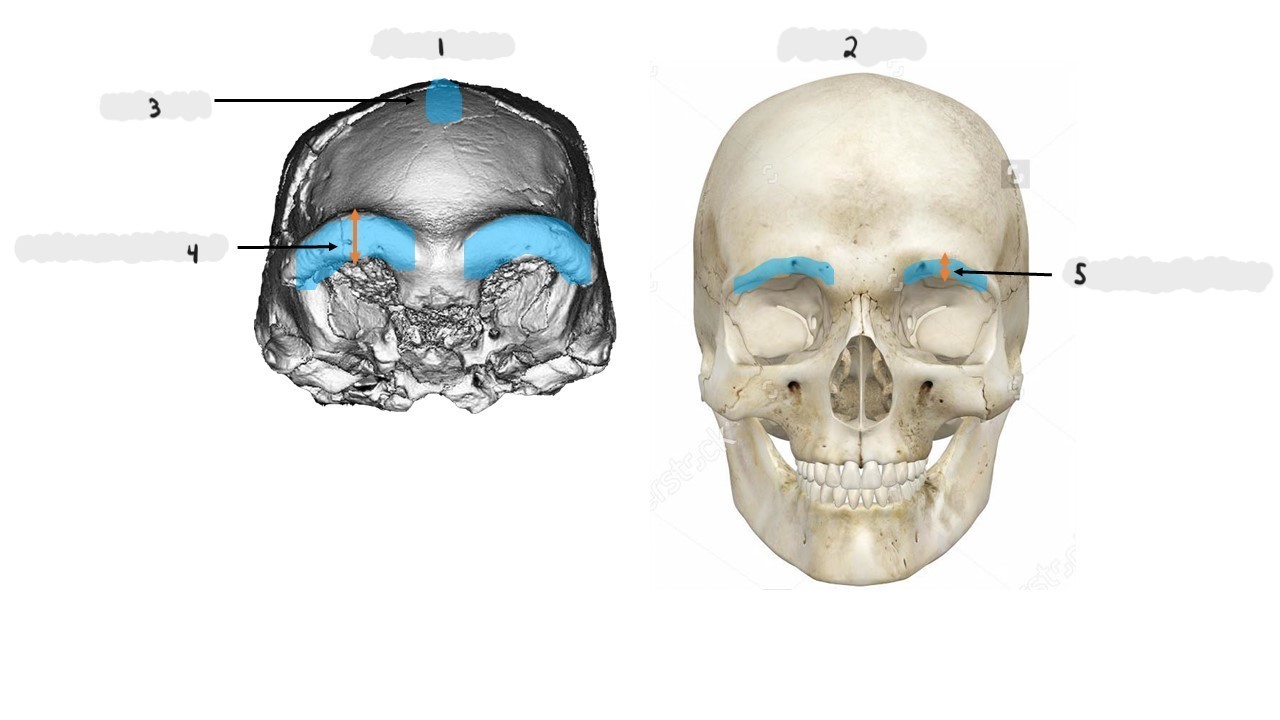
Homo erectus, Homo sapiens, sagittal keel, post-orbital convergence
Label
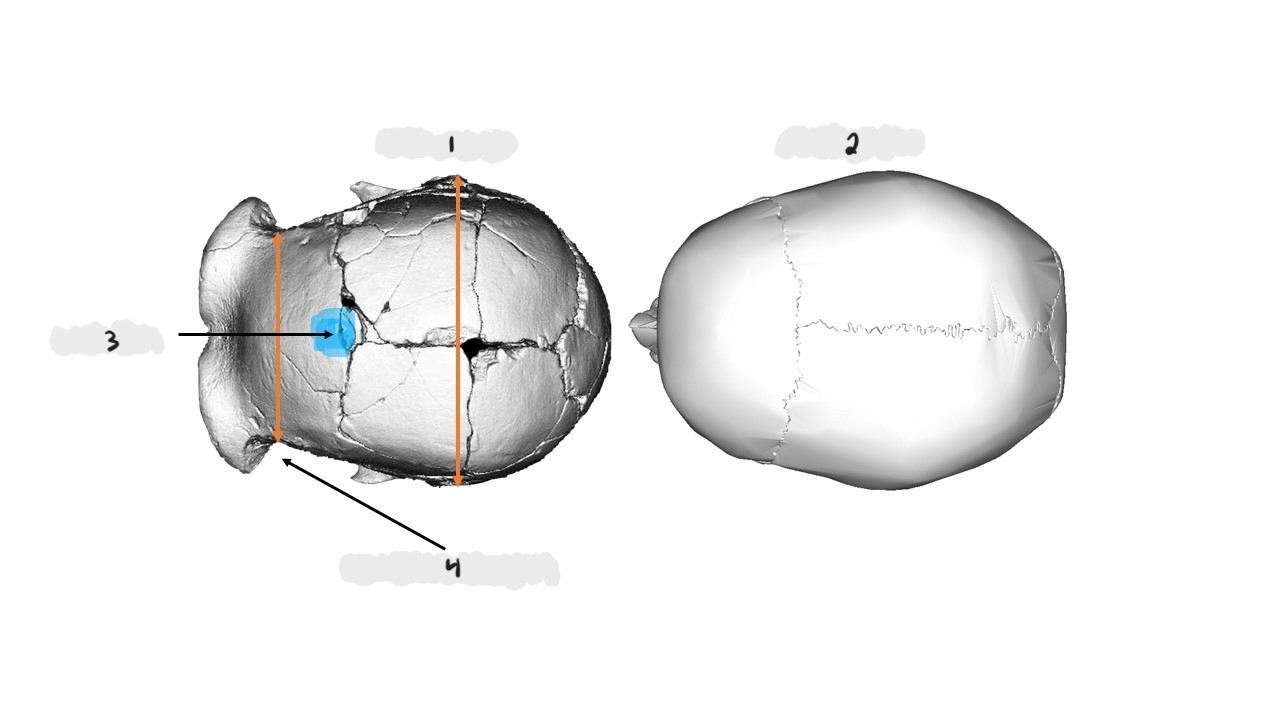
Homo erectus, Homo sapiens, nuchal torus, widest at base, widest at middle
Label
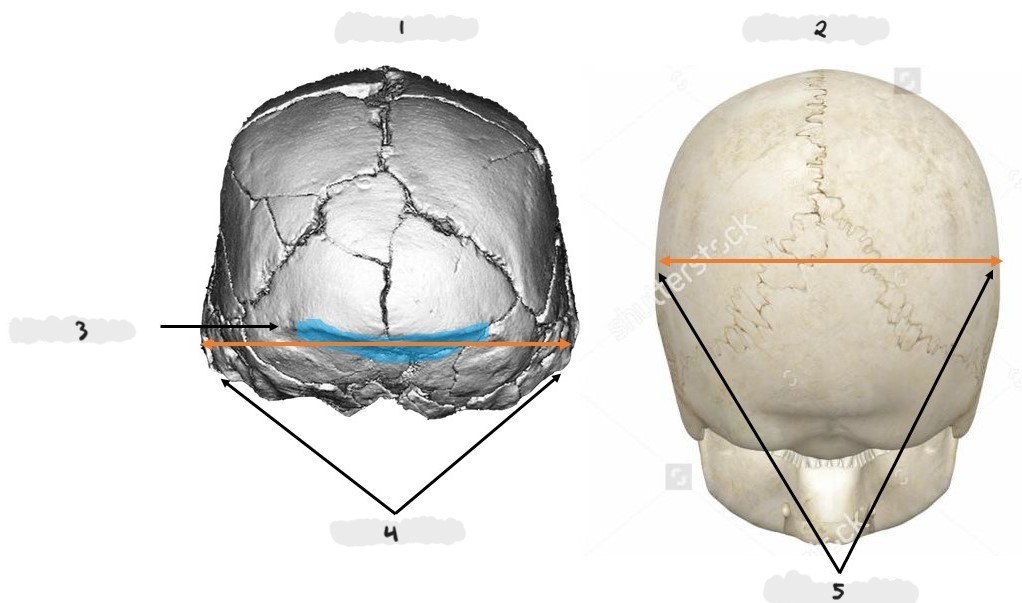
Homo erectus, Homo sapiens, angled occipital region, rounded occipital region
Label
larger muscle attachments, smaller muscle attachments, gorilla, chimpanzee, human, tall and pointy, thinner, prognathic, procumbent, short and round, thicker, orthognathic, small, orthognathic, yes, rounded cusps, extremely thick
Label

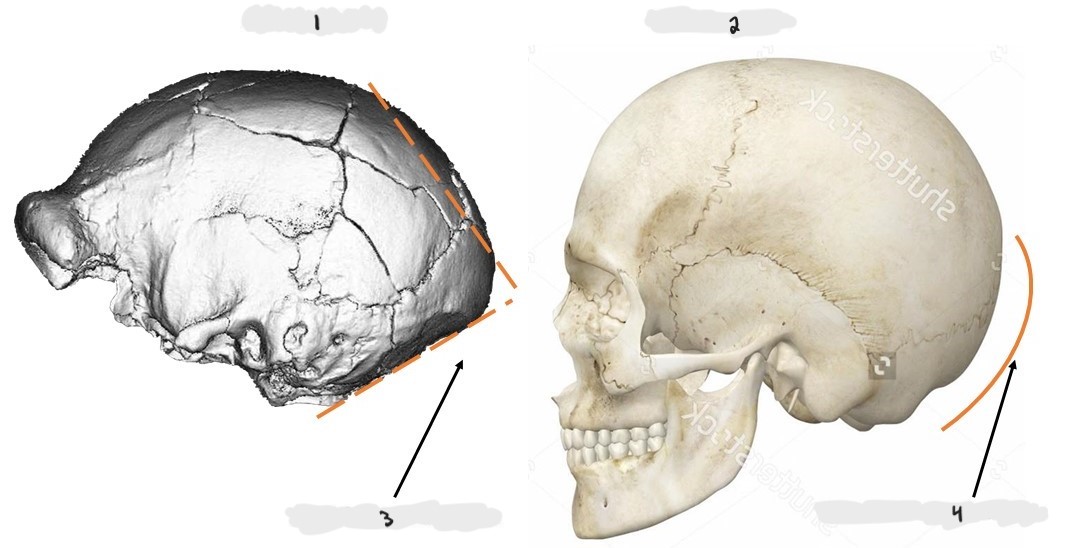
H. neanderthalensis; no chin; large, shovel-shaped incisors; inflated cheeks (no canine fossa); high, wide, and large nose; double-arched browridges
Label
H. neanderthalensis; H. sapiens; long and low vault; robust, double-arched browridges; midfacial projection; no chin; retromolar space; occipital bun; large cranial capacity; forehead; chin; round occipital
Label
Relative
Paleomagnetism: relative or absolute?
Absolute
OSL: relative or absolute?
Absolute
Argon-argon: relative or absolute?
Relative
Lithostratigraphy: relative or absolute?
Relative
Tephrostratigraphy: relative or absolute?
Relative
Biostratigraphy: relative or absolute?
Absolute
Potassium-argon: relative or absolute?
Absolute
Radiocarbon (carbon-14): relative or absolute?
Absolute
Uranium series: relative or absolute?
Absolute
Thermoluminescence: relative or absolute?
Paleomagnetism
Dates when the earth’s magnetic polarity flipped
OSL
Dates sediments that were buried and no longer exposed to light
Argon-argon
Dates volcanic eruptions
Lithostratigraphy
Dates based on correlation of rock units
Tephrostratigraphy
Dates volcanic ash layers
Biostratigraphy
Dates based on faunal succession
Potassium-argon
Dates volcanic sediments
Radiocarbon (carbon 14)
Dates living tissues that incorporated carbon via carbon dioxide
Uranium series
Dates carbonate sediments like stalagmites and flowstones in caves, also bones and teeth
Thermoluminescence
Dates burnt stone tools
1.3×10^9 years
Argon-argon half-life
1.3×10^9 years
Potassium-argon half-life