A2. forces
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
force
a push or a pull, describes the interaction between bodies
change the motion of an object – set it in motion or stop it from moving
change the shape or size of a body
Measured in Newtons, vector
weight (formula)
W = mg
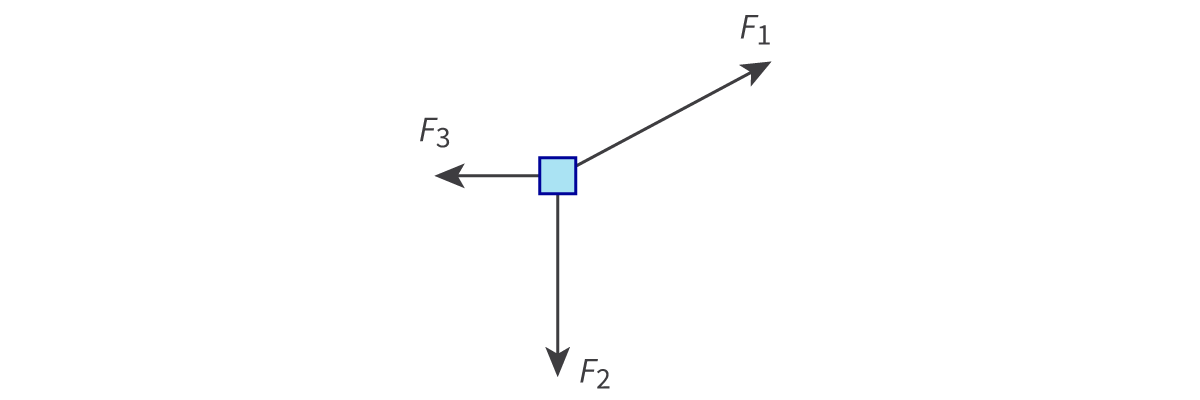
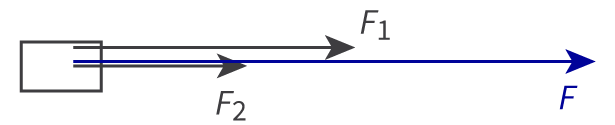
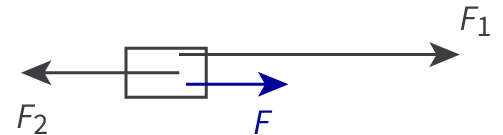
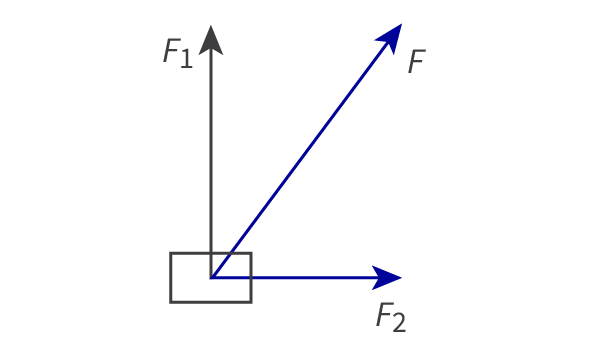
free-body diagrams
Fnet = F1 + F2
Fnet = F1 - F2
Fnet = (F12 - F22)1/2
newton’s first law of motion
every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight line unless compelled to change its state by the action of an external force
newton’s second law of motion
the acceleration of an object depends upon two variables – the net force acting on the object and the mass of the object
newton’s third law of motion
for every action (force) in nature there is an equal and opposite reaction
Electric force
interaction between two charged particles, can be attractive or repelling
Magnetic force
interaction between two poles of a magnetic field, north and south, can repel or attract
Normal force
perpendicular to the surface that an object contacts
Frictional force
A force between two surfaces when in contact. It impedes motion and results in heating
static friction
The frictional force that acts between two bodies rest. μs = F /N
dynamic friction
The frictional force that acts between two bodies moving relative to each other μdFn = F
Tension force
The force experienced by a rope (or wire, etc.) attached to a fixed point when the rope is pulled from the other end, or the force experienced by a rope when it is pulled from both ends.
elastic restoring force
The force that counteracts the force extending or compressing a spring and restores the spring to its natural length.
Hooke’s law
The displacement of a spring is directly proportional to the force exerted on the spring. (F =-kx)
viscous drag force
The resistive force opposing the motion of a body inside a fluid
Buoyancy
The force exerted by a fluid on an object partly or wholly immersed in the fluid, that counteracts the weight of the body.