Sports Equipment Final
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
The most common midsole foam is:
ethylene vinyl acetate
Which foaming technique can result in trace contaminants left behind in the foam
chemical foaming
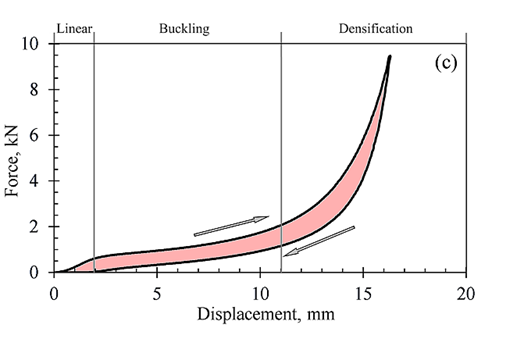
the curve below shows deformation of a midsole foam during loading and unloading. the pink area between the lines represents
energy loss
ethylene vinyl acetate is a:
copolymer
cross linking of EVA midsole foam will make the polymer:
harder
polyurethane is commonly formed by reacting __
a polyol with an isocyanate
what is the order of typical energy return in midsole foams
EVA<TPU<PEBAX
the common structural aspect of all superfoams is:
a polymer with alternating hard and soft segments
A foam made by a supercritical foaming process can result in improved energy return and more stable performance
True
A large moment of inertia will ______________
reduce twisting of the driver head
The highest performing shoes have energy return values on the order of ___________.
80-90%
The coefficient of restitution of a driver ___
describes a measurement of how efficiently a golf club’s face transfers energy to the ball when it strikes
the densest (least porosity) microstructure of a driver will result from:
forging
the strongest parts of a driver can be expected to result from:
forging
which of the following is true about sintering
the reason sintering occurs (i.e. the driving force) is to reduce the surface energy by particle coalescence
grooves in irons are intended to _
impart back spin to the golf ball
sheet wound composite shafts __
will have a “spine” that will affect behavior
the face of a driver is bulged (not flat) __
to straighten the trajectory of an off-center ball strike
dimples can vary in diameter and depth. deep dimples generate _ than (as) shallow dimples
less spin
a higher spinning golf ball will experience _ than (as) a slower spinning golf ball
more lift
smaller diameter dimples generally give the ball _ and better control in the wind
a lower trajectory
larger diameter dimples give the ball a _ flight time
longer
the most common golf ball core material is
polybutadiene
surlyn, a common golf ball cover material is an example of a(n) _
ionomer
dimples on a golf ball create __
more turbulence at the ball surface
in a three piece golf ball where each layer has a different density, if a layer is non-concentric it will affect the _ of the ball
center of gravity
knots in wood decrease strength because
they increase the fraction of off axis cellulose fibers
which is true about bat hoop mode frequency
higher performing bats tend to have lower hoop mode frequencies
which of the following is true
ash bats are more prone to single piece failures than maple bats
the size of a tennis racket “sweet spot can be increased by __”
increasing the frame stiffness
the maximum coefficient of restitution in a tennis racket is __
near the throat of the racket
the dead spot (with minimal energy return) is located __
near the tip of the racket
composite tennis racket frames are __
hollow
some tennis strings are multifilamentary. the flexibility and elasticity of the string depends on the angle at which the filaments are wound. a tighter wind yields __
more flexible and elastic string
tennis strings undergo viscoelastic creep __
regardless of their use level
incorporation of piezoelectrics in tennis rackets for vibration control is an example of __
active damping
countervail carbon fiber composite incorporating viscoelastic material is an example of
passive damping