Atoms and the Periodic Table
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Democritus
-tiny invisible particles
-"atomos"
John Dalton
-atoms of different elements are different masses
-combinations in specific ratios
J.J. Thomson
-negative charges
-scattered through a positively charged mass
Ernest Rutherford
-nucleus was discovered as a dense positive mass
-rest of the atom was mostly empty space
Niels Bohr
-electrons move in specific energy levels or orbits
Erwin Schrödinger
-electrons are found in space around the nucleus where they are most likely to be found
James Chadwick
-discovered neutral charges called neutrons
Dalton's atomic theory
1) Everything is made of atoms, which are the indivisible building blacks of matter and cannot be destroyed.
2) All atoms of an element are identical.
3) The atoms of different elements vary in size and mass.
4) Compounds are produced through different whole-number combinations of atoms.
5) A chemical reaction results in the rearrangement of atoms in the reactant and product compounds.
Numbers 1 & 2 are no longer accepted because of the existence of subatomic particles and isotopes.
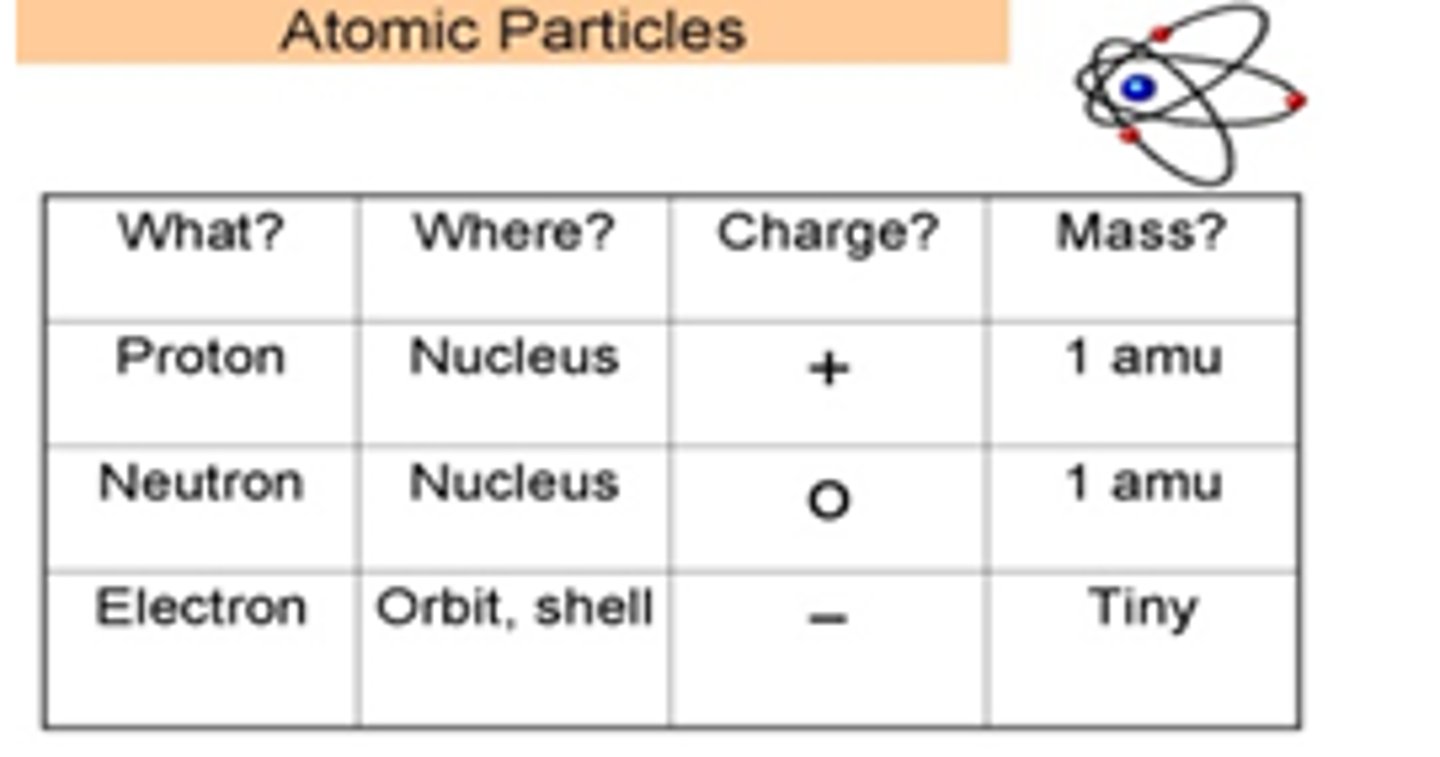
Atom
smallest particle of an element that is still that element
Nucleus
small positively charged center of an atom
Subatomic Particles
smaller than an atom -- protons, neutrons, electrons
Quarks
6 types that make up protons and neutrons -- grouped in pairs
Electron Cloud
the area around the nucleus of an atom where elecrons are most likely to be found
Atomic mass unit
amu
Atomic Number
number of protons in an atom
Isotopes
atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons
Average atomic mass
the weighted average mass of all the naturally occurring isotopes of an element
Mass Number
protons + neutrons
Writing Isotopes
ex) Carbon - 12
Chart
Who created the periodic table?
Dmitri Mendeleev
What did Mendeleev arrange the elements by?
atomic mass
What does periodic mean?
repeating
What did Mendeleev do to his periodic table when certain elements didn't fit in the right columns?
left empty spaces for unknown elements
Who fixed the periodic table?
Henry Moseley
What did Moseley do to change the periodic table?
rearranged the table based on increasing atomic number
Define Periodic Table
arrangement of elements by increasing atomic number and periodic changes in physical and chemical properties
What is a period on the periodic table?
horizontal rows of elements on the periodic table
How are periods numbered?
1-7
What do periods represent?
the number of electron shells in an element
What is a group on the periodic table?
vertical columns of elements on the periodic table
How are groups numbered?
1-18
What do groups represent?
the number of valence electrons in an element
What are energy levels?
areas where electrons are found around the nucleus
When an electron is closer to the nucleus, it has ______ energy. When an electron is farther from the nucleus, it has ______ energy.
lower; higher
Where is a valence electron?
outer energy level
What is the maximum number of electrons that can go into each energy level?
Level 1 = 2
Level 2 = 8
Level 3 = 18
Level 4 = 32
What is maximum number of electrons that can be in the valence electron shell of an atom?
8 (exception, level 1 holds 2)