Ancient Greece and Etruscan
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
BIG IDEAS in GREECE
Figure - idealized naturalism (both idealized & naturalistic)
look real BUT perfect
Military accomplishments
Known for paintings & bronze, but neither survive because they were destroyed by conquering cultures
bronze taken and melted to create swords
Temple worship - gods live inside, sacrifice on porch
ARCHAIC PERIOD
800-480 BCE
City-States
Homer writes the Iliad and the Odyssey
Sudden BOOM in population and material goods
ART FOR AESTHETIC PURPOSES
VASE PAINTING TRADITIONS - ARCHAIC
Horizontal lines - registers
Narrative art
Black glazed human figures on red clay (problem b/c the figures are not as detailed and the people are white, not black)
Profile faces
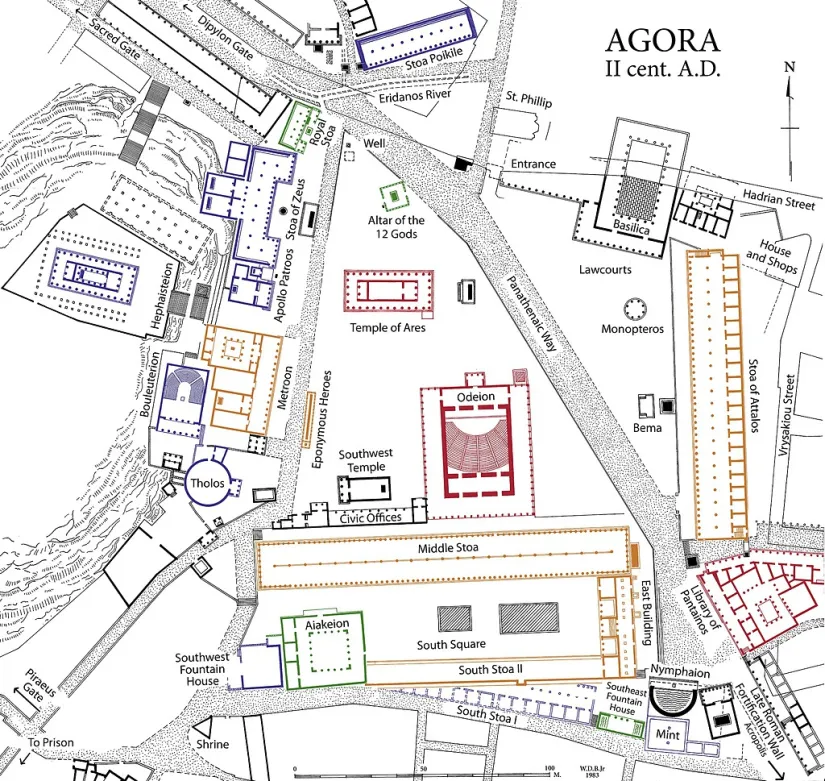
“Athenian Agora” Archaic; 600 BCE
“Gather place” or “assembly”
Athletic, artistic, spiritual, and political events
Resources to build → shows power
Begin Doric Column usage
Stoa - Agora
Started this: Display paintings showing Greek military triumph BEHIND colonnades
Public space later copied by Romans in Forum of Trajan & House of Vettii
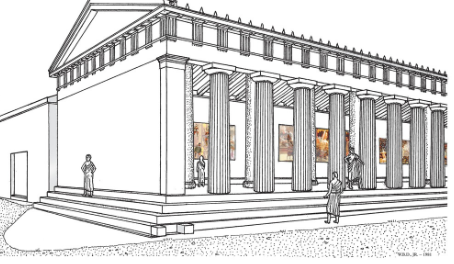
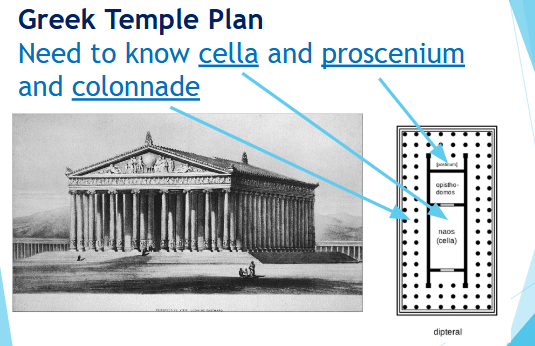
Greek Temple Plan:
look at notebook
Polytheistic - Zeus, Hera, Athena, etc.
Proscenium = porch
front porch
animal sacrifice
pouring of libations
Greek Theater - also has proscenium and later influences design of COLOSSEUM
cella = location of where the statue of the god, visited, private worship
believe statued = physcial connection to god (like Darshan & Lakshaman Temple)

“Anavysos Kouros” 530 BCE; Archaic Greek, Marble with paint
Kouros = young man
More naturalistic muscles, smoother transitions
Still stylized hair and archaic smile, even weight distribution
Archaic smile represents the transcendence into immortality
Inscribed at base - “Stay and mourn at the tomb of dead Kroisos, whom raging Ares destroyed one day as he fought in the foremost ranks”
commemorates his bravery as a soldier
Grave marker for dead soldier

“Peplos Kore” 530 BCE; Archaic Greek; Marble with paint
Kore - statue of a young female, usually grave markers or temple votive figures
Peplos - style of dress
Stance is rigid, clothing is blocky
Naturalistic touch = characteristic of Archaic
Perhaps represents Athena or an acolyte to her, hand would’ve held a symbol to let us know
Classical Greece CONTEXT
480-323 BCE
510 BCE - Persian Invasion
City-States become rivals → Olympic Games become POPULAR
Polykleitos writes The Canon - mathematical proportions of perfect human figure using the pinky
Naked DUDES ARE ALL THE RAGE

“Bronze Doryphoros” 440 BC; Polykleitos; Classical Greece
Spear - Bearer → ideal warrior
CONTRAPPOSTO STANCE
Relaxed face, naturalistic idealized muscles
no more Archaic smile
Insipient Movement
Mathematical Proportion (Polykleitos)

“Niobedes Krater” Classical Greece; 460 BCE; Clay; red-figure technique
NEW TECHNIQUE - red figure painting
MORE FINE DETAIL AND NATURALISTIC
Three-quarter view of face, figures move around space (not stuck on register)
more interactive space
Context - Apollo and Artemis shooting children of Niobe w/ arrows because Niobe bragged about being superior to gods; Hercules surrounded by Athena and heroes
Didactic artwork - teaches a lesso, specifically to not insult the gods
Influenced by paintings
Krater - mixes water and wine (shape of vase) for temple worship
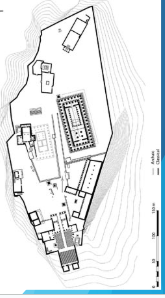
“Acropolis” Athens, Classical Greece; 445 BCE; Marble
CONTEXT:
Complex modelled after Agora
Dedicated to Athena, but Poseidon fought for it (shows that they are so good that gods are fighting over them)
Birthplace of LIMITED democracy, not equal
Wavy lines - located HIGH on a hill
Overlooking city, seen from afar - shows power and dominance
Separated from unimportant/low class
Closer to Heaven
Gods lived on Mount Olympus

Parthenon - Acropolis
Temple for Athena, housed a 40 ft high statue (home of Goddess, NOT for worship)
Doric temple, rectilinear
Emphasis on ideal proportions and mathematics - corrects flaws in our vision
ENTASIS - buldge in columns (corrects flaws in our vision)
Sacred and secular (nonreligious) mixed - also housed treasure, stored valuables
Decorated with scenes of war and Athenian triumph

East Pediment - Parthenon
Narrative - Poseidon fighting Athena for sponsorship of Athens
Poseidon uses war tactics (triton) while Athena uses peace (olive branch)
Duality of divine rule - JUST LIKE EGYPT (TUTANKHAMUN’S TOMB), NEAR EAST (STANDARD OF UR), AND NDOP OF KING MISHE
Human figure - idealized, naturalistically rendered, folds of drapery create shadows
Notice the sloped shape - created to fit into the triangular pediment


Cella - Parthenon Acropolis
40 ft high statue (of Athena), decorated in gold
2 storied columns - later used in Roman Forum of Trajan
Visited alone, not in gorups
Ritual located on porch (proscenium)

Plaque of the Ergastines - Frieze, Parthenon
Toga - later influences Buddhists
Different levels of relief (both high and low)
overlapping = DEPTH

“Nike Adjusting Her Sandal” - Acropolis
Athena Nike = pose showing victory
Insipient movement, almost awkward
Wet drapery - erotic, but allows one to see both the human form and the drapery, showing that the creator/sculptor had the skill to create both the human form and the drapery
Originally had wings (created balance)

“Grave Stele of Hegeso” 410 BCE; Classical Greece; marble and paint
Servant handing Hegeso box of jewelry
Domestic setting - woman’s place
“Hegeso, Daughter of Proxenos” women defined by male relationships
Trianlge on top = pediment
Ionic columns
Special attention to drapery
Idealized naturalism (like Archaic)
Return to funerary markers, most sculptors were put to work on the Parthenon
Hellenistic Greece
323-31 BCE
AKA Antigonid Empire AKA Macedonian
“Hellas” Greek word for Greece
After Alexander the Great dies and right before Rome invades
Culture spreads through the Greek-speaking world
Three Power Dynasties - Persian, Egyptian, Antigonids (Hellenistic Greek)
Ruled by Kings - wealth put on display

“Winged Victory of Samothrace” Hellenistic Greece; 190 BCE; Marble
Formal analysis - wet drapery, VERY DRAMATIC STANCE & MOVEMENT
Athena
Believed to be part of a fountain honoring naval victory
Placed on coast (naval victory)
Interacts with environment - wind blowing drapery (ultimate naturalism)

“Seated Boxer” Hellenistic Greece; 100 BCE; Cast BRONZE
Found on display in Rome - Baths of Constantine
Monument to athlete victory - but NOT idealized - it was NATURALISTIC
broken nose, cauliflower ear, cuts on face
Insipient movement (like Fang Byeri)
captures the figure doing something and as if they are about to do something
Beard - hercules
likely held inset eyes - like Eshnunna Votive figures
Extensive wear on fingers and toes - ritual healing of athletes

“Great Altar of Zeus and Athena” Pergamon, Turkey; 175 BCE; Hellenistic Greek; Marble
Built by Greek King Eumenes II
to display power
Altar in acropolis, next to library and palace, representing the truth and divine rule
Frieze depicts narrative of gigantomachy (Gods fighting Giants) - allegory for Greece fighting Persia
enemis depicted strong in order to emphasize that the Greeks were stronger by winning
Gods = Greece
Titans = Persia
Triumph of civilization over Barbarism
Wide stairs like Audience Hall
Ionic columns

Frieze of Athena - Great Altar at Pergamon
Less about harmony and serenity, more about movement and strong feeling
Battle portrayed through swirling drapery, contorted bodies
war = chaotic (like Night Attack)
Extremely high relief
Overlapping, dynamic use of space
Leadership is divine, power over enemies is absolute
Warning to those who may want to join enemy
Triumph over chaos

Estruscan Context
Etruria - Italy
600-200 BCE
Originally a GREEK territory, but won independence
Close to sea for trade, exchange culture/ideas/ ART
Foundation for Roman Empire

“Temple of Minerva” Veii, Italy; 500 BCE; Wood, mudbrick, rock
Greek influence - cella, proscenium, doric columns
New - THREE room cella (triple cella), no stylobate all around
Rome going to like this idea
Minerva = Roman version of Athena
Sculpture on TOP - theater for gods AND community
NOT inpediment
Later influences Rome & Sistine Chapel

“Appolo” from Temple of Minerva; Vulca (artist); 500 BCE; Painted terracotta
Greek-like: archaic smile, somewhat rigid stance, stylized hair and drapery (like Anavysos Kouros)
BUT more MOTION than typical Archaic Greek art
Life size - likely acted out a mythic event
Probably fought Hercules with an audience of other sculptures
Context - audience = Gods & the people, placed on roof, backdrop of sky

“Tomb of the Triclinium” Tarquinia, Italy; 480 BCE; Volcanic Rock and Fresco
Ritual: 3 days you would have eaten with the dead, but after the body decomposes, you would then cremate the body and put the ashes into a sarcophagus. This process helps to ease the transition to the afterlife.
Necropolis (like Giza)
House for afterlife in necropolis
Fresco - painting on wet plaster - INNOVATION
permanence; allowed for paintings to be more permanent
Checker ceiling - references ritual party tents - meal givien during funerary week
afterlife is good, no more pain and responsibility

Dancers and Diners - Tomb of the Triclinium
Ancient Mediterranean - composite stance, registers
Elite - fine food, servants, fine robes
Gender - males painted darker (more outside), females painted lighter (stayed inside)
Convivial Atmosphere - cheerful, jolly, afterlife is a GREAT thing to enjoy
people seen DANCING due to convivial atmosphere

“Sarcophagus of the spouses” Etruscan, 520 BCE, Terra Cotta
Archaic Smile - content with death
held cremated remains of high status individuals
Couple reclines on cushion like they would at banquet
Shows obvious affection/intimacy
like Akhenaton and Family
Convivial - social sphere, positive
man darker, women lighter
Women enjoy more status
Rome - The Republic Period
509 - 27 BCE
Rome takes over the Etruscans, Greeks, and most of the Mediterranean
Governed by Divine Kings and Senate (limited democracy)
Assimilated Greek Gods (Zeus → Jupiter, Poseidon → Neptune, Athena → Minerva)

“Doryphoros (Spear Bearer)” Roman copy (marble) of a Greek original (bronze); 450 BCE
Rome conquers Greece and brings back and copies their art
THISI S THE ROMAN MARBLE COPY
triumph over Greece, false sense of culture
Original design by Polykleitos in BRONZE
Polykleitos wrote the Canon where he talked about the mathematical proportion of the perfect human figure in relation to the pinky
Contrapposto stance

“Alexander Mosaic” from the House of Faun, Pompeii; Rebublic Rome; 100 BCE; Mosaic
2 cultures fighting - Greek (Alexander the Great) and Persia (darius
Elite class wants to look both educated AND cultures
ITS A COPY based on Greek painting Philoxenes of Eretria
Tells a GREEK story - Alexander the Great (Greek) vs Darius (Persia)
Patron looks CULTURED - appreciation of Greek artwork
Patron looks educated - knowledge of current events and history
FORMAL ANALYSIS:
-Thousands of tiles (million and a half) - naturalism
Dynamic composition - movement in opposite directions
Some go forward, some go backward, some turning
Intense emotion - worry, fear, anger
CONTEXT:
Darius (Persia) retreats from battle with Alexander (Greece) in Battle of Issus
Calm leader against chaos
Alexander wears no armor and has no weapon
divine approval
Climax of war, many casualties - emotion

“Hed of a Roman Patrician” Republic Roman; 75 BCE; Marble
Patrician = civil servant
Specific person - served in Senate
Virtues of public career - age, serious, stress of hard work
Veristic portrait - absurdly realistic, real life traits are exaggerated, emphasis on wrinkles and flaws (stress from wroking for gov’t
Deep respect for family, tradition, and ancestry - one of original citizen families
Given DURING LIFE after retirement and worshipped by family after death because it was a model for what the family members should be like
like portrait of sin sukju
Imperial Rome
27 BCE - 96 BCE
Emperor Augustus brings stability, peace, and economic prosperity
Less republic/Senate, more DIVINE LEADER
Sophisticated civil engineering and architecture (architecture = display of power through control of resources and power)
System of law and government - much like Western World
Art is public and used as propaganda

“Augustus of Prima Porta” Imperial Roman, 1st Cent. CE; Marble
FUNCITON - POLITCAL PROPAGANDA
controls image of ruler

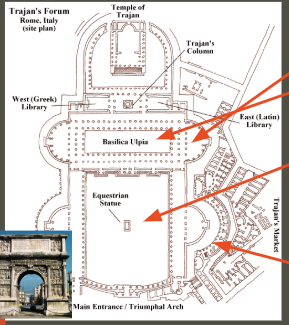
“Forum of Trajan” Rome; Italy; 110 CE; Apollodorus of Damascus; Brick and concrete and marble
Trajan “the good Emperor” - built after his death, he is deified in the Temple by hadrian
City civic center - school, court of law, market, army drills, audience chambers, library
Trajan markets - gathering of trade materials from conquered cultures
Contained exotic and imported stone - proceeds from military accomplishment, on display in Rome
showed they are cultured
SUCCESS of IMPERIAL rule * after battle
Apollodorus of Damascus - context
Military engineer - bulit Danube river bridge that won a battle for Trajan
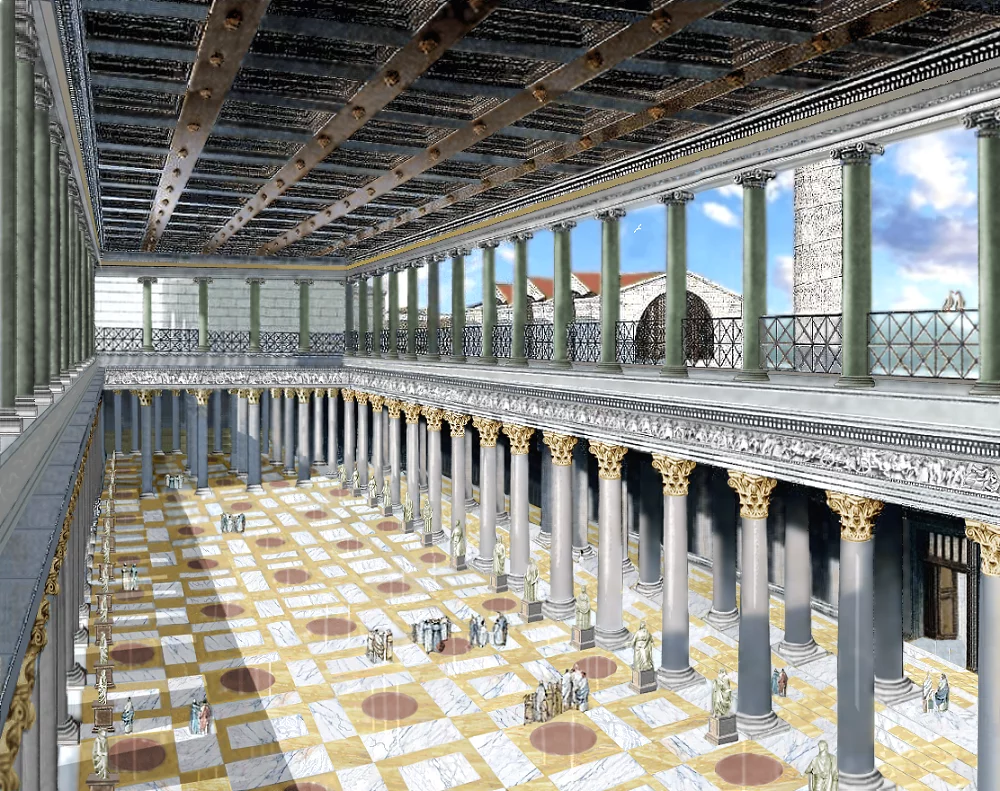

Basilica Ulpia - Forum of Trajan
Secular (non-religious) - civic and law
Apse: semi-circle section on either end
Two stored column interior - references Greek temples
Clerestory references Temple of Amun-Ra
Corinthian capitals
Will later influence Christian churches

Column of Trajan
Narrative art (Dacian Was) in relief sculpture using continuous registers
Both Trajan and enemy are strong
shows that the Romans are STRONGER
Trajan in oratory stance (like Augustus), calm victor
Next to library - truth, righteousness
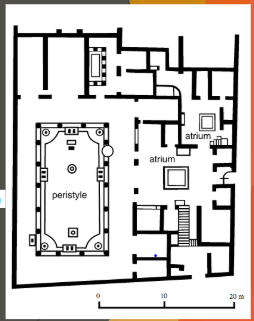
“House of Vettii” Pompeii; Imperial Roman; 2nd century BCE; Cut stone and fresco
Context: highly stratified society, both owners were former slaves (newly rich)
Focus of the homes is the atrium wiht garden
show of wealth/status
Function - DOMESTIC, also receive clients for work
HOUSE OF VETTII FRESCOES:
Documented Greek and Roman mythology
Were considered modern or trendy for the time - noveau riche

The garden
Atrium - references the STOA from Agora in Athens, Greece
Displays art (behind COLONNADE)
Wealth - garden (plants bloom yaer round)
Doric columns
Want to appear WEALTHY to look successful to clients

“Colosseum” (og name = Flavian Amphitheater); Rome, Italy; Imperial Roman; 70 CE; Stone and CONCRETE
Built by Emperor Vespasian from stolen Jewish treasures
Sports events, plays, and political gatherings
like Agora
Concrete - INNOVATION- lightweight building materials
Invention: Romn Barrel Arch AND the Keystone
Velarium = large awnings
CONTEXT:
orginally named Flavian Amphitheater
Given name Colosseum after Giant statue of Nero (Sun God) ‘The Colossus”
Top Columns: Corinthian - Rome is dominant
Middle Columns: Ionic columns
Bottom Columns: Doric (Tuscan) - Greek, historic foundation (starts w/ Greek culture and architecture → Roman

“Pantheon” Imperial Roman; 120 CE; Concrete
Temple to ALL Gods, later converted into a church
Central plan, proscenium
Columns imported from Egypt
INTERIOR:
Wanted to impress viewers w/ an unexpectadly large interior space
concrete allows to have a large space without the need of hypostyle hall design because concrete is lightweight
Oculus - open window at top; allows light to shine on gods and emperors
Combined statues of emperors and gods - DIVINE RULE
28 sections of coffers - perfect #; also lessens weight of concrete dome
Later influence HAGIA SOPHIA
Central space
large interior
dome on top
Originally built as a Christian Church

“Ludovisi Battle Sarcophagus” Imperial Roman; 250 CE; Marble
Purchased by Cardinal Ludovisi
Piling of figures and crowding of space - distancing from Classical Greece
Replace cremation with burial - Christianity
Reference to Persian God Mithras - light, truth and victory over death