Philosophy 100 Midterm
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Epistemology
The Study of Knowledge
How do we know what we know?
What is the distinction between truth and falsity?
Is there objective truth?
Value Theory
The Study of Goodness
Value Theory - Three Subdivisions
Ethics, Political Philosophy, and Aesthetics
Ethics
Moral goodness. What is a moral action? (Value Theory)
Political Philosophy
Justice as a value. What is a just social order? (Value Theory)
Aesthetics
Beauty as a value. Is beauty a quality in objects autonomous from the human mind? (Value Theory)
Metaphysics
The Study of Existence/Reality
What is the nature of things (micro/macro)?
Is there a God?
Are Humans free?
Logic
The Study of Correct Argumentation
What are the rules for rational argumentation?
How can you identify fallacious reasoning?
How to Read Philosophy (4 Steps)
1) Identifying types of philosophical claims
2) Distinguishing the parts of an argument
(premises and conclusions) and how they fit
together.
3) Identifying key concepts and significant
examples
4) Reading with a charitable lens/avoiding a straw
man
Argument (Definition)
an inference from a premise(s) to a conclusion
Argument (Example)
Socrates is a man. (Premise)
Ever man is mortal. (Premise)
Therefore, Socrates is mortal. (Conclusion)
Gramsci
Spontaneous vs. Critical Philosophers
Philosophers create new concepts/words or restructure a vague/undertheorized concept/word
Principle of Charity
Always give another person's argument the benefit of
the doubt, meaning the most rational interpretation
possible
Straw Man Fallacy
Creates a “cartoon” version of an argument
Plato
Knowledge vs. Opinion
Non-philosophers only care about particulars (things in the world)
Particulars change so one can only hold opinions about them (opinions are an unstable understanding)
Philosophers care about both particulars and universals (things that make particulars intelligible)
You can know universals since they don’t change
Assumptions
The intellectual principles and values that an author assumes in their argument
Implications
Conclusions that would also follow if we do/do not agree with the argument
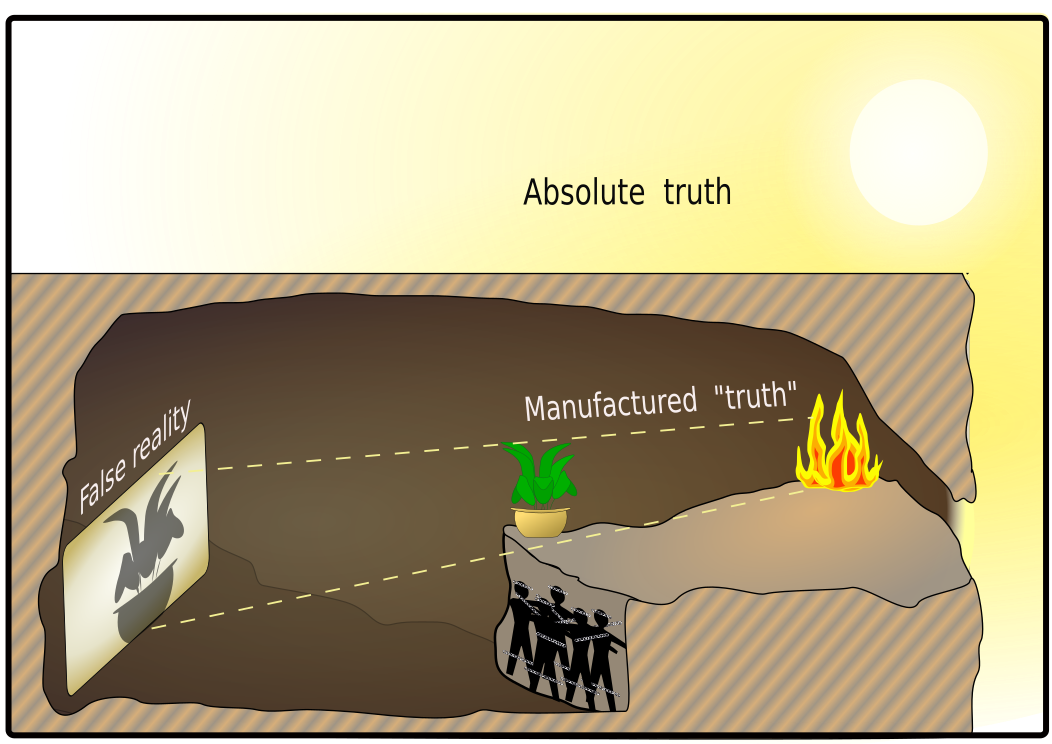
Allegory of the Cave
Aristotle
3 forms of friendship (utility, pleasure, and complete)
good in itself vs. good for
other ends (intrinsic vs. extrinsic goods)Complete friendship: Reciprocated goodwill, end is internal to relation, rare
and slow, only possible for virtuous people
Friendship is…
Most necessary for life
A natural phenomenon
Any union that binds people together for a good
Montaigne
• Equality (not respect) (unlike family relation)
• Communication (secrets, critique)
• Free will (not obligatory)
• Gentle and calm attraction (unlike lovers)
• More exposure = more enjoyment (unlike lovers)
• Spiritual bond
• Gender-specific
• “Blending of souls” (only one friend)
Teleology
the study of ends or purposes
Eudaimonia
the condition of human flourishing or of living well
Sufficient vs. Necessary conditions
Sufficient Conditions: Enough to fulfill that goal
Necessary Conditions: You need this thing to fulfill the goal, but it may not be everything you need
A priori vs. a posteriori
A priori: Knowable independently of experience
A posteriori: Knowable on the basis of experience
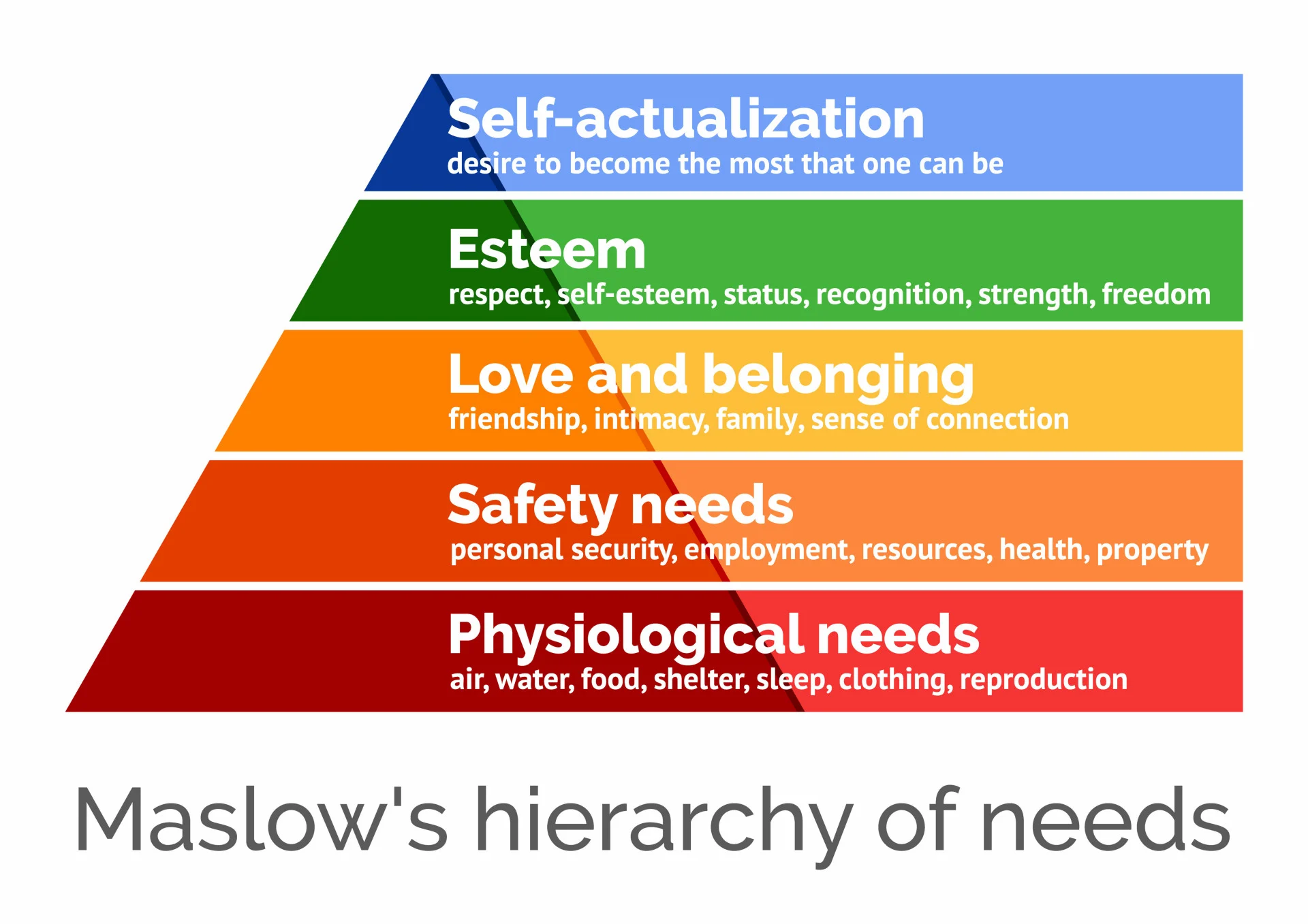
Maslow
• Love as “eros”/passion
Maslow’s view of passion as the basis of full self-actualization:
• Comes after other needs are met; not automatic, requires metamotivation/needs
• Driven by a value system bigger and “outside oneself”; servant to higher ideals
• Eros as fulfilling “inner requiredness” that one belongs to/one can’t will it or serve it as duty – one is
meant for this purpose and the purpose is meant for oneself (calling or fundamental identity)
• Available to anyone but one must search and find this passion and reach this highest form of
selfhood through submission to it, not because of secondary or external factors
Fromm Argumentative Foils
Love is caused by ”being loveable”
Love is focused on finding an “object”, a commodity exchange in a market
Love is experienced as a sudden, intense emotion
Fromm’s Idea of Art
• Theory, practice, focus of ultimate
concern
• I.e., knowledge and effort
• The development of our capacity/faculty
(internal power)
Fromm’s Conditions of All Human Beings
• Transcend nature
• Have self-consciousness and separateness
• Human isolation causes shame, guilt, anxiety
Fromm’s Common Solutions to Human Isolation
Orgiastic States (Drugs, Alcohol, Sex)
Group Conformity
Creative Activity (Productive Work)
Fromm’s Mature vs Immature Unions
Mature: Preserves individual integrity/is an
expression of human freedom, taps into inherent powers of a person, gives one’s aliveness, produces love, requires character development, has care, responsibility, respect, knowledge
Immature: Symbiotic unions, Activity that is guided by others for external motivations, has dependency, narcissistic omnipotence, desire to exploit others or hoard
Fromm’s Symbiotic unions
Biological (mother/child) AND Psychological (masochistic, sadist)