Chapter 8: Reactions of Alkenes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
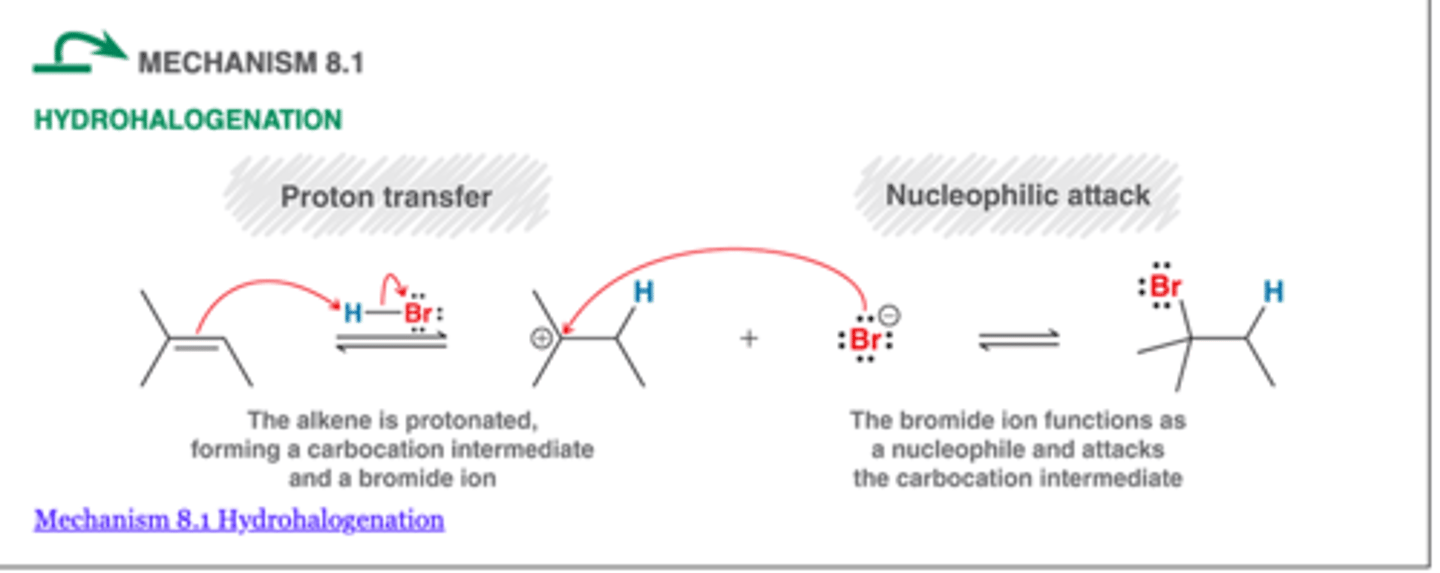
Hydrohalogenation
-the addition of HCl or HBr to a multiple bond to give an alkyl halide product
-Markovnikov addition: HBr
-Anti-markovnikov addition: HBR and ROOR
-1 chiral center=pair of enantiomers possible
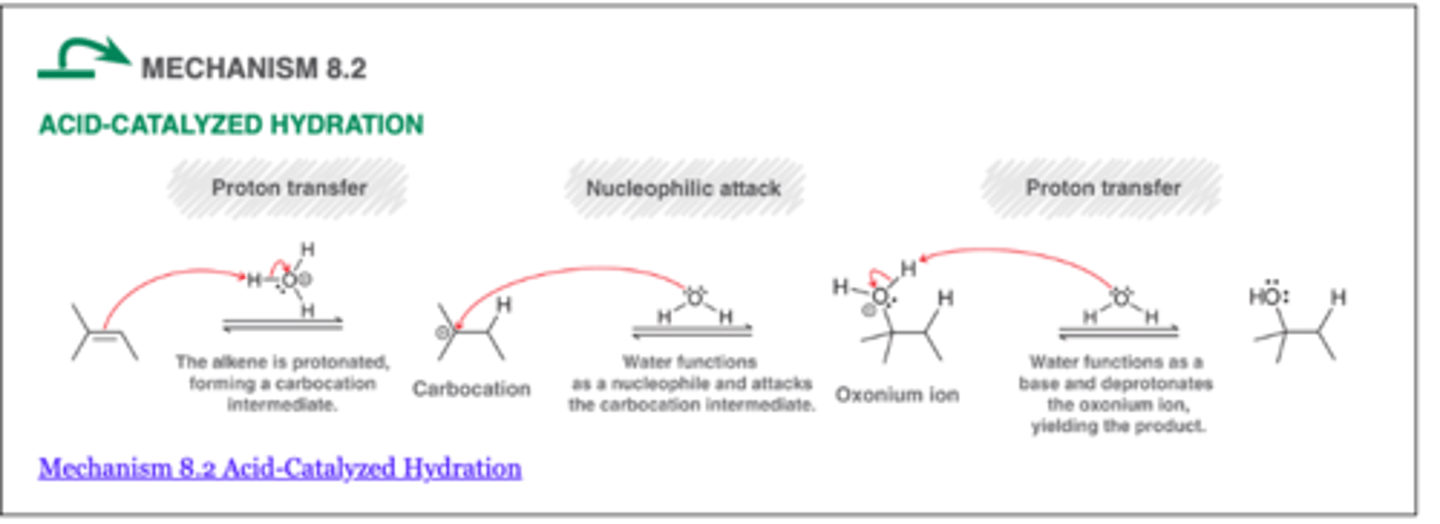
Acid Catalyzed Hydration
- used to convert alkenes to alcohols
- Markov regioselevtivity
- carbocation rearrangements are possible
- When a new chiral center is generated, a racemic mixture of enantiomers is expected
H20, H+, H2SO4 (aq)
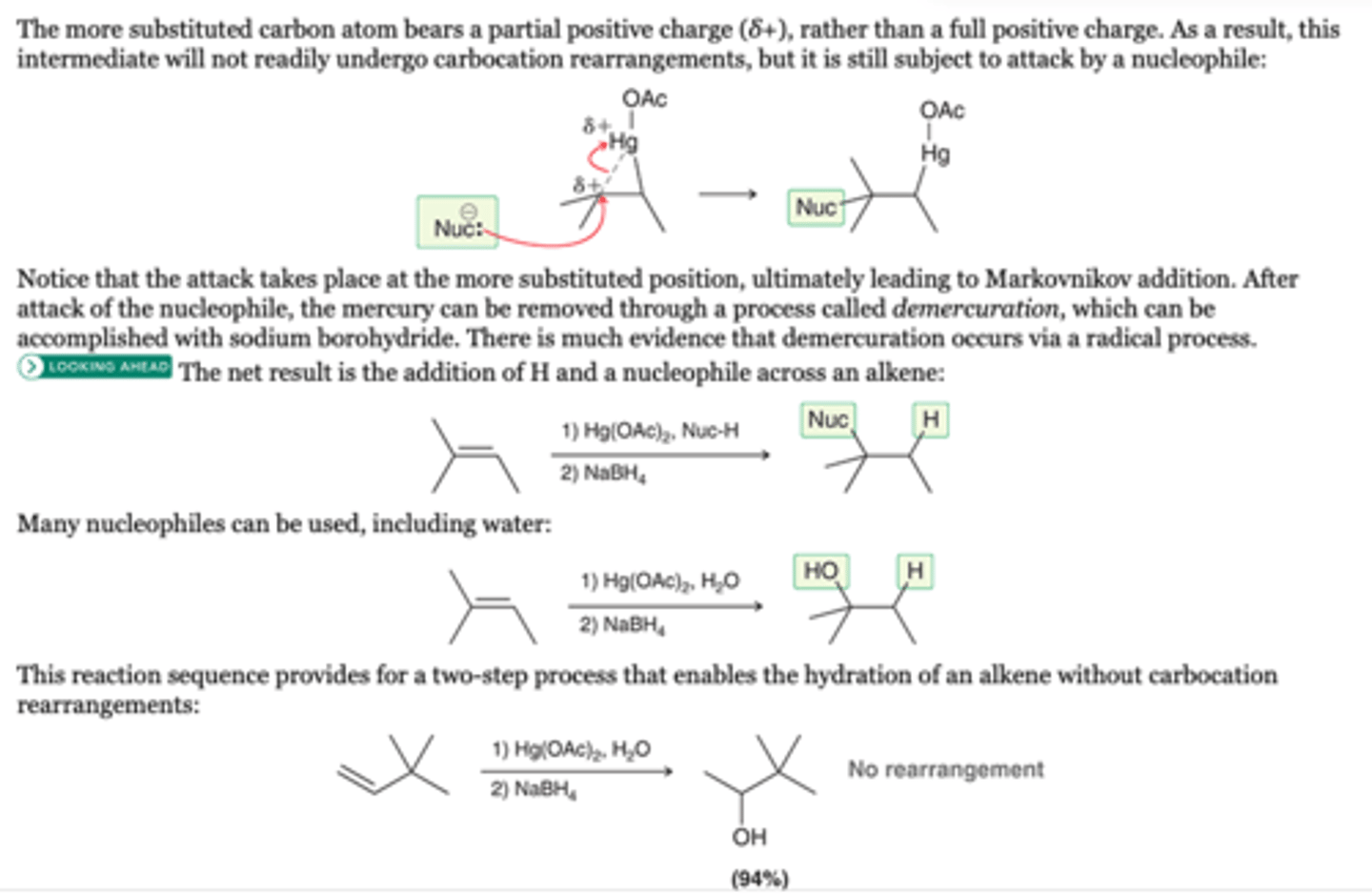
Oxymercuration-Demercuration
-Will not undergo carbocation rearrangements
-Nucleophile attacks the most substituted position
-Markovnikov addition
1. Hg(OAC)2, H20
2. NaBH4
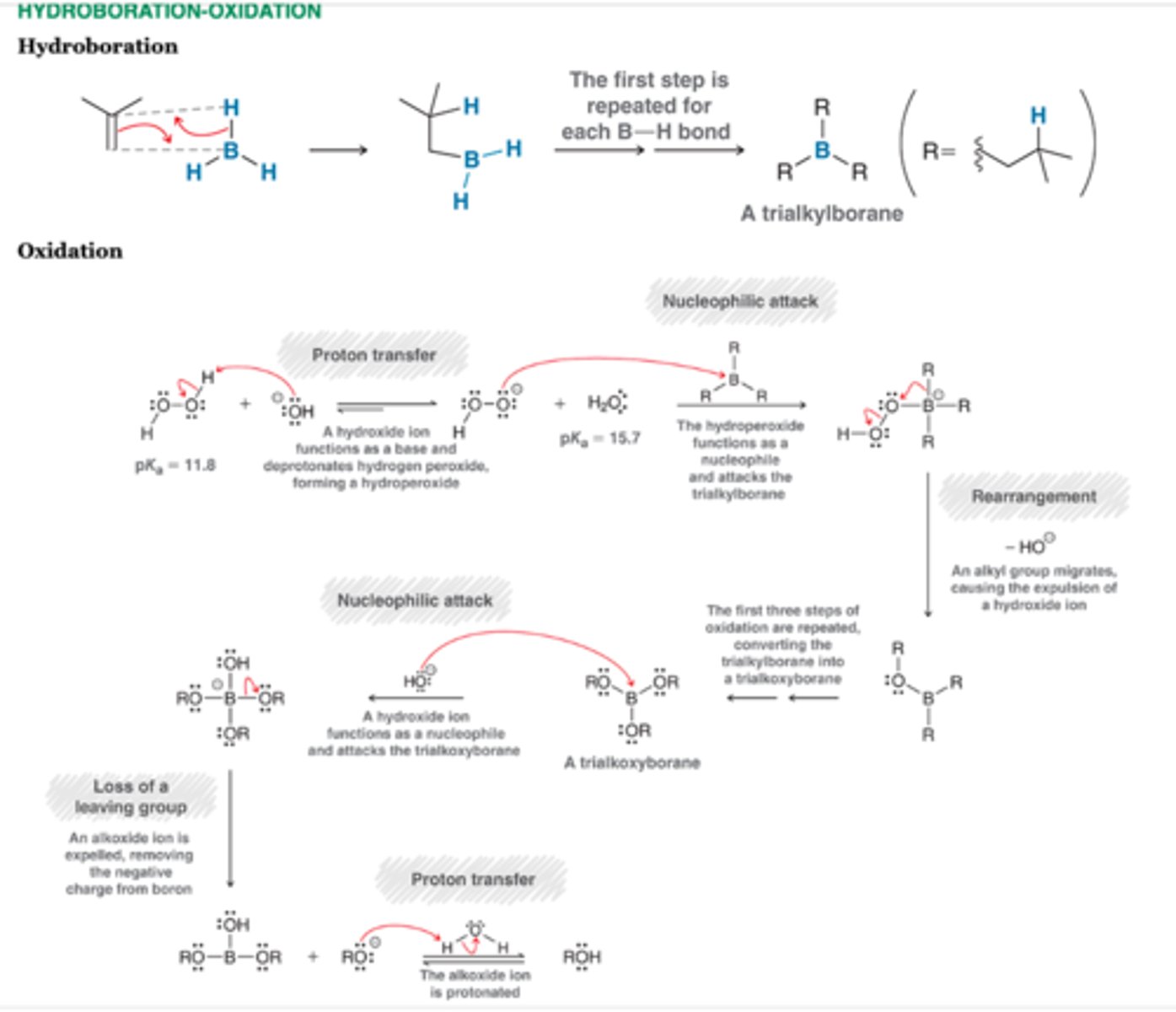
Hydroboration Oxidation
-Anti-Markovnikov addition
-Undergoes Syn addition
-BH2 is installed at less substituted position and OH is installed at the less substituted position
-1 chiral center= racemix mixture
-2 chiral centers= syn addition
1. BH3, THF
2. H202, NaOH
Catalytic Hydrogenation
-reduces alkenes to alkanes
Zero chiral centers: syn requirement is not relevant. Only one product formed
One chiral center: Both possible enantiomers are formed
Two chiral centers: The requirment for syn addition determines which pair of enantiomers is obtained. (Be careful of meso compounds)
1. H2, Ni
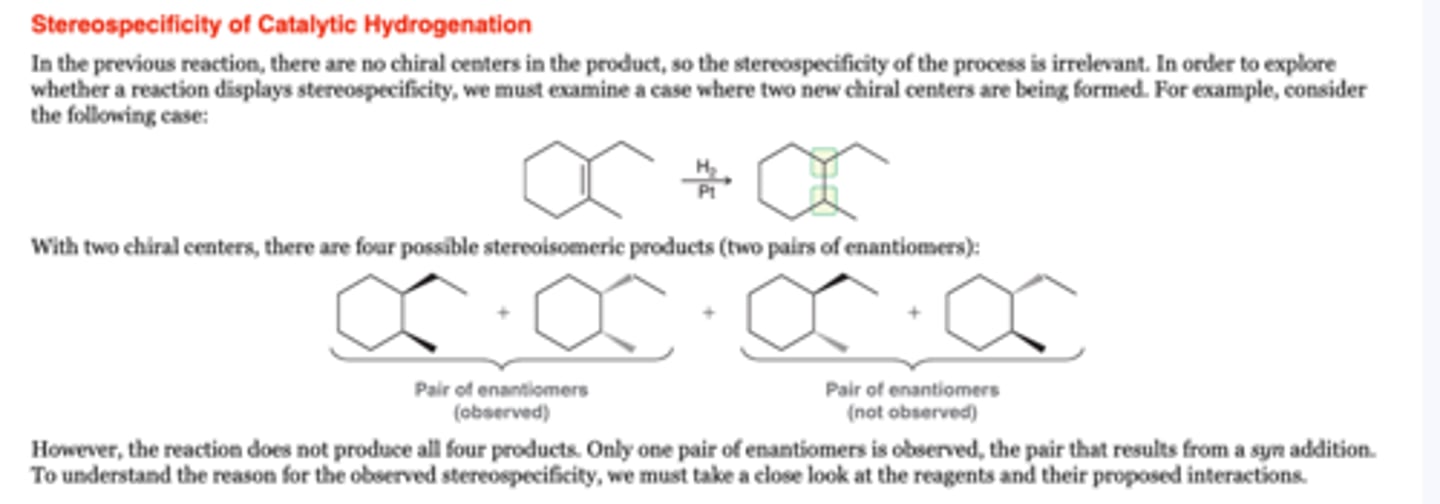
Halogenation
-involves the addition of X2 (either Br2 or Cl2) across an alkene.
-For most simple alkenes, halogenation appears to proceed via an anti-addition
-The stereochemical outcome for halogenation reactions is dependent on the configuration of the starting alkene
1. Br2 or Cl2
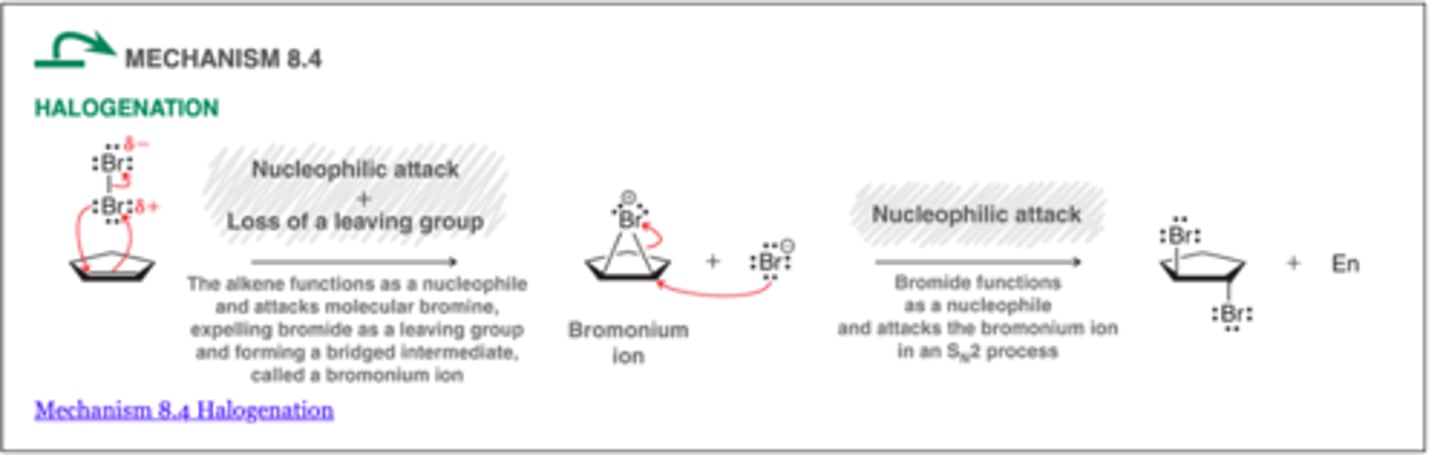
Halohydrin Formation
-Installs OH at the more substituted position
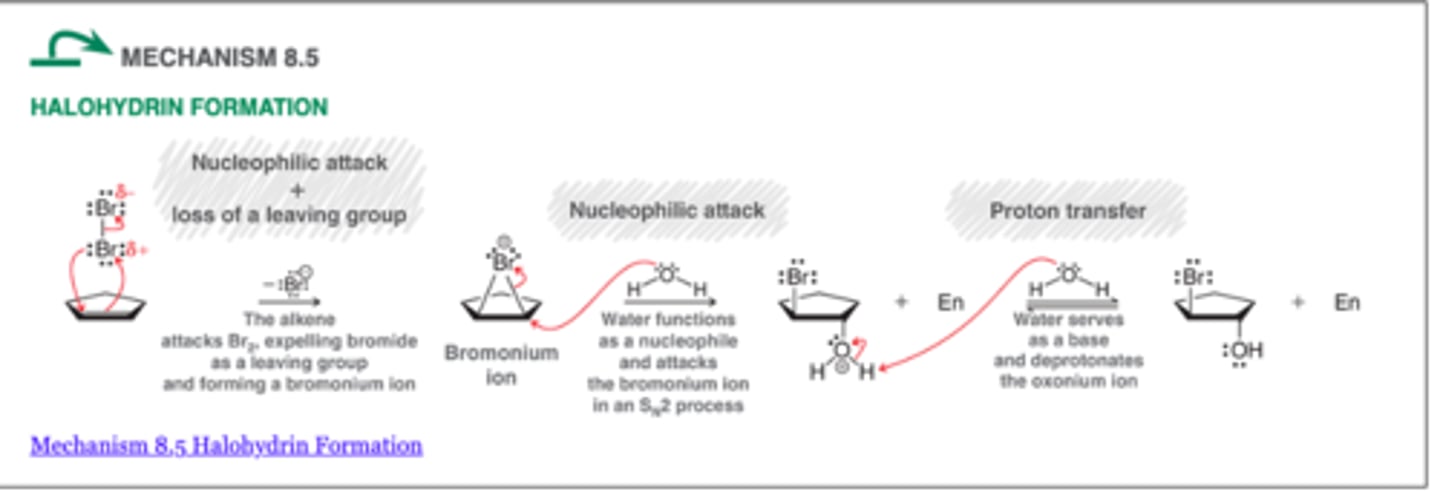
Anti Dihydroxylation
What's added: OH and OH
Regioselectivity: N/A
Stereoselectivity: anti
Intermediate: don't worry about it
Rearrangement: not possible
anti-addition becomes irrelevant with one chiral center
1. RCO3H
2. H3O+
Syn Dihydroxylation
1. OsO4
2. NaHSO3, H2O
or
1. KMnO4
2. NaOH cold
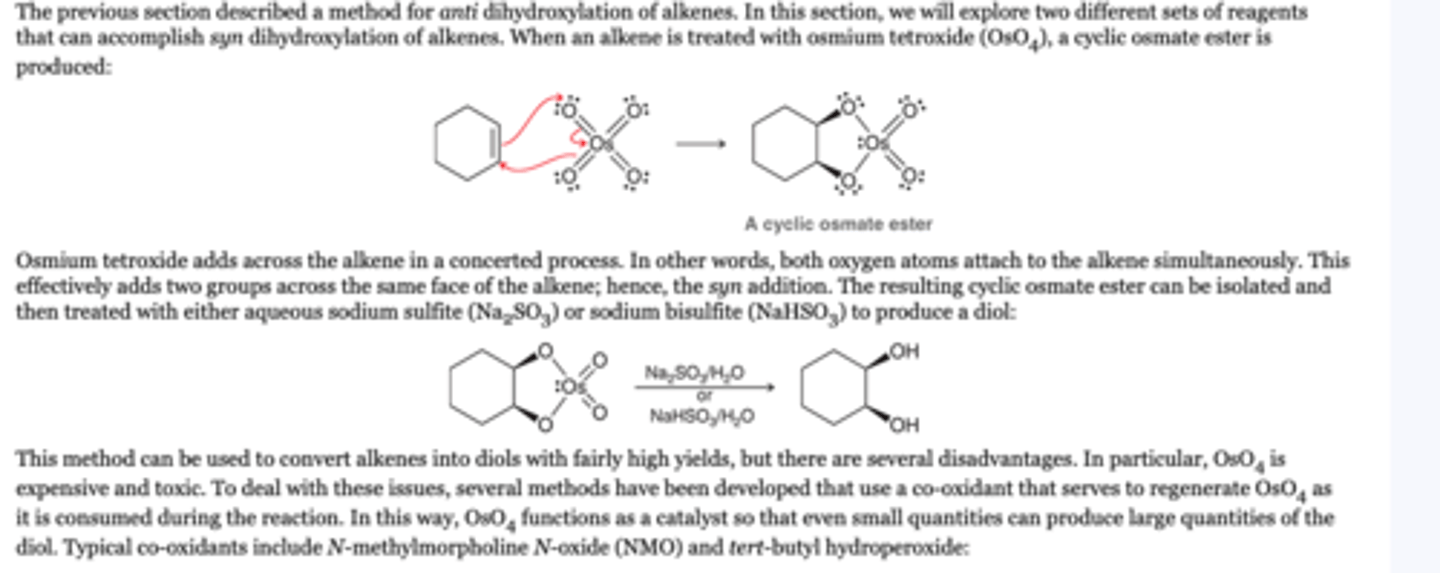
Oxidative Cleavage
-the C=C bond is completely split apart to form two C=O bonds. Therefore, issues of stereochemistry and regiochemistry become irrelevant.
1. O3
2. DMS or Zn/H20
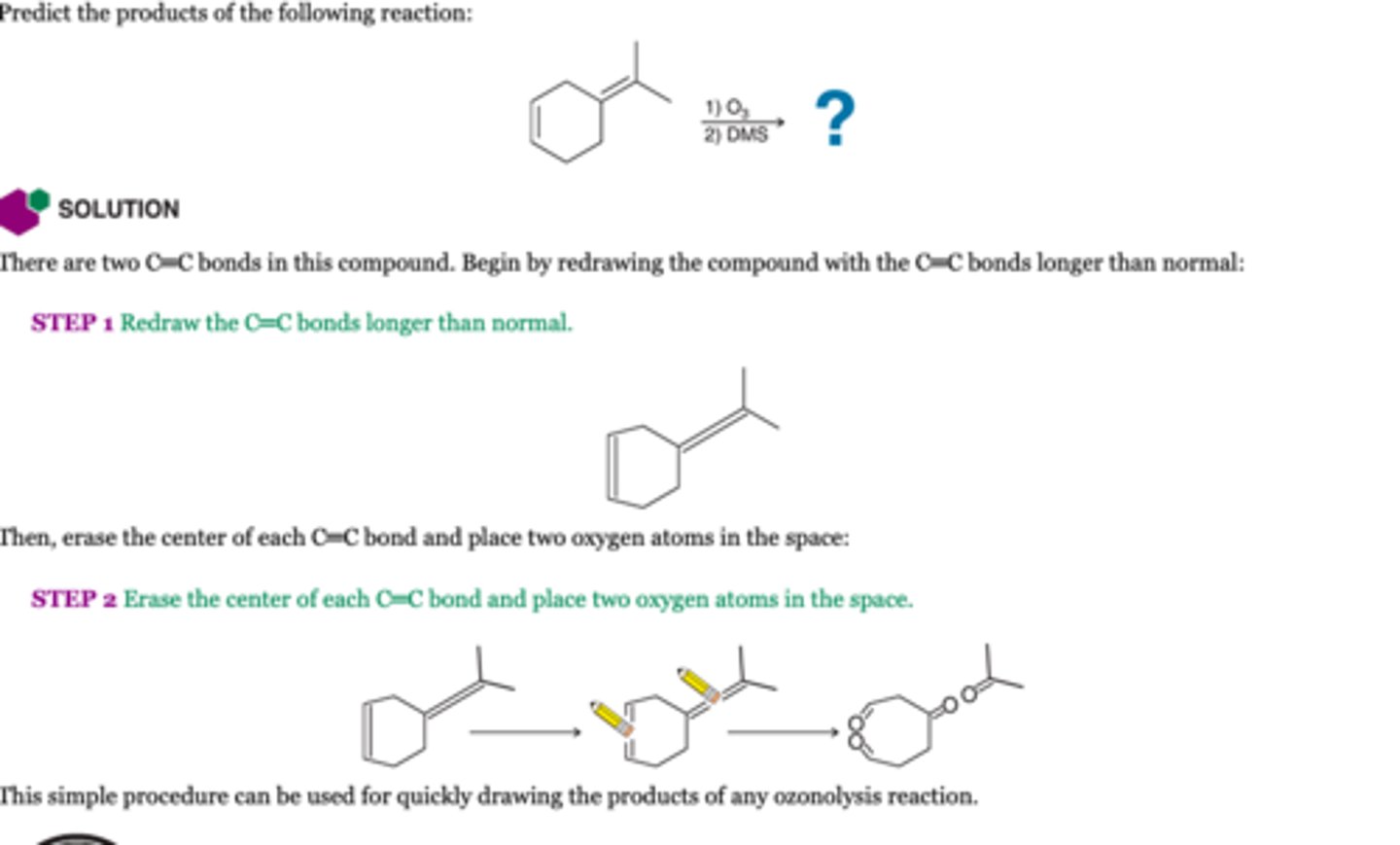
Oxidative Cleavage by KMNO4
-KMNO4 is a strong oxidizing agent
-If KMNO4 makes a aldehyde it is further oxidized to RCO2H
-IF KMNO4, makes a formaldehydte it is oxidized to formic acid but it decomposes to CO2 which is the final product
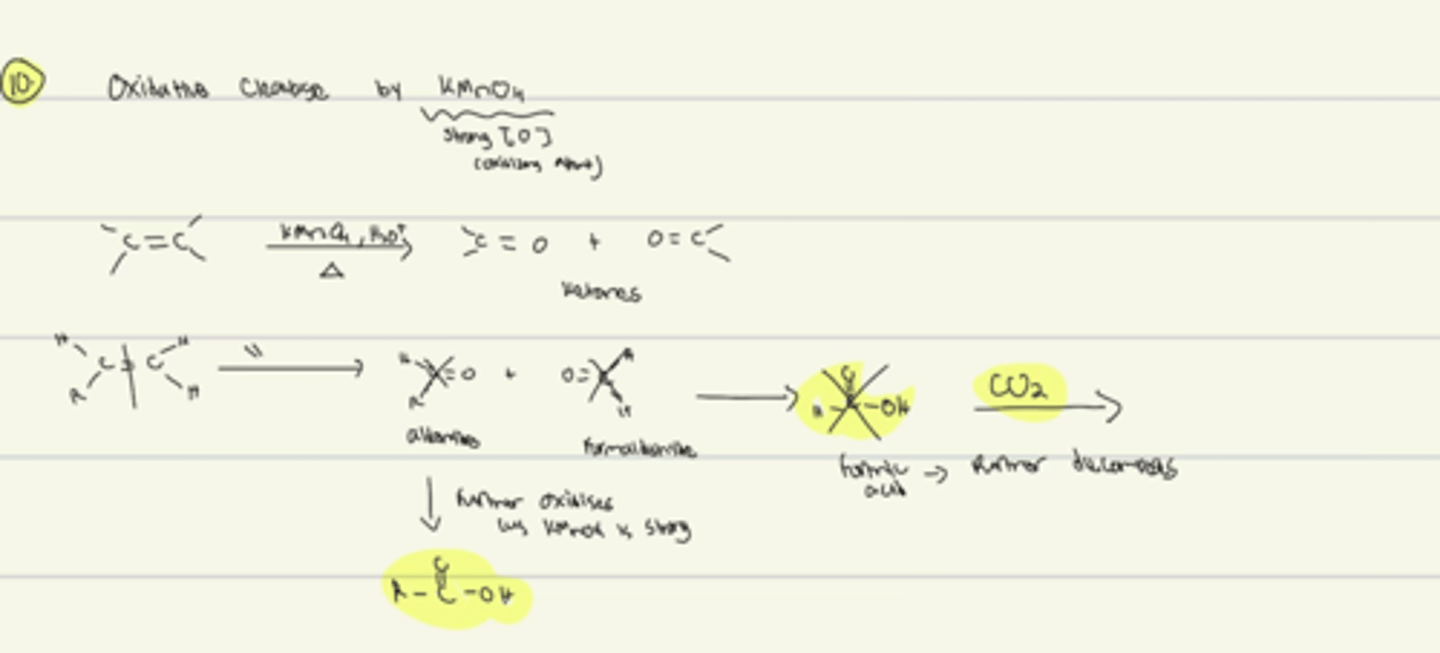
Oxidation/Reduction
Oxidation: number of oxygen increases OR number of hydrogen decreases
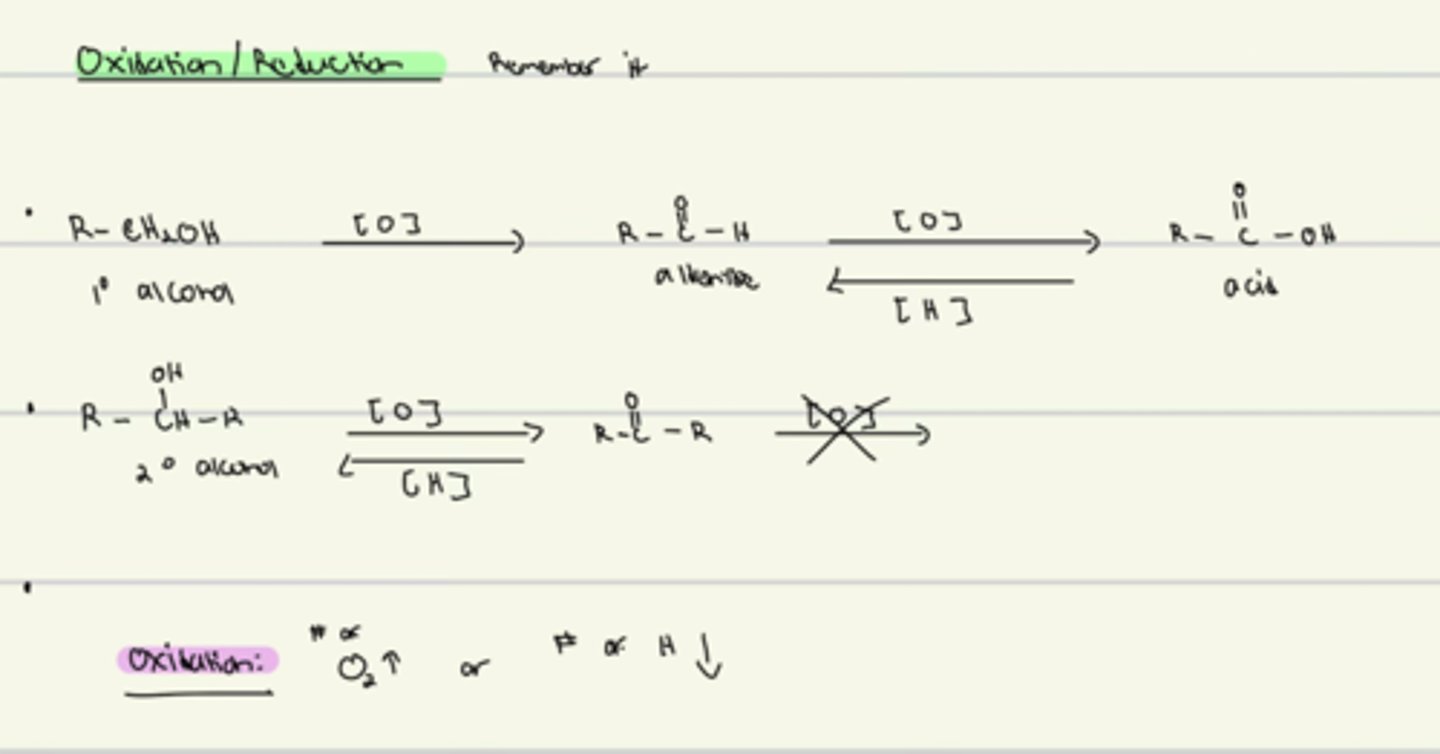
TsCl, pyridine can be used on a ____and ____alcohol
primary and secondary but not tertiary
Primary alcohol undergoes ____while secondary and tertiary undergo ____
E2, E1 (H2SO4)
Primary alcohol undergoes _____while secondary and tertiary undergo____
SN2, SN1 (HBr)
If FINAL carbons is less than STARTING carbons during synthesis, use...
1) O3
2) DMS