Anatomy - Reproductive System Quiz
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/79
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
1
New cards
largest sex cell ; female body
eggs (ova)
2
New cards
smallest sex cell ; male body
sperm
3
New cards
how much of the DNA does each sex cell have?
half
4
New cards
spermatogenesis
the process of producing sperm
5
New cards
know the labeling
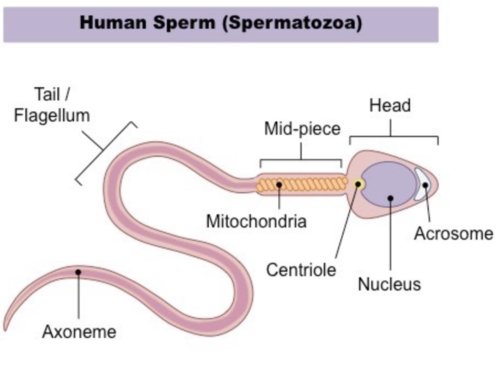
6
New cards
head of sperm contains
nucleus (with DNA) and enzymes to help sperm enter egg
7
New cards
midpiece of sperm contains
mitochondria that produce ATP to move flagellum
8
New cards
flagellum of sperm (tail) function
movement
9
New cards
Oogenesis
production of egg cells ; occurs in ovaries
10
New cards
Fertilization
fusion of the sperm and egg cells
11
New cards
new cell created by fertilization
zygote
12
New cards
masculine hormone
testosterone
13
New cards
feminine hormone
estrogen
14
New cards
seminiferous tubules
site of sperm production
15
New cards
scrotum
protects and regulates temperature of testes
16
New cards
epididymis
where sperm are stored/finish maturing, damaged sperm are broken
17
New cards
vas deferens
18" tube that carries sperm from epididymis to seminal vesicle ; can also store sperm for months
18
New cards
seminal vesicles + ejaculatory duct
produce seminal fluid
19
New cards
semen consists of
seminal fluid and sperm + some prostate secretions (prevent urinary tract infections)
20
New cards
prostate
gland surrounding urethra that releases secretions to prevent urinary infections with semen
21
New cards
urethra
runs away from bladder, through prostate, to end of penis ; does not release semen/urine at the same time
22
New cards
cowper's glands
secrete fluid into urethra to neutralize acid from urine (male)
23
New cards
penis
surrounds urethra and contains erectile tissue (fills with blood during erection)
24
New cards
circumcision
males are born with foreskin on distal end of penis ; circumcision removes it
25
New cards
ovaries
make ova (1/month after puberty), produce estrogen and progesterone
26
New cards
fallopian tubes
5" long path from uterus ; not connected to ovaries but fingerlike fimbriae capture egg when released ; where fertilization occurs
27
New cards
uterus
provides protection, nutrition, and waste removal for developing baby ; contracts to expel fetus at birth
28
New cards
layers of uterus
myometrium (thickest, smooth muscle) and endometrium (inner lining, has glands and blood vessels, thickens for pregnancy or sheds if no pregnancy)
29
New cards
cervix
"neck" between uterus and vagina ; secretes mucus to allow or block sperm ; dilates during labor
30
New cards
vagina
passage for menstrual fluids ; receives penis and sperm ; forms birth canal
31
New cards
hymen
elastic membrane surrounding vagina ; purpose unknown
32
New cards
bartholin's glands
secrete fluids to reduce friction during intercourse (female)
33
New cards
clitoris
contains erectile tissue and dense nerve clusters
34
New cards
labia
outermost skin and fat tissue
35
New cards
menarche
female's first period
36
New cards
menopause
end of menstruation ; between ages 40-50
37
New cards
ovarian cycle
produces eggs for fertilization
38
New cards
follicular phase (ovarian cycle)
starts on first day of bleeding/menses ; lowest hormones ; FSH rises and follicles develop in ovaries ; estrogen rises and endometrium thickens ; ~day 14 LH peaks and egg releases
39
New cards
ovulation
egg is released from ovary ; ~day 14 of ovarian cycle
40
New cards
luteal phase (ovarian cycle)
egg-less follicle grows+yellows and becomes corpus luteum, producing progesterone to grow uterine wall ; pregnancy=CL grows, thick lining for embryo ; no pregnancy=CL shrivels, progesterone falls, menstruation occurs when endometrium sheds
41
New cards
uterine cycle
prepares uterus for pregnancy
42
New cards
menses phase (uterine cycle)
first day of cycle ; reduced blood flow to endometrium, it sheds via vagina ; lasts 3-5 days
43
New cards
proliferative phase (uterine cycle)
after menses to ~day 14 (ovulation) ; endometrial lining regrows
44
New cards
secretory phase (uterine cycle)
from ovulation to first day/menses ; hormone levels drop, progesterone and estrogen from corpus luteum cause more growth of endometrial lining
45
New cards
epidural
medicine placed near spinal cord that can ease pain during labor
46
New cards
episiotomy
cutting of the vaginal opening ; may be done to prevent tearing during birth
47
New cards
breach birth
infant does not come out head first
48
New cards
baby after birth
covered in fine hair called lanugo and waxy substance called vernix
49
New cards
meconium
sticky black substance of swallowed amniotic fluid + digestive secretions ; will show up in baby's first diaper
50
New cards
mammary lobes
15-25 lobes that radiate around nipple ; produce the milk when a woman is lactating
51
New cards
lactiferous ducts
milk passes into the lactiferous ducts, which open to the outside of the nipple
52
New cards
areola
"nipple" ; infant's sucking stimulates more milk production
53
New cards
breastfeeding benefits
milk contains sufficient vitamins, proteins, fats, antibodies ; physical/eye contact is good for mother/baby ; mother can lose pregnancy weight faster ; uterus shrinks
54
New cards
What are the purposes of the human reproductive system?
To produce the healthiest eggs and sperm for the continuation of our species ; also for pleasure for humans ; not required for us to stay alive
55
New cards
How is a new human being formed from 2 parents, on a cellular level?
They combine their DNA through the single sperm meeting the egg (sperm uses enzymes+momentum to make it through), which creates a zygote, starting the formation of a human ; (fertilization)
56
New cards
What organs make up the male reproductive system?
testes, epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles/ejaculatory ducts, urethra, cowper's glands, penis
57
New cards
What organs make up the female reproductive system?
ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, myometrium, endometrium, cervix, vagina ; external=hymen, bartholin's glands, clitoris, labia
58
New cards
When are males fertile? Females?
Males are fertile every day from puberty until death ; females are only fertile during their ovulation phase (after puberty) which is roughly two weeks after their period
59
New cards
What is a "menstrual period" and why does it occur?
3-5 days long ; marks start of ovarian and uterine cycles ; happens from puberty until menopause ; if a female is not pregnant, the endometrial lining is not needed for protection of the egg, so it sheds and exits via vagina
60
New cards
What is the difference between ovulation and menstruation?
menstruation prepares and takes care of the uterus if a female is not pregnant ; ovulation produces eggs for the female to become pregnant
61
New cards
What are the stages of labor and birth?
water breaks, baby is delivered through contractions as a vaginal birth/C section/breach birth, placenta is expelled within a half hour after the birth
62
New cards
Compare vaginal delivery to a C section
vaginal delivery-baby exits normally, head first, through vaginal canal ; C section-baby gets stuck, usually flipped wrong way, taken out through lower abdomen
63
New cards
infertility
inability to conceive a baby
64
New cards
testicular trauma
Testicle is hurt by force; can cause bleeding, bruising, temporary or long-term infertility
65
New cards
testicular torsion
Testicle rotates, cutting off circulation to it; causes severe pain and swelling
66
New cards
Erectile dysfunction
Male cannot get or keep an erection firm enough for sexual intercourse
67
New cards
Benign prostatic hypertrophy
Non-cancerous prostate gland enlargement that can cause painful or difficult urination
68
New cards
Abruptio placentae
When placenta detaches from endometrium before delivery, depriving the baby of oxygen and nutrients; symptoms include uterine pain, bleeding, early contractions
69
New cards
Amenorrhea
Lack of a menstrual period for more than 3 months or extremely delayed period/puberty
70
New cards
PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome)
Complicated disorder causing enlarged and cyst-covered ovaries; symptoms include infertility, irregular menstruation, excess hair growth, acne, weight gain
71
New cards
Ectopic pregnancy
Pregnancy that occurs outside the endometrium; vaginal bleeding or irregular bleeding and abdominal pain are common
72
New cards
Endometriosis
Endometrial lining grows outside the uterus; can cause pain, irregular periods, and sometimes infertility
73
New cards
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Bacterial infection of the blood causing fever, low blood pressure, vomiting, and/or rash
74
New cards
PMS (pre-menstrual syndrome)
Symptoms that occur prior to menstruation: mood swings, carbohydrate cravings, fatigue, irritability or depression, bloating, and/or tender breasts
75
New cards
PMDD (pre-menstrual dysphoric disorder)
Severe extension of PMS to the point of disrupting work and relationships
76
New cards
Miscarriage
Spontaneous loss of pregnancy before 20th week; abdominal pain, abnormal bleeding are signs; depression may follow
77
New cards
Pre-eclampsia/eclampsia
Pregnancy complication; can be fatal for mother and fetus; starts with high blood pressure and can progress to seizures or coma if untreated
78
New cards
HIV/AIDS
Virus passed via body fluids, symptoms similar to the flu (sore throat, fatigue, vomiting, rash); HIV causes AIDS which hinders body's immune system leading to death
79
New cards
prostate, testicular, penile (disorder)
cancer
80
New cards
breast, ovarian, cervical, uterine/endometrial (disorder)
cancer