MICROBIO CEE - Virology
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Viruses that do not have membranes
Naked Viruses
Naked DNA Virus examples
Papillomavirus
Adenovirus
Parvovirus
Polyomavirus
Naked RNA virus examples
Calicivirus
Picornavirus
Reovirus
Hepevirus
Characteristics of most DNA Viruses
Double stranded
Icosahedral
Linear DNA
Replicated in the Nucleus
ALL DNA VIRUSES ARE DOUBLE STRANDED EXCEPT______
PARVOVIRUS
ALL DNA VIRUSES ARE ICOSAHEDRAL EXCEPT____
POX VIRUS (COMPLEX)
ALL DNA VIRUSES HAVE LINEAR DNA, EXCEPT ____
HEPADNA, POLYOMA, PAPILLOMA
ALL DNA VIRUSES REPLICATED IN NUCLEUS, EXCEPT ___
POX VIRUS
ALL RNA VIRUSES ARE SINGLE STRANDED EXCEPT ______
REOVIRUS
ALL RNA VIRUSES REPLICATE IN THE CYTOPLASM EXCEPT _____
RETROVIRUS AND INFLUENZA VIRUS
Disease associated:
herpes labialis (cold sores)
temporal lobe encephalitis
sporadic encephalitis
Herpes simplex virus-1
Other info:
latent in trigeminal ganglia
Herpes simplex virus-1
Disease associated:
Herpes genitalis, neonatal herpes
Herpes simplex virus-2
Other info:
latent in sacral ganglia
Herpes simplex virus-2
Disease associated:
chickenpox, shingles
postherpetic neuralgia
VaricellaZoster virus (HHV-3)
Other info:
Latent in dorsal root or trigeminal ganglia
VaricellaZoster virus (HHV-3)
Disease associated:
“kissing disease”
Mononucleosis
Lymphomas
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Epstein-Barr virus (HHV-4)
Other info:
(+) Monospot test
Use of amoxicillin in mononucleosis can cause characteristic maculopapular rash
Epstein-Barr virus (HHV-4)
Disease associated:
AIDS retinitis
Cytomegalovirus (HHV-5)
Other info:
“owl eye” intranuclear inclusions
Cytomegalovirus (HHV-5)
Disease associated:
Roseola infantum (exanthem subitum)
Human herpesviruses 6 and 7
Disease associated:
Kaposi sarcoma
Seen in HIV/AIDS and transplant patients.
Human herpesvirus 8
DNA Viruses family examples (7)
Herpesviruses
Poxvirus
Hepadnavirus
Adenovirus
Papillomavirus
Polyomavirus
Parvovirus
Disease associated:
Smallpox
Cowpox
Molluscum contagiosum
Poxvirus
Other info:
largest DNA virus
Poxvirus
Disease associated:
Acute or chronic hepatitis
Hepa-B virus
Hepadnavirus
Disease associated:
Febrile pharyngitis
Adenovirus
Disease associated:
HPV–warts
cervical cancer
Papillomavirus
Disease associated:
JC virus
BK virus
Polyomavirus
Disease associated:
“slapped cheek” rash in children
erythema infectiosum, or fifth disease
Parvovirus
Positive or negative sense single-stranded RNA virus?
• In the host cell, the ____ of the virus is directly translated into Viral proteins.
positive-sense RNA single-stranded RNA virus
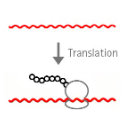
Positive or negative sense single-stranded RNA virus?
•It is not readable by the host ribosome.
• First, the _____(3'-to-5')
is converted into positive-sense RNA
(5'-t0-3') by viruses RNA-dependent
RNA polymerase.
negative-sense RNA single-stranded RNA virus
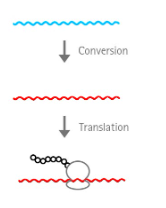
NEGATIVE STRAND-RNA VIRUSES
mnemonic
"Always Bring Polymerase Or Fail Replication"
NEGATIVE STRAND-RNA VIRUSES examples
Arenaviruses
Bunyaviruses
Paramyxoviruses (Measles, Mumps, RSV,Parainfluenza)
Orthomyxoviruses (Influenza A&B)
Filoviruses (Ebola)
Rhabdoviruses (Rabies)
Disease/virus associated:
Rotavirus- diarrhea in children
Reoviruses
Disease/virus associated:
Poliovirus
Echovirus
Rhinovirus- “common cold”
Coxsackievirus - aseptic meningitis
HAV - acute viral hepatitis
Picornaviruses
aseptic meningitis is caused by
Coxsackievirus
acute viral meningitis is caused by
HAV
Also known as the “common cold”
Rhinovirus
Disease/virus associated:
HEV
Hepevirus
Disease/virus associated:
Norovirus—viral gastroenteritis
Caliciviruses
Disease/virus associated:
HCV
Dengue
Zika virus
Flaviviruses
Disease/virus associated:
Chikungunya virus
Rubella
Togaviruses
Disease/virus associated:
HIV—AIDS
Retroviruses
Disease/virus associated:
“Common cold,” SARS, MERS
Coronaviruses
Disease/virus associated:
Influenza virus
Orthomyxoviruses
Disease/virus associated:
Parainfluenza
RSV
Measles, Mumps
PaRaMyxoviruses
Disease/virus associated:
Rabies
Rhabdoviruses
Disease/virus associated:
Ebola/Marburg hemorrhagic fever
Filoviruses
Disease/virus associated:
LCMV
Lassa fever encephalitis
Arenaviruses
Disease/virus associated:
California encephalitis
Bunyaviruses
Disease/virus associated:
HDV is a “defective” virus
Delta virus
Family of HAV
RNA picornavirus
Family of HBV
DNA hepadnavirus
Family of HCV virus
RNA flavivirus
Family of HDV virus
RNA deltavirus
Family of HEV
RNA hepevirus
What hepatitis virus?
High mortality in pregnant women
HEV
Hepatitis virus families
HAV
HBV
HCV
HDV
HEV
What are common agents that transmitt infection from the mother to fetus?
Toxoplasma gondii
Rubella
Cytomegalovirus
HIV
Herpes simplex virus-2
Syphilis
MOT: Cat feces or ingestion of undercooked meat
Toxoplasma gondii
Maternal manifestations:
Usually asymptomatic;
lymphadenopathy (rarely)
Toxoplasma gondii
MOT: Respiratory droplets
Rubella
Maternal Manifestations:
Rash, lymphadenopathy,
polyarthritis, polyarthralgia
Rubella
MOT: Sexual contact, organ transplant
Cytomegalovirus
Maternal manifestations:
Usually asymptomatic;
mononucleosis-like illness
Cytomegalovirus
MOT: Sexual contact, needlestick
HIV
Maternal manifestations:
Variable presentation depending on CD4+ cell count
HIV
MOT: Skin or mucous membrane contact
Herpes simplex virus-2
Maternal manifestations:
Usually asymptomatic; herpetic (vesicular) lesions
Herpes simplex virus-2
MOT: Sexual contact
Syphilis
Maternal manifestations:
Chancre (1º) and disseminated rash (2°) are the two stages likely to result in fetal infection
Syphilis
Neonatal manifestations: Blue muffin rash
Toxoplasma gondii,Rubella, Cytomegalovirus
Neonatal manifestations:
Classic triad: chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, and intracranial calcifications, +/-"blueberry muffin" rash
Toxoplasma gondii
Neonatal manifestations:
Classic triad: abnormalities of eye (cataracts BI) and ear (deafness) and congenital heart disease (PDA); +/-"blueberry muffin" rash.
Mnemonic: "I (eye) ❤ ruby (rubella) earrings"
Rubella
Neonatal manifestations:
Hearing loss, seizures, petechial rash, "blueberry muffin" rash,chorioretinitis, periventricular calcifications
Cytomegalovirus
Neonatal manifestations:
Recurrent infections, chronic diarrhea
HIV
Neonatal manifestations:
Meningoencephalitis, herpetic (vesicular) lesions
Herpes simplex virus-2
Neonatal manifestations:
Often results in stillbirth, hydrops fetalis; if child survives, presents with facial abnormalities (eg, notched teeth, saddle nose, short maxilla), saber shins, CN VIII deafness
Syphillis