1.2 Developments in Dar al-Islam, 1200-1450 (and Abrahamic Religions)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
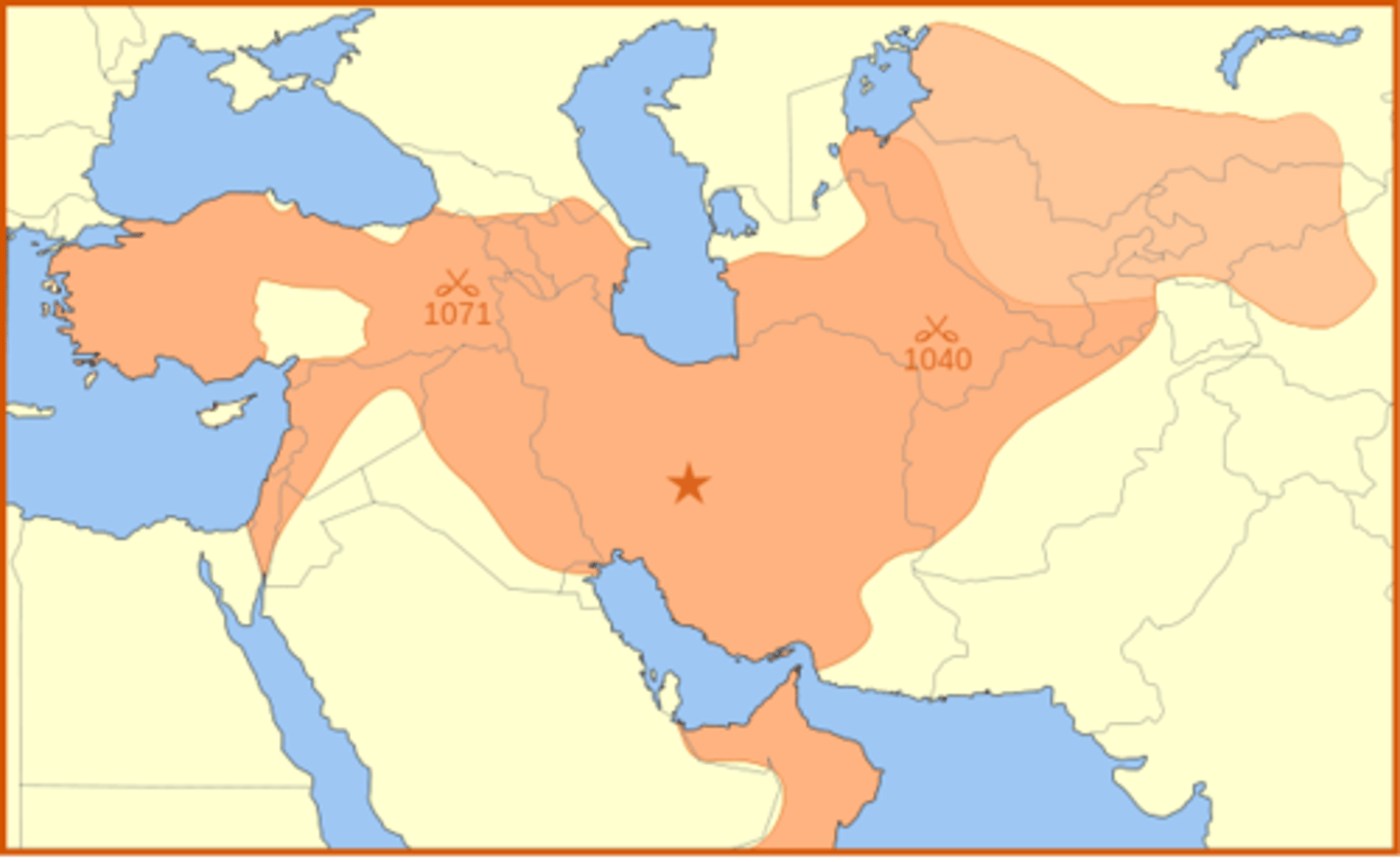
Seljuk Empire
Middle East, 11th-12th centuries
}Turkic empire ruled by sultans in Persia and modern-day
Iraq
} Established Turks as major ethnic group carrying Islam
across Eurasia, along with Arabs and Persians
} Demonstrated weakness of Abbasid caliphate in its later
years; sultans held real power in the empire
} Helped to spread the influence of Islam throughout the region
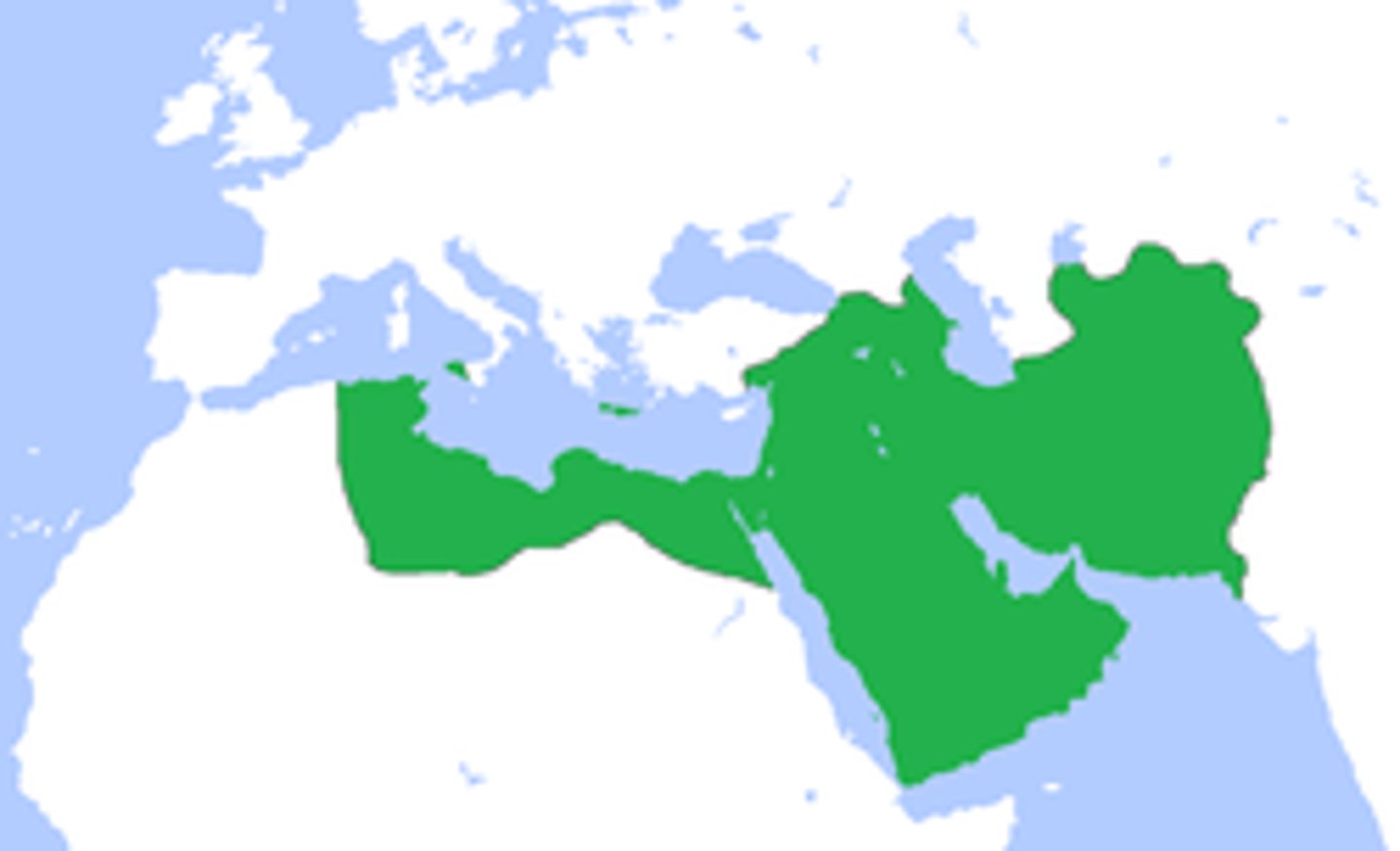
Abbasid Caliphate
(750-1258 CE) The caliphate, after the Umayyads, who focused more on administration than conquering. Had a bureaucracy that any Muslim could be a part of.
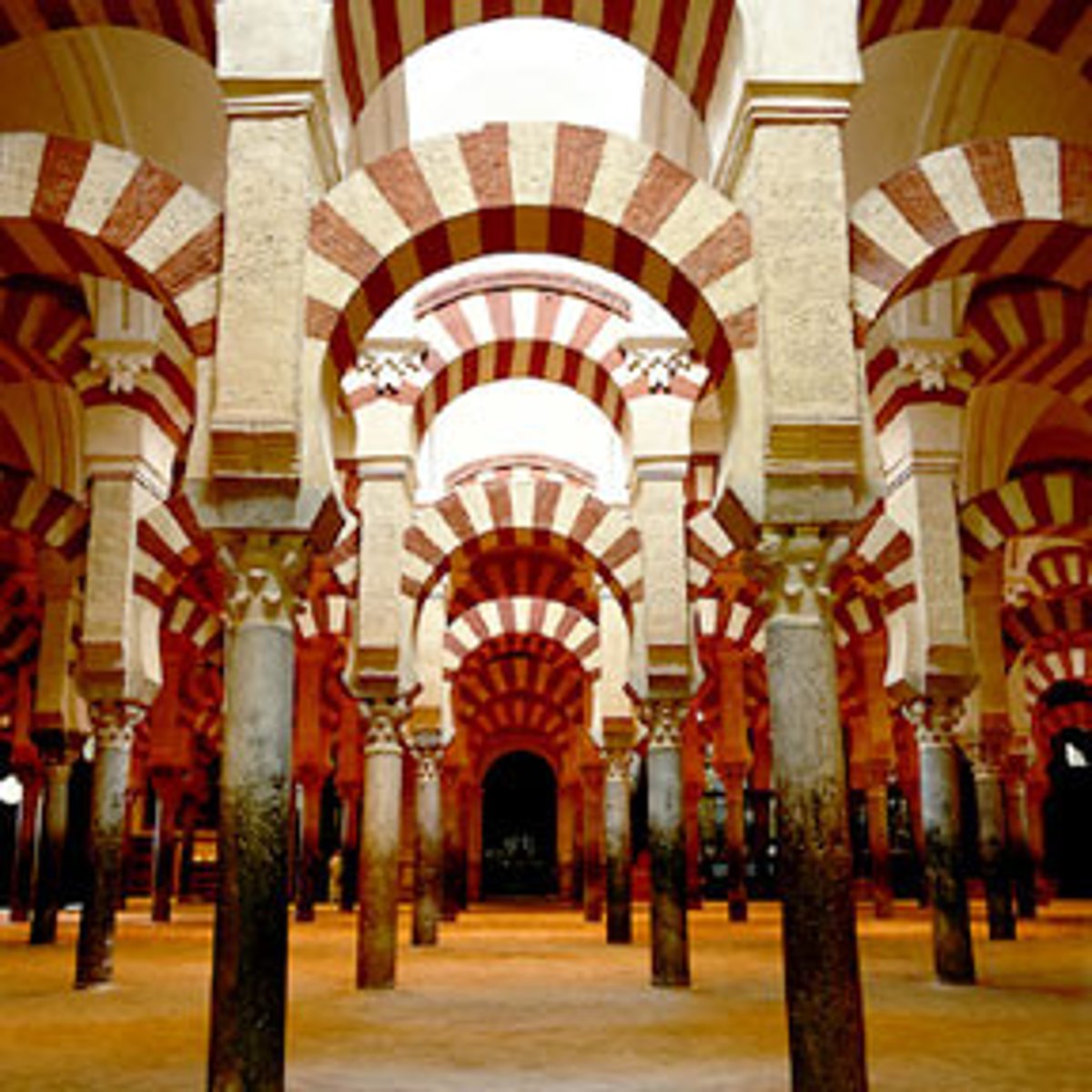
Cordoba Caliphate
(929-1031) capital of Muslim Spain, an economic center, hundreds of workshops, culture and learning flourished there.

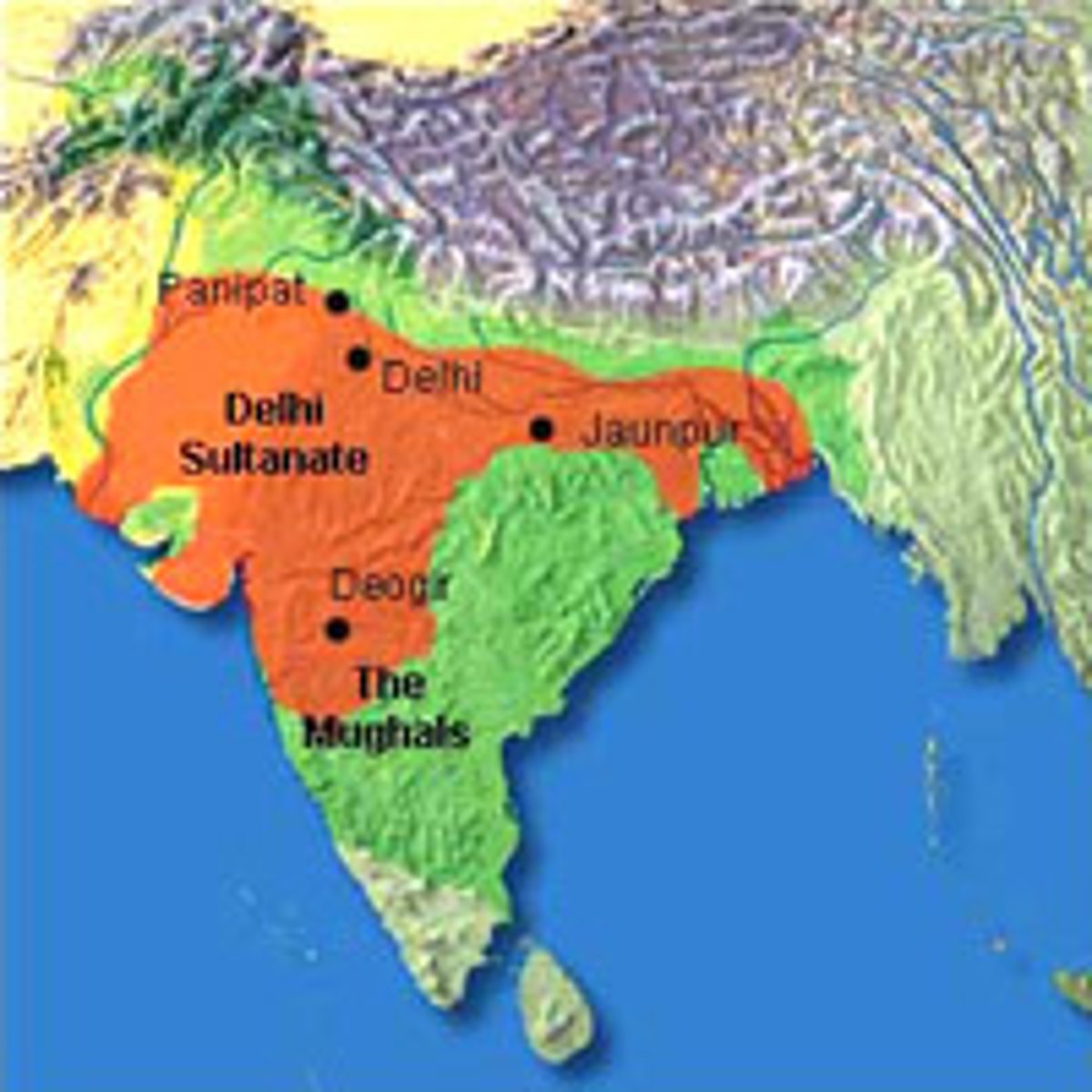
Delhi Sultanate
The first Islamic government established within India from 1206-1520. Controlled a small area of northern India and was centered in Delhi.
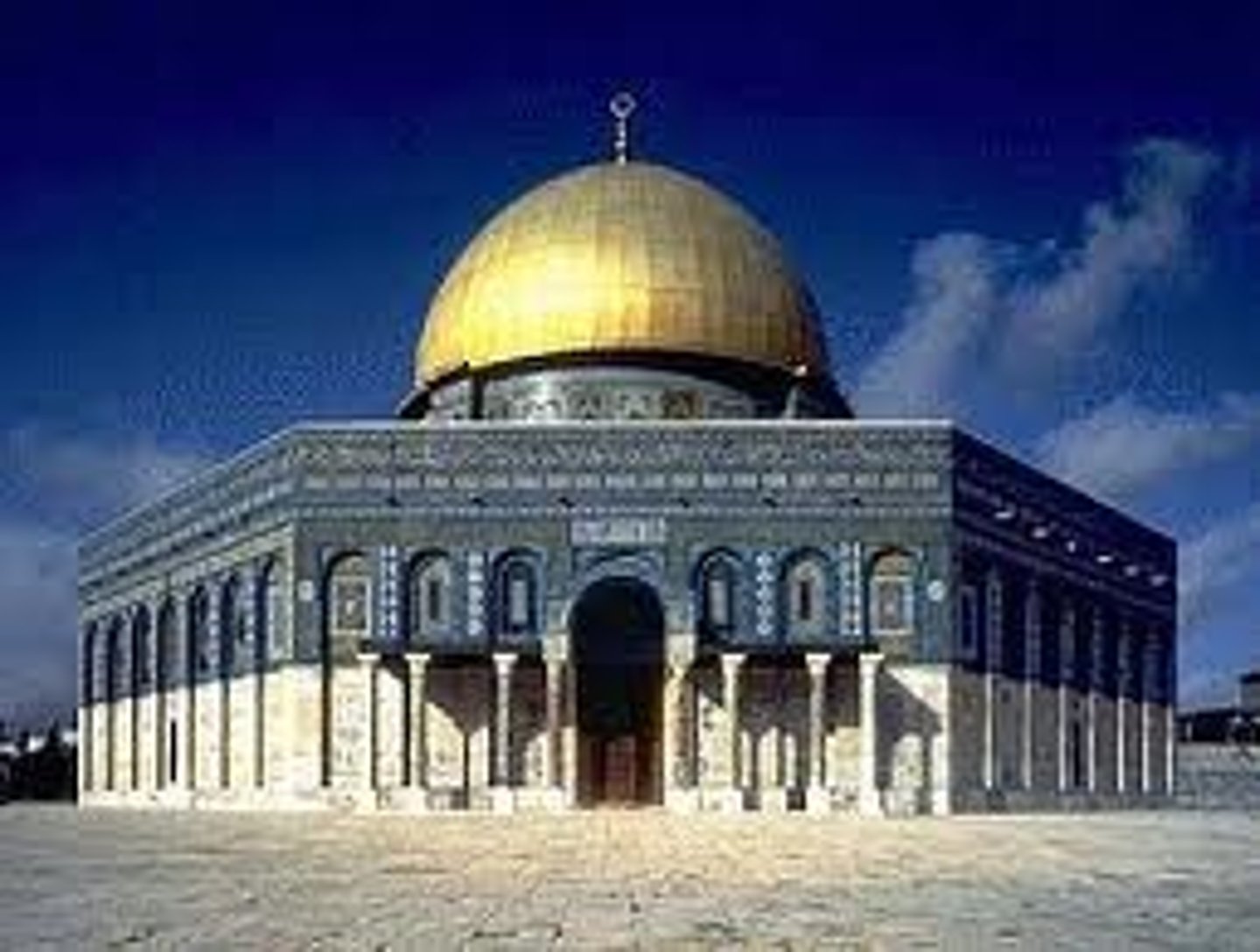
Caliph/Caliphate
A supreme political and religious leader in a Muslim government, successor to Muhammad.

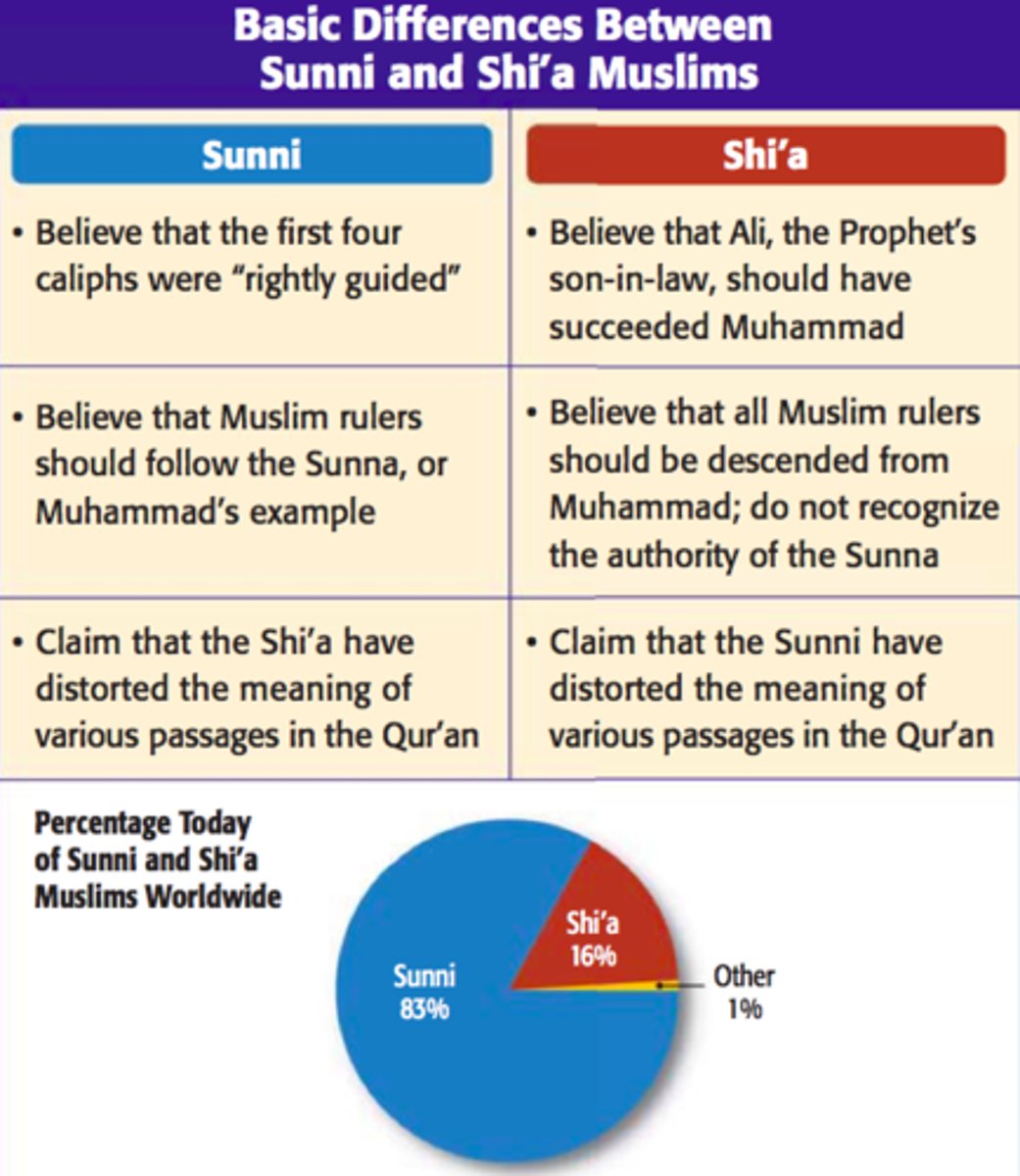
Sunni Muslims
Majority of the Muslims; believe successor of Muhammad can be an elected caliph.
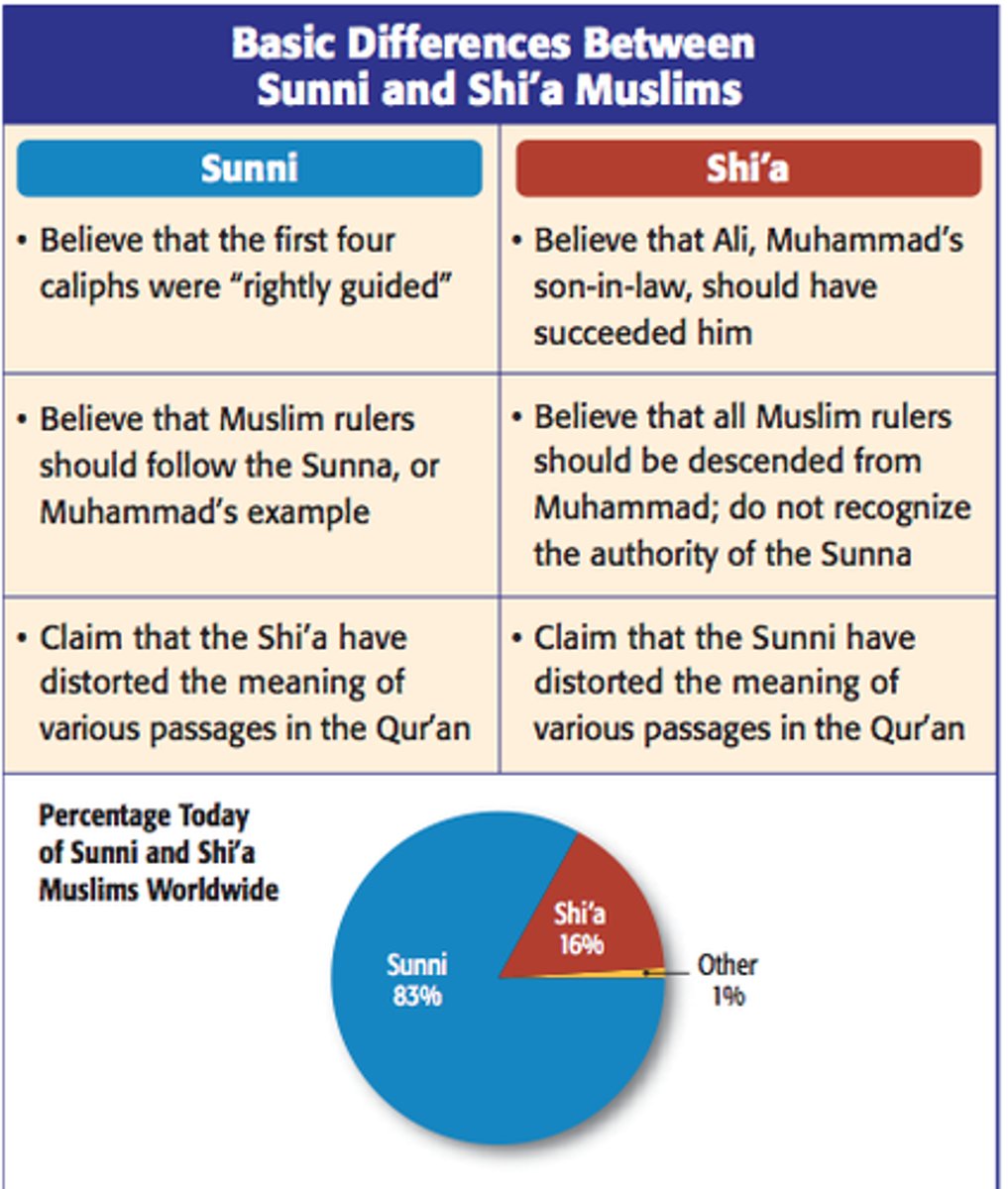
Shia Muslims
Believe that the leader of the Islamic faith should be a direct descendant of the prophet Muhammad.
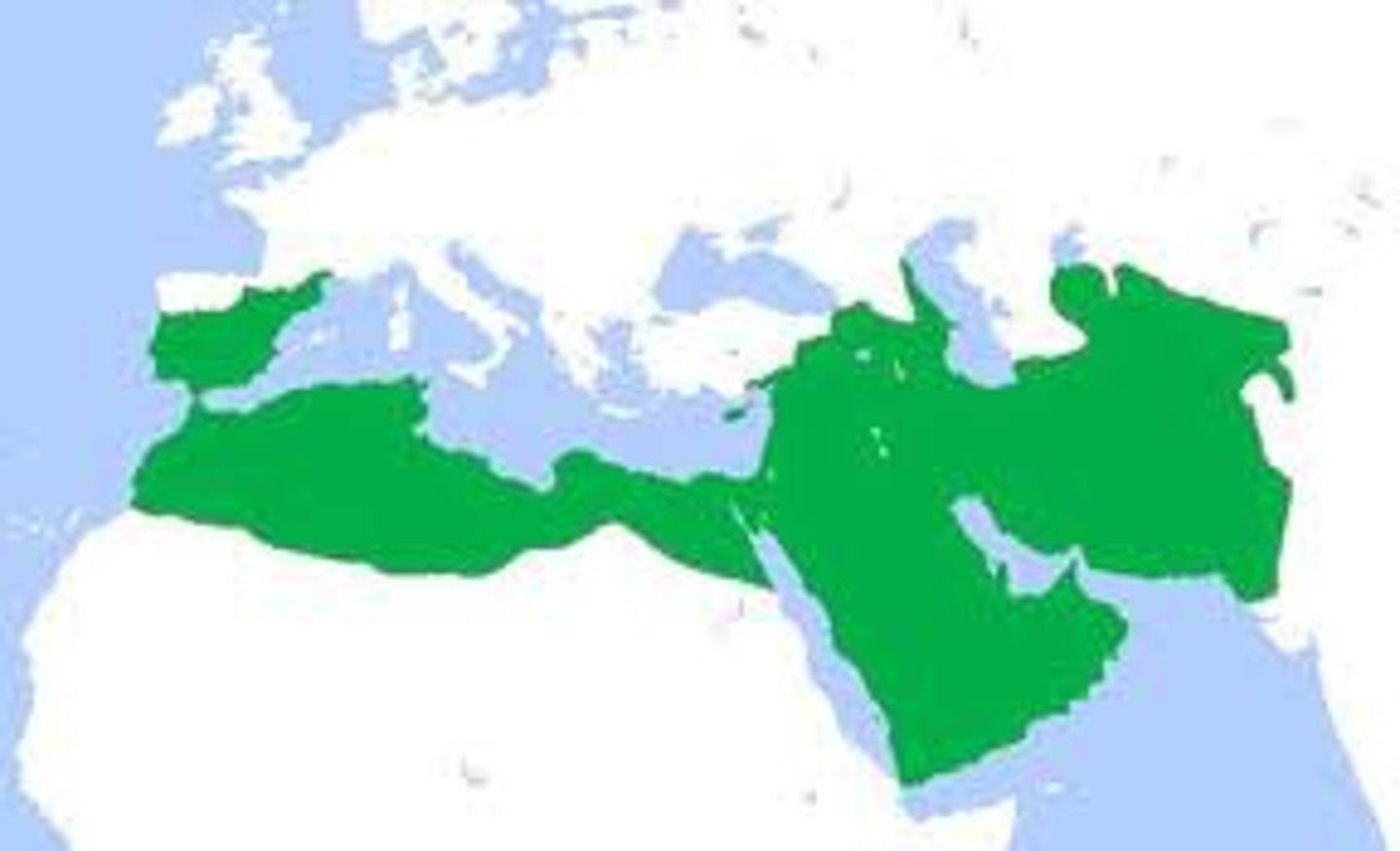
Dar al-Islam
an Arabic term that means the "house of Islam" and that refers to lands under Islamic rule.
Abrahamic Religions
3 religions that regard Abraham as their ancestor in faith: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.

Christianity
A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior.
Judaism
the monotheistic religion of the Jews having its spiritual and ethical principles embodied chiefly in the Torah and in the Talmud.

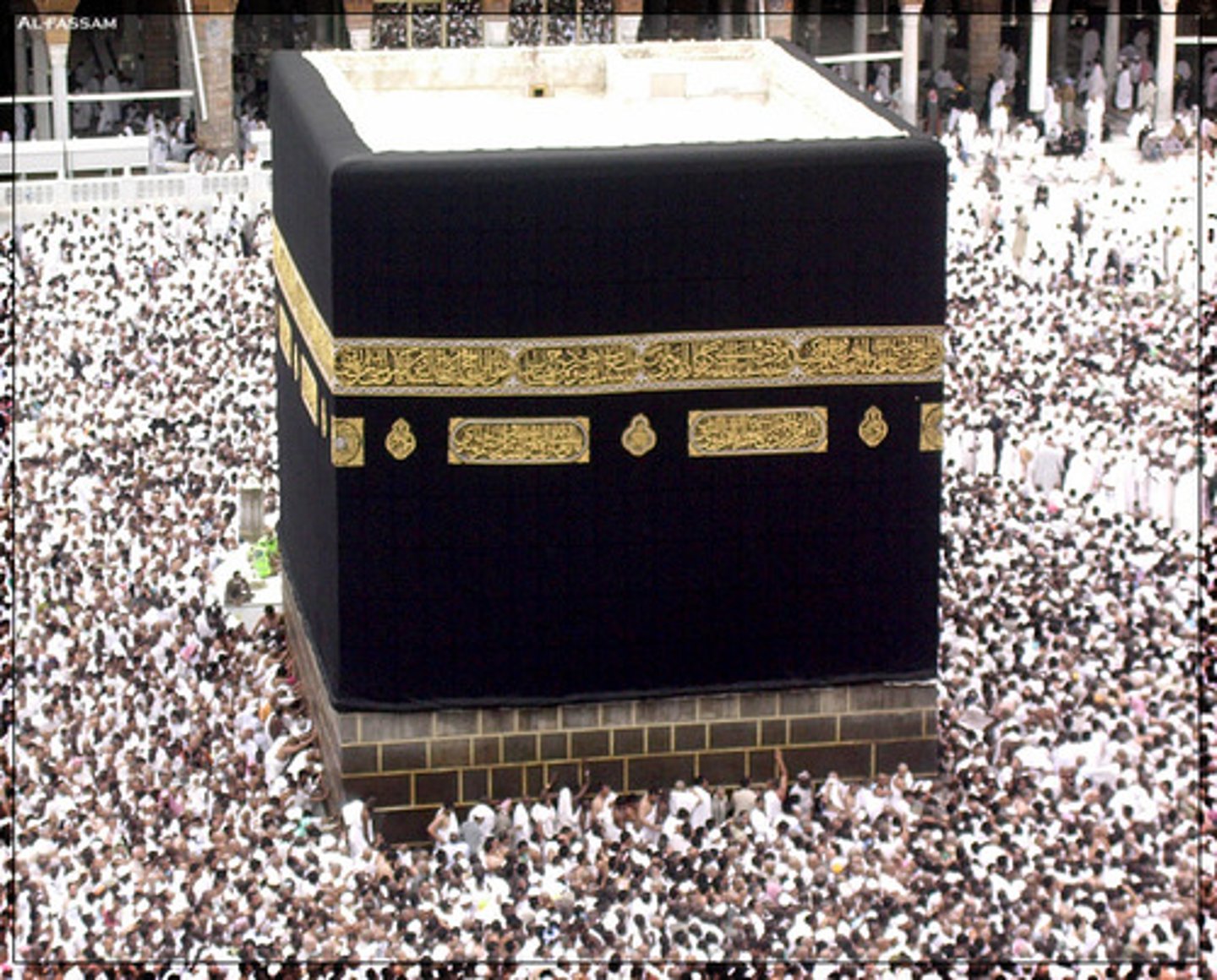
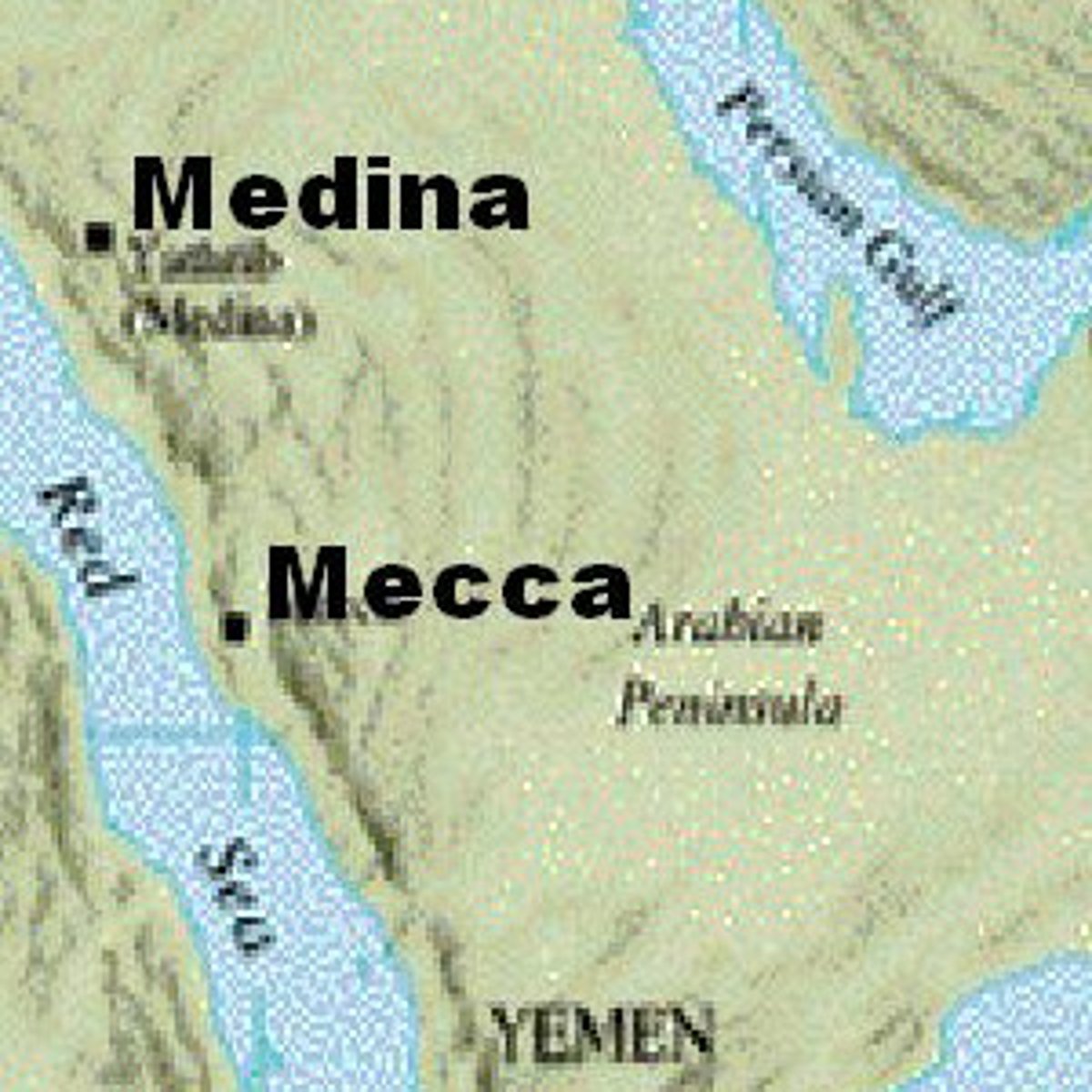
Mecca
City in western Arabia; birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad, and ritual center of the Islamic religion.

Medina
City in western Arabia to which the Prophet Muhammad and his followers emigrated in 622 to escape persecution in Mecca.
Prophet Muhammad
the founder of Islam, believed to be the last true prophet sent by God, wrote the Koran which were his revelations.

Quran (Koran)
the sacred writings of Islam revealed by God to the prophet Muhammad during his life at Mecca and Medina.

Five Pillars
The obligatory religious duties of all Muslims; confession of faith, prayer, fasting during Ramadan, zakat, and hajj.

Sharia
Body of Islamic law that includes interpretation of the Quran and applies Islamic principles to everyday life.

Jizya (tax)
tax paid by Christians and Jews who lived in Muslim communities to allow them to continue to practice their own religion.
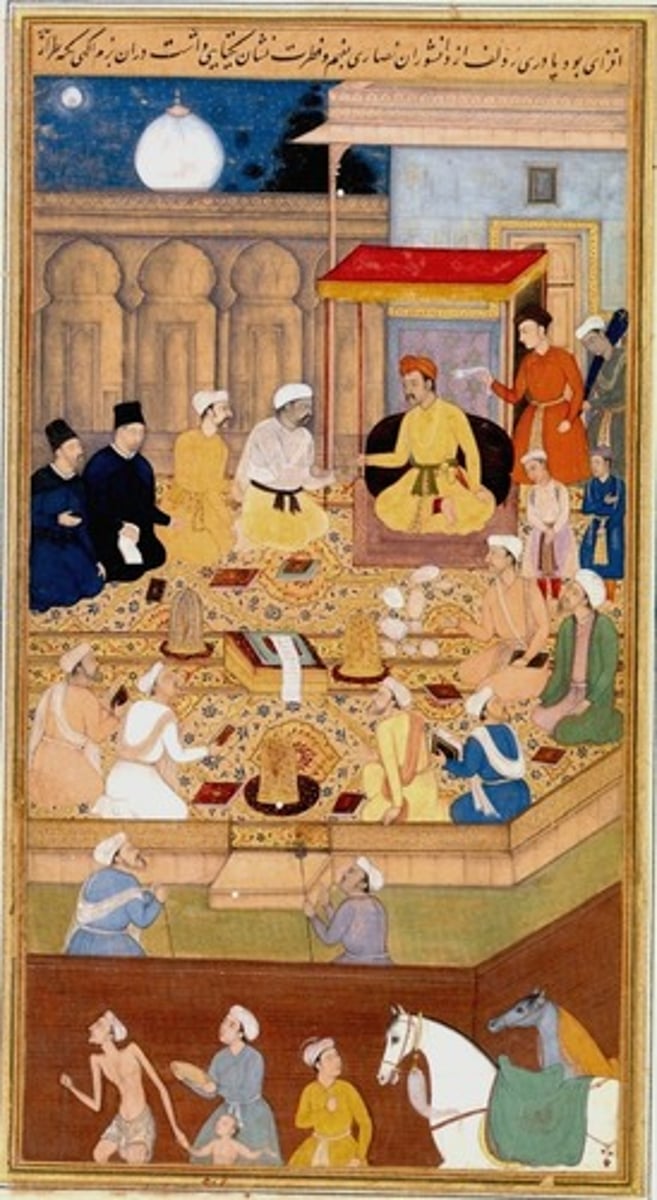

Harun al-Rashid
Most famous of the Abbasid caliphs (786-809); renowned for sumptuous and costly living recounted in The Thousand and One Nights.
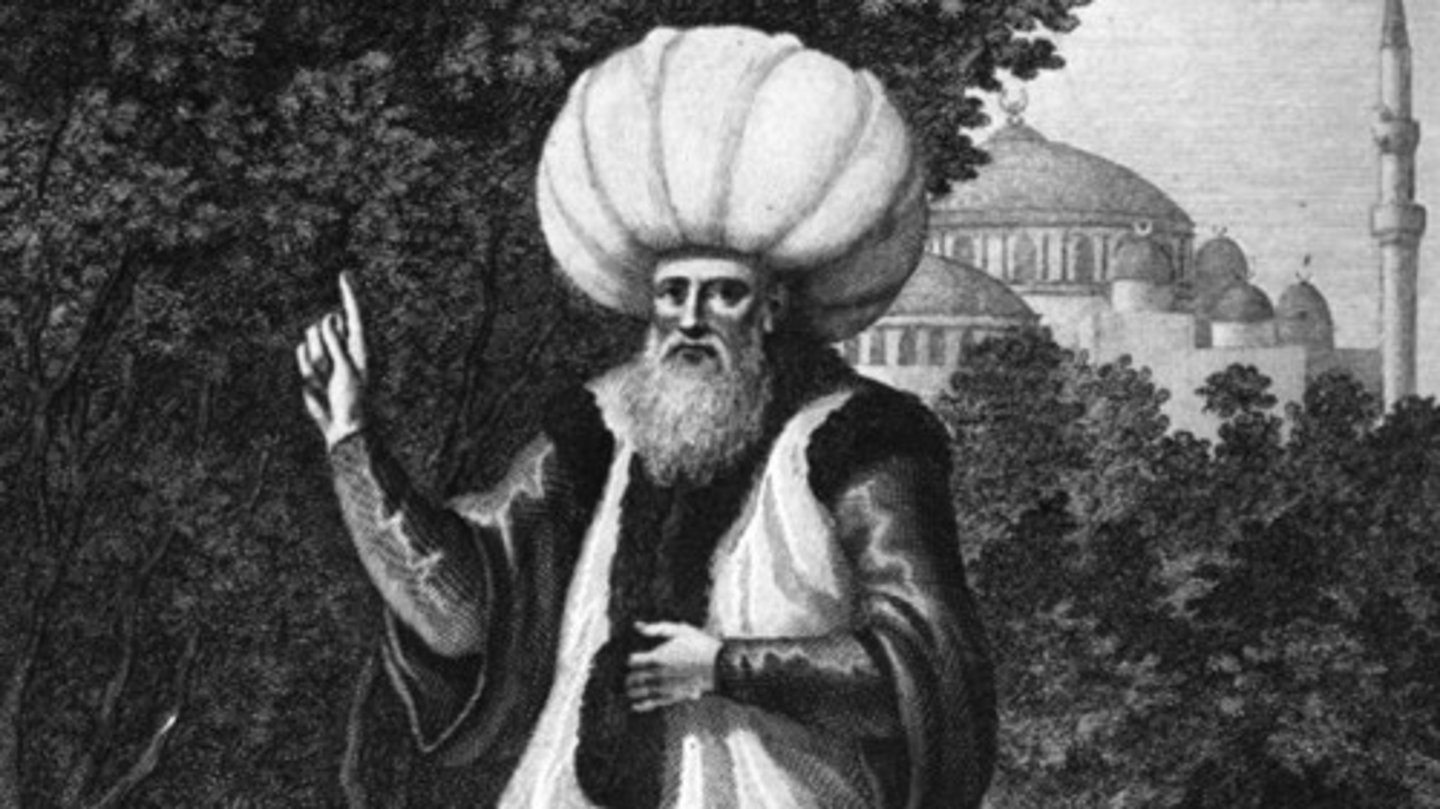

Sufi
A Muslim who seeks to achieve direct contact with God through mystical means.

Ibn Rushd
Spanish-Arab philosopher; also known as Averroes; influenced by Aristotle, his best known writings explore the relationship between reason and faith.

House of Wisdom (Baghdad)
Combination library, academy, and translation center in Baghdad established in the 800s.

"The Thousand and One Nights"
A group of tales narrated by a fictional princess, many are set in Baghdad, include romances, fables, adventures, best known for Aladdin and the magic lamp

Scholasticism
A philosophical and theological system, associated with Thomas Aquinas, devised to reconcile Aristotelian philosophy and Roman Catholic theology in the thirteenth century.

Nicene Creed
(Christianity) a formal creed summarizing Christian beliefs.

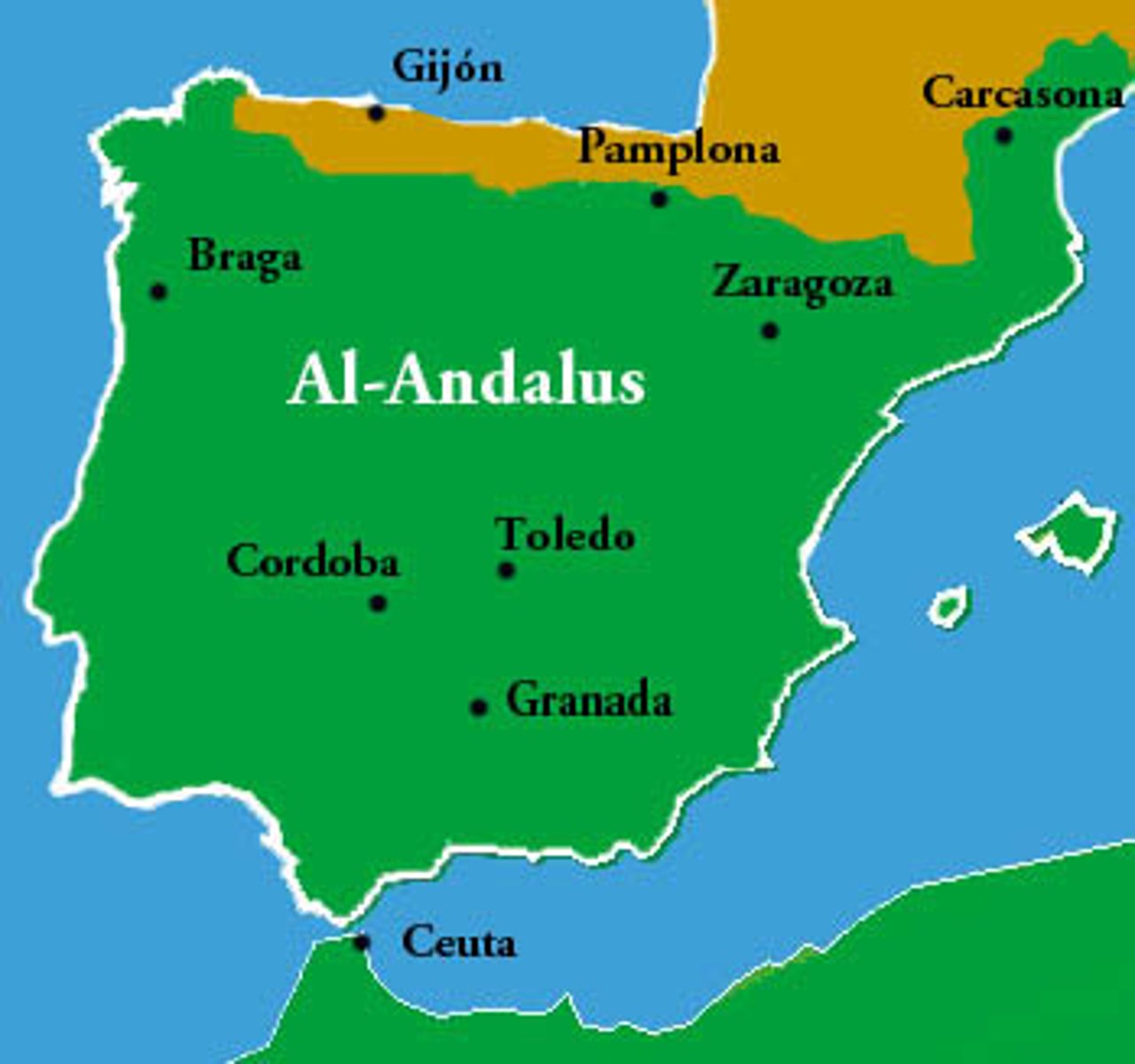
Al-Andalus
A Muslim-ruled region in what is now Spain, established by the Berbers in the eighth century A.D.