MRAD 4218 Module 7 Pathology
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Urinary Pathologies
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
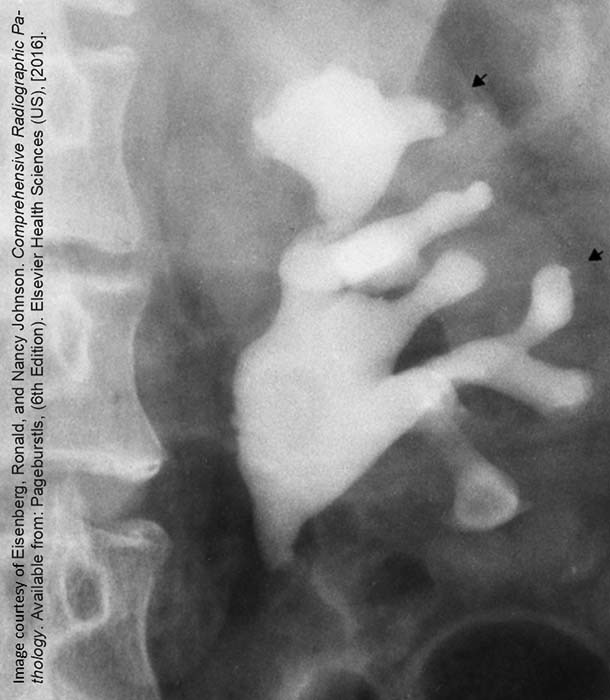
Pyelonephritis: Retrograde Urography
Shows blunting and blurring of the calyces

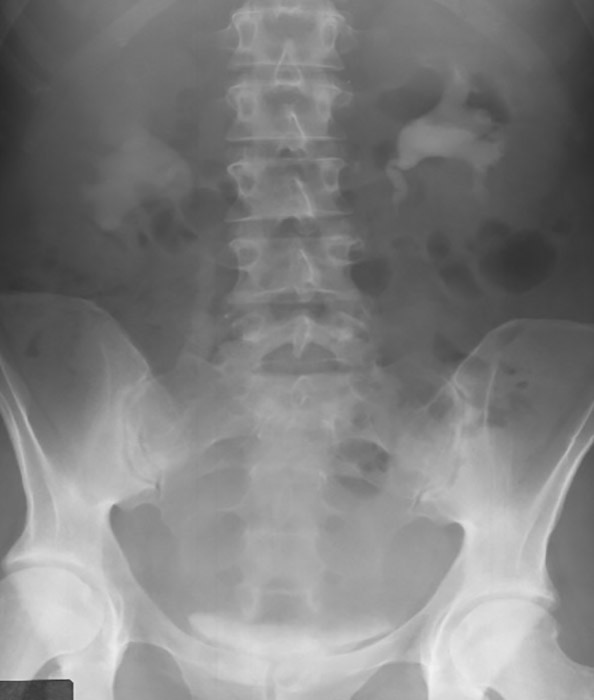
Pyelonephritis: Intravenous Urography
Demonstrates the right infected kidney
Ureter appears widened and there appears to be a mass in the abdomen
Hazy appearance of the right contrast filled renal pelvis compared to the left
Due to edema

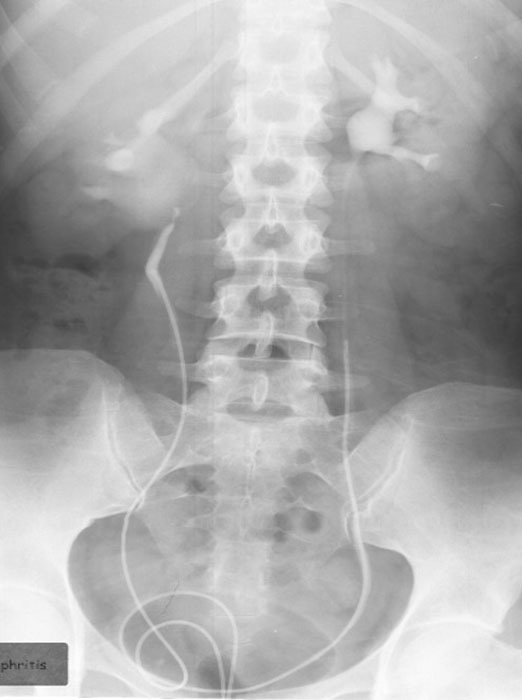
Pyelonephritis: Retrograde Urography
Infected right kidney w/ haziness and dilation of the contrast filled renal pelvis

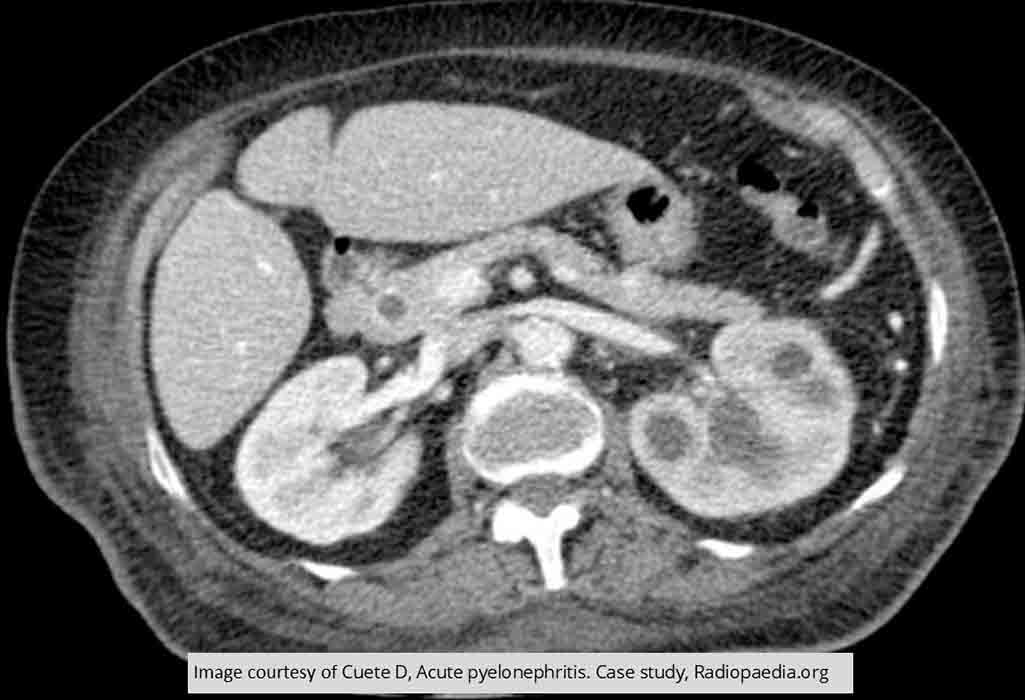
Pyelonephritis: CT w/ Contrast
Image shows enlargement of the calyceal areas surrounded by edema in the left kidney
Left kidney appearance is quite spotty
Indicates decrease of renal function of the left kidney

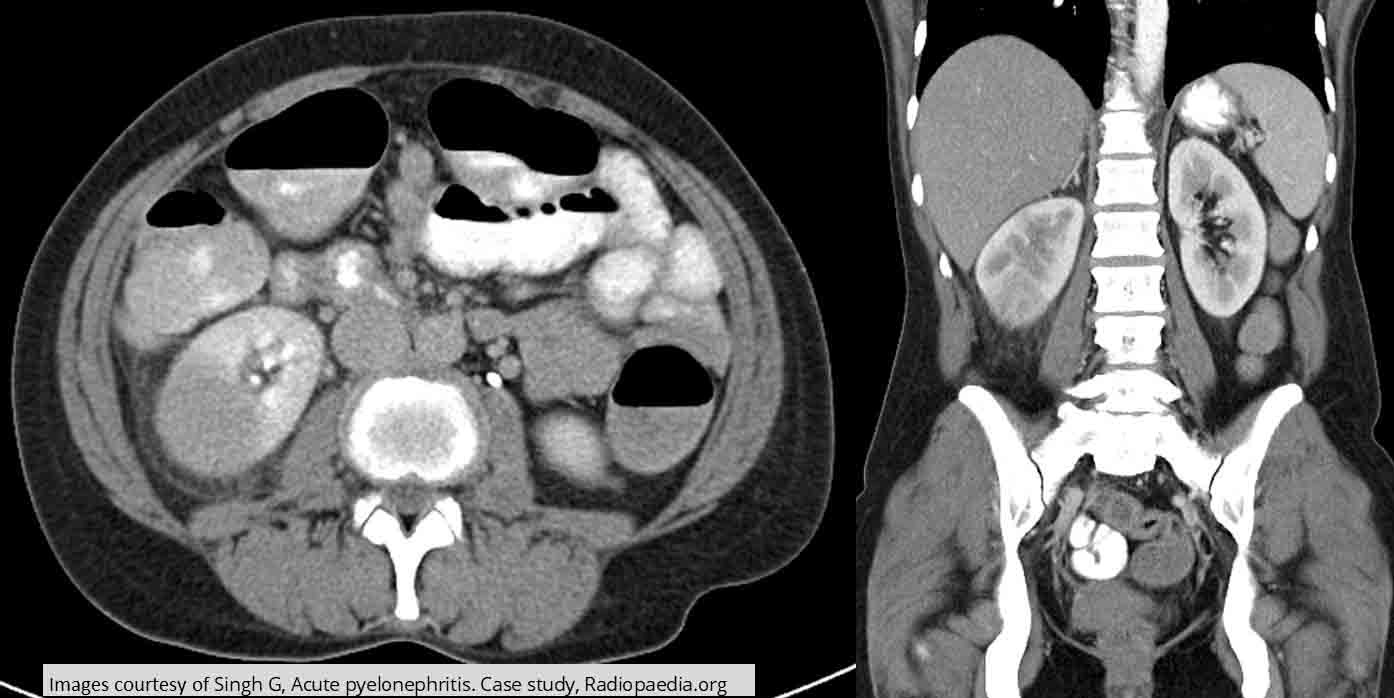
Pyelonephritis: CT Non Contrast
Shows edema throughout the right kidney consistent w/ infection

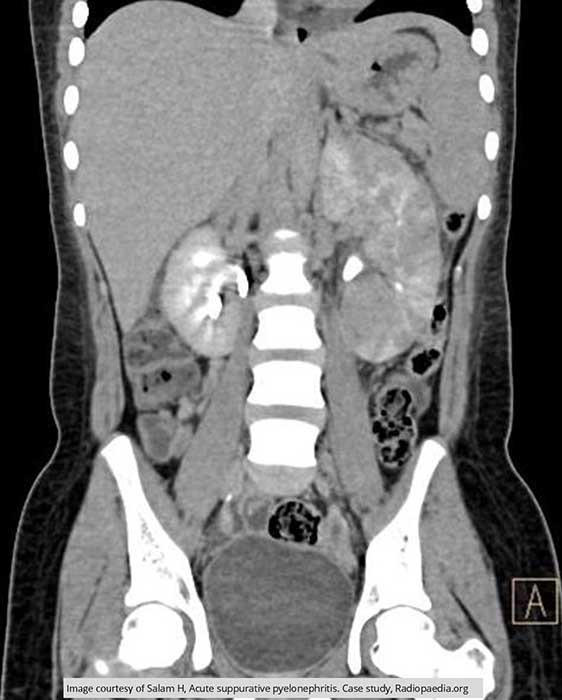
Pyelonephritis: CT w/ Contrast
Coronal image demonstrates the enlargement of the left kidney caused by the infection
Very little functioning of the left kidney

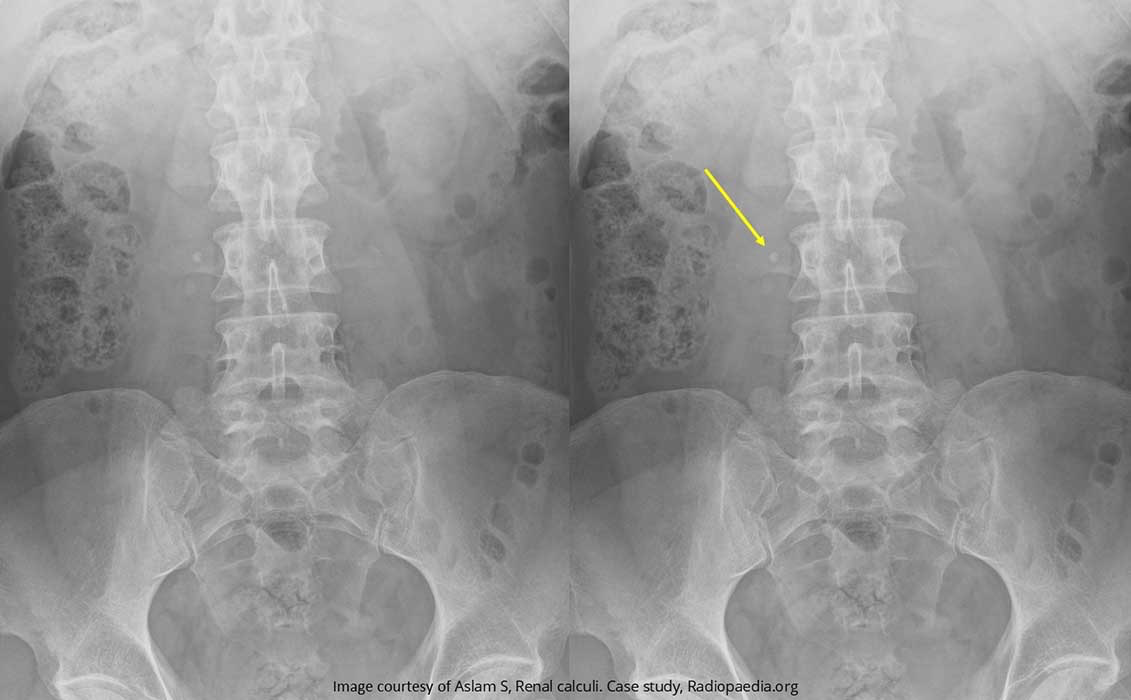
Renal Calculi: Stone sitting on the right transverse process of L3

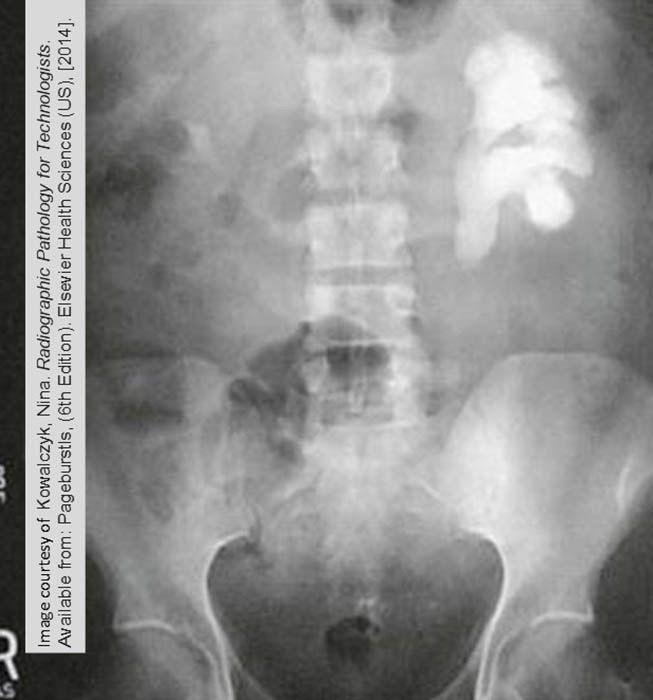
Renal Calculi: Staghorn Calculus
Taken over the renal pelvis and calyces

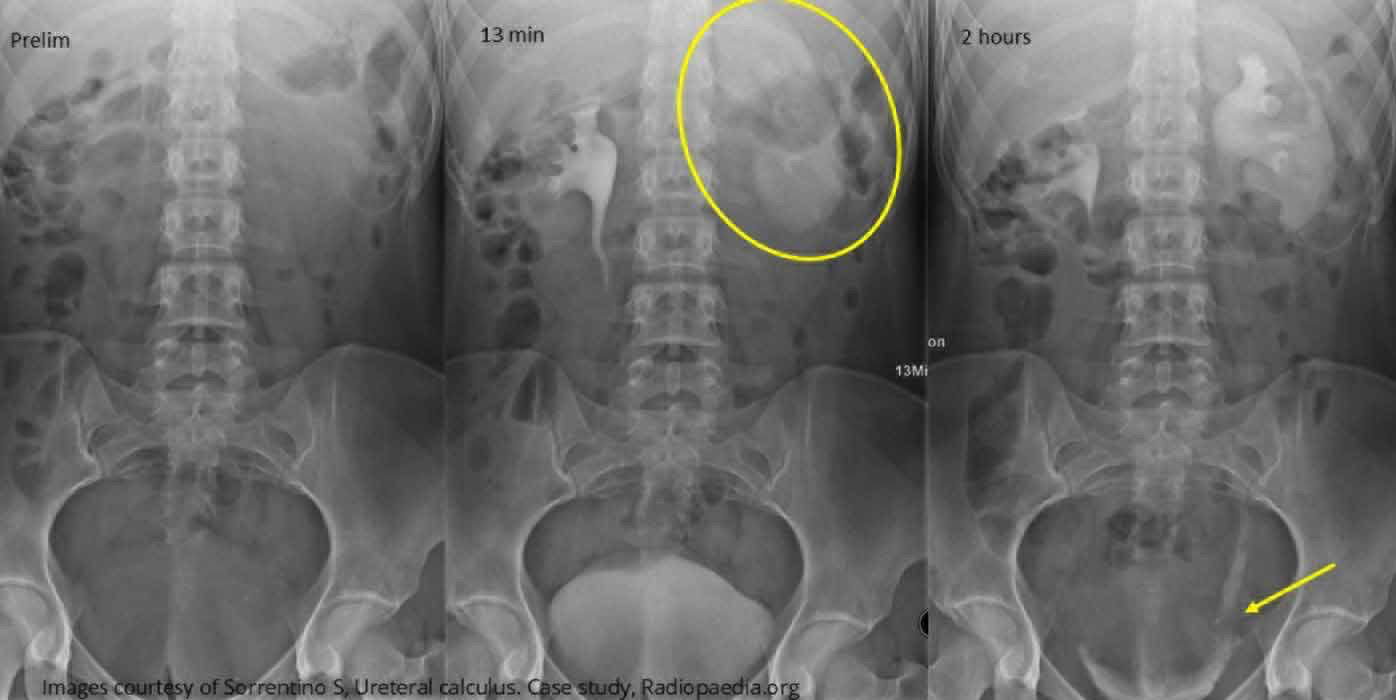
Renal Calculi: Intravenous Urography
Timed sequence of images is showing the delayed function of the left kidney due to a stone in the lower ureter (yellow arrow)

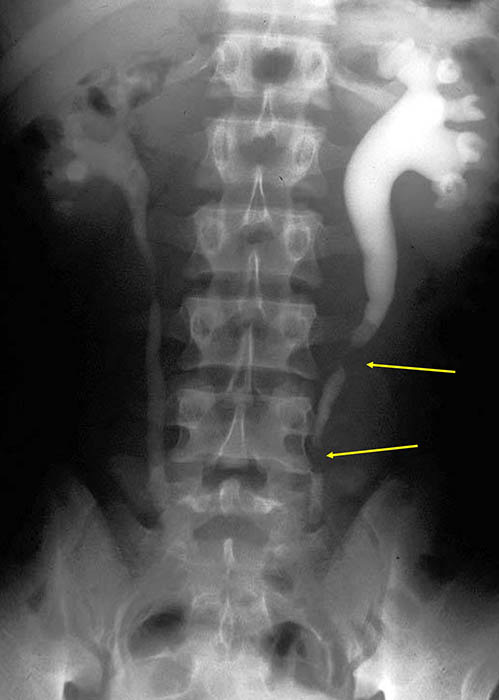
Renal Calculi: Image demonstrates the back up of contrast caused by two radiolucent stones (yellow areas) in the ureter

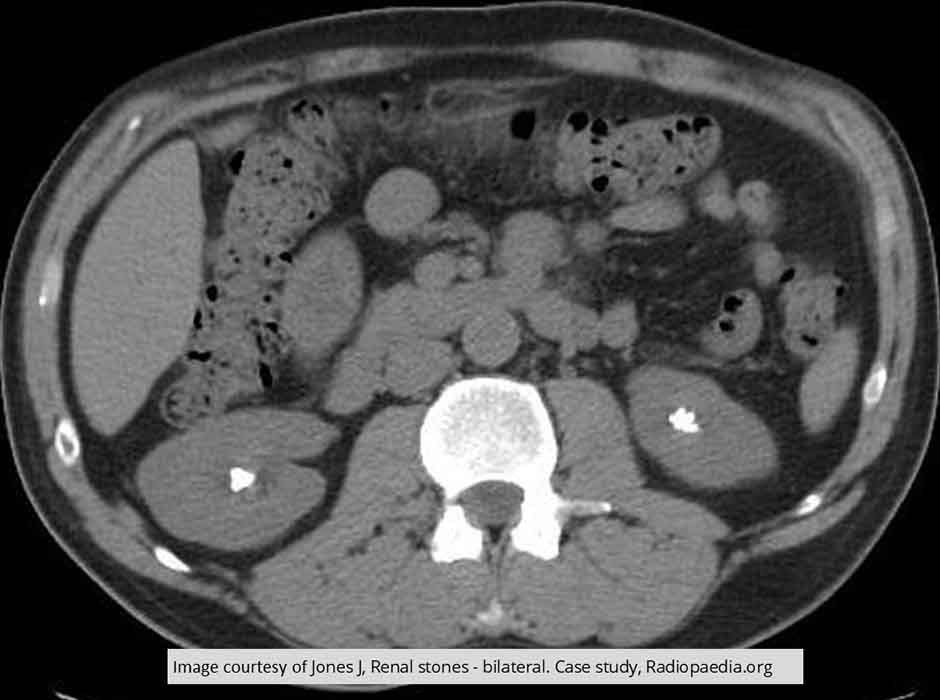
Renal Calculi: Non-contrast CT
Bilateral renal calculi seen within the renal pelvis

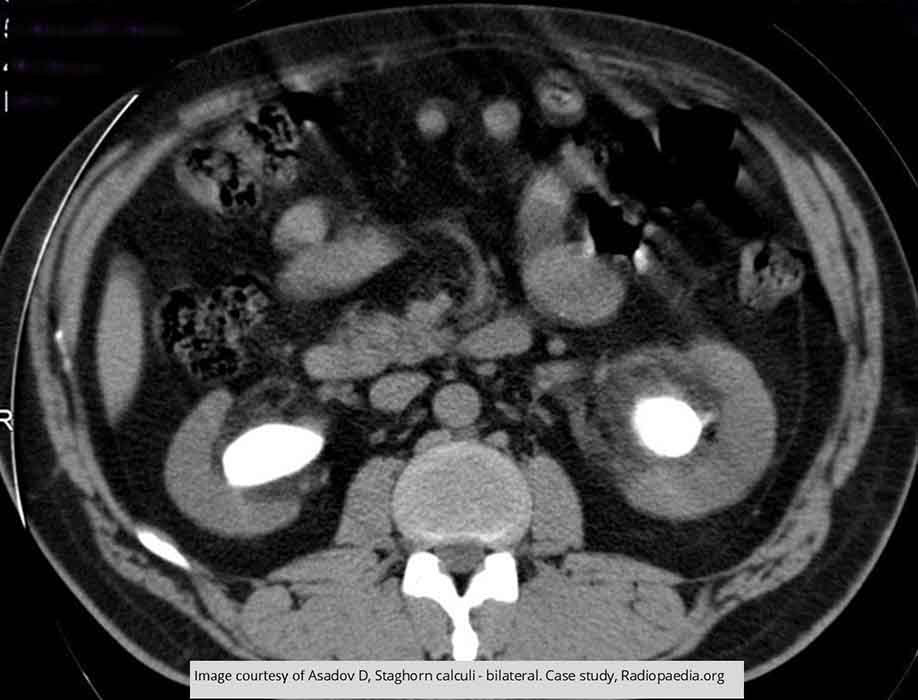
Renal Calculi: CT Staghorn Calculi
Demonstrates the entire renal pelvis filled w/ renal calculus, bilaterally

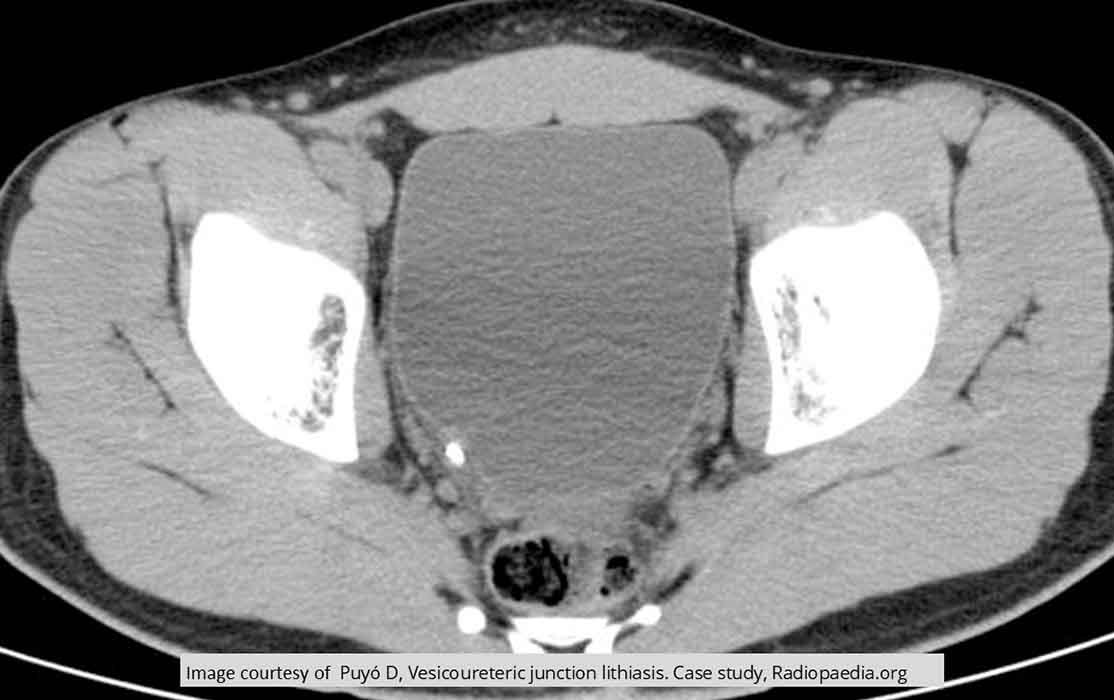
Renal Calculi: Non-contrast CT
Stone in the UVJ, one of the most common sites for renal calculi to get stuck

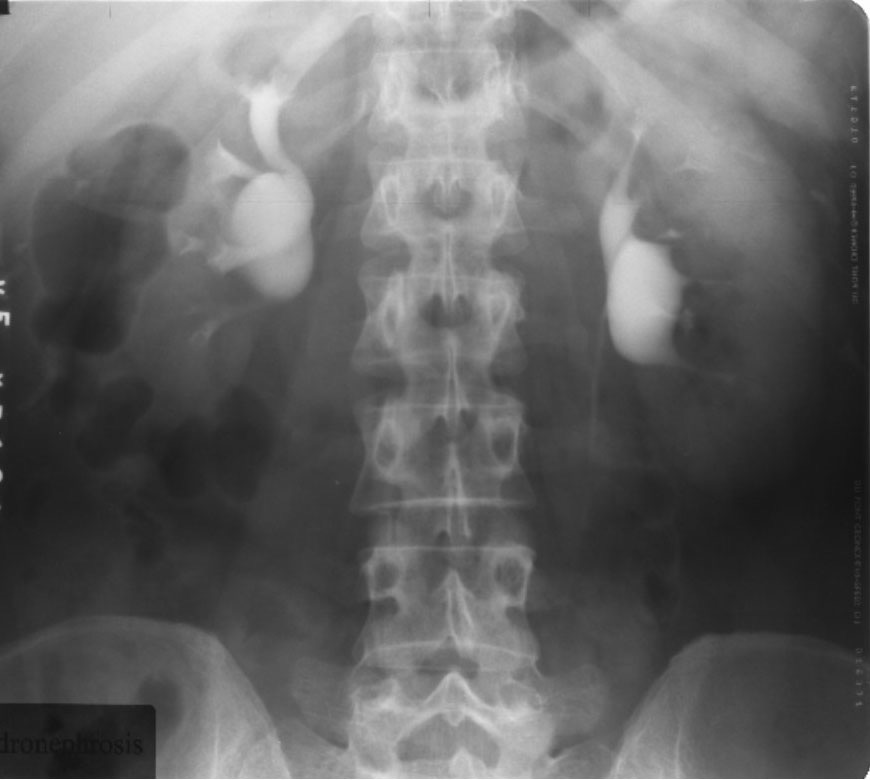
Hydroureter/Hydronephrosis: Intravenous Urography
Demonstrates bilateral hydronephrosis
The right is more dilated than the left

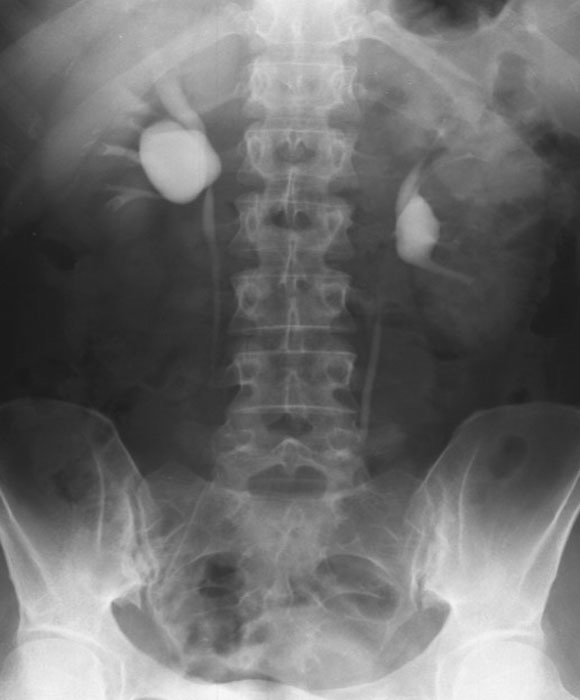
Hydroureter/Hydronephrosis: Right sided hydronephrosis
Notice the contrast enhancement of the entire kidney - due to the hydronephrosis slowing down the ability to filter out contrast from the blood
No obvious dilation of the ureter

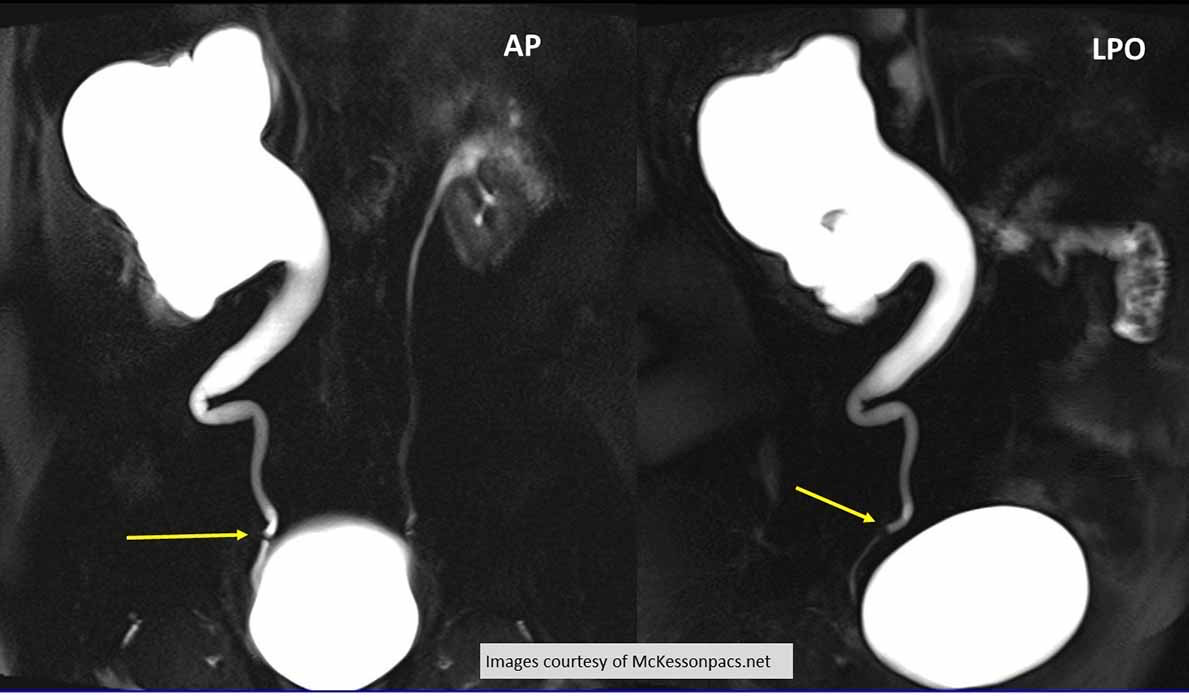
Hydroureter/Hydronephrosis: Retrograde urography
Demonstrates a stone that has caused severe Hydroureteronephrosis
Radiolucent renal calculus seen (yellow arrow)
LPO will help visualize the right distal ureter free from SI of the bladder

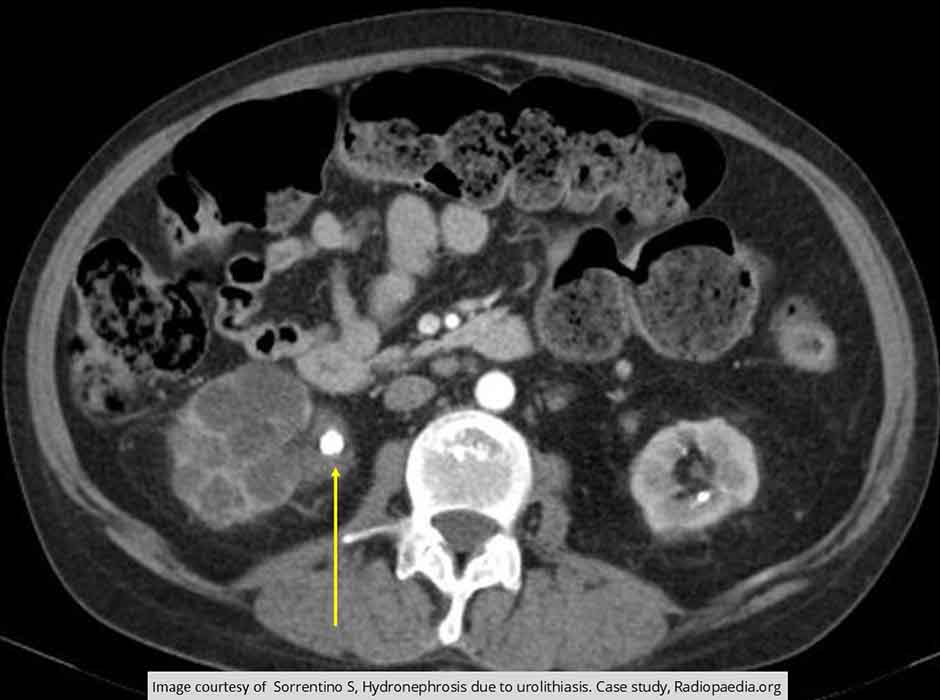
Hydroureter/Hydronephrosis: CT w/ Contrast
Demonstrates an obstructive renal calculus in the right renal pelvis (yellow arrow) causing dilation of the calyces
Note the enlargement of the kidney

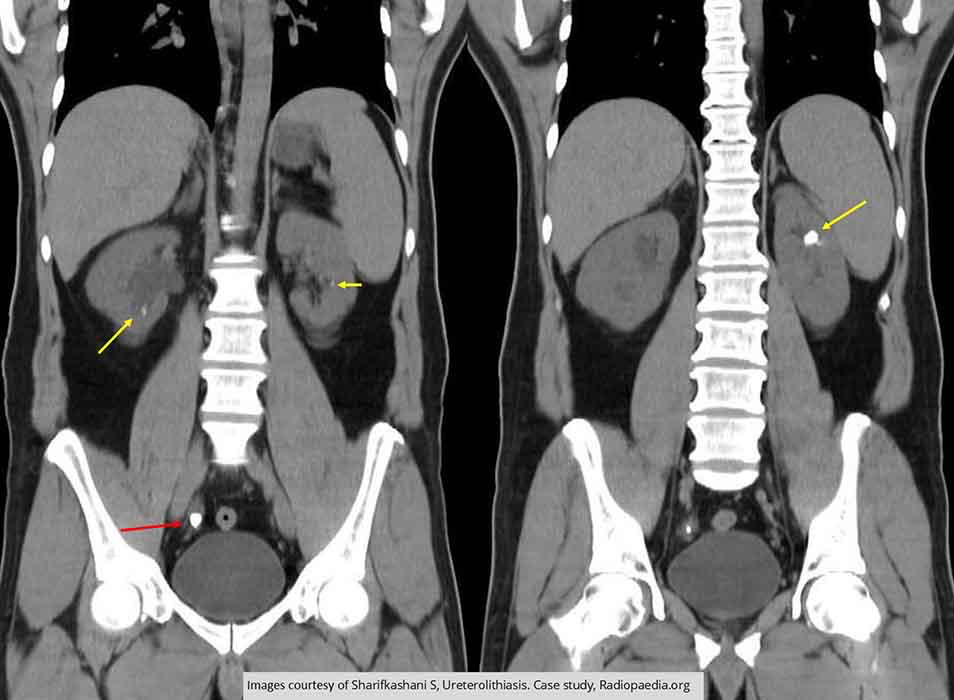
Hydroureter/Hydronephrosis: CT non contrast
2 coronal slices demonstrating multiple renal calculi (yellow arrows) bilaterally
Red arrow is causing Hydroureteronephrosis
Note the dilation of the right renal pelvis

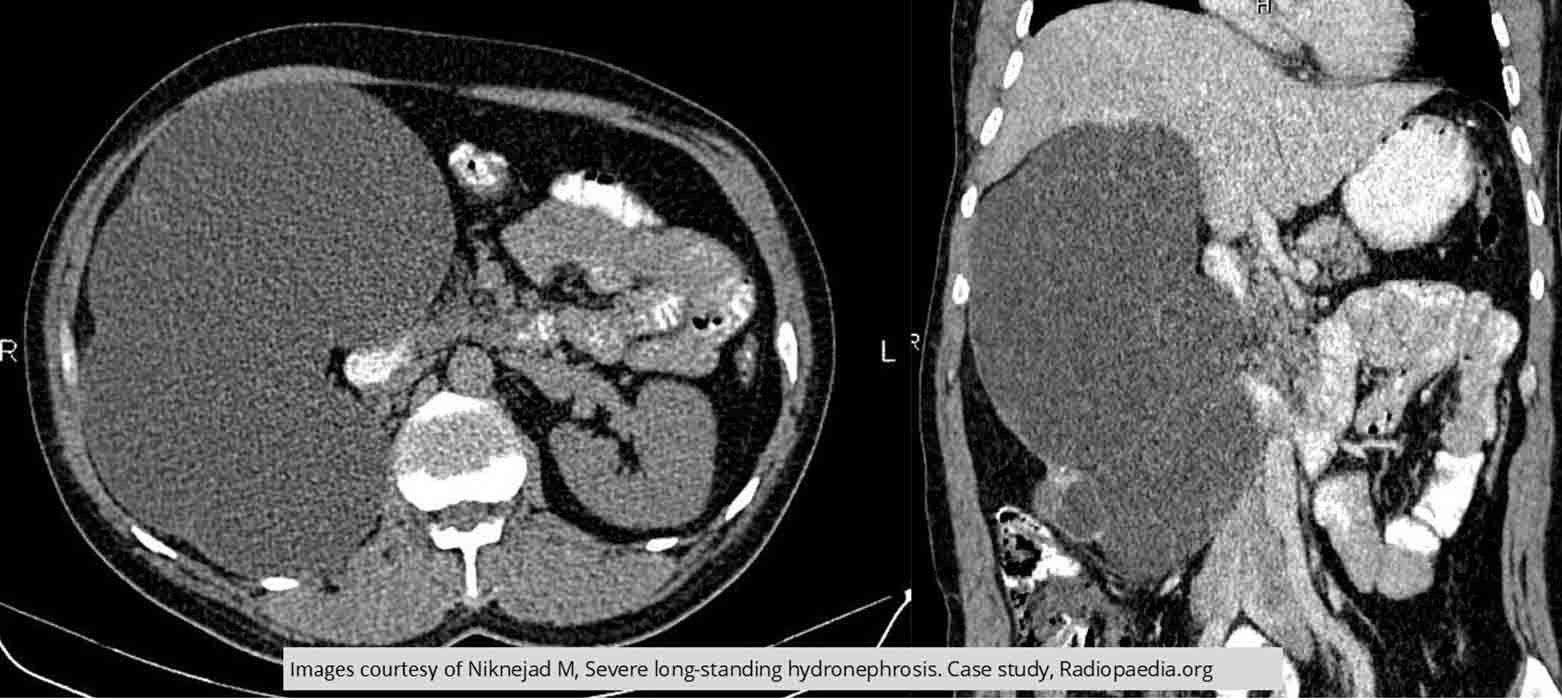
Hydroureter/Hydronephrosis: CT Hydronephrosis
Massive long standing hydronephrosis caused by a 32mm calculus in the right renal pelvis
Non-functioning kidney

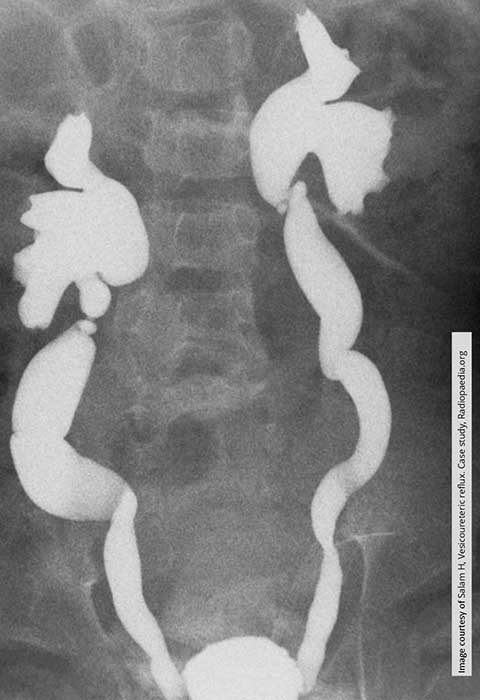
Vesicoureteral Reflux: Massive ureterovesical reflux in this child w/ hydroureteronephrosis bilaterally

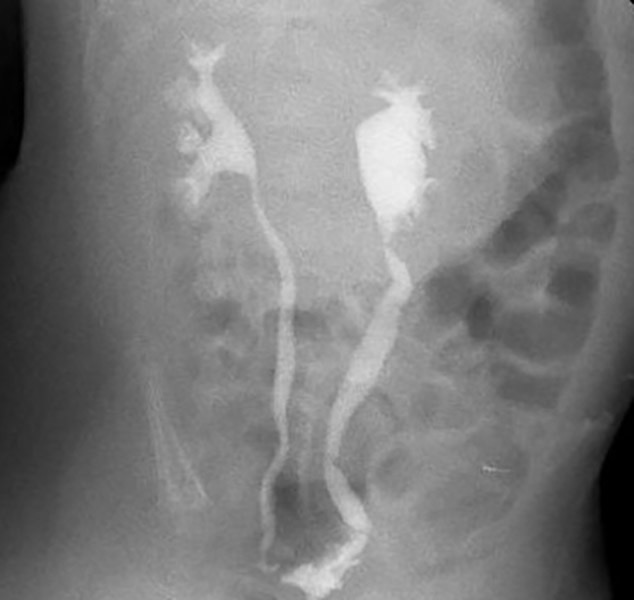
Vesicoureteral Reflux:Bilateral reflux w/ a very small bladder in this infant
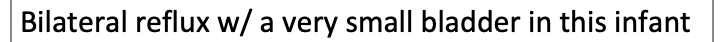
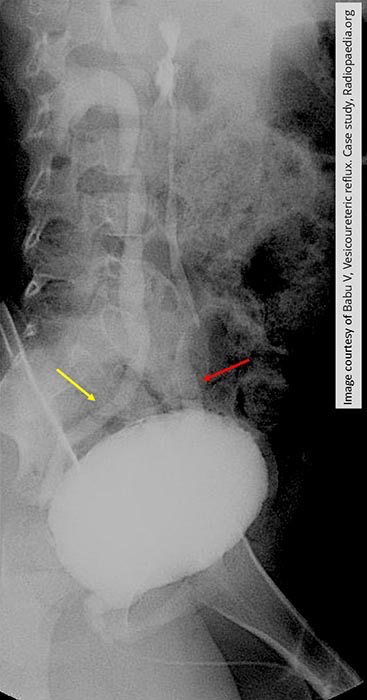
Vesicoureteral Reflux: Bilateral reflux w/ the right side (yellow arrow) causing hydroureteronephrosis
Left side is only demonstrating hydronephrosis
Irregular outline of the bladder indicates thickening and scarring of the bladder most likely due to repeated bladder infections

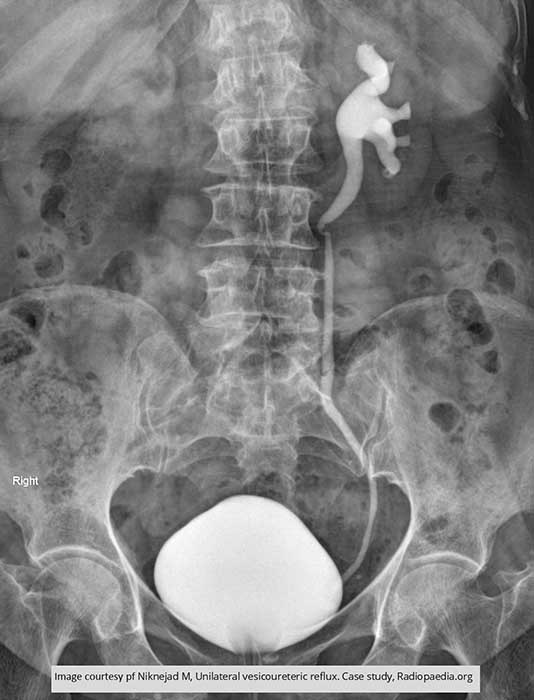
Vesicoureteral Reflux: Demonstrates unilateral reflux in adult patient

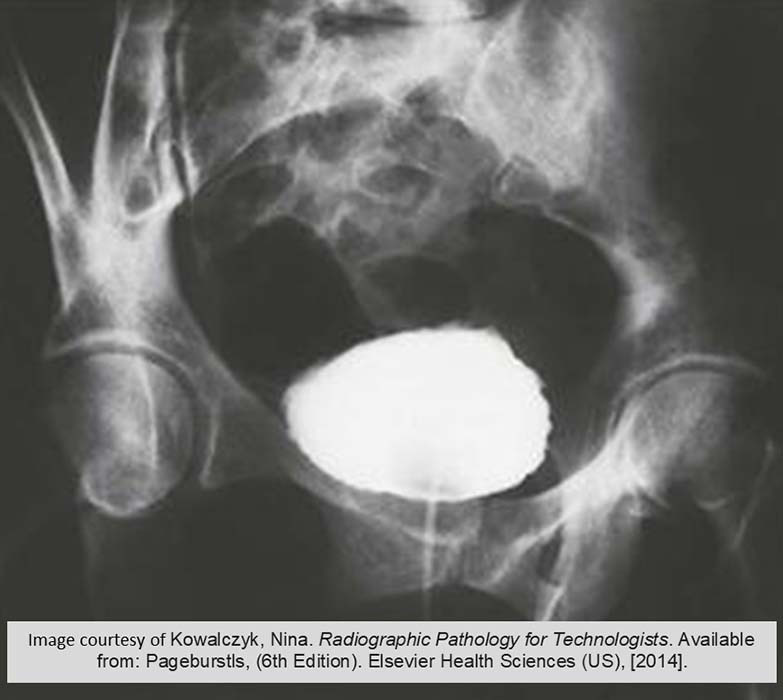
Cystitis: Cystogram
Demonstrates the roughened inner surface

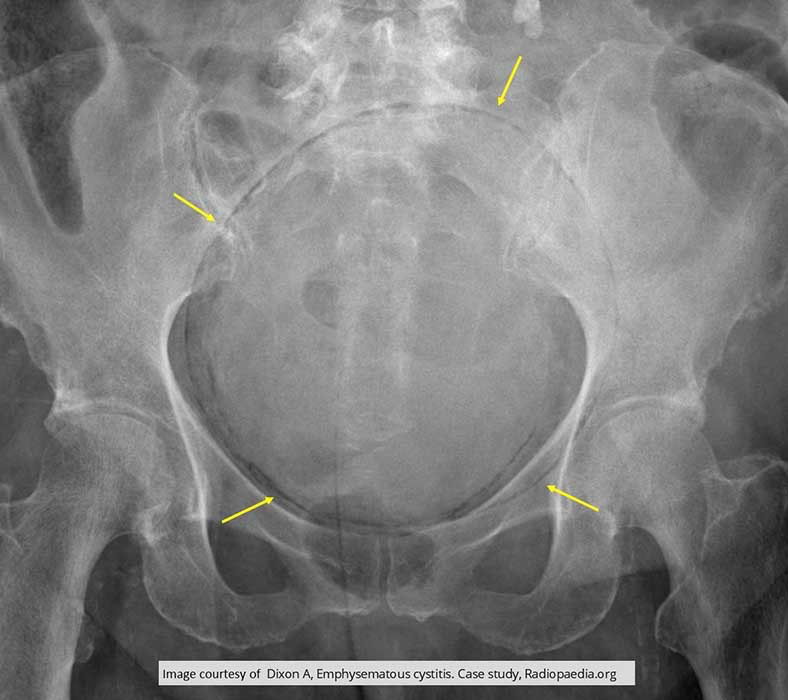
Cystitis: Pelvis Radiograph
Yellow arrow demonstrates the lucent air within the bladder of this patient w/ Emphysematous Cystitis

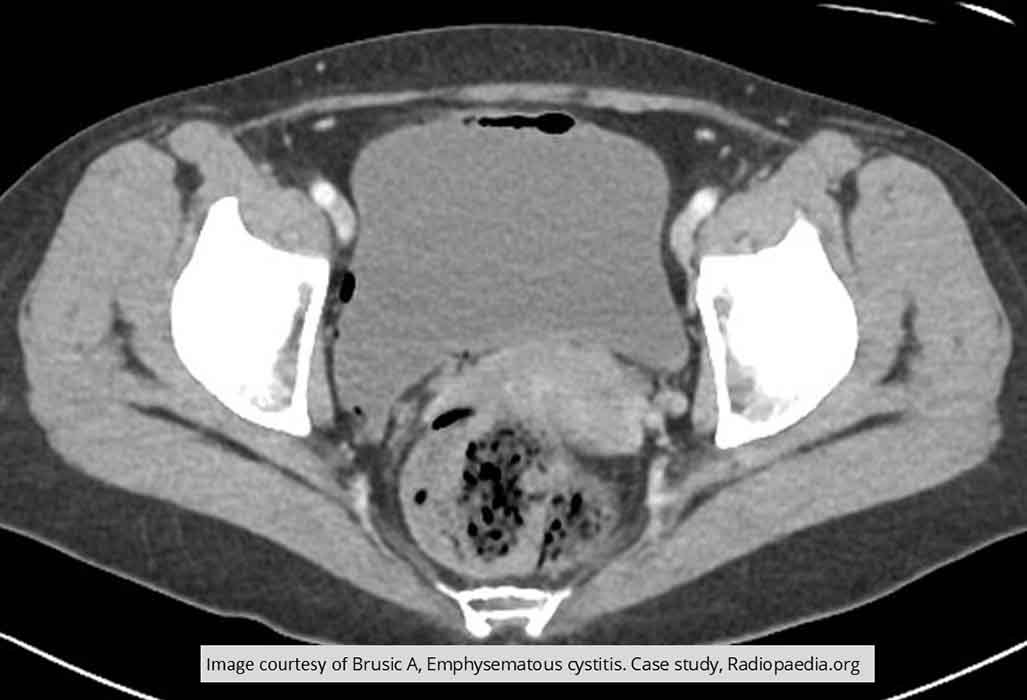
Cystitis: Air demonstrated within the bladder wall of this PT w/ Emphysematous Cystitis

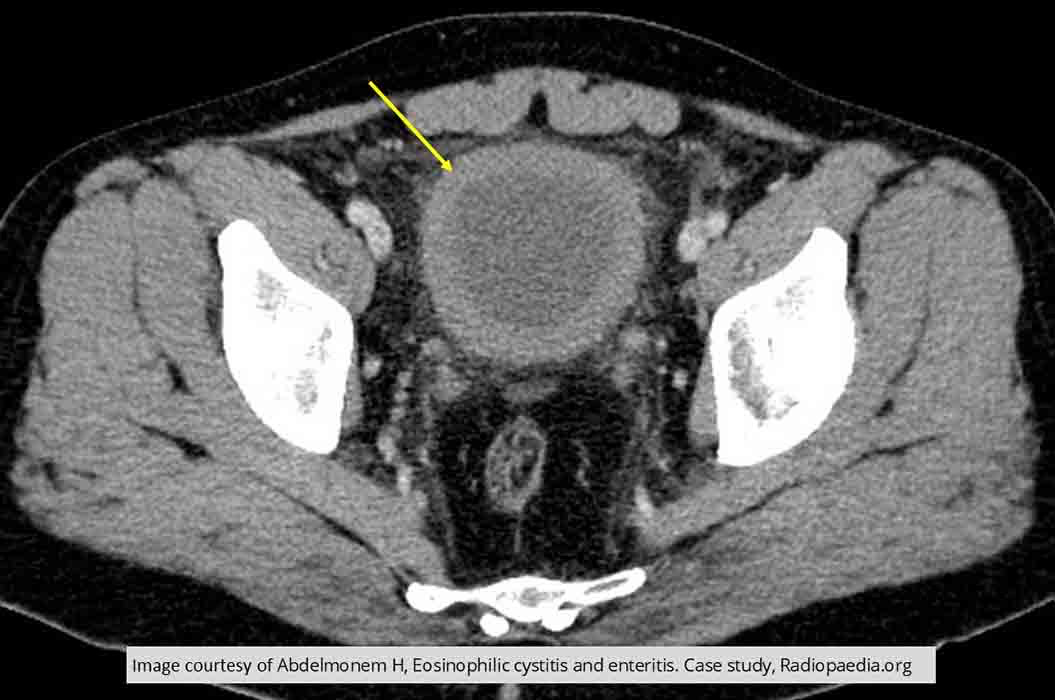
Cystitis: Thickened bladder wall

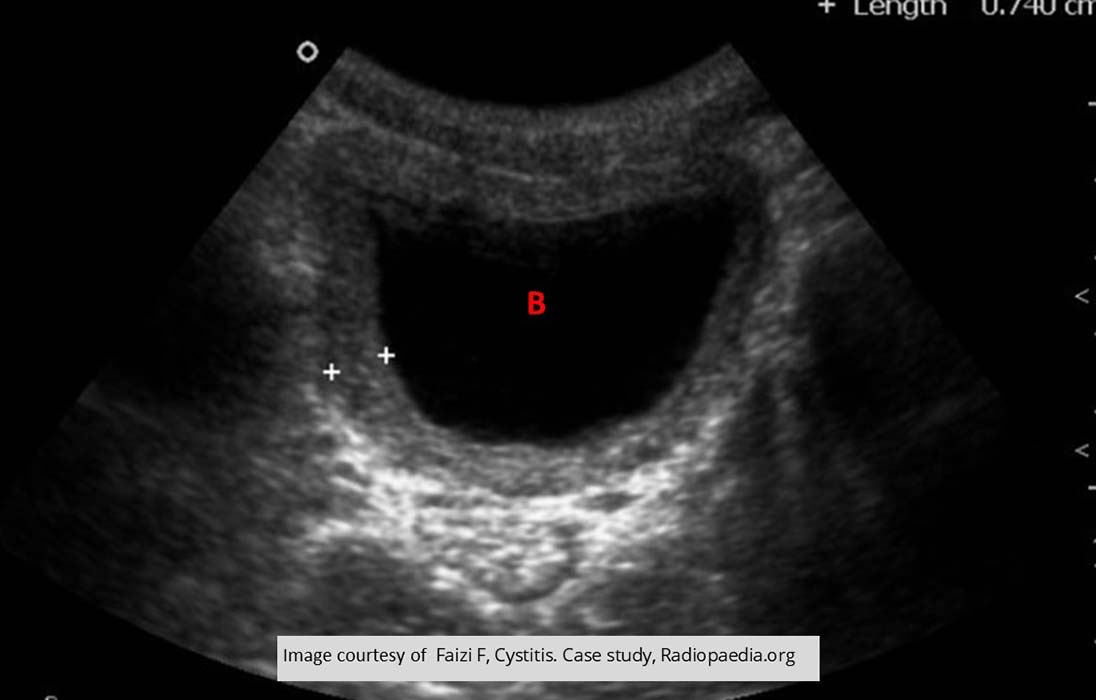
Cystitis: thickened bladder wall
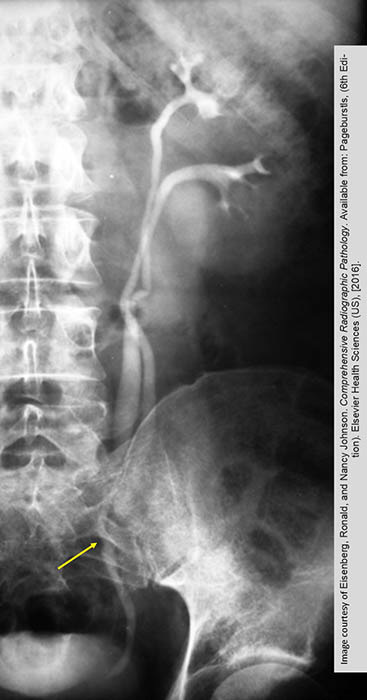
Duplication: Intravenous Urography
Incomplete duplication as the upper and lower ureter unite at the pelvic brim (yellow arrow)

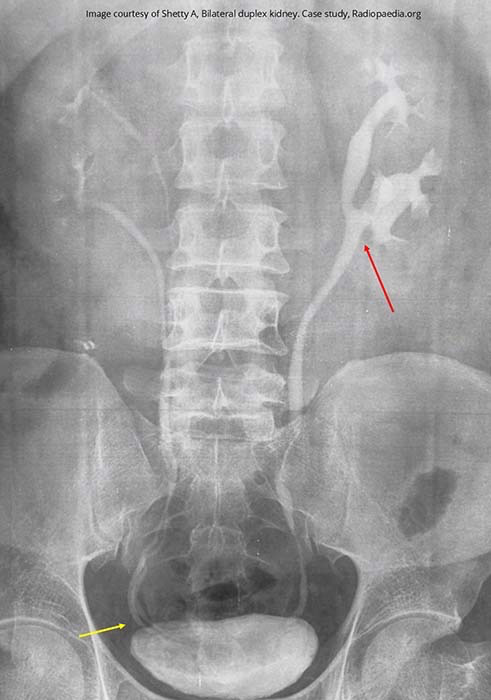
Duplication: Bilateral duplex system
Left side of the ureters merge at the level of L3 = incomplete duplication
Right side has a complete duplication as both right ureters are still seen in the lower pelvis (yellow line) continuing posterior into the bladder

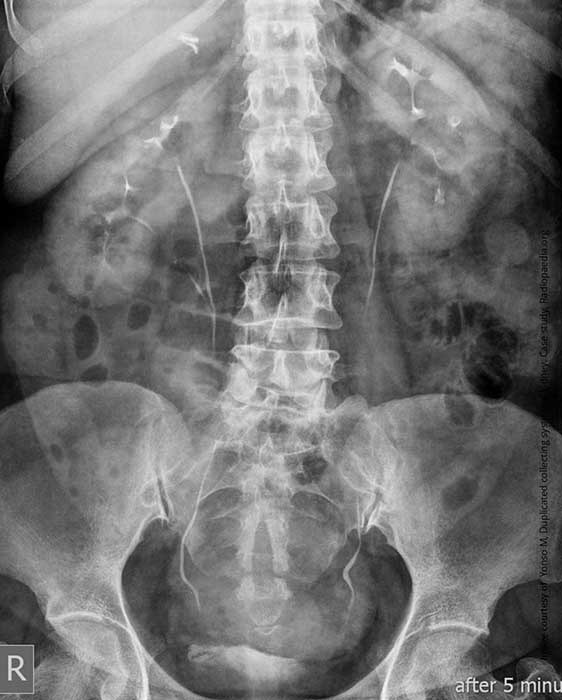
Duplication: Single side duplication on right side w/ ureters uniting at the level of L4/5 joint space

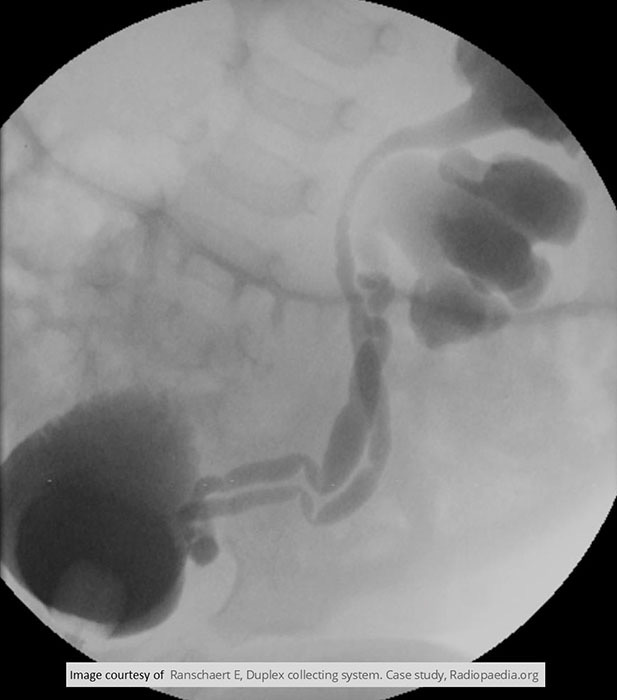
Cystography
Massive left sided hydronephrosis seen w/ duplex collecting system
Ureters are fused just prior to the UVJ

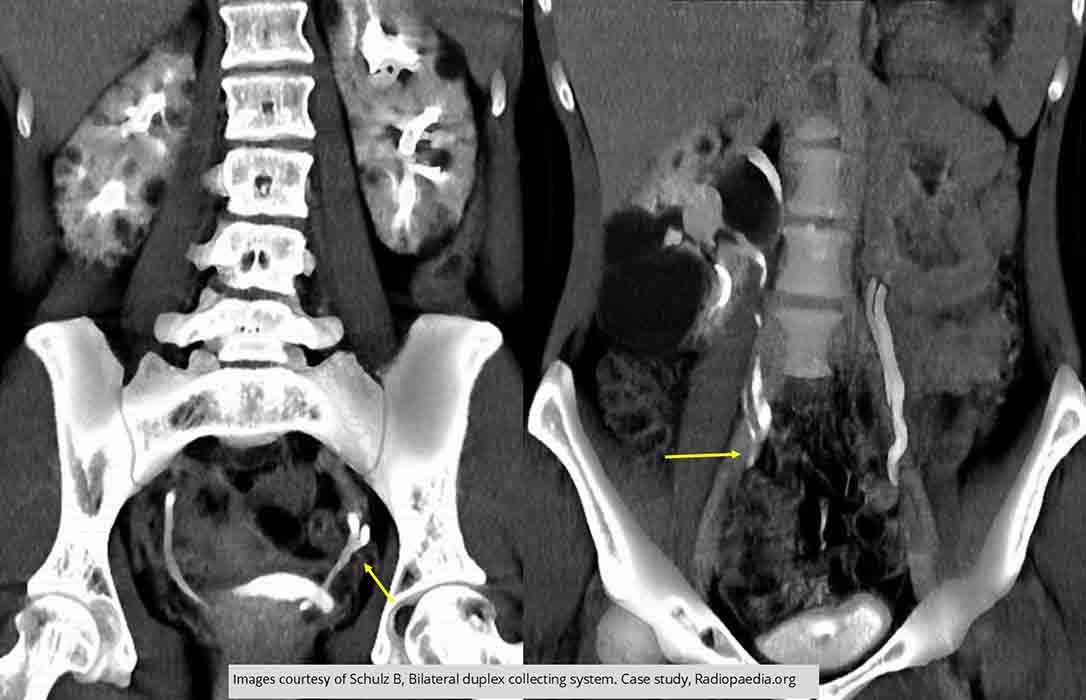
Duplication: Both ureters on both sides fuse prior to entry into the bladder
Multiple cysts seen in both kidneys

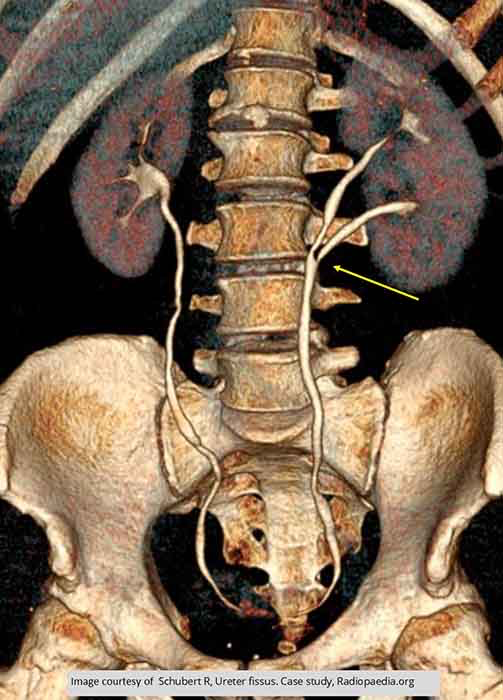
Duplication: Incomplete duplication with the ureter uniting

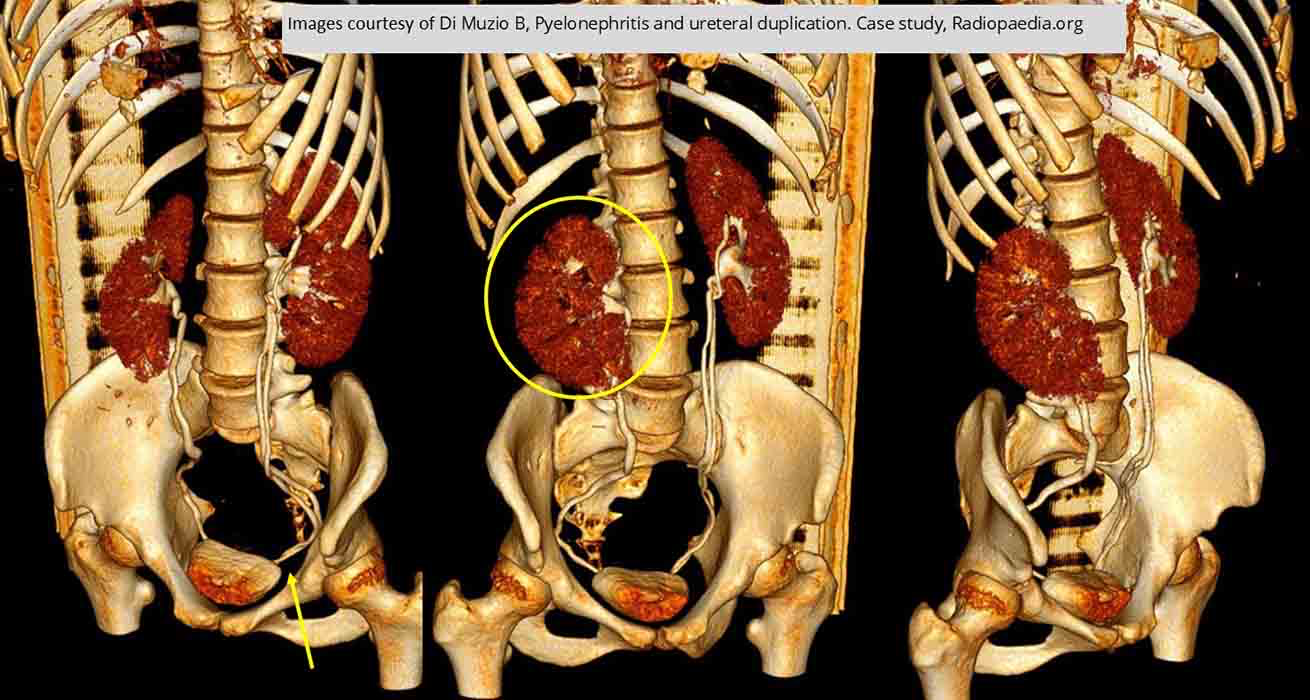
Duplication: Duplication on the left side
Right side demonstrates pyelonephritis

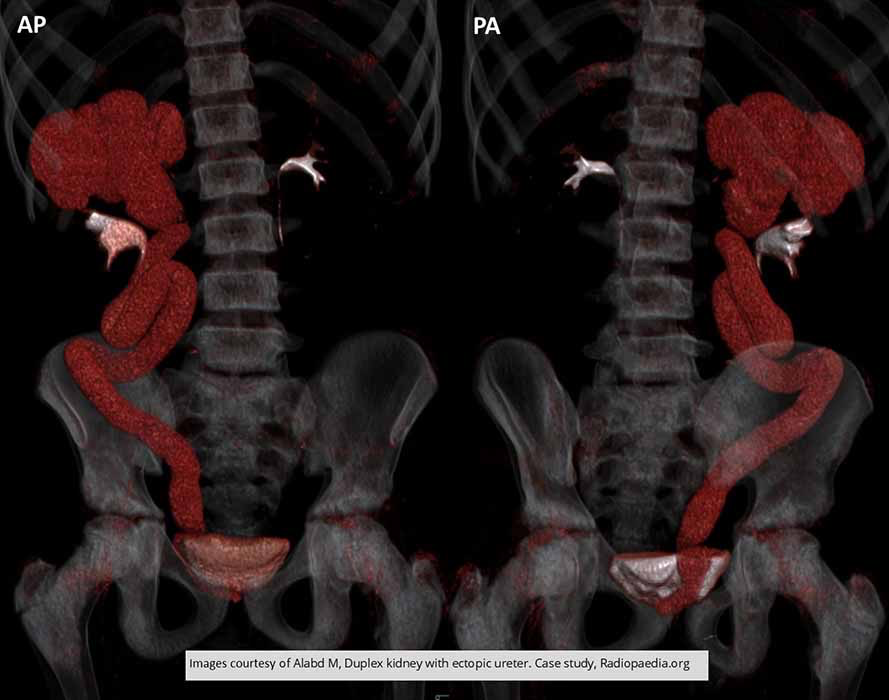
Duplication: Right side duplication
Note the upper pole and ureter demonstrates hydronephrosis/hydroureter due to the insertion site of the ureter - it enters at the prostatic urethra, thus is unable to empty properly

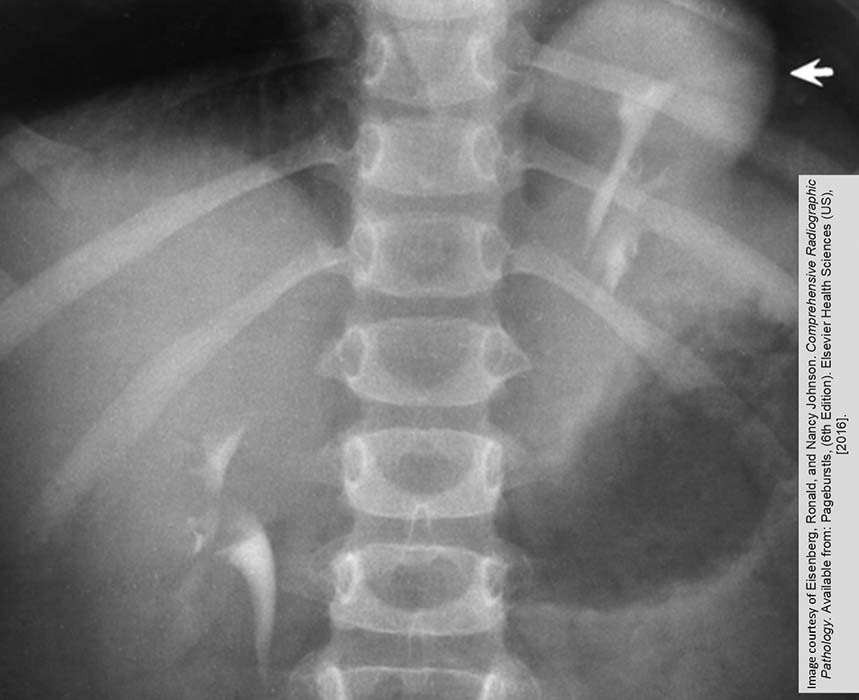
Ectopic Kidney: Thoracic Kidney
Arrow indicates a portion of the kidney above the diaphragm
Note the kidney is mal-rotated as the renal pelvis is pointed more anterior than medially

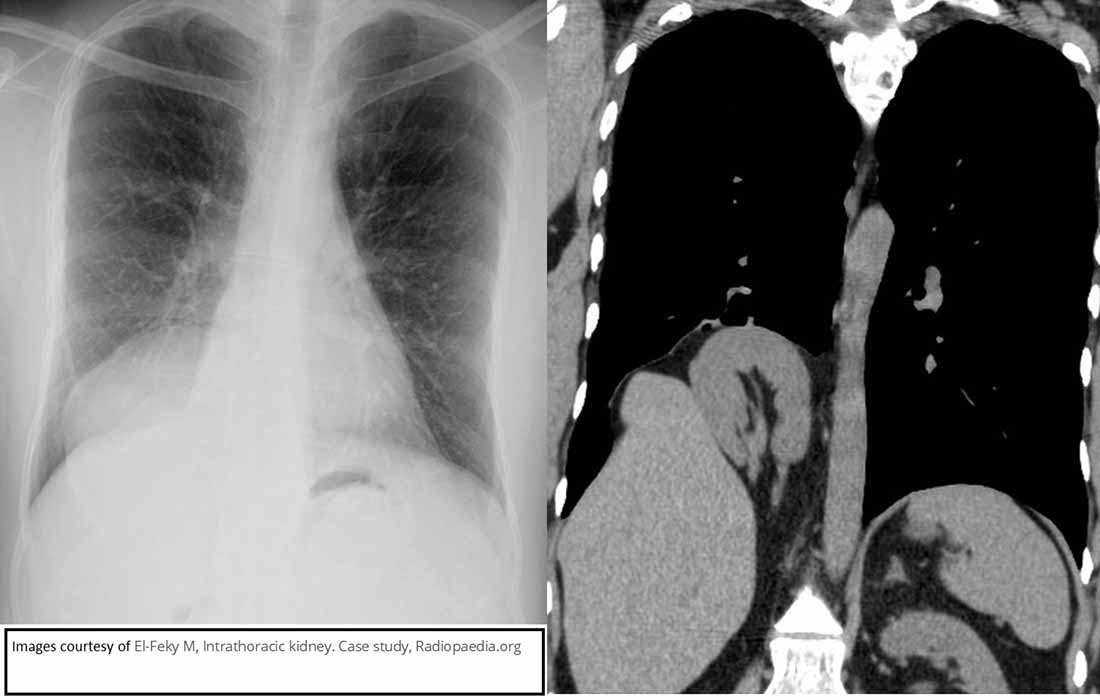
Ectopic Kidney: Thoracic Kidney
Chest and associated CT demonstrating a thoracic ectopic kidney

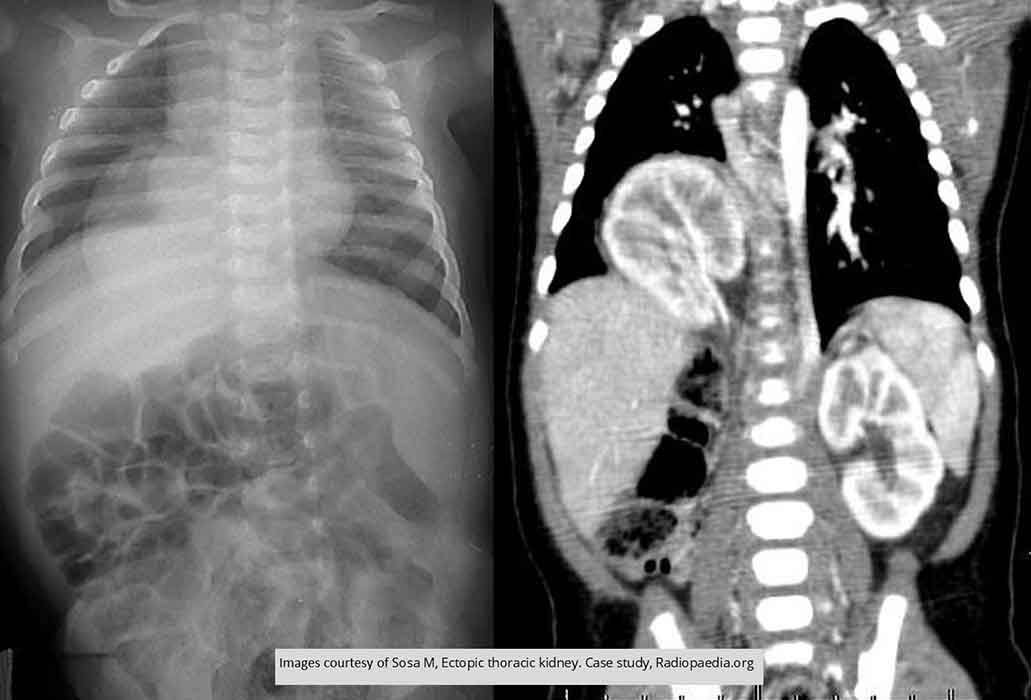
Ectopic Kidney: Thoracic Kidney
Intrathoracic right kidney, through a posterior defect at right hemidiaphragm

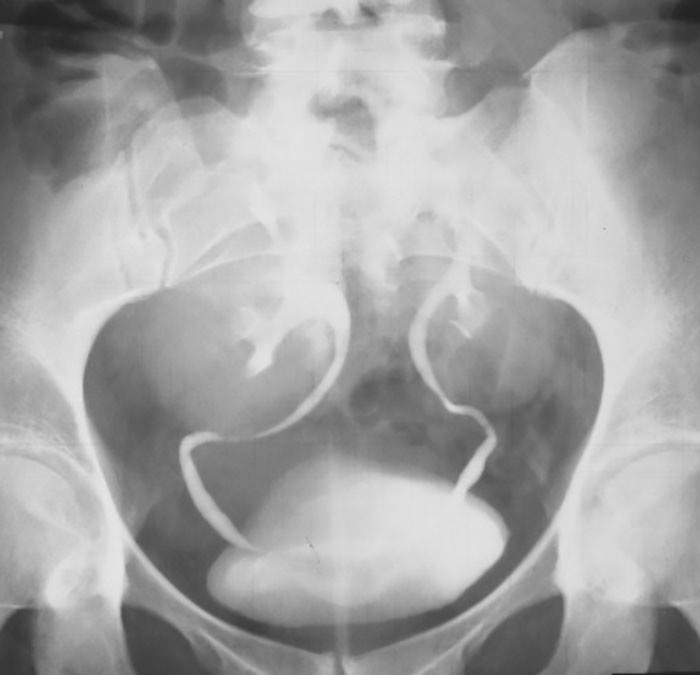
Ectopic Kidney: Bilateral Pelvic Kidney
Neither kidney ascended from the pelvis

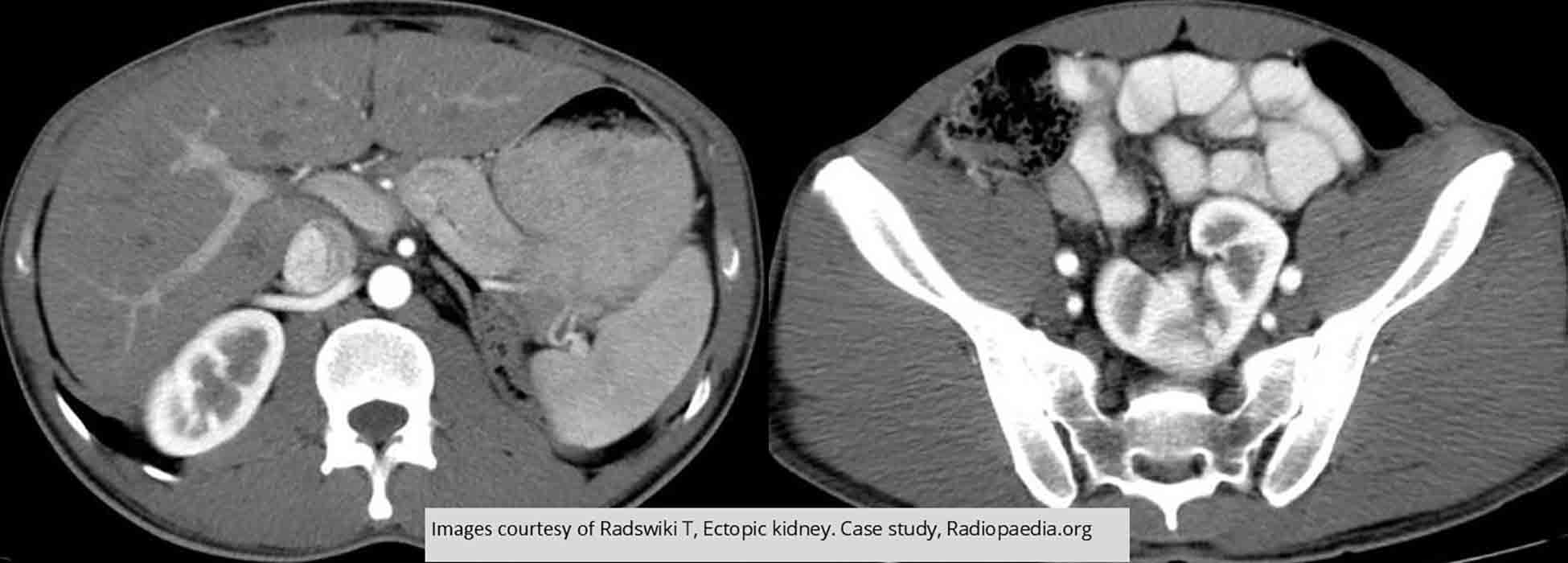
Ectopic Kidney: Right kidney is in normal position, left kidney is in pelvis

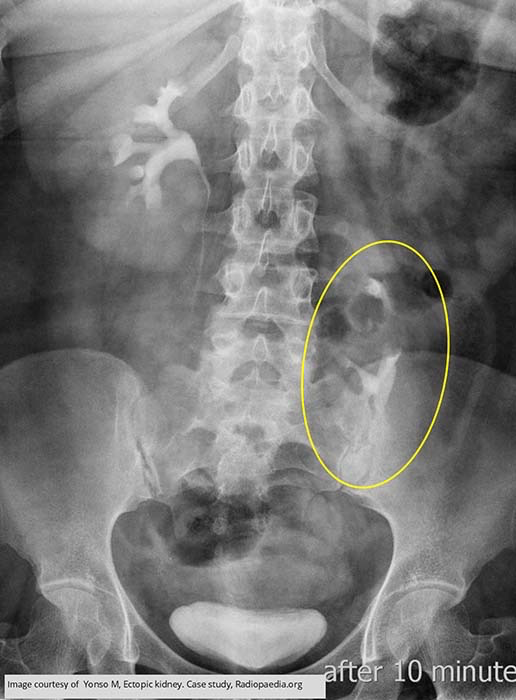
Ectopic Kidney: Left kidney partially ascended but still considered pelvic

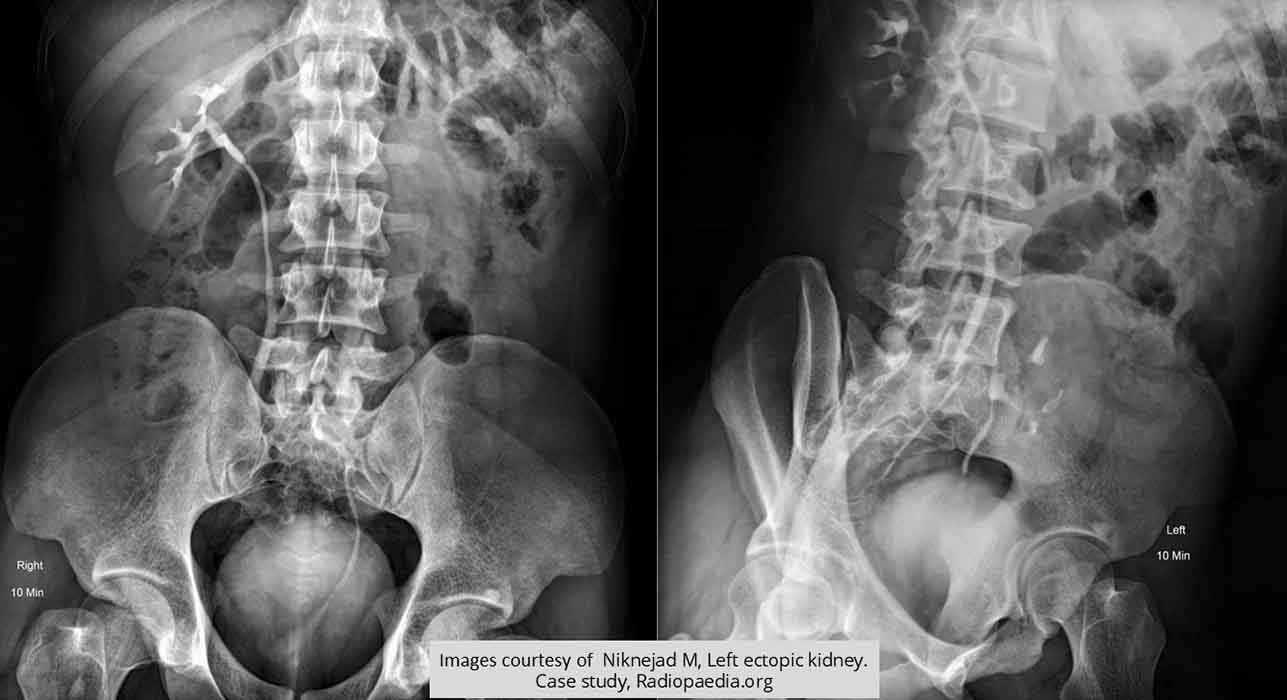
Ectopic Kidney: Pelvic kidney better visualized in LPO

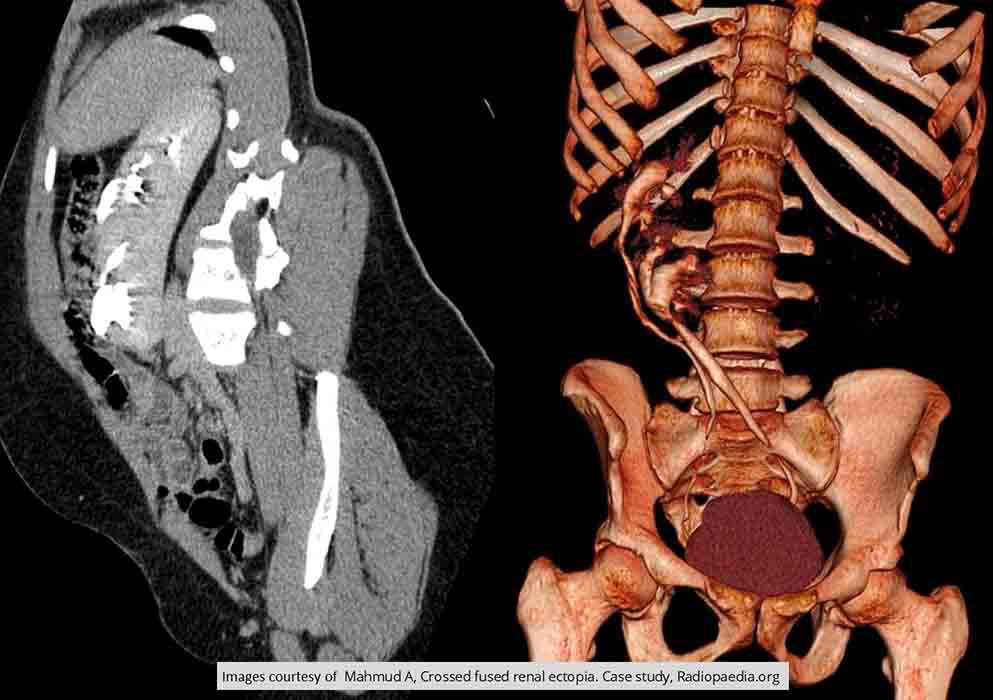
Ectopic Kidney:Cross fused ectopia
Left kidney has ascended to the right side
Two kidneys are fused together

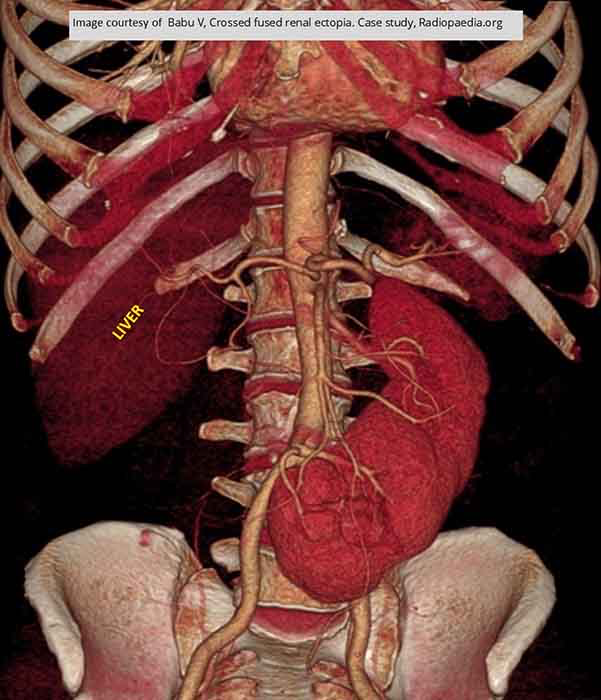
Ectopic Kidney: Right kidney has crossed and fused to the left kidney

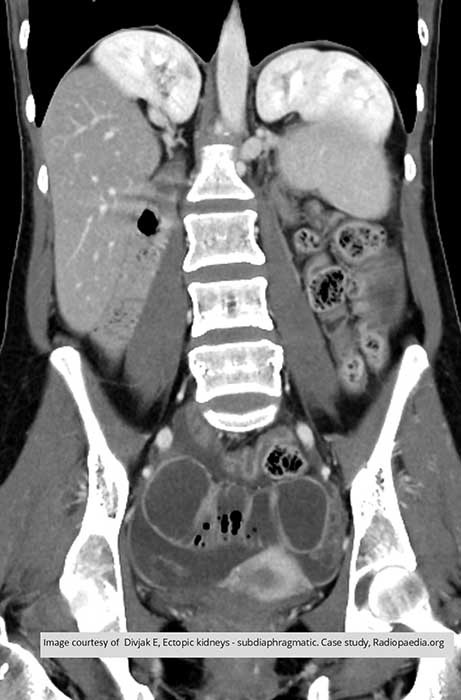
Ectopic Kidney: Not quite into the thoracic cavity but would be considered thoracic based on their location

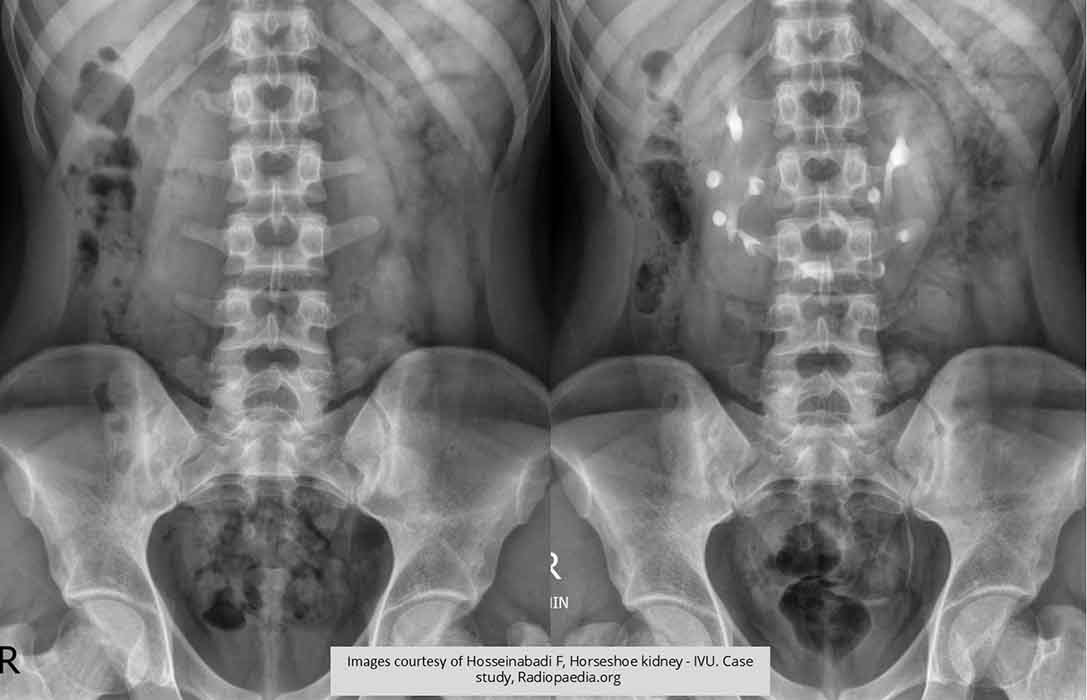
Horseshoe Kidneys:
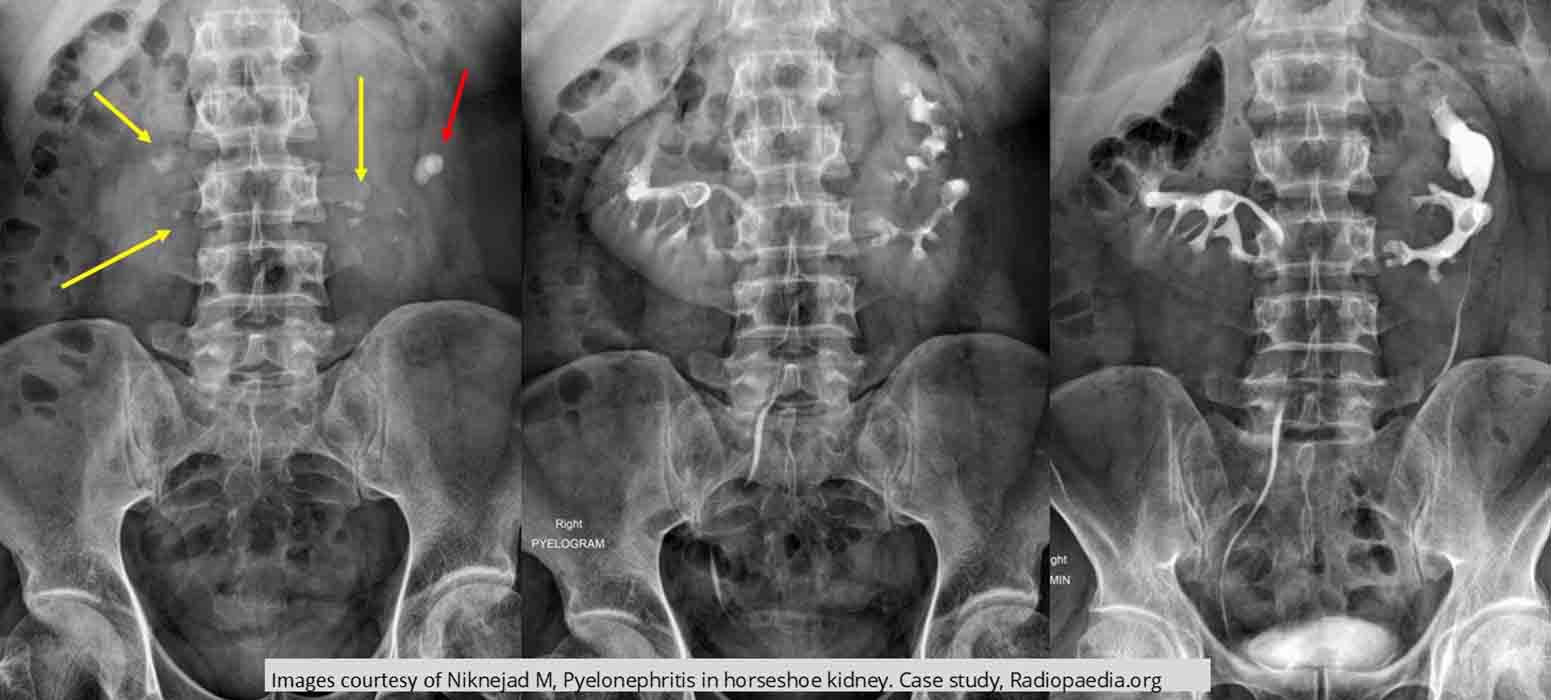
Horseshoe Kidneys: AXR demonstrates multiple renal calculi (yellow arrow)
Red arrow indicates a large calculi causing hydronephrosis
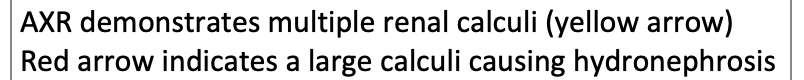
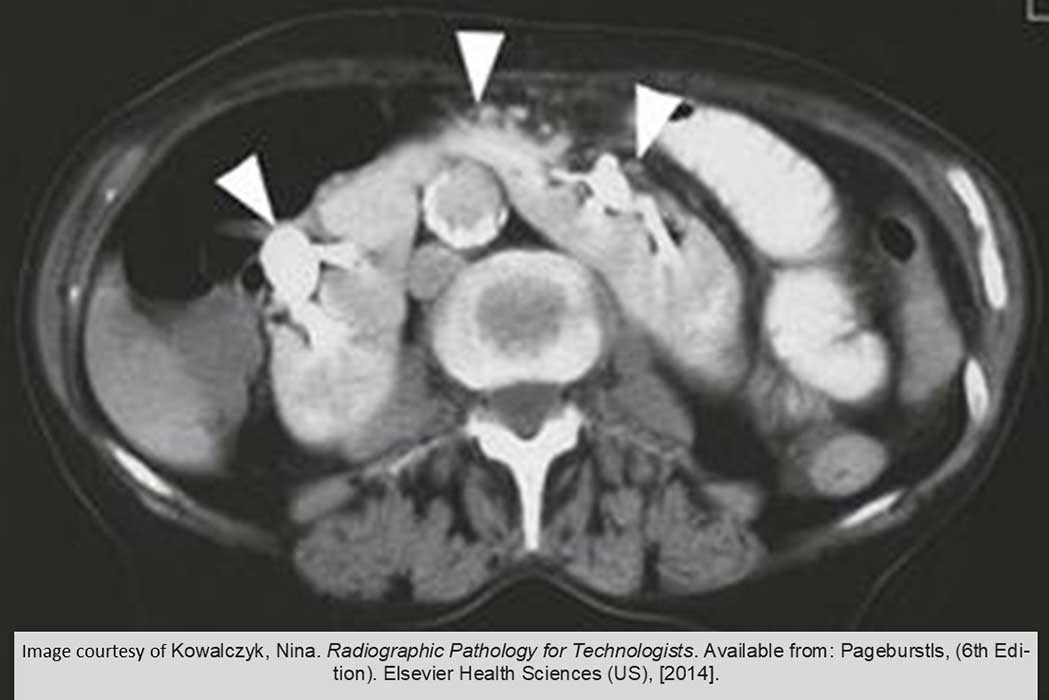
Horseshoe Kidneys: Shows hydronephrosis in both kidneys (arrowheads) as well as demonstrating the isthmus (center arrowhead)

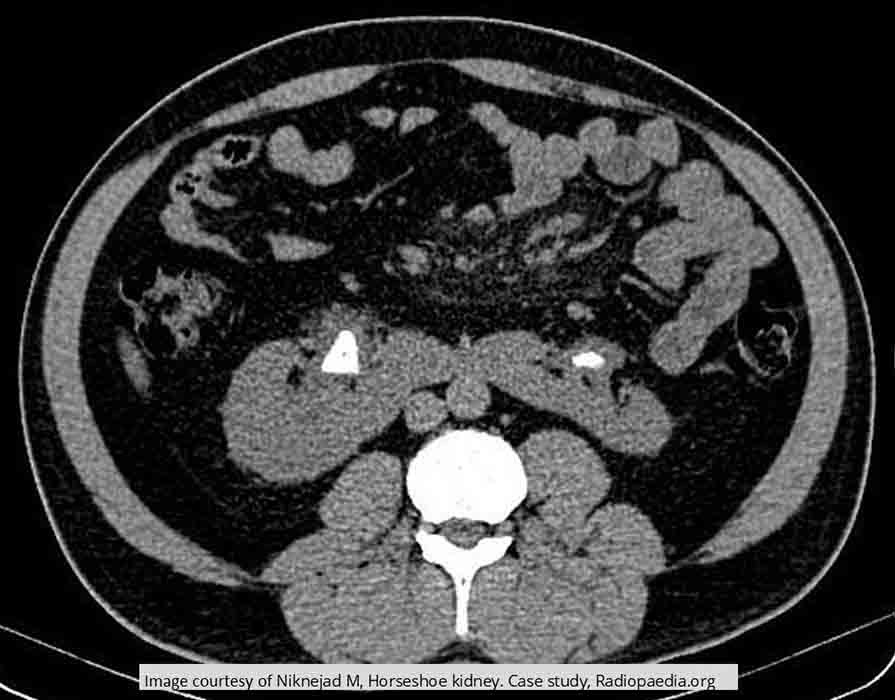
Horseshoe Kidneys: Non contrast image shows a 23mm sone in the RT pelvis and a 13mm stone in the LT pelvis

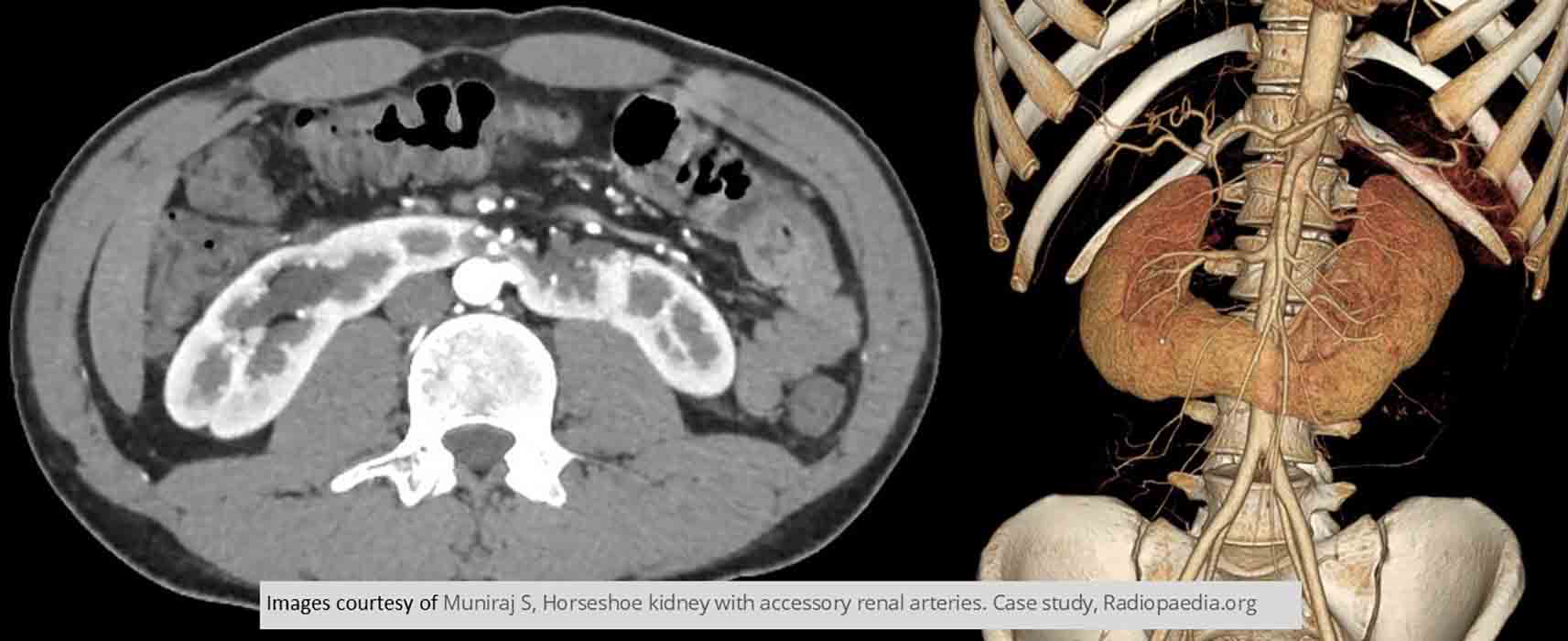
Horseshoe Kidneys:
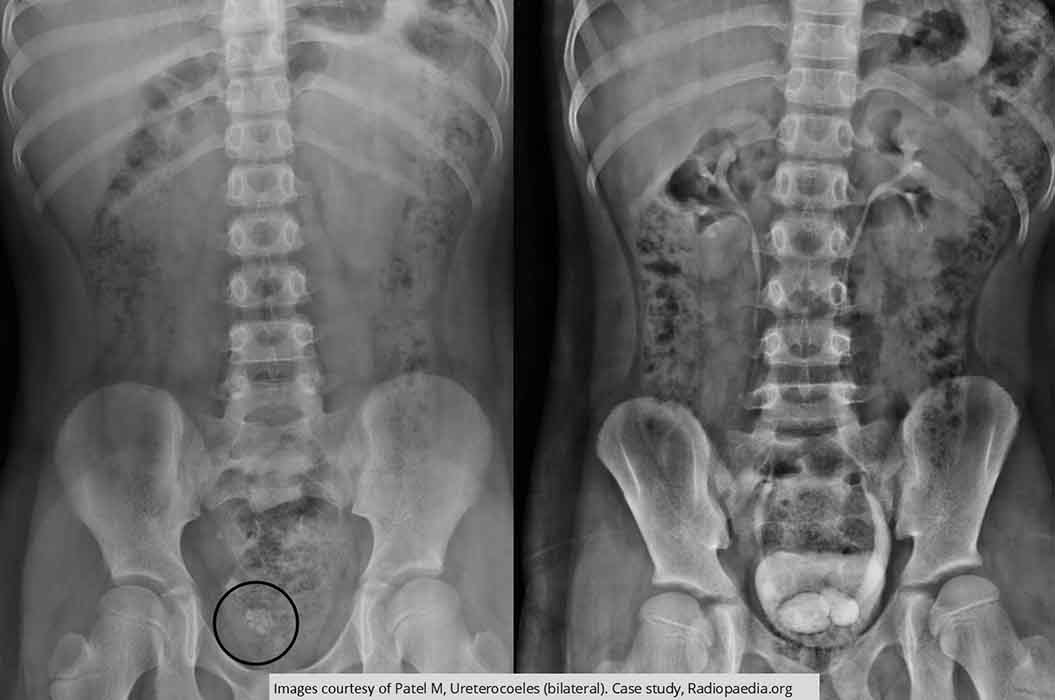
Ureterocele: Renal calculi present in pelvis on the non-contrast image
Bilateral "cobra heads" seen in the bladder indicating ureteroceles
The right one is in the same area as the renal calculi
The left ureter has some moderate dilation associated w/ the ureterocele

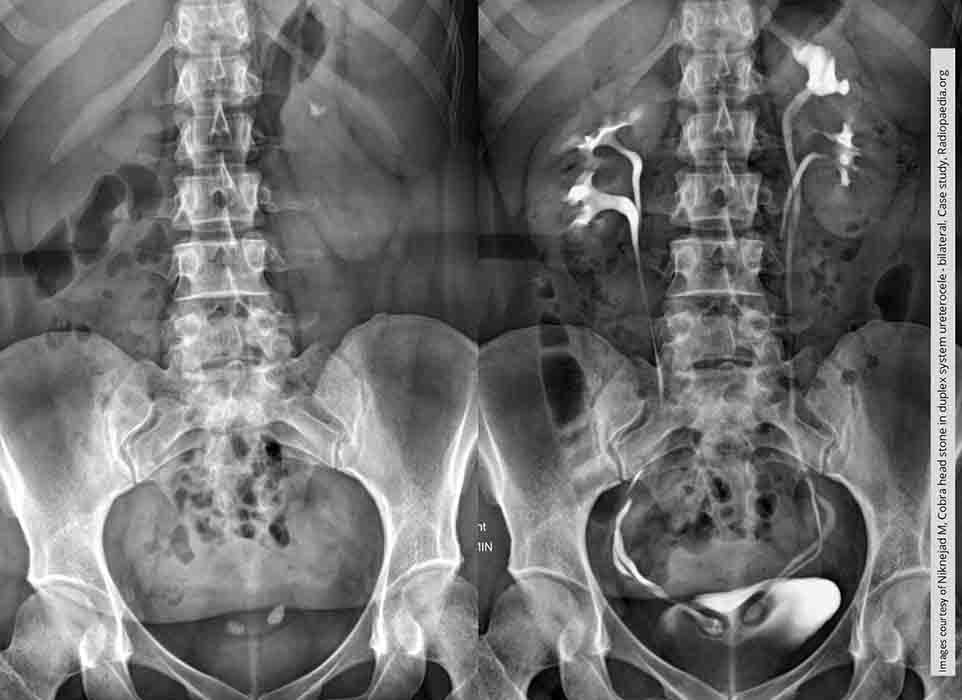
Ureterocele: Non-contrast image has 2 suspect areas (renal calculi) which confirmed on the contrast image to be sites of bilateral ureteroceles
Notice each of these kidneys is duplex in origin. Therefore the ureters coming from the superior pole would be the ones w/ the ureteroceles

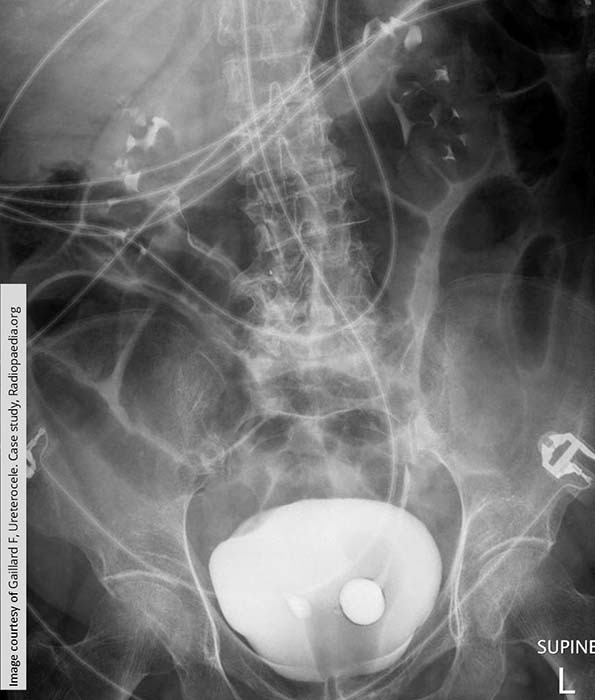
Ureterocele: Bilateral ureteroceles w/ the left being substantially larger than the right

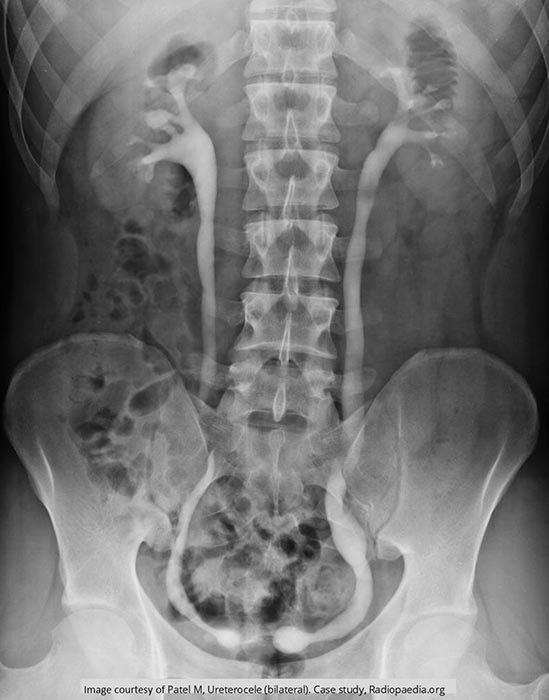
Ureterocele: Bilateral ureteroceles seen, each w/ hydroureteronephrosis

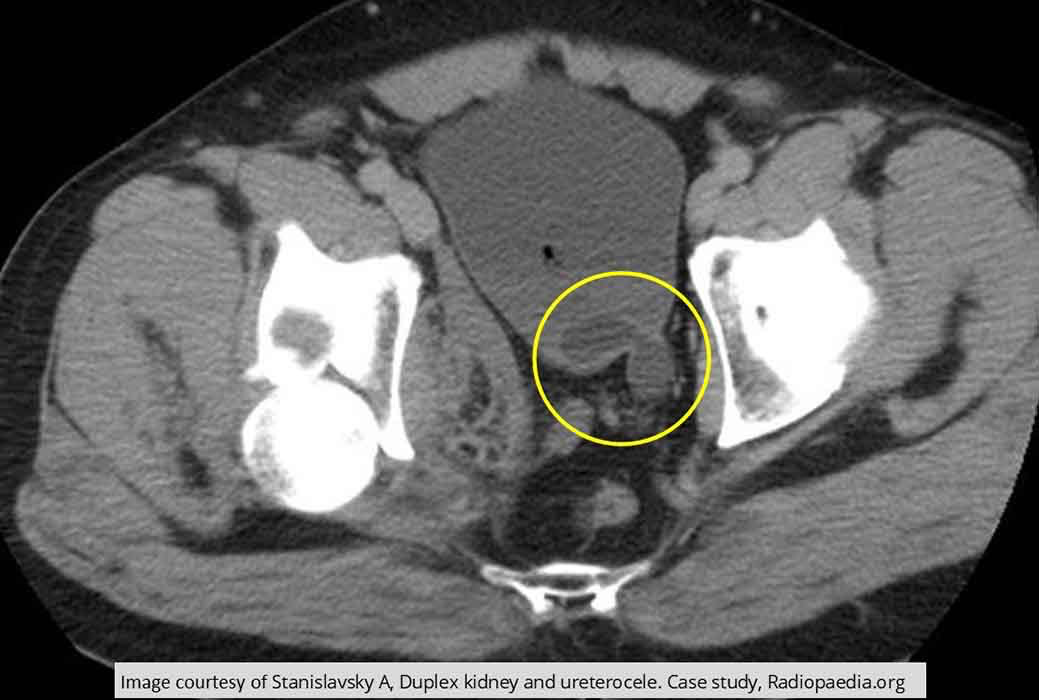
Ureterocele: Ureterocele was an incidental finding
Prolapse right through the UVJ

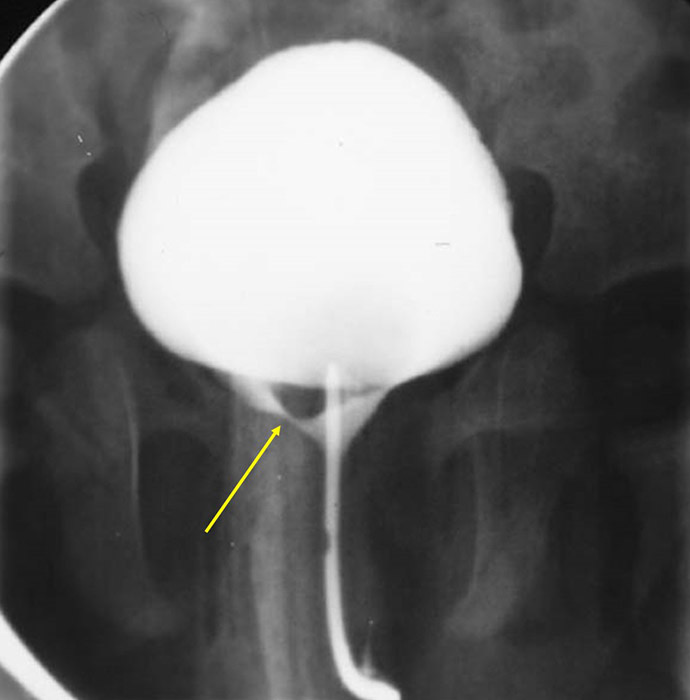
Ureterocele: Voiding Cystourethrography
Image shows a large ureterocele (yellow arrow) partially obstructing the urethra on this image

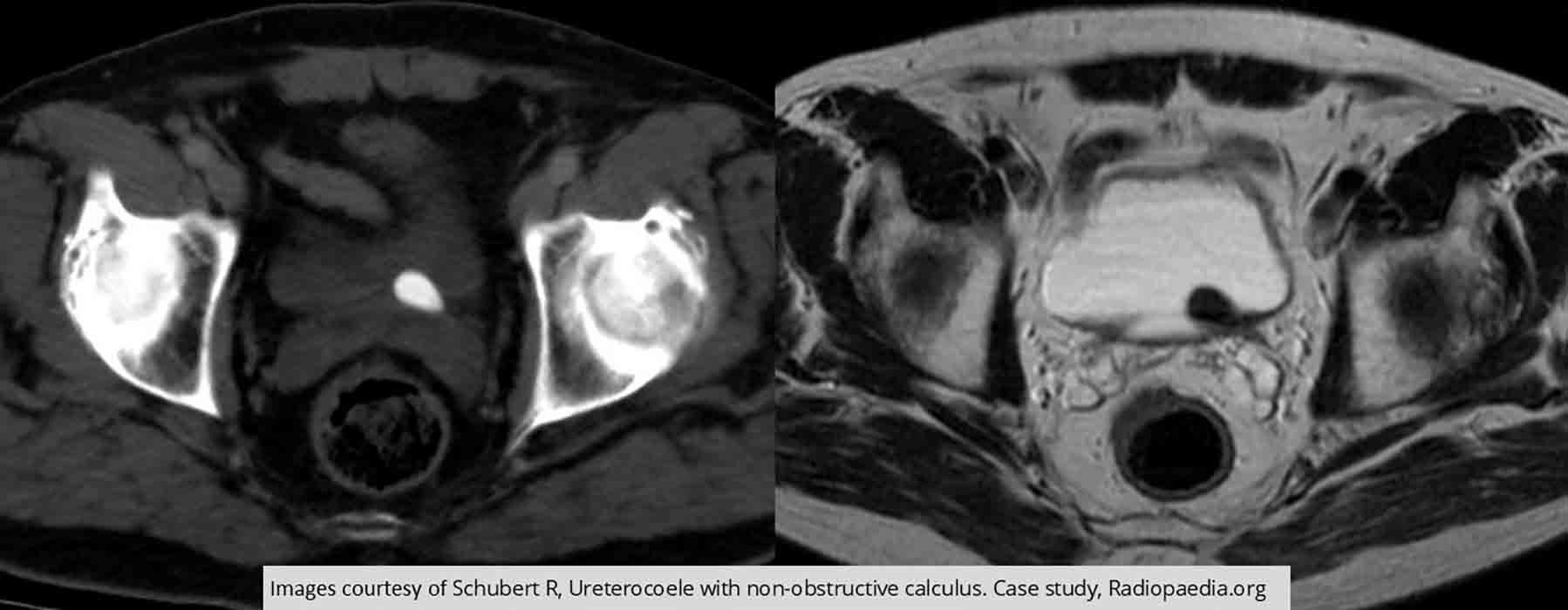
Ureterocele: Large renal calculus seen on CT
MR shows that there is a ureterocele present at that site
Prolapse through the UVJ

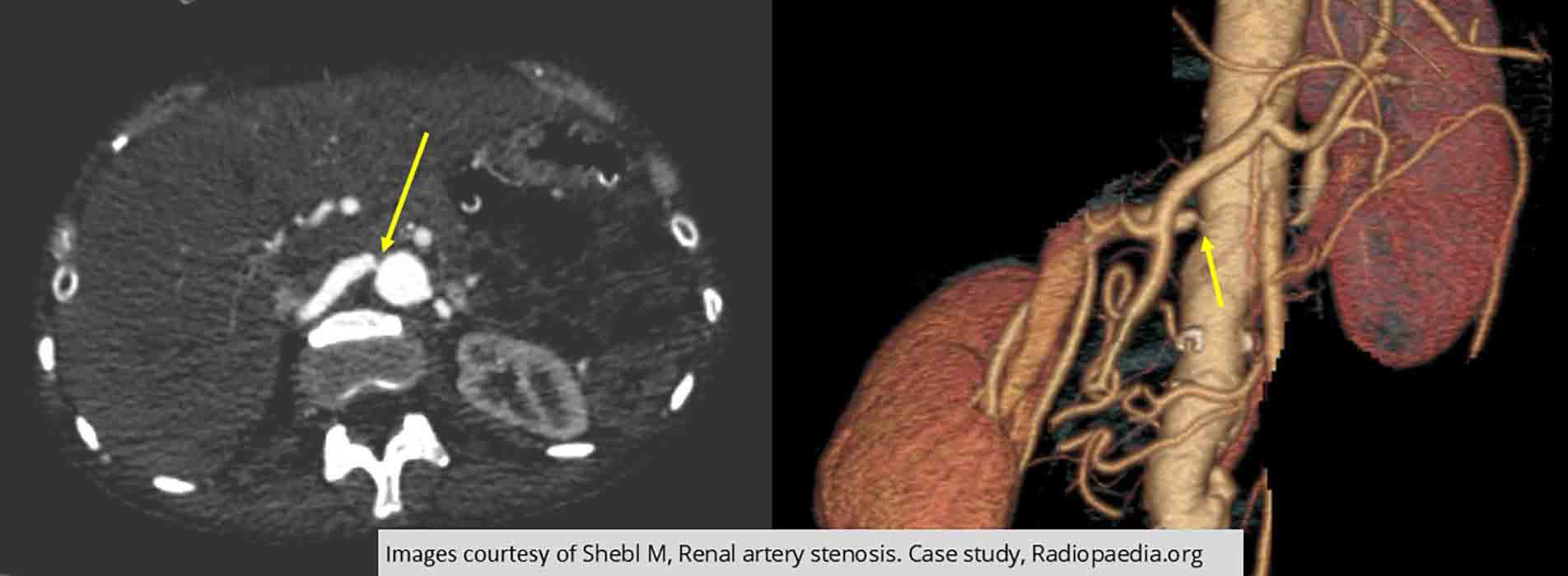
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: Renal artery narrowing on the right side (yellow arrows)

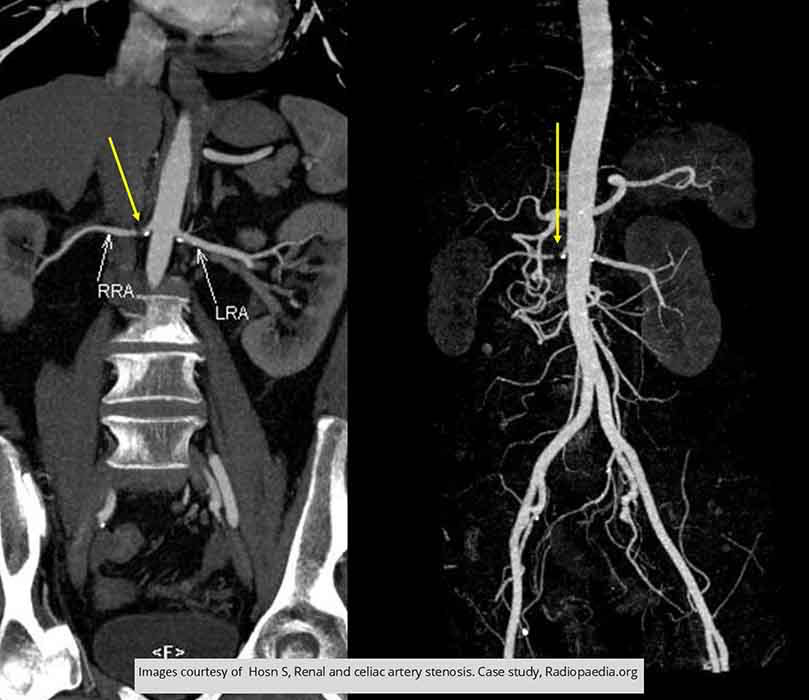
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: Right sided stenosis

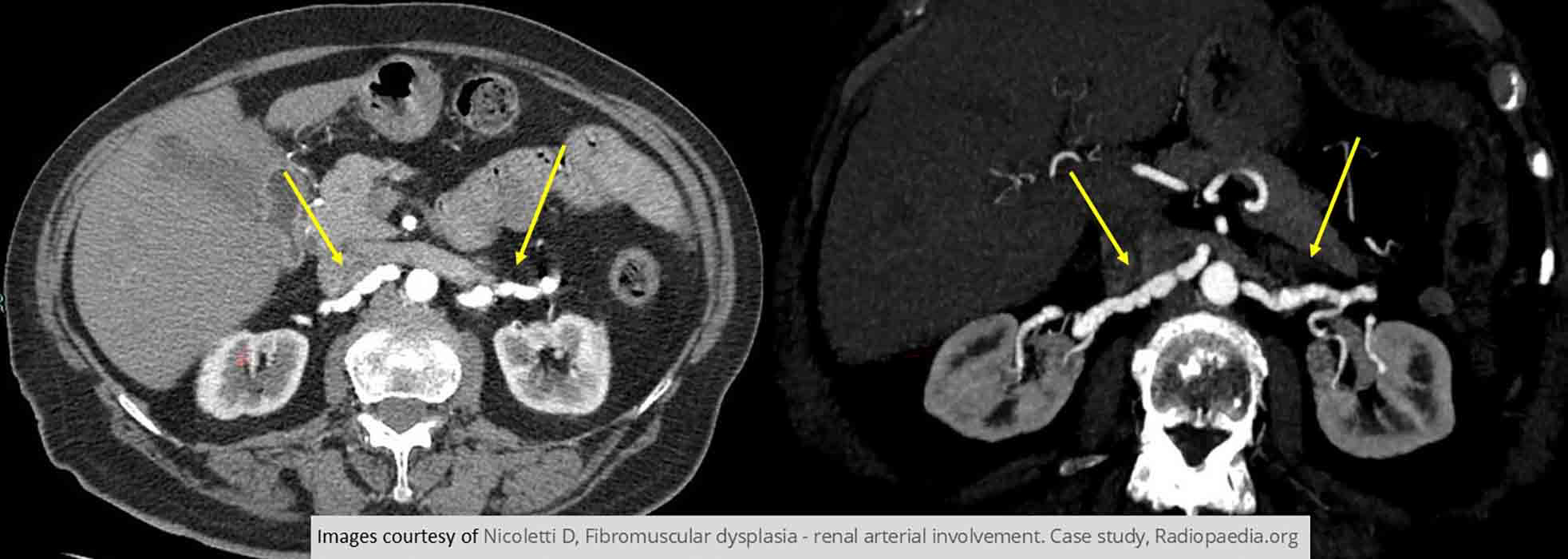
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: PT w/ Fibromuscular dysplasia demonstrating bilateral renal stenoses

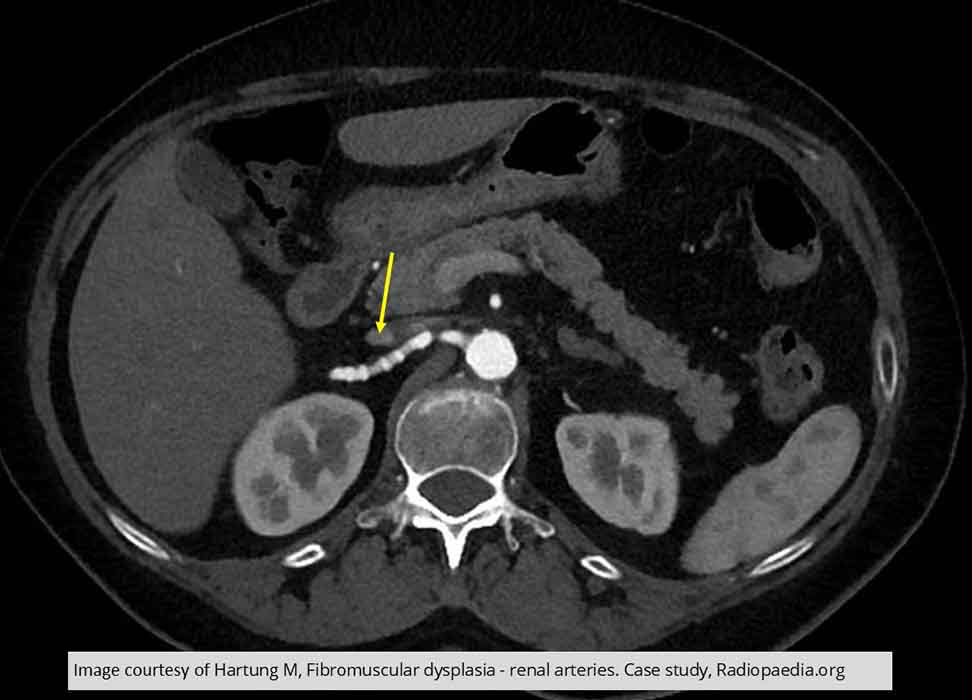
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: String of beads demonstrated on PT w/ Fibromuscular dysplasia

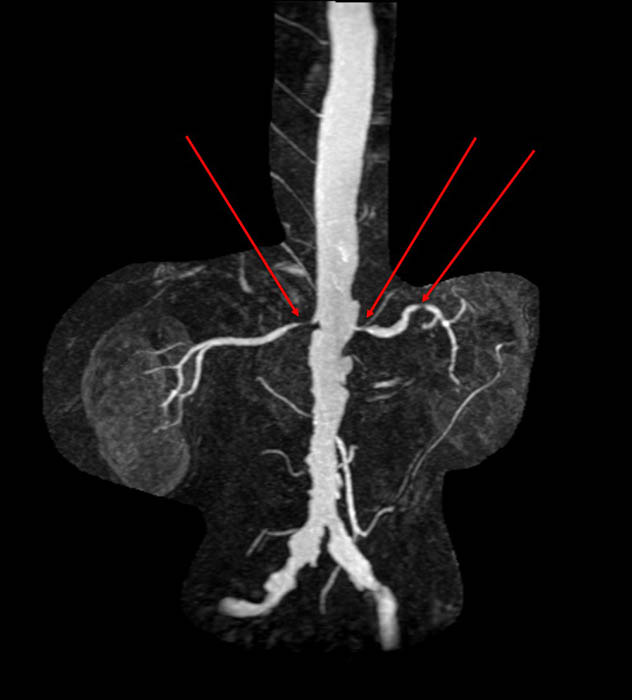
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: Multiple stenoses areas (red arrows) in both renal arteries

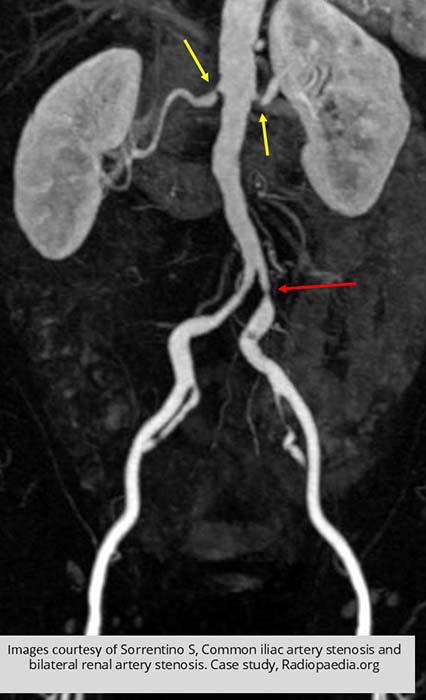
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: Bilateral stenoses (yellow arrows) seen in this MR image
LT iliac artery stenosis

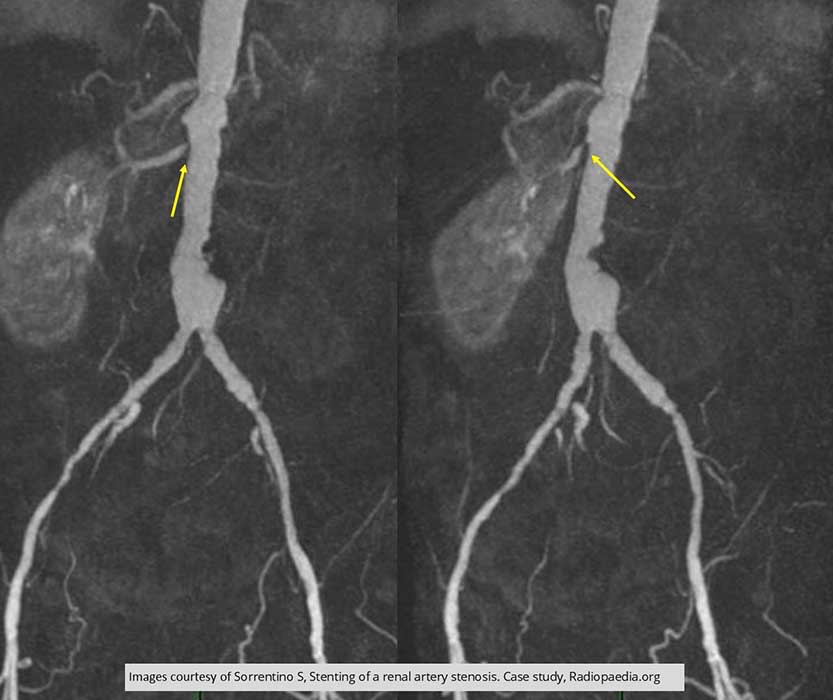
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: Unilateral RT renal stenosis demonstrated (yellow arrows)

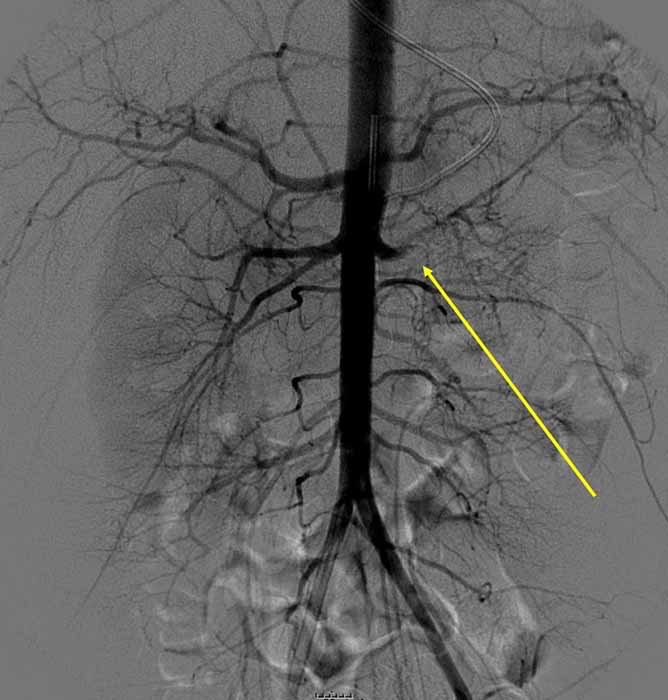
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: Left fully occluded renal artery (yellow arrow)

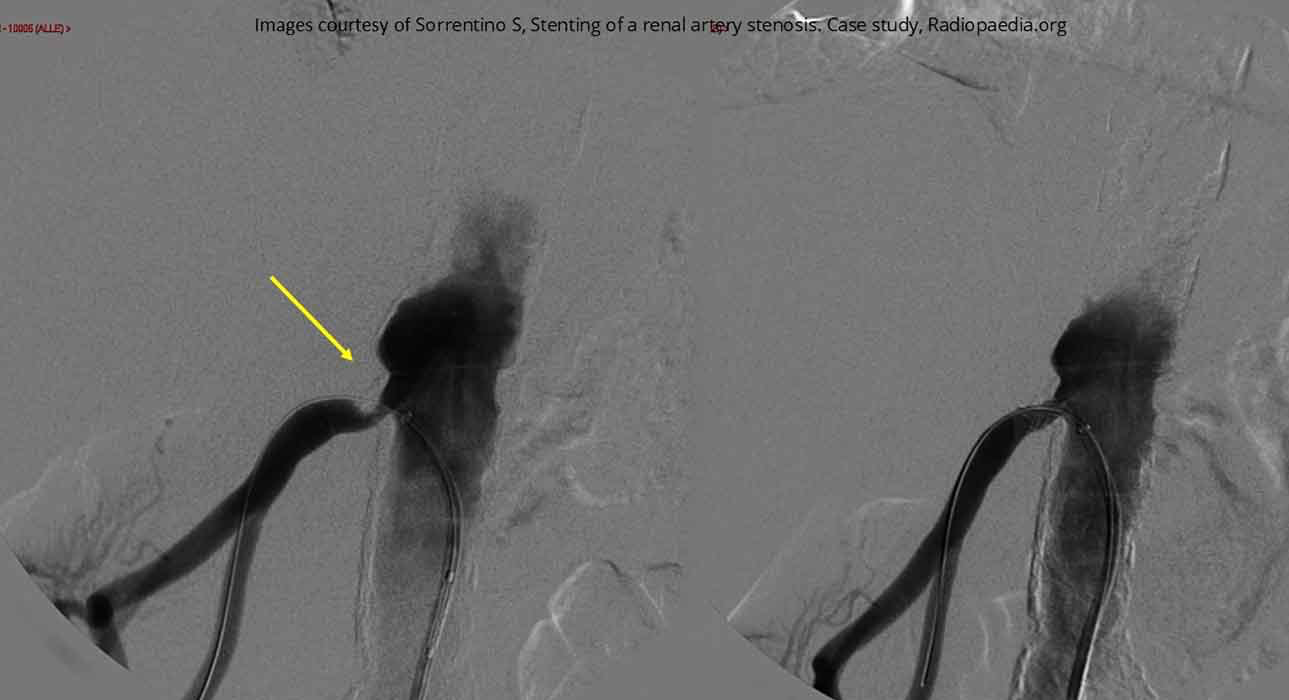
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: Pre and post stent insertion

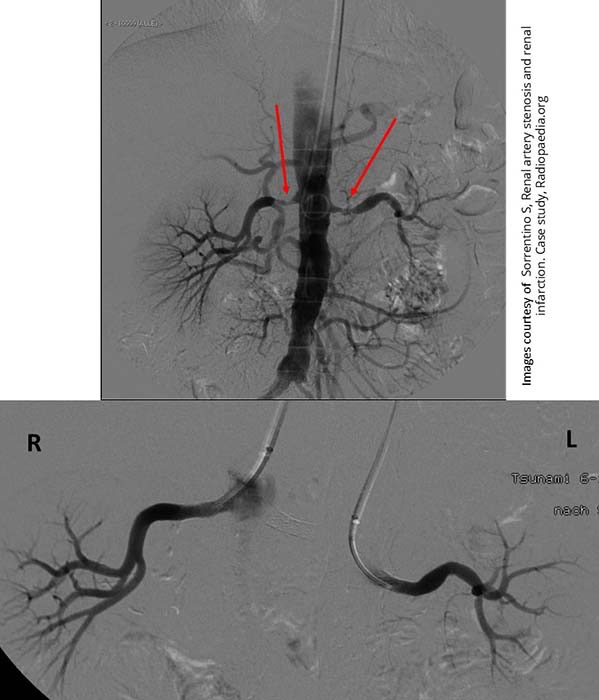
Renal Hypertension/Stenosis: Bilateral stenoses w/ stent insertion

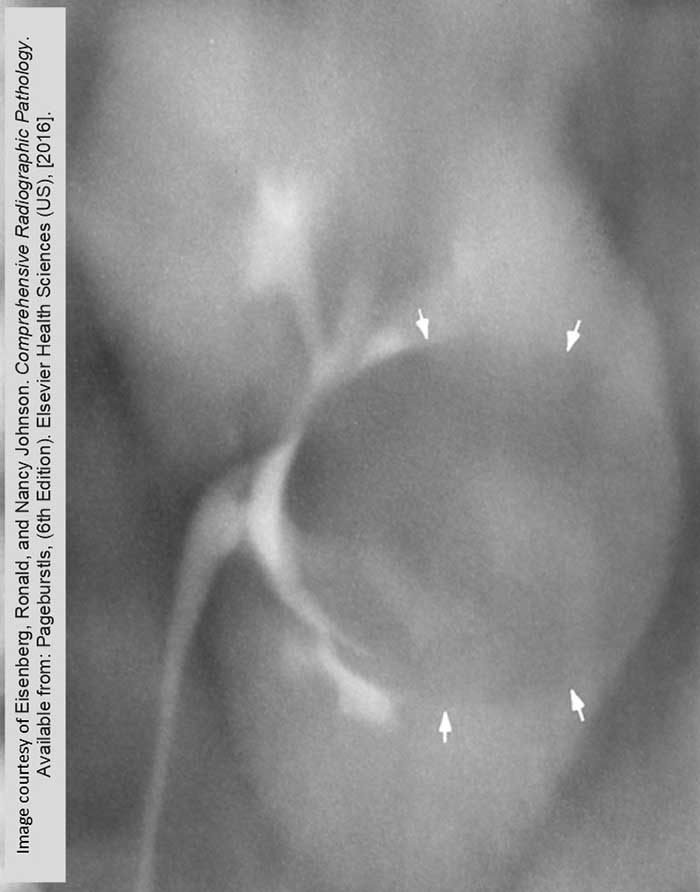
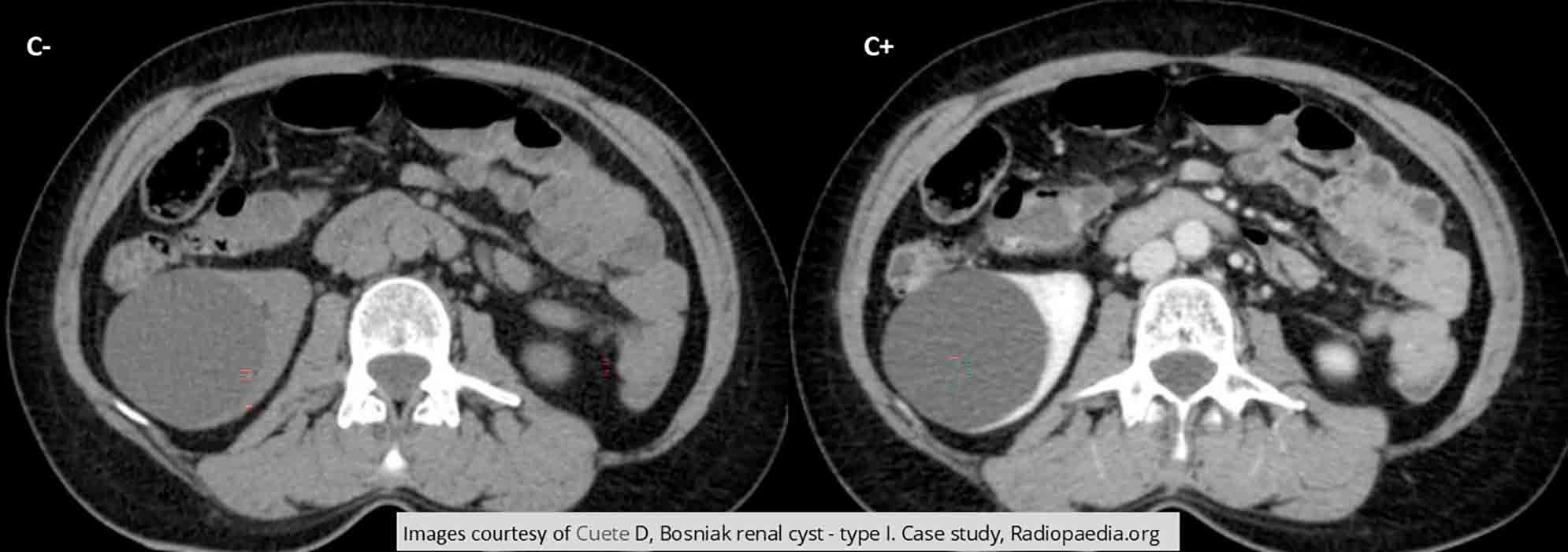
Renal Cyst
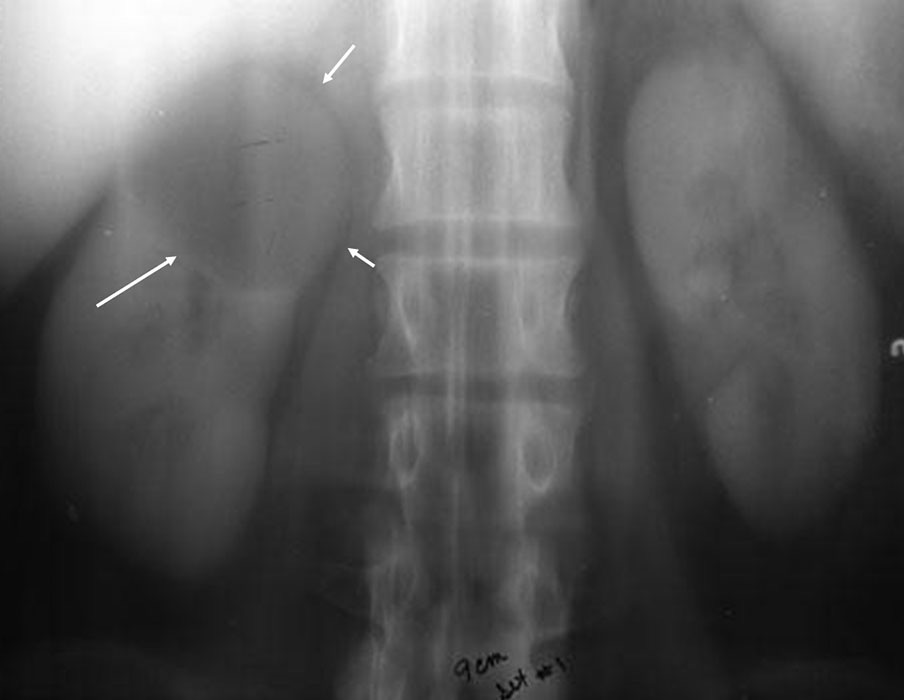
Renal Cyst: Large renal cyst in the right kidney - somewhat unusual as most times they are found in the lower pole

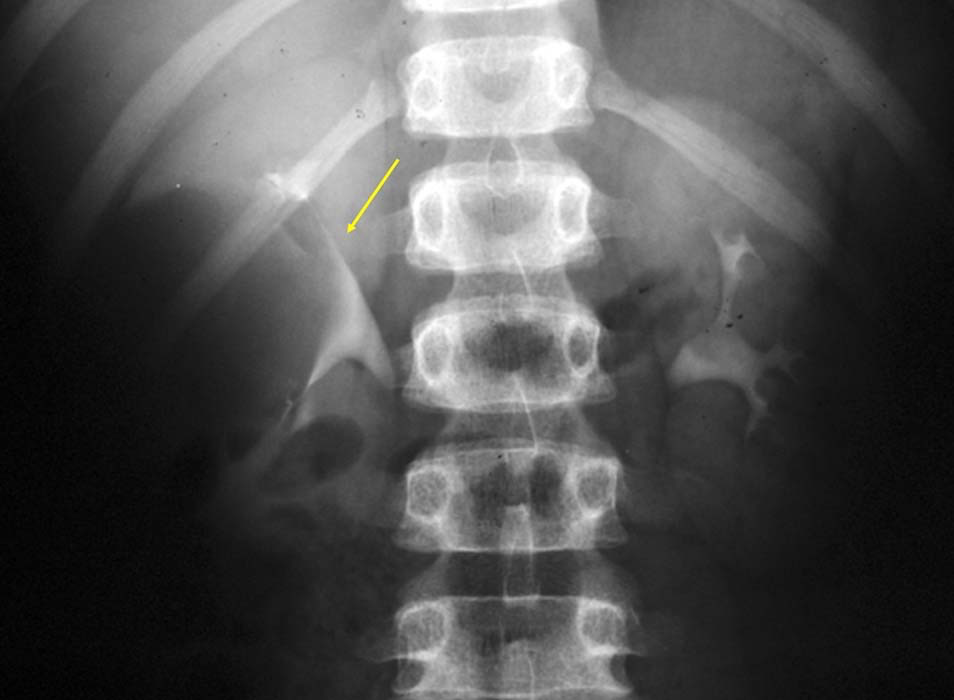
Renal Cyst: Note the stretched calyces as normal tissue is being stretched by the large cyst in the right kidney

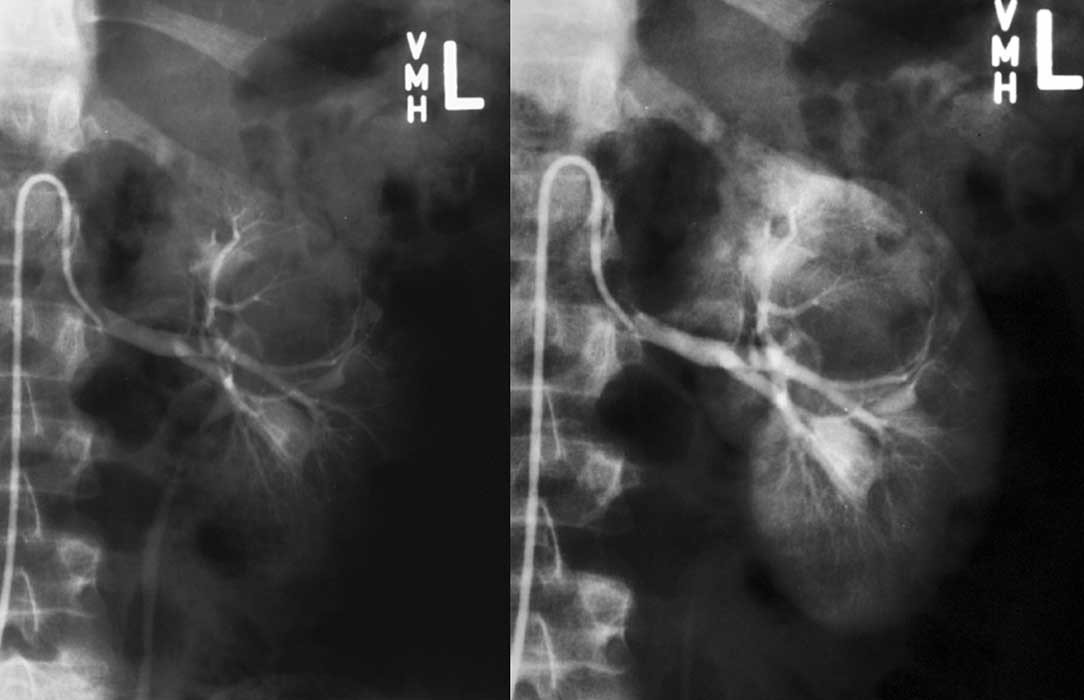
Renal Cyst: Angiography
Note the cyst itself does not fill w/ contrast
The cyst is displacing normal kidney tissues in these images

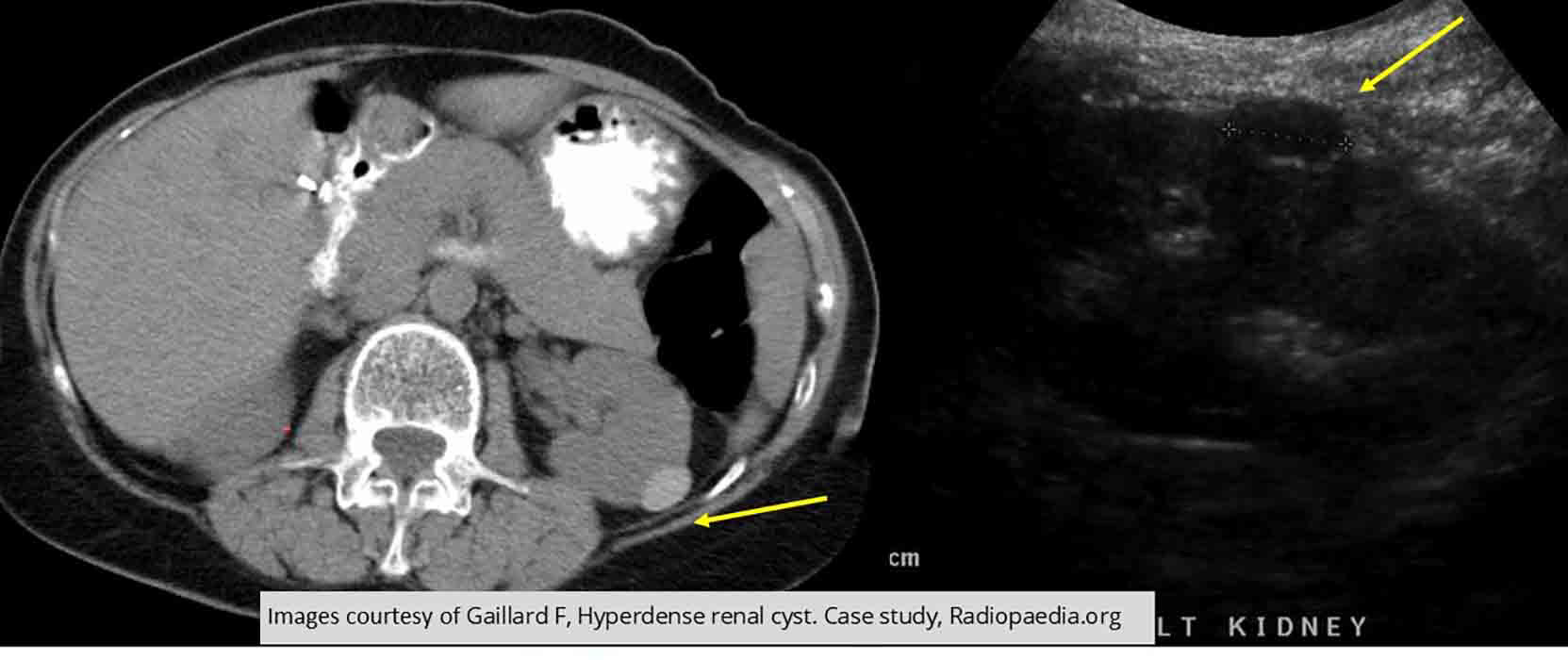
Renal Cyst: US and CT
Comparative images demonstrating a slightly hyperdense cyst
US demonstrates that it is still fluid filled

Renal Cyst: CT
Tumor does not enhance w/ contrast

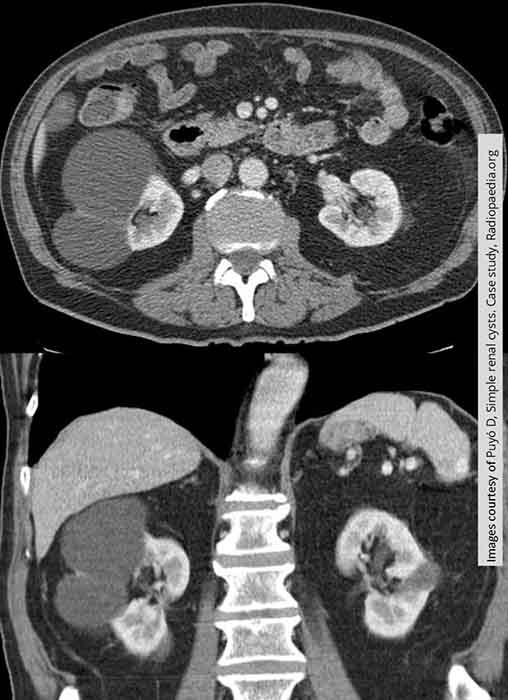
Renal Cyst: 2 cysts in the right kidney, one in the left

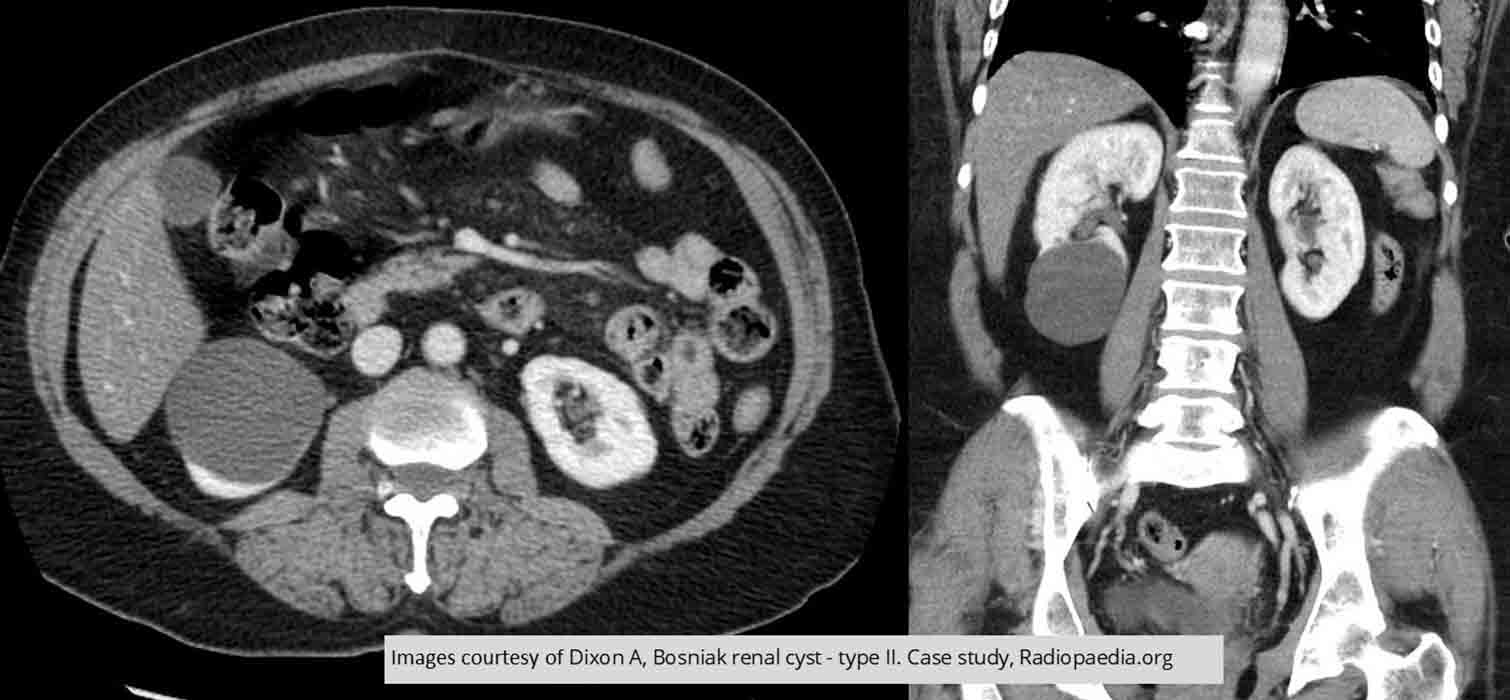
Renal Cyst: Non-enhancing right lower pole renal cysts
There are some slight linearities within it may indicate that it is multicameral

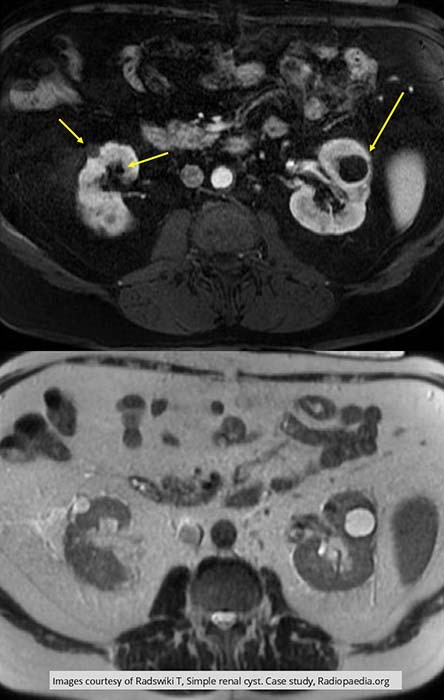
Renal Cyst: Multiple bilateral cysts
Top image is T1 w/ no enhancement
Bottom image is T2 w/ enhancement of the cysts

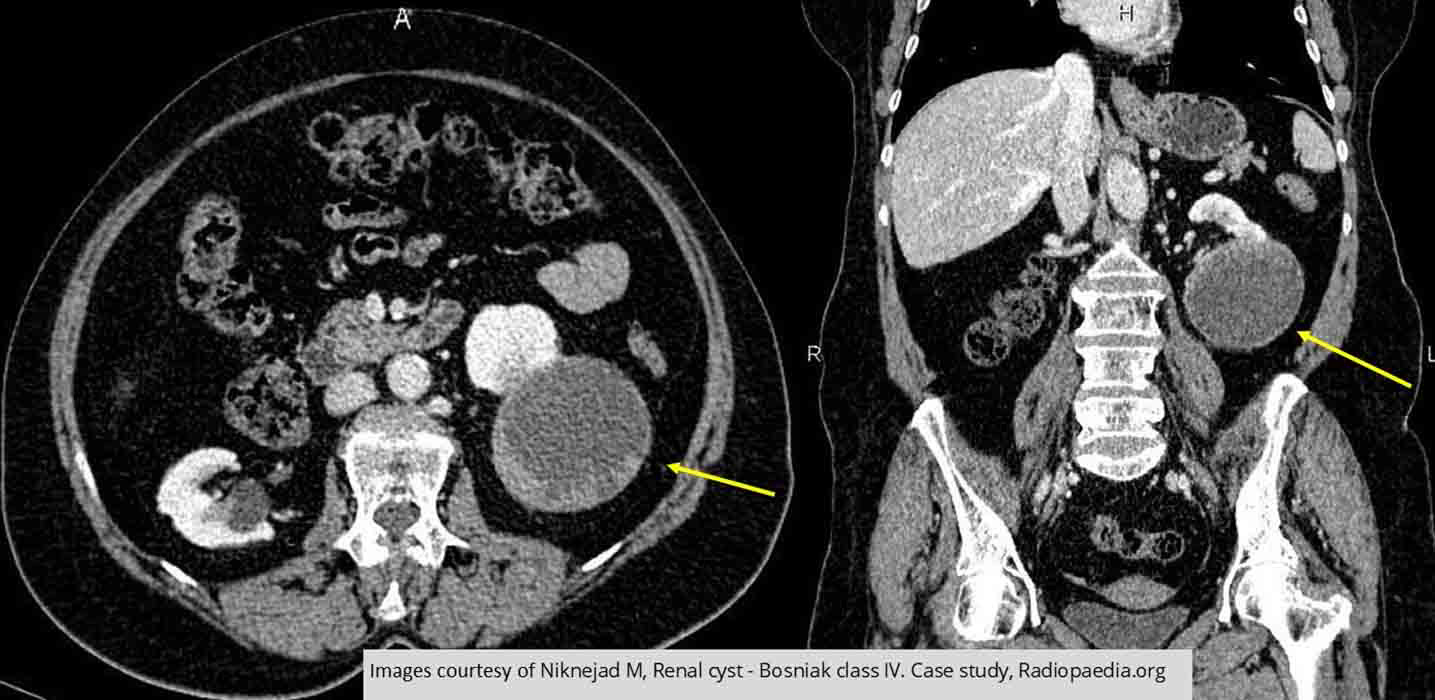
Renal Cyst: TYPE IV Cyst
This is malignancy
Note the uneven thickening of the walls
Have enhanced under contrast as per the report
Report also indicated some calcification as well as "eccentric soft tissue components" within the cyst

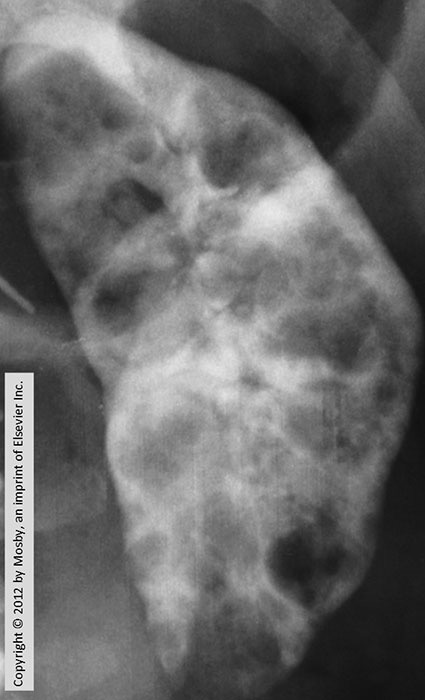
PKD
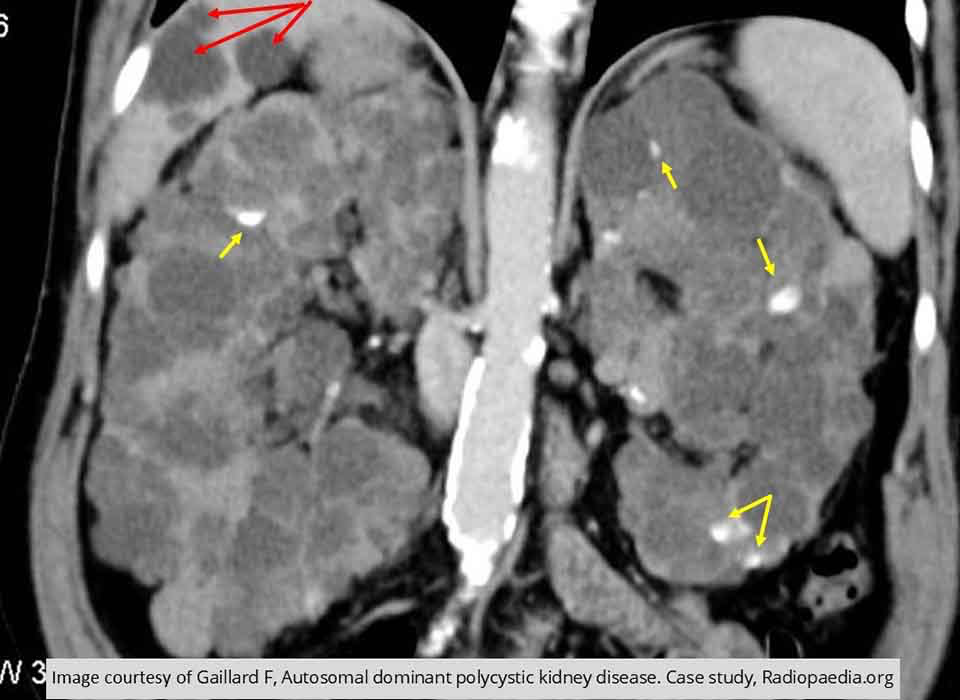
PKD: Demonstrates non-enhancing cysts Note all the areas of calcification with the kidneys (yellow arrows)
Notice the cysts in the liver (red arrow)

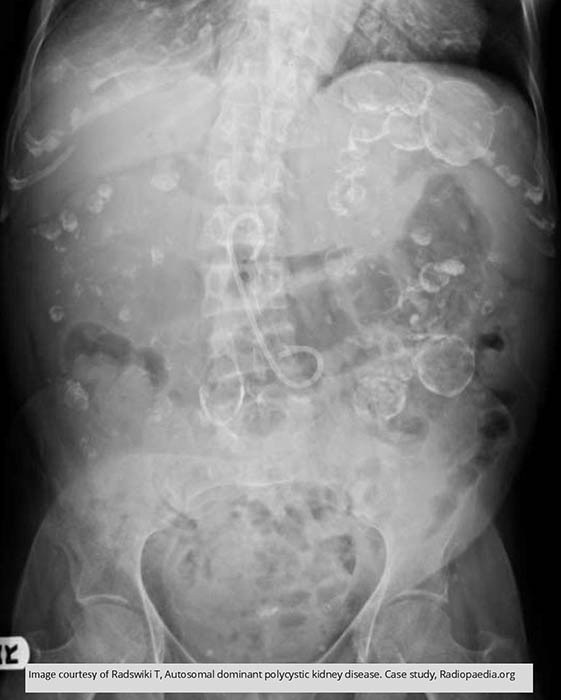
PKD: Multiple calcification throughout the abdomen representing cyst calcifications in this PKD patient

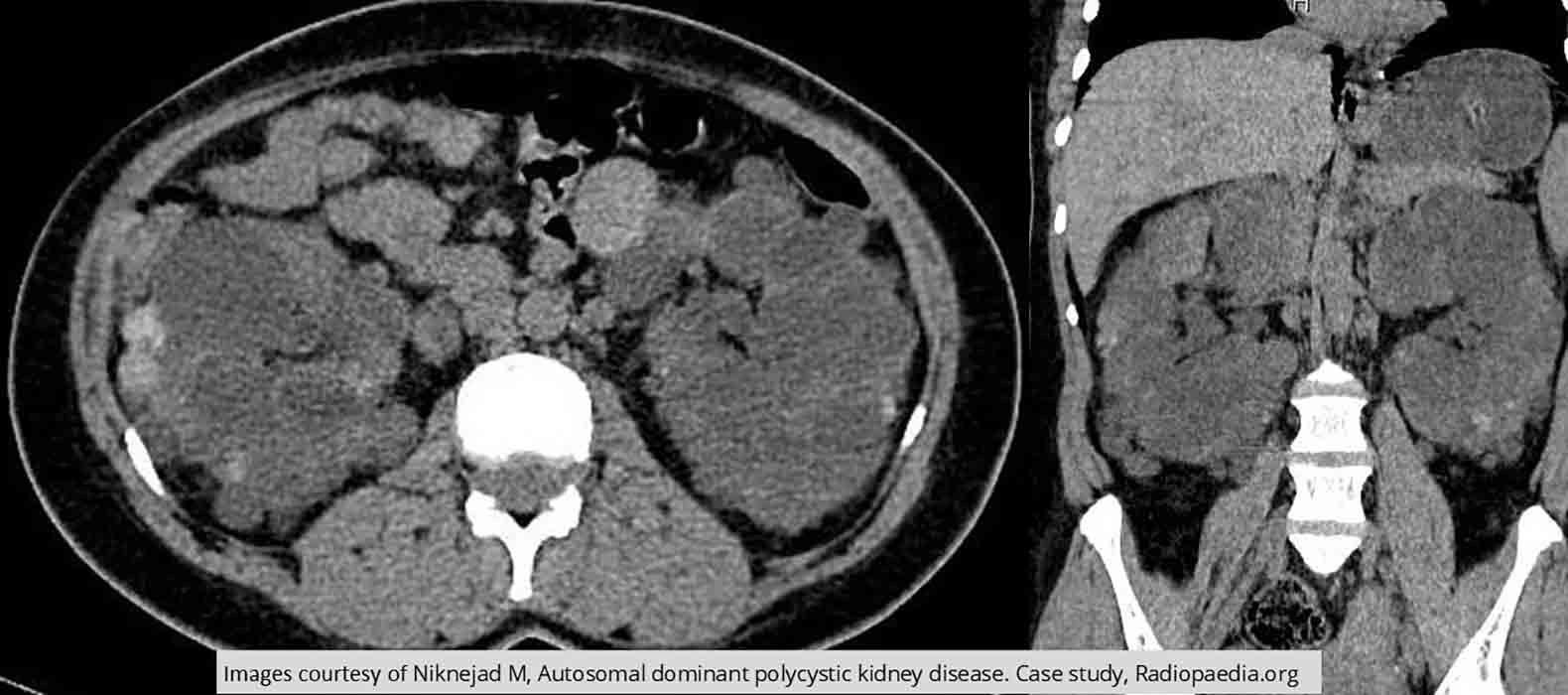
PKD: Enlarged kidneys with multiple cysts throughout

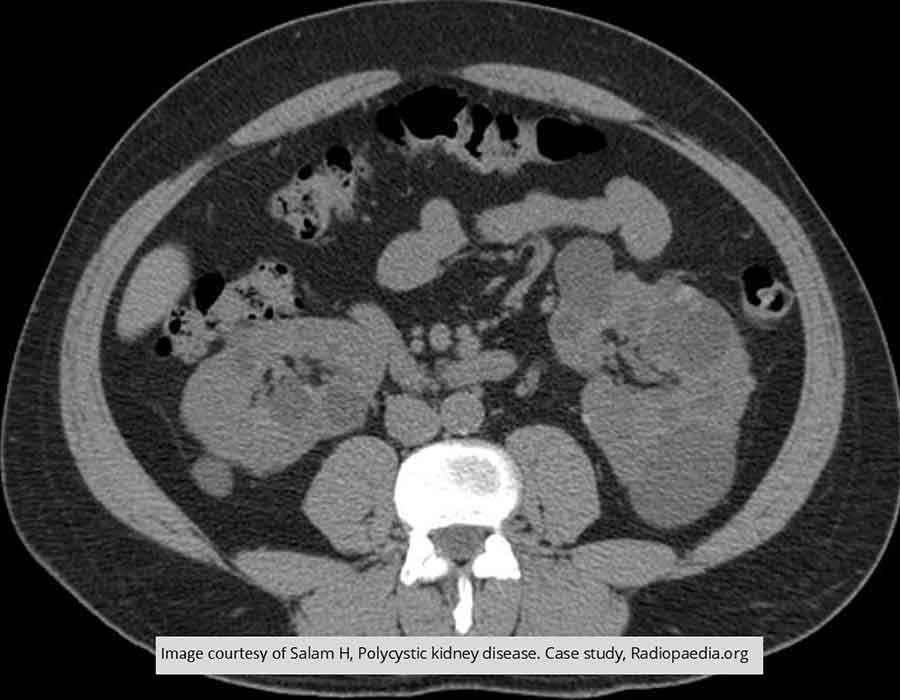
PKD: Note the multiple cysts in both kidneys
Notice the odd shape these cysts have given the left kidney

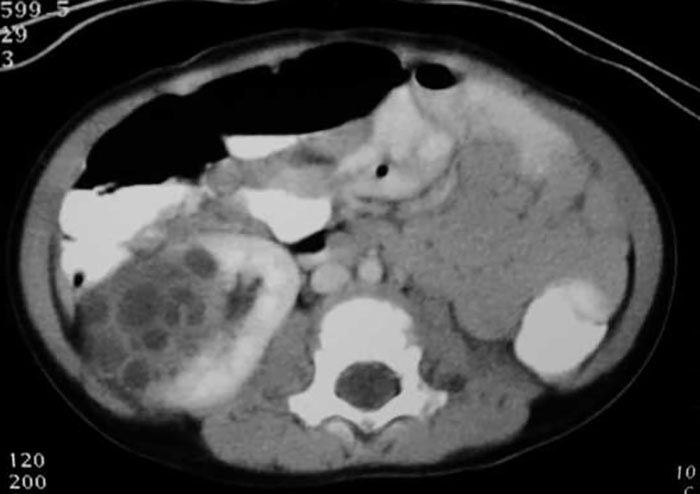
PKD: Right kidney very enlarged
Mass of cysts and the tissue surrounding them is non functioning

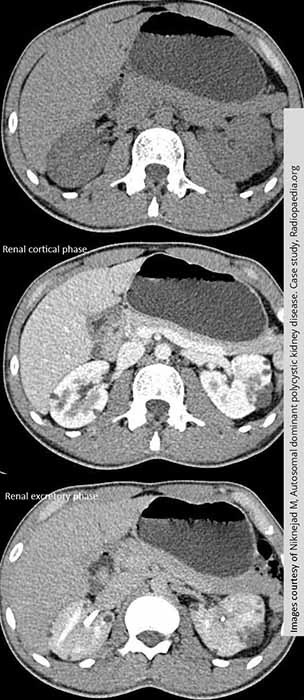
PKD: In the non contrast scan, the cyst are barely visible
Multiple cysts seen when contrast is introduced

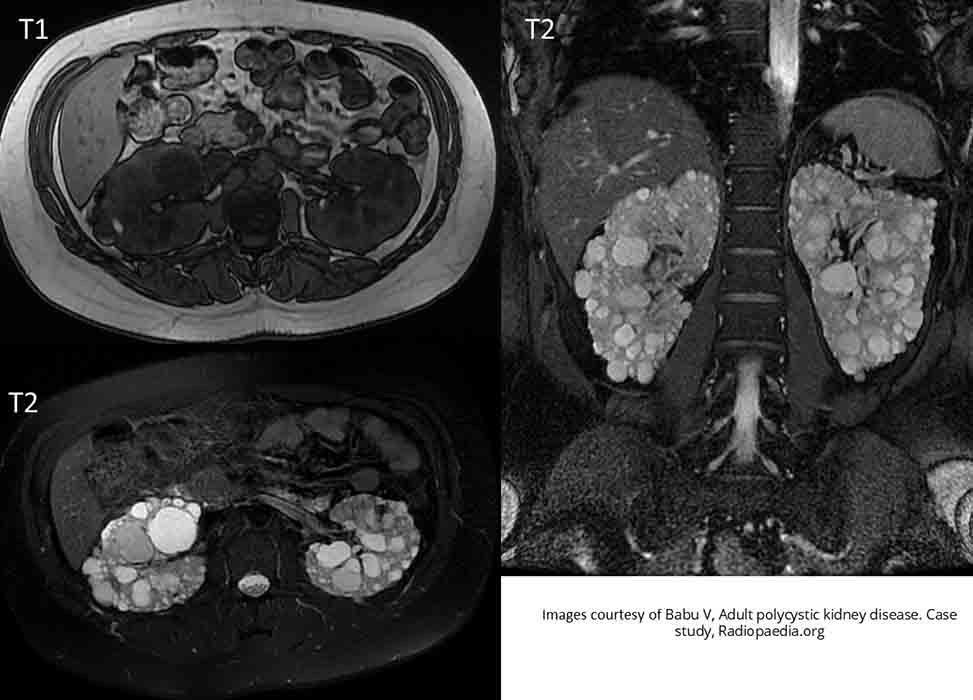
PKD: T1 images show no enhancement
T2 give a great indication of how extensive the PKD

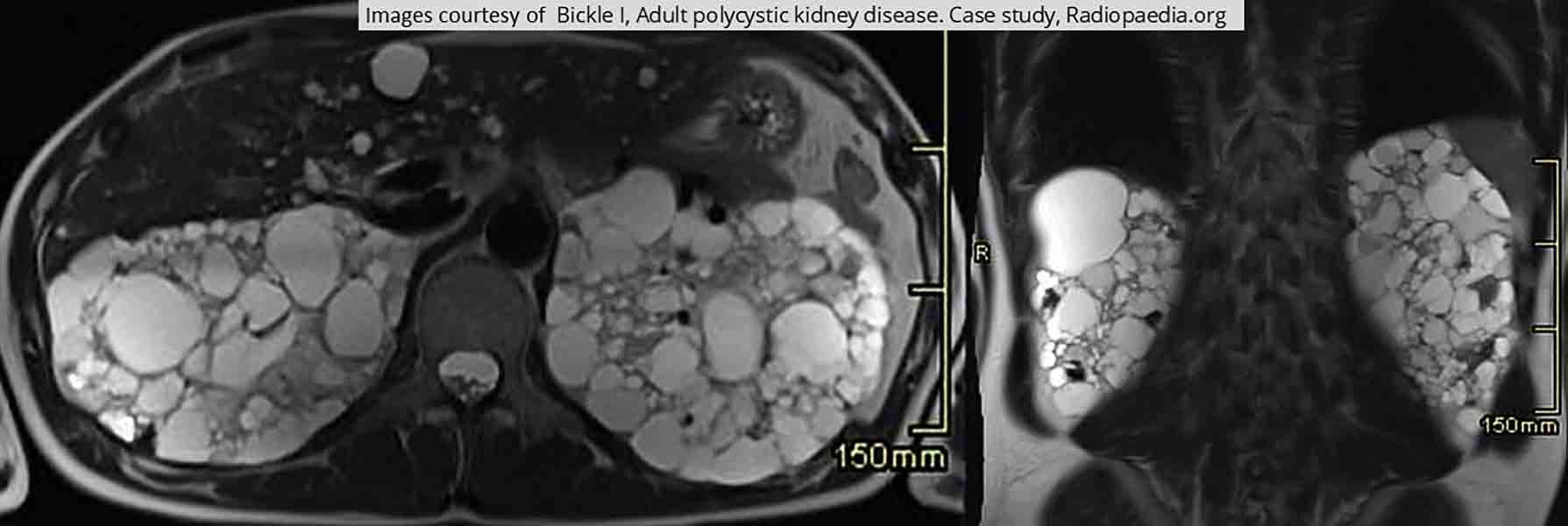
PKD: Massively enlarged distorted kidneys seen on this T2 image

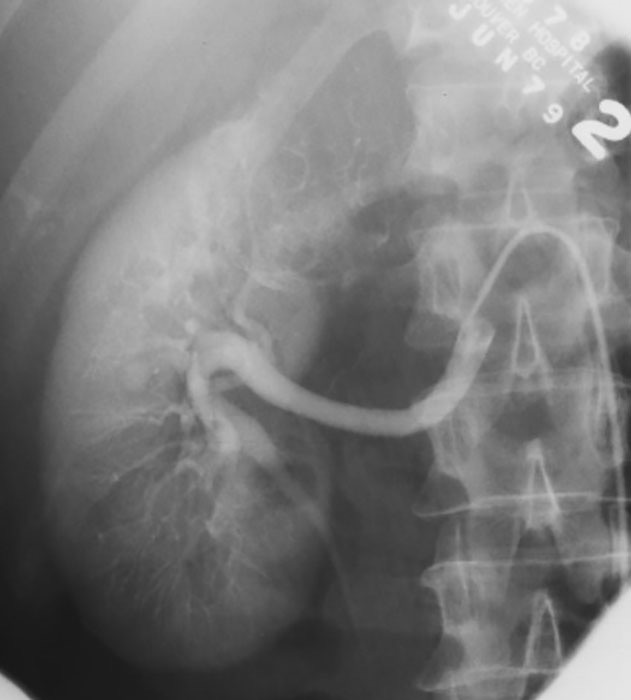
RCC
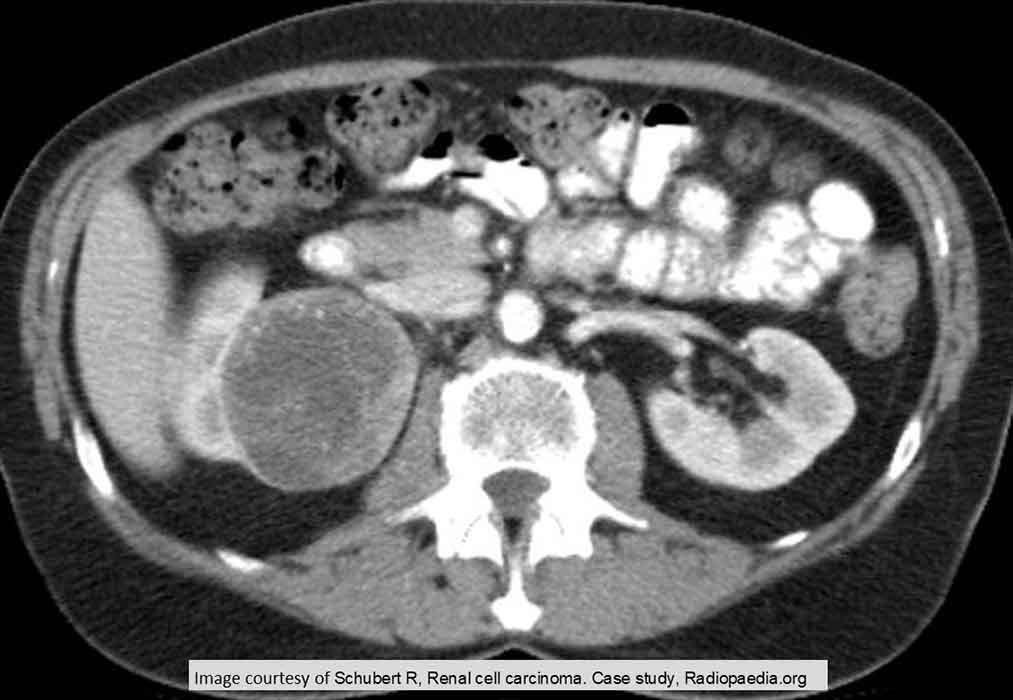
RCC: Right sided lesion
Notice the non-homogeneous nature of the tumor and the thick, uneven walls of it

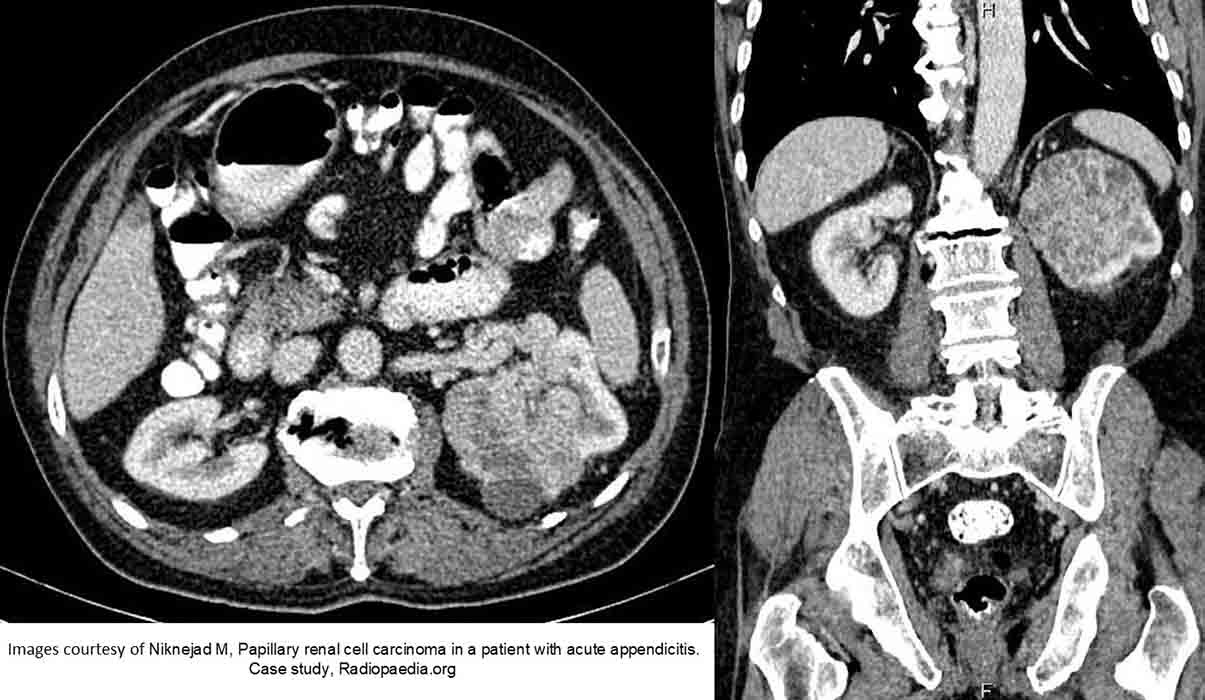
RCC: Left sided lesion
Enlarged tumor w/ decreased function, when compared to the right side
Most of the normal structure has been destroyed

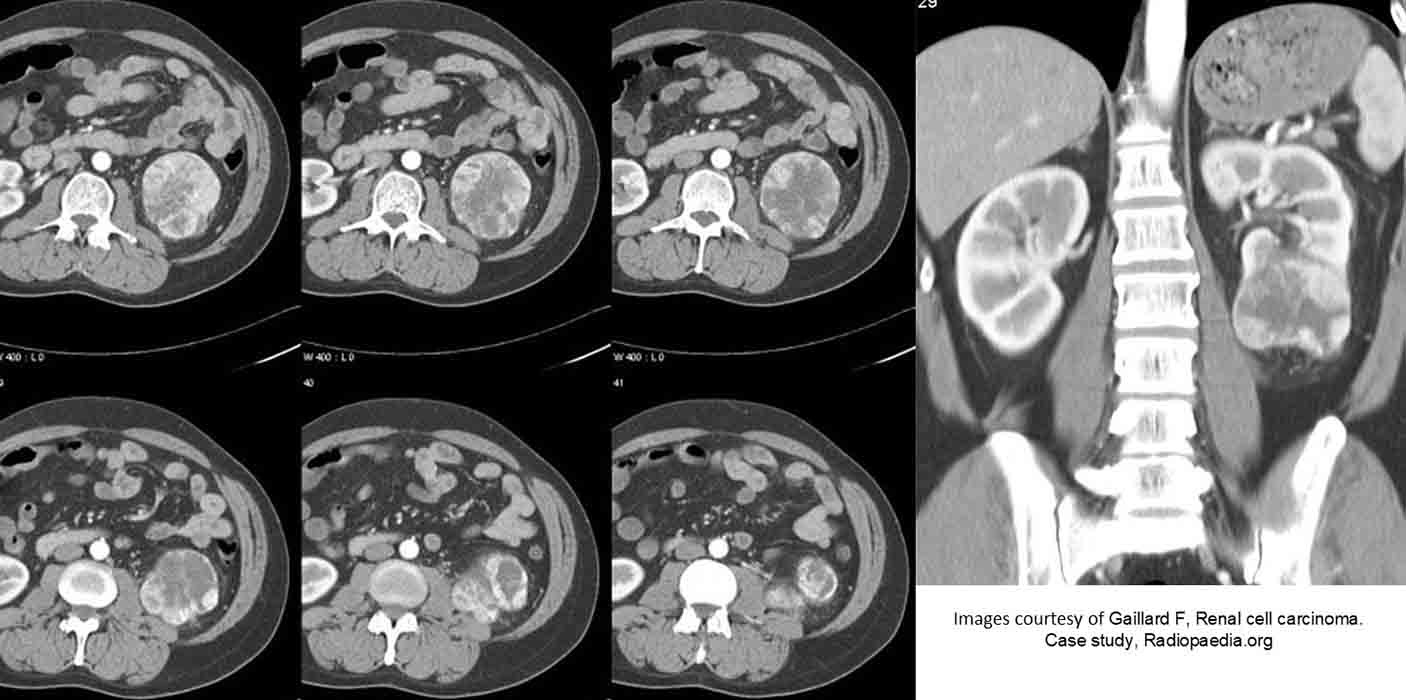
RCC: Multiple slices demonstrating an enlarged tumor mass w/ some necrosis in the inferior portion of it

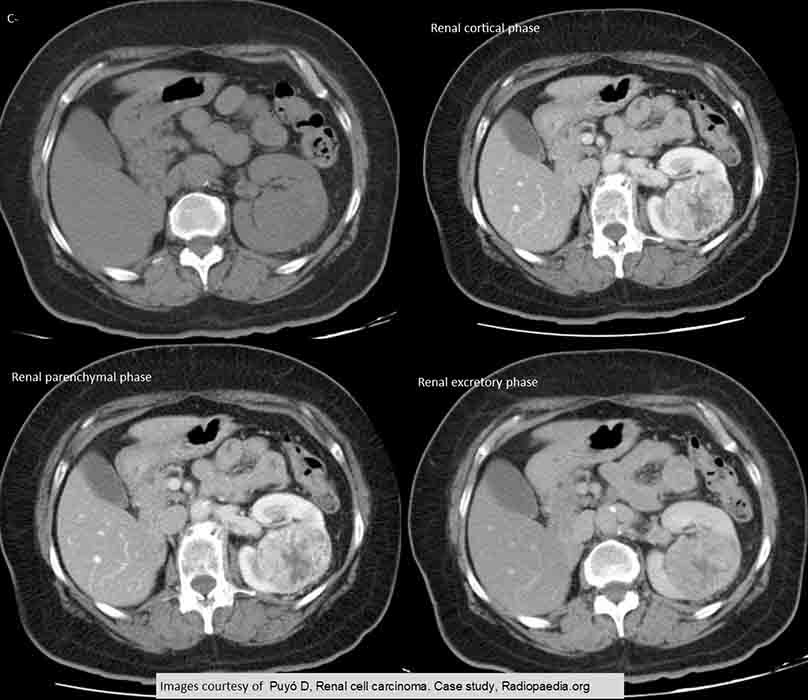
RCC: 4 scan phases
Non-contrast the tumor blends in w/ the rest of the kidney
Necrotic tissue is seen in both the cortical and parenchymal phases

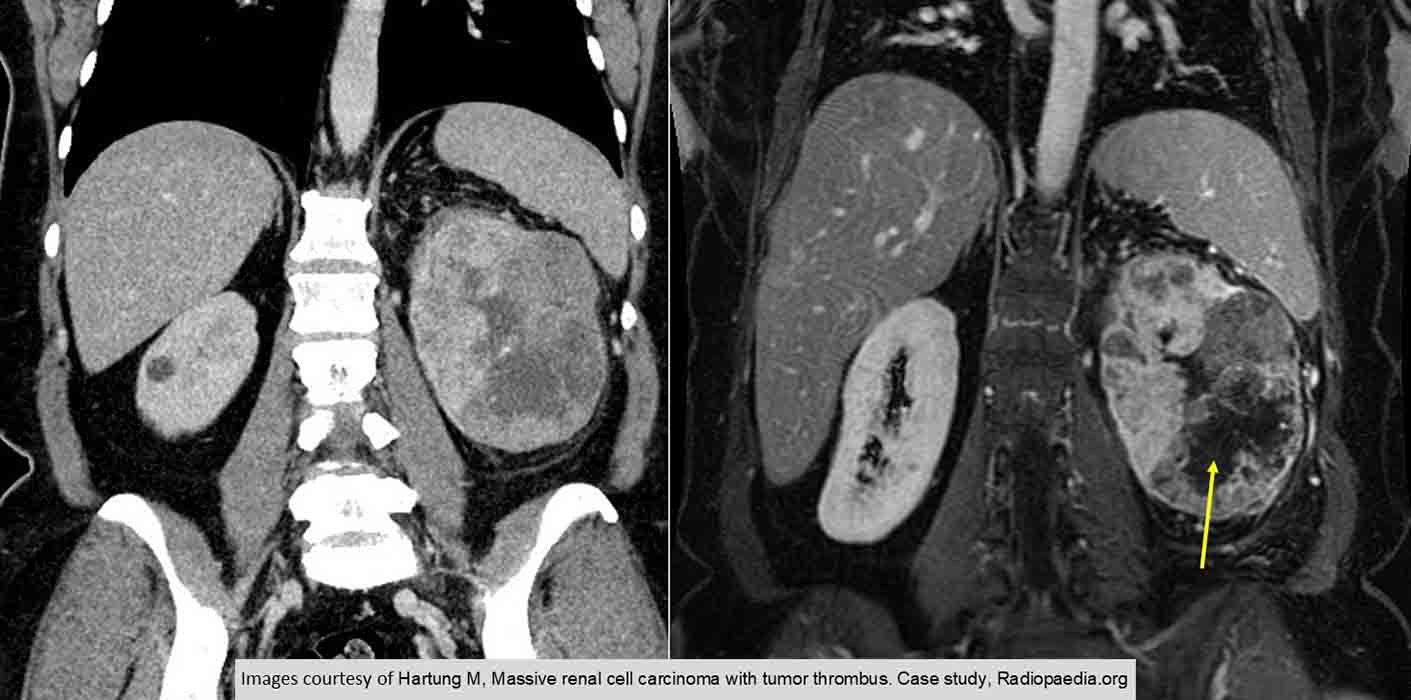
RCC: Demonstrates the necrosis very well

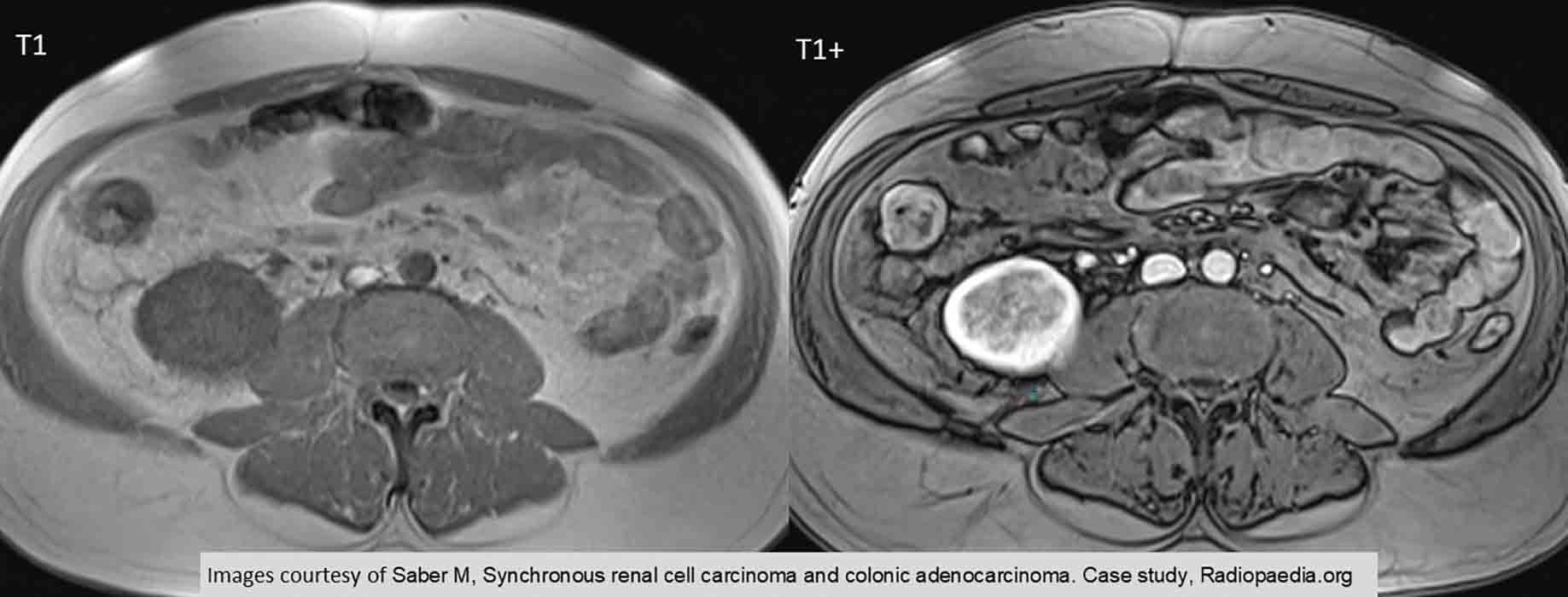
RCC: T+ demonstrates the arterial enhancement of the kidney as well as the non-homogenous density of the tumor

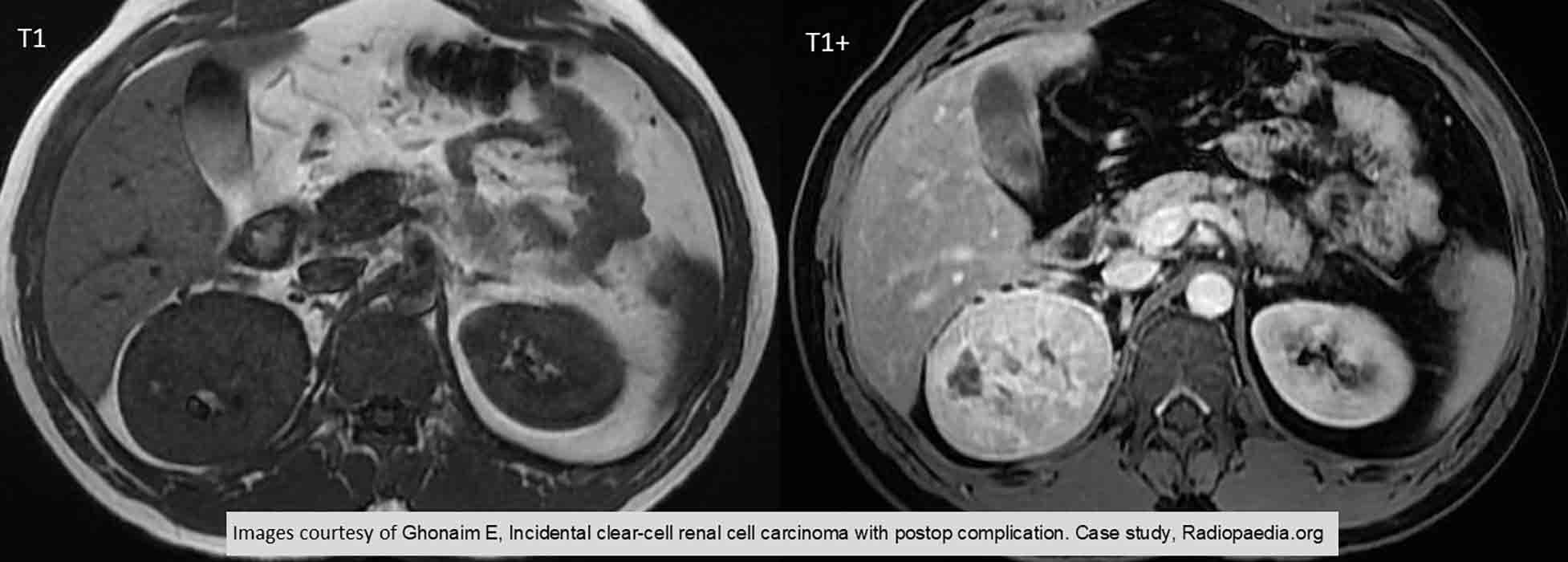
RCC: In the arterial enhancement image, there is very uneven enhancement and an area of necrosis in the lateral margin of the right kidney

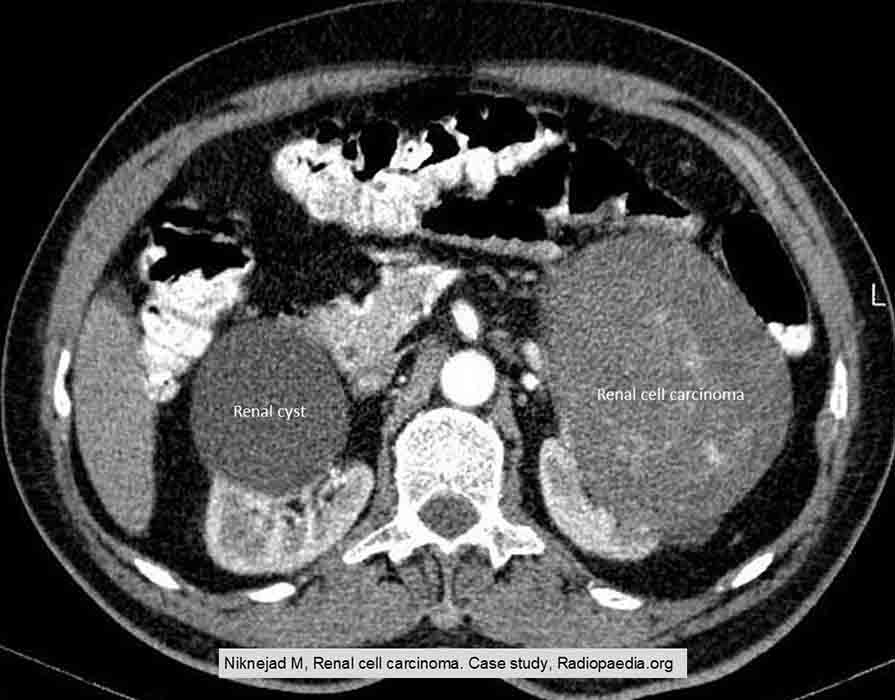
RCC: Cyst vs. Tumor
Note the smooth, rounded border of the cyst compared to the tumor which is not as delineated

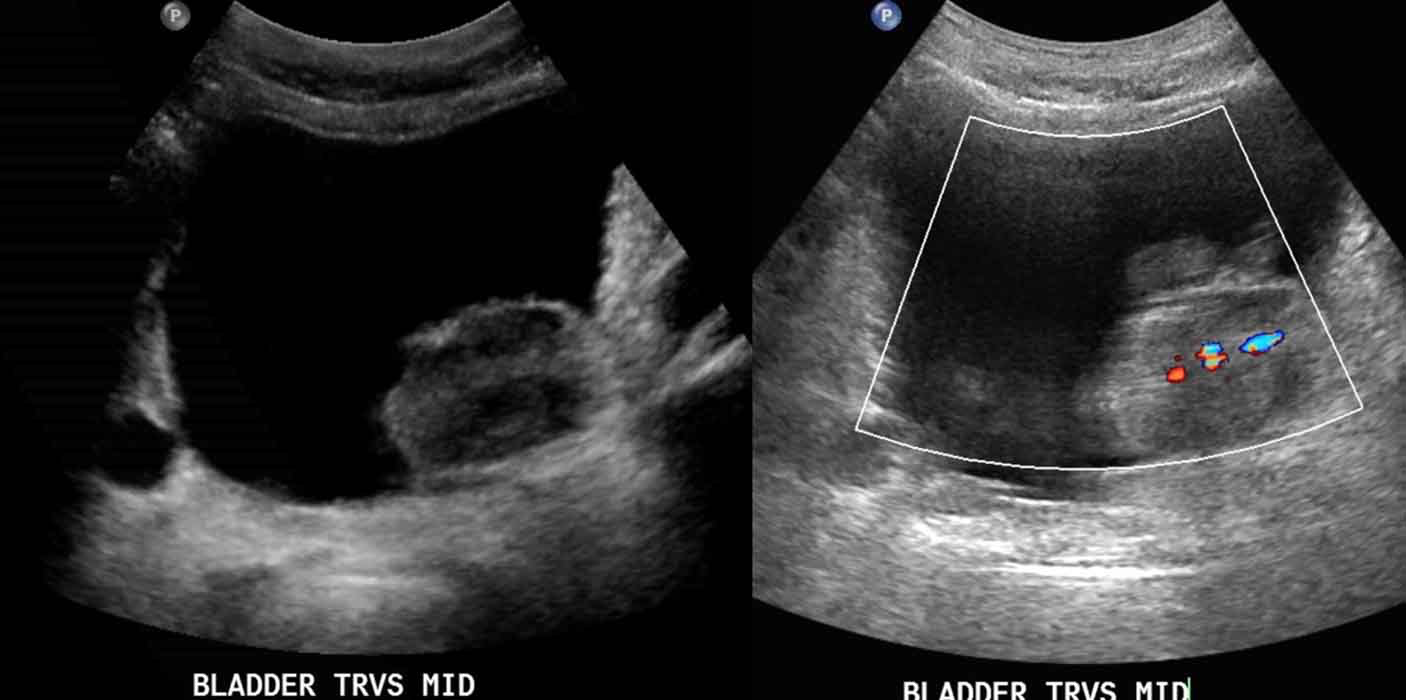
Bladder Carcinoma: Demonstrates a superficial bladder cancer w/ vascularization seen in the doppler image
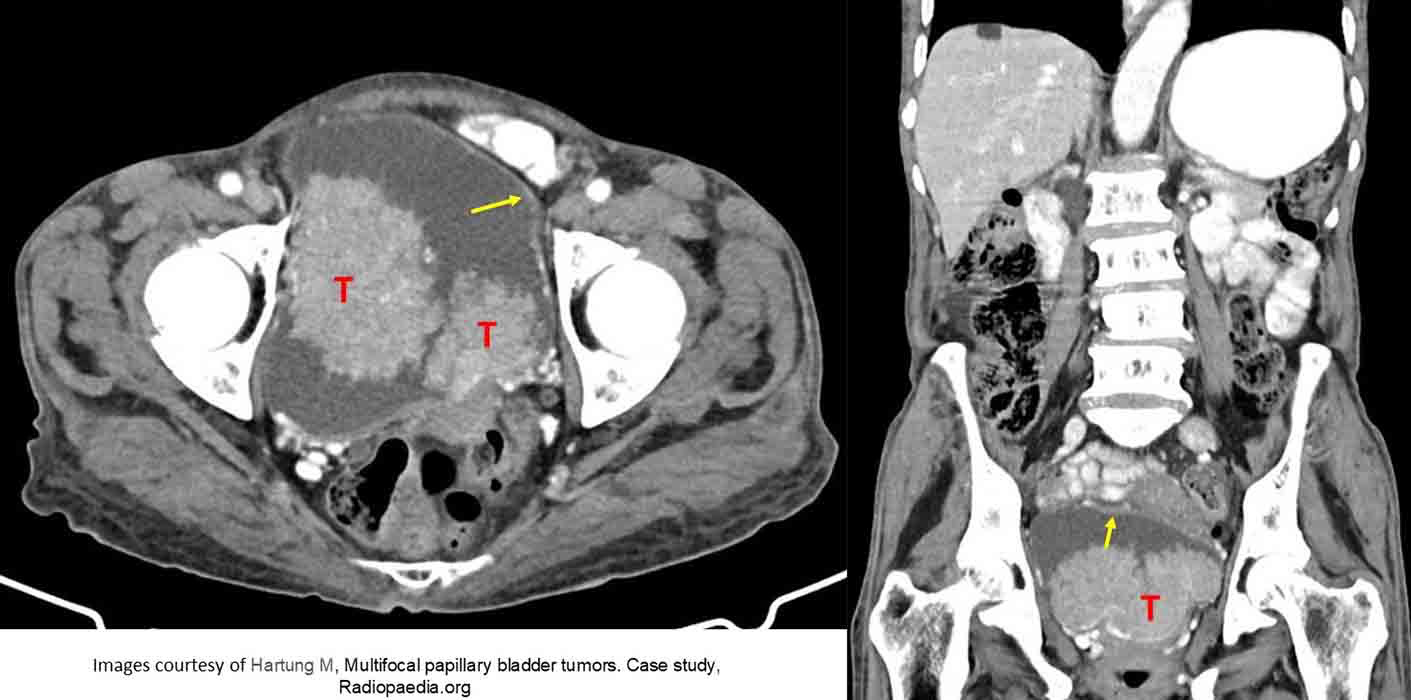
Bladder Carcinoma: Two superficial bladder masses
Note they are similar in HU to the bladder wall (yellow arrow)

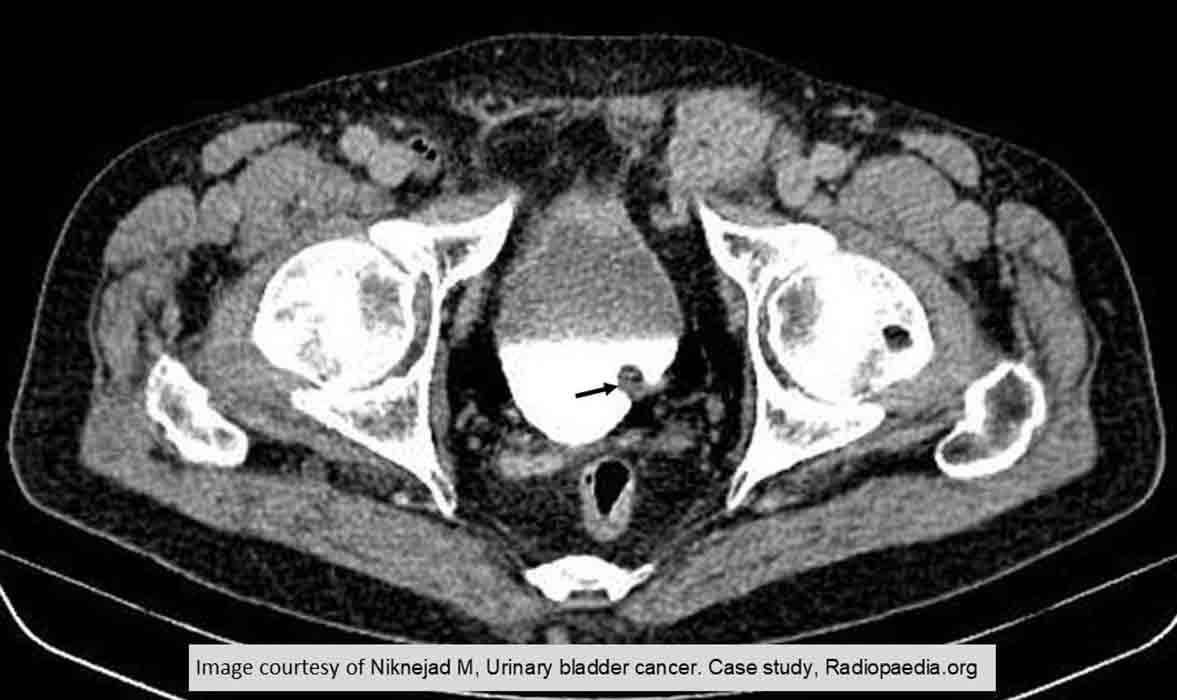
Bladder Carcinoma: Very small superficial tumor as indicated by the black arrow

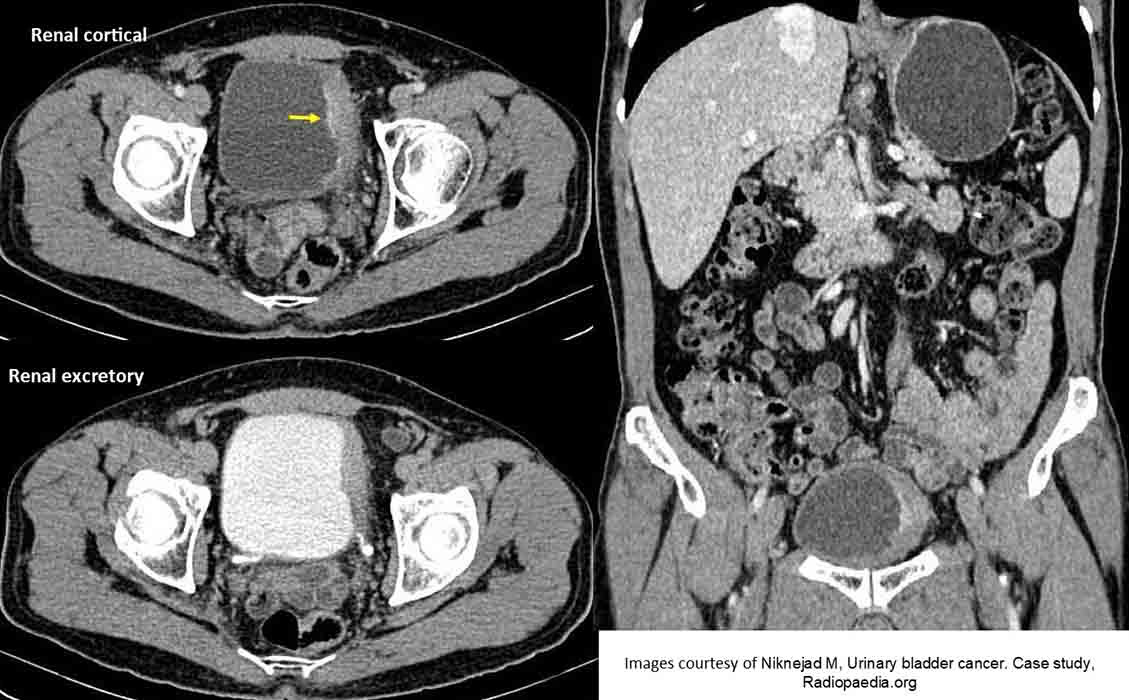
Bladder Carcinoma: Invasive bladder cancer
Note the fine line of "crusted" calcification (yellow arrow) as well as the irregular thickened wall on the left side
