RCP 370 Ch. 7 Assessment of the Cardiovascular System
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
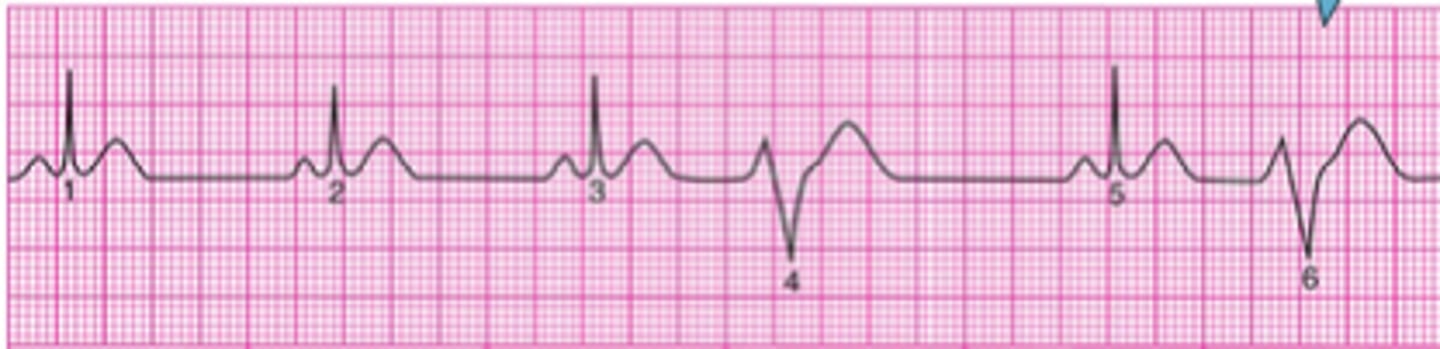
P wave
Depolarization of the atria
QRS complex
Depolarization of the ventricles
T wave
ventricular repolarization
how to calculate regular rhythm
- Count the number of large boxes on the ECG strip between two QRS complexes. Then 300 divided by large boxes (300/boxes).
- Count the wave and time by 10
Regular heart rhythm
300
Assessing HR boxes
- each small box is 0.2
- 3 sec = 15 boxes
- 6 sec = 30 boxes
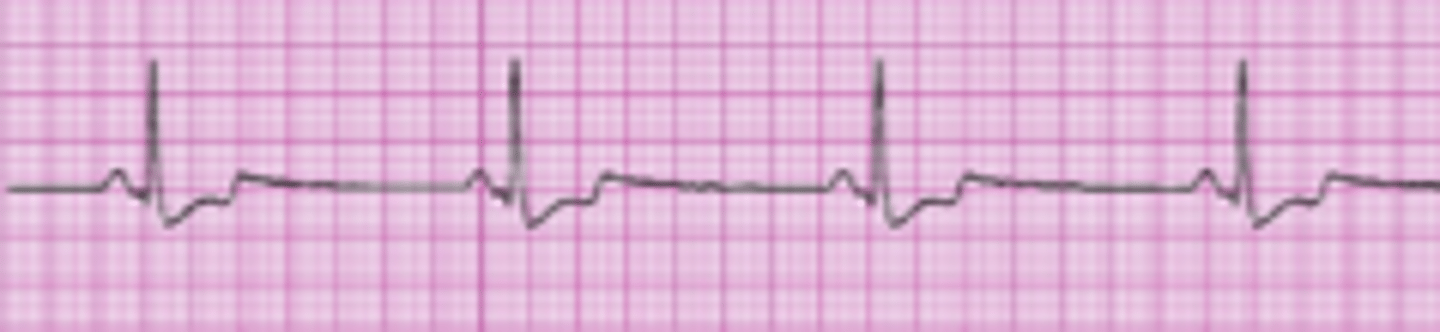
Sinus Bradycardia
- <60 bpm
- Common causes: weakened or damaged SA node, hypoxemia, increased ICPs, OSA.
- Severe cases: decreased CO, BP, and tissue hypoxia.
- poor capillary refill, cold, clammy and depressed sensorium.
- Treatment: Atropine and oxygen
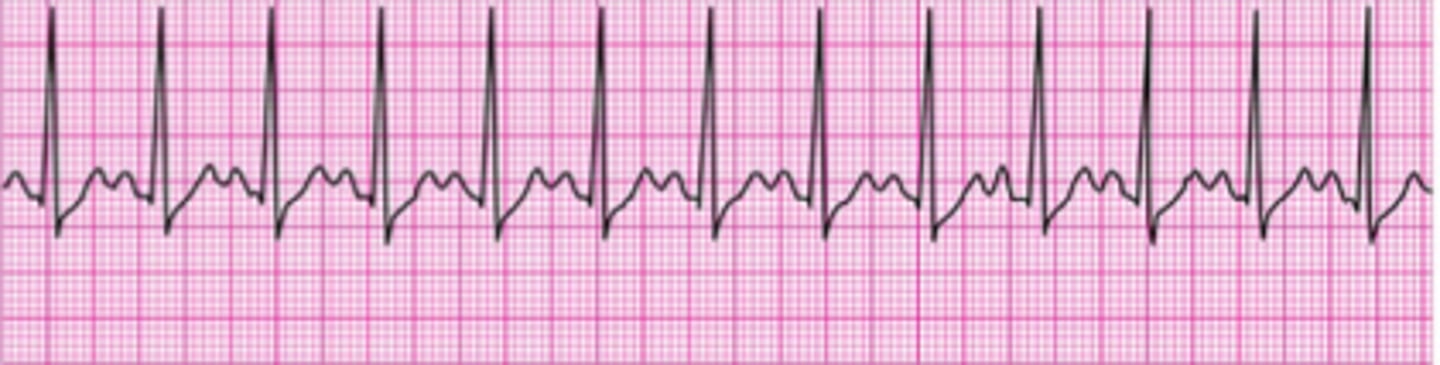
Sinus Tachycardia
- >100 bpm
- Common causes: severe anemia, hyperthermia, hemorrhage, pain, fever, anxiety, sympathomimetic or parasympathetic Drug Administration.
- Treatment: treat underlying cause, hypoxemia = administer oxygen therapy.
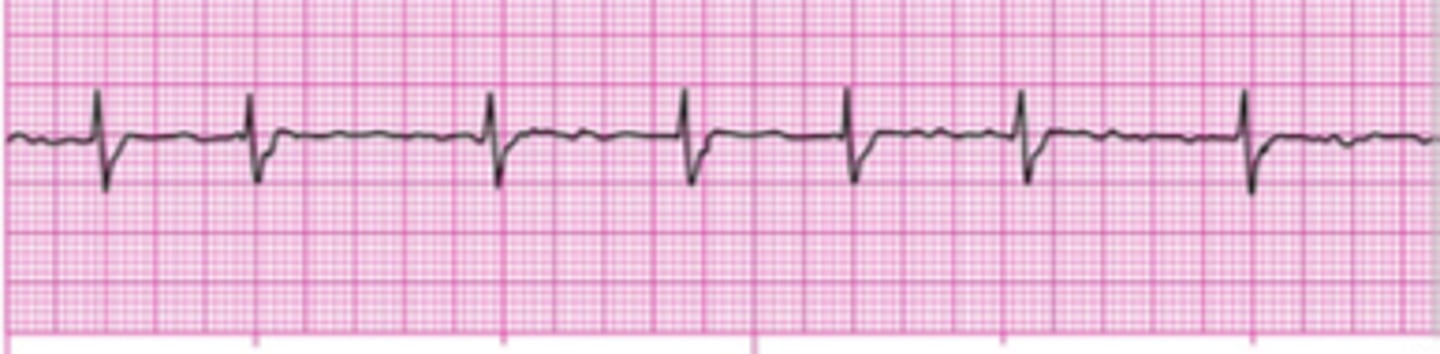
Atrial Flutter
Normal P wave are absent
and replaced by two or more
regular saw-tooth waves,
atria fires rapidly.
- Normal QRS complex
- Atrial rate is usually constant,
250-350 bpm
- Ventricular rate is in the
normal range
- Causes: hypoxemia, damage
to essay node and congestive
heart failure
- Treatment: Digoxin, beta
blockers, calcium channel
blockers.
Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial contraction are disorganized (quivering).
- No visible P wave
- Atrial rate ranges from 350-700 bpm
- Atria is clot
- Causes: hypoxemia, damage to SA node also seen in OSA.
- Treatment: digoxin, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, anticoagulants and thrombolytics.
Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC)
- The QRS complex is wide, bizarre, and unlike the normal QRS complex Is not preceded by a P wave
- The regular heart rate is altered by a PVC. May be very irregular when there are many PVCs
- Common causes – Myocardial disease, hypoxemia, acidemia, hypokalemia, CHF. Also noted during theophylline, alpha stimulant and beta agonist toxicity.
- Treatment: oxygen, lidocaine
Bigeminal PVC
PVC after a normal heartbeat
Trigeminal PVC
PVC after q 2 heartbeats
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach)
- P wave is not seen
- QRS complex = wide and bizarre
- Ventricular rate ranges from 150 to 250 bpm
- Blood pressure & LOC is often decreased during ventricular tachycardia -> medical emergency
- With pulse -> cardioversion, lidocaine, amiodarone
- Without a pulse -> defib, compressions, epinephrine & amiodarone
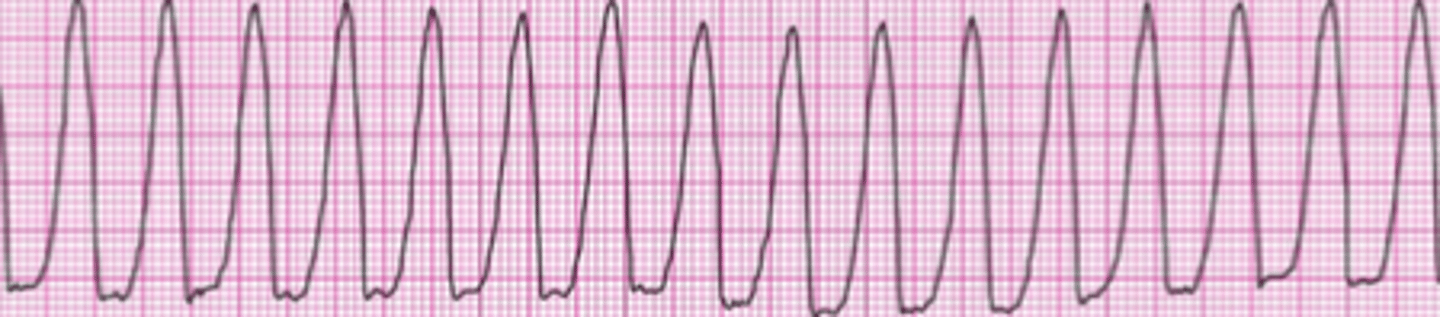
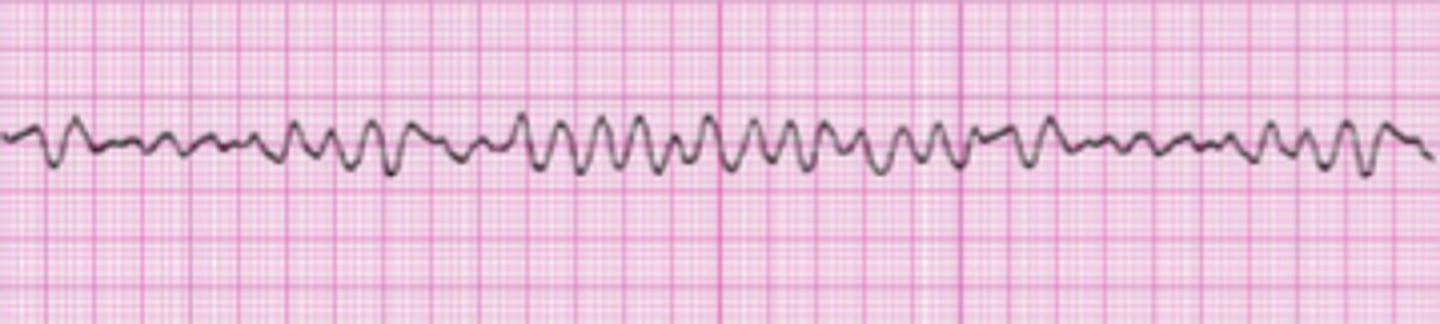
Ventricular Fibrillation
- Chaotic electrical activity and cardiac activity
- Ventricles quiver
- There is no perfusion beat-producing rhythm
- The is no cardiac output or blood pressure.
- The patient will die in minutes without treatment – CODE
BLUE
- Treatment: Defibrillation and CPR until ROSC
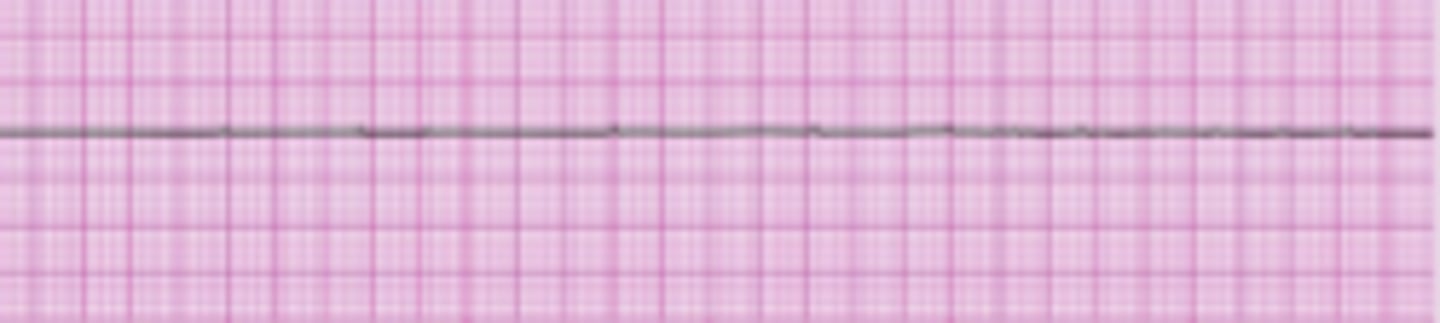
Asystole (Cardiac Standstill)
- The complete absence of electrical and mechanical activity
- Cardiac output stops, and the blood pressure falls to zero.
- The ECG tracing appears as a flat line
- Treatment: CPR and ACLS
Most Common Causes Of Cardiac Arrest
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Asystole
Hemodynamics
The forces that influence the circulation of blood
Invasive Cardiovascular Monitoring Assessments
- Invasive monitoring = assessment and treatment of critically ill patients.
(1) intracardiac pressures and flows via a pulmonary artery catheter
(2) arterial pressure via an arterial catheter (systemic) (3) central venous pressure via a central venous catheter
(4) coronary artery pathology (e.g., the use of the procedure coronary angiography
Systemic Arterial Catheter
The most commonly used mode of invasive hemodynamic monitoring
• Referred to as an a-line
• More accurate than cuff pressures
• Measures:
- Continuous systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial blood pressure
Fluctuations in blood pressure
- Data for guidance of therapy decisions for hypotension or hypertension ABG blood draws
CVP
2-6 mmHg
PAP (pulmonary artery pressure)
- 15-35/5-15
- 25/10
PCWP (pulmonary capillary wedge pressure)
4-12 mmHg
Cardiac Output (CO)
4-8 L/min
Stroke Volume
40-80 mL
Stroke volume index
40 ± mL/beat/m2
Cardiac Index
3.0 ± 0.5L/min/m2
Pulmonary vascular resistance
50-150 dynes × sec × cm-5
Systemic vascular
resistance
800-1500 dynes × sec × cm−5