NSAIDs
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors: Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Acetaminophen
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors
Aspirin and related drugs
Aspirin protects against MI and stroke
Inhibit__prostaglandin synthesis_________; mediator of the inflammatory reactions ___
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors USE
Suppress inflammation
relieve pain_______
Reduce fever
Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors AE
Gastric ulceration ________
Bleeding_______________
Renal impairment
Four adverse effects of cyclooxygenase inhibitors
Gastric Ulceration
Bleeding___________
Renal Impairment
May cause _MI and Stroke
COX 1 COX 2
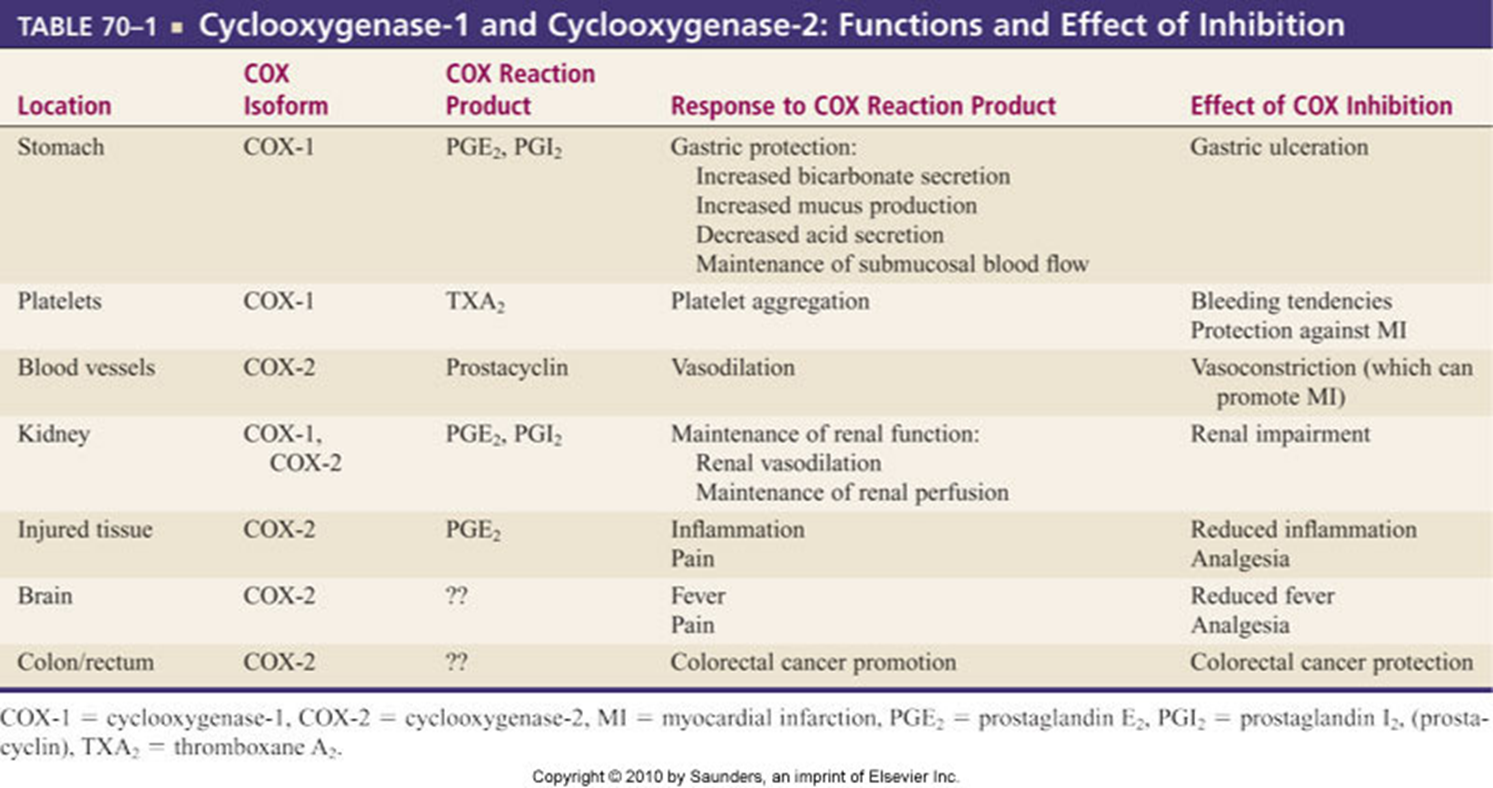
COX 1 (Housekeeper)
Protects gastric mucosa
Supports renal fxn
Promotes platelet aggregation __________
COX 2
Produced at tissue injury sites.
Mediates inflammation________________
Receptors sensitized to painful stimuli
Mediates fever and pain perception _____
Vasodilitation
COX I
Protects Gastric Mucosa
Supports renal fxn__
Promotes platelet aggregation________
COX I Inhibited
Gastric erosion and ulceration________
Bleeding tendencies_
Renal __impairment
COX II
Produced at tissue injury sites.
Mediates inflammation__
Receptors sensitized to painful stimuli
Mediates fever and pain perception__________
Vasodilitation
COX II Inhibited
Inflammation is suppressed.
Pain is alleviated _____
Fever is ____reduced_____
Protection against colorectal cancer
Vasoconstriction
Drugs with anti-inflammatory properties
NSAIDs: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Aspirin
Ibuprofen___________________
Naproxen
Celecoxib__________________
NSAIDs: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Aspirin
NSAIDs: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Ibuprofen
NSAIDs: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Naproxen
NSAIDs: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Celecoxib
Drugs without anti-inflammatory properties
Acetaminophen
Para-aminophenol derivative_____
1st gen NSAIDS
Aspirin (P)
Aspirin (P)
Inhibits COX I and COX II
Suppresses pain & inflammation; promotes gastric ulceration, bleeding and renal imp___
2nd gen NSAIDS
coxibs
coxibs
Inhibits COX2 only. Suppresses pain and inflammation with increased Stroke and MI risks.
Effects of NSAIDS
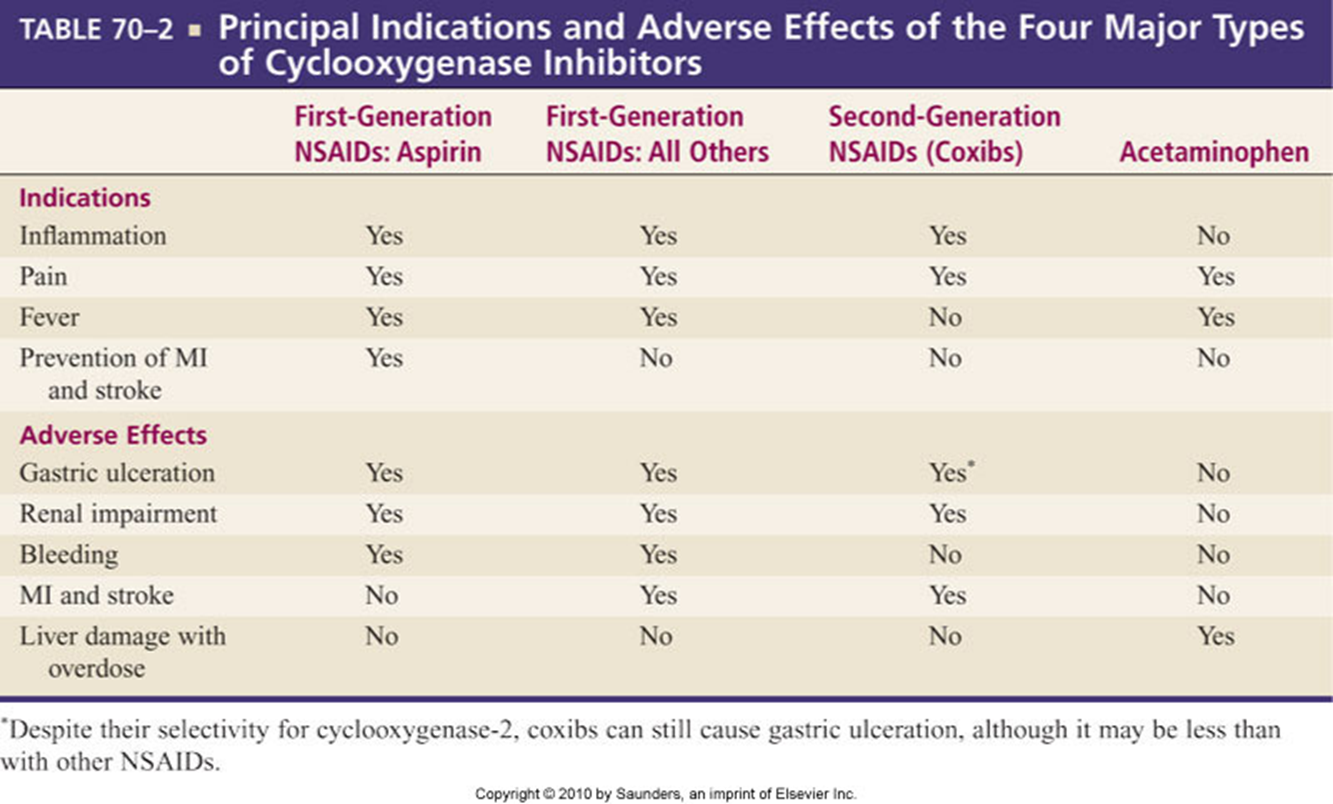
First-Generation NSAIDs
Inhibit COX-1 and COX-2
First-Generation NSAIDs: Tx inflammatory disorders
RA_________________________
OA________________________
Bursitis______________________
Alleviate mild to moderate pain
Suppress fever
Relieve dysmenorrhea
First-Generation NSAIDs: Risk
Suppress inflammation but have risk of serious harm
NSAID-induced ulcers
Aspirin (Salicylates)
Nonselective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase
Irreversible inhibitor of COX
Aka Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA)
Aspirin Therapeutics:
Analgesic
Small doses_____________
Antipyretic
Small doses
Anti-inflammatory
Large doses___________________
Suppression of platelet aggregation
Protects in thrombotic disorders
Dysmenorrhea
Aspirin AE
GI
Distress__________________
Heartburn
Nausea___________________
NI: Food of full glass of water
Bleeding_________________
Renal impairment
Salicylism (aspirin overdose)__________
HOLD the ASA
Reye’s syndrome____________________
Encephalopathy
Pregnancy
Postpartum ___hemorrhage_______
May prolong labor
Hypersensitivity reaction
Patient teaching: Box 16-3
Contraindications – use aspirin (overdose), acholol
Aspirin Drug interactions
Anticoagulants
warfarin and heparin _______
Glucocorticoids
Promote gastric ulceration
Omeprazole reduces GI risk__
Alcohol
Increases the risk of GI bleeds___
Ibuprofen
Reduces aspirin’s antiplatelet fxn
ACE inhibitors and ARBS_______
Acute poisonings
Salicylism
Nonaspirin First-Generation NSAIDs
Aspirin-like drugs
fewer GI, renal, and hemorrhagic effects than aspirin __________
20+ nonaspirin NSAIDs available
(all similar, but for unknown reasons, patients tend to do better on one drug or another)
Inhibit COX-1 and COX-2
inhibition is reversible (unlike with aspirin)
Principal indications
RA_____________________
OA_____________________
Do not protect against ____MI and stroke___
Increase the risk of thrombotic events.
Minimize CV risk: Lowest dose for the shortest time.
ex: indomethacin (Indocin)
First-Generation NSAIDs (Propionic Derivatives)
Drugs that inhibit prostaglandin synthesis in the CNS and PNS systems.
Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) (P)
Inhibits cyclooxygenase_______________
Anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic props _______
Tx: Fever, ___mild to mod, arthritis _________
Risk for MI and Stroke
Naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn)
Inhibits cyclooxygenase
Selective for COX I
Long half life
Tx: arthritis, dysmenorrhea, mild to moderate pain _______.
A/E: GI disturbances, increase MI and Stroke
Selective: Lower risk
First-Generation NSAIDs (Propionic Derivatives)
Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) (P)
Naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn)
First-Generation NSAIDs (Propionic Derivatives): Uses
Mild to moderate pain
Dysmenorrhea
OA and RA
Initial gout attacks
Fever in children > than age 6
First-Generation NSAIDs (Propionic Derivatives): AE
Dyspepsia________
Dry mouth
Heartburn
Nausea
Constipation______
Epigastric pain
GI ulceration_______
Gingerval hyperplasia
Nephrotoxicity
Elevated BUN__and creatinine
First-Generation NSAIDs (Propionic Derivatives): Contraindications
Sensitivities to ibuprofen and salicylates
Drugs that increase the effects of Ibuprofen:
Anticoagulants
Drugs that have an additive analgesic effects
Codeine
Oxycodone
Additive gastric irritant:
Corticosteroids
Patient Teaching:
Take the drug with food or fluid
Drink fluid daily when taking the drug regularly
Report any signs of bleeding to the practitioner
Alcohol, Ginger, Garlic, Ginkgo and Feverfew
increase bleeding risk
Oxicam Derivatives Drugs
meloxicam (Mobic) (P)
Piroxicam (Feldene)
Oxicam Derivatives
COX I and COX 2 Inhibitor
Anti-inflammatory, Analgesic, and Antipyretic effects___
Uses: ___OA and RA______
Onset: 1 hour
Peak: 5 to 6 hours
-Contraindications
Allergies_________
Creatinine clearance less than 20ml/min is not recommended.
Oxicam Derivatives AE
SOB
Bronchospasm______
Hemoptysis
Hematuria
Bleeding_________
Decreased platelets
Decreased H & H
Bone marrow depression_
Edema
N/V
Diarrhea__
Black Box:
CV Events/GI Bleed
Acetic Acid Derivatives Drug
indomethacin (Indocin) (P)
Acetic Acid Derivatives Uses
RA_________________________
OA_________________________
Bursitis
Tendonitis
Gout
ketorolac (Toradol)
Anti-inflammatory effects; more severe adverse effects that propionic acid derivatives.
Powerful analgesic______________
No respiratory depression or physical depression
A/E: Peptic ulcers, GI bleeds, Prolonged bleeding time
Acetic Acid Derivatives AE
H/A
Dizziness
Insomnia
Gi Bleeds_______
Abdominal pain
Distention
Transient ileus _____
Renal impairment
Decreased clotting time
Acetic Acid Derivatives Contraindications
Hypersensitivity
Hx of GI bleeds
Status post CABG_
Acetic Acid Derivatives: Parenteral Formulations are contraindicated
Bleeding
Thrombocytopenia
Coagulation defects
Drugs that increase indomethacin effects:
Phenytoin___
Salicylates
Sulfonamides_
Sulfonyureas
Drugs used with indomethacin that increase the risk of bleeding:
Salicylates
Anticoagulants
Lithium
Second-Generation NSAIDs (COX-2 Inhibitors)
Just as effective as traditional NSAIDs at suppressing inflammation and pain
Somewhat lower risk for GI side effects
May have bleeding_____________
Gastroduodenal ulcers
Can impair renal fxn
Cause HTN and Edema
Increase the risk for MI and stroke__, two coxibs withdrawn from use:
rofecoxib____ (Vioxx) and valdecoxib______ (Bextra)
Use of celecoxib has sharply declined
Celecoxib (Celebrex)
Second-generation COX-2 inhibitor
Fewer adverse effects than first-generation drugs
Because of cardiovascular risks, last-choice drug for long-term management of pain.
Celecoxib (Celebrex) Use
Osteoarthritis _________
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
Acute pain_____________
Dysmenorrhea
Celecoxib (Celebrex) AE
Gastroduodenal Ulcer____________
Cardiovascular Effects
Does not inhibit COX-1
Aggregation-----Not suppressed
Inhibits COX 2---promoting vasoconstriction
Renal toxicity_______________________
Impairs renal fxn
COX 2 inhibited
Sulfonamide allergy
Use in pregnancy
May close may cause premature closure of ductus arteriosus____
Celecoxib (Celebrex): Drug interactions
Warfarin
May decrease diuretic effects of furosemide_______
May decrease ___antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors___
May increase ___levels of lithium ____
Narrow therapeutic range
Levels of celecoxib may be increased by fluconazole
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) Therapeutic uses:
Analgesic, antipyretic
Does not have any anti-inflammatory or antirheumatic actions
Not associated with Reye’s syndrome __
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) MOA
Inhibits prostaglandin synthesis _____ in central nervous system
-> reduce fever and pain
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) AE
Very few at normal doses
Hepatotoxicity____________________
With overdose or in patients with liver failure
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) Overdose
Hepatic necrosis
S/S of hepatic failure, coma, death
Early symptoms: N/V, diarrhea, sweating, abdominal pain
The effect of ----__harmful, poisonous__------ or toxic substances on the liver resulting in liver damage.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) Treatment for overdose:
N-acetylcysteine (Mucomyst) ______
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) Drug interactions
Alcohol
increase the risk of liver injury from acetaminophen____
Warfarin
Increases bleeding ___warfarin metabolism is inhibited _________
AHA Statement on COX Inhibitors
Most COX inhibitors
Especially COX-2 inhibitors, increase the risk for MI and stroke.
AHA___recommends a stepped-care approach_____
Four basic steps
Nondrug measures
Acetaminophen/Aspirin
Ibuprofen/Naproxen
Last resort----COX 2 Inhibitor