HPS111 - Introduction to Psychology
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Define psychology
Scientific study of behaviour and mental processes.
History of psych? (Early + 20th century - main focus, and 3 areas)
Early ideas - Internal processes
Philosophers, biological explanations + psychodynamics.
20th century - behaviour
Behaviourism, humanism, modern neuroscience
Biopsychosocial model
Cognitions + behaviour may best be explained by the interaction between biology, psychology and social factors.
Types of psychologists (3)
Clinical psychologist
Organisational psychologist
Registered psychologist
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Brain + spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) and Somatic Nervous System
Complex system of nerves outside the CNS.
Involves skeletal muscles under voluntary control.
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
Involves smooth muscles under involuntary control.
- Homeostasis
ANS Applications
Parasympathetic regulates involuntary muscle movements - heart rate, breathing, etc.
Sympathetic is activated when encountering a stressor - being chased, scared, etc.
Macro + micro influences
Macro - culture, social norms, groups
Micro - Indivs. like family, romantic partners, work colleagues
Encephalisation quotient (EQ)
Metric of relationship between intelligence + brain size.
Brain mass/body mass
Limitation of EQ
Chihuahua's have the highest EQ, as they have oversized cranial volume relative to body size.
Cerebral cortex
Outermost layer of brain, contains higher-order abilities eg. language learning + complex thinking (uniquely human)
Corpus callosum + split brain surgery
Bridge of neural tissue between two hemispheres.
Corpus callosum is cut so hemi's cannot communicate (to isolate seizures in severe epilepsy)
Reflexes
Simple responses to the environment (1:1)
eg. touching smth hot, knee-tap reflex
Instincts
More complex response than reflex, more than 1:1
INBUILT, NOT LEARNED
eg. whale migration, turtle hatchlings heading towards sea
Limitations of neurobiological approaches (3)
1. 'Description' of what happened is not able to provide an 'explanation' for why.
2. Danger than current approach is just modern phrenology
3. Brain areas don't act in isolation
Neurons + glial cells
- Individual nerve cells which make up the brain + NS
- Provide nutrients to neurons + structural support to NS
Sensory, motor + interneurons
Transmit info. from sensory receptors to brain
Transmit info. from brain to body for functioning
Transmit info. from one neuron to another
Neuron structure (9)
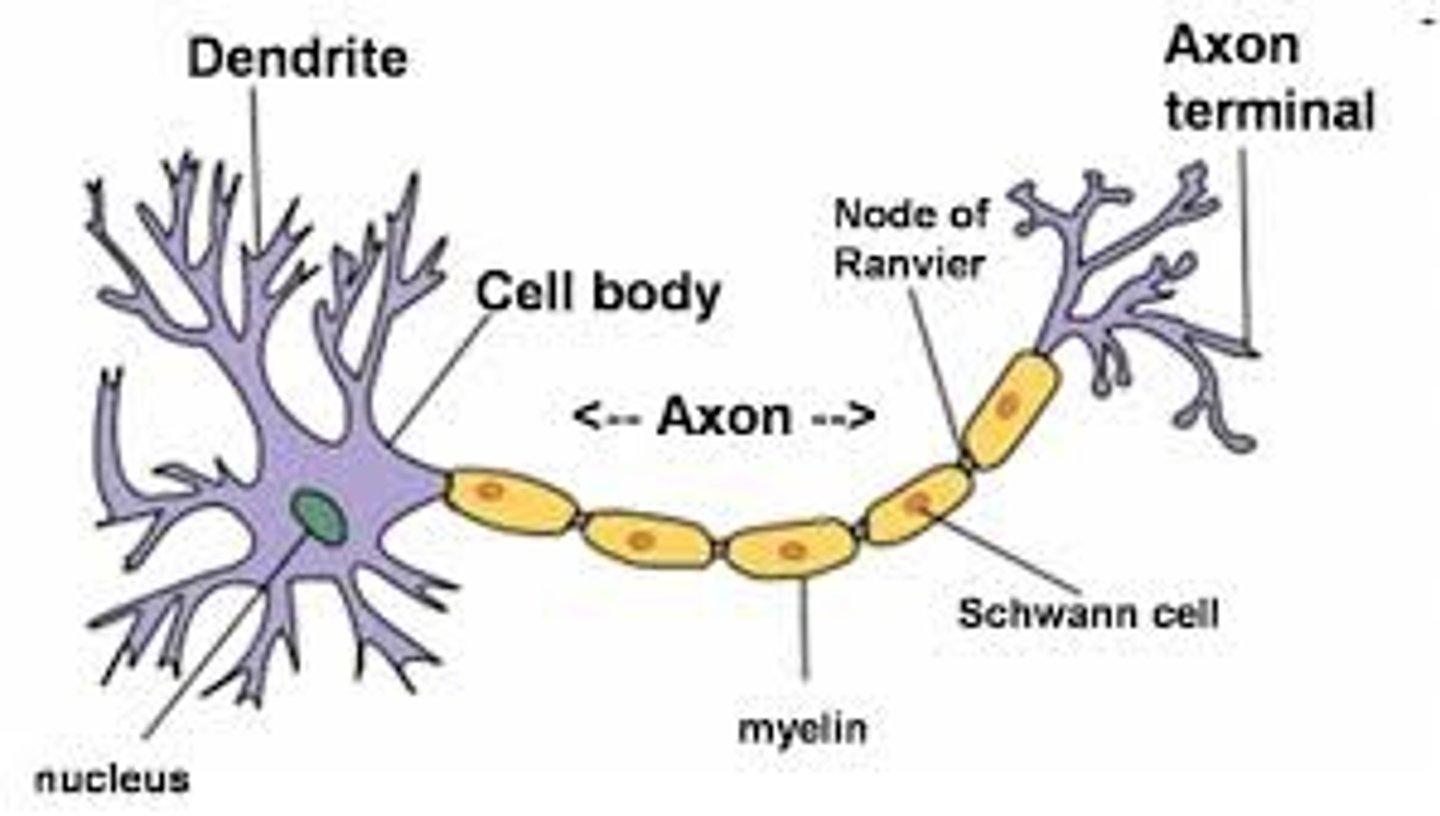
Grey + white matter (+ where each found)
Cell bodies + dendrites (outside of brain)
Myelinated axons of neurons which transmit info from grey areas (inside of brain, corpus callosum + spinal cord all white)
Neuronal communication - STEP A (def + 2)
- How dendrites + cell bodies receive info. from other neurons
1. Graded potentials are either excitatory (depolarising) or inhibitory (hyperpolarising)
2. All EPSP's or IPSP's converge at the axon hillock, with the general consensus of these signals translating to an "all-or-nothing" action potential
Neuronal communication - STEP B (def + 3)
- Processes which info. travels from axon hillock to terminal buttons via electrical intra-neuronal communication.
1. Excitatory threshold is reached, depolarisation causes the action potential.
2. Refractory period of hyperpolarisation occurs, enabling action potential to continue moving in the right direction.
3. Repeats at all Nodes of Ranvier through saltatory communication.
Neuronal communication - STEP C (2)
- How electrical signal turns into a chemical signal for communication across the synapse.
1. Neurotransmitters sit in vesicles in the terminal buttons.
2. Action potential will trigger these vesicles to move down the terminal buttons, fuse with the membrane and release the NT's into the synapse.
Ion (def, charges and names)
Molecule or chemical with a charge
Positive = cation
Negative = anion
Diffusion
Passive movement of a substance down a concentration gradient.
Electrostatic pressure
Passive attraction of oppositely charged ions + repulsion of similarly charged ions.
Charge at rest of intracellular + extracellular environment?
Intracellular - Negative (resting membrane potential = -70 millivolts)
Extracellular - Positive
Depolarisation + hyperpolarisation
D - causes inside of cell to become LESS NEGATIVE (+)
H - causes inside of cell to become MORE NEGATIVE (-)
What is the threshold for excitatory stimulation at the axon hillock?
-55 to -65 millivolts
Refractory period
Short period of temporary hyperpolarisation, where ion channels are unable to open which allows the action potential to flow in the right direction.
What type of communication is the signal using moving down the axon, and definition.
Saltatory communication - Each node acts as a booster continuing the signal along the axon (leaping between nodes)
Synaptic vesicles
Contain neurotransmitters
Descend down terminal button -> fuse w/ cell membrane + release NT's into synapse.
Lock-and-key principle (3)
- Specific neurotransmitters will bind to specific receptor sites based on shape.
- Chemical communication is much slower than electrical communication within neurons, as it is not goal-directed behaviour.
- Binding -> postsynaptic neuron will experience depolarisation (excitatory) or hyperpolarisation (inhibitory)
Clearing the synapse (3)
- Re-uptake sites in the presynaptic neuron.
- Enzymes in the synapse to break down NT's.
- NT's float off and out of the synapse.
Sensation (2)
Awareness resulting from stimulation of a sense organ.
- PHYSICAL effects of an environmental stimulus on our NS ('receptor cells'
Perception (2)
Organisation + interpretation of sensations
- PSYCHOLOGICAL effects of an environmental stimulus on our NS.
Sensory transduction
The process in which physical energy from the environment is converted into neural activity which can be interpreted by the NS.
Sensory receptors of the eye?
Cones - detect + compare colour (central part of retina)
Rods - Sensitive to light (periphery of retina) - useful @ night + in periphery vision.
Monocular depth cues
Relative motion/Motion parallax - Infer object depth based on speed they move past.
Occlusion - When one object blocks vision of another.
Binocular depth cues
Convergence + divergence - Extent our eyes need to "cross" to focus on an object.
Binocular disparity - Slight difference between images received by each eye.
Chemoreceptors
Transduce chemicals in food/air into "taste" and "smell".
Haptics
Touch
-> comfort
-> threat
-> intimacy
Gestures (def + 3)
Convey internal states through hand, arm and head movements.
-> Adaptors - self-touching behaviours (fidgeting)
-> Emblems - Agreed-upon meanings in cultures (thumbs-up)
-> Illustrators - Complement verbal messages
Facial expressions
Convey emotion + set the tone for communication (match facial expression to speech content)
Posture (2)
-> acknowledge others
-> express interest/dominance
Eye contact (4)
-> interest/intimidation
-> monitors feedback
-> pupil dilation
(cultures use eye contact differently)
Vocalics (vocal qualities) (4)
-> pitch
-> pace
-> volume
-> vocal quality
Proxemics (space and distance)
Close = comfort + attraction
Distant = lack of connection
Personal presentation + environment
- Physical characteristics
- Adorned + surrounding artefacts (jewellery = marital status, religious beliefs, etc.)
B.F. Skinner LA Theory
LA occurs through operant conditioning (reinforcement)
Eg. "Mum" = mother's attention, association btw. word + response (LA = environment/nurture)
Noam Chomsky LA Theory
LA Device - Innate LA ability (LA = genetics/nature)
The Classical Model (Wernick-Lichtheim Model)
Broca's area - Speech production (Frontal)
Wernicke's area - Language comprehension (Temporal)
Limitation of Classical Model (2)
- lexical level, doesn't contribute "how?"
- Broca's aphasia can occur without damage to Broca's area (+ Wernicke's)
Dual Stream Model (3)
Dorsal Stream - Phonological processing.
Ventral Stream - Semantic (word meaning) processing
- Includes many brain parts, simultaneously + across both hemis.
Linguistic determinism
Language DETERMINES thought processes.
eg. time conceptualised ^ or <-->
Linguistic relativity
Language INFLUENCES thought processes.
Emotions (def + 2)
Moment to moment responses to any eliciting event.
Primary - Initial response
Secondary - Feel emotion about unresolved primary emotion eg. feeling guilty about feeling jealous
Mood (3)
- Longer-lasting
- Trait-like w/ less extreme changes
- Personality can impact mood.
Affect
Umbrella term for emotion, mood + stress response.
3 aspects of emotion
Appraisal (cognitive/thought) - relevant? good, bad, neutral? (labels our feelings)
Arousal (physiological/feeling) - Increased heart rate, pupil constriction, etc. (can be confusing w/out appraisal
Behaviour - what we do to express or regulate the emotion.
Intrapersonal and interpersonal functions of emotions
Intra - Adaptive eg. widening eyes or scrunching nose
Inter - Communicate w/ others how we feel eg. smiling, or work to create a change in the environment eg. glaring
Fredrickson's broaden + build theory
When we feel more positive emotions, our thinking and vision broadens.
Parts of the brain responsible for emotion? (4)
1. The limbic system - Deep brain structures involved in emotion, memory, regulation + motivation.
2. Cingulate cortex - Experience + expression of emotion
3. DLPFC - Emotion regulation + goal-directed behaviour
4. No 'emotional centres' in the brain
Motivation
A process that influences the direction, persistence + vigour of goal-directed behaviour.
Self-determination theory (3)
3 fundamental human needs
1. Competence - View self as competent, learn + improve new skills
2. Autonomy - Making free choices
3. Relatedness - Form meaningful relationships
Selective attention
Allows us to attend to only the most relevant/one source of info. while ignoring others.
Parallel vs. serial processing
P - Differ on only one feature - several stimuli @ once to find which is different
S - Differ by multiple features - Attend to one target at time to search for both features.
Components of working memory (4)
Phonological loop - Briefly stores sound info.
Visuospatial sketchpad - Briefly stores visual + spatial info.
Episodic buffer - Temporary storage space where info. from slave systems + LTM can be manipulated.
Executive control - Controls sequence of actions performed in other subsystems.
Serial position effect
Primacy effect - Remember words from beginning (Rehearsal -> LTM)
Recency effect - Remember words from end (still in working memory)
Theories of forgetting
1. It never reached LTM
2. Retrieval failure
3. Memory decay
4. Interference
Proactive and retroactive interference
P - Past material interferes w/ recall of new material eg. saying old phone number instead of new phone number
R - New info. interferes w/ ability to recall earlier info. eg. can't remember old phone number
Songlines
Ancient stories passed down through generations of FN Australians + hold important historical, geographical and political info.
Intelligence (3)
The capacity to learn from experience
Using meta-cognitive processes to enhance learning
The ability to adapt to the surrounding environment.
CHC Theory of Intelligence
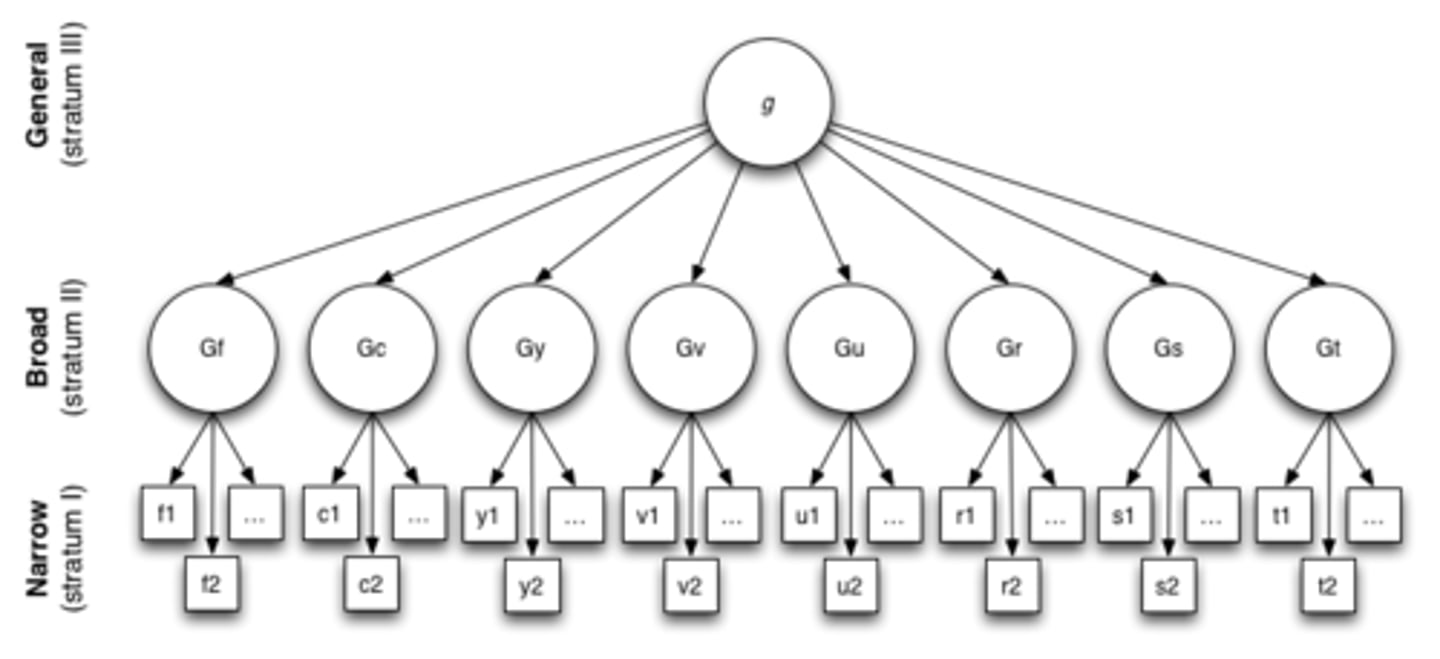
Fluid + crystallised ability (defs + theory of origin)
F - Ability to solve novel problems
C - How we use learned skills, knowledge + experiences (education)
CHC Theory of Intelligence
Limitations of Gardner's theory (2)
- Separating intelligences w/ no relationships
- Very hard to measure the constructs