AP Biology Unit 2 Cell Structure and Function
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
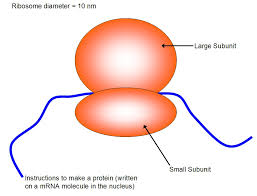
Ribosomes
Cellular Structures responsible for synthesizing proteins
Cytoplasm (Or Cytosol)
Jelly like substance that fills the inside of cell
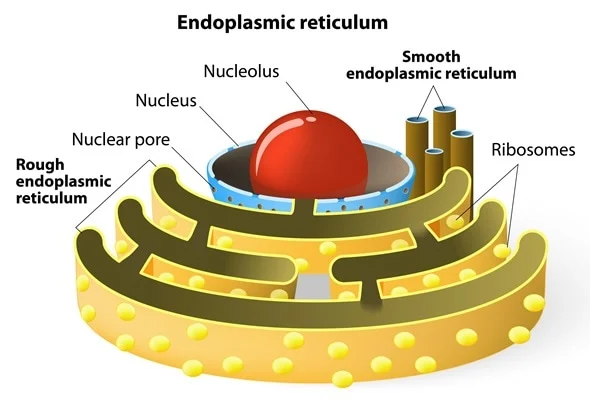
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Network of Membranes; considered the highway of the cell as materials travel through its membrane. Two types: Smooth ER(responsible for lipid synthesis, smooth surface), Rough ER(responsible for protein synthesis, surface filled with Ribosomes)
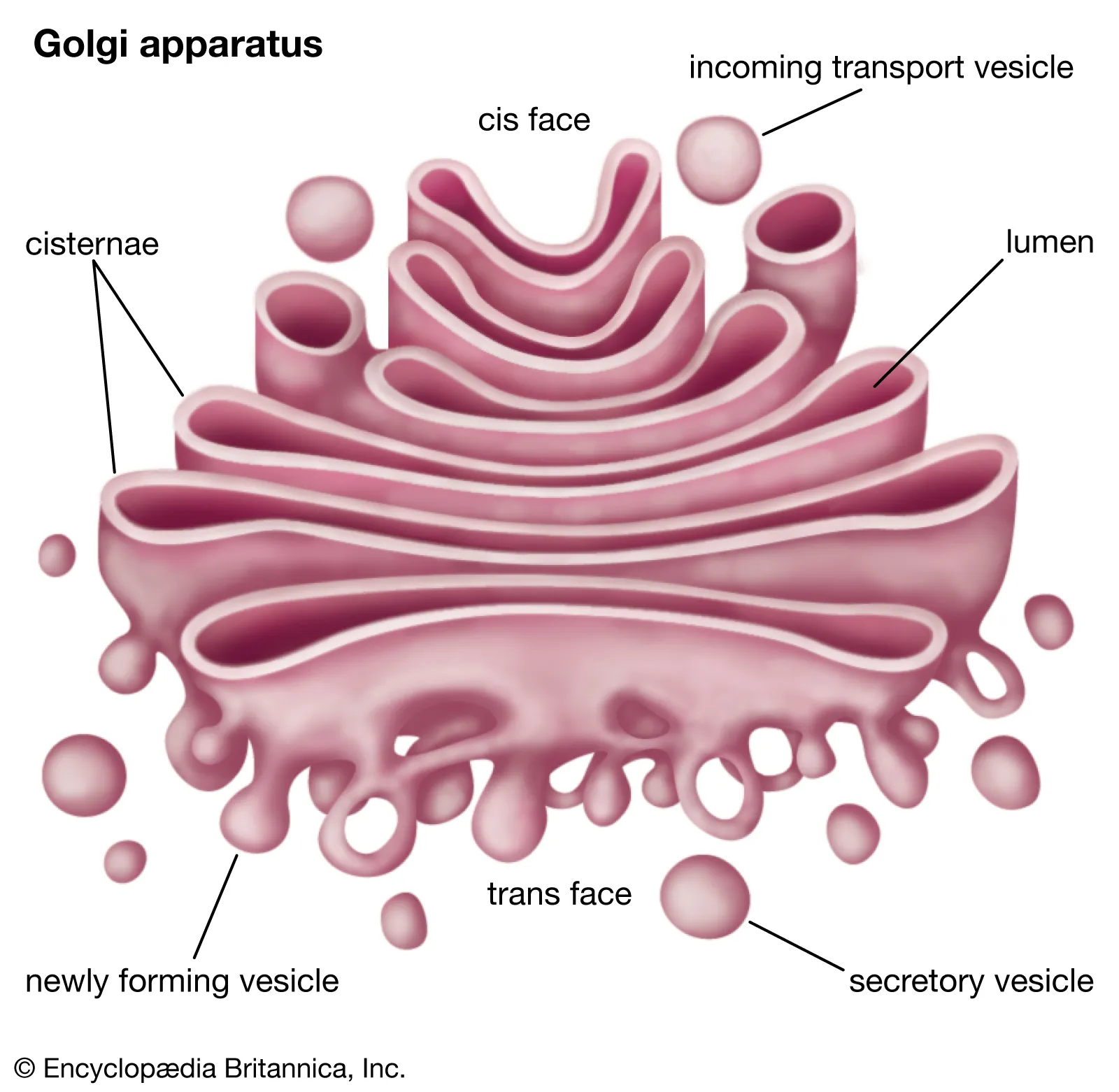
Golgi Complex (or Apparatus)
Set of membrane sacs responsible for processing, packaging, and shipping out produced proteins (think UPS headquarters)
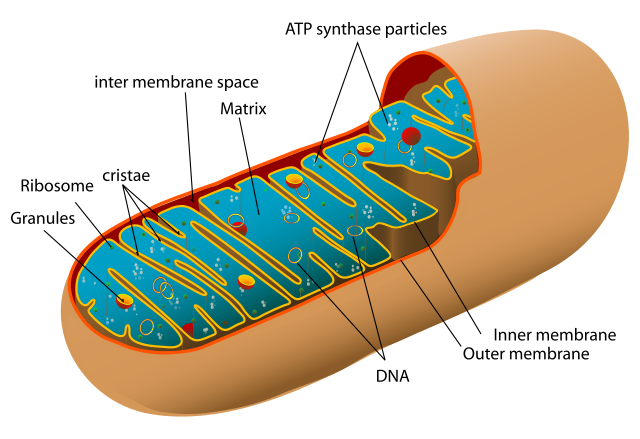
Mitochondria
Cell organelle responsible for cellular respiration/ATP production (Found in Both Animal/Plant cells)
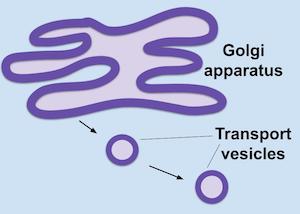
Vesicles
Small membrane sacs used as transport vehicles within the cell
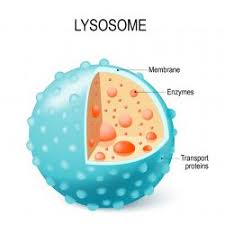
Lysosomes
Cell organelle containing digestive enzymes to breakdown materials (Animal Cells only)
Vacuole
Storage unit of the cell; water, nutrients, waste
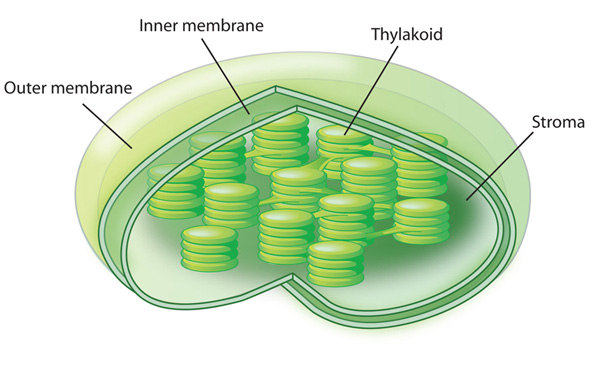
Chloroplast
Specialized PLANT cell organelles responsible for Photosynthesis
Mitochondrial Membrane
Mitochondria consists of an inner/outer mitochondrial membranes, creating an inner-membrane space
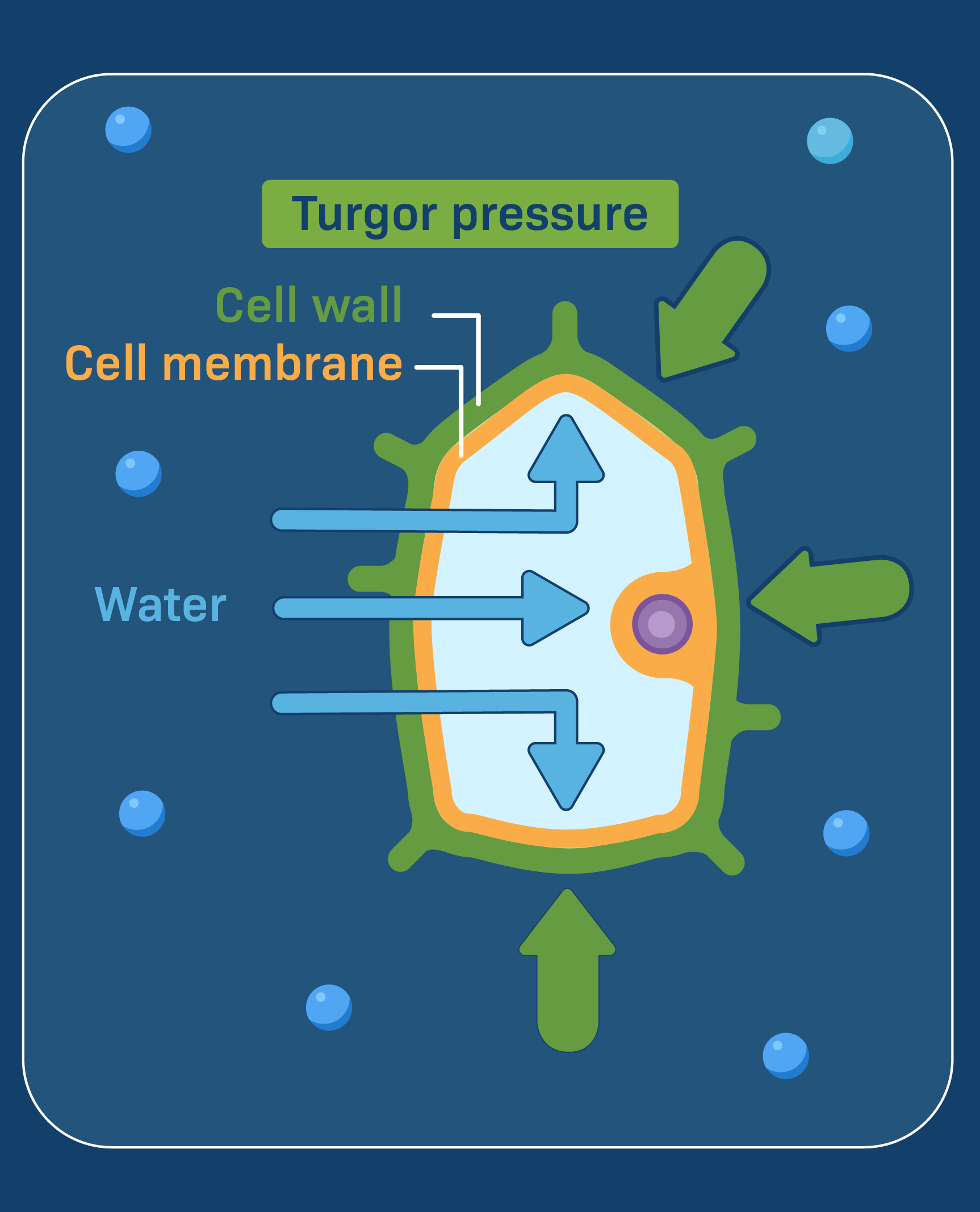
Turgor Pressure
Force exerted on a plant’s cell wall
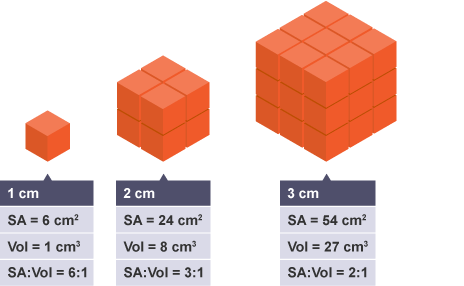
Surface Area-Volume Ratio
Ratio of a cell’s surface area to it’s volume. Influences how efficient substances are exchanged across a cell’s surface.
Surface area of a Sphere
R = radius
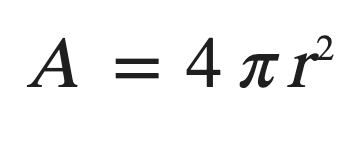
Surface Area of a Cube
S = side length of cube
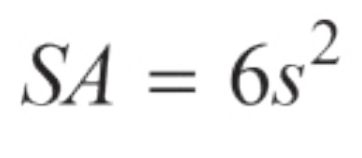
Surface Area of a Cylinder
H = height
R = radius
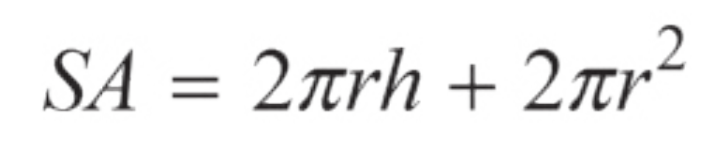
Surface Area of a Rectangular Solid
l = length
w = width
h = height
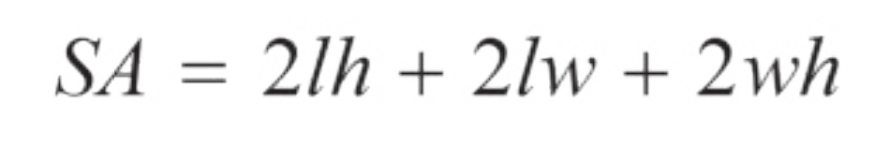
Volume of a Sphere
R = radius
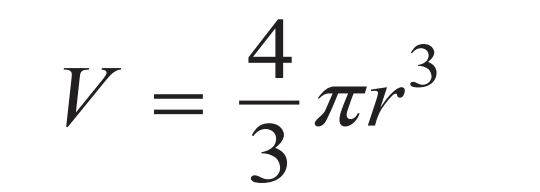
Volume of a Rectangular Solid
l = length
w = width
h = height
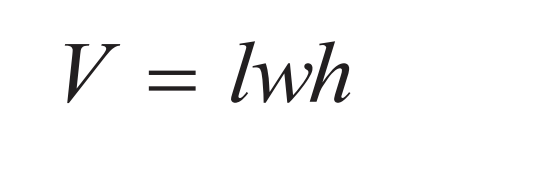
Volume of a Cylinder
r = radius
h = height
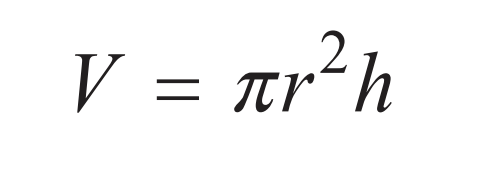
Volume of a Cube
s = side length of cube
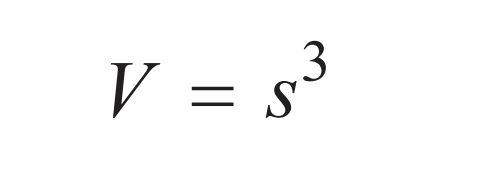
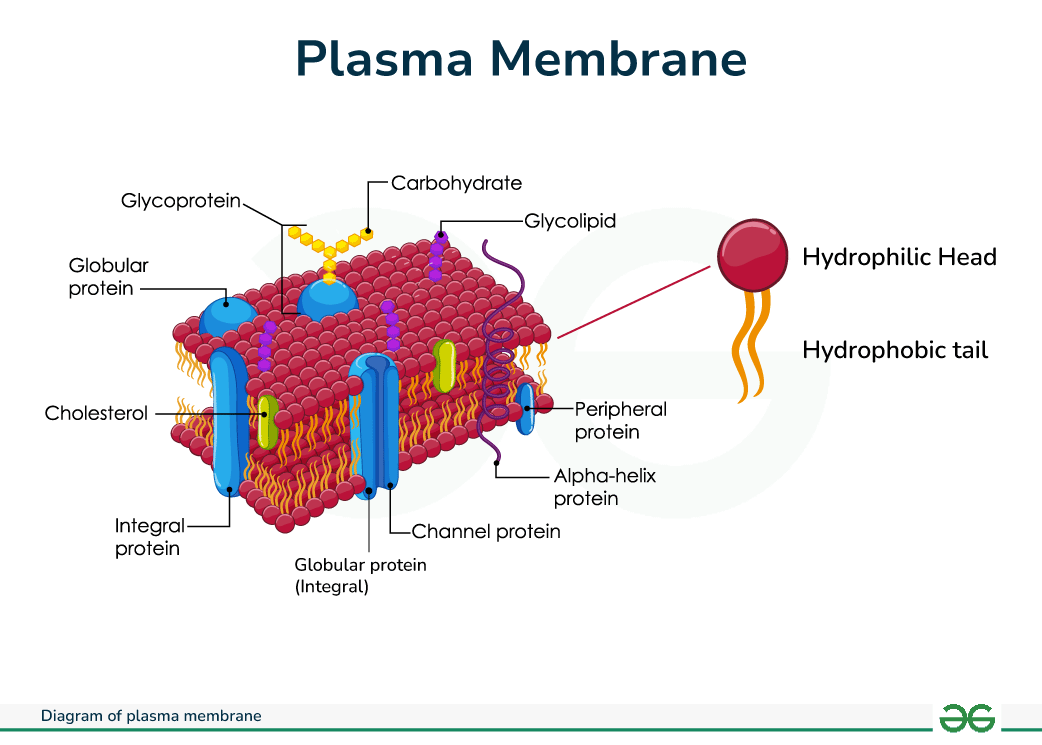
Plasma Membrane (AKA Cell Membrane)
Composed of phospholipid bilayer (double layer of phospholipids) and other proteins/lipids. Physical barrier between external environment and the inner cell organelles and regulates entry/exit of substances
Membrane Folds
Structures in the cell that are folded to increase Surface Area → Increased Efficiency in Organelle Processes
Heat Exchange
Process by which an organism maintains their body temperature by losing or gaining heat
Nutrient Exchange
Movement of essential substances (oxygen, glucose, amino acids) into cells and the removal of waste products (Carbon Dioxide)
Waste Elimination
Process in which organisms eliminate waste products from their body, ensuring homeostasis.
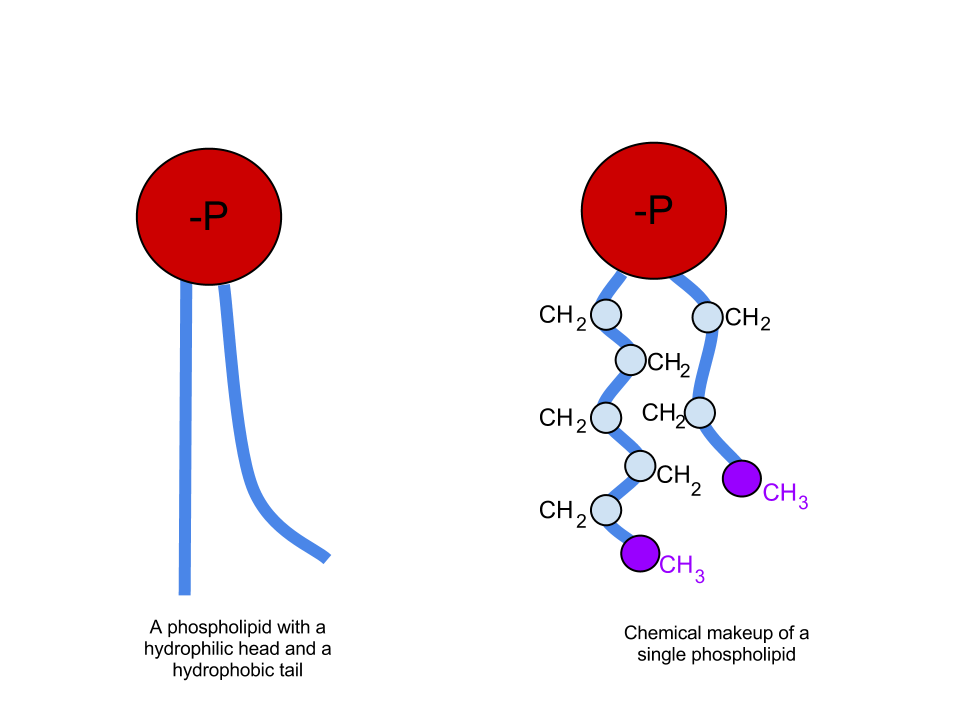
Phospholipids
Composed of a phosphate hydrophilic head and a fatty acid hydrophobic tail, forms the structure of the cell membrane
Hydrophobic
Substances that HATE water (oils, fats, waxes, fatty acid tails)
Hydrophilic
Substances that LOVE water (polar molecules, charged molecules, phosphate head)
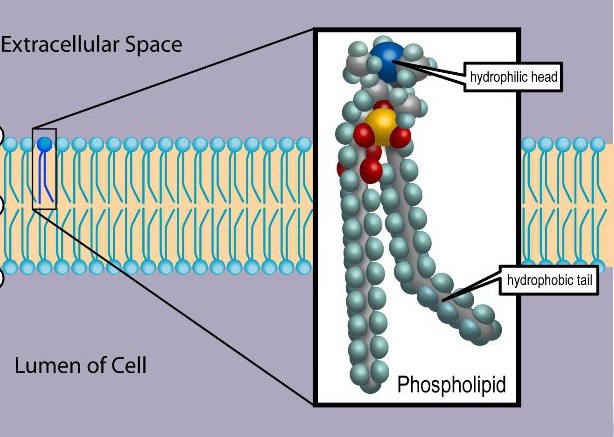
Phosphate Head
Polar hydrophilic end of the phospholipid bilayer, stick out in cell membrane
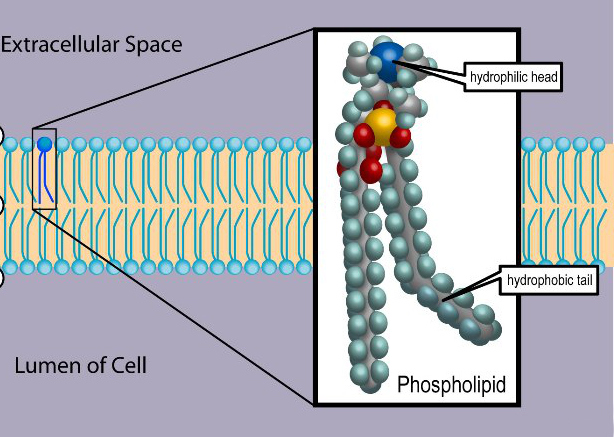
Fatty Acid Tail
Non-polar hydrophobic end of phospholipid bilayer, stays inside of the cell membrane
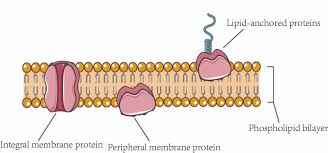
Embedded Proteins
Proteins that are permanently embedded in the cell membrane and span the entire membrane. Used for transport of substances across the membrane, cell-signaling, and cell recognition
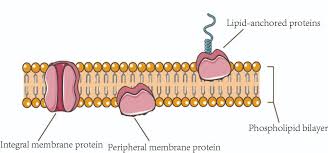
Peripheral Proteins
Proteins that are attached to the membrane, BUT are only attached to either the hydrophilic side or hydrophobic side.
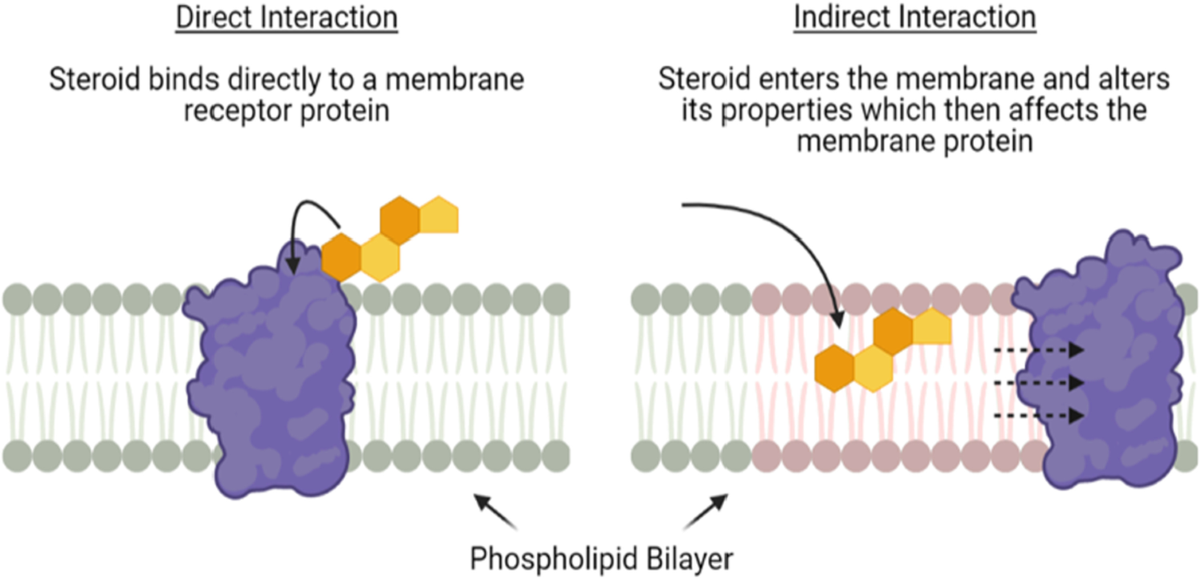
Steroids Role in Cell Membrane
Diffuses into the lipid part of the membrane. Used to maintain fluidity according to the external temperature of the environment
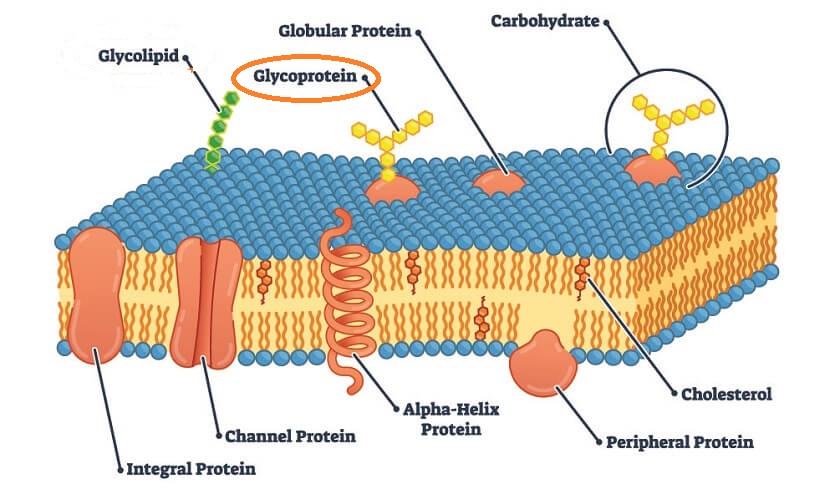
Glycoproteins/Glycolipids
Proteins and Lipids with one or more carbohydrates attached. Can be used as surface receptors on Cell Membrane

Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes the structure of the cell membrane as a fluid structure with multiple components being added on to the main bilayer.
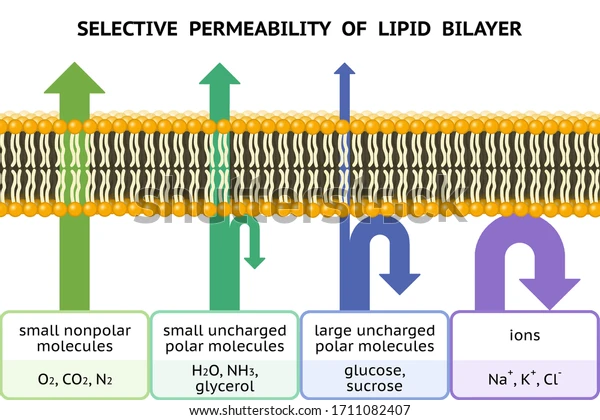
Selective Permeability
A membrane’s ability to allow some molecules to pass through while blocking other molecules based on a molecule’s polarity.
External Environment
Surrounding Conditions that influence a cell’s survival.
Internal Environment
Refers to the fludity inside of the cells.
Nonpolar Molecules
Oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, Fatty Acids
Hydrophilic Molecules
Glucose, some Amino Acids, Sodium chloride, Sodium hydroxide
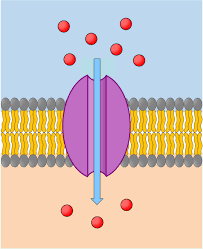
Channel Proteins
Proteins that allow transportation of specific molecules through the plasma membrane
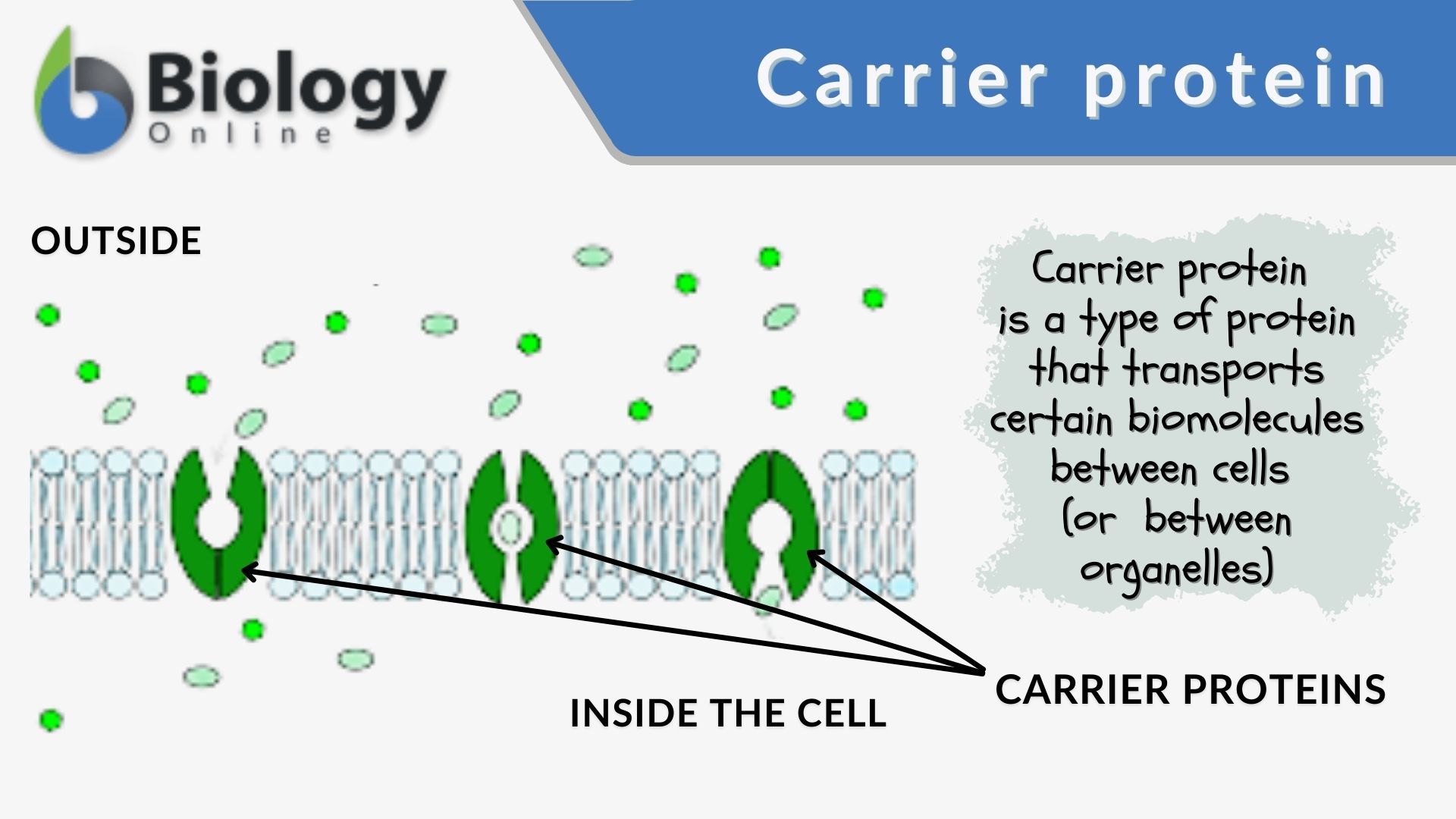
Carrier Proteins
Proteins on the membrane that bind to a surface, change its shape, and carry it across the cell membrane
Solutes
Substances that are dissolved in the presence of a solvent, usually water
Water
Can be used to dissolve solutes
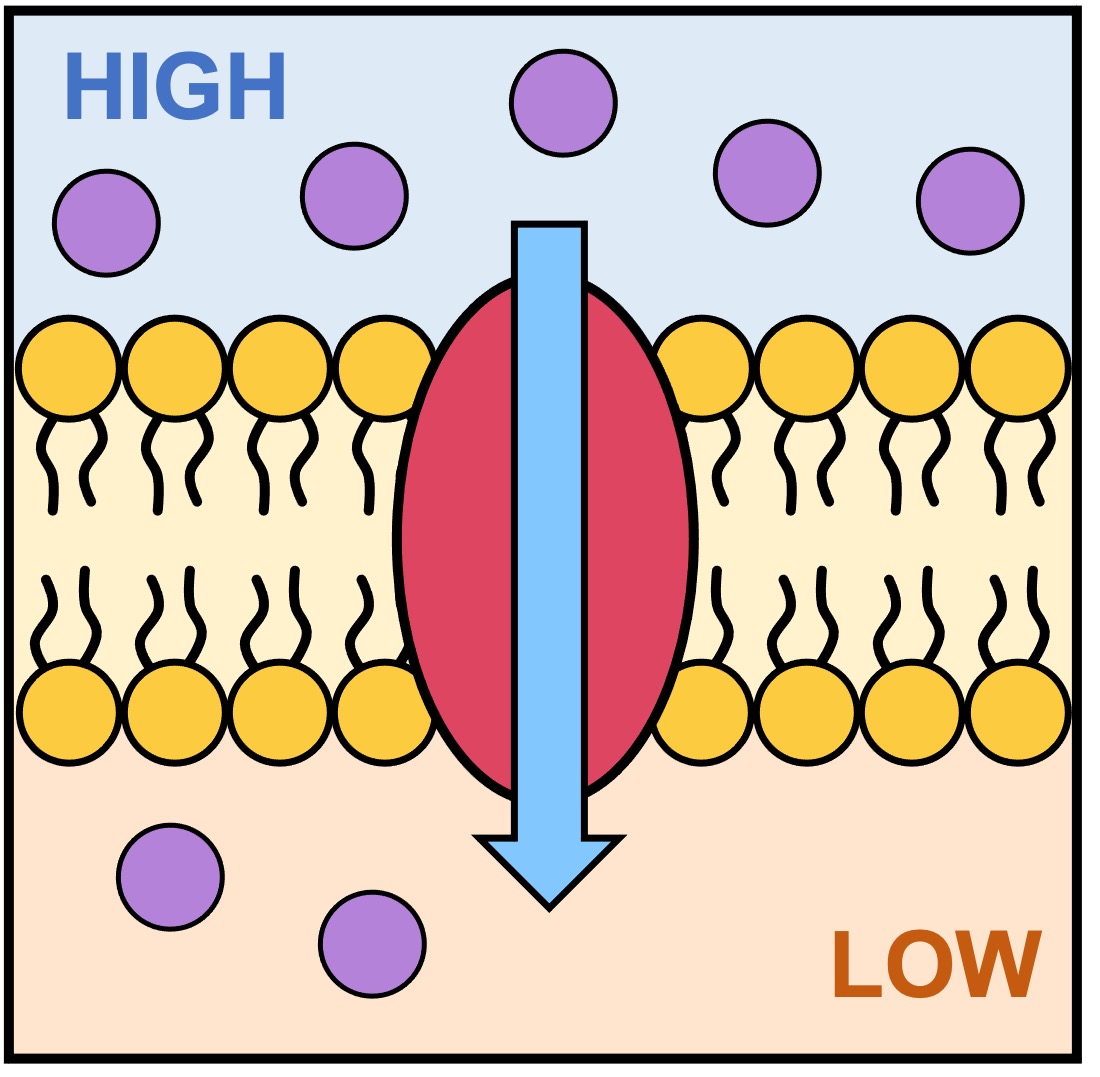
Passive Transport
Transportation of molecules across the cell membrane from high concentration to low concentration. Doesn’t require energy
Metabolic Energy
Energy released through metabolic processes, primarily to produce ATP
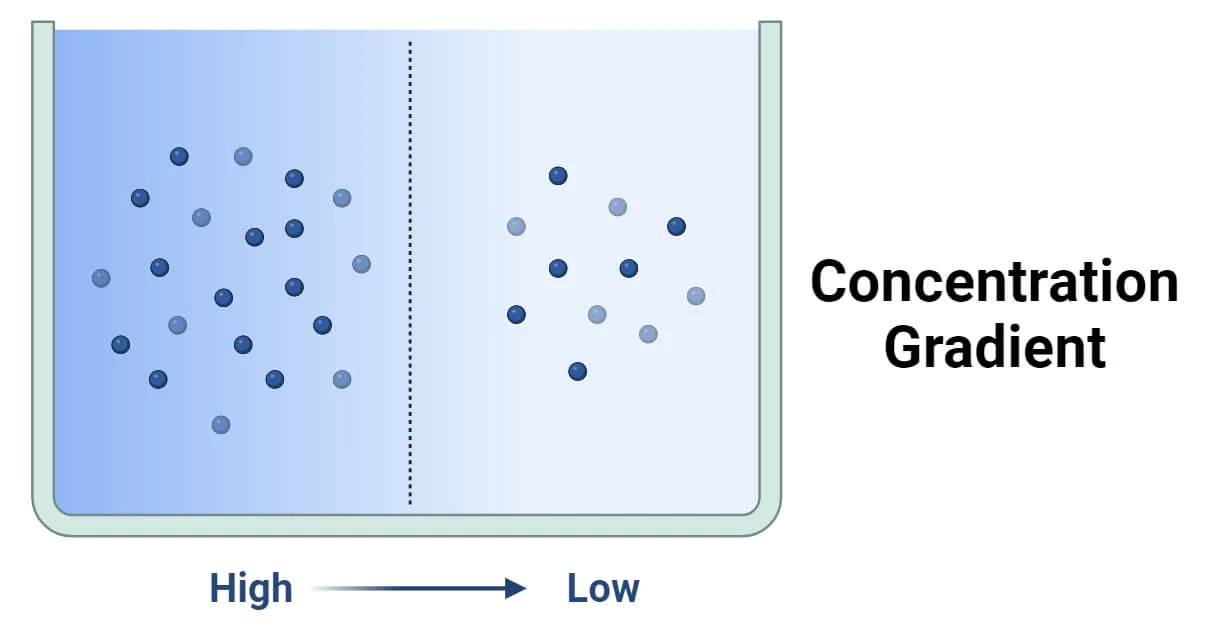
Concentration Gradient
Movement from solutes from a high concentration to a low concentration
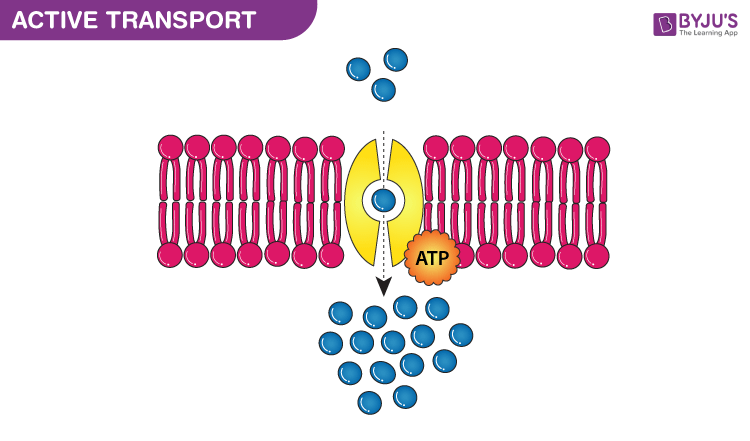
Active Transport
Type of membrane transport in which Energy in the form of ATP is used to move molecules from low concentration to high concentration.
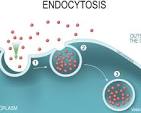
Endocytosis
Cell takes in material from the external environment and engulfs it with the cell membrane, creating a vesicle
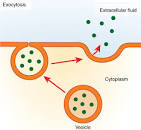
Exocytosis
Cell packs waste and other unnecessary materials into a vesicle, fuses the vesicle into the cell membrane and releases the vesicle into the external environment
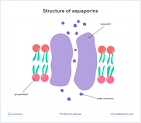
Aquaporins
Membrane proteins that serve as channels for water. Allowing for water transport across the cell membrane
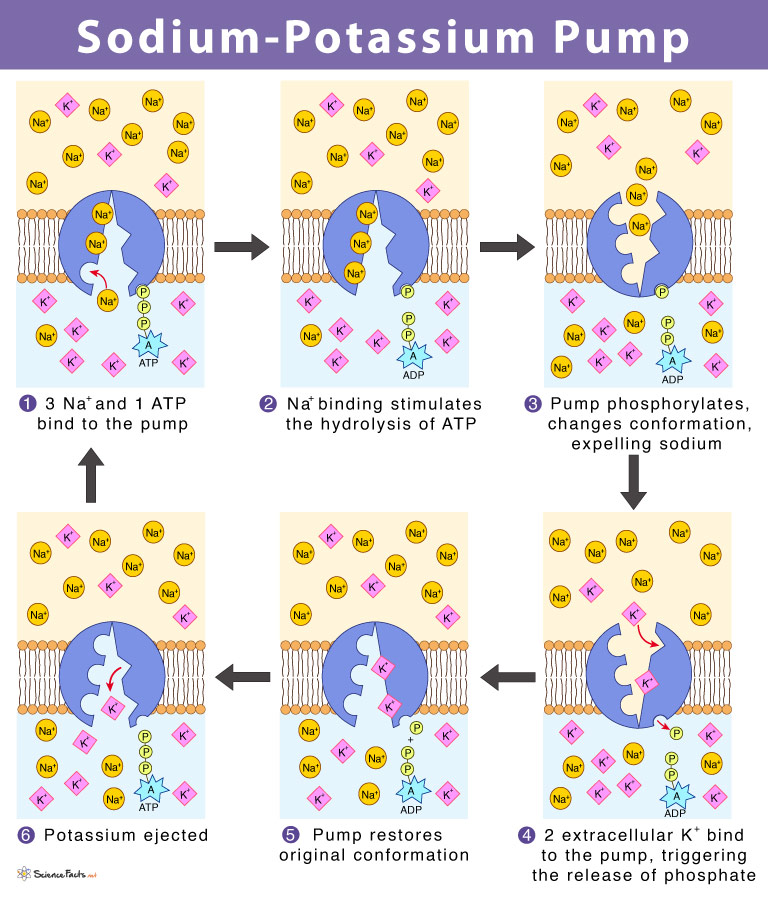
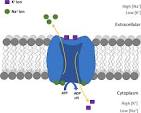
Na-K Pump
Membrane protein that actively transports Sodium/Potassium ions across cell membrane using energy from ATP hydrolysis
ATPase
Protein that uses ATP hydrolysis (ATP → ADP) to move ions across cell membrane
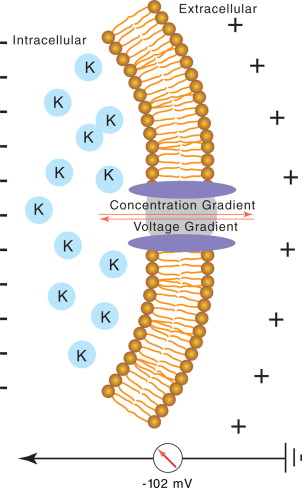
Membrane Potential
Difference in electrical charge between inside and outside of a cell’s membrane
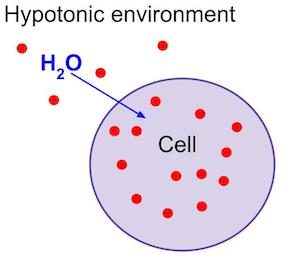
Hypotonic Solution
Solution that has a lower solute concentration compared to another solution. In terms of water potential of a cell, Water moves into the cell and the cell bursts
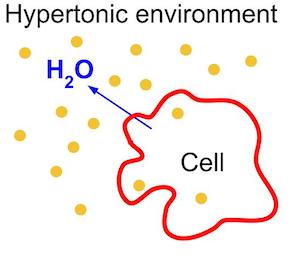
Hypertonic Solution
A solution that has a higher solute concentration compared to another solution. In terms of water potential of a cell, Water moves out of the cell and the cell shrinks
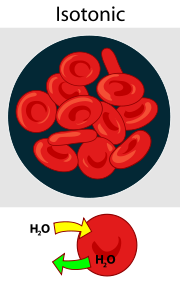
Isotonic Solution
Solution has equal amounts of solutes compared to another solution. This allows for a net flow of water in between solutions
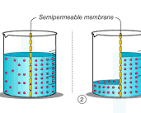
Osmosis
Movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from low solute concentration to high solute concentration
Pressure Potential
Physical pressure exerted on a cell’s wall by the cell’s content, including water
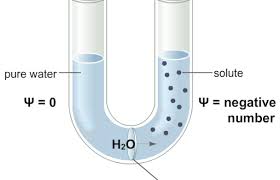
Water Potential
Tendency of water to move from one area to another due to various factors including solute concentration and pressure
Water Potential Formula

True or False: In an open container, the water potential is equal to the solute concentration of the container
True
Solute Potential
The influence of dissolved solutes on water’s ability to move across the membrane
Solute Potential Formula

Homeostasis
Organism/Organelle’s ability to maintain a stable internal environment
Kelvin Calculation
Given Degree in celsius + 273
Molar Concentration
The amount of solute (in moles) per unit volume of solution
Ions
Atom or molecule that has a net charge due to loss/gain of electrons
Membrane-Bound Organelles
Specialized structures within the cell that are enclosed by their own membrane. Ex: Mitochondria, ER, Golgi Body (note: ONLY FOUND IN EUKARYOTIC CELLS)
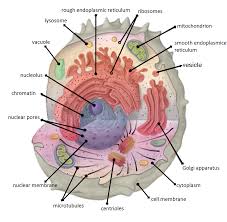
Compartmentalization
Separation of cellular functions into specific membrane-bound organelles to enhance efficiency
Internal Membranes
Specific Organelles have membranes that separate them from the rest of the cell, setting up compartmentalization
Intracelullar Metabolism
Chemical process that happens within the organelles of the cell that break down substances for energy
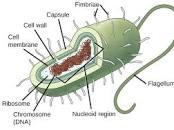
Prokaryote Cells
Bacterial Cells that have a plasma membrane, but no internal membrane-bound organelles
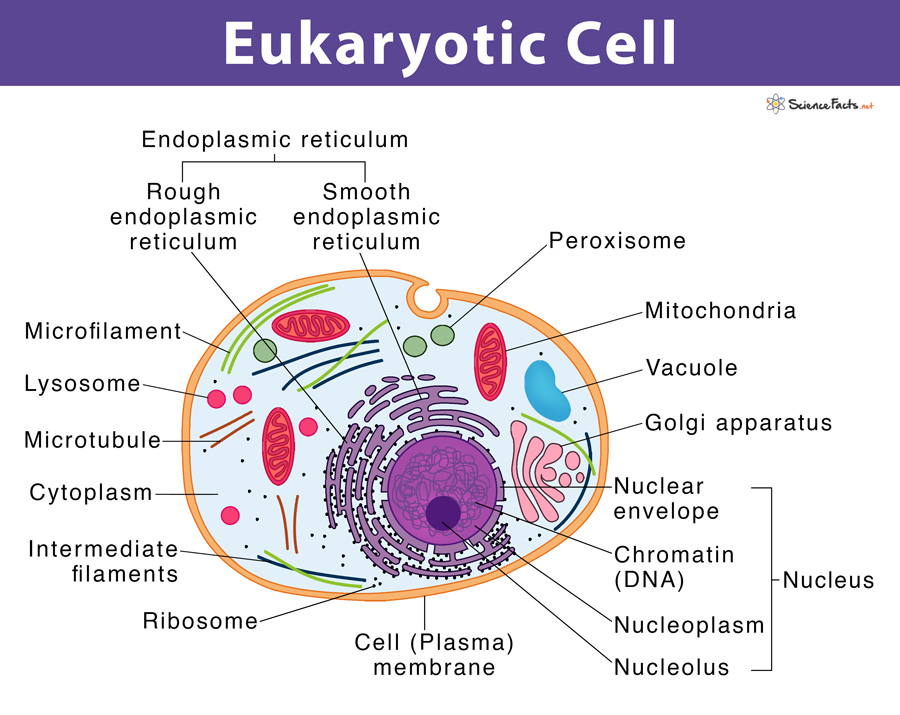
Eukaryotic Cells
Animal/Plant Cells that uses internal membrane-bound organelles
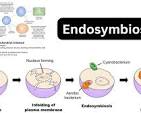
Endosymbiotic Theory
Some eukaryotic organelles like the Mitochondria originated as prokaryotic cells until they were engulfed by larger Eukaryotes, establishing a symbiotic relationship which would evolve later on into the internal membrane-bound organelles.