cell molec
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
|
share the same basic chemistry.
The inner membrane of the mitochondrion when examined with transmission electron microscopy appears _
folded with a large surface area to allow energy production (ATP synthesis) to take place.
|
the composition of the membrane
The organelle shown in the figure is the ___________ and one of its main functions is to______
Golgi apparatus; package and modify proteins, such as glycosylation, for secretion
|
self-replicatory.
The defining property that differentiates prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells is their
lack of a nucleus
The cellular process by which vesicles are secreted from cells is called:
exocytosis.
|
nerve
|
house the DNA and ribosome synthesis machinery.
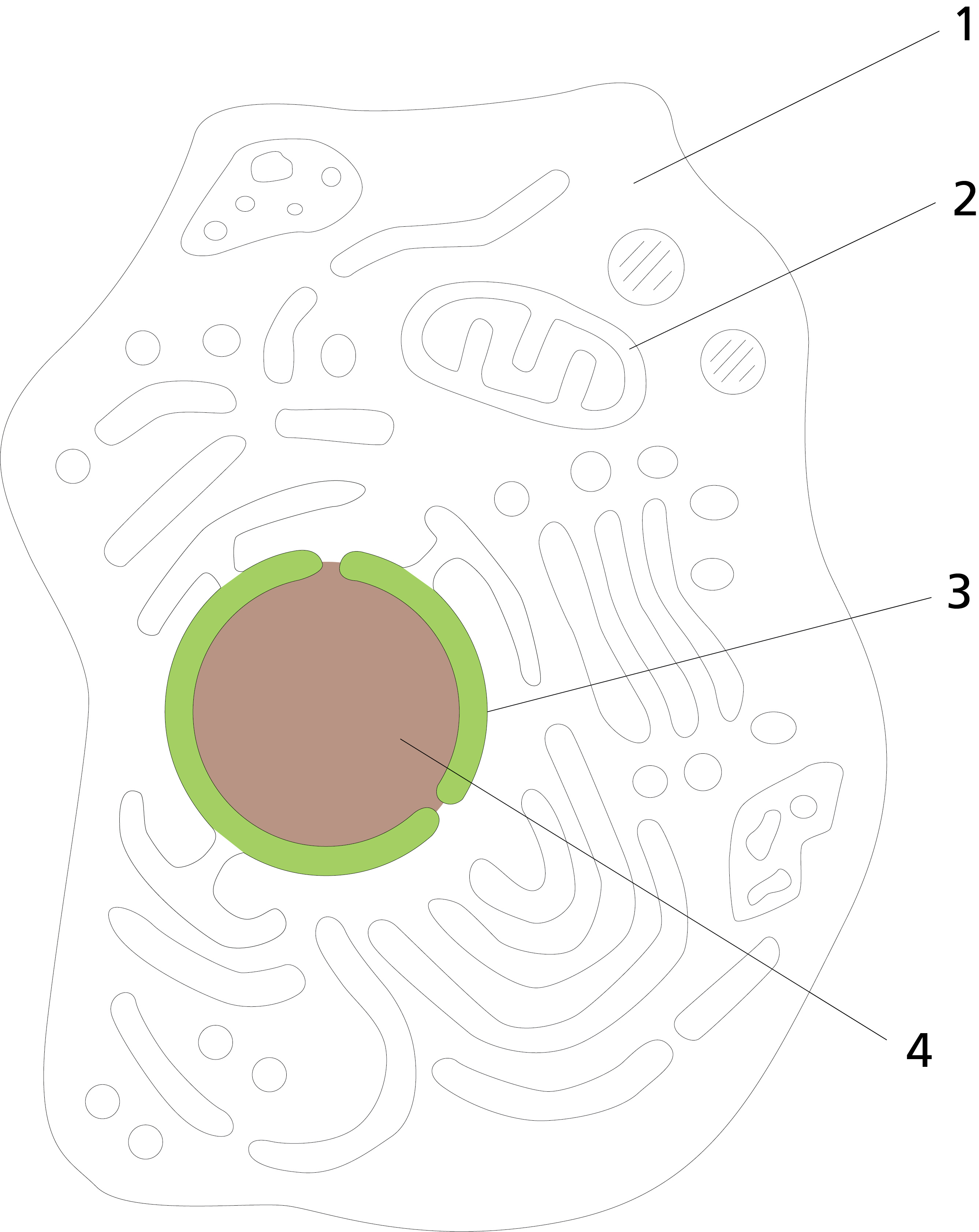
|
nuclear envelope
Substances that do not form polar bonds are likely to be:
hydrophobic
A molecule with a large number of polar covalent bonds is likely to
be highly soluble in water.
What is the function of proteins inside cells?
they can serve as structural support, they can play a role in ligand recognition and signal transduction, &
they can reduce bacterial loads through forming barriers on cells
Which of these sugar molecules is NOT a monomer:
sucrose (monomers are ribose, glucose, and fructose)
Hydrolysis is________to _____molecular bonds.
addition of water - break
|
glycogen (found in plants is cellulose, starch, and pectin)
Where are glycoproteins mainly found?
bound to the outer plasma membrane
Long polymers are made from single subunits in cells using a ___________ reaction, which ___________ water.
condensation; releases
Triacyglycerols are ______
the most common fat storage molecules in cells
|
N, C
Gibbs free energy is more likely negative when_____
entropy increases and enthalpy is low
Energy carriers are activated__
during the breakdown of molecules
Gibbs free energy is negative when___
bonds are broken
An enzymatic reaction will most likely proceed if_____
the activation energy is lower than the energy expended to promote a reaction.
𝚫G indicates__
the change in a reaction from substrate to product
Equilibrium refers to a state where____
reactants and products do no longer change
The 2nd law of thermodynamics stipulates that____
entropy increases
In Catabolism, molecules are____whereas in Anabolism molecules are_______
broken down; synthesized
Enzymes__
lower the activation energy without participating in the reaction between two reactants leading to a product.
|
NADH, NADPH, & ATP
An antibody interacts with an antigen through_
its heavy and light chain variable region
The first amino acid to be discovered was__
Asparagine from Asparagus in 1806.
A glycoprotein _
may participate in viral transfection, is assembled in the Golgi apparatus, locates within the plasma membrane with the sugar moeity facing to the extracellulars space.
What is the difference between a peptide and a protein?
Peptides are made up of linear amino acid chains.
|
quaternary
Hydrogen bonding between NH and C=O groups of every 4th amino acid within the polypeptide backbone results in which type of folding pattern?
α helix (D)
Which of the following represents secondary structures in a protein?
a-helix
A protein can interact with water and lipds because____
it has polar and hydrophobic amino acids
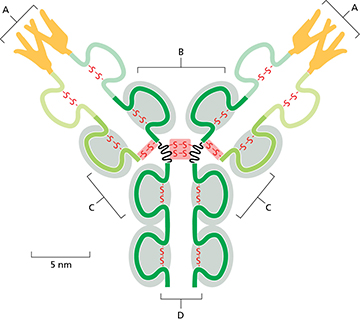
The figure below shows a depiction of an antibody. Which label correctly identifies the region(s) of the antibody that contains variable amino acids for binding of a specific antigen?
A
Beta sheets adopt___
coiled formations, antiparallel orientations, or parallel confirmations.
The function of a feedback mechanism is to
turn on/off the synthesis of a gene or product.
Which of the following is true about a negative feedback loop?
The last enzyme in a chain of enzymatic reactions signals to a previous enzyme to stop the enzymatic reaction.
Which of the following is INCORRECT regarding how enzymes lower the activation energy of a reaction?
Enzymes reduce the free energy of the products of the reaction. (Correct: Enzymes encourage the substrates to change shape toward a transition state that favors the reaction, Enzymes align substrates to promote a reaction between them, & Enzymes rearrange electrons in the substrates in a way that favors the reaction.)
How does phosphorylation of a protein affect its activity?
could increase or decrease the activity
Disulfide bonds stabilize protein shape outside the cell by__
covalent bonds between cysteines.
What are glycochains used for by cells?
All of the above: They form mucus in the intestine to transport food molecules, They serve as cell surface recognition factors, They create structural support for plant cells
How does binding of a signaling molecule to its receptor affect its activity?
All of the above: Binding may activate the protein, Binding may inactivate the protein, Binding may change its conformation.
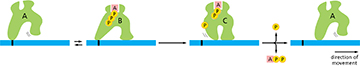
Shown below is the ATP hydrolysis cycle of a motor protein. What sentence BEST describes the state of the motor protein in "C"?
The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP caused a conformational change in the protein.
|
affinity chromatography
The word "nucleoside" refers to____
the nitrogen base and sugar ring
Which of the following is found at the ends of eukaryotic genomes?
telomeres
|
centromeres
The technique whereby DNA is amplified is called________
PCR
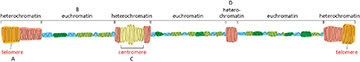
Shown below is a schematic of an interphase chromosome. Which region is most likely to contain the highest density of genes?
B
Which of the following is a function of the protein component of chromosomes?
It packages the DNA strands.
The description of the DNA double helix was__
a combined effort of multiple scientists including Watson and Crick, Wilkins, and Franklin.
___________ is a sequence of DNA that contains the information required for making a particular functional RNA or protein.
A gene
The nucleolus__
assembles ribosomal RNA and proteins into ribosomes from 10 chromosomes that form a loop structure at their tip
|
chromosomal staining and analysis
Which of the following describes the chromosomal makeup of a somatic cell of a human biological male?
22 pairs of autosomes + 1 X chromosome + 1 Y chromosome
|
DNA polymerase can cut out improperly base-paired nucleotides and add the correct one during synthesis.
The bonds that link two DNA strands together are
hydrogen bonds
What is the name of the DNA sequence where replication begins?
replication origin
Which double-strand break repair mechanism is a simple ligation mechanism?
nonhomologous end joining
What is the function of a topoisomerase in DNA replication?
It relieves the tension in DNA strands
Shown below is a replication bubble. At which location is the DNA polymerase adding nucleotides in a continuous manner
A and D
The sequence at which DNA replication begins tends to have which characteristic?
AT-rich
The energy for the polymerization reaction in DNA synthesis is powered by
the breaking of high-energy phosphate bonds in the deoxynucleotides.
|
3′–TCGAGCTAGCCGAT–5′
How are the primers from which DNA synthesis starts different from the DNA itself?
The primers are made up of RNA not DNA.
At which step of gene expression can cells amplify the number of copies of a protein made from a single gene?
both transcription and translation
Export of RNA from the nucleus requires the RNA to have which characteristic(s)?
5′ cap and poly-A tail
The splicing of introns out of an mRNA molecule is catalyzed by
RNA molecules that base pair with the splice sites to promote intron removal, called the splicesome.
Why does RNA polymerase make more mistakes than DNA polymerase?
RNA polymerase does not have proofreading activity
How do tRNAs become attached to the correct amino acid?
aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
What is the benefit of protein synthesis in polyribosomes?
More protein can be produced from a single RNA
|
mRNA
Which nucleic acid often base pairs with itself to fold into complex three-dimensional shapes in the cell?
RNA
The catalytic sites for peptide bond formation during translation is found in which part of the ribosome?
large subunit RNAs
The reading frame to use for translating an mRNA into functional protein is determined by the
location of an AUG.
|
promoter
A housekeeping gene is a gene whose cellular function is
important for processes found in all cell types.
The figure below depicts which of the following mechanisms that cells use to maintain their identity through cell divisions?
positive feedback
The regulatory control of a gene product after transcription is called
post-transcriptional control.
Excess amounts of the amino acid tryptophan result in downregulation of the expression of the enzymes required for its synthesis due to
the repressor binding to the operator.
In the cell, enhancer sequence functions are limited in their range of action by the formation of ___________ that hold specific genes and enhancers in close proximity.
loops
Which of the following statements is correct regarding ATP driven pumps?
Eukaryotic cells contain a variety of ATP driven pumps including Na+/K+ ATPase, Ca++ ATPase and H+ ATPase.
Noncoding RNAs include all of the following EXCEPT
mRNA (true for: rRNA, tRNA, regulatory RNAs)
|
mRNA; translation
Transplanting the nucleus of an epithelial cell into an egg cell lacking genetic information leads to the formation of
a normally developing embryo.
How do retroviruses work?
they carry RNA that is transcribed into DNA for genomic integration using reverse transcriptase
A SNP is_____
a single nucleotide polymorphism which causes slighlty different traits in individuals.
Germline mutations that are deleterious are likely to
be lost from a population.
Which of the following mechanisms for genetic change involves the acquisition of genetic material from another organism?
horizontal transfer
|
Viruses can leave the cell and move to other cells and organisms; mobile genetic elements generally just move around the genome within in a cell.
A relatively small number of ________gave rise to eukaryotic protein diversity.
exons
A mutation in the ___________ of the gene encoding the enzyme lactase enables expression of this gene in adults.
regulatory sequence
How do gene duplications arise?
DNA replication causes misalignment of repetitive sequences which then leads to unequal crossing over
Mobile genetic elements___
encode the components they need for movement
The total size of the human genome is approximately ___________ base pairs
3.2 billion