10.9 - Excretory System
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
what is the primary role of the excretory system?
to filter out metabolic wastes from the body and eliminate them as urine
the excretory system also aids the body in retaining water and solutes
how many kidneys do humans have?
2
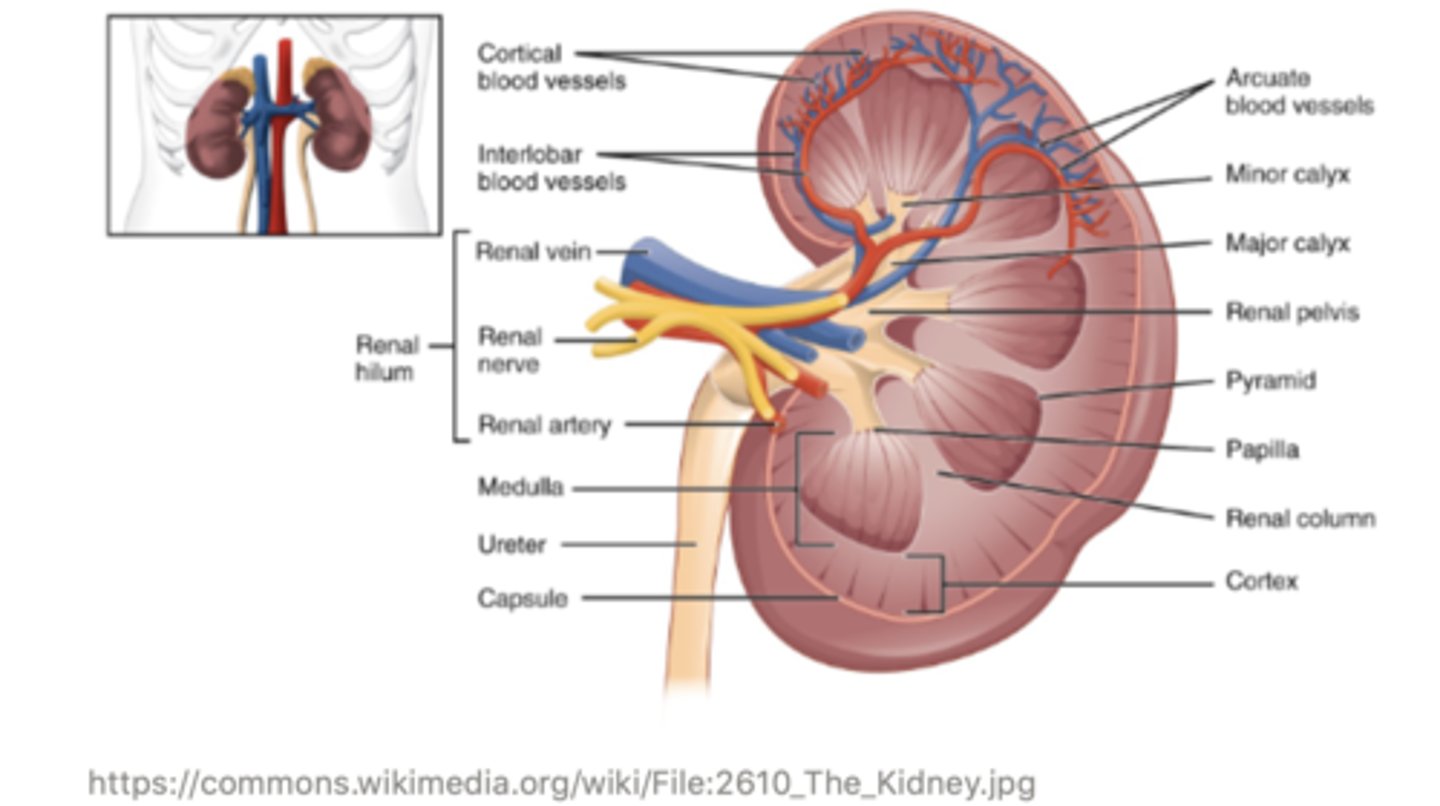
the outer portion portion of the kidney is called the ______ , and this is where blood enters
cortex
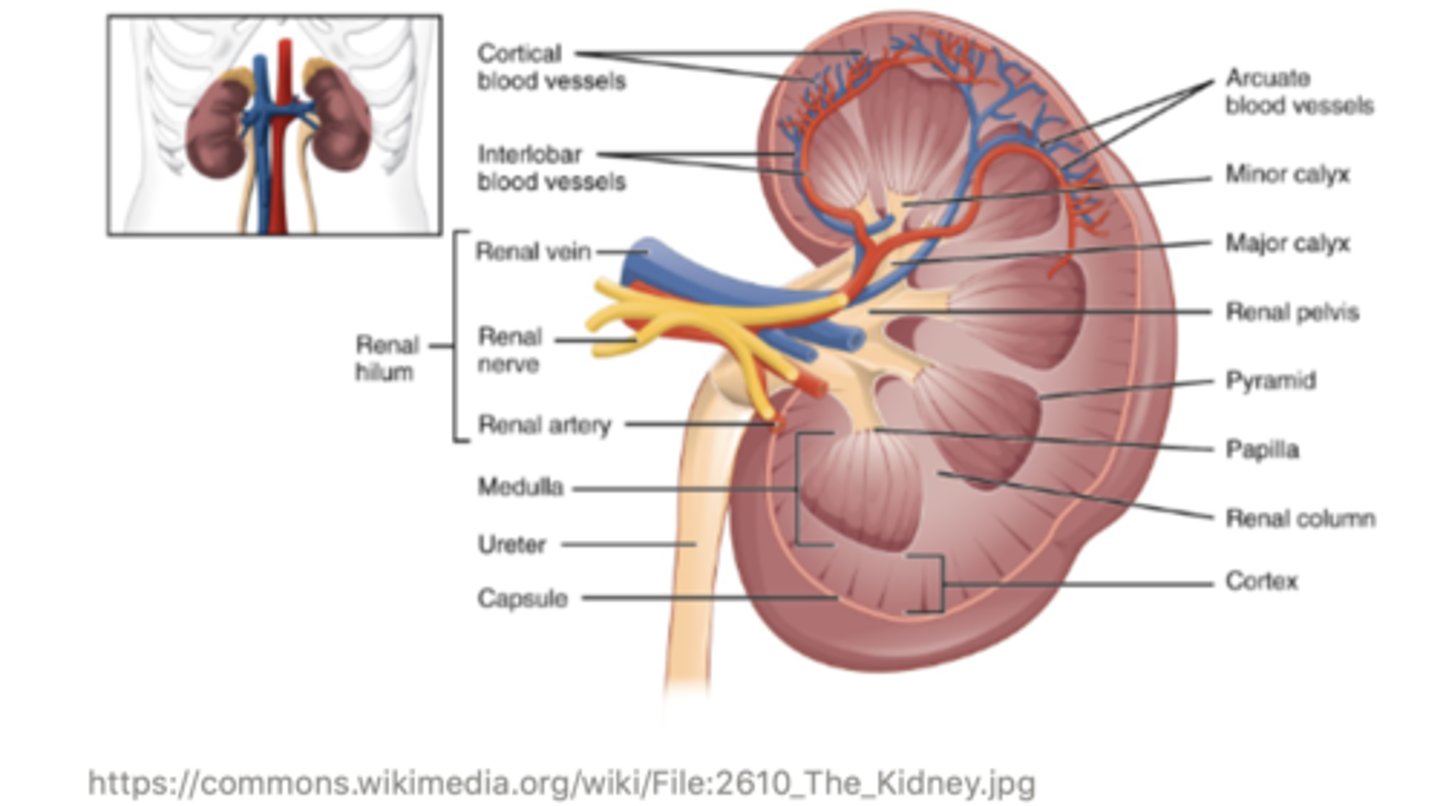
the middle portion of the kidney is called the ______
medulla
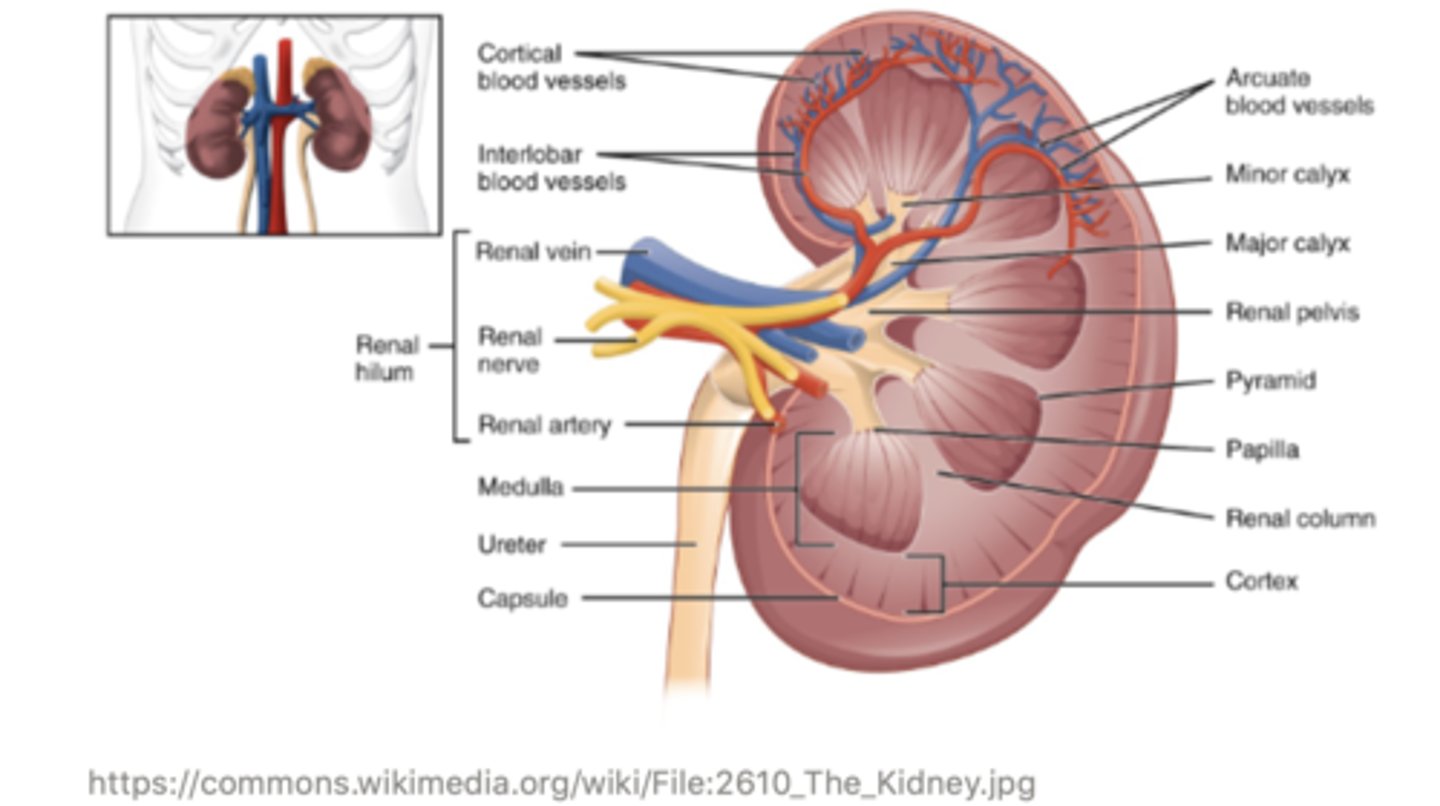
the very inner portion of the kidney is called the ______, and this is where filtrate exits the kidney
pelvis
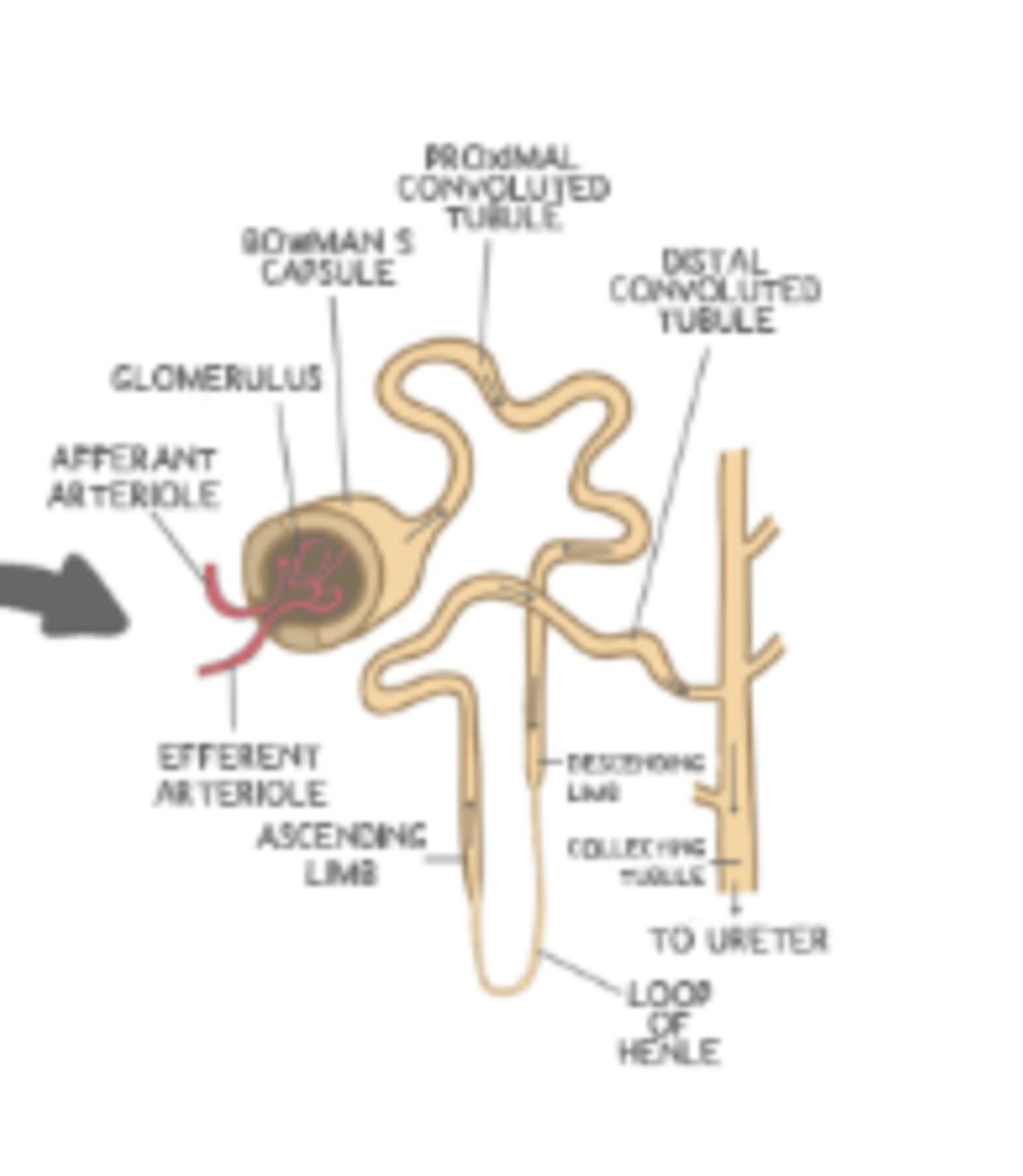
a ______ is the single, functional unit of the kidney
nephron
kidneys are made of thousands of individual nephrons!
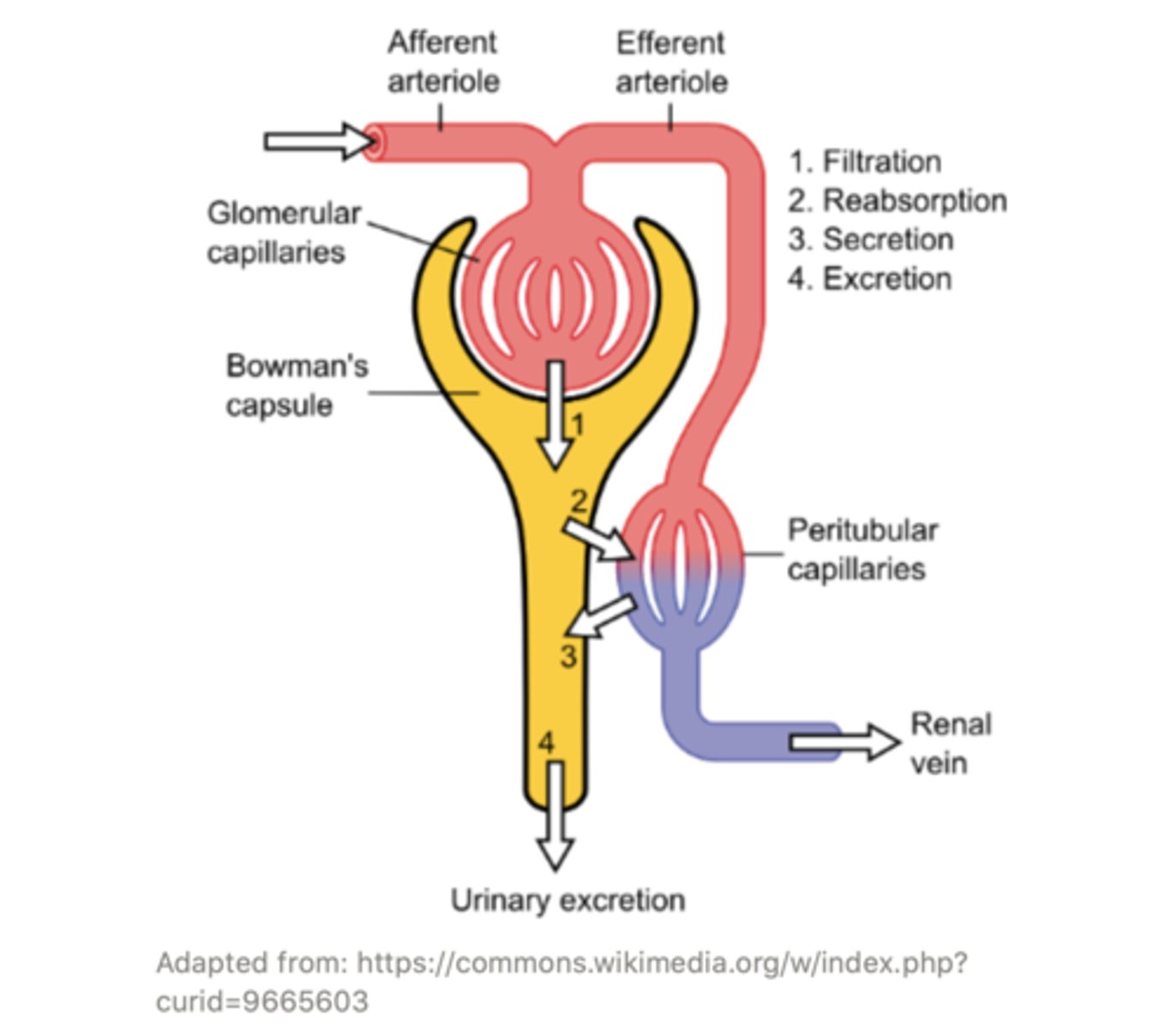
what are the 4 main processes that occur in the kidneys?
filtration; reabsorption; secretion; excretion
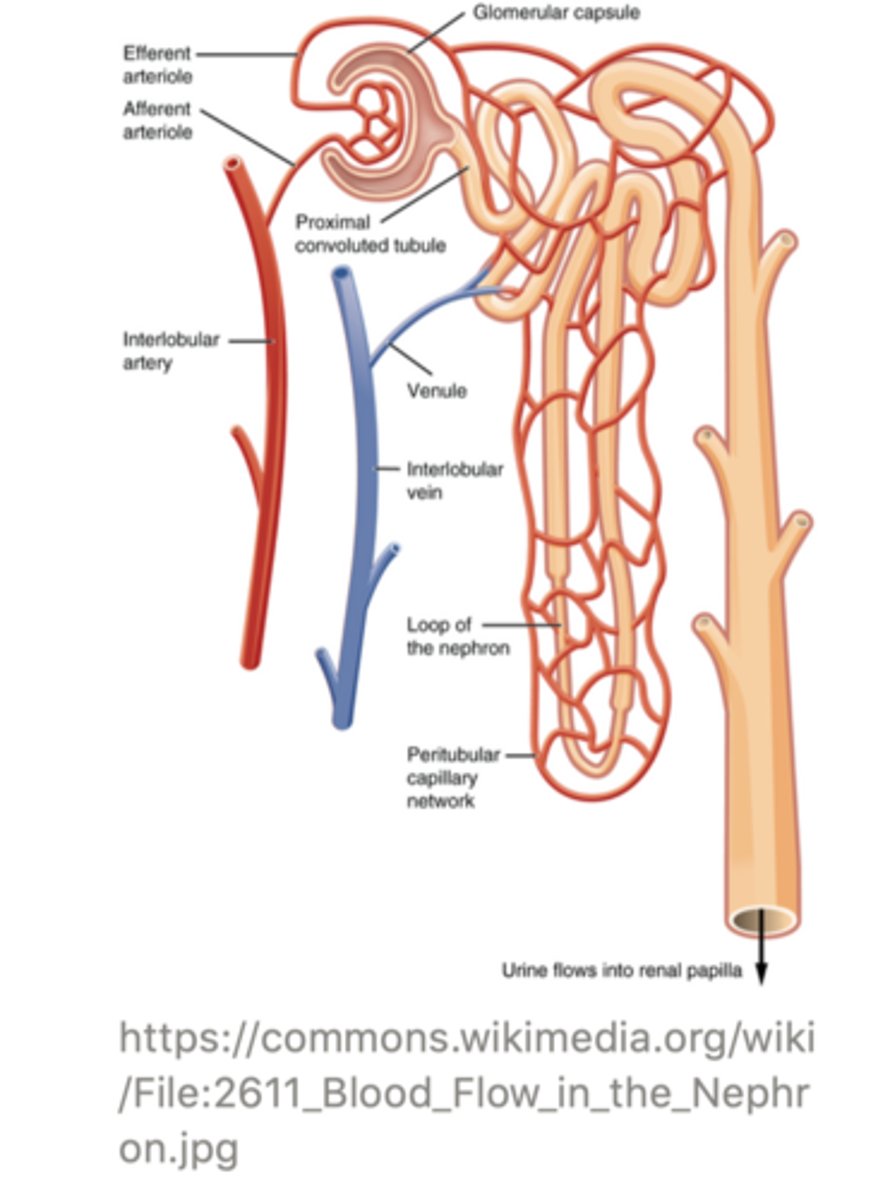
the excretory process begins when blood flows from the body and into the ______ artery, which branches off into the ______. From there it is led into the ______
renal artery (interlobular artery is an accepted answer too) --> afferent arteriole --> glomerulus
the ______ is a ball/collection of blood vessels located in the renal cortex of the kidney
glomerulus
the glomerulus is strategically located adjacent to the ______
Bowman's capsule
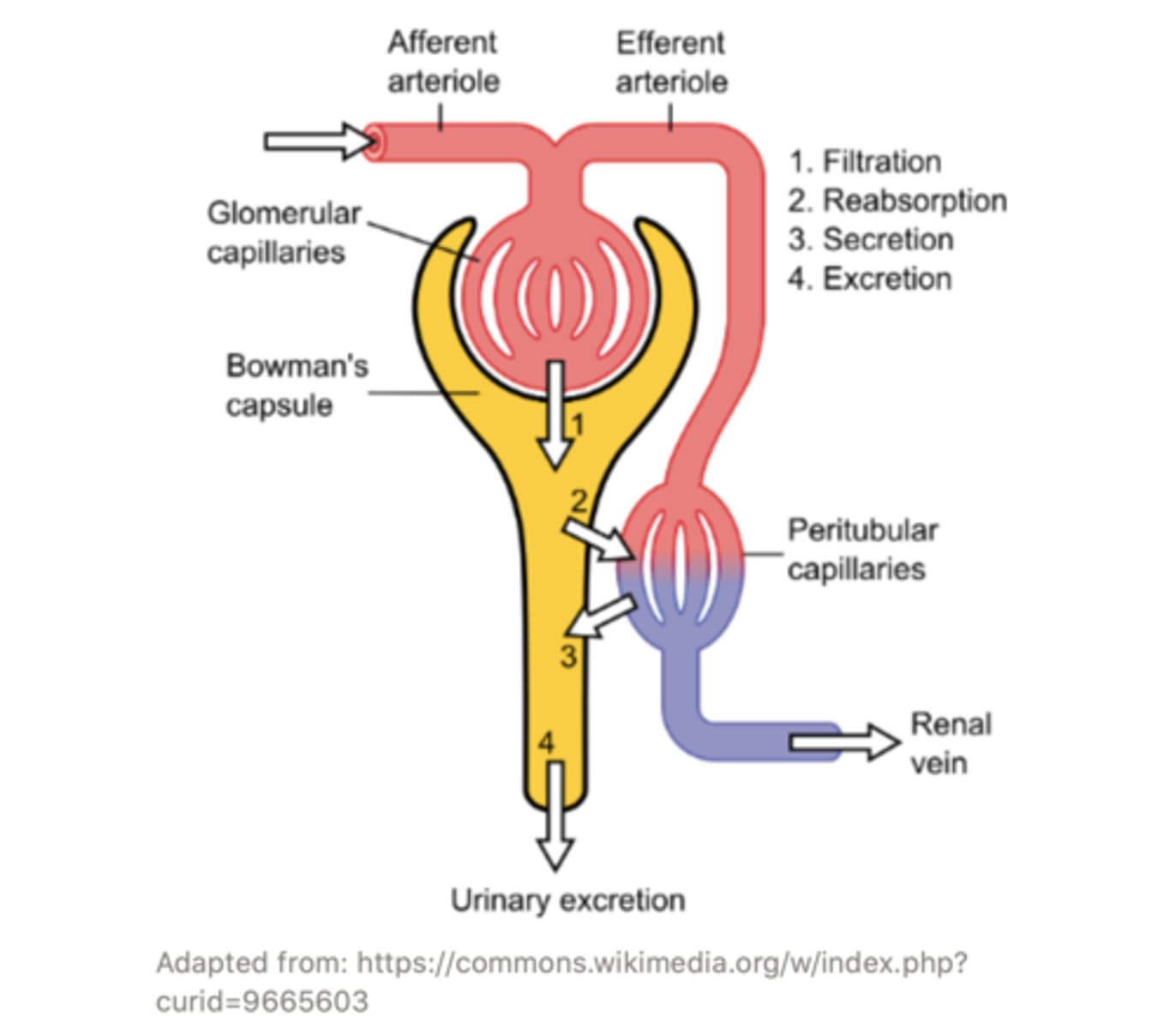
together, the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule are known as the ______
renal corpuscle
the substances that filter from the blood and into the Bowman's capsule are known as ______
filtrate
smaller substances can pass into the Bowman's capsule while the larger substances that cannot pass into the Bowman's capsule remain in the glomerulus. This process is called ______
filtration
the glomerulus acts like a sieve - it allows small substances (like _______ and ______) to pass into the Bowman's capsule while it keeps larger substances (like ______ and ______) in the blood
water; solutes; proteins; blood cells
the Bowman's capsule has ______ (hint: long, foot-like processes) that wrap around the glomerulus
podocytes (podo = foot or foot-like part)
the podocytes form ______ (hint: 'window' or 'opening'). Some of these slits are large enough for certain small substances to pass through but small enough to prevent other large ones from passing through the Bowman's capsule
fenestrations (fenestra = window; opening)
blood within the glomerulus leaves the renal corpuscle via the ______ _______
efferent arteriole
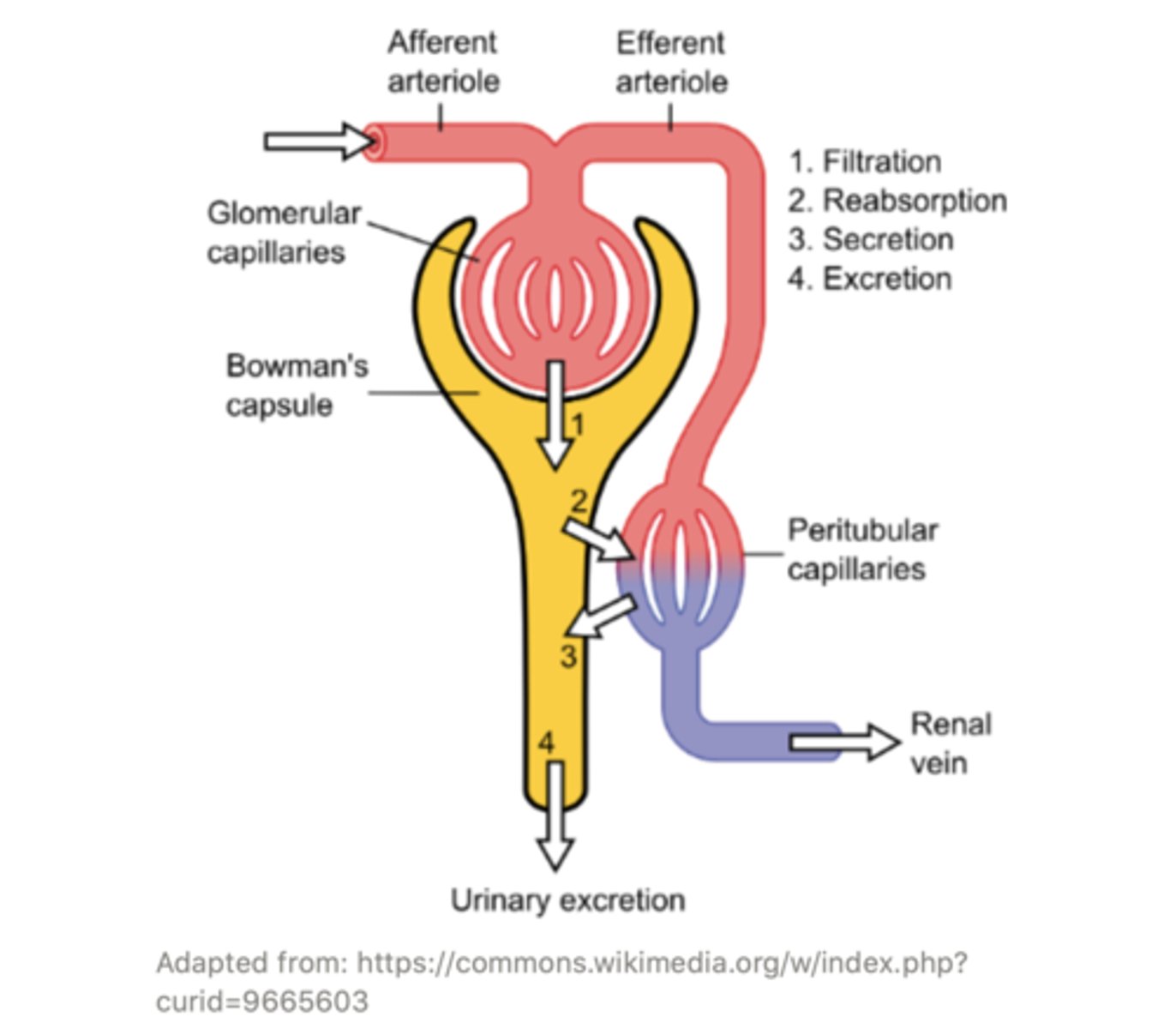
the efferent arteriole goes on to form a set of capillaries called the ______ capillaries
peritubular
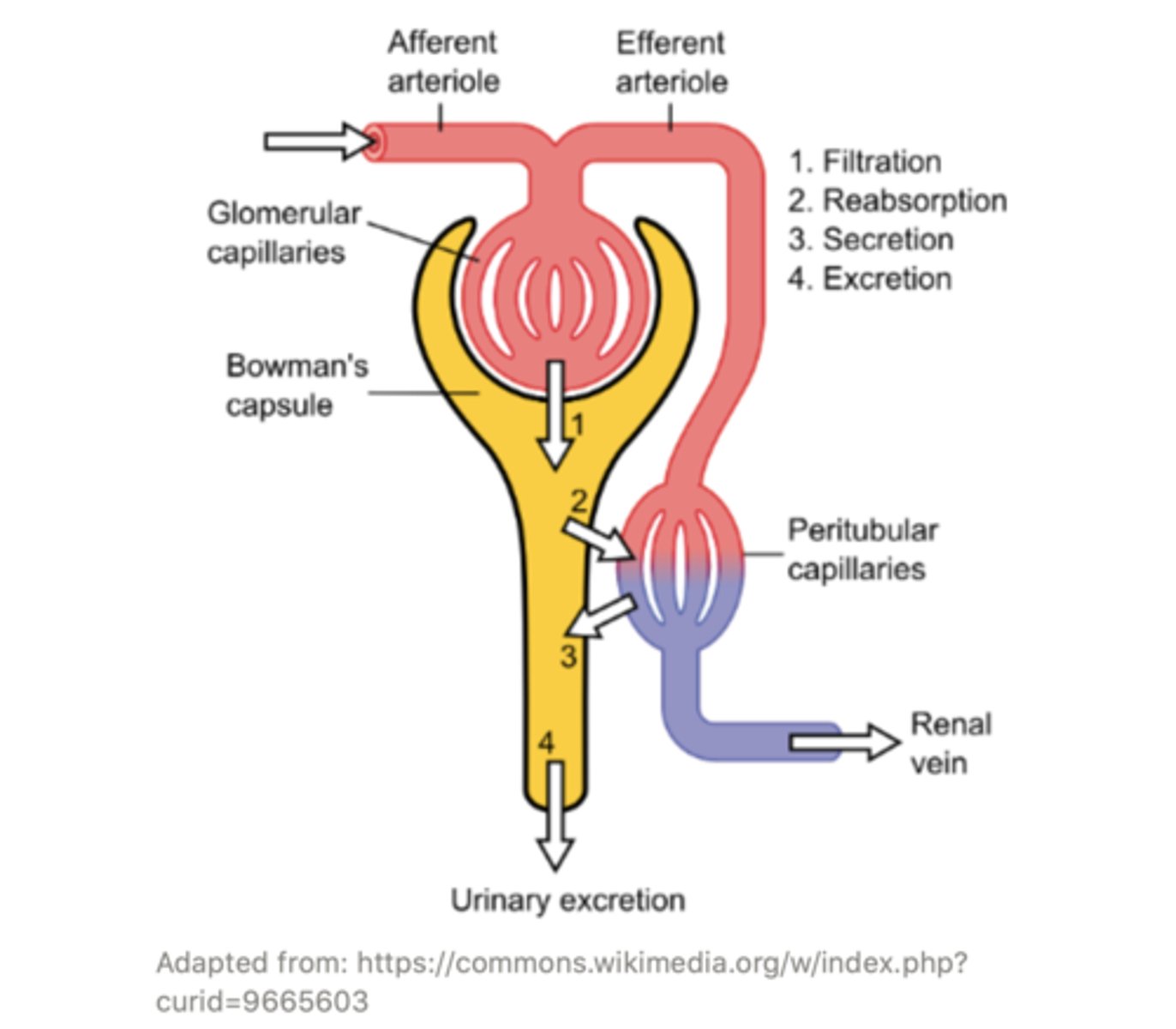
the ______ capillaries surround the different tubules of the nephron and exchange water, salts, and other important molecules with them. This modifies the content of the filtrate through processes of ______ and ______
peritubular;
reabsorption; secretion
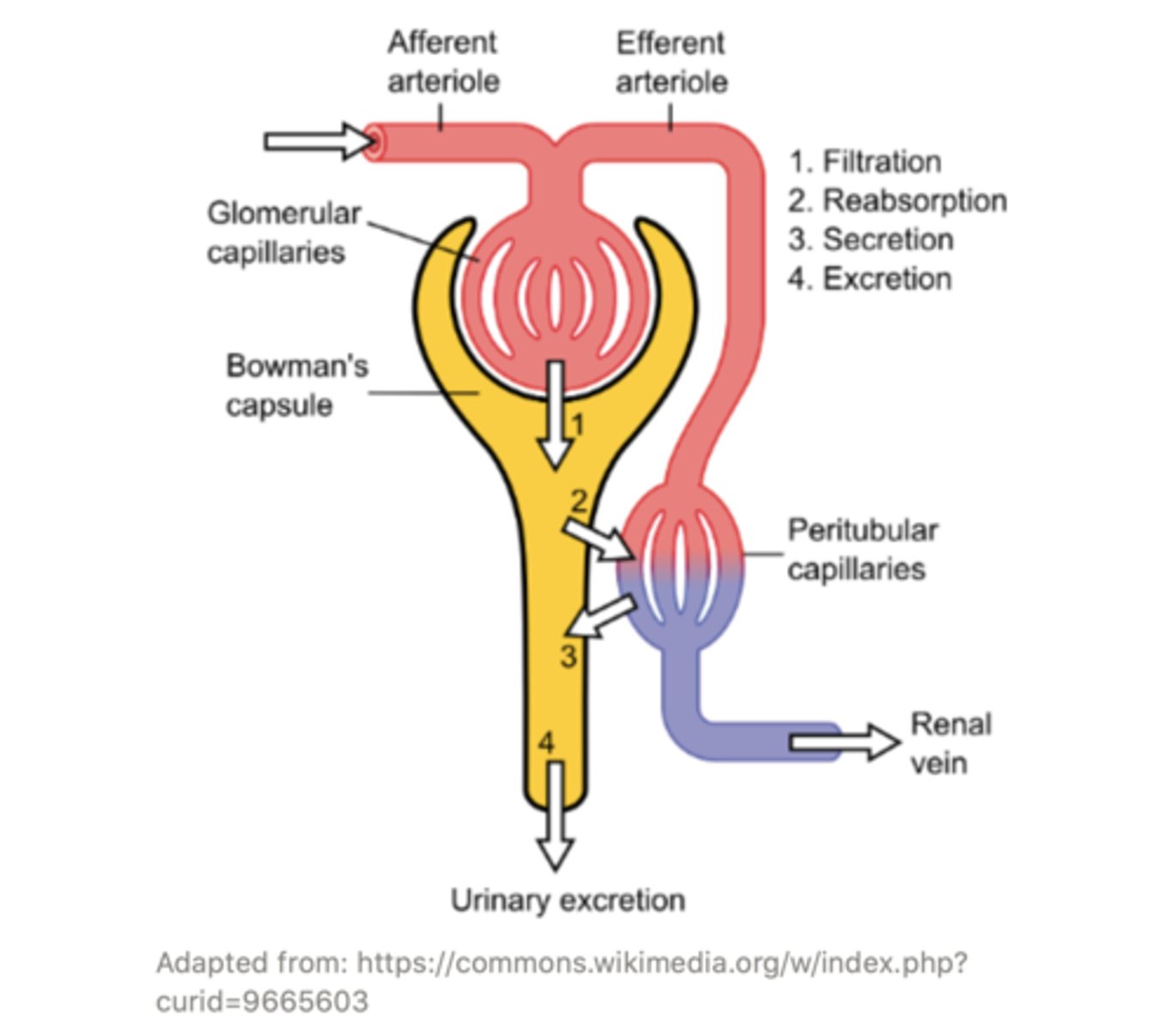
what is the mnemonic to remember the order of the afferent arteriole vs. the efferent arteriole in the kidney?
A comes before E in the alphabet, so the Afferent arteriole comes before the Efferent arteriole in the kidney (afferent enters and efferent leaves)
the process of the removal of water and solutes from filtrate back into the blood vasculature is called ______
reabsorption
reabsorption occurs from the ______ up to and including the ______
proximal convoluted tubule (predominantly); collecting duct
filtrate flows from the Bowman's capsule to the ______, then into the ______
proximal convoluted tubule; loop of Henle (descending limb is also an acceptable answer)
the _____ is the part of the nephron that descends from the cortex of the kidney to the medulla
loop of Henle
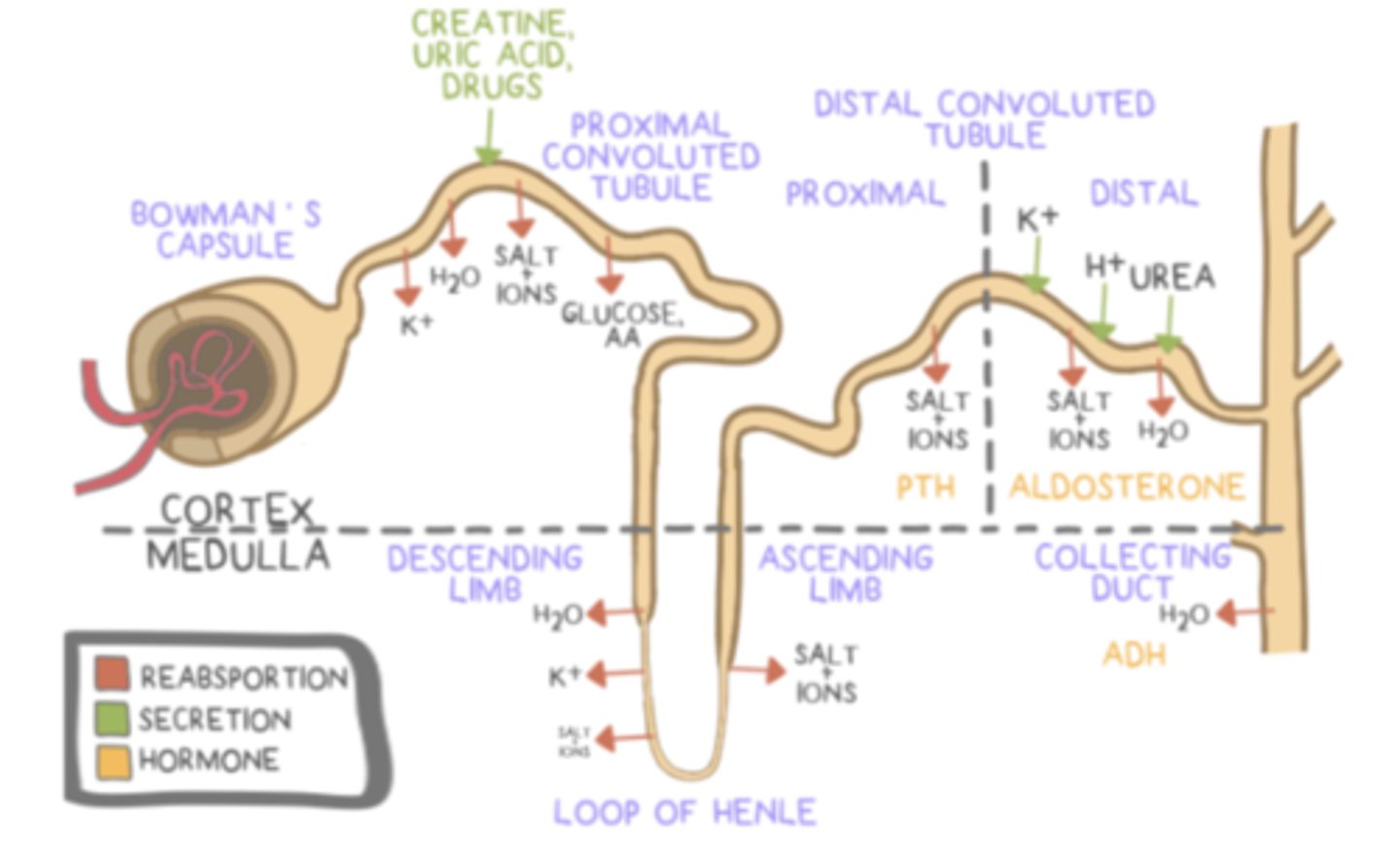
the descending limb of the loop of Henle has a _____ permeability to water and _____ permeability to solutes
high; low
the ______ limb of the loop of Henle has a high permeability to water and low permeability to solutes
descending
as filtrate travels down the descending limb it becomes ______ concentrated
more
(because water leaves the filtrate)
the water that leaves the descending limb is absorbed back into the blood supply by the ______, which are blood capillaries that run adjacent and parallel to the loop of Henle
vasa recta
this is our body's way of reabsorbing and retaining water!
the ascending limb of the loop of Henle has a very ______ permeability to water and ______ permeability to solutes
low; high
the ______ limb of the loop of Henle has a very low permeability to water and high permeability to solutes
ascending
as filtrate travels up the ascending limb it becomes ______ concentrated
less (because solutes leave the filtrate)
the solutes that leave the ascending limb are absorbed back into the blood supply by the ______, which are blood capillaries that run adjacent and parallel to the loop of Henle
vasa recta
this is our body's way of reabsorbing and retaining important salts
the process of the transfer of solutions from the blood vasculature directly into the nephron tubule filtrate secretion is called ______
secretion
via the process of ______ certain (usually harmful) substances are extracted from the blood, specially from the ______ capillaries, and taken up by the nephrons directly
secretion; peritubular
secretion occurs in the ______ (predominantly) and the ______
distal convoluted tubules (predominantly); proximal convoluted tubules
the proximal convoluted tubule is located between the ______ and the _____ of the loop of Henle
renal corpuscle (Bowman's capsule is an acceptable answer too); descending limb
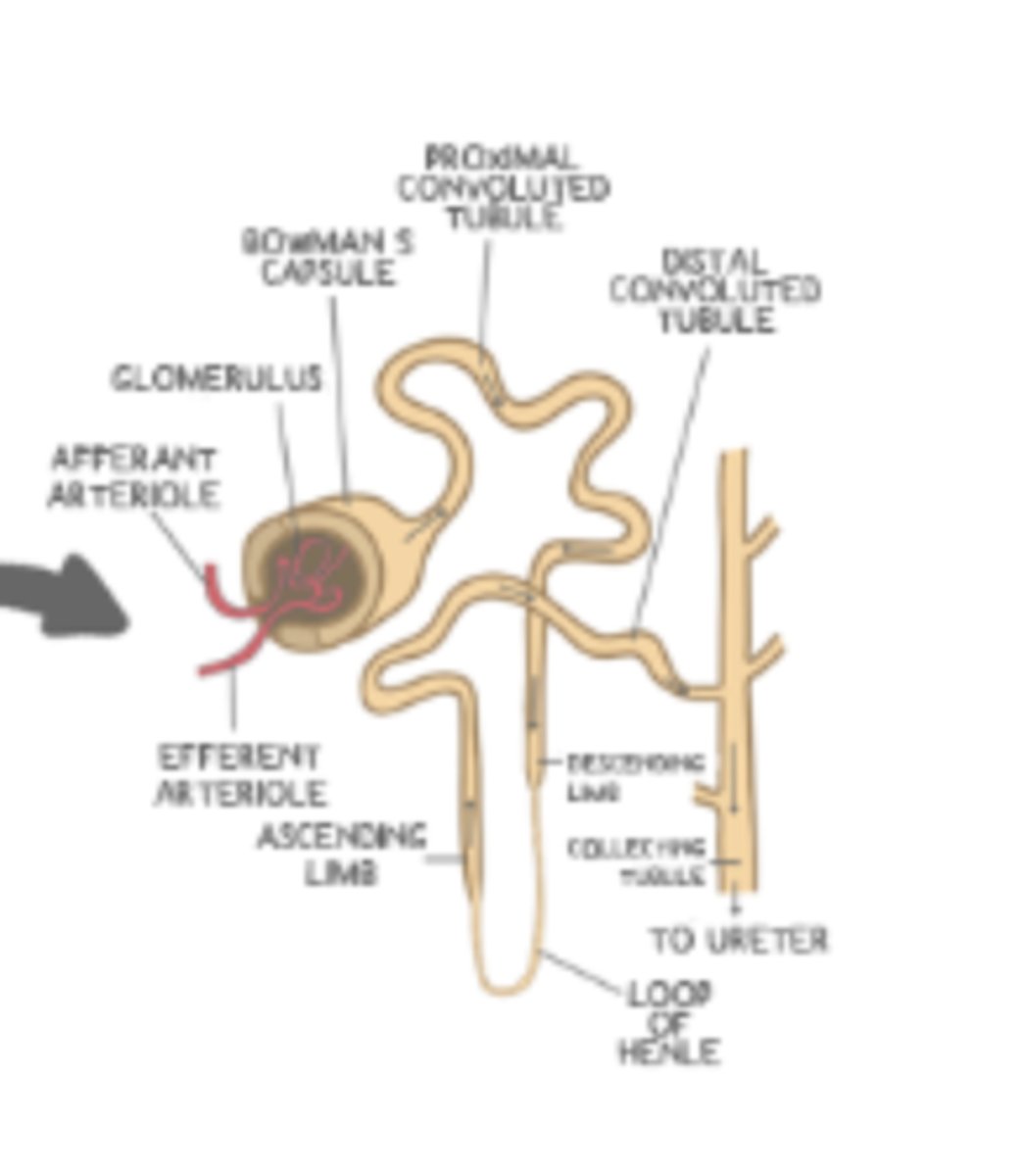
the distal convoluted tubule is located between the ______ of the loop of Henle and the ______
ascending limb; collecting duct
the process by which the filtrate (after filtration, reabsorption and secretion have occurred) is removed from the body as urine is called ______
excretion
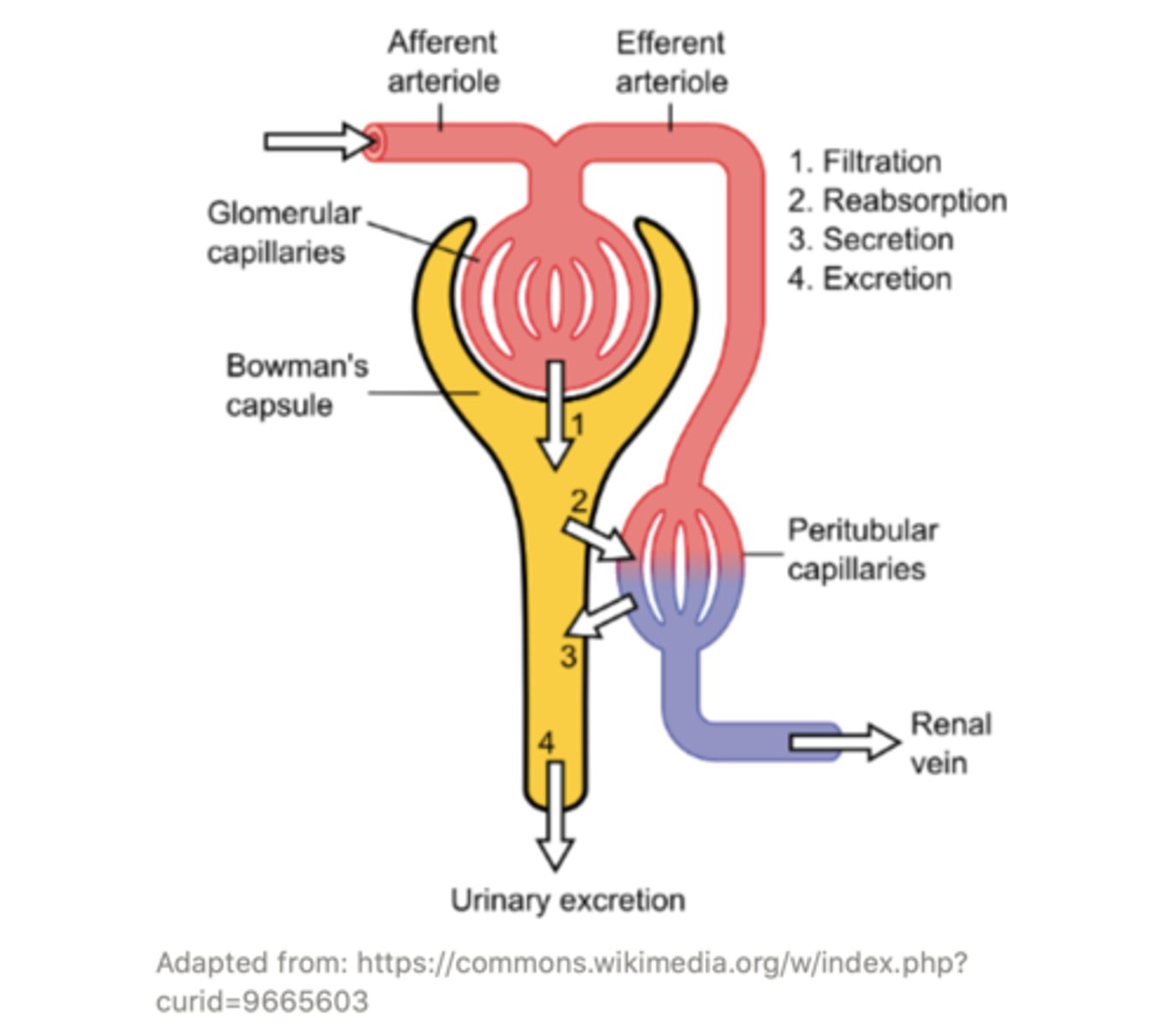
After filtration, reabsorption, and secretion, the filtrate is called ______ and is excreted
urine
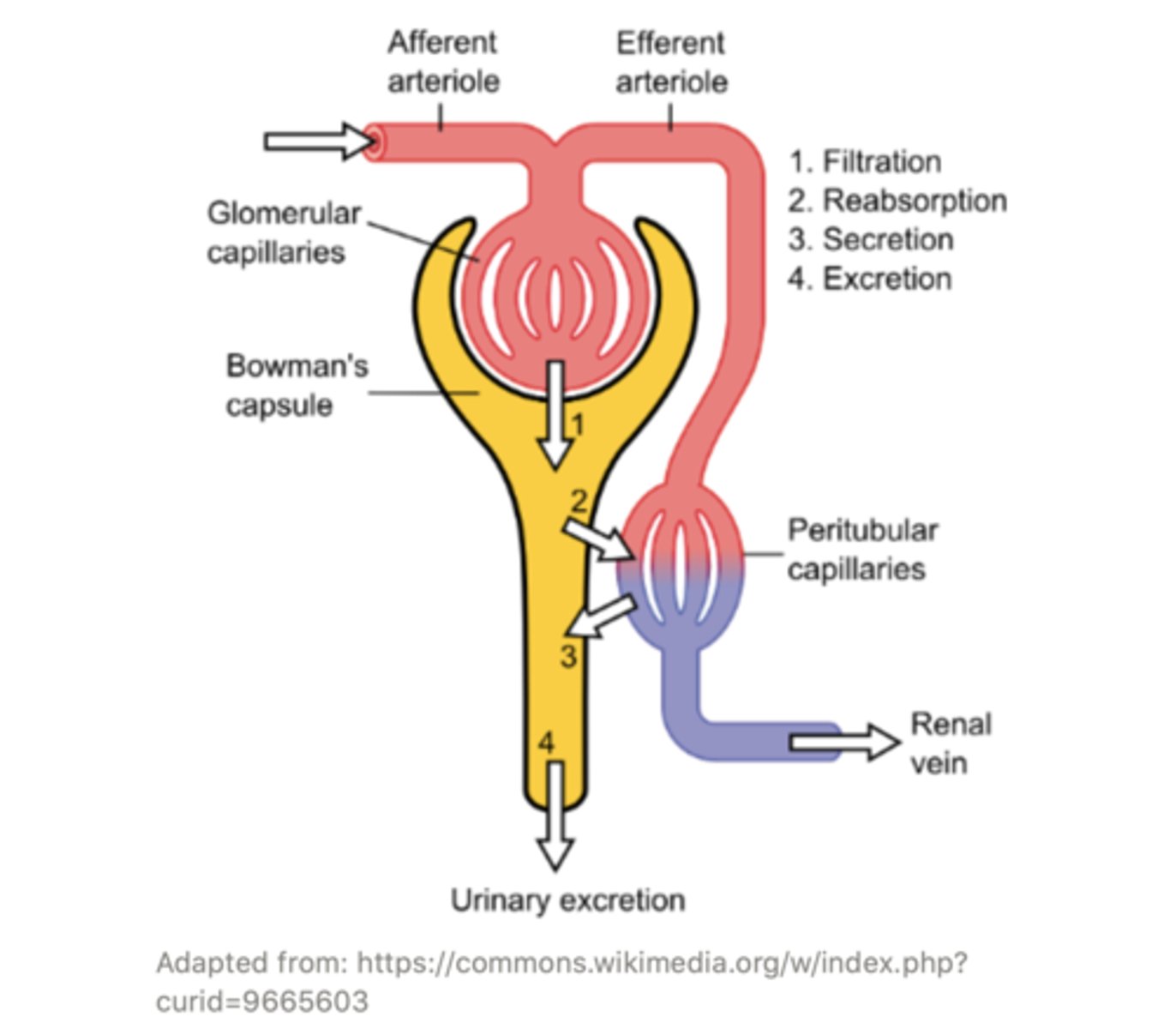
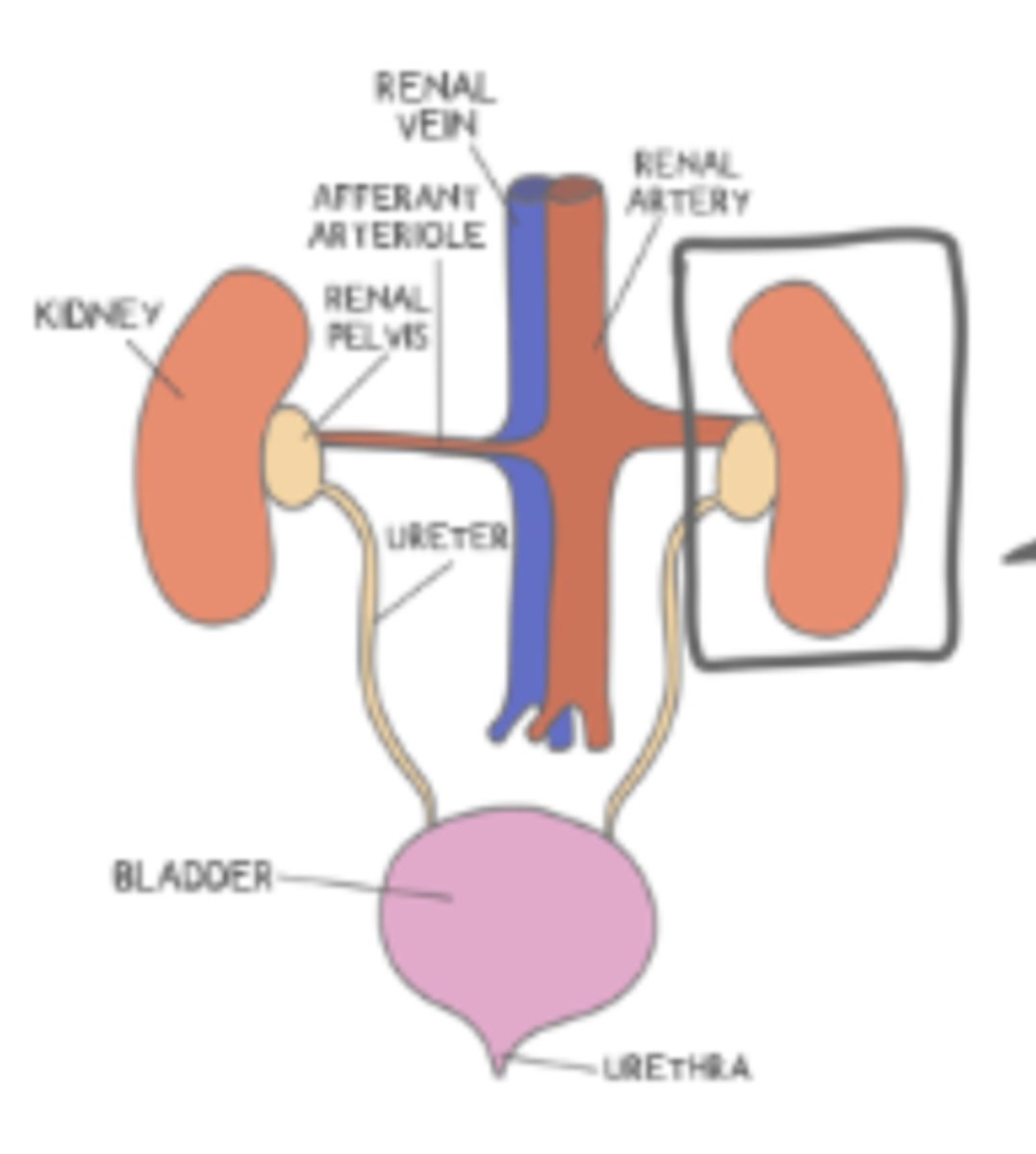
the ______ collects filtrate from several different nephrons. The ______ leads to the renal pelvis, and from there goes to the ______
collecting duct; collecting duct; ureter
the ______ is the connecting passageway between the kidneys and the urinary bladder
ureter
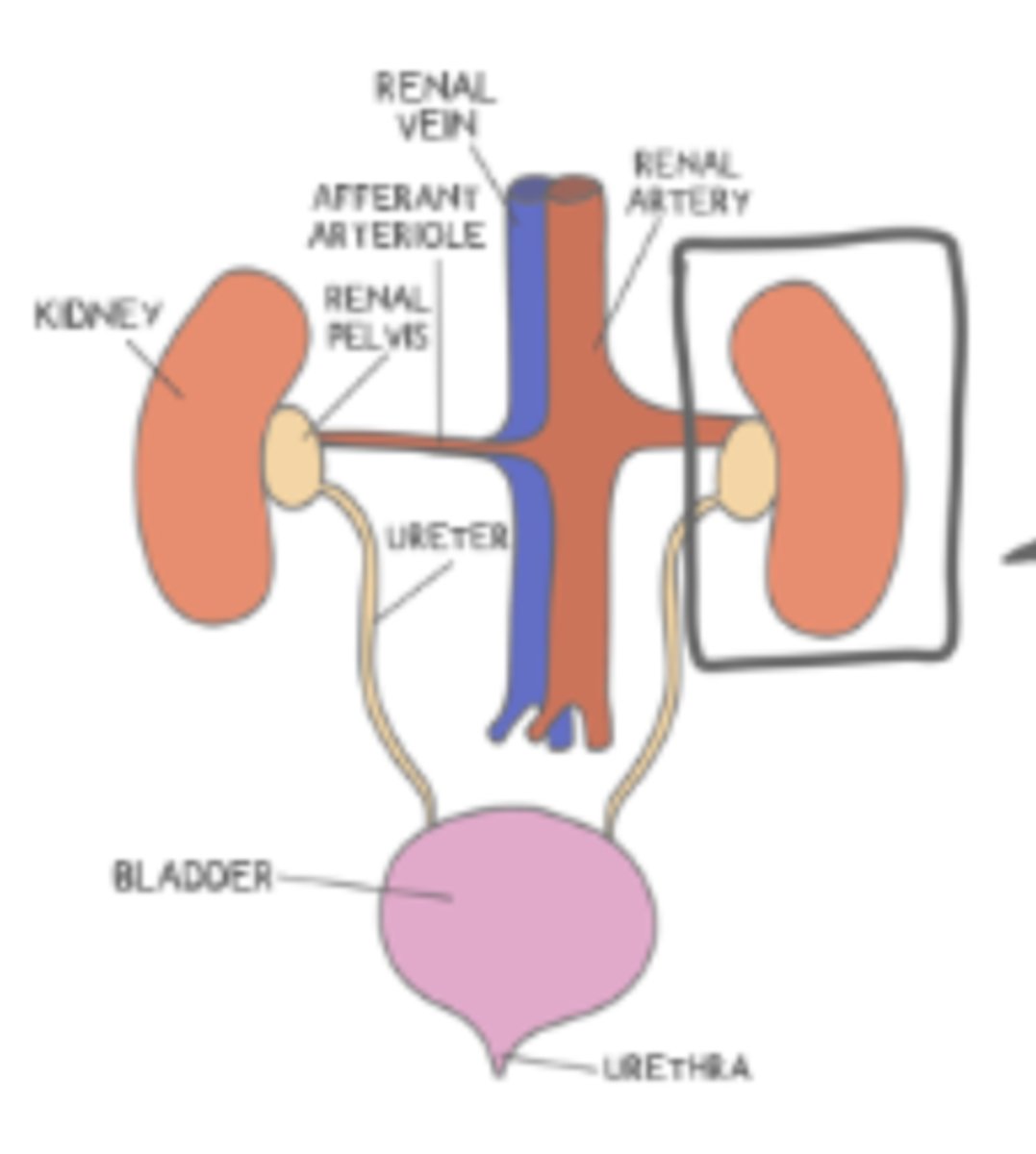
the _____ is where the urine is temporarily stored until the body signals for it to be excreted, and when this signal comes, the fluid flows to the ______
urinary bladder; urethra
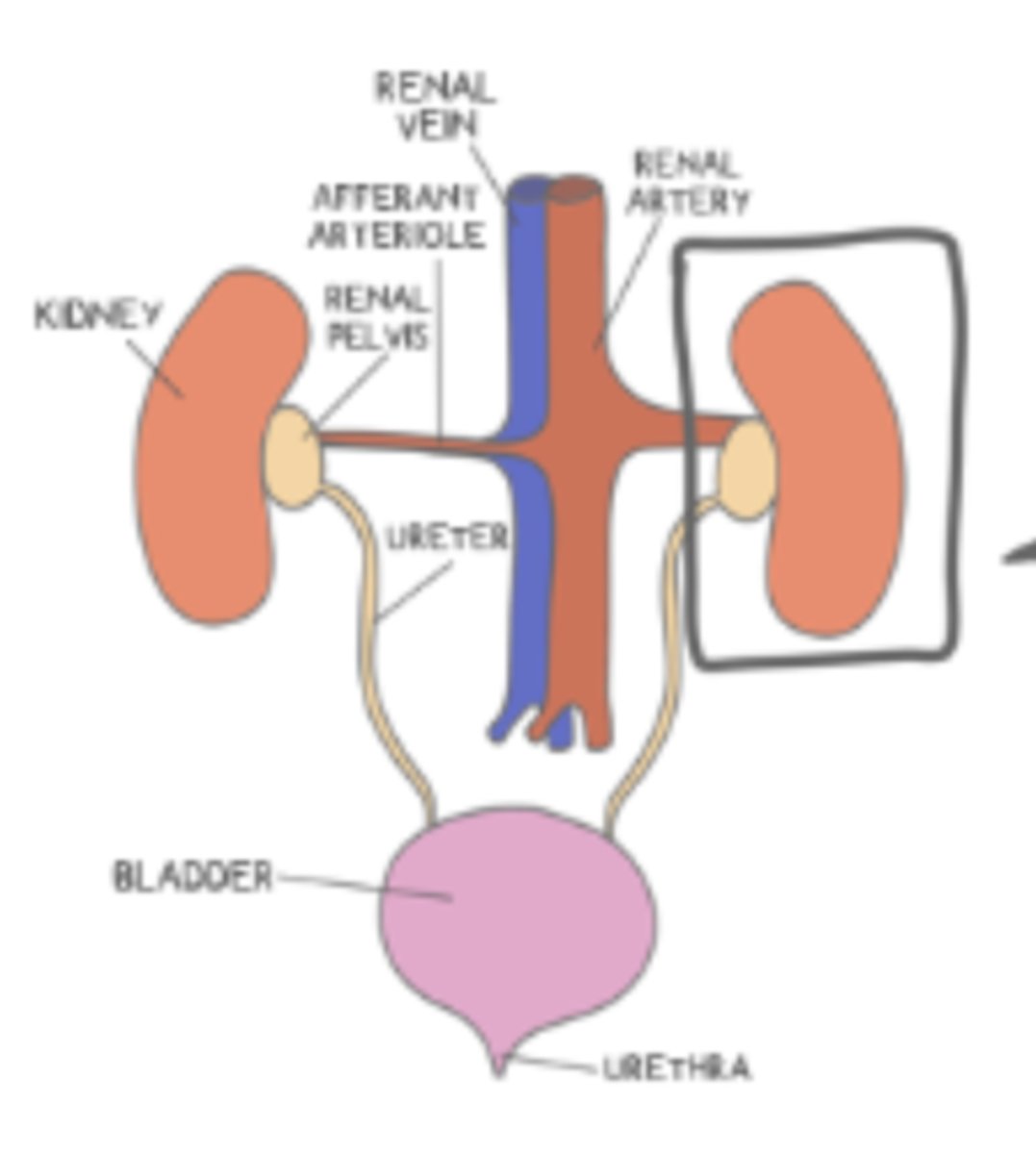
the _____ is where the urine is excreted and exits the body
urethra
parathyroid hormone (PTH) ______ calcium levels in the blood
increases
parathyroid hormone (PTH) increases calcium levels in the blood by stimulating reabsorption of calcium in the ______ (hint: part of the kidney), and causing the ______ to release calcium
nephron tubules; bones
calcitonin _____ calcium levels in the blood
decreases
calcitonin lowers calcium levels in the blood by ______ reabsorption of calcium in the nephron tubules, and causing the ______ to absorb calcium
inhibiting; bones
(calcitonin is released by the thyroid gland)
parathyroid hormone and calcitonin have the ______ effects on calcium levels in the blood
opposite
aldosterone is considered a _____ hormone, and is produced by the adrenal _____
mineralocorticoid; cortex
aldosterone functions to increase ______ and ______ reabsorption and to increase ______ secretion
increase sodium (Na+) and water (H2O) reabsorption; increase potassium (K+) secretion
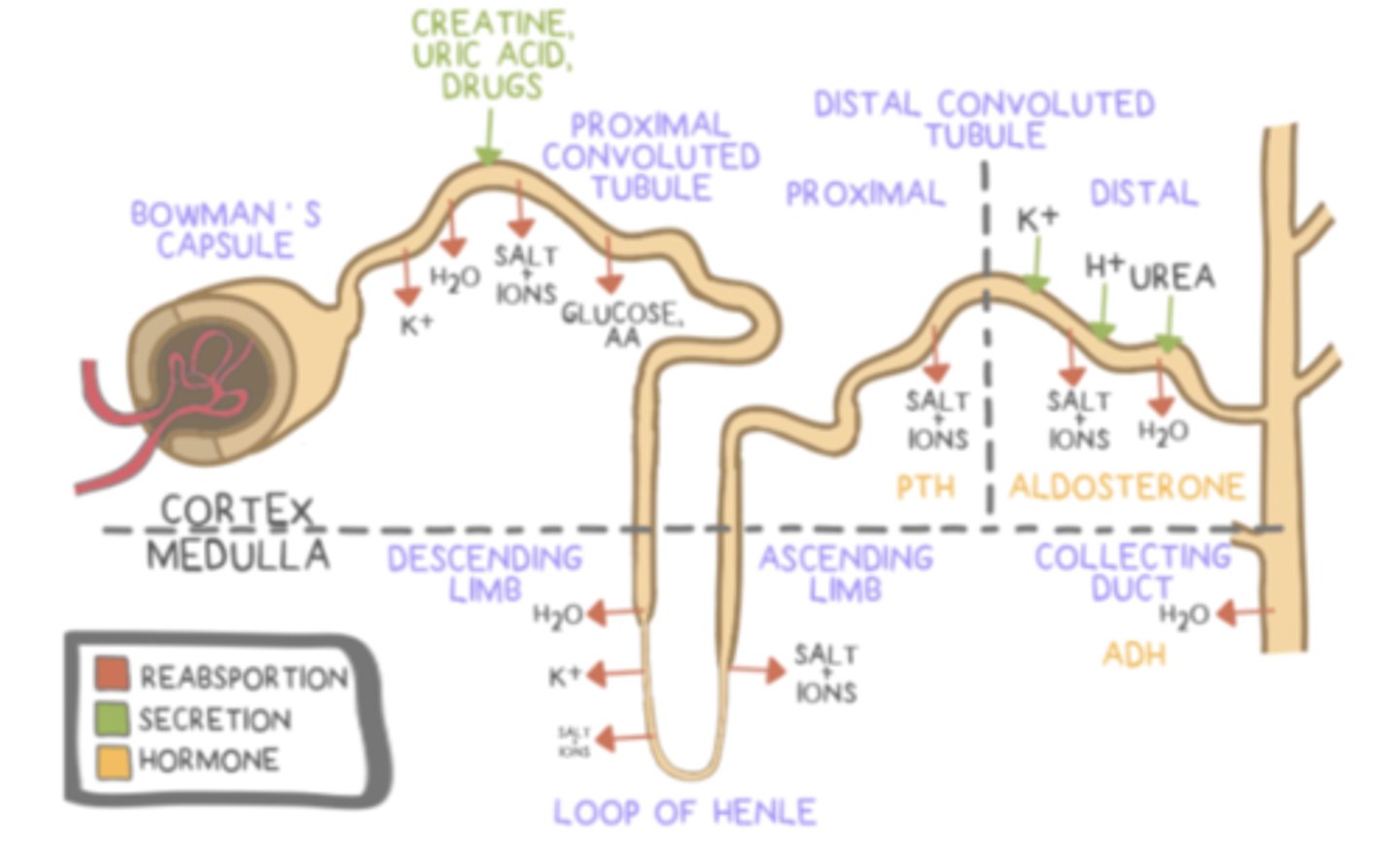
aldosterone functions in the ______ of the nephron and in the ______
distal convoluted tubule; collecting duct
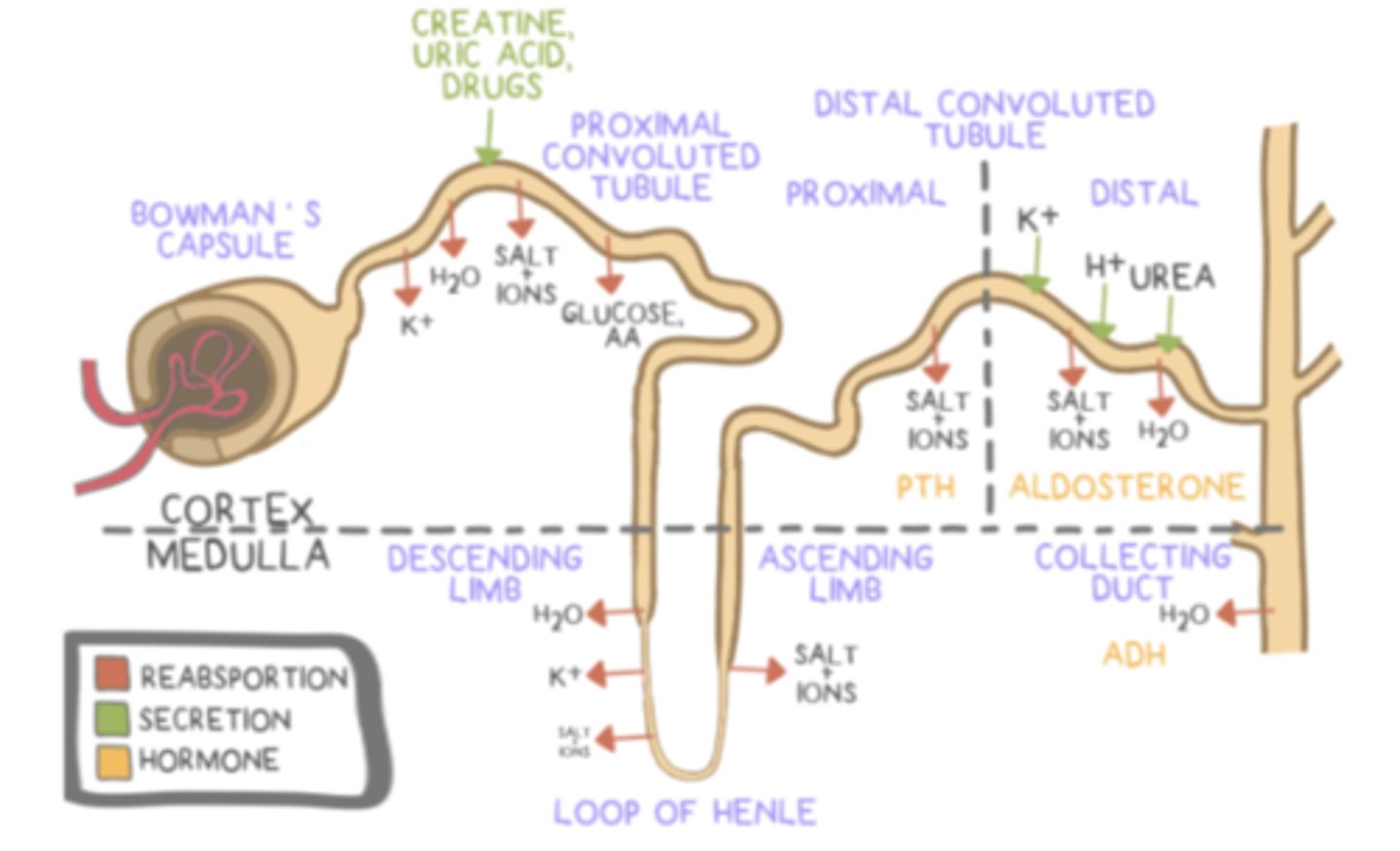
antidiuretic hormone (ADH/vasopressin) prevents ______ (production of urine)
diuresis = production of urine
antidiuretic hormone (ADH/vasopressin) is produced by the ______; however, it is stored in the ______
hypothalamus; posterior pituitary
the hypothalamus stimulates the ______ to release antidiuretic hormone (ADH/vasopressin) when the extracellular fluid volume is _____
posterior pituitary; low
antidiuretic hormone (ADH/vasopressin) causes ______to insert into the ______, which allows more water reabsorption
aquaporins; collecting duct
(less water goes into the urine, leading to very concentrated urine)
the special cells in the afferent arteriole near the glomerulus are called ______, and they can detect changes in blood pressure and sodium levels
juxtaglomerular cells (juxta = nearby)
when blood pressure or blood sodium is low, these cells release ______
renin
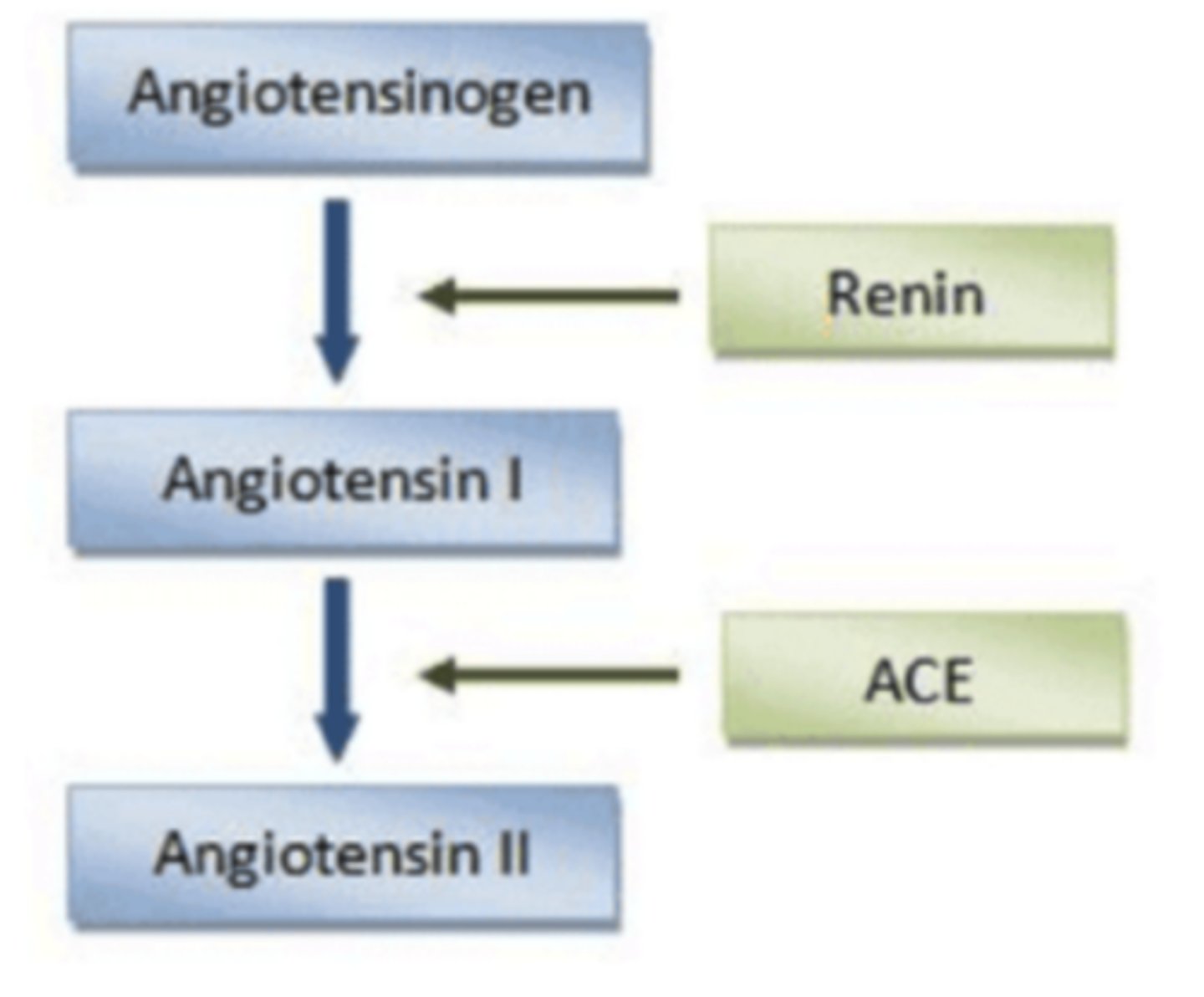
renin is an ______ which acts on ______ to activate it to the form angiotensin I
enzyme; angiotensinogen
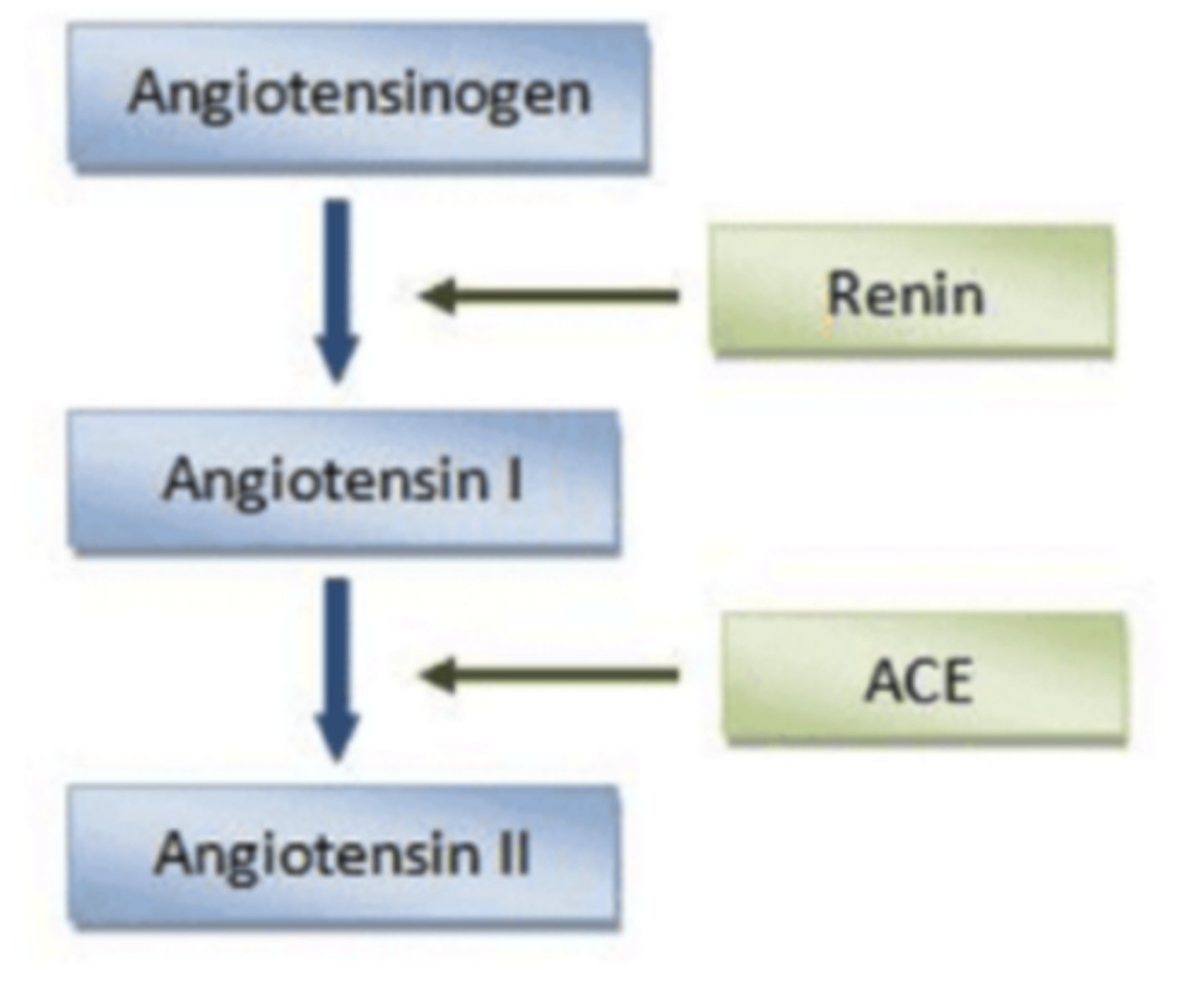
a different enzyme called ______ acts on angiotensin I to convert it to ______, which is the active form of the hormone
angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE); angiotensin II
atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), which is made by atrial cells in the heart, has what three main effects in order to reduce blood volume and pressure?
1. Increases the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
2. Decreases sodium reabsorption and increase sodium excretion
3. Inhibits renin and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)