auburn biology 1021 lab final
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Lab 1: What did caffeine do to the heart rate of Daphnia?
Caffeine sped up the heart rate
Lab 1: What did ethanol do to the heart rate of the Daphnia?
Ethanol slowed it down
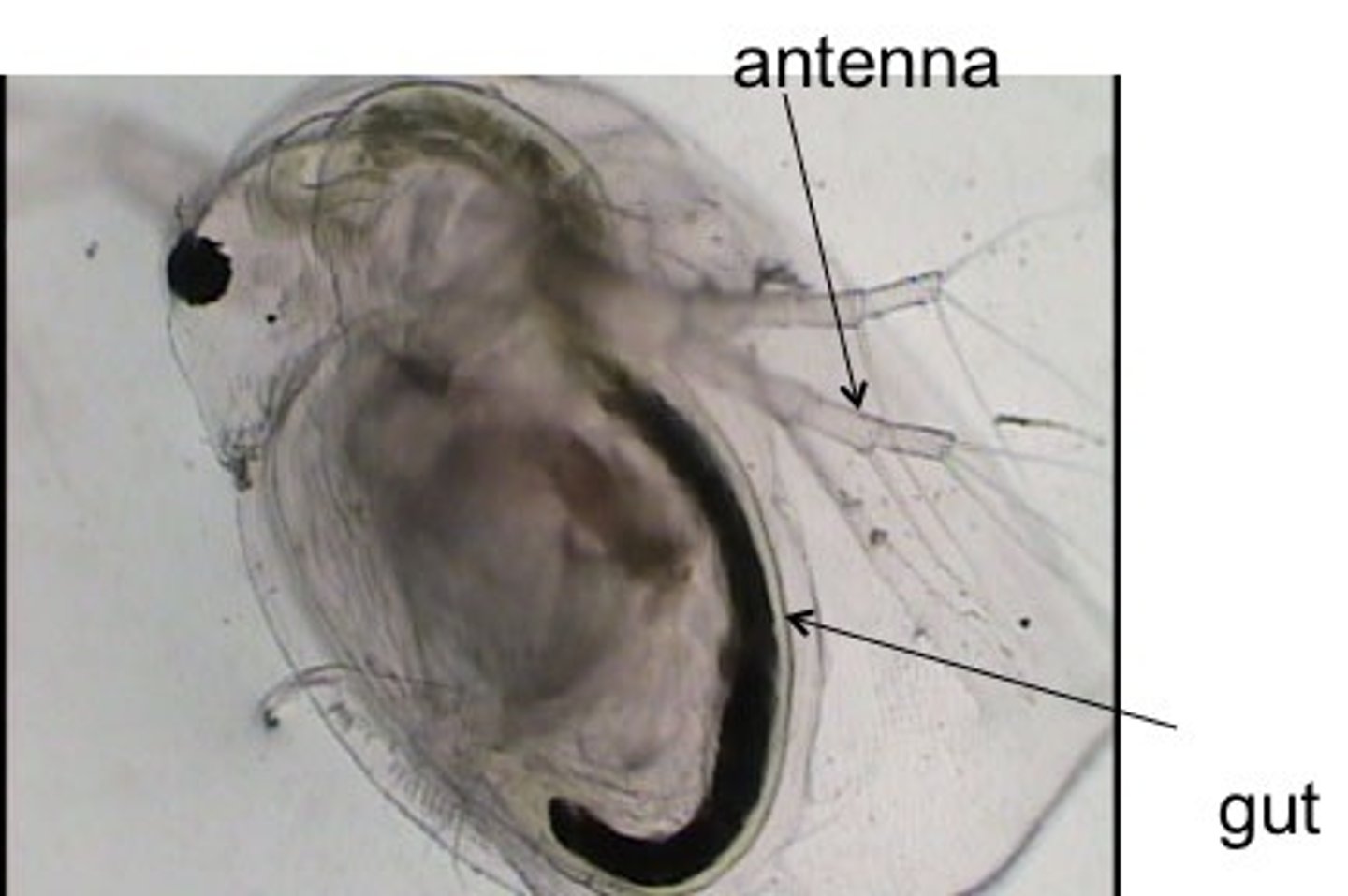
Lab 1: Anatomy of daphnia
Lab 1: Know major parts of dissecting scope
Look in lab manual (1-4)
Lab 1: One or more factors that the scientist varies during the experiment
Independent variable
Lab 1: A feature that the scientist measures in order to determine if it changes in response to the independent variable
Dependent variable
range
median
mean
mode
difference between highest and lowest value
number in the middle
average
number that occurs the most
Lab 2: What solutions are used to test for the 4 types of organic molecules?
Iodine -- polysaccharide (starch)
Benedict's Reagent -- Sugar
Brown Paper Bag and Vegetable Oil--Lipids
Biuret Test - protein
Lab 2: What does a positive test look like for the vegetable oil test for lipids? Negative?
Positive vegetable oil test: 1 layer
Negative vegetable oil test: 2 layers
Lab 2: What does a positive test look like for the Biuret test for proteins? negative?
Positive Biuret Test: violet color
Negative Biuret Test: pinkish
Lab 2: What does a positive test look like for the Benedict's Reagent for sugar?
NEGATIVE: BLUE any other color is positive
green: very low
yellow: low
yellow/orange: medium
orange: high
red/orange: very high
Lab 2: What does a positive test look like for the Iodine test for polysaccharides (starch) ?
Purple/blue/black indicates starch is present
Lab 2: Know functional groups
See lab manual
Don't worry about molecules in self test -- be able to identify functional groups in those molecules tho
Lab 3: Study metric system chart
lab manual
Lab 3: What is the formula for Celsius to Fahrenheit?
F= (9/5)C + 32
Lab 3: What is the formula for Fahrenheit to Celsius?
C= 5/9 (F- 32)
Lab 3: Compound scope magnification equation
Eyepiece magnification X scope magnification
Lab 3: Resolution equation (know how to plug in numbers)
r = 0.61 (lambda)/ N.A.
r: resolution
lambda: wavelength of light _ 0.54 micrometers = lambda
N.A.: numerical aperture of the objective lens
Lab 3: Know major parts of compound microscope
lab manual
Lab 3: How do you estimate the length of a specimen?
low power: 4.2 mm
medium power: 1.4 mm
high power: 0.35 mm
multiply estimated length/ how much of field specimens takes up to the length of the field
Lab 4: Be able to identify cells and cell conditions
Lab manual/ in slides
Lab 4: Be able to identify items from cell ultrastructure images
Examples in lab manual and on canvas
Lab 5: How does the size of the molecule affect the rate of diffusion?
The larger the size of the molecule, the less distance is traveled when diffused w/ another molecule
Lab 5: How does the temperature of the molecule affect the rate of diffusion?
The rate of simple diffusion is increased when the temperature is increased
Lab 5: Why did some bags lose weight in the dialysis bag experiment?
Hypotonic: inside bag
Hypertonic: outside bag
dH2O is moving from hypotonic to hypertonic
(dH2O in NaCl)
Lab 5: Why did some bags gain weight in the dialysis bag experiment?
Hypertonic: inside bag
Hypotonic: outside bag
dH2O is moving from hypotonic environment to hypertonic
(NaCl in dH2O)
Lab 5: Why did the salt solution plasmolyze Elodea and what did it look like?
Salt solution is hypertonic compared to plant cells
The cells looked like the inside had shrunk but the cell wall remained the same size
Lab 6: What are enzymes and what do they do?
Enzymes are proteins
They make reactions occur more rapidly by lowering activation energy
Lab 6: Product used in the reaction
Benzoquinone
Lab 6: Enzyme used in reaction
Catechol oxidase
Lab 6: Substrate used in reaction
Catechol
Lab 6: How did the temperature affect enzyme activity for the enzyme used in this lab?
Higher temperature reduces activity
Lab 6: How did the pH affect enzyme activity for the enzyme used in this lab?
pH<4 or pH> 8 reduces activity
Lab 7: Yeast undergoes ______ when it is lacking _____
Fermentation, O2
Lab 7: CO2 is a by product of ____
Fermentation
Lab 7: Crickets and beans perform ________ to make _______
Respiration, energy
Lab 7: Crickets and beans inhale ____ to produce _____
O2, CO2
Lab 7: How does measuring CO2 production relate to respiration and fermentation in yeast, germinating beans, and crickets?
When each respirates they produce CO2
Lab 7: What is the difference between aerobic respiration and fermentation
Fermentation only occurs when O2 isn't present `
Lab 7: The process by which organisms get energy (ATP) from their food molecules
Cellular respiration
Lab 7: Produces 2 molecules of ethanol, 2 molecules of CO2, and 2 molecules of ATP for every molecule of glucose that enters glycolysis
Alcohol fermentation
Lab 7: Produces 2 molecules of lactic acid (lactate) and 2 ATPs are produced for every molecule of glucose that undergoes glycolysis
Lactic acid fermentation
Lab 7: What does the heat of respiration represent?
The heat lost during respiration
Lab 7: What is the bromythbol blue experiment?
It changes color in the presence of CO2
More CO2 in light because light causes photosynthesis which releases CO2
Elodea grown in light=yellow= much produced
Elodea grown in dark= green - some CO2 produced
Blue= no CO2 present
Lab 8: how does chromatography work and which pigments were separated from the leaf?
chromatography papers have fibers of a certain size
-carotene, chlorophyll A, and chlorophyll B
1. orange-yellow
2. yellow
3. grassy yellow
4. yellow green
Lab 8: what is fluorescence and what causes it?
long wavelength of light produced by electron as it falls to a lower level
Lab 8: what colors are useful for photosynthesis and what are least useful?
green = not useful
-only color reflected in plants
all others are absorbed
Lab 8: what is the difference between reflect and absorbed light?
reflected: colors seen
absorbed: colors not seen
Lab 8: where is starch stored?
plant's vacuole
Lab 8: how does light vs dark affect starch storage?
light does not affect starch storage
Lab 8: how does measuring O2 level relate to photosynthesis?
plants produce oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis
Lab 9/10: What happens in mitosis?
a 4-stage process that creates 2 identical cells from one original cell
Lab 9/10: first and longest stage of mitosis
-chromosomes become visible
-centrioles separate and move to opposite poles of the cell
prophase
Lab 9/10: second stage of mitosis
-chromosomes line up across the center of the cell
-become connected to the spindle fiber at their centromere
metaphase
Lab 9/10: 3rd stage of mitosis
-sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are pulled a part
anaphase
Lab 9/10: 4th stage of mitosis
-chromosomes gather at opposite ends of the cell (lose distance rod-like shapes).
-2 new nuclear membranes form around each other of the 2 regions of DNA and the spindle fibers disappear
telophase
Lab 9/10: process that follows the last stage of mitosis
-2 complete copies of DNA now in different regions of one cell (cell membrane pinches and divides in 1/2)
-result: 2 individual cells that are identical to the original call
cytokinesis
Lab 9/10: a period of cell growth and normal activity
-between mitosis and cell cycle
interphase
Lab 9/10: meiosis:
-DNA coils into chromosomes
-nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear
-mitotic spindle forms
-synapsis (crossing-over) occurs
prophase 1
Lab 9/10: meiosis:
-tetrads line up randomly along midline
-spindle fibers attach to centromere of each homologous chromosome
metaphase 1
Lab 9/10: meiosis:
-homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles of the cell
anaphase 1
Lab 9/10: meiosis:
-chromosomes reach opposite end of cell and cytokinesis begins
meiosis 1
Lab 9/10: meiosis:
-spindle fibers form and move to the chromosomes toward the midline of the dividing cell
prophase 2
Lab 9/10: meiosis:
-chromosomes move to midline of the diving cell
-facing opposite poles of dividing cell
metaphase 2
Lab 9/10: meiosis:
-chromatids separate
-move toward opposite poles of the cell
anaphase 2
Lab 9/10: meiosis:
-nuclear membrane forms around the chromosomes in each of the 4 new cells
telophase 2
Lab 9/10: be able to identify different mitotic/meiotic stages in cell slides and structures
noted on the slides posted on canvas
Lab 9/10: containing 2 complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent (somatic cells)
diploid
Lab 9/10: having a single set of unpaired chromosomes (gametes/sex cells)
haploid
Lab 9/10: know what is on the charts from the lab 9 self-test and meiosis chart
lab manual
Lab 11: questions will be like those on the
genetics 1-4 homework assignments
Lab 11: both alleles for a trait are dominant in an individual
homozygous dominant
Lab 11: both alleles for a trait are recessive in an individual
homozygous recessive
Lab 11: differing alleles for a trial in an individual (Yy)
heterozygous
Lab 11: the different forms of a gene.
allele
Lab 11: the genetic constitution of an organism with respect to a trait; for a single trait on an autosome, an individual can be homozygous for a dominant trait, heterozygous, or homozygous recessive trait
genotype
Lab 11: the physical appearance of an organism with respect to a trait
phenotype
Lab 11: Know how to predict genotypic and phenotypic ratios for "monohybrid" crosses (really meaning concern with a single gene), and how to work backwards to determine the likely genotypes of parents (it helps a lot if you can do Punnett squares)
look online or in handout for help
Lab 11: Know how to predict phenotypic ratios for "dihybrid" crosses (really meaning crosses with two independently inherited genes), and how to work backwards to determine the likely genotypes of parents (it helps a lot if you can do Punnett squares, and if you treat each gene separately)
look online or in handout for help
Lab 11: what is an x-linked (sex-linked) trait and how do you determine the parental genotypes of given offspring phenotypes?
*genes for these traits occur on the X chromosomes.
-no heterozygous state in males
-only females can be carriers
Lab 11: at least 50% of people have specific trait
autosomal dominant
Lab 11: skips at least one generation
autosomal recessive
Lab 11: specific traits skips at least one generation, usually found in males
x-linked
Lab 11: know how to identify parts in pedigrees
*read info above and in handout
Lab 11: know how to do chi-square tests for genetic crosses
look at equation in handout
Lab 12: how do electrophoresis work? look in manual to in detail information
they can be used to analyze hemoglobin in blood in order to detect the carrier of a genetic disease
Lab 12: What is sickle cell anemia?
an autosomal recessive trait, a patient with this as fewer red blood cells than a person with normal hemoglobin
Lab 12: genotype sickle cell anemia:
H^AH^A
person has normal hemoglobin, no disease
Lab 12: genotype sickle cell anemia:
H^AH^S
person is a "carrier"; half of their hemoglobin is normal; self is abnormal; these people usually aren't anemic
Lab 12: genotype sickle cell anemia:
H^SH^S
person has a sickle cell anemia and thus has very severe anemia
Lab 12: what cell barriers had to be disrupted to get the DNA out of the cells, and ow were those barriers disrupted? (strawberry experiment)
-the cell membrane and cell wall had to be disrupted
-smashing the strawberry disrupted the cell wall and the cell membrane was disrupted by the soap in the detergent
Lab 12: what caused the strawberry DNA to precipitate?
the alcohol added to the solution then causes the DNA to precipitate out
Lab 12: What does the DNA in the strawberry look like?
white, cloudy or find stringy substance
Lab 13: Hardy Winberg equilibrium equation
p^2 + 2pq + q^2 =1
(for 2 alleles A & a)
Lab 13: what does "p" represent?
Frequency of A
Lab 13: what does "q" represent?
frequency of a
Lab 13: What does "p^2" represent?
frequency of AA
Lab 13: What does "q^2" represent?
frequency of aa
Lab 13: What does "2pq" represent?
frequency of Aa
Lab 13: What does "p+q" represent?
frequency of individuals