Block II: Conceptual Modelling
4.7(7)Studied by 186 people
Card Sorting
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:16 PM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
1
New cards
A relative association...
a. ...establishes a relationship between the static methods of a class.
b. ...establishes a relationship between the interface of a class.
c. ...establishes a relationship between the instances of a class.
d. ...establishes a relationship between the statics attributes of a class.
e. Leave question blank
a. ...establishes a relationship between the static methods of a class.
b. ...establishes a relationship between the interface of a class.
c. ...establishes a relationship between the instances of a class.
d. ...establishes a relationship between the statics attributes of a class.
e. Leave question blank
c
2
New cards
A conceptual model can be defined as follows:
a. a graphical view of the requirements.
b. it is a kind of implied version of a real-world domain.
c. a diagram of objects and relationships in our system.
d. leave this question blank.
e. it is a kind of system process view.
a. a graphical view of the requirements.
b. it is a kind of implied version of a real-world domain.
c. a diagram of objects and relationships in our system.
d. leave this question blank.
e. it is a kind of system process view.
a
3
New cards
Select the CORRECT definition:
a. a class diagram is an integrated set of elements, subsystems or assemblies that accomplish a defined objective.
b. leave this question blank
c. a class diagram shows the structure of a system under a certain situation.
d. an object diagram captures and specifies the system vocabulary (elements, relationships and structures).
e. a class diagram captures and specifies the system vocabulary (elements, relationships and structure)
a. a class diagram is an integrated set of elements, subsystems or assemblies that accomplish a defined objective.
b. leave this question blank
c. a class diagram shows the structure of a system under a certain situation.
d. an object diagram captures and specifies the system vocabulary (elements, relationships and structures).
e. a class diagram captures and specifies the system vocabulary (elements, relationships and structure)
e
4
New cards
According to the Liskov substitution principle:
a. All the instances of a superclass are also instances of a subclass.
b. leave this question blank.
c. the definition of a subclass is applicable to an interface.
d. all instances of a subclass are also instances of the superclass.
e. the definition of a subclass is applicable to a superclass.
a. All the instances of a superclass are also instances of a subclass.
b. leave this question blank.
c. the definition of a subclass is applicable to an interface.
d. all instances of a subclass are also instances of the superclass.
e. the definition of a subclass is applicable to a superclass.
d
5
New cards
What kind of relationships can appear in a class diagram to represent a conceptual model?
a. association, dependency, aggregation, composition and generalisation.
b. leave this question blank.
c. association and dependency.
d. association, dependency, aggregation, composition, and contracting.
e. association and contracting
a. association, dependency, aggregation, composition and generalisation.
b. leave this question blank.
c. association and dependency.
d. association, dependency, aggregation, composition, and contracting.
e. association and contracting
a
6
New cards
The weak generalization or realisation...
a. it is not an alternative to. multiple inheritance that is not support in most of programming languages.
b. leave this question blank.
c. it increases the degree of dependency.
d. it is equivalent to a composition with 1-n multiplicity.
e. it reduces the reuse of data and code.
a. it is not an alternative to. multiple inheritance that is not support in most of programming languages.
b. leave this question blank.
c. it increases the degree of dependency.
d. it is equivalent to a composition with 1-n multiplicity.
e. it reduces the reuse of data and code.
e
7
New cards
which is an application of an association class?
a. restrict the access to the instances of the association.
b. add extra information to an association.
c. reduce the multiplicity of some association.
d. establish association roles.
e. leave this question blank.
a. restrict the access to the instances of the association.
b. add extra information to an association.
c. reduce the multiplicity of some association.
d. establish association roles.
e. leave this question blank.
b
8
New cards
which is NOT a desired property of a model?
a. predictive.
b. comprehensive
c. linear
d. precise
e. leave this question blank
a. predictive.
b. comprehensive
c. linear
d. precise
e. leave this question blank
c
9
New cards
what is aggregation?
a. it is a kind of non-shared composition.
b. it serves us to represent a kind of generalization process.
c. it is a type of association that represents a "whole-part" relationship, transitive and asymmetric.
d. it is the set of operations to solve a problem or reach an objective.
e. leave this question blank
a. it is a kind of non-shared composition.
b. it serves us to represent a kind of generalization process.
c. it is a type of association that represents a "whole-part" relationship, transitive and asymmetric.
d. it is the set of operations to solve a problem or reach an objective.
e. leave this question blank
c
10
New cards
A conceptual model can be defined as follows:
a. a diagram of objects and relationships in our system.
b. It is a kind of simplified version of a real-world problem.
c. a graphical view of the requirements.
d. it can be a reflexive association at a class-level but not in a sub-class level
a. a diagram of objects and relationships in our system.
b. It is a kind of simplified version of a real-world problem.
c. a graphical view of the requirements.
d. it can be a reflexive association at a class-level but not in a sub-class level
c
11
New cards
Which is NOT a desired property of a model?
a. comprehensive
b. analytical
c. precise
d. predictive
a. comprehensive
b. analytical
c. precise
d. predictive
b
12
New cards
what type of classes can exist according to the different types of objects?
a. physical, historical, tangible.
b. physical, logical, tangible.
c. historical, logical and tangible
d. physical, logical and historical
a. physical, historical, tangible.
b. physical, logical, tangible.
c. historical, logical and tangible
d. physical, logical and historical
d
13
New cards
What is aggregation?
a. it is a type of generalization that represents a "whole-part" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
b. it is a type of association that represents a "is-a" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
c. it is a type of generalization that represents a "is-a" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
d. it is a type of association that represents a "whole-part" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
a. it is a type of generalization that represents a "whole-part" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
b. it is a type of association that represents a "is-a" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
c. it is a type of generalization that represents a "is-a" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
d. it is a type of association that represents a "whole-part" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
d
14
New cards
Which is an application of an association class?
a. reduce the multiplicity of some association.
b. establish association roles.
c. add extra information to an association
d. restrict the access to the instances of the association
a. reduce the multiplicity of some association.
b. establish association roles.
c. add extra information to an association
d. restrict the access to the instances of the association
c
15
New cards
given a class hierarchy, select the CORRECT answer:
a. it does not have neither instances nor multiplicity.
b. it represents a pure relationship between instances.
c. It represents a pure relationship between interfaces.
d. a class can only have one parent class.
a. it does not have neither instances nor multiplicity.
b. it represents a pure relationship between instances.
c. It represents a pure relationship between interfaces.
d. a class can only have one parent class.
a
16
New cards
according to the semantics of an association, which is NOT a type of association?
a. inheritance
b. N-ary
c. composition
d. aggregation
a. inheritance
b. N-ary
c. composition
d. aggregation
b
17
New cards
The weak realisation or generalisation implies:
a. the degree of reuse is increased.
b. the degree of dependency is decreased.
the performance is decreased.
d. all answers are false
a. the degree of reuse is increased.
b. the degree of dependency is decreased.
the performance is decreased.
d. all answers are false
b
18
New cards
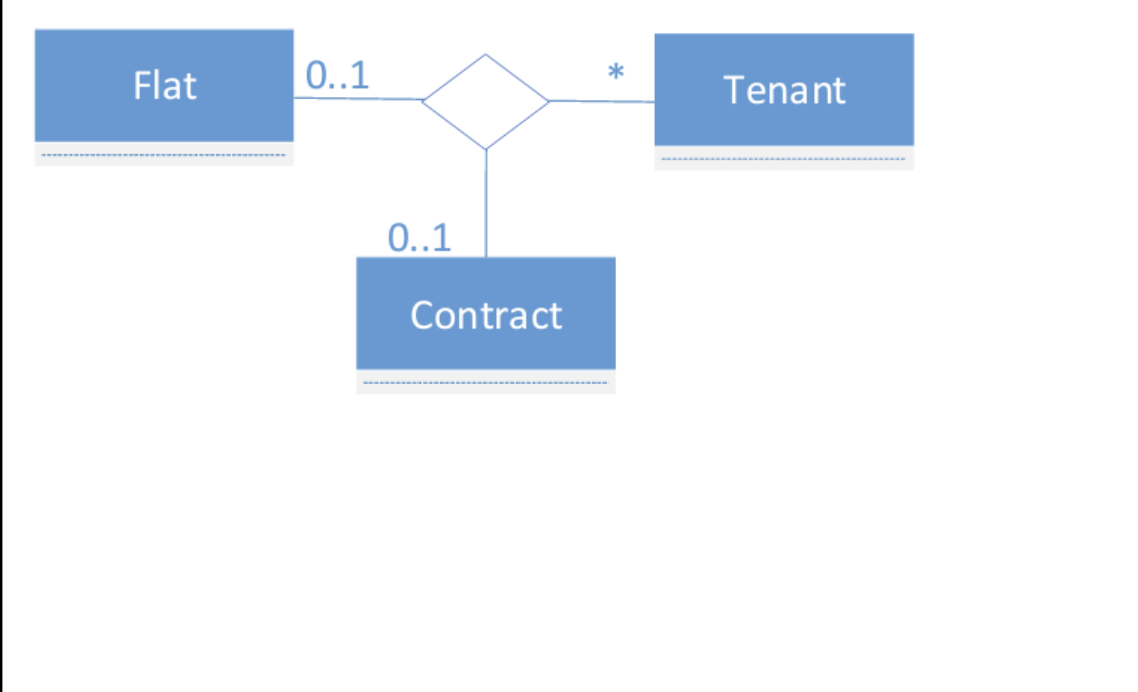
Given the next UML class diagram, select the CORRECT interpretation:
a. a flat can be rented by several tenants under the same contract.
b. a flat can be rented by several tenants under different contracts.
c. a tenant can rent two flats under the same contract.
d. a tenant can rent one flat under different contracts.
a. a flat can be rented by several tenants under the same contract.
b. a flat can be rented by several tenants under different contracts.
c. a tenant can rent two flats under the same contract.
d. a tenant can rent one flat under different contracts.
a
19
New cards
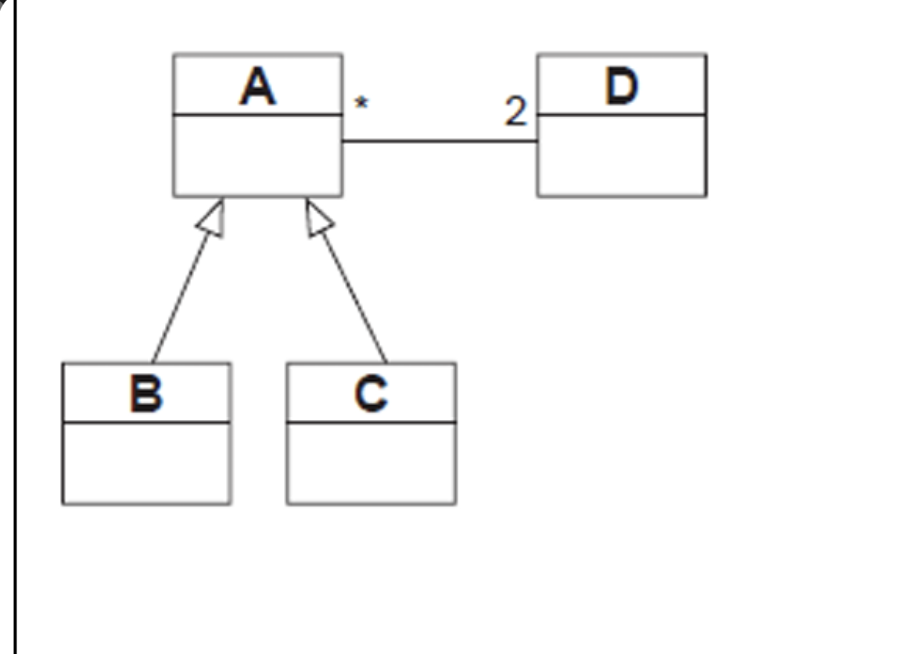
given the next UML class diagram, select the CORRECT interpretation.
a. one object of D must be associated with at least one object of C or B.
b. one object of A must be associated with an object of D.
c. one object of B must be associated wit exactly 2 objects of D.
d. two objects of D must be associated with multiple objects of A.
a. one object of D must be associated with at least one object of C or B.
b. one object of A must be associated with an object of D.
c. one object of B must be associated wit exactly 2 objects of D.
d. two objects of D must be associated with multiple objects of A.
c
20
New cards
which is an application of an association class?
a. reduce the multiplicity of some association
b. establish association roles
c. add extra information to an association
d. restrict the access to the instances of the association
a. reduce the multiplicity of some association
b. establish association roles
c. add extra information to an association
d. restrict the access to the instances of the association
c
21
New cards
from a conceptual point of view...
a. a datatype represents a concept within a system
b. a datatype can only keep constant or variable values.
c. a class represent a concept within the system
d. a class can only keep constant and immutable values.
a. a datatype represents a concept within a system
b. a datatype can only keep constant or variable values.
c. a class represent a concept within the system
d. a class can only keep constant and immutable values.
c
22
New cards
given a class hierarchy, select the CORRECT answer:
a. it represents a pure relationship between classes.
b. the level of abstraction is reduced.
c. a subclass only inherits superclass protected properties.
d. a subclass can only have a parent class
a. it represents a pure relationship between classes.
b. the level of abstraction is reduced.
c. a subclass only inherits superclass protected properties.
d. a subclass can only have a parent class
a
23
New cards
what is aggregation?
a. it is a type of generalisation that represents a "whole-part" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
b. it is a type of association that represents a "whole-part" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
c. it is a type of association that represents a "is-a" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
d. it is a type of generalisation that represents a "is-a" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
a. it is a type of generalisation that represents a "whole-part" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
b. it is a type of association that represents a "whole-part" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
c. it is a type of association that represents a "is-a" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
d. it is a type of generalisation that represents a "is-a" transitive and asymmetric relationship.
b
24
New cards
A reflexive association...
a. .. establishes a relationship between the interfaces of a class.
b. .. establishes a relationship between the instances of a class.
c. .. establishes a relationship between the static attributes of a class.
d. ... establishes a relationship between the static methods of a class.
a. .. establishes a relationship between the interfaces of a class.
b. .. establishes a relationship between the instances of a class.
c. .. establishes a relationship between the static attributes of a class.
d. ... establishes a relationship between the static methods of a class.
b
25
New cards
select the CORRECT statement...
a. if the requirements are specified with graphical techniques, the derived conceptual model is always complete.
b. a detailed conceptual model can contain classes that are not stated in the requirements.
c. a descriptive model generated by a reverse engineering process is complete.
d. non-functional requirements are not represented in a conceptual mode.
a. if the requirements are specified with graphical techniques, the derived conceptual model is always complete.
b. a detailed conceptual model can contain classes that are not stated in the requirements.
c. a descriptive model generated by a reverse engineering process is complete.
d. non-functional requirements are not represented in a conceptual mode.
b
26
New cards
A rule of thumb t model class attributes...
a. if the range of values is large, an attribute will fit better.
b. if the range of values is large, a subclass will fit better.
c. if the range of values is large, an enumeration will fit better.
d. if the range of values is large, an interface will fit better
a. if the range of values is large, an attribute will fit better.
b. if the range of values is large, a subclass will fit better.
c. if the range of values is large, an enumeration will fit better.
d. if the range of values is large, an interface will fit better
a
27
New cards
An n-ary association...
a. it eases the navigability
b. aggregation is not allowed.
c. it cannot be, at the same time, a class association.
d. the minimum multiplicity must be 1
a. it eases the navigability
b. aggregation is not allowed.
c. it cannot be, at the same time, a class association.
d. the minimum multiplicity must be 1
b
28
New cards
given an UML class diagram stating an inheritance relationship between a superclass A and subclass A1. Which of the following statements is CORRECT?
a. establish the navigability is optional.
b. establish the name is mandatory
c. the subclass A1 inherits some of the properties of A.
d. the subclass A1 inherits all the properties of A.
a. establish the navigability is optional.
b. establish the name is mandatory
c. the subclass A1 inherits some of the properties of A.
d. the subclass A1 inherits all the properties of A.
d
29
New cards
Select the INCORRECT statement regrind data types
a. they can be primitive data types or enumerated.
b. they can contain operations
c. they are general-purpose
d. it is possible to create instances, although they are anonymous, without identity.
a. they can be primitive data types or enumerated.
b. they can contain operations
c. they are general-purpose
d. it is possible to create instances, although they are anonymous, without identity.
b
30
New cards
Which is an application of an association class?
a. reduce the multiplicity of some associations.
b. establish association roles.
c. add extra information to an association.
d. restrict the access to the instances of the association.
a. reduce the multiplicity of some associations.
b. establish association roles.
c. add extra information to an association.
d. restrict the access to the instances of the association.
c
31
New cards
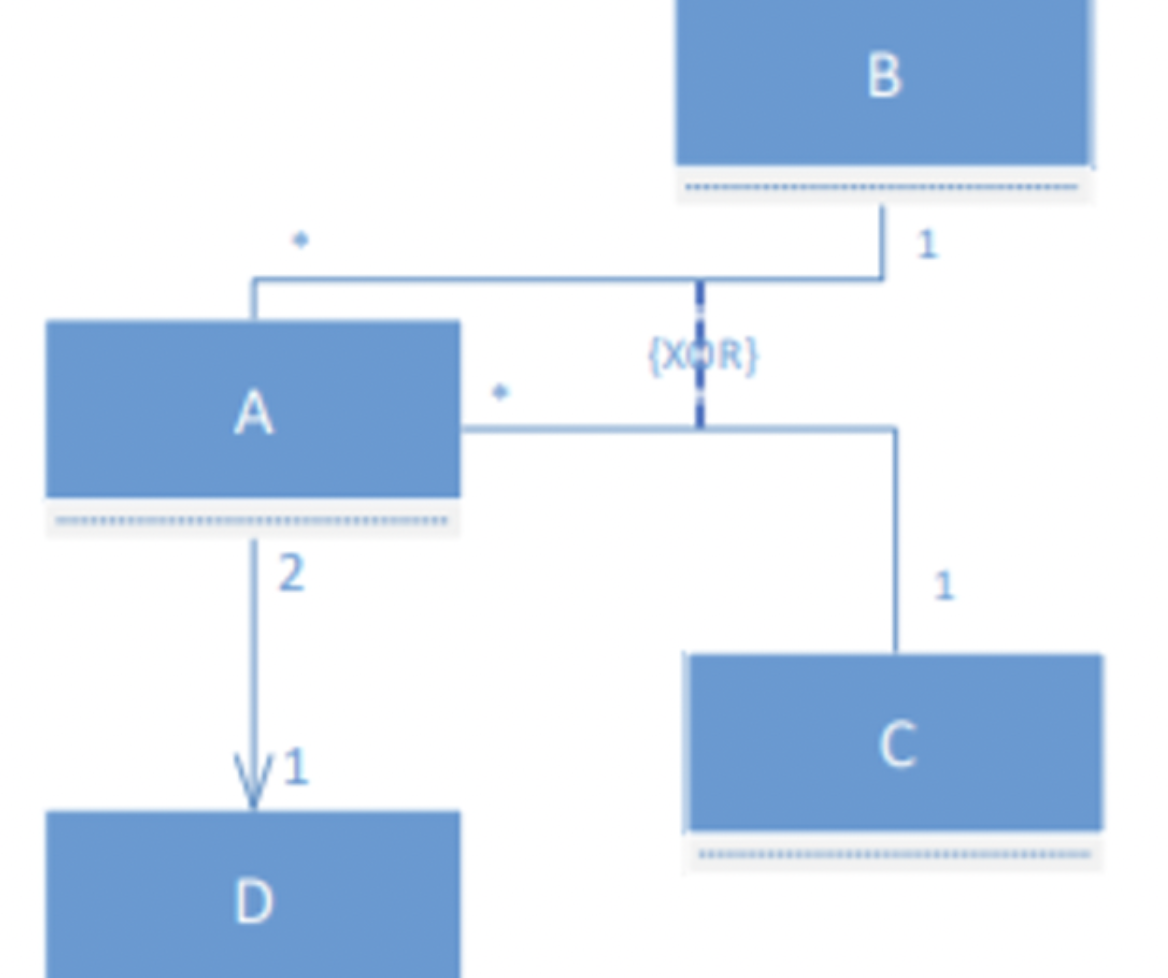
Given the next UML class diagram, select the INCORRECT interpretation.
a. An instance of A is associated with exactly 1 instance of B or 1 instance of C.
b. The association between A and D is navigable from A to D.
c. An instance of A is associated with exactly 2 instances of D.
d. An instance of B may be associated with n instances of A.
a. An instance of A is associated with exactly 1 instance of B or 1 instance of C.
b. The association between A and D is navigable from A to D.
c. An instance of A is associated with exactly 2 instances of D.
d. An instance of B may be associated with n instances of A.
c
32
New cards
Select the CORRECT statement regarding navigability
a. it specifies the possibility of sending messages to the attributes of a class.
b. it specifies the possibility of creating instances of a class and access static methods.
c. it specifies the ability of a source instance to create attributes and operations of instances.
d. it specifies the ability of a source instance to access attributes and operations of instance.
a. it specifies the possibility of sending messages to the attributes of a class.
b. it specifies the possibility of creating instances of a class and access static methods.
c. it specifies the ability of a source instance to create attributes and operations of instances.
d. it specifies the ability of a source instance to access attributes and operations of instance.
d
33
New cards
A reflexive association..
a. .. establishes a relationship between the interfaces of a class.
b. .. establishes a relationship between the instances of a class.
c. .. establishes a relationship between the static attributes of a class
d. .. establishes a relationship between the static methods of a class
a. .. establishes a relationship between the interfaces of a class.
b. .. establishes a relationship between the instances of a class.
c. .. establishes a relationship between the static attributes of a class
d. .. establishes a relationship between the static methods of a class
b
34
New cards
if both, abstract classes and interfaces, serve to specify operations, when should we select between the use of an abstract class or an interface?
a. abstract classes represent a better option if we want to reuse data and some operations.
b. interfaces represent a better option if we want to reuse data and some operations.
c, it does not matter, the result will be the same in terms of number of instances, extensibility, etc.
d. it does not matter, in both cases the state of the parent class or interface is inherited
a. abstract classes represent a better option if we want to reuse data and some operations.
b. interfaces represent a better option if we want to reuse data and some operations.
c, it does not matter, the result will be the same in terms of number of instances, extensibility, etc.
d. it does not matter, in both cases the state of the parent class or interface is inherited
a
35
New cards
which is not a desired property of a model?
a. comprehensible
b. analytical/expensive
c. precise
d. predictive
a. comprehensible
b. analytical/expensive
c. precise
d. predictive
b
36
New cards
One attribute is...
a. equivalent to a bidirectional association
b. equivalent to a unidirectional association
c. equivalent to a reflexive association
d. none are correct
a. equivalent to a bidirectional association
b. equivalent to a unidirectional association
c. equivalent to a reflexive association
d. none are correct
b
37
New cards
what is a model?
a. a graphical representation of a set of interconnected elements
b. a graphical representation of the elements of a system
c. a collection of elements that fulfil a specific functionality
d. an abstraction of a system, a complete and consistent simplification of the real system, for a better understanding of it.
a. a graphical representation of a set of interconnected elements
b. a graphical representation of the elements of a system
c. a collection of elements that fulfil a specific functionality
d. an abstraction of a system, a complete and consistent simplification of the real system, for a better understanding of it.
d
38
New cards
Select the INCORRECT one:
a. an association allows to invoke justo one method
b. any association has a double meaning: dynamic and static
c. in associations are preferred nouns over verbs
d. an attribute that is a class is equivalent to a unidirectional accusation
a. an association allows to invoke justo one method
b. any association has a double meaning: dynamic and static
c. in associations are preferred nouns over verbs
d. an attribute that is a class is equivalent to a unidirectional accusation
b
39
New cards
Select the INCORRECT one:
a. an association allows to invoke justo one method
b. any association has a triple meaning: dynamic, static and dimensional
c. in associations are preferred nouns over verbs
d. an attribute that is a class is equivalent to a unidirectional accusation
a. an association allows to invoke justo one method
b. any association has a triple meaning: dynamic, static and dimensional
c. in associations are preferred nouns over verbs
d. an attribute that is a class is equivalent to a unidirectional accusation
b
40
New cards
which are considere characteristics of the analysis process with objects and classes?
a. use a simplified notation
b. classes, attributes and methods are domain concepts
c. all of them are CORRECT
d. it is a specification tool
a. use a simplified notation
b. classes, attributes and methods are domain concepts
c. all of them are CORRECT
d. it is a specification tool
c
41
New cards
what is an aggregation?
a. it is a non-shared composition
b. it is a non-shared inheritance
c. it is a special type of association that represents a whole-par relationship, transitive and asymmetric.
d. the methods and operations required to solve a problem.
a. it is a non-shared composition
b. it is a non-shared inheritance
c. it is a special type of association that represents a whole-par relationship, transitive and asymmetric.
d. the methods and operations required to solve a problem.
42
New cards
what types of classes exist depending on the represented object?
a. historical, logical and tangible
b. physical, logical and historical
c. physical, logical and tangible
d. physical, historical and tangible
a. historical, logical and tangible
b. physical, logical and historical
c. physical, logical and tangible
d. physical, historical and tangible
b
43
New cards
conceptual modelling can be defined as:
a. a graphical view of the requirements
b. simplification of real-world phenomena
c. a diagram with the objects related to our project and the relationships between them
d. formal representation of the operations of a system
a. a graphical view of the requirements
b. simplification of real-world phenomena
c. a diagram with the objects related to our project and the relationships between them
d. formal representation of the operations of a system
a
44
New cards
given a class hierarchy, select the CORRECT answer:
a. the subclass inherits the protected properties of the superclass
b. represents a pure relationship between classes
c. the abstraction level is reduced
d. it can be interpreted as a whole.part relationship
a. the subclass inherits the protected properties of the superclass
b. represents a pure relationship between classes
c. the abstraction level is reduced
d. it can be interpreted as a whole.part relationship
a
45
New cards
select the CORRECT answer:
a. a system is an encapsulation of a model with a graphical representation of its elements
b. a system is the graphical representation of a set of interconnected elements
c. a system is an abstraction of a model, a complete and consistent simplification of the real system, for a better understanding of it.
d. a system is a set of organized elements to fulfil a specific functionality.
a. a system is an encapsulation of a model with a graphical representation of its elements
b. a system is the graphical representation of a set of interconnected elements
c. a system is an abstraction of a model, a complete and consistent simplification of the real system, for a better understanding of it.
d. a system is a set of organized elements to fulfil a specific functionality.
d
46
New cards
what is a composition?
a. it is a special type of aggregation representing an "is-a" relationship
b. it is a special type of specification representing a "is-a" relationship
c. it is a special type of generalisation representing a "whole-part" relationship and asymmetric
d. c. it is a special type of association representing a "whole-part" relationship and asymmetric
a. it is a special type of aggregation representing an "is-a" relationship
b. it is a special type of specification representing a "is-a" relationship
c. it is a special type of generalisation representing a "whole-part" relationship and asymmetric
d. c. it is a special type of association representing a "whole-part" relationship and asymmetric
d
47
New cards
In a composition...
a. there are not any special restrictions regarding multiplicity
b. copy and delete operations are kept
c. the multiplicity can only be 0...1 or 1...1, same as aggregation
d. can be a reflexive relationship, but not for subclasses.
a. there are not any special restrictions regarding multiplicity
b. copy and delete operations are kept
c. the multiplicity can only be 0...1 or 1...1, same as aggregation
d. can be a reflexive relationship, but not for subclasses.
b
48
New cards
Regarding the differences between classes and datatypes, please select the INCORRECT answer:
a. the population is finite and variable while the population of a datatype is finite or infinite but constant.
b. a class can be simple or structured while a datatype is always simple.
c. the attributes of a class are fixed or variable while the values of a datatype are fixed and immutable.
d. a class can be part of a unidirectional (one-way) or bidirectional (two-way) associations while a datatype can only be part of unidirectional associations.
a. the population is finite and variable while the population of a datatype is finite or infinite but constant.
b. a class can be simple or structured while a datatype is always simple.
c. the attributes of a class are fixed or variable while the values of a datatype are fixed and immutable.
d. a class can be part of a unidirectional (one-way) or bidirectional (two-way) associations while a datatype can only be part of unidirectional associations.
b
49
New cards
how can we decide if a domain concept is modelled as a class or as a datatype? select the INCORRECT answer
a. a domain concept will be always modelled as a class since concepts are always abstract.
b. a domain concept will be modelled as a class or as a datatype depending on the target system. Therefore, the type of modelling is domain dependent.
c. a domain concept will be modelled as an object if it represents a concrete domain instance.
d. a domain concept will be modelled as a class if it represents a family of instances and not just a concrete concept.
a. a domain concept will be always modelled as a class since concepts are always abstract.
b. a domain concept will be modelled as a class or as a datatype depending on the target system. Therefore, the type of modelling is domain dependent.
c. a domain concept will be modelled as an object if it represents a concrete domain instance.
d. a domain concept will be modelled as a class if it represents a family of instances and not just a concrete concept.
a
50
New cards
select a characteristic that does NOT define a reflexive association.
a. a reflexive (or recursive) association) is a kind of association in which both ends are start and finish in the same class.
b. the links can connect instances of different classes or events an instance with itself.
c. it is a kind of association that represents a whole-part, transitive and asymmetric relationship transitive.
d. in a reflexive association, the role names are mandatory to distinguish the ends of the relationship.
a. a reflexive (or recursive) association) is a kind of association in which both ends are start and finish in the same class.
b. the links can connect instances of different classes or events an instance with itself.
c. it is a kind of association that represents a whole-part, transitive and asymmetric relationship transitive.
d. in a reflexive association, the role names are mandatory to distinguish the ends of the relationship.
d
51
New cards
regrind composition..
a. it serves to represent encapsulation but not restricted access to a class.
b. it is a kind of non-shared aggregation.
c. it does not propagate deletion operations.
d. it can hold any type of multiplicity.
a. it serves to represent encapsulation but not restricted access to a class.
b. it is a kind of non-shared aggregation.
c. it does not propagate deletion operations.
d. it can hold any type of multiplicity.
b
52
New cards
given a software system in which we have a database to store the information about users and an externa program that is used by administrators to manage the database, it is necessary to consider the administrators as a user in the conceptual modelling?
a. yes, we must consider administrators as users, and they can appear in diagrams and documents such as the requirements specification.
b. end -users must appear since they are actors, but administrators must not appear since they are using an external application to manage the database.
c. end.users must not appear, but administrators must since they must perform operations to keep the system running.
d. none of them must appear since they are external agents.
a. yes, we must consider administrators as users, and they can appear in diagrams and documents such as the requirements specification.
b. end -users must appear since they are actors, but administrators must not appear since they are using an external application to manage the database.
c. end.users must not appear, but administrators must since they must perform operations to keep the system running.
d. none of them must appear since they are external agents.
b
53
New cards
a possible rule of thumb for the property model
a. if a range (set of possible values) is very large, an attribute would be better
b. If the range (possible set of values) is very large, a subclass would be better.
c. if the range (set of possible values) is enumerated an attribute would be better.
d. None of the above is correct
a. if a range (set of possible values) is very large, an attribute would be better
b. If the range (possible set of values) is very large, a subclass would be better.
c. if the range (set of possible values) is enumerated an attribute would be better.
d. None of the above is correct
a
54
New cards
An attribute is...
a) Equivalent to a bidirectional association.
b) Equivalent to a unidirectional association.
c) Equivalent to a reflexive association.
d) None of the above is correct.
a) Equivalent to a bidirectional association.
b) Equivalent to a unidirectional association.
c) Equivalent to a reflexive association.
d) None of the above is correct.
b
55
New cards
What is called aggregation?
a) It is a special type of association that represents a transitive and asymmetric whole-part relationship.
b) It is a type of non-shared composition.
c) To the functions and operations required to solve a problem or achieve an objective.
d) None of the above.
a) It is a special type of association that represents a transitive and asymmetric whole-part relationship.
b) It is a type of non-shared composition.
c) To the functions and operations required to solve a problem or achieve an objective.
d) None of the above.
a
56
New cards
A hierarchy of classes:
a) It is a pure relationship between classes.
b) It has no instances or multiplicity.
c) The subclass inherits all the properties of the superclass.
d) All of the above are correct. *A hierarchy of classes: It is a relationship
a) It is a pure relationship between classes.
b) It has no instances or multiplicity.
c) The subclass inherits all the properties of the superclass.
d) All of the above are correct. *A hierarchy of classes: It is a relationship
d
57
New cards
From a conceptual point of view...
a) A data type represents a concept within the boundaries of the system.
b) A data type can only contain fixed or variable values.
c) A class represents a concept within the boundaries of the system.
d) A class can only contain fixed and immutable values.
a) A data type represents a concept within the boundaries of the system.
b) A data type can only contain fixed or variable values.
c) A class represents a concept within the boundaries of the system.
d) A class can only contain fixed and immutable values.
c
58
New cards
An n-ary relationship...
a) It facilitates navigation.
b) Does not allow aggregation.
c) It cannot be an association class at the same time.
d) The minimum multiplicity must be 1.
a) It facilitates navigation.
b) Does not allow aggregation.
c) It cannot be an association class at the same time.
d) The minimum multiplicity must be 1.
b
59
New cards
Weak generalization implies that...
a) Reuse is increased.
b) Dependence is decreased.
c) Yield decreases.
d) All of the above are false.
a) Reuse is increased.
b) Dependence is decreased.
c) Yield decreases.
d) All of the above are false.
d
60
New cards
Multiplicity can be defined as...
a) In a binary association, the multiplicity of an association end specifies the number of target instances that can be linked to a single source instance through association.
b) In a binary association, the multiplicity specifies the capacity that an instance of the source class to access all instances of the target class via the instances of the
association that connects them.
c) In a binary association, the multiplicity of an association end specifies the type of target instances that can be linked to multiple source instances through association.
d) In a binary association, the multiplicity specifies the capacity that an instance of
class source to access some instances of the target class via the instances of the association
that connect them.
a) In a binary association, the multiplicity of an association end specifies the number of target instances that can be linked to a single source instance through association.
b) In a binary association, the multiplicity specifies the capacity that an instance of the source class to access all instances of the target class via the instances of the
association that connects them.
c) In a binary association, the multiplicity of an association end specifies the type of target instances that can be linked to multiple source instances through association.
d) In a binary association, the multiplicity specifies the capacity that an instance of
class source to access some instances of the target class via the instances of the association
that connect them.
a
61
New cards
In a binary association, the multiplicity of an association end...
a) Specifies the number of target instances that can be interleaved with multiple instances origin through association.
b) Specifies the ability of an instance of the source class to access instances of the target class by means of the association instances that connect it.
c) Represents the number of classes that can be intertwined within the same class diagram.
d) Specifies the number of destination instances that can be interleaved with a single instance
origin through association.
a) Specifies the number of target instances that can be interleaved with multiple instances origin through association.
b) Specifies the ability of an instance of the source class to access instances of the target class by means of the association instances that connect it.
c) Represents the number of classes that can be intertwined within the same class diagram.
d) Specifies the number of destination instances that can be interleaved with a single instance
origin through association.
a
62
New cards
A class diagram takes care of:
a) Illustrate the structure of the system through particular situations.
b) Capture and specify vocabulary of the system: elements, relations and structure.
c) Graphically represent the algorithm or process.
d) None of the above.
a) Illustrate the structure of the system through particular situations.
b) Capture and specify vocabulary of the system: elements, relations and structure.
c) Graphically represent the algorithm or process.
d) None of the above.
b
63
New cards
What is a model?
a) Abstraction or simplification of reality.
b) A way of programming.
c) It is a type of requirement.
d) It is a correspondence between requirements and classes.
a) Abstraction or simplification of reality.
b) A way of programming.
c) It is a type of requirement.
d) It is a correspondence between requirements and classes.
a
64
New cards
A model is...
a) A graphical representation of a set of interconnected elements.
b) An abstraction of a system.
c) A collection of elements organized to fulfill a specific purpose.
d) A simplification of the requirements.
a) A graphical representation of a set of interconnected elements.
b) An abstraction of a system.
c) A collection of elements organized to fulfill a specific purpose.
d) A simplification of the requirements.
b
65
New cards
Which of these relationships can NOT contain a class diagram?
a) Inheritance
b) Aggregation
c) Composition
d) Reflexive associations.
a) Inheritance
b) Aggregation
c) Composition
d) Reflexive associations.
a
66
New cards
A model...
a) It is a collection of elements organized to fulfill a specific purpose.
b) It is an abstraction of a system, that is, a (complete and consistent) simplification of the real system, which serves to understand it better.
c) It is the graphic representation of a set of interconnected elements.
d) None of the above.
a) It is a collection of elements organized to fulfill a specific purpose.
b) It is an abstraction of a system, that is, a (complete and consistent) simplification of the real system, which serves to understand it better.
c) It is the graphic representation of a set of interconnected elements.
d) None of the above.
b
67
New cards
What properties are desirable in a model?
a) Understandable, Accurate, Cheap and Predictive.
b) Comprehensive, Precise, Abstract and Predictive.
c) Understandable, Abstract, Cheap and Predictive.
d) Understandable, Extensive, Cheap and Predictive.
a) Understandable, Accurate, Cheap and Predictive.
b) Comprehensive, Precise, Abstract and Predictive.
c) Understandable, Abstract, Cheap and Predictive.
d) Understandable, Extensive, Cheap and Predictive.
a
68
New cards
The class diagram is an element of:
a) Conceptual modeling.
b) The architectural model.
c) Requirements analysis.
d) None of the above.
a) Conceptual modeling.
b) The architectural model.
c) Requirements analysis.
d) None of the above.
a
69
New cards
How can the multiplicity symbol '*' also be expressed in an association relation of a
UML diagram?
a) 0..*.
b) 1..*.
c) 1..1.
d) Another way
UML diagram?
a) 0..*.
b) 1..*.
c) 1..1.
d) Another way
a
70
New cards
What does "conceptual model" mean?
a) It is a graphic view of the information contained in the requirements.
b) It is the fundamental organization of a system embodied in its components, the relationships
between them and with the environment, and the principles that guide their design and evolution.
c) It is a description of the steps or activities that must be carried out to carry out some process.
d) It is the systematic application of scientific and technological knowledge, methods and experiences
software design, implementation, testing and documentation.
a) It is a graphic view of the information contained in the requirements.
b) It is the fundamental organization of a system embodied in its components, the relationships
between them and with the environment, and the principles that guide their design and evolution.
c) It is a description of the steps or activities that must be carried out to carry out some process.
d) It is the systematic application of scientific and technological knowledge, methods and experiences
software design, implementation, testing and documentation.
a
71
New cards
About actor associations-system:
a) Are those in which the two ends of the association are linked to the same class.
b) Represents modeled entities within the system.
c) Represents associations with entities external to the system.
d) Represents a whole relationship-part.
a) Are those in which the two ends of the association are linked to the same class.
b) Represents modeled entities within the system.
c) Represents associations with entities external to the system.
d) Represents a whole relationship-part.
c
72
New cards
Desirable properties of a model:
a) Understandable, accurate, predictive and cheap.
b) Fast, understandable and cheap.
c) Colorful, precise, coherent and cheap.
d) Simple, fast and cheap.
a) Understandable, accurate, predictive and cheap.
b) Fast, understandable and cheap.
c) Colorful, precise, coherent and cheap.
d) Simple, fast and cheap.
a
73
New cards
What is a model?
a) It is an abstraction of a system, that is, a simplification of the real system, which serves to understand it better.
b) It is a collection of elements organized to fulfill a specific purpose.
c)It is an internal globalization of the real system, which serves to store requirements.
d) It is the graphic representation of a set of interconnected elements, a partial view of
a model.
a) It is an abstraction of a system, that is, a simplification of the real system, which serves to understand it better.
b) It is a collection of elements organized to fulfill a specific purpose.
c)It is an internal globalization of the real system, which serves to store requirements.
d) It is the graphic representation of a set of interconnected elements, a partial view of
a model.
a
74
New cards
Find the bogus property of the view attribute definition in class:
a) It is a property shared by members of the same class.
b) Each attribute has a different value for each object.
c) The attributes of the same class always have the same value.
d) None are false.
a) It is a property shared by members of the same class.
b) Each attribute has a different value for each object.
c) The attributes of the same class always have the same value.
d) None are false.
c
75
New cards
What does the following expression “ 1..* ” mean in an association?
a) One and only one.
b) From one to many.
c) From one to many (including zero).
d) All except one.
a) One and only one.
b) From one to many.
c) From one to many (including zero).
d) All except one.
b
76
New cards
what is an attribute?
a) property shared by the objects of a class
b) Distinctive quality of a class.
c) Function that can be applied to the objects of a class.
d) Exclusive ownership of an object of a class.
a) property shared by the objects of a class
b) Distinctive quality of a class.
c) Function that can be applied to the objects of a class.
d) Exclusive ownership of an object of a class.
a
77
New cards
UML can be defined as:
a) A graphical modeling language focused on the field of software engineering.
b) A standard that defines the guidelines to be followed in the requirements engineering process.
c) A modeling language that allows describing a software product through diagrams,
textual descriptions and code snippets.
d) All of the above are true.
a) A graphical modeling language focused on the field of software engineering.
b) A standard that defines the guidelines to be followed in the requirements engineering process.
c) A modeling language that allows describing a software product through diagrams,
textual descriptions and code snippets.
d) All of the above are true.
a
78
New cards
Mark the answer that does NOT correspond to the characteristics of a reflexive association.
a) A reflexive (or recursive) association is one in which the two ends of the association they are attached to the same class.
b) Links can connect two different instances of the same class, or even one instance With itself.
c) It is a special type of association that represents a relationship all-part, transitive and asymmetric.
d) In a reflexive association role names are mandatory, in order to distinguish the two ends of the association.
a) A reflexive (or recursive) association is one in which the two ends of the association they are attached to the same class.
b) Links can connect two different instances of the same class, or even one instance With itself.
c) It is a special type of association that represents a relationship all-part, transitive and asymmetric.
d) In a reflexive association role names are mandatory, in order to distinguish the two ends of the association.
c
79
New cards
Indicate the true sentence regarding the composition:
a) Implement encapsulation, but not restricted access.
b) It behaves as a non-shared aggregation.
c) Does not propagate delete operations.
d) Admits any type of multiplicity.
a) Implement encapsulation, but not restricted access.
b) It behaves as a non-shared aggregation.
c) Does not propagate delete operations.
d) Admits any type of multiplicity.
b
80
New cards
Regarding modeling in UML, associations...
a) They are always symmetrical, and therefore the roles between the classes are interchangeable.
b) They are always asymmetric, since they are equivalent to ordered pairs, and therefore the roles between the
classes are not interchangeable.
c) If they are reflexive, they can be symmetric.
d) Asymmetric associations can only be unidirectional.
a) They are always symmetrical, and therefore the roles between the classes are interchangeable.
b) They are always asymmetric, since they are equivalent to ordered pairs, and therefore the roles between the
classes are not interchangeable.
c) If they are reflexive, they can be symmetric.
d) Asymmetric associations can only be unidirectional.
b
81
New cards
Select the INCORRECT answer:
a) An attribute whose type is a class is equivalent to a one-way association.
b) A single association allows the invocation of many operations.
c) Every association has a triple meaning: dynamic aspect, static aspect and dimensional.
d) In associations, static names (nouns) are preferable, reserving names dynamics (verbs) for operations.
a) An attribute whose type is a class is equivalent to a one-way association.
b) A single association allows the invocation of many operations.
c) Every association has a triple meaning: dynamic aspect, static aspect and dimensional.
d) In associations, static names (nouns) are preferable, reserving names dynamics (verbs) for operations.
c
82
New cards
According to the Barbara Liskov substitution principle:
a) The definition of the subclass is applicable to the superclass.
b) All objects of the subclass are also of the superclass.
c) All objects of the superclass are also of the subclass.
d) None of the other options is correct.
a) The definition of the subclass is applicable to the superclass.
b) All objects of the subclass are also of the superclass.
c) All objects of the superclass are also of the subclass.
d) None of the other options is correct.
b
83
New cards
What is multiple generalization?
a) It is the generalization in which a class generalizes several subclasses at the same time. It can't be done
implement in some object-oriented programming languages.
b) It is the same as multiple classification.
c) It is the generalization in which a class C inherits from a class B which in turn inherits from a class A, and so on, forming a multilevel hierarchy.
d) It is the generalization in which a class specializes several superclasses at the same time.
a) It is the generalization in which a class generalizes several subclasses at the same time. It can't be done
implement in some object-oriented programming languages.
b) It is the same as multiple classification.
c) It is the generalization in which a class C inherits from a class B which in turn inherits from a class A, and so on, forming a multilevel hierarchy.
d) It is the generalization in which a class specializes several superclasses at the same time.
d
84
New cards
What types of classes are there according to the objects represented?
a) Physical, Logical and Historical.
b) Historical, Logical and Tangible.
c) Physical, Historical and Tangible.
d) Physical, Logical and Tangible.
a) Physical, Logical and Historical.
b) Historical, Logical and Tangible.
c) Physical, Historical and Tangible.
d) Physical, Logical and Tangible.
a
85
New cards
Weak realization or generalization...
a) Reduce dependency.
b) Decreases reuse.
c) Alternative to multiple generalization, not supported by many languages.
d) All of the above are correct.
a) Reduce dependency.
b) Decreases reuse.
c) Alternative to multiple generalization, not supported by many languages.
d) All of the above are correct.
d
86
New cards
In relation to the difference between Class and Data Type (datatype), indicate the INCORRECT answer:
a) The population of a Class is finite and variable, while the population of a Data Type is finite or infinite, but in any case constant.
b) a class can be simple or structured while a data type must always be simple.
c) The attributes of a Class are fixed or variable, while the values of a Data Type are fixed and immutable.
d) A Class can participate in unidirectional or bidirectional associations, while a Data Type can only participate in unidirectional associations.
a) The population of a Class is finite and variable, while the population of a Data Type is finite or infinite, but in any case constant.
b) a class can be simple or structured while a data type must always be simple.
c) The attributes of a Class are fixed or variable, while the values of a Data Type are fixed and immutable.
d) A Class can participate in unidirectional or bidirectional associations, while a Data Type can only participate in unidirectional associations.
b
87
New cards
How to decide without a concept of the domain should be modeled as a class or as a data type? Point out the
wrong answer.
a) A domain concept will always be modeled as a class, since concepts are by their nature abstract nature itself.
b) A concept of the domain will be modeled as a class or as a data type depending on the system in which it is used, therefore, the difference is relative to the system in question.
c) A domain concept will be modeled as an object if it represents a concrete instance of the domain.
d) A concept of the domain will be modeled as a class if it represents a family or type of things,
more than one concrete thing.
wrong answer.
a) A domain concept will always be modeled as a class, since concepts are by their nature abstract nature itself.
b) A concept of the domain will be modeled as a class or as a data type depending on the system in which it is used, therefore, the difference is relative to the system in question.
c) A domain concept will be modeled as an object if it represents a concrete instance of the domain.
d) A concept of the domain will be modeled as a class if it represents a family or type of things,
more than one concrete thing.
a
88
New cards
In a reflexive relationship it is shown:
a) The relationship between the interfaces of that class.
b) The relationship between the instances of that class.
c) The relationship between the static attributes of that class.
d) The relationship between the static methods of that class.
a) The relationship between the interfaces of that class.
b) The relationship between the instances of that class.
c) The relationship between the static attributes of that class.
d) The relationship between the static methods of that class.
b
89
New cards
What types of relationships can be identified on a class diagram to represent a model
conceptual?
a) Association, Dependency, Aggregation, Composition and Hiring.
b) Association, Dependency, Aggregation, Composition and Generalization.
c) Association and Dependency.
d) Association and Generalization.
conceptual?
a) Association, Dependency, Aggregation, Composition and Hiring.
b) Association, Dependency, Aggregation, Composition and Generalization.
c) Association and Dependency.
d) Association and Generalization.
b
90
New cards
A generalization is:
a) The relationship between a general element and a specific element, where the specific element you can add information and must be consistent with the general element.
b) The specification of a set of connections between instances (links) that represent the structure and communication possibilities of the system.
c) The function or transformation that can be applied to the objects of a class.
d) The property shared by the objects of a class.
a) The relationship between a general element and a specific element, where the specific element you can add information and must be consistent with the general element.
b) The specification of a set of connections between instances (links) that represent the structure and communication possibilities of the system.
c) The function or transformation that can be applied to the objects of a class.
d) The property shared by the objects of a class.
a
91
New cards
In a UML model there is an inheritance relationship between a superclass A and a subclass A1 of
is. Which of the following statements is correct?
a) Setting the navigability of the relationship is optional.
b) Setting the relation name is mandatory.
c) Subclass A1 inherits only some of the properties of superclass A.
d) Subclass A1 inherits all the properties of superclass A.
is. Which of the following statements is correct?
a) Setting the navigability of the relationship is optional.
b) Setting the relation name is mandatory.
c) Subclass A1 inherits only some of the properties of superclass A.
d) Subclass A1 inherits all the properties of superclass A.
d
92
New cards
Point out the INCORRECT statement about data types.
a) They can be primitive or enumerated data types.
b) They can have operations.
c) They are of general domain.
d) Instances can be created, although they are anonymous, without identity.
a) They can be primitive or enumerated data types.
b) They can have operations.
c) They are of general domain.
d) Instances can be created, although they are anonymous, without identity.
b
93
New cards
What is an application of association classes?
a) Reduction of the cardinality of the association.
b) Establishment of the roles of the association.
c) Adding information to an association.
d) Restriction of access to the instances of the association
a) Reduction of the cardinality of the association.
b) Establishment of the roles of the association.
c) Adding information to an association.
d) Restriction of access to the instances of the association
c
94
New cards
Select the CORRECT option regarding the navigability of an association:
a) It offers the possibility of sending messages in both directions.
b) It offers the possibility of declaring variables that are of type public class.
c) It is the ability of an instance of the source class to create instances of the target class
through the bodies of the association.
d) It is the ability of an instance of the source class to access instances of the class destination through the instances of the association.
a) It offers the possibility of sending messages in both directions.
b) It offers the possibility of declaring variables that are of type public class.
c) It is the ability of an instance of the source class to create instances of the target class
through the bodies of the association.
d) It is the ability of an instance of the source class to access instances of the class destination through the instances of the association.
d
95
New cards
Which is NOT a desirable property of a model?
a) Understandable
b) Analytical
c) Precise
d) Predictive
a) Understandable
b) Analytical
c) Precise
d) Predictive
b
96
New cards
Select the INCORRECT answer:
a) An attribute whose type is a class is equivalent to a one-way association.
b) A single association allows the invocation of a single operation.
c) Every association has a double meaning: dynamic aspect and static aspect.
d) In associations, static names (nouns) are preferable, reserving names dynamics (verbs) for operations.
a) An attribute whose type is a class is equivalent to a one-way association.
b) A single association allows the invocation of a single operation.
c) Every association has a double meaning: dynamic aspect and static aspect.
d) In associations, static names (nouns) are preferable, reserving names dynamics (verbs) for operations.
a
97
New cards
Which is NOT a desirable property of a model?
a) Understandable
b) Accurate
c) expensive
d) Predictive
a) Understandable
b) Accurate
c) expensive
d) Predictive
c
98
New cards
Given a hierarchy of classes, mark the CORRECT answer:
a) Represents a pure relationship between instances.
b) The level of abstraction is reduced.
c) The subclass inherits all of the properties of the superclass.
d) It can be interpreted as a relationship “all-part".
a) Represents a pure relationship between instances.
b) The level of abstraction is reduced.
c) The subclass inherits all of the properties of the superclass.
d) It can be interpreted as a relationship “all-part".
c
99
New cards
Mark the CORRECT statement:
a) If the requirements are specified using graphic techniques, the generated model is complete.
b) A detailed conceptual model may contain classes that are not listed in the requirements.
c) A descriptive model generated through reverse engineering techniques is always complete.
d) Non-functional requirements have no representation in a conceptual model.
a) If the requirements are specified using graphic techniques, the generated model is complete.
b) A detailed conceptual model may contain classes that are not listed in the requirements.
c) A descriptive model generated through reverse engineering techniques is always complete.
d) Non-functional requirements have no representation in a conceptual model.
b
100
New cards
In relation to the differences between Class and Data Type (datatype), mark the INCORRECT answer:
a) The population of a Class is finite and variable, while the population of a Data Type is finite or infinite, but in any case constant.
b) The attributes of a Class are fixed or variable, while the values of a Data Type are fixed and immutable.
c) A Class can be simple or structured, while a Data Type must always be simple.
d) A Class can participate in unidirectional or bidirectional associations, while a Data Type can only participate in unidirectional associations
a) The population of a Class is finite and variable, while the population of a Data Type is finite or infinite, but in any case constant.
b) The attributes of a Class are fixed or variable, while the values of a Data Type are fixed and immutable.
c) A Class can be simple or structured, while a Data Type must always be simple.
d) A Class can participate in unidirectional or bidirectional associations, while a Data Type can only participate in unidirectional associations
c