Physics A-Level -MODULE 5: Newtonian world and astrophysics
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
159 Terms
Thermal Equilibrium
Energy is transferred from a region of high temperature to a region of low temperature.
When 2 objects are in contact with each other and they are of the same temperature, there is no net transfer of energy between them.
Brownian motion
The molecules of a gas travel in random directions with random velocity
Internal energy
The sum of the randomly distributed kinetic and potential energies associated with the atoms or molecules which make up a substance
Absolute zero
0 Kelvin, the point where all molecules in a substance stop moving completely and have minimum internal energy
Specific Heat Capacity
The energy required per unit mass to increase the temperature of a substance by 1 Kelvin
Specific Latent Heat of Fusion
The energy required per unit mass to change the phase of a substance from solid to liquid WITHOUT a change in temperature
Specific Latent Heat of Vaporisation
The energy required per unit mass to change the phase of a substance from liquid to gas WITHOUT a change in temperature
Avogadro’s constant
The number of PARTICLES in 1 mole of a substance (6.02 × 10²³)
Kinetic theory of gases
As collisions between atoms and the wall of the container are perfectly elastic (no net conversion of kinetic energy into other forms), atoms rebound from wall at same speed they travel in at
Boyle’s Law
For a fixed mass of gas at a constant temperature, the pressure is inversely proportional to volume
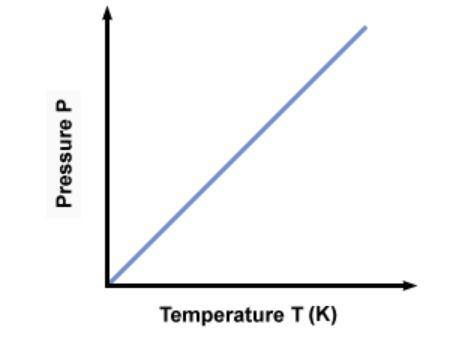
Charles’ Law
For a fixed mass of gas at a constant volume, the pressure is proportional to temperature
Pressure Law
For a fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure, the temperature is proportional to volume
Root mean square
Used to find pressure of a gas at a microscopic level
Ideal gas
One that obeys Boyle’s law with complete precision
Perfect gas
A real gas under conditions that Boyle’s law is a valid description of its behaviour
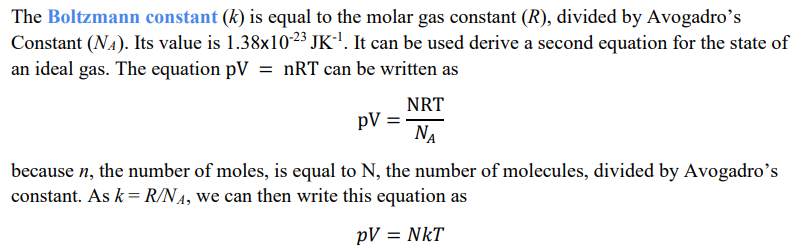
Boltzmann constant
Equal to the molar gas constant (R) divided by Avogadro’s constant (6.02 × 10²³)
Molar gas constant
Physical constant that relates the energy and temperature if a gas to the amount of substance.
How can you convert between Kelvin and Celsius?
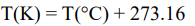
What is the equation for specific heat capacity?
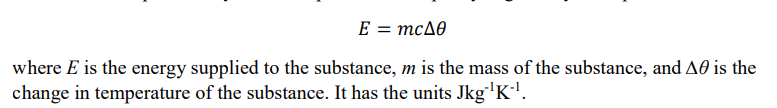
What is the equation for specific latent heat?

How do you calculate the number of moles in a given substance?
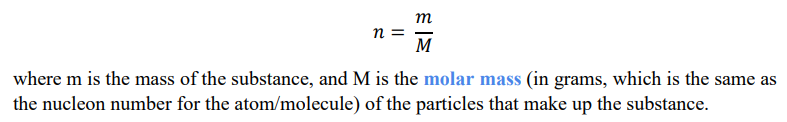
What equation is given when combining the ideal gas laws?

Derive a second equation for the state of an ideal gas using Boltzmann’s constant
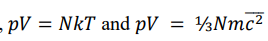
Relate these pressure equations to derive a new formula
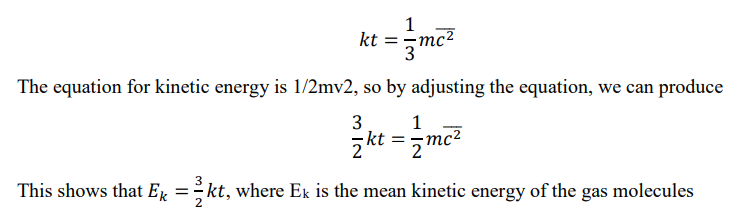
What is the equation for root mean square speed, and what can it be used to find?

What is the average force exerted on an atom by a wall given by? (perfectly elastic)
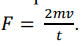
In terms of energies, what occurs when a substance is heated but remains in the same state?
The KE of the molecule increases, but the PE remains the same
In terms of energies, what occurs when a substance changes state?
The PE increases, but the KE remains the same
Why does the temperature stay the same when a substance changes state?
Thermal energy is used to overcome the electrostatic bonds between molecules
What are the 5 assumptions in the kinetic theory of gases?
The gas contains a large number of atoms which move with random, rapid motion (Brownian motion)
The volume of the gas atoms is negligible when compared to the total volume of the gas
All collisions between atoms, with other atoms, and with the walls of the container they are in, are perfectly elastic
The time taken for atoms to collide is negligible, compared to the time between collisions
The electrostatic forces between atoms are negligible, except for when the atoms are colliding (EPE at max = 0J)
What is the graph used to represent Boyle’s law?
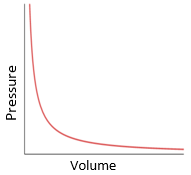
What is the graph used to represent Charles’ law?
What is the graph used to represent the pressure law?
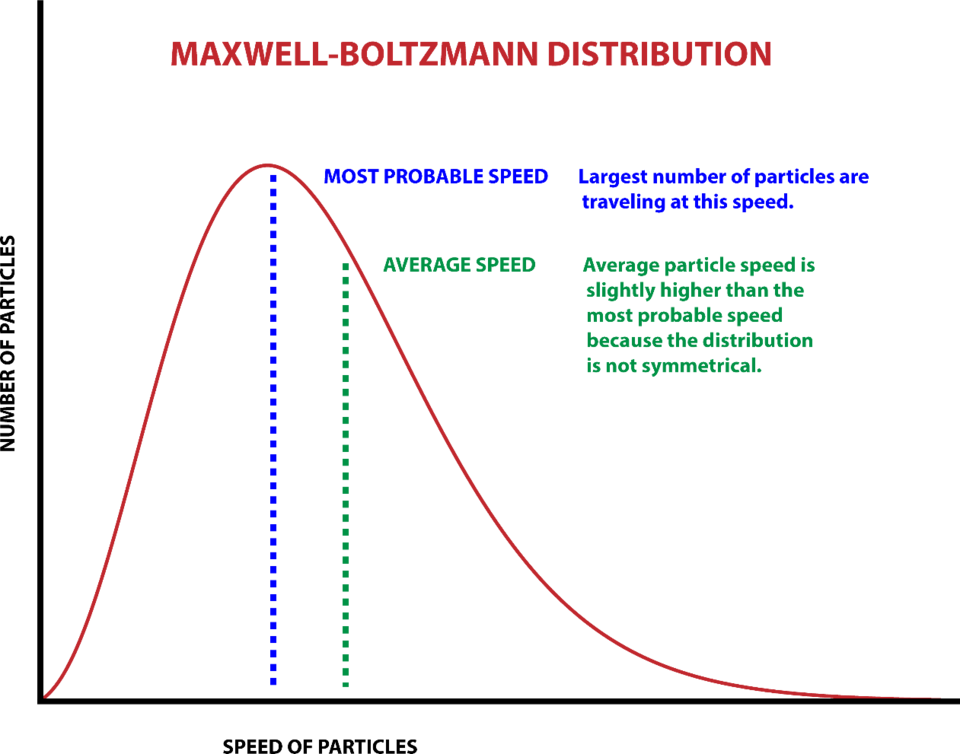
What does the Maxwell Boltzmann distribution represent?
Shows the number of molecules with each speed, against speed c
The area under the graph = total number of molecules
As temperature of gas increases, the peak of the graph shifts to a higher speed, and there is a greater distribution
What is Newton’s 1st Law?
An object in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by a resultant force
What is Newton’s 2nd Law?
The net force acting on an object is directly proportional to the rate of change of momentum, and is acting in the same direction
What is Newton’s 3rd Law?
When 2 objects interact they exert equal and opposite forces on each other.
(These forces are always the same type, and have the same magnitude but they act on different objects and in opposite directions)
How can Brownian motion be observed?
Smoke particles are visible under a microscope, and exhibit random motion
Random motion is exhibited due to collisions with the molecules in air
This results in a transfer of momentum in random ways
How can you determine specific heat capacity using the method of mixtures?
Known masses of 2 substances at different known temperatures mixed together until thermal equilibrium is reached
The final temperature is measured
The energy transfer from the hotter substance is the same as the energy transfer to the cooler substance, so the specific heat capacity equation can be equated for both substances
If SHC of one of the substances is known, then it can be determined for the other substance
How can you determine specific heat capacity using the electrical heater method?
Known mass of a substance is heated by an electrical heater with known power (or measured pd and current) for a given time
The initial and final temperatures of the substance are measured
We can rearrange the equation shown to find c as we know that the energy transfer = VIt
An insulator is used around the substance to minimise external energy transfer, increasing accuracy
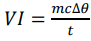
How can you determine specific latent heat?
Electrical heater with known power heats the object
When an object is changing phase, temperature remains constant
So temperature is monitored and the duration where the temperature is constant is used as the time when calculating the energy transferred to the substance
How can you investigate Boyle’s Law?
A sealed syringe can be filled with gas and connected to a pressure gauge
The syringe can be used to vary the volume of the container, and the values for volume and pressure recorded
When a graph of pressure against 1/V is plotted, a straight line graph should be produced, showing a constant relationship
To increase the accuracy, the syringe should be lowered slowly so that no heat is produced from friction
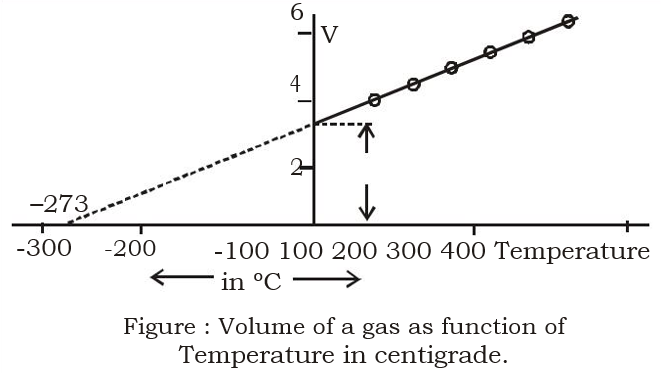
How can you estimate absolute zero?
A sealed container of air, connected to a pressure gauge, is placed in a water bath
Temperature of water is varied, and the values of temperature and pressure are recorded
When pressure is plotted against temperature, a linear graph will be produced
At absolute zero, the gas molecules will have no kinetic energy, so there will be no collisions with the container walls, resulting in there being no gas pressure
By extrapolating the graph back, the x-intercept can be found, and this is equal to absolute zero
Angular velocity
An object’s rate of change of angular position
Centripetal acceleration
The acceleration of an object moving in circular motion.
(Any object in circular motion must have an acceleration since the direction of the object, and therefore its velocity, is constantly changing)
Centripetal force
The resultant force responsible for an object moving in circular motion; centripetal forces always act towards the centre of the object’s rotation.
Frequency
The inverse of time period; the number of rotations per unit time
Period
The time taken for one whole rotation
Radian
A unit of angle, where 2pi is equal to one complete angular rotation
How do you convert an angle from degrees to radians?
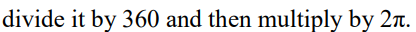
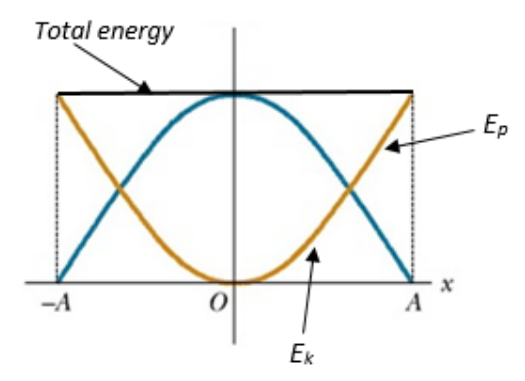
What is the equation used to convert between frequency and period?
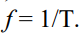
What is the equation used to calculate angular velocity in relation to the angle the object has travelled through?
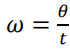
In a time of 1 period, T, the object will complete a full circle, with an angle equal to 2pi. How is the represented in an equation?
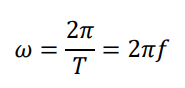
What formula gives the speed v of an object moving in a circle of radius r?
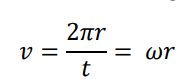
How is centripetal acceleration calculated?
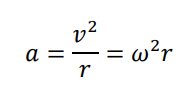
How is centripetal force calculated?
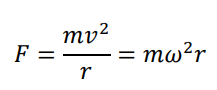
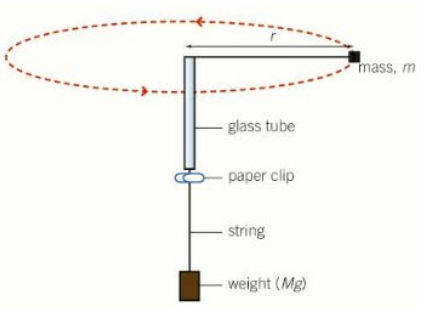
What is the 8 step technique to determine/ investigate circular motion?
Tying a bung, with mass m, to a piece of string and threading it through a glass tube
The other end of the string has a weight, with mass M, suspended from it
This provides the centripetal force, F = Mg, as the tension throughout the string is constant
The string is whirled in a circle, and the time taken for a complete rotation is recorded
The mass of the weight is altered and the experiment repeated
We can equate two equations to get: Mg = (mv²/r)
By measuring the radius of the circle, and using time for one complete oscillation, the velocity can be determined
When v² is plotted against M, a straight line graph which passes through the origin should be produced
Simple harmonic motion
A type of oscillation where the acceleration of the oscillator is directly proportional to the displacement from the equilibrium position.
Displacement (x)
The distance from the equilibrium position
Amplitude (A)
The maximum displacement
Period (T)
The time taken to complete one full oscillation
Frequency (f)
The number of oscillations per unit time
Phase difference (phi)
The fraction of an oscillation between the position of two oscillating objects
Angular frequency (w)
The rate of change of angular position
Isochronous oscillation
An oscillator in SHM where the period of the oscillation is continuously equal and therefore the period is independent of the amplitude.
Energy transfer rule in SHM
Energy is exchanged between the kinetic and potential forms, but the total energy stays the same due to energy being conserved.
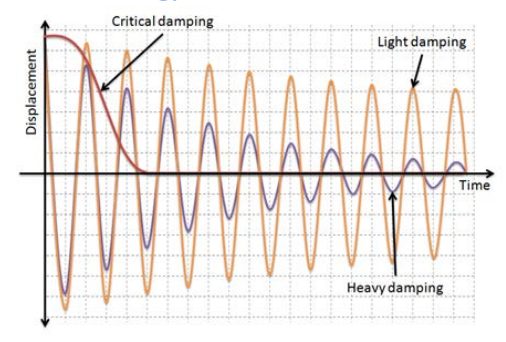
Damping
The process by which the amplitude of the oscillation decreases over time; this is due to energy loss to resistive forces such as drag or friction
Critical Damping
Object stops before one complete oscillation
Heavy damping
Amplitude decreases dramatically
Light damping
Amplitude decreases exponentially
Natural frequency
When an object oscillates without external forces being applied (aka free oscillation)
Periodic driving force
Force applied to an object causing forced oscillation to occur at a specific frequency
Resonance
When the driving frequency is equal to natural frequency, causing an increase in amplitude
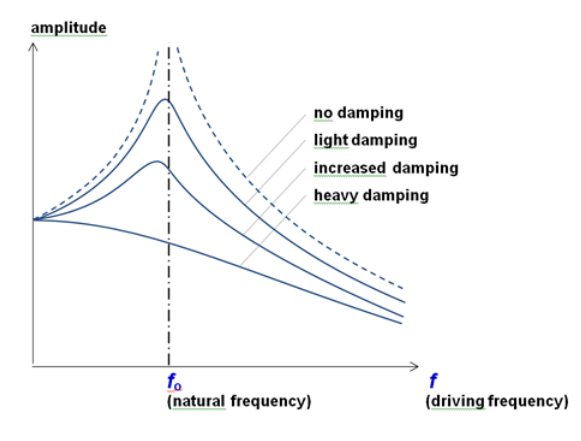
What is a resonance graph and how does it relate amplitude, natural frequency, and damping?
When driving frequency = natural frequency, resonance occurs
This is when the amplitude of the oscillation rapidly increases, and if there is no damping, the amplitude will continue to increase until the system fails
As damping is increased, the amplitude will decrease at all frequencies, and the max amplitude occurs at a lower frequency
What is the key equation for simple harmonic motion?
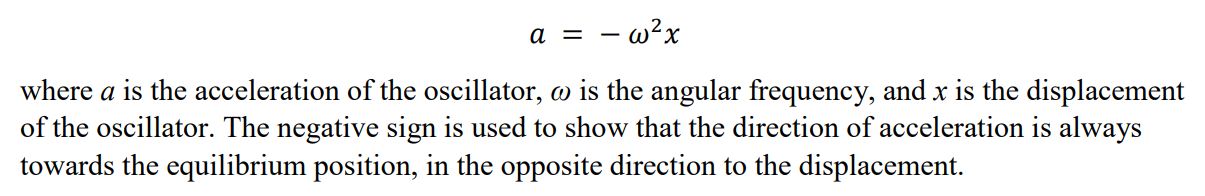
What are the 2 equations that can be used to determine the displacement of a simple harmonic oscillator?
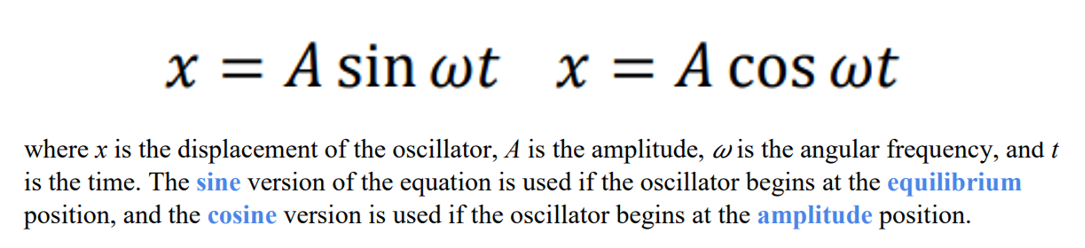
How can the velocity of an oscillator be calculated?
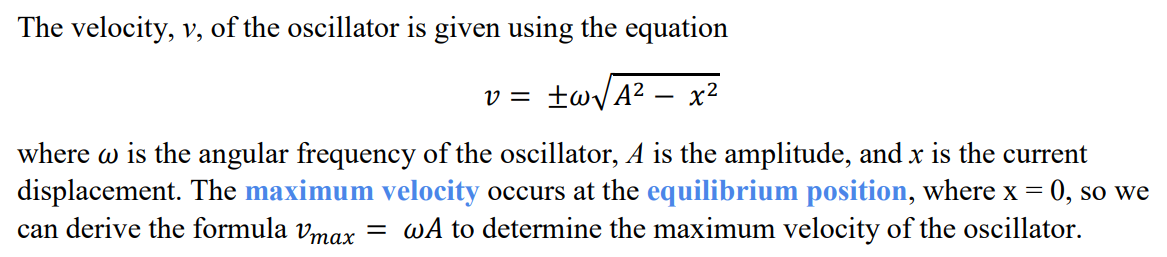
How is phase difference calculated?
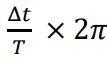
How is angular frequency calculated?
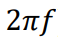
Draw a graph that represents energy changes in an oscillating system (SHM)
Draw a graph that represents critical, heavy, and light damping
How is resonance investigated?
Suspended mass between two springs attached to an oscillation generator.
Millimetre ruler can be placed parallel to spring-mass system, measuring amplitude.
Driver frequency slowly increased at intervals from 0.
Mass will oscillate with increasing amplitude, reaching maximum amplitude when driver frequency of the system is equal to the natural frequency of the system.
Amplitude will decrease again when frequency is further increased.
The system experiences damping from the air so amplitude shouldn't continue to increase until system failure.
To increase accuracy, system can be filmed, and amplitude value recorded from video stills as it can be difficult to determine while mass is oscillating.
Escape velocity
The minimum velocity required by an object to be able to escape a gravitational field of a mass when projected vertically from its surface.
Field lines
A line representing the path that a mass would take when placed within a field
Geostationary satellite
A satellite that orbits above the equator with a 24 hour period, meaning that it will always remain above the same position on the Earth; they orbit approx. 36,000 km above the surface of the Earth
Gravitational Field Strength
The force per unit mass exerted on a small test mass placed within the field
Gravitational Field
A region surround a mass in which any other object with mass will experience an attractive force
Gravitational Potential Energy
The component of an object’s energy due to its position in a gravitational field
Gravitational Potential
The work done per unit mas required to move a small test mass from infinity to that point
Kepler’s 1st Law
The orbit of every planet is an ellipse with the Sun at one of the foci:
All the planets have slightly elliptical orbits
The orbits of comets are much more elongated
Kepler’s 2nd Law
A line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas during equal intervals of time
Objects travel faster when they are closer to the Sun
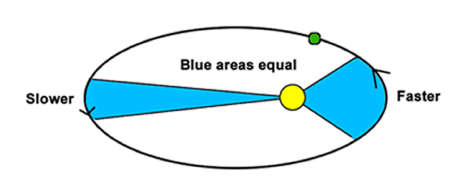
Kepler’s 3rd Law
The squares of the orbital periods of planets are directly proportional to the cubes of the radii of the orbits
Newton’s Law of Gravitation
The force between two masses is proportional to the product of the masses involved and inversely proportional to the square of the separation of masses.
What is the equation for gravitational field strength, g?
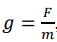
What is the formula representing Newton’s Law of Gravitation?
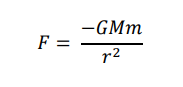
Which formula shows that the field strength for an object doesn’t depend on the mass of the object in orbit around the 1st object?
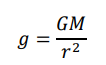
Derive a formula for the time period of an orbit using both gravitational field equations and circular motion equations

How is gravitational potential calculated?
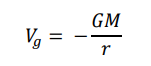
How is gravitational potential energy derived?
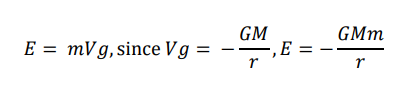
How is escape velocity calculated?
