NMR Spectroscopy 6.3.2
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
practical uses of NMR
MRI scan
what isotopes are identified
¹³C
¹H
why is carbon 13 and a proton used in NMR
uneven number of nucleons which absorb radio waves
what shift to go for ?
always go for highest shift
what do the peaks show in carbon NMR
the number of different carbon environments
what is the reference point in carbon NMR
Tetramethyl silane ( TMS)
why is TMS used in NMR
gives a single sharp peak
inert ( doesn’t react with sample)
volatile ( separated from sample easily)
TMS displayed formula
Si(CH₃)₄
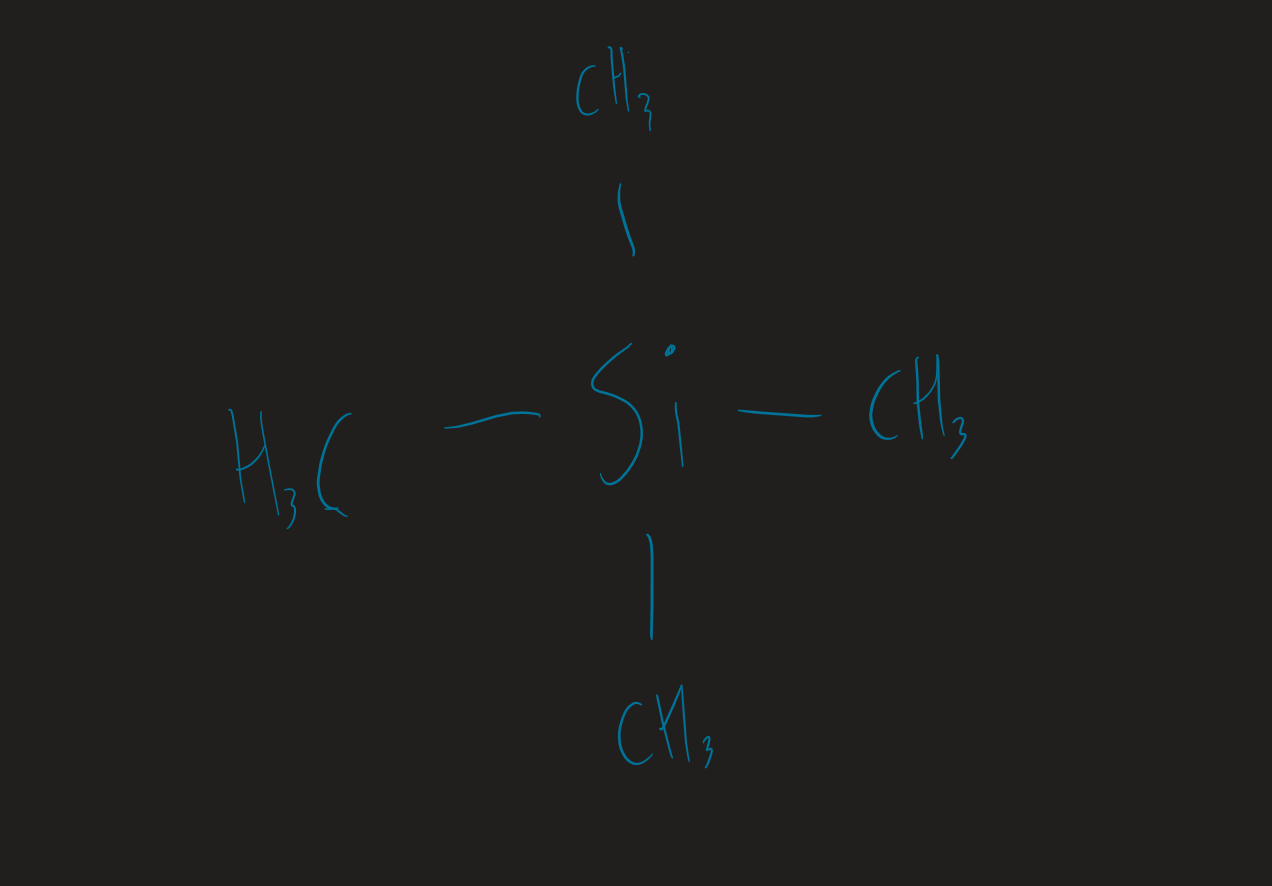
what does carbon environment mean
number of carbon atoms attached to different atoms ( what the atom is attached to aswell)
when do methyl groups have the same carbon type
attached to same carbon
what type of solvent is used in Proton NMR
Deuterated solvent ( CDCl₃)
why are Deuterated solvents used ?
have a even number of nucleons so doesn’t produce signal
How to prepare a Proton NMR
molecule dissolved in Deuterated solvent ( CDCl₃)
with TMS as reference peak
what causes peak at O
TMS reference peak
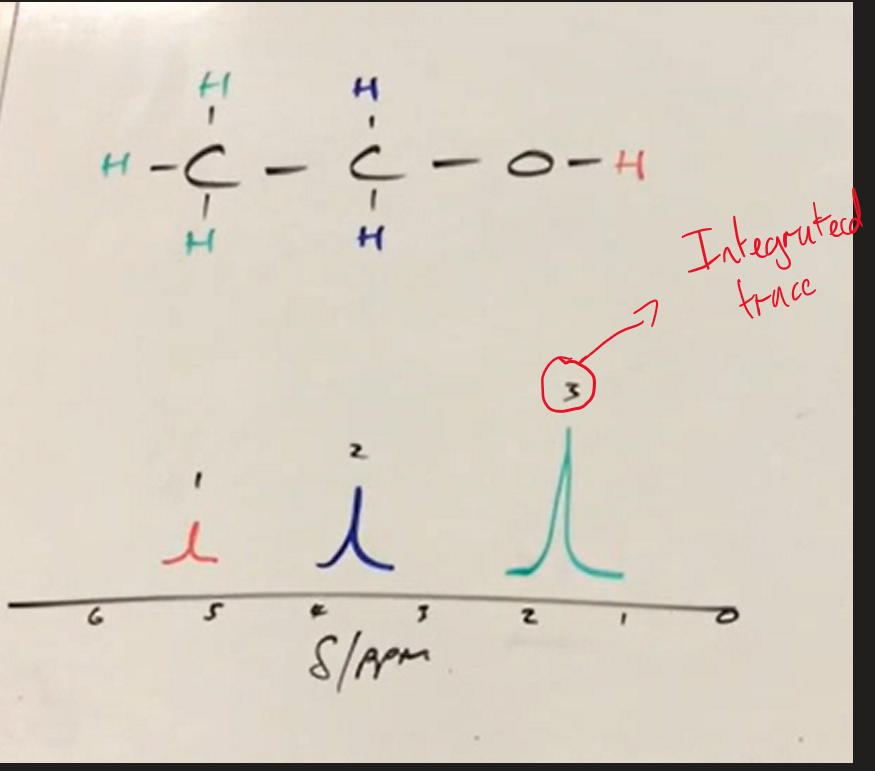
what is the Integrated Trace
gives information about relative proportion of each hydrogen type
what does Integrated trace show about hydrogen
Ratio of Hydrogens in each hydrogen Type
Integrated trace / R.P. A Image
number above peak
what causes proton splitting
adjacent different proton types attached to carbon
How to work out splitting patterns of Proton type
Count number of adjacent proton in different environment = n
add 1 → n + 1 = splitting pattern
Splitting pattern of proton with no adjacent protons
1
n = 0
n + 1 = 1
peak splitting patterns names
peak splits into 1 → singlet
peak splits into 2 → Doublet
peak splits into 3 → Triplet
peak Splits into 4 → quartet
many peaks → Multiplet
Proton splitting ( IMAGE)
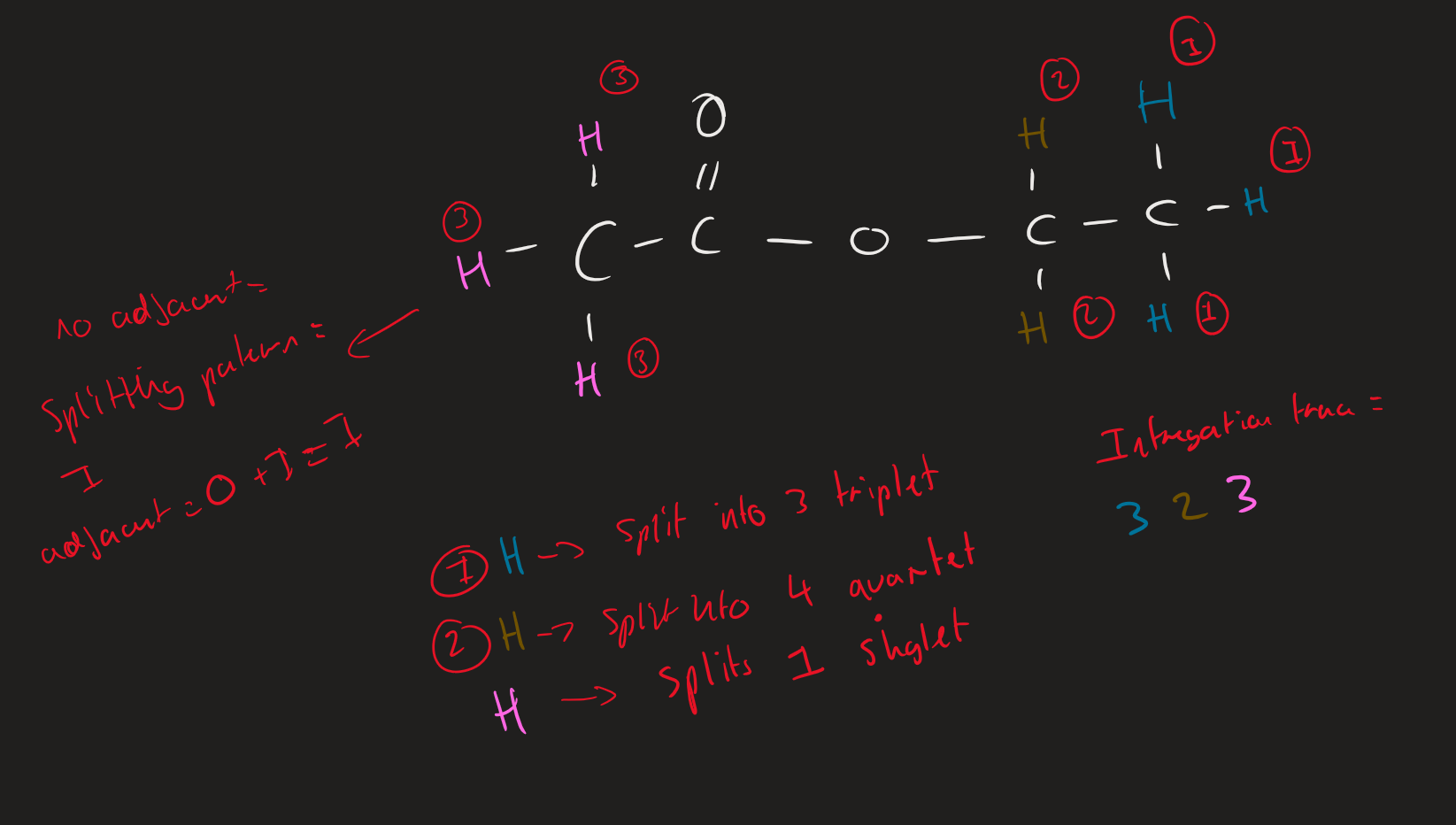
How to remove Alcohol OH and amine NH peaks
add D₂O → removes all NH and OH peaks
what is the splitting pattern for OH and NH peak
always singlet
disadvantage of NH / OH peak
Mask other peaks
¹H NMR spectrum what to look for first
Always look for Benzene
aldehyde
carboxylic acid
¹H NMR spectrum what does a triplet quartet anywhere on the spectrum show
ethyl group → (CH₃CH₂)
always 3:2
¹H NMR spectrum what does benzene integration number show
the hydrogens on benzene
other hydrogens been substituted
¹H NMR spectrum how to identify benzene
Multiplet at 6-8 ppm
¹H NMR what does a single peak show
Hydrogen no adjacent hydrogens
¹H NMR what does a doublet peak show
there's a adjacent single hydrogen
¹H NMR what does a singlet (R.P.A of 9) show
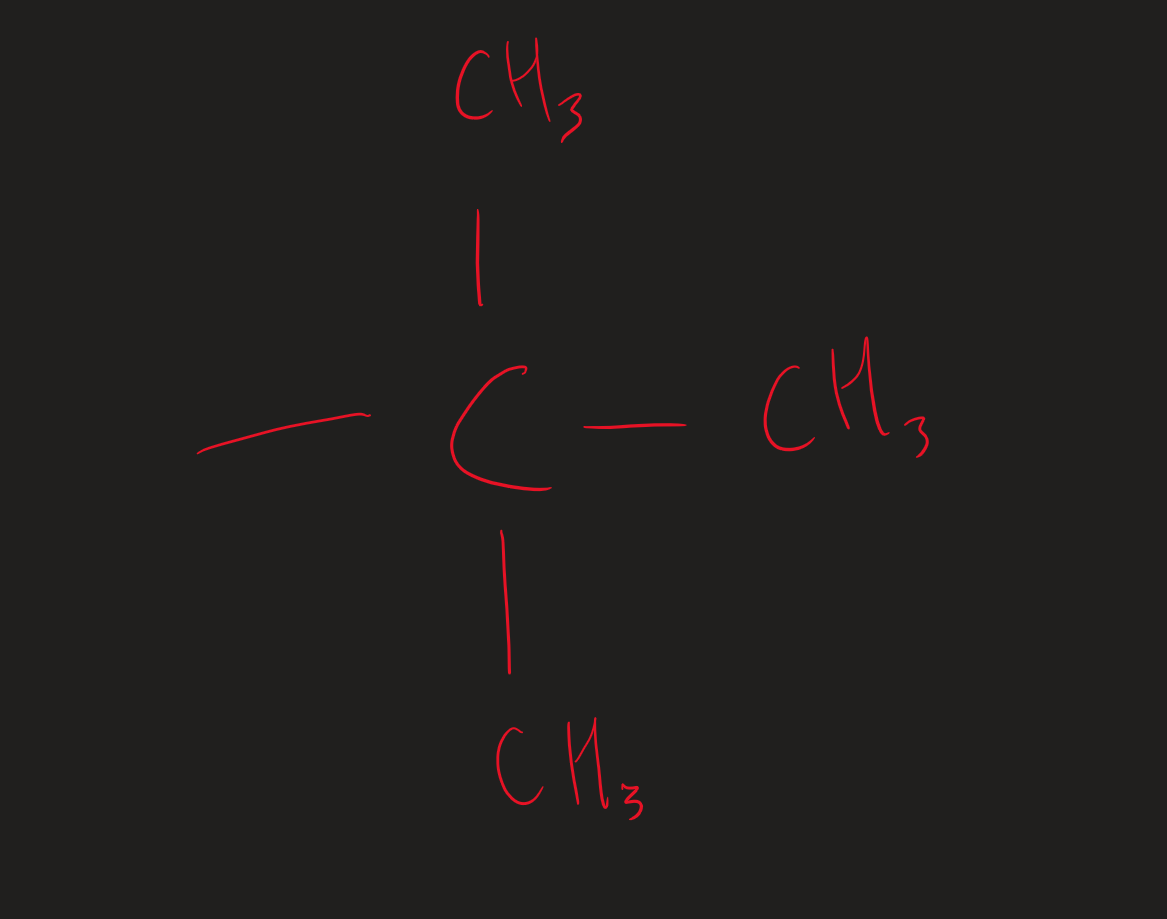
¹H NMR what does a singlet peak (R.P.A of 1) show
OH ( alcohol group)
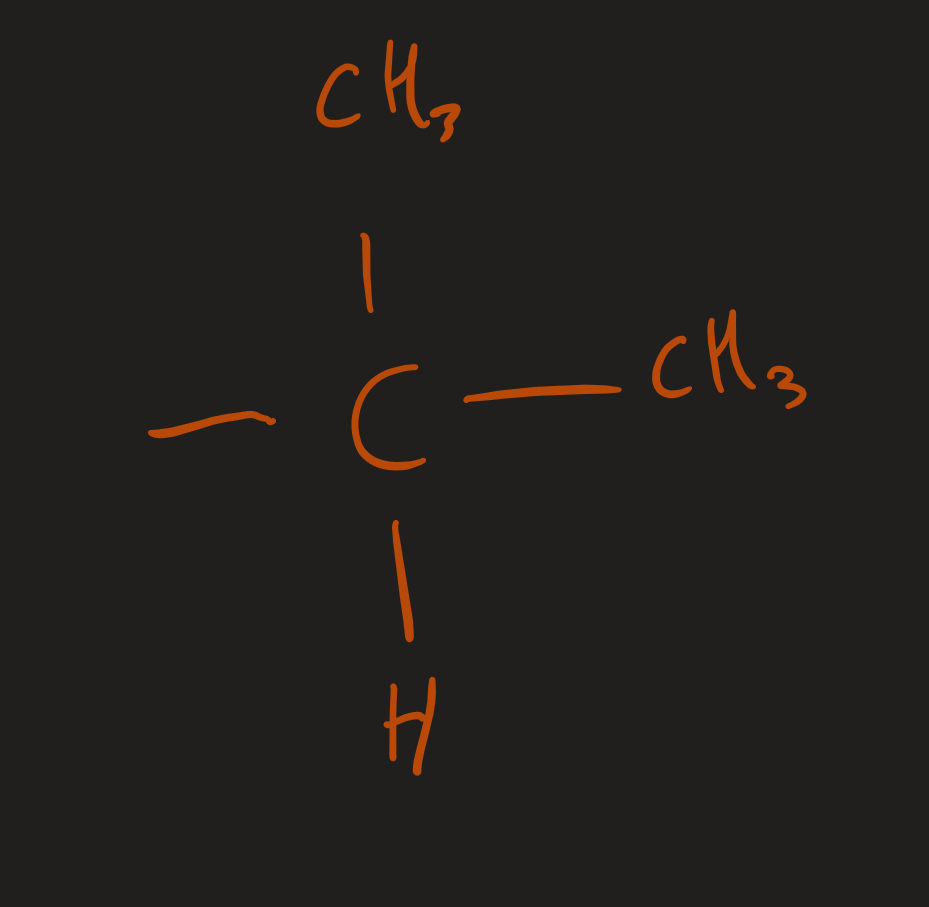
¹H NMR spectrum what does a doublet (RPA 6) Multiplet (RPA 1) show
CH(CH₃)₂
What are the phases in TLC
Mobile phase
Stationary phase
TLC what is the stationary phase
silica
TLC what is the mobile phase
solvent
TLC what separates the molecules
Relative adsorption
TLC what do isomers produce
similar adsorption to stationary phase
large spots caused by merging smaller spots
Control variables in a TLC experiment
Same solvent
Same stationary phase
Control variables in Gas chromatogram
Same temperature
same pressure
same diameter of column
¹H NMR spectrum what does a triplet triplet RPA 2 mean
CH₂CH₂
¹H NMR spectrum what does a Doublet ( RPA 3)- Quartet ( RPA 1)
CHCH₃
¹H NMR what does a singlet (R.P.A of 6) show
C(CH₃)₂
What is the Mobile phase in Gas chromatography
helium
what is the stationary phase in Gas chromatography
liquids such as Large chain alkanes
Gas chromatography molecule and retention time relationship
More non polar = Longer retention time
( non-polar more soluble in alkanes)
Gas chromatography what does the peaks show
Number of compounds in the mixture
What do two molecules having similar retention times mean in Gas chromatography
Isomers
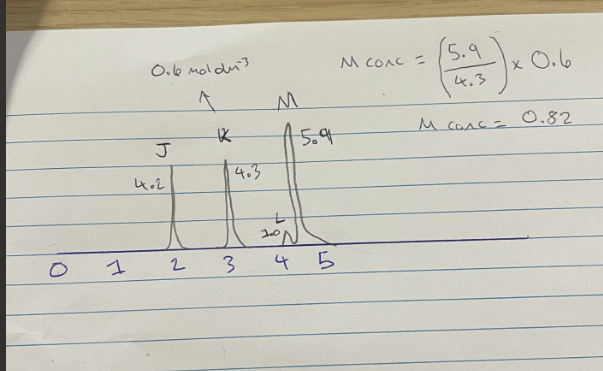
How to use Gas chromatography to work out concentrations
(ratio of compound (x) / ratio of known concentration ) x concentration
How to use Gas chromatography to work out concentrations (IMAGE)
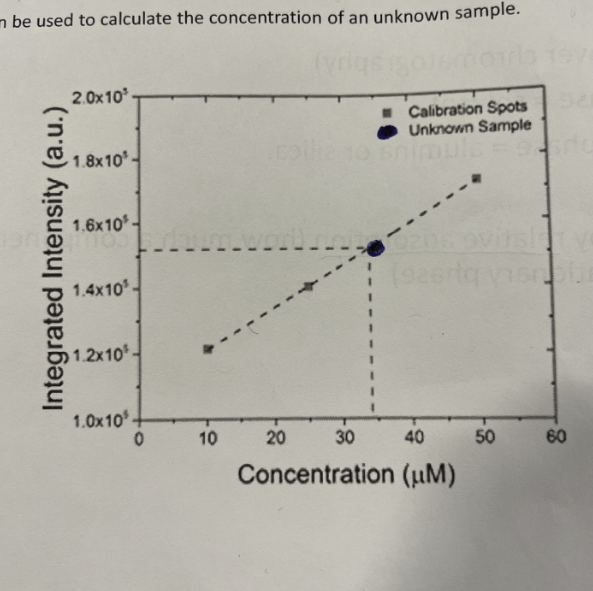
How to use Calibration curve to calculate concentration
Gas chromatography if stationary phase is liquid how are molecules separated
By relative solubility
How does D₂O work
replace protons with D atoms which have even number of nucleons → produces no signal
difference between separation in gas chromatography and TLC
TLC → Relative adsorption
Gas → Relative solubility