psy5240 exam 4
4.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/60
Earn XP
Last updated 6:07 PM on 4/11/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
1
New cards
relationships and geography
### -you are more likely to meet someone who lives close by than across town (geography)
### -study found more than half of participants met at school, work, church, or a party
\-Mere-exposure effect – repeated exposure to any stimulus, including a person, leads to greater liking for that stimulus (time)
### -study found more than half of participants met at school, work, church, or a party
\-Mere-exposure effect – repeated exposure to any stimulus, including a person, leads to greater liking for that stimulus (time)
2
New cards
attractiveness and dating history
women: deemed more attractive have more dates
men: attractiveness is more based on their success than looks
* looks r important for men towards women then it is for women evaluating men
\
men: attractiveness is more based on their success than looks
* looks r important for men towards women then it is for women evaluating men
\
3
New cards
homophily
the tendency to have contact with people who are equal in social status.
* matching phenomenon
* race/ethnicity, education/SES, age, and religion \[in that order\]
- We get positive reinforcement from others agreeing with us
-Others’ agreement bolsters our sense of rightness
* We anticipate positive interactions with those people
* matching phenomenon
* race/ethnicity, education/SES, age, and religion \[in that order\]
- We get positive reinforcement from others agreeing with us
-Others’ agreement bolsters our sense of rightness
* We anticipate positive interactions with those people
4
New cards
interpersonal marketplace
choosing partners whose social worth matches our own.
* their attractiveness and success is highly coordinated with their partners
* women rated most attractive in high school were more likely to have husbands with high income and education.
* their attractiveness and success is highly coordinated with their partners
* women rated most attractive in high school were more likely to have husbands with high income and education.
5
New cards
reinforcement theory
Byrne’s law of attraction
* our attraction to another person is based on the reinforcements outweighing the punishments
* more simplified: we like people who are nice to us frequently more than people who are not.
\-preferring people who are similar to us because the interaction is rewarding.
* we prefer people who are similar (race, education, age, religion) and are good looking
* our attraction to another person is based on the reinforcements outweighing the punishments
* more simplified: we like people who are nice to us frequently more than people who are not.
\-preferring people who are similar to us because the interaction is rewarding.
* we prefer people who are similar (race, education, age, religion) and are good looking
6
New cards
how intimacy affects relationships
* Involves commitment, feelings of closeness and trust, and self-disclosure
In intimate relationships the focus is often on closeness and sharing in three areas
* Affective: feelings
* Cognitive: thoughts
* Physical: touching (not necessarily sexual)
In intimate relationships the focus is often on closeness and sharing in three areas
* Affective: feelings
* Cognitive: thoughts
* Physical: touching (not necessarily sexual)
7
New cards
intimacy and self-disclosure
Self-disclosure – involves telling your partner some personal information about yourself
* leads to reciprocity
* couples that practice self-disclosure are more satisfied
* promotes intimacy
* self-disclosure of emotions are heavily related to intimacy
* leads to reciprocity
* couples that practice self-disclosure are more satisfied
* promotes intimacy
* self-disclosure of emotions are heavily related to intimacy
8
New cards
Components of triangular theory of love
Robert Sternberg
3 parts:
* Intimacy:
The emotional component of love
* Passion:
The motivational component of love
* Decision or commitment:
The cognitive component of love
3 parts:
* Intimacy:
The emotional component of love
* Passion:
The motivational component of love
* Decision or commitment:
The cognitive component of love
9
New cards
triangular theory of love cont.
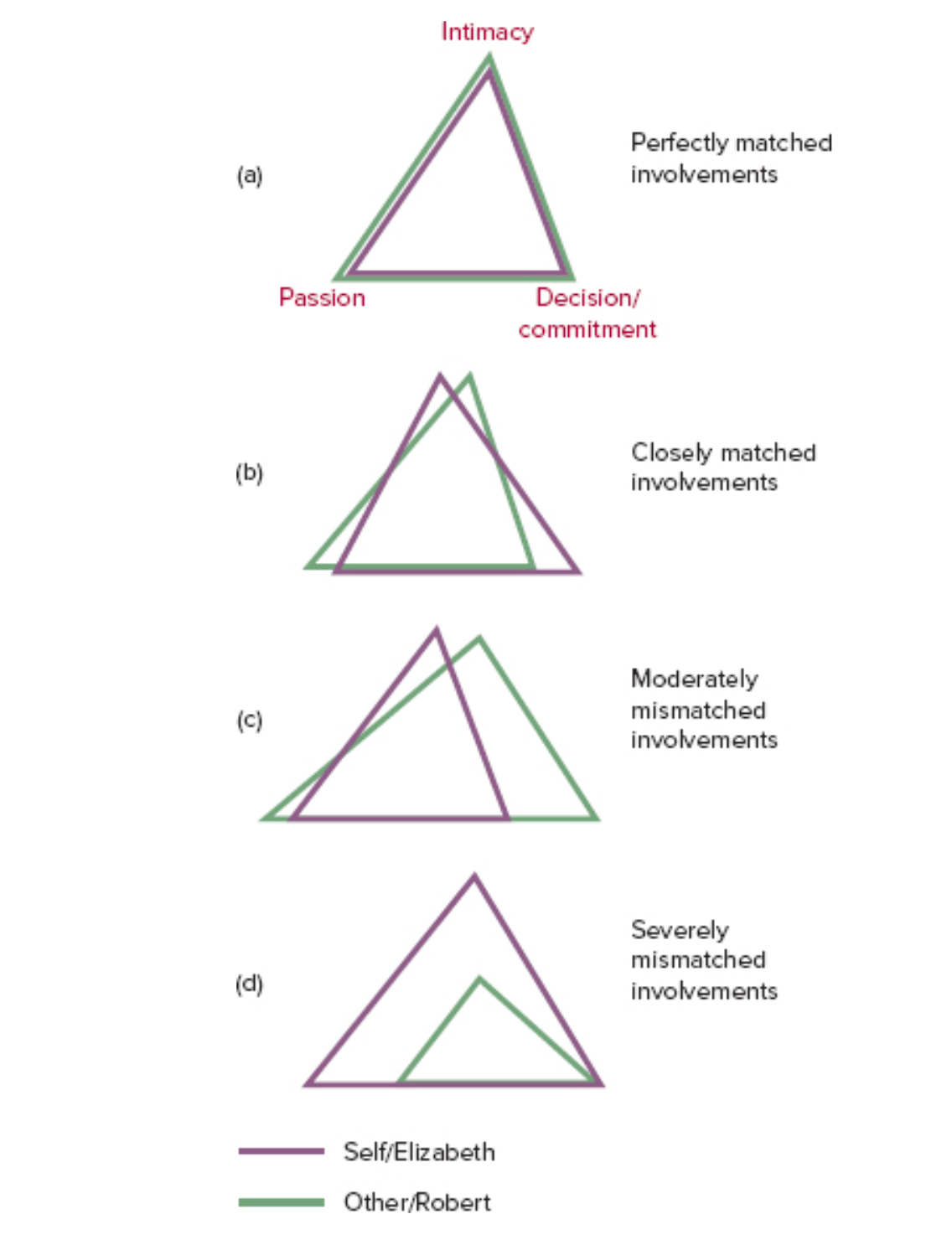
\-top point of triangle is intimacy, left is passion, right is decision
\-shows how people can be well matched or mismatched
\-when there is a good match between the partners love, they are more satisfied
* mismatched triangles show dissatisfaction in the relationship
\-shows how people can be well matched or mismatched
\-when there is a good match between the partners love, they are more satisfied
* mismatched triangles show dissatisfaction in the relationship
10
New cards
attachment theory of love
* Based on research with infant attachment to parents
\- These early bonds, whether secure and pleasant or insecure and unpleasant, profoundly affect us for the rest of our lives, particularly with regards to forming loving attachments to others as adults
\
3 styles of attachment:
* secure lovers
* fearful or avoidant lovers
* preoccupied or anxious-ambivalent lovers
\- These early bonds, whether secure and pleasant or insecure and unpleasant, profoundly affect us for the rest of our lives, particularly with regards to forming loving attachments to others as adults
\
3 styles of attachment:
* secure lovers
* fearful or avoidant lovers
* preoccupied or anxious-ambivalent lovers
11
New cards
secure lovers
\-Find it easy to get close to others and are comfortable having others close to them
\-Mutual dependency feels right to them
\-Do not fear abandonment
* 53% of adults
\-Mutual dependency feels right to them
\-Do not fear abandonment
* 53% of adults
12
New cards
fearful or avoidant lovers
* Are uncomfortable feeling close to another person or having that person feel close to them
* Find it difficult to trust or depend on a partner
\- 26% of adults
* Find it difficult to trust or depend on a partner
\- 26% of adults
13
New cards
preoccupied or anxious-ambivalent lovers
* Want desperately to get close to a partner but often find the partner does not reciprocate the feelings, perhaps A-A lovers scare others away
* Are insecure in relationships, worry that the partner does not love them
\-20% of adults
* Are insecure in relationships, worry that the partner does not love them
\-20% of adults
14
New cards
intent vs impact
intent:
* what the speaker means
impact:
* what the other person thinks you mean
\
effect communication occurs when the speakers impact matches their intent.
* what the speaker means
impact:
* what the other person thinks you mean
\
effect communication occurs when the speakers impact matches their intent.
15
New cards
intersectionality
Simultaneously considering the meaning and consequences of multiple categories of identity differences, and disadvantages
\-race,gender, social class, sexuality
\-race,gender, social class, sexuality
16
New cards
gender binary
concept of gender only having two categories , male and female.
17
New cards
how does one adopt the beliefs and customs of a new culture?
\-acculturation
\
\
18
New cards
nonverbal cues
\-ability to read body language
\-women are better at this
\-men and women differ verbally and nonverbally
\
\-women are better at this
\-men and women differ verbally and nonverbally
\
19
New cards
which gender is more likely to want emotional involvement before premarital intercourse?
women
20
New cards
stereotype
a generalization about a group of people that distinguishes them from others
\
\
21
New cards
gender role
set of norms, or culturally defined expectations, that define how people of one gender ought to behave
22
New cards
socialization
* The ways in which society conveys to the individual its norms or expectations for his or her behavior
23
New cards
gender identity
the individual and psychological sense of maleness or femaleness
24
New cards
sexual identity
develops during adolescence and becomes fixed
\
\-you sense of self in relation to you sexuality
\-gender identity and sexual orientation
\-straight, gay, bi, pan
\
\-you sense of self in relation to you sexuality
\-gender identity and sexual orientation
\-straight, gay, bi, pan
25
New cards
sexual orientation
– A person’s erotic and emotional orientation toward members of his or her own gender or members of the other gender
26
New cards
coming out
– The process of acknowledging to oneself, and then to others, that one is gay or lesbian
27
New cards
homophobia
– A strong, irrational fear of homosexuals; negative attitudes and reactions to homosexuals
28
New cards
anti-gay prejudice
– Negative attitudes and behaviors toward gays and lesbians that do not rise to the level of homophobia
29
New cards
native american tribes and third gender
\-two spirit: manly hearted women
* exceptionally independent and aggressively could take on
\-beyond male and female
* women could express masculine traits and activities while dressing and living as a women.
\
* exceptionally independent and aggressively could take on
\-beyond male and female
* women could express masculine traits and activities while dressing and living as a women.
\
30
New cards
how do men and women differ in aggressiveness?
* Men are generally more aggressive
* True for all types of aggression (physical, verbal, fantasy)
\-True for all ages (most pronounced in preschool age children – gets less so in adulthood)
* -men are taught to take the lead
* -women are taught to be chaste and not engage in sex
* True for all types of aggression (physical, verbal, fantasy)
\-True for all ages (most pronounced in preschool age children – gets less so in adulthood)
* -men are taught to take the lead
* -women are taught to be chaste and not engage in sex
31
New cards
how do men and women differ in communication style?
\-they differ verbally and non-verbally
* -women are better at reading non-verbal cues
* -men tend to not communicate their needs verbally
\
\
* -women are better at reading non-verbal cues
* -men tend to not communicate their needs verbally
\
\
32
New cards
how do men and women differ in masturbatory behavior and porn?
\-men are more likely to masturbate
\-men are more likely to use porn
* men and women respond similarly to erotic material, but sometimes women are unaware of their own arousal
\-men are more likely to use porn
* men and women respond similarly to erotic material, but sometimes women are unaware of their own arousal
33
New cards
how do researchers get the most honest answers from women in research?
in self reports men tend to exaggerate while women minimize their responses
* the bogus pipeline gave the most honest reporting from women and men
* the bogus pipeline hooks them up to a fake polygraph or lie detector machine.
* the bogus pipeline gave the most honest reporting from women and men
* the bogus pipeline hooks them up to a fake polygraph or lie detector machine.
34
New cards
what parts of the female gender role can interfere with their sexual functioning?
* our culture has tighter restrictions on a womens sexuality than men
* double standard
\-female have a less obvious arousal response than men causing them to be less aware of their own arousal
\-the word clitoris is missing from sex textbooks, talks from parents and teachings
\-because women’s gentials are hidden they are less likely to masturbate and develop their full sexual potential.
\
* double standard
\-female have a less obvious arousal response than men causing them to be less aware of their own arousal
\-the word clitoris is missing from sex textbooks, talks from parents and teachings
\-because women’s gentials are hidden they are less likely to masturbate and develop their full sexual potential.
\
35
New cards
LGB verbal abuse
55% report experiencing verbal harassment
28% are verbally harassed by family members
* -these incidents take a psychological toll
28% are verbally harassed by family members
* -these incidents take a psychological toll
36
New cards
how gender stereotypes in the media affect young girls and boys
\-shows male and females in stereotypical gender roles
* the messages reinforced childrens stereotyped ideas on gender
* toys are gendered in kids minds
* videos games show men are violent and women as hookers or sexual objects
* the messages reinforced childrens stereotyped ideas on gender
* toys are gendered in kids minds
* videos games show men are violent and women as hookers or sexual objects
37
New cards
sexual fluidity
changes that occur over time in sexual attraction, identity, and behavior
* bisexual to lesbian
* bisexual to lesbian
38
New cards
how are gay and lesbian relationships different from straight?
they do not vary from heterosexual relationships
39
New cards
how have homosexuals been treated during different periods of time?
\-discrimination was institutionalized
1980: some states laws were passed to prohibit housing discrimination
1990 congress passed hate crimes statistics act
* the federal gov. has not passed any laws banning discrimination
1980: some states laws were passed to prohibit housing discrimination
1990 congress passed hate crimes statistics act
* the federal gov. has not passed any laws banning discrimination
40
New cards
gay and lesbian parenting
\-gay fathers better adjust with kids than straight
* many kids with gay parents grow up to be straight
* gay parents can develop healthy kids just the same as straight
* many kids with gay parents grow up to be straight
* gay parents can develop healthy kids just the same as straight
41
New cards
stress of hiding ones sexuality
higher rates of depression and suicide attempts
42
New cards
how do prenatal hormones affect sexuality?
prenatal hormones (androgen) influences the brain and can reflect sexual orientation
\-high levels of androgen cause an attraction to women (mostly males)
lower levels of androgen can cause an attraction to men(mostly females)
\-high levels of androgen cause an attraction to women (mostly males)
lower levels of androgen can cause an attraction to men(mostly females)
43
New cards
normal to paraphilia
A mild, or even a strong preference for an object is within the normal range of sexual behavior, but is abnormal if it becomes an extreme necessity
\-abnormal behavior is rare and not practiced by many
\-abnormal behavior is rare and not practiced by many
44
New cards
paraphilia
sexual activities other than normal sex with consenting adults.
\-unusual, unconventional sexual behavior
Effects:
* Injury to partner (sadism, pedophilia)
* Arrest/incarceration (job loss, divorce)
* Self-injury (masochism)
* Social/sexual relationships may suffer (unwilling partner)
* Unusual behavior may become major activity (exhibitionistic acts, fetish objects)
* Death
\-unusual, unconventional sexual behavior
Effects:
* Injury to partner (sadism, pedophilia)
* Arrest/incarceration (job loss, divorce)
* Self-injury (masochism)
* Social/sexual relationships may suffer (unwilling partner)
* Unusual behavior may become major activity (exhibitionistic acts, fetish objects)
* Death
45
New cards
how individuals with fetishes behave and what they might collect
fixation on some object rather than a human, and attach great erotic significance to that item
collect:
* cross-dressing
* womens underwear, bras, stockings, shoes or other clothing items
* media materials
* or objects
behave:
* holding,rubbing, smelling an object
* asking partner to wear an item
* perfer or require item during sex
collect:
* cross-dressing
* womens underwear, bras, stockings, shoes or other clothing items
* media materials
* or objects
behave:
* holding,rubbing, smelling an object
* asking partner to wear an item
* perfer or require item during sex
46
New cards
transexual
relating to a transgender person or someome who had. sex reassignment
47
New cards
transvestite
Simply involves dressing as a member of the other gender (NOT ABNORMAL)
* Transsexuals while in transition
* Drag queen
* Drag kings
* Female impersonators
* Perhaps adolescent boys expressing confusion and frustration
* Transsexuals while in transition
* Drag queen
* Drag kings
* Female impersonators
* Perhaps adolescent boys expressing confusion and frustration
48
New cards
transvestic fetishism
the individual has recurrent and intense sexual arousal from cross-dressing, as manifested by fantasies, urges, or behavior
* cause significant distress or impairment in life
* masturbate while cross dressed
* cause significant distress or impairment in life
* masturbate while cross dressed
49
New cards
why is the term sexual addiction criticized?
the term addiction has very specific definitions among perfessionals and the term for sexual addiction to not meet the definition in some ways.
* no physical withdrawl symptoms
* addiction can come from illegal or destructive behavior
* no physical withdrawl symptoms
* addiction can come from illegal or destructive behavior
50
New cards
S & M behavior
* Dominance and submission
* An interaction that involves a consensual exchange of power – the dominant partner uses his or her power to control and sexually stimulate the passive partner
* Master/slave, naughty child
* An interaction that involves a consensual exchange of power – the dominant partner uses his or her power to control and sexually stimulate the passive partner
* Master/slave, naughty child
51
New cards
why do non-true sadist and masochists engage in SM behavior?
* Is rare as a sexual disorder
* More common in milder, nonparaphiliac forms
* Fantasies of behavior are more common than actual behavior
* Partners usually engage in both roles
* Men report being interested since childhood
* Women report being introduced to the behavior by their partner
* More common in milder, nonparaphiliac forms
* Fantasies of behavior are more common than actual behavior
* Partners usually engage in both roles
* Men report being interested since childhood
* Women report being introduced to the behavior by their partner
52
New cards
why do people engage in masochist behavior?
* not precisely known
* learning theory: experiencing punishment as a child or whenever and gettin aroused from it reinforces the behavior
* learning to associate pain with sexual arousal
* learning theory: experiencing punishment as a child or whenever and gettin aroused from it reinforces the behavior
* learning to associate pain with sexual arousal
53
New cards
what is the suggested strategy for encounter an exhibitionist?
\-exposes genitals to unsuspecting person or stranger
* remain calm and suggest they should seek professional help
* they get aroused off the shocked reaction from strangers
* remain calm and suggest they should seek professional help
* they get aroused off the shocked reaction from strangers
54
New cards
what is most likely for a voyeur to engage in and what turns him on?
* arousal from watching an unsuspecting person undressing themselves
* \
* \
55
New cards
hypersexuality
Refers to an excessive, insatiable sex drive in either a man or a woman; leads to compulsive sexual behavior; person is never satisfied by behavior
men: satyriasis
women: nymphomania
men: satyriasis
women: nymphomania
56
New cards
asphyxiophilia
* Involves creating or enhancing sexual arousal by cutting off one’s oxygen supply
\-Strangulation by a rope around the neck
\-Pillow against the face
\- Plastic bag over the head
\- Is a very dangerous behavior
\- Death rate of between 250 to 1000 per year in U.S.
\-Strangulation by a rope around the neck
\-Pillow against the face
\- Plastic bag over the head
\- Is a very dangerous behavior
\- Death rate of between 250 to 1000 per year in U.S.
57
New cards
frotteurist
the individual has recurrent and intense sexual arousal from touching or rubbing against a nonconsenting person, as manifested by fantasies, urges, or behavior
* Occurs in crowded places – subways, elevators, buses
* Perpetrator:
* Rubs genitals against victim’s thighs/buttocks
* Fantasizes about loving, caring relationship
* Could fondle genitalia or breasts with hands (technically toucherism)
\
* Occurs in crowded places – subways, elevators, buses
* Perpetrator:
* Rubs genitals against victim’s thighs/buttocks
* Fantasizes about loving, caring relationship
* Could fondle genitalia or breasts with hands (technically toucherism)
\
58
New cards
necrophiliac
sex with a dead body
59
New cards
exhibitionist
sexual arousal from the exposure of one’s genitals to an unsuspecting individual
* Sometimes masturbates while exposing himself
* Generally makes no attempt to have contact
* Accounts for most of the arrests for sex crimes
* May have desire to shock the victim
* Sometimes masturbates while exposing himself
* Generally makes no attempt to have contact
* Accounts for most of the arrests for sex crimes
* May have desire to shock the victim
60
New cards
asexuality and textbook statements
\
– The absence of a sexual orientation – a person whose sexual orientation is toward neither men nor women
* Defined as a lack of sexual attraction to a person of either sex
* Different from not engaging in sexual behavior
* Asexuals are also different from celibates
* May be a disorder rather than a paraphilia (2006)
#### • the authors think of them as having a sexual variation
– The absence of a sexual orientation – a person whose sexual orientation is toward neither men nor women
* Defined as a lack of sexual attraction to a person of either sex
* Different from not engaging in sexual behavior
* Asexuals are also different from celibates
* May be a disorder rather than a paraphilia (2006)
#### • the authors think of them as having a sexual variation
61
New cards
love as a story
* love is war
* garden story (love needs ongoing cultivation)
* associated with high satisfaction
* business story (employer and employee)
* horror (terrorizer and victim)
* garden story (love needs ongoing cultivation)
* associated with high satisfaction
* business story (employer and employee)
* horror (terrorizer and victim)