Macroeconomic objectives, circular flow of income, AD introduction
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
GDP
Gross Domestic Product- the total market value of all final goods and services produced annually in an economy
Economic growth
The ability of the economy to increase the value of goods and services
Recession
A period of temporary economic decline during which trade and industrial activity are reduced, generally identified by a fall in GDP in two successive quarters (6 months)
Inflation
A general increase in prices and fall in the purchasing value of money.
Unemployment
Measures the number of people who are able to work and are economically active, but do not have a job during a period of time.
Exchange rate
The principle value of a currency in one country compared with the value in another
Government budget
A type of plan of a country's tax revenues and government expenditures over a period of time.
National debt
The total amount of money that a country's government has borrowed, by various means-the sum of government deficits over time.
Income distribution
How the nation's total income is distributed among its population among various groups of the population such as the poor and the rich.
Environmental sustainability
A management approach that involves developing strategies that both sustain the environment and produce profits for the company
Supply-side policies
Government policies designed to promote market forces in order to increase economic growth. They are policies which are aiming to shift the PPF for the economy outwards. Supply-side policies aim to increase productivity and/or competition in product or labour markets. They can also be interventionist
Demand-side policies
Fiscal policy is the manipulation of government spending and taxation to affect total demand in the economy
Monetary policy: is the use of changes in the base rate of interest and the money supply to influence the rate of growth of total demand and the rate of price inflation.
Income (Y)
The flow of money measured per unit of time (£ per year)
Wealth
The total value of money and other assets and stock.
Aggregate Demand
The total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time and any given price level.
Consumption (C)
Spending by households on goods and services, with the exception of purchases of new housing
Savings ratio (S)
The ratio of personal saving to household disposable income (Expressed as a percentage)
Investment (I)
Spending on capital equipment, inventories, and structures, including household purchases of new housing
Government spending (G)
Goods and services that government buys
Net exports (X-M)
Spending on domestically produced goods by foreigners (exports) minus spending on foreign goods by domestic residents (imports)
Index Number equation
(raw number/base year raw number)
discretionary income
Income available for spending and saving after an individual has purchased the basic necessities of food, clothing, and shelter
Circular flow of income
The flow of goods and services between households and firms and their corresponding payments in money terms.
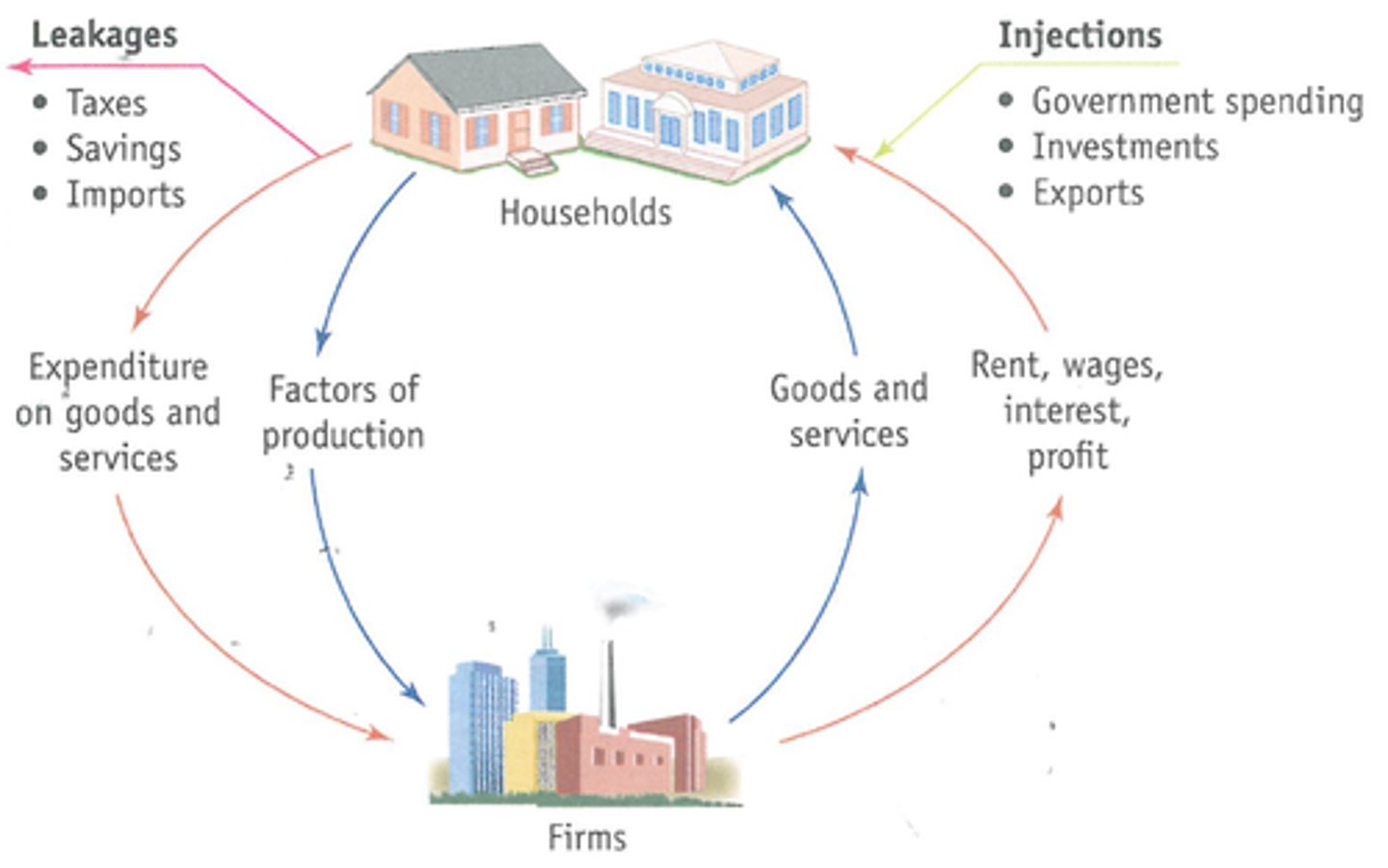
National Income (Y)
The value of income paid by firms to households in return for land, labour and capital
National Output (O)
The value of the flow of goods and services from firms to households
National Expenditure (E)
The value of spending by households on goods and services
Leakages from the circular flow of income
Leakages occur when households put some income aside in savings (S); to pay government tax (T); Buy foreign made products: imports (M)
Injections into the circular flow of income
Government spending (G)
Investment (I)
Exports (X)
Real disposable income (Yd)
Income after taxes and welfare benefits, adjusted for the effects of inflation
Aggregate demand equation
AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
consumer confidence
the extent to which people are optimistic or pessimistic about the future health of the economy including interest rates, prices, incomes and jobs.
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
The change in consumer spending arising from a change in disposable income, for every extra pound, how much is spent on consumption.
negative supply shock
An unexpected decrease in the availability of a key resource that temporarily decreases productivity and increases the cost of production. This forces producers to higher prices. An example of this is oil following Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
Accelerator Theory
The theory of investment that says that current investment spending depends positively on the expected future growth of real GDP, or the shrinking of real GDP. Firms will ramp up capital investment when economic growth is occurring in order to increase production of goods, while they will make it smaller in recessions due to a falling demand.
Animal Spirits
Psychological factors that lead to changes (optimism or pessimism) in the mood of consumers or businesses, thereby affecting consumption, investment, and GDP. The theory was coined by John Maynard-Keynes.
Interest Rate
The price of money, i.e. cost to borrowers and the reward to savers.
Housing equity
Difference between current market value of property and outstanding mortgage owed on the home.