GENETICS EXAM 2 (aLLeles interactions)
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
•Genes are the physical units of heredity
the physical units of heredity
chromosomes are
long molecules of doubl- stranded DNA
genes are on what
chromosomes
2 copies of each sexually reproducing chromosome (2 copies of each gene)
diploid
alleles are
alternative forms of a gene
each gene may have?
multiple alleles in a population
alleles encode what type of gene product
different version
each diploid individual can be homozygous, which means
2 gene copies are same allele
A1 AND A1
each diploid individual can be heterozygous , which means
2 gene copies are different alleles
genotype
the genetic makeup of an organism
allele combination, what allele combination do you have
phenotype
the observable traits of an organism
what you see
natural selection acts on the phenotype which is determined by the underlying genotype
evolution
one phenotype is favored, the frequencies of alleles associated with each phenotype change across generations
wild type
the allele that occurs most frequently in the population
normal allele
mutant allele
any alleles whose DNA sequence differs from the wild type allele
diff in DNA sequence
encodes diff RNA OR PROTEIN
GENE INTERACTION
genes and alleles interact to influence phenotype
dominance
relationship between 2 alleles of the same gene
complete dominance
phenotype of only one allele is visible in a heterozygote
in dominant alleles the phenotype is observed in
the homozygous and heterozygous genotypes
in recessive alleles the phenotype is observed in
only when HOMOzygous
phenotypes are a consequence of
the activities of the protein products produced by the alleles of a gene
dominance is determined by the
activity of protein products of the alleles
gene dosage
key to determining dominance
more copies of a gene there are, more gene product will be produced when that gene is expressed
haplosufficient
in diploids , genes only require a single copy for a normal level of function
a gene is haplosufficient when
the person is carrying one functional allele and one non-functional allele (heterozygotes) , they will display the wild type phenotype (WILD TYPE ALLELE IS DOM)
a gene is haploinsufficient when
a perosn is carrying one functional allele and one non- functional allele (heterzygotes), they will display the mutant phenotype (MUTANT PHENOTYPE IS DOMINANT)
mutant alleles can be; loss of function
complete loss of a functional gene product
mutant alleles can be; gain- of- function
acquires a new function
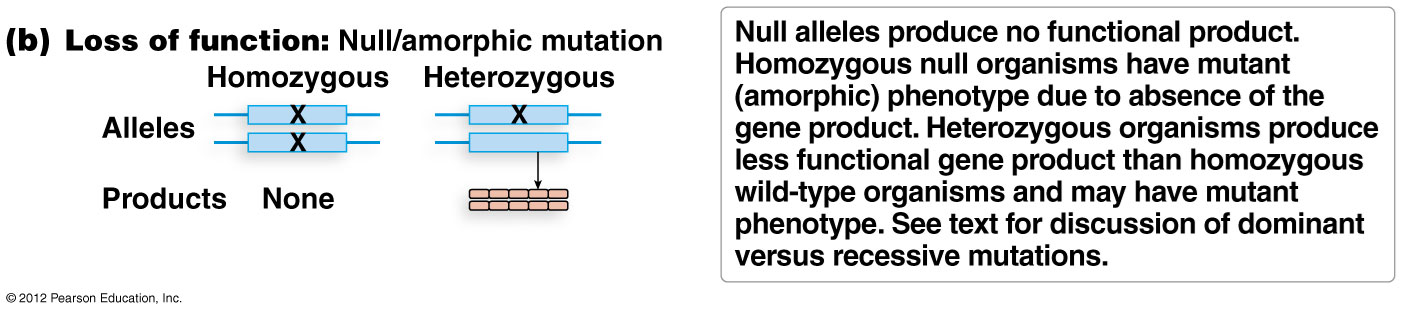
loss of function mutations; null mutaiton
lethal when homozygous
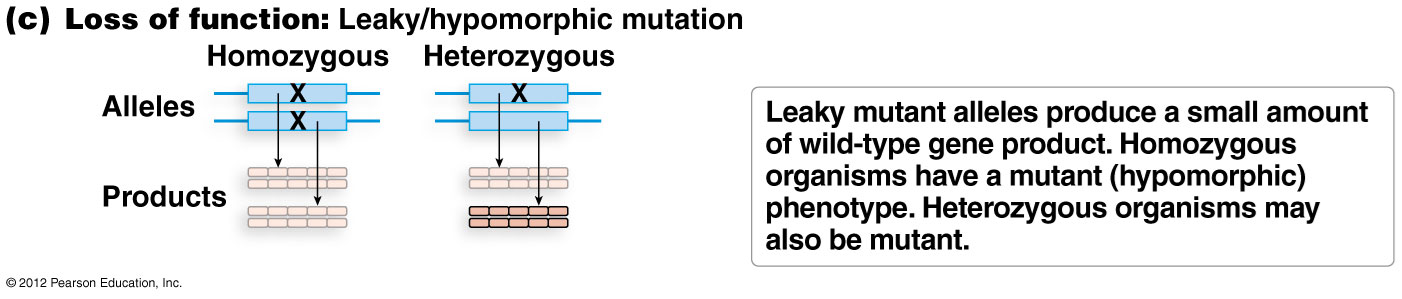
loss of function mutations; leaky mutation
results in a partial loss of function due to decreased gene product
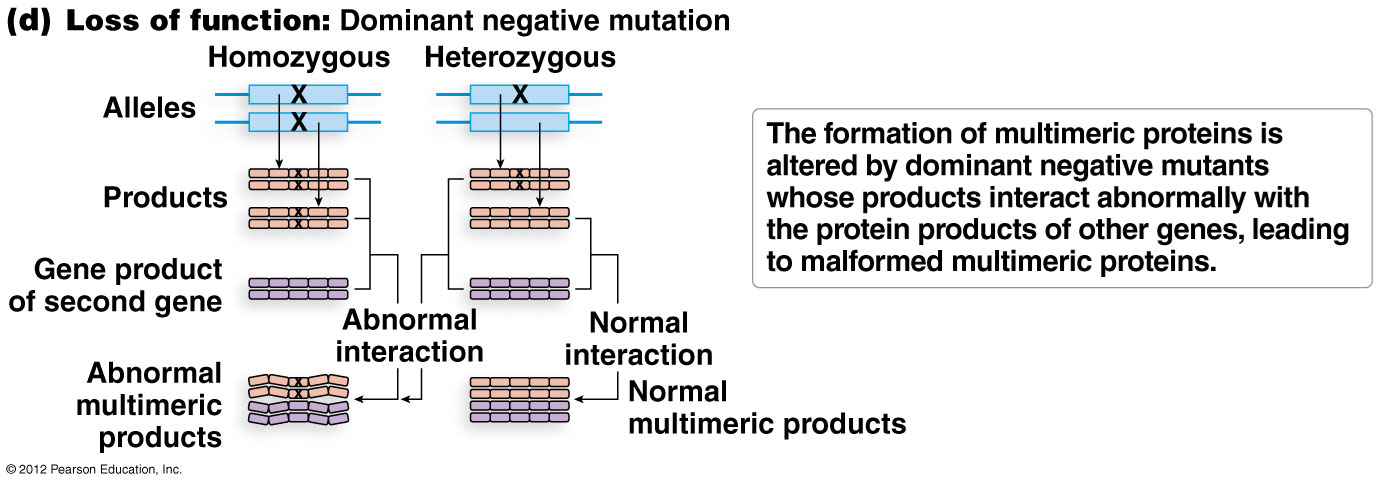
dominant negative mutations
multimeric proteins, composted of 2 or more polypeptides join together to form a functional protein
have a spoiler effect on the protein as a whole (one bad apple spoils the whole bunch)
gain of function mutations; hypermorphic
mutations produce more gene product than normal

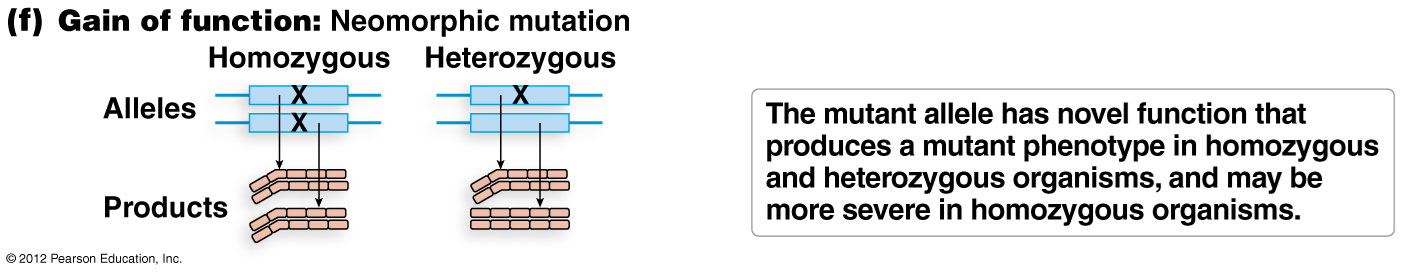
gain of function mutation- neomorphic
gene product with novel function not found in the wild type
incomplete dominance
heterozygous people display phenotypes intermediate to either homozygous phenotype po
HETERO ARE INTERMEDIATE
codominance
heterozygotes with different phenotype than that of either homozygote
NOT PHENOTYPE
OWN THING NOT INTERMEDIATES
ABO ALLELES; IA ,IB AND i
IA AND IB- ARE COMPLETELY DOM OVER THE i allele
CODOMINANT WITH EACHOTHER
type A
pressense of one antigen on the blood cell surface
type B
the presence of a different antigen
type AB people
have both antigens
type O
people have neither
wild type C allele
full coat of color
completely dom over all the others
c ch
dilute phenotype, called chinchilla
incompletely dominant over c h
c h
called himalayan, little pigment on the body but full color on the extremities
c
fully recessive null , white phenotype
lethal mutations
single- gene mutations that cause death that are inherited as alleles