Chapter 2 : Crime and Deviance
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2.1 How are crime and deviance defined and measured?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
what are the ideas of classical criminology?
focuses on the crime
believes that there is no difference between a criminal and non-criminal (free will)
ensures that the punishment fits the crime
what are the ideas of positivism?
focuses on the criminal
believes that criminals are different (determinism)
ensures that the punishment / therapy suits the offender
what are the ideas of durkheim?
crime is a normal part of society
crime is not only influenced by economic factors, but also cultural factors
as modern societies become more individualised, crime may also decrease
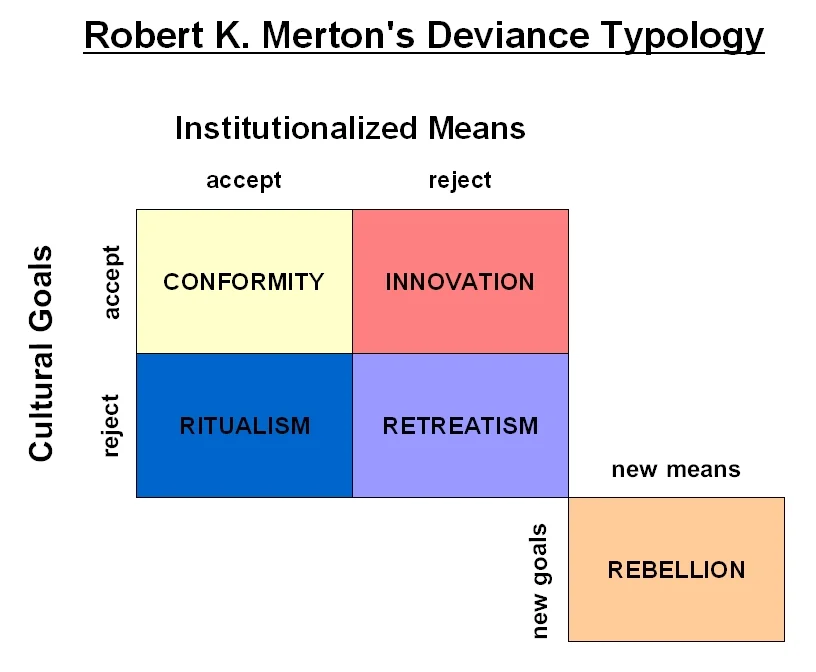
what are the ideas of merton’s strain theory?
society has taught us goals (e.g. have money, power) but at the same time systematically blocked the opportunities for many people to achieve these goals
this leads to them being in the state of anomie
being in this state was more likely to lead to trying to achieve these goals through illegitimate means
what is meant by the term ‘anomie’ according to durkheim?
a breakdown of social norms
this will lead to individuals being in a state of confusion or sense of purposeless
they may feel disconnected from social values, goals and expectations of society
what is meant by the term ‘anomie’ according to merton?
when people are unable to live up to the norms of society
caused by a strain between what they expect out of life and what they were actually getting
what are the ideas of subculture theory?
refers to a group of people who exist outside of mainstream culture (e.g. criminals)
might’ve started young by following parents before it turns to following peers
they form their own cultural frameworks that normalise deviant behaviour (e.g. breaking windows, stealing)
what are the ideas of interactionism?
focuses on the question ‘why are some actions seem as criminal/deviant in the first place and why are some individuals labelled as criminals’
moves from focusing on crime to deviance
moves from looking at criminal behaviour to looking at how society reacts
focuses more on the subjective experience, how agents of social control identify and reinforce behaviours that are deviant
suggests that being stereotyped or labelled as deviant or a criminal may in fact encourage them to reinforce the stereotype
what are the ideas of marxism/radical criminology?
argues that the injustice of capitalism is a cause of crime and deviance
we should not label the crimes of the lower class, their actions are the result of the conditions they are forced to live with
by identifying the crimes of lower class and allowing the media to create moral panic about it, it camouflages the crimes of the powerful (tax evasion, fraud)
the criminal becomes a critic of society, rebelling against the injustice of the capitalist system by committing crimes
what are the ideas of left realism?
people often romanticise a crime/deviance (making criminals appear more relatable by exaggerating their struggles, shifting the focus from their actions or motives)
many victims of crime are often working class (poor) or women, this could lead to people forgetting the victims
what are the ideas of right realism?
turned the question to ‘what can we do to try and control crime?’
wilson & kelling ‘broken windows’ theory
as fear builds up, informal social control goes down which allows petty crime to infiltrate
suggests methods such as zero tolerance policy and situational crime prevention
what does wilson & kelling state in ‘broken windows’ theory?
crime and disorder are closely related, the physical environment had an impact on fear of crime and the sense of safety
e.g. broken windows in houses → problem can escalate, leading to more serious crimes happening → a sense of unease from residents
what is the zero tolerance policy?
remove any physical or social cues within environments that cause fear
e.g. having harsh punishments for minor crimes such as graffitiing
what is situational crime prevention?
manipulating spaces and reducing crime without having to deal with the underlying causes of crime
e.g. installing CCTVs, adding barbed wires / gates as a deterrence
what is a crime?
a legal wrong that can be followed by criminal proceedings, which may result in punishment
e.g. murder
what is deviance?
behaviour disapproved by most people in a society or group, which does not conform to shared norms and values
e.g. not lining up
what is social order?
general conformity to the shared norms and values, so that society is peaceful and predictable
what is social control?
the process by which people are made to obey the rules of a society
this is done by agencies of social control, institutions that serve to ensure conformity
it can be informal and formal
what is formal social control?
it is carried out by the government, armed forces and the criminal justice system, including the police, the courts and the prison service
what is informal social control?
it is carried out by agencies such as the education system, the family, the peer group, the media and religion
we are often less aware of it, but it is arguably more important and effective than formal social control
what is meant by crime being socially constructed?
crime is defined by social norms and power structures rather than being inherently wrong
it is not necessarily universal or agreed upon by everyone
crime being socially constructed also reflects different attitudes that are found towards what is considered deviant at a particular point
what is meant by crime being relative?
(because crime is socially constructed, it must be relative)
crime can vary according to time, culture and context
give one example of crime/deviance being relative in terms of time (homoesexuality)
we no longer see homosexuality as deviant or a crime, the sexual offences 1967 decriminalised private homosexual acts between men over 21 years
the marriage (same sex couples) act 2013 extended marriage to same sex couples in england and wales
give a second example of crime/deviance being relative in terms of time (child labour)
in the past, child labour was seen as the norm
this is then changed by the factory act, which forbid children under 9 years of age to work, as well as children not allowed to work before 7am and after 7pm during school hours
to now, it is illegal to hire children under the age of 13
give a third example of crime/deviance being relative in terms of time (US alcohol consumption)
during the prohibition era , while the consumption of alcohol was still legal, any production, transportation or sale of alcohol were banned
the law was then repealed in the 21st amendment, now only some states still prohibit selling alcohol, while most states allow drinking over the age of 21
give one example of crime/deviance being relative in terms of culture (gang subculture)
the majority of society views gang behaviour as deviant, or even criminal
e.g. violence, being involved in criminal behaviour, selling drugs
however, members in the gang believe that what they are doing is acceptable, and their behaviours are considered as norms in their subculture
give a second example of crime/deviance being relative in terms of culture (marriage customs)
in the UK, child marriage is seen as illegal. However, in countries like Niger, child marriages are considered a norm in their society
76% of girls in Niger are married or entered a union before the age of 18, 28% under the age of 15, which most are done under customary law
give a third example of crime/deviance being relative in terms of culture (shoes indoors)
mainly in the US, it is considered normal to wear your outdoor shoes into the house instead of changing for slippers or just wearing socks
however, in many south east asia countries such as japan and taiwan, wearing your outdoor shoes into the house is considered deviant and is seen as disrespectful or unhygienic
give one example of crime/deviance being relative in terms of context (murder)
killing another person in a civilian setting is universally condemned as murder, and typically results in a criminal prosecution
however, in a wartime setting, killing an enemy is often seen as a heroic act and the person may been rewarded with medals or honours
give another example of crime/deviance being relative in terms of context (wearing a swimsuit)
wearing a swimsuit is considered the norm when you are at the beach or a swimming pool
however, it is seen as deviant behaviour if you wear it in formal settings such as the office or in church
give a third example of crime/deviance being relative in terms of context (smoking)
since the introduction of health act 2006, smoking in enclosed public spaces such as restaurants or shops are now illegal
however, smoking in spaces such as the streets or inside private homes are still allowed
what is official crime statistics?
published by the government and is made up of two types of data
one is the police recorded crime statistics, involves statistics produced from police, court and prison records
another is the crime survey for england and wales, which collects data about victim’s experiences of crime during the previous year
all of these are collected by the home office and published by the office for national statistics
what is police recorded crime statistics?
records kept by the police and other official agencies
they are published by the home office every 6 months and have been collected since 1857
they are sometimes used as a definitive measure of the amount of crime which has taken place, but only includes crime which the police are aware and have recorded of
what is some strengths of police recorded crime statistics?
they cover the whole population and go back many years, so trends and patterns can be identified
they are up to date and standardised, the time lag between occurrence of crime and reporting results tends to be short, which provides an indication of emerging trends
easy to access and have already been compiled, useful in identifying the effectiveness of laws and anti-crime policies
what is one weakness of police recorded crime statistics? (dark figure)
they only include crimes that are recorded by the police, failing to account for the ‘dark figure’ of unreported and unrecorded crime
the dark figure of crime refers to all unrecorded crime, which may contain ‘victimless’ crimes such as drug offences where no one is likely to report to the police
other crimes may not be recorded due to the fear or shame of the victim, the lack of awareness that a crime has even been committed
what are three supporting statistics for ‘dark figure of crime’?
a survey on mumsnet found that 83% of those who had been raped or sexually assaulted did not report it to the police, half said they would be too ashamed to report it and 70% said they think the media is unsympathetic to women who report rape
in 2012, kier starmer said that 9 out of 10 rapes and other sexual attacks were never reported to the police, arguing its because victims do not believe the criminal justice system can help them
in 2014, the ministry of justice revealed that the conviction rate for sexual offences was just 55%
what is another weakness of police recorded crime statistics? (police discretion)
this refers to the fact that the police can exercise choice in whether they record an incident that has been reported to them, as well as in which category of crime they record it (by using manipulation techniques)
it is argued that police exercise this discretion in recording crime because of the political pressures on them to improve their clear-up rates and meet targets om reducing certain types of crime
this leads to a misleading figure of the overall crime rate, potentially causing some types of people to be wrongfully arrested
what is one of the manipulation techniques used in police recorded crime statistics? (coughing)
encouraging an offender to admit to a number of offences in return for being charged for a less serious offence, resulting in a reduced sentence
this would greatly improve the ‘clear-up rate’ for the police force
what is another of the manipulation techniques used in police recorded crime statistics? (cuffing)
also known as (no-criming)
referring to when crimes that have been initially reported and recorded down, being removed from the statistics at a later date
this may be because the officers did not believe the complainant or there is simply not enough evidence
however, it has been alleged that in order to improve figures, officers may inappropriately take crime of the books, or even persuade the victim to withdraw their allegation
what is the third manipulation technique used in police recorded crime statistics? (skewing)
forces putting resources into those areas measured by performance indicators, to the detriment of other areas
what are two supporting evidences for police discretion?
james patrick - analysed data from the met police, found that even serious sexual offences were routinely ‘no-crimed’ and burglary was commonly downgraded to a lower type of offence
farrington and dowds - analysed random samples of police records in nottinghamshire, staffordshire and leicestershire, found that nottinghamshire was more likely to record thefts under the value of £10, while the other two deemed it as minor and did not record them
hence, nottinghamshire’s crime rate was much higher in statistics, shows that there may be distortions in statistics due to local priorities
what is the third weakness for police recorded crime statistics? (socially constructed)
marxists and interactionsists question the validity of police recorded crime statistics since the definition of crime is socially constructed, rather than objective facts
the police may also subconsciously or consciously display bias depending on the social status of the victim, as well as dependent on how they interpret the role of the police in deciding how to interpret and enforce the law
what are two examples to support marxists’ and interactionists’ criticism of police recorded crime statistics?
murder of Stephen Lawrence - met police displaying institution racism
Gill’s study on working class communities suggested that victims who were poor were treated more negatively by the police, black communities also complained the police do not take racist crimes against them seriously