THERMODYNAMICS
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Thermodynamics
a branch of physical chemistry which deals with the heat, temperature and physical properties of matter
Ions in lattices
are held together by ionic bonds
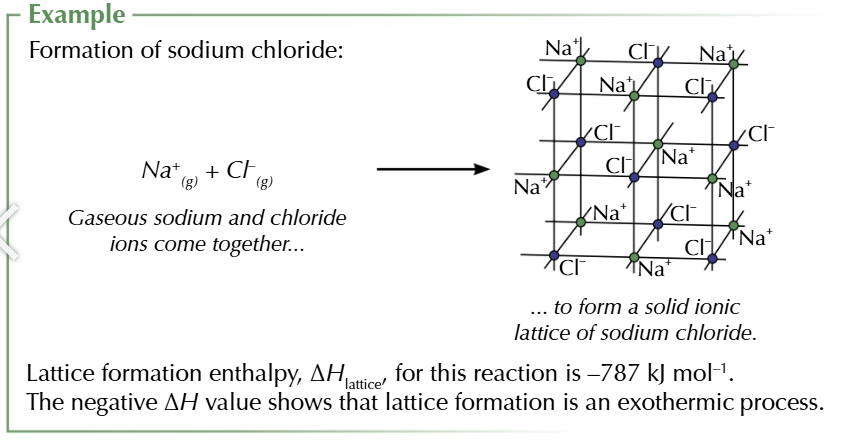
lattice formation enthalpy
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound in formed from its gaseous ions
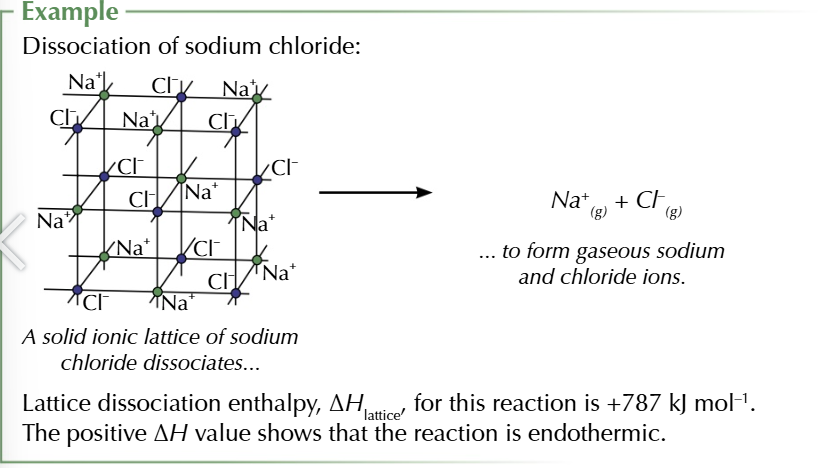
lattice dissociation enthalpy
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a solid ionic compound is completely dissociated into its gaseous ions
lattice enthalpy can’t be measured directly
instead you have to combine the enthalpies from a number of other processes to work out the lattice enthalpy
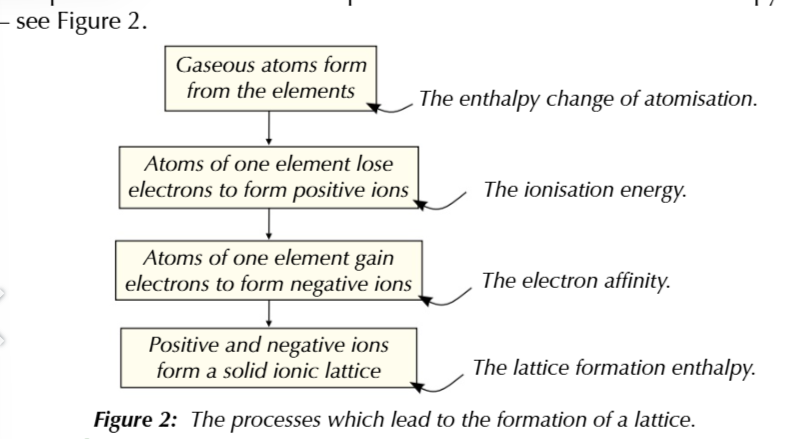
lattice enthalpy=
atomisation+ionisation+electron affinity+formation
Enthalpy change of formation
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states
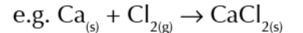
bond dissociation enthalpy
enthalpy change when all bonds of the same type in 1 mole of gaseous molecules are broken
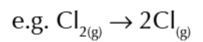
enthalpy change of atomisation of an element
the enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atoms is formed from an element in it standard state
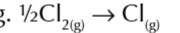
enthalpy change of atomisation of a compound
enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound in its standard state is converted to gaseous atoms
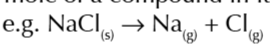
first ionisation energy
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ion is formed from 1 mole of gaseous atoms

second ionisation energy
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous 2+ ions is formed from 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions
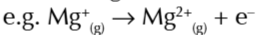
first electron affinity
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions is made from 1 mole of gaseous atoms
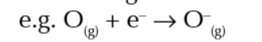
second electron affinity
enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous 2- ions is made from 1 mole of gaseous 1- ions
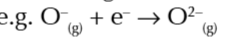
enthalpy change of hydration
enthalpy change when 1 mole of aqueous ions is formed from gaseous ions
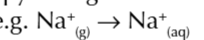
enthalpy change of solution
enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic substance dissolves in enough solvent to form an infinitely dilute solution
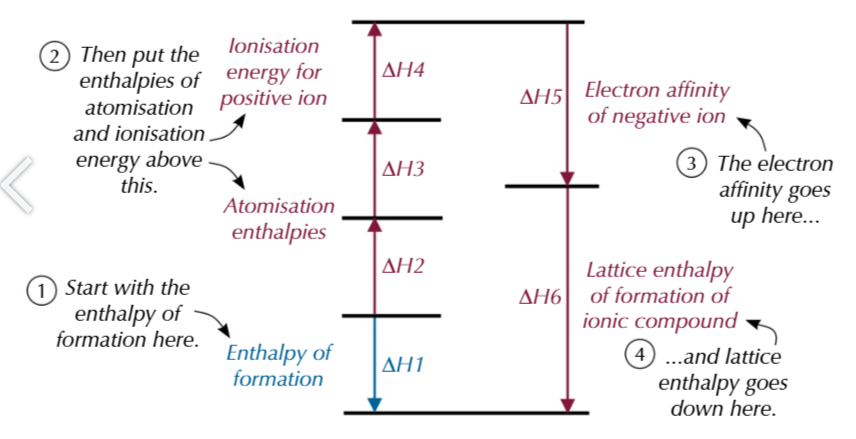
born-haber cycle
enthalpy of Formation
enthalpies of Atomisation
enthalpies of Ionisation
electron Affinity
lattice enthalpy of ionic compounds
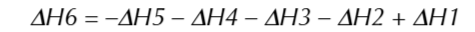
Hess’ law
total enthalpy change of a reaction is always the same no matter which route is taken
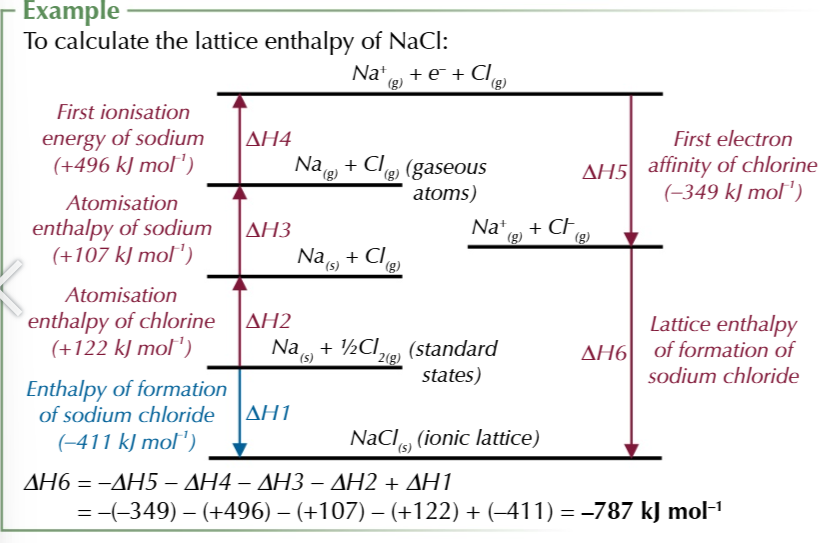
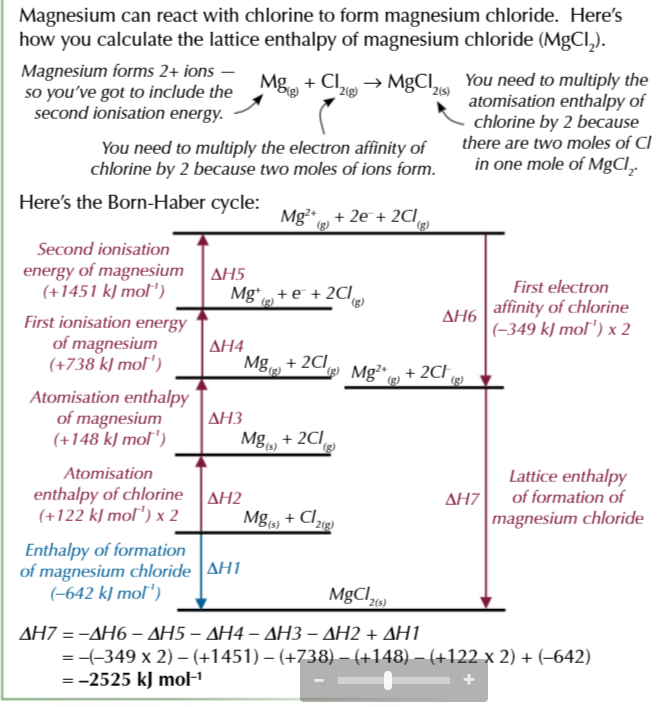
born haber cycles for compounds containing group 2 elements have an extra step
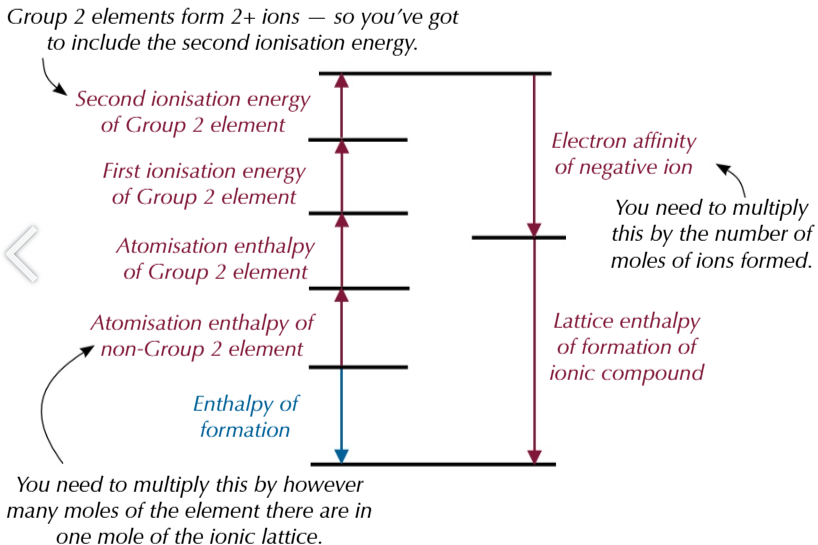
purely ionic model of lattice assumptions:
all ions are spherical
all ions have evenly distributed charge around them
theoretical enthalpy is always different from experimental enthalpy
this is evidence ionic compounds usually have some covalent character
positive and negative ions in lattice are usually exactly spherical
positive ions polarise neighbouring ions to different extents, the more polarisation there is the more covalent the bonding will be

2 things happen when a solid ionic lattice dissolves in water
Lattice enthalpy of dissociation: bonds between ions break to make gaseous ions, endothermic
Enthalpy change of hydration: bonds between ions and water are made, exothermic
water can form bonds with ions because it is polar
oxygen is more electronegative that hydrogen, so it draws the bonding electrons towards itself, creating a dipole
positive ions form weak bonds
with the partial negative charge on the oxygen atom of water
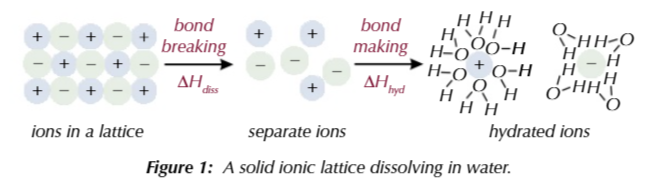
negative ions for weak bonds
with the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom of water
enthalpy change of solution is the overall effect…
…on the enthalpy of bond breaking and bond making
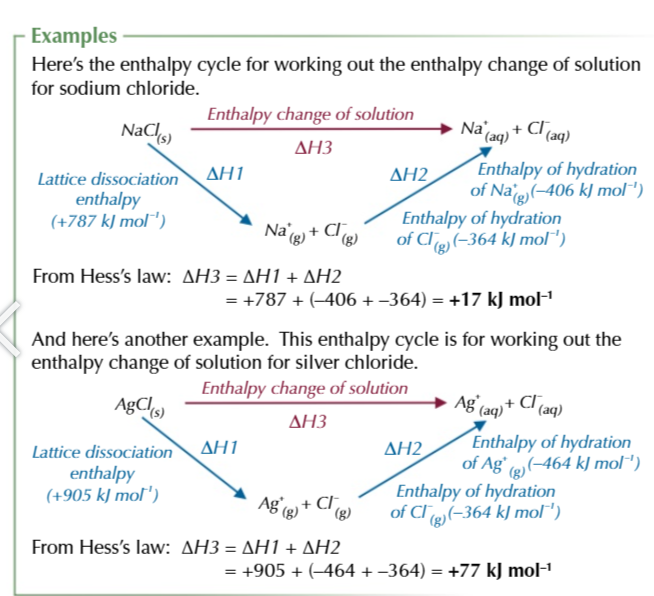
enthalpy change of solution can be calculated
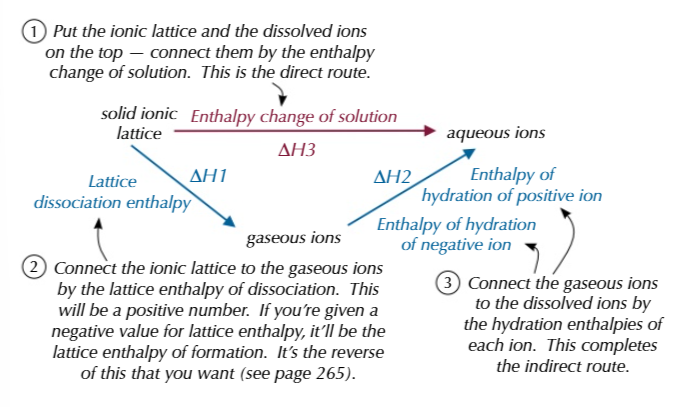
Enthalpy of hydration of positive and negative ions - lattice dissociation enthalpy
entropy
the measure of the number of ways that particles can be arranged and the number of ways that the energy can be shared out between the particles
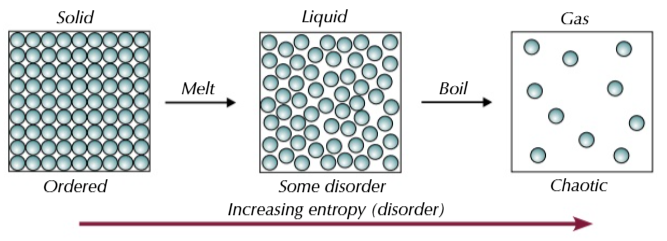
dissolution
dissolving a solid also increases its entropy as dissolved particles can move freely as they are no longer held in place
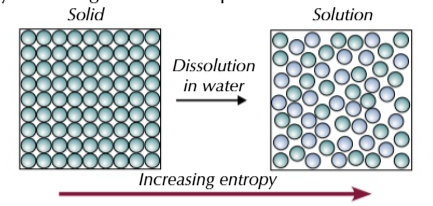
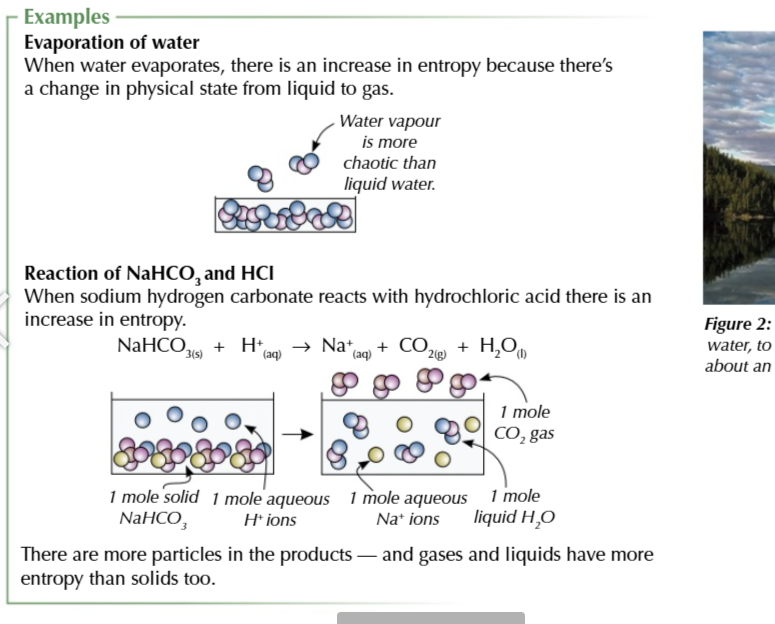
more particles means more entropy
the more particles there are the more ways they and their energy can be arranged
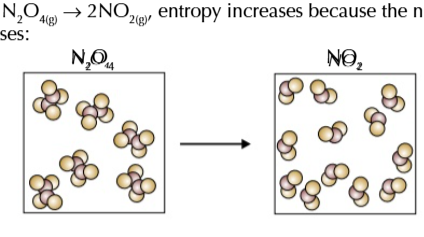
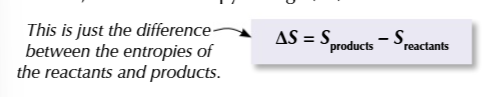
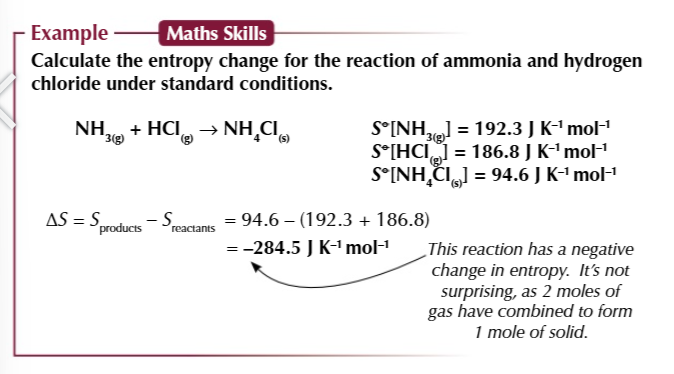
calculating entropy change
products - reactants
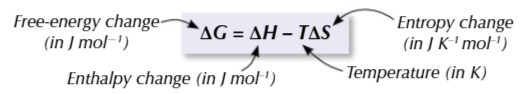
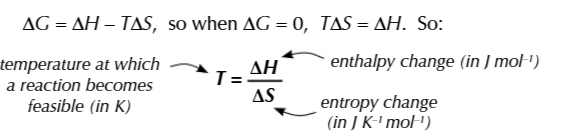
free energy change
is a measure used to predict whether a reaction is feasible
a reaction is feasible when
ΔG is negative or equal to 0
negative ΔG doesn’t guarantee a reaction will occur or tell you about its rate
the reaction may only be theoretically feasible, with an extremely high activation energy or have such a slow rate you wouldn’t be able to notice tis happening at all

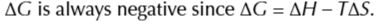
exothermic reactions and POSITIVE ENTROPY change
these reactions are feasible at any temperature
endothermic reactions and has a NEGATIVE ENTROPY change
these reactions are not feasible at any temperature
if the reaction is endothermic and entropy is positive
the reaction will only be feasible above a certain temperature

if the reaction is exothermic and enthropy is is positive
reaction is only feasible below a certain temperature

when ΔG is 0
a reaction is JUST feasible
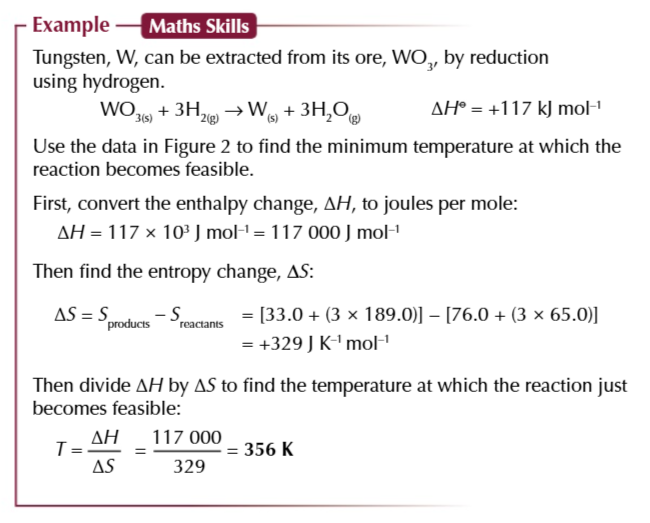
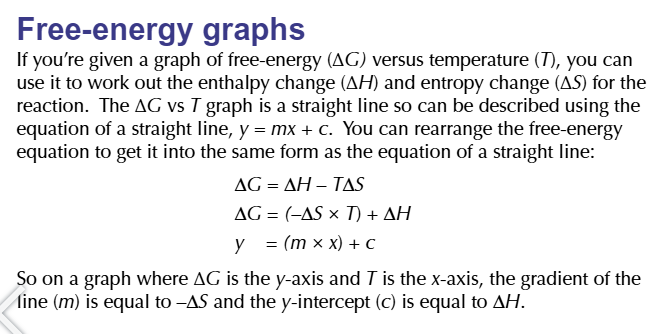

variation in ionisation energy, FROM STRONGEST TO WEAKEST
O2+>O> O- >O2-
CATION>NEUTRAL ELEMENT>ANION