Biological molecules: nutrients + energy requirements + food tests
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Carbohydrates (what elements are they made out of? Molecular structure. What is its function in the body? Foods that are rich in carbohydrates?)
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen.
Starch and glycogen are large, complex carbohydrates which are made up of simple sugars (e.g. glucose, maltose, sucrose) joined in a long chain. Glucose is a monosaccharide, while sucrose is a disaccharide (made of 2 monosaccharides, glucose and fructose).
Provide us with energy to carry out reactions (respiration).
Bread, pasta, rice…
Glucose and other types of simple sugars belong to one group of carbs: they are all simple sugars.
Glucose is found naturally in sweet tasting foods like vegs and fruits. Other foods countain diff types of sugar:
fruit sugar = fructose, milk sugar = lactose, table sugar = sucrose
What are the 2 main physical properties of sugar? What is the main sugar transported through plant stems?
They all taste sweet and are soluble in water
Sucrose
We get most of our carbs from not sugars. It is a polymer of ____
Starch
Glucose -- made of long chains of glucose moleules joined together
Why is starch a food storage in many plants? Animal tissues dont have starch, but what other carb similar to it and has the same function do they have?
It is an insoluble molecule (and large as well)
Glycogen
Complex/large carbs like starch and glycogen have to be broken down into simple sugars during digestion to be absorbed.
What is another carb (also a polymer of glucose) that humans cannot digest? Why? What do we use it instead of being a source of energy like other carbs?
Cellulose
Our gut doesn't make the enzyme needed to break down cellulose molecule.
It forms dietary fibre or 'roughage'.
Lipids (what elements are they made out of? Molecular structure. What is its function in the body? Where are lipids important? Foods that are rich in lipids?)
Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
1 glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids
Long term energy store, insulation (fat under the skin reduces heat loss), protection from mechanical damage (fat around organs like kidneys, heart)
Important in cell membranes, hormones and the nervous system.
Oils, butter, cheese…
How are animal lipids different from plant lipids? Lipids are essential, but too much especially a type call saturated fats leads to…
Animal lipids (animal fat) is solid at room temp, liquid if warmed up
Plant lipids (oils) are usually liquid at room temp
Heart disease
Proteins (what elements are they made out of? Molecular structure. What is its function in the body? Foods that are rich in proteins?
✨CHONISSS✨ Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulfur.
Made out of chains of amino acids.
Used for growth and repair of cells and tissues (+ many compounds like enzymes are made from proteins)
Meat, eggs, fish…
The ___ of a protein is very important in allowing it to carry its function. How is this decided?
Shape
Order of amino acids
What is a balanced diet?
A diet in which the essential nutrients are consumed in the right proportion.
What essential nutrients are needed in a balanced diet?
Carbs, proteins, lipids
Minerals: iron and calcium
Vitamins A, D, C
Water
Dietary fiber
Calcium (uses in the body, sources and consequences of deficiency)
Strong teeth, bones and involved in blood clotting.
Milk, cheese, eggs…
OSTIA-QUE-TIENE-POROSSS Osteoporosis (weakening and hollowing of bones)
Iron (uses in the body, sources and consequences of deficiency)
Make haemoglobin in red blood cells (carry oxygen).
Leafy veg (spinach), red meat, liver.
Ana-Emma Anaemia (feeling tired)
Vitamin A (uses in the body, sources and consequences of deficiency)
For vision, especially night vision. Makes a chemical in the retina and protects the eye.
Carrots, fish, liver
Night blindness
Vitamin C (uses in the body, sources and consequences of deficiency)
Essential for collagen — healthy skin, hair, teeth, bones and gums. Makes fibres of connective tissue (bonds cells together)
Green vegetables, citrus fruits, strawberries.
Scared of being CURVYYY
Scurvy (wounds fail to heal, bleeding)
Vitamin D (uses in the body, sources and consequences of deficiency)
Aids absorption of calcium.
Oily fish, red meat, exposure to sunlight
Rickets
Fibre (uses in the body, sources and consequences of deficiency)
Isn't digested but helps muscles in gut move food through intestines by providing bulk (roughage) (muscles has¡ve something to push against)
Fruit, vegetables, wholegrain products.
Constipation
Water (uses in the body, sources and consequences of deficiency)
Needed for chemical reaction to take place in cells.
Water, fruits, drinks.
Fatigue, death.
Energy requirements:
Generally the greater a person’s weight the more energy that person needs. This is why men, with a greater average body mass, need more energy than women
How does energy requirements vary in different people? Activity levels, age. pregnancy
Activity levels: active people need more energy because of increased muscle activity
Age: children need more energy, because they are growing but they are small.
Teenagers need the most energy because their body is growing at its fastest rate.
Old people less energy because their metabolic rate is slower.
Pregnancy: more energy because they have a baby developing in their wombs + extra weight they have to carry
However it is not only the recommended energy requirements that vary with age, sex and pregnancy but also the content of the diet.
What nutrient might a pregnant woman need extra of and why? What about younger women during menstruation and why?
Pregnant women may need extra iron and calcium in their diet, for the growth of the fetus
In younger women, the blood loss from menstruation can result in anaemia, producing a need for extra iron in the diet.
How do you prepare a food sample?
Break up (crush) the food using pestle and mortar.
Transfer to a test tube and add distilled water.
Mix the food and the water by stirring with a glass rod.
Filter the mixture using a funnel and filter paper, collecting the solution.
This takes the solid residue so that the color changes do not get distorted.
Describe the test for glucose
- Prepare food sample (grind if needed) and transfer it into a test tube.
- Prepare a hot water bath (75°C).
- Use a pipette to add drops of Benedict's solution into the test tube.
- Place the test tube into the water bath and wait.
- A positive test will show a colour change from blue to brick red (green ~> yellow in lower concentrations)
Describe the test for starch
- Prepare food sample and transfer it into a test tube/spotting tile
- Add drops of iodine solution using a pipette.
- Shake if in test tube to make sure all the contents are mixed together.
- Positive result: colour change from brown/orange to blue-black.
Describe the test for proteins
Prepare food sample and transfer into a spotting tile/test tube.
Add drops of biuret solution using a pipette.
Shake if in test tube.
Positive test shows a colour change from blue to lilac/purple
Describe the test for lipids
- Prepare food sample (grind if needed) and transfer into a test tube.
- Mix food sample with 2cm^3 of ethanol and equal volume of cold water.
- Shake.
- Positive test shows a cloudy white emulsion forming.
TRIPLE: practial
How can we measure the energy content in a food sample?
What is energy content measured in?
By burning the sample of food. The longer it burns the more energy it has.
In kilojoules (kJ)
What kind of food do we expect will burn the longest?
Lipids (1 gram of fully oxidised fat produces ≈ 39kJ)
Proteins (1 gram of fully oxidised protein produces ≈ 18kJ)
Carbs ( 1 gram of fully oxidised carb produces ≈ 17kJ)
Foods with a high percentage of of lipid contain a large amounts of energy.
Others, like fruits and vegetable have a much lower energy content, why?
They are mainly composed of water which doesn’t have energy
What is the equation to find the energy per gram of food?

A teacher tells some students to carry out an experiment to compare the energy values of 2 biscuits.
Describe a suitable method the students could use for their experiment (4)
Note: comments in cursive isnt on the mark scheme but i think it is worth to put here.
MP1: measure out same volume/mass of water and put in a boiling tube
MP2: use sample of biscuits of the same mass/known mass using a balance and spear the sample on a mounted needle
MP3: ignite biscuit and hold under boiling tube of water/eq
MP4: relight if goes out/continue until completely burnt/eq
MP5: use thermometer to measure increase in water temperature/measure initial and final temp of water/eq
MP6: highest temperature rise has most energy
al parecer allow mp 1,2,5,6 from equation
energy = (mass of water x temp rise x 4.2) ÷ mass of biscuit
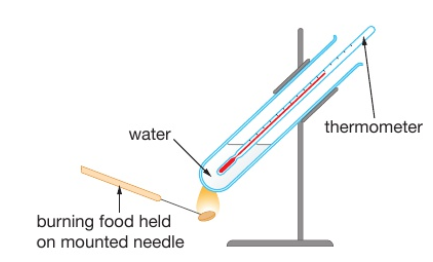
When we measure the final temp of the water how can we make sure that it is correct?
Stir with a stirring rod to distribute the heat evenly