Chem exam 1 finals review
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
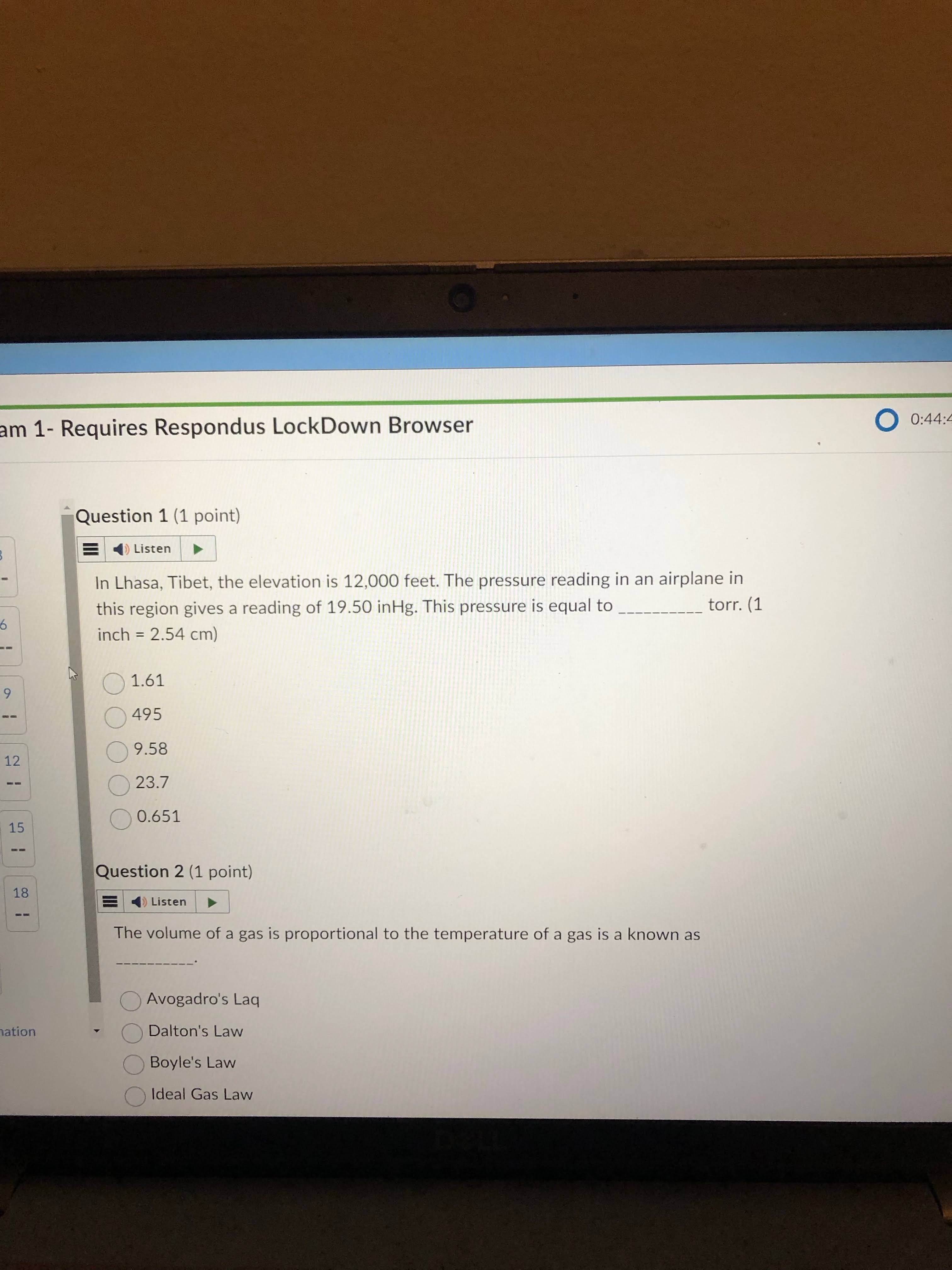
the answer is 495.
this means that you can ignore the HG and focus on the units of measurement. so go from in to cm to mm to atm to torr
name all the gas laws and the old men connected to them
p times v= pervert boyle
p divided by t= gay boy penis toucher
v divided by t= charles watching tv
V/n = avogadros
now talk about what each gas law is saying and provide example
boyle says: pressure and volume inversely related . this is why putitng finger over syringe hole and then pushing down the plunger you will see as volume decreases, pressure increases.
charles says: temp and volume directly related. this is why balloon shrink in cold temperature since gas molc moving slower. also why balloons expand in warm temps since gas molc move faster and spread out more
gay says: temp and pressure directly related. this is why tires shrink in cold weather as the molc wont bounce against walls and will move slower. hot weather makes them expand the walls more energetically.
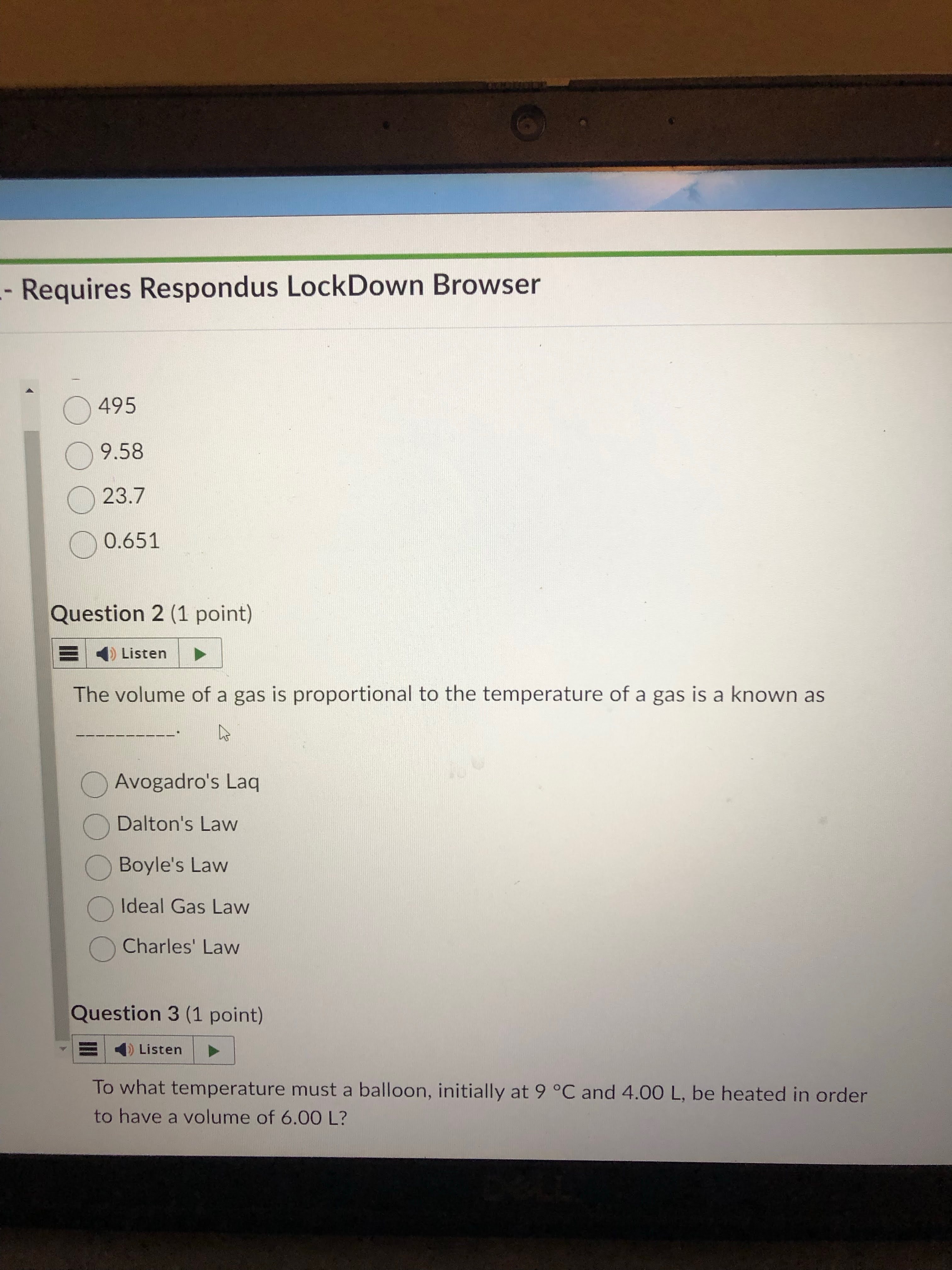
charlie watching tv and seeing the chocolate factory ad
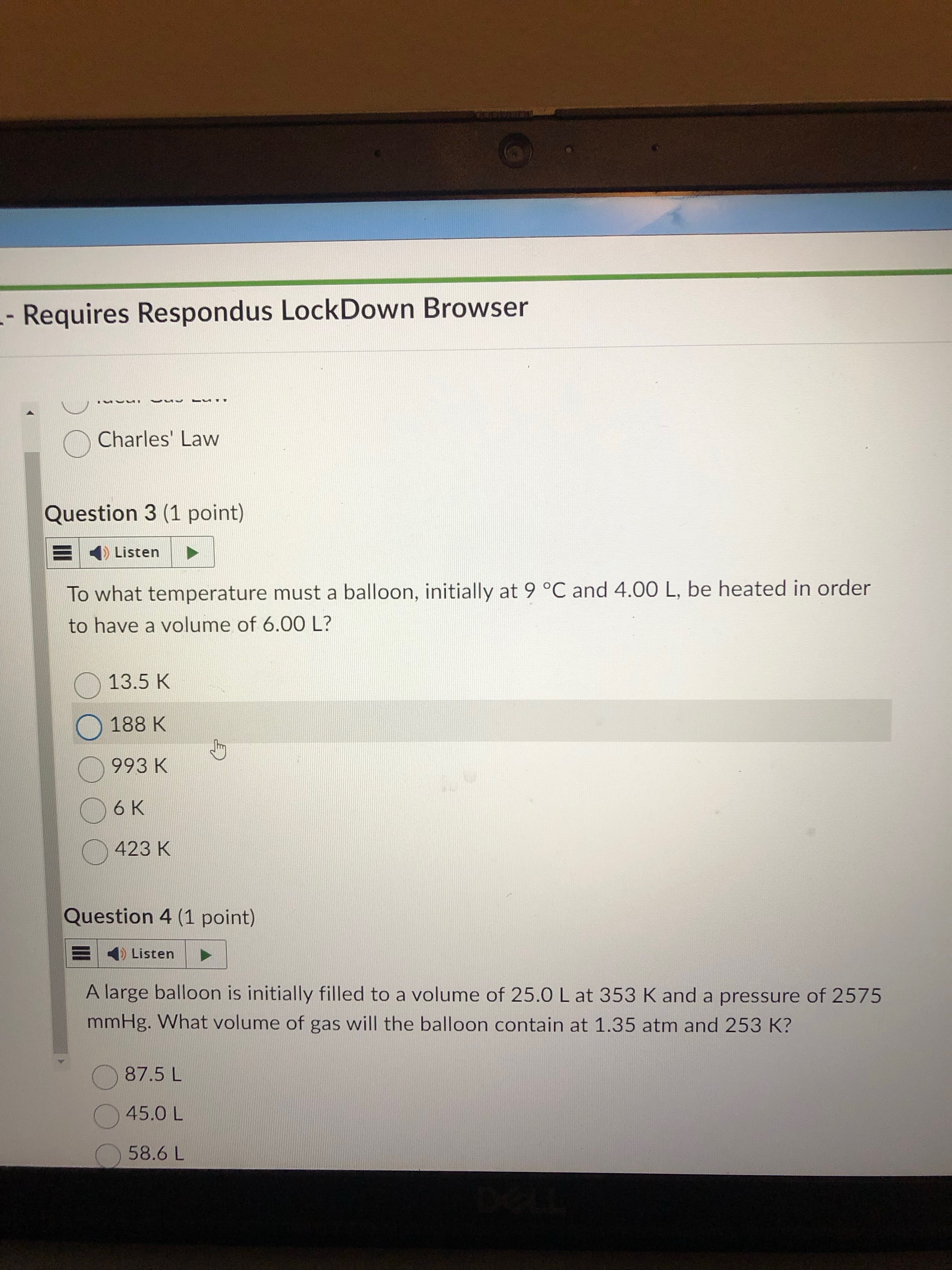
just do v/t formula
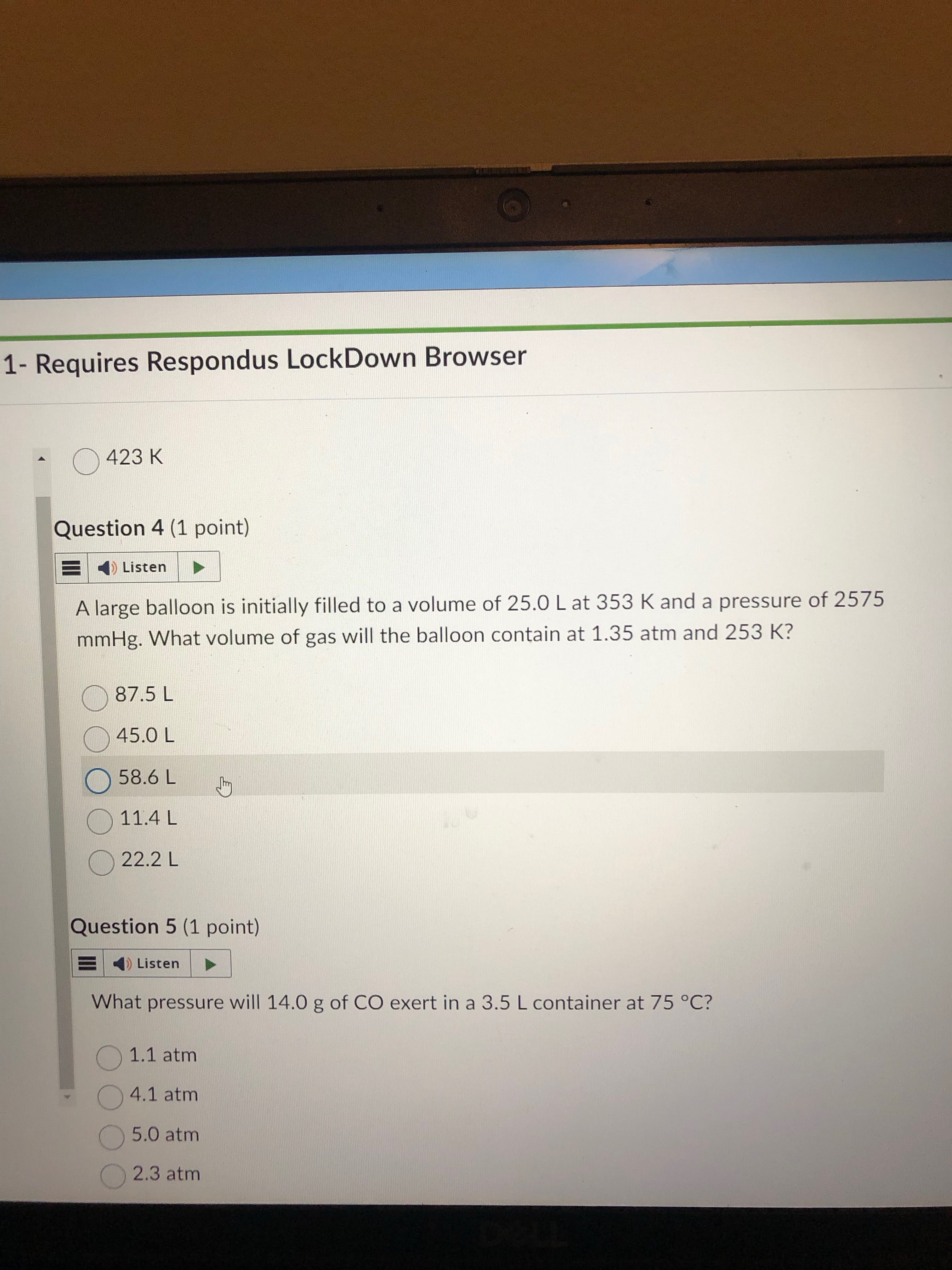
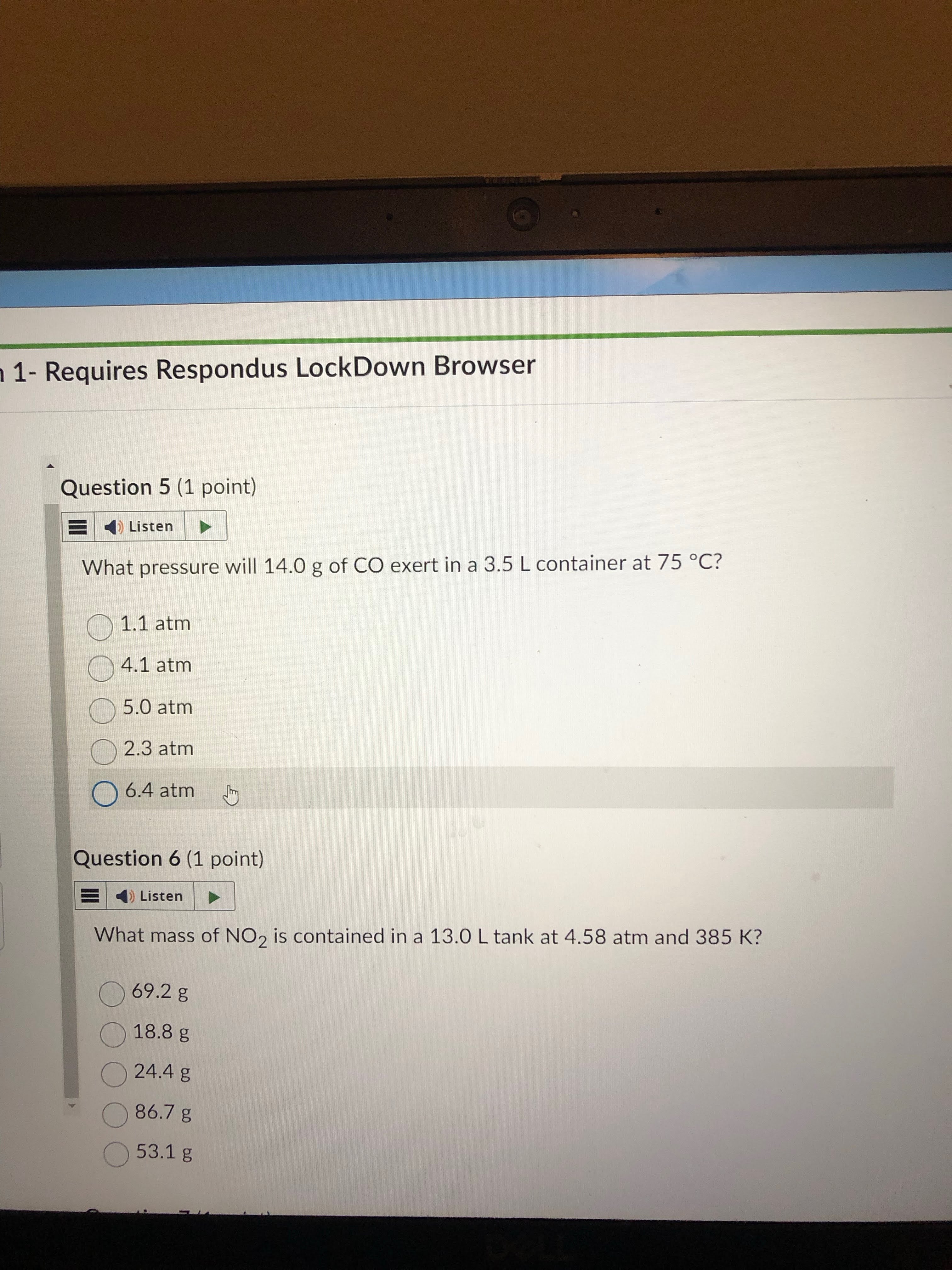
4.1 atm. just plug and chug into pv=nrt. change t and n to correct formats
0.50 × 0.08206 × 348.15 / 3.5
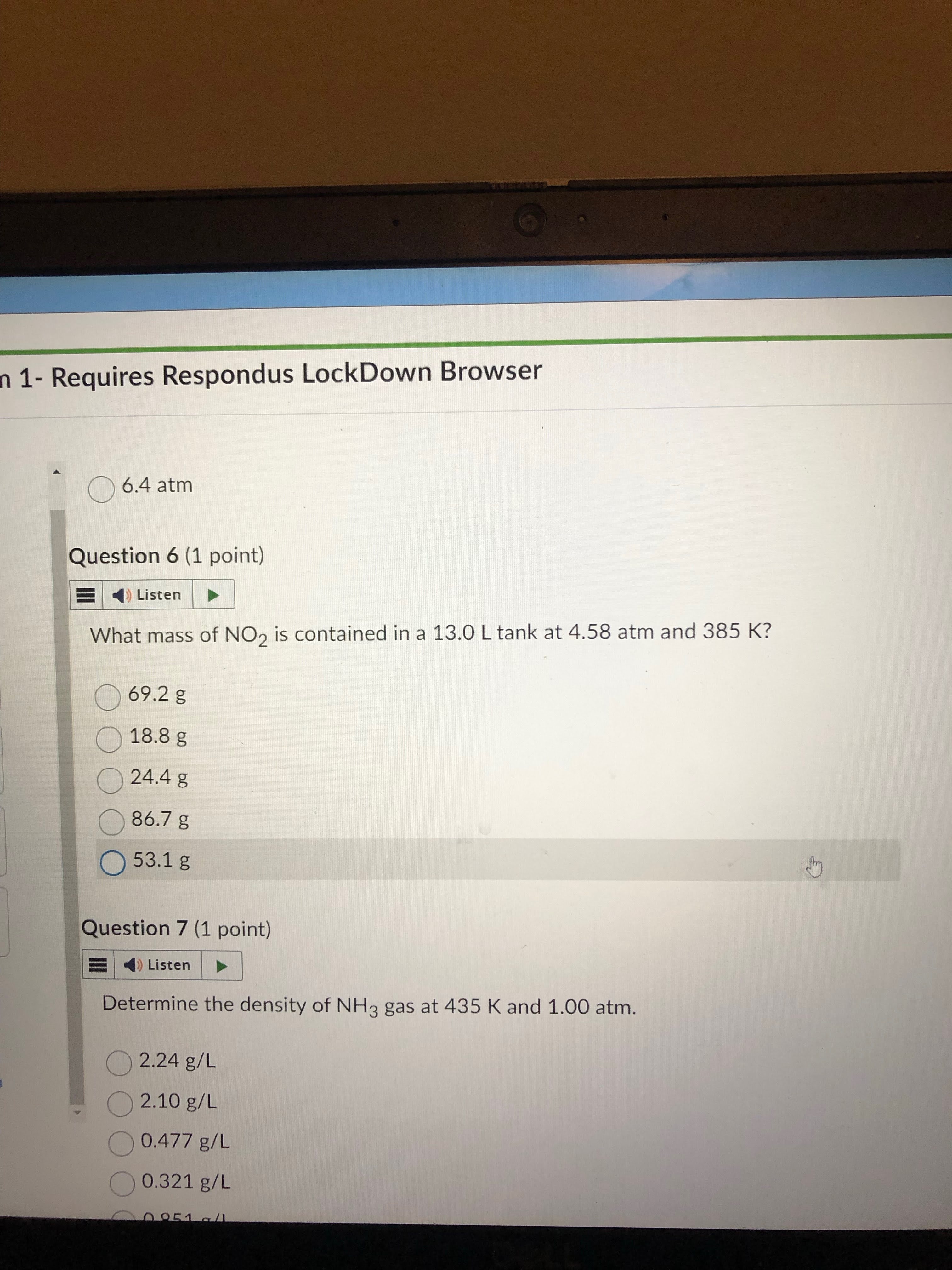
plug and chug. you get mols as answer so must convert mol to g using molar mass.
answer = 86.7
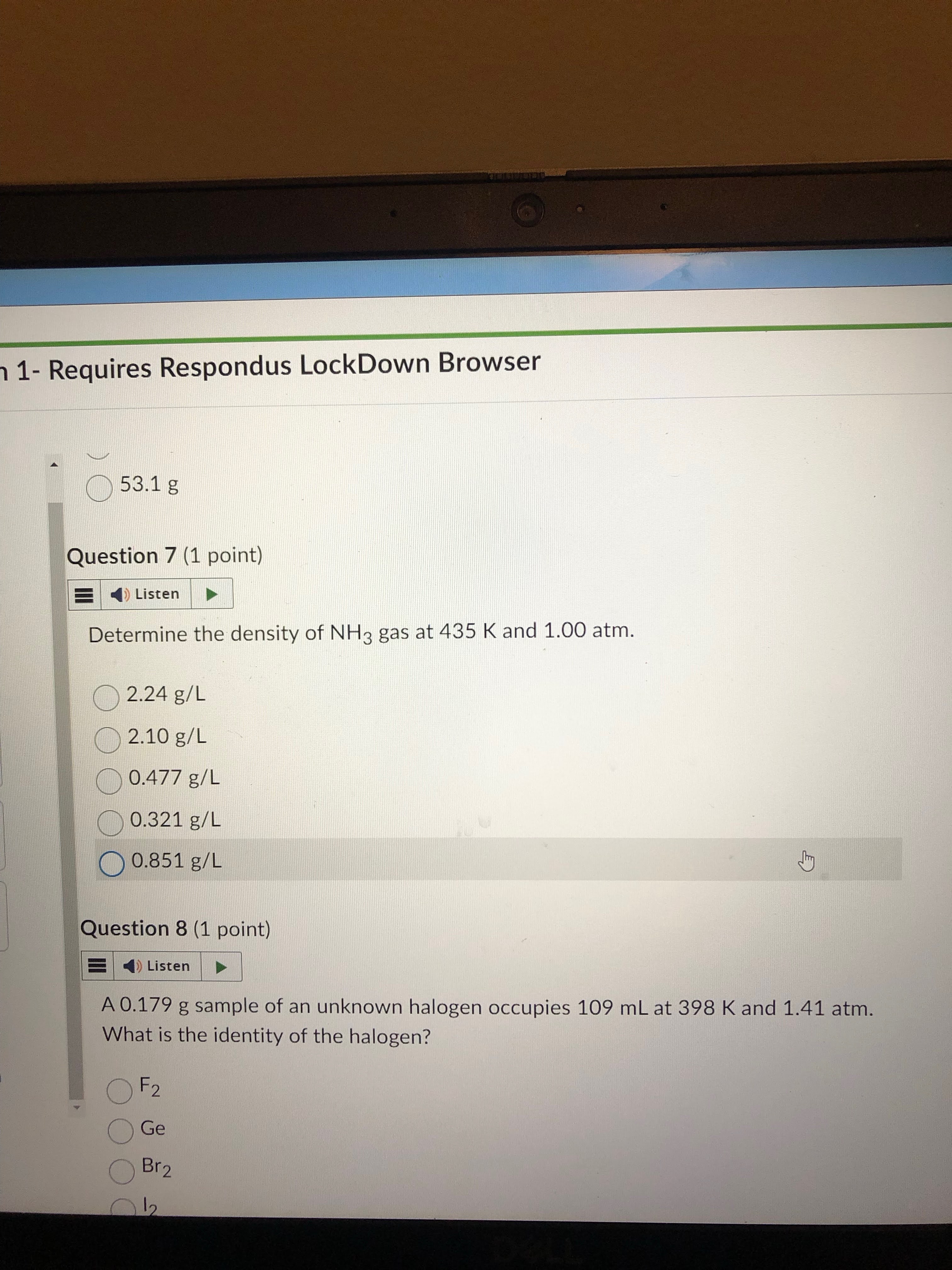
remember the ideal gas law w/ respect to density. find molar mass by given gas. then just plug and chug.
answer= 0.477 g/L
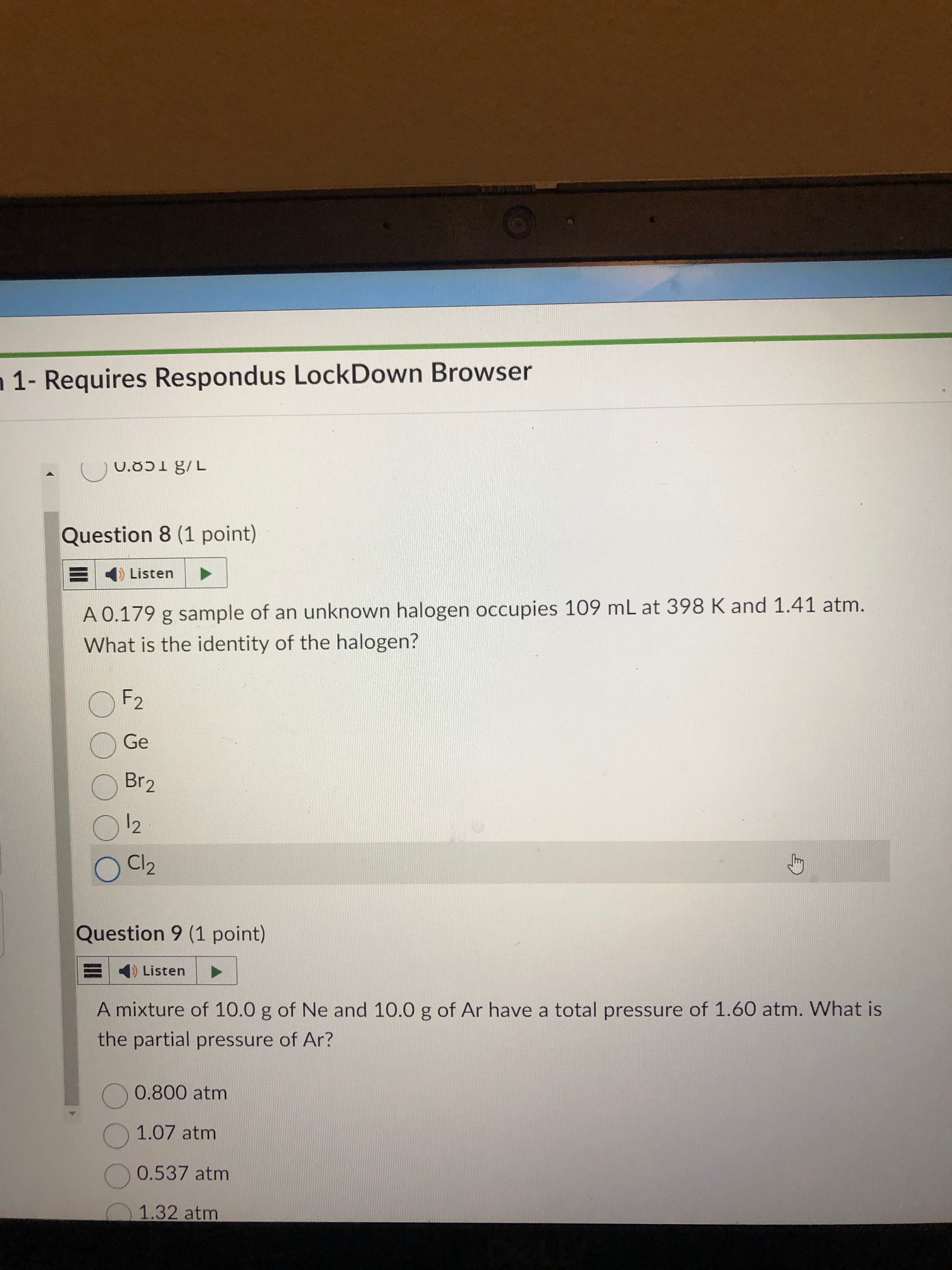
1- must find mols of given gas first
2- find each of the options’ MM. then you can mult each by the amount of mols. this will give you the grams of the unknown halogen
answer= f2
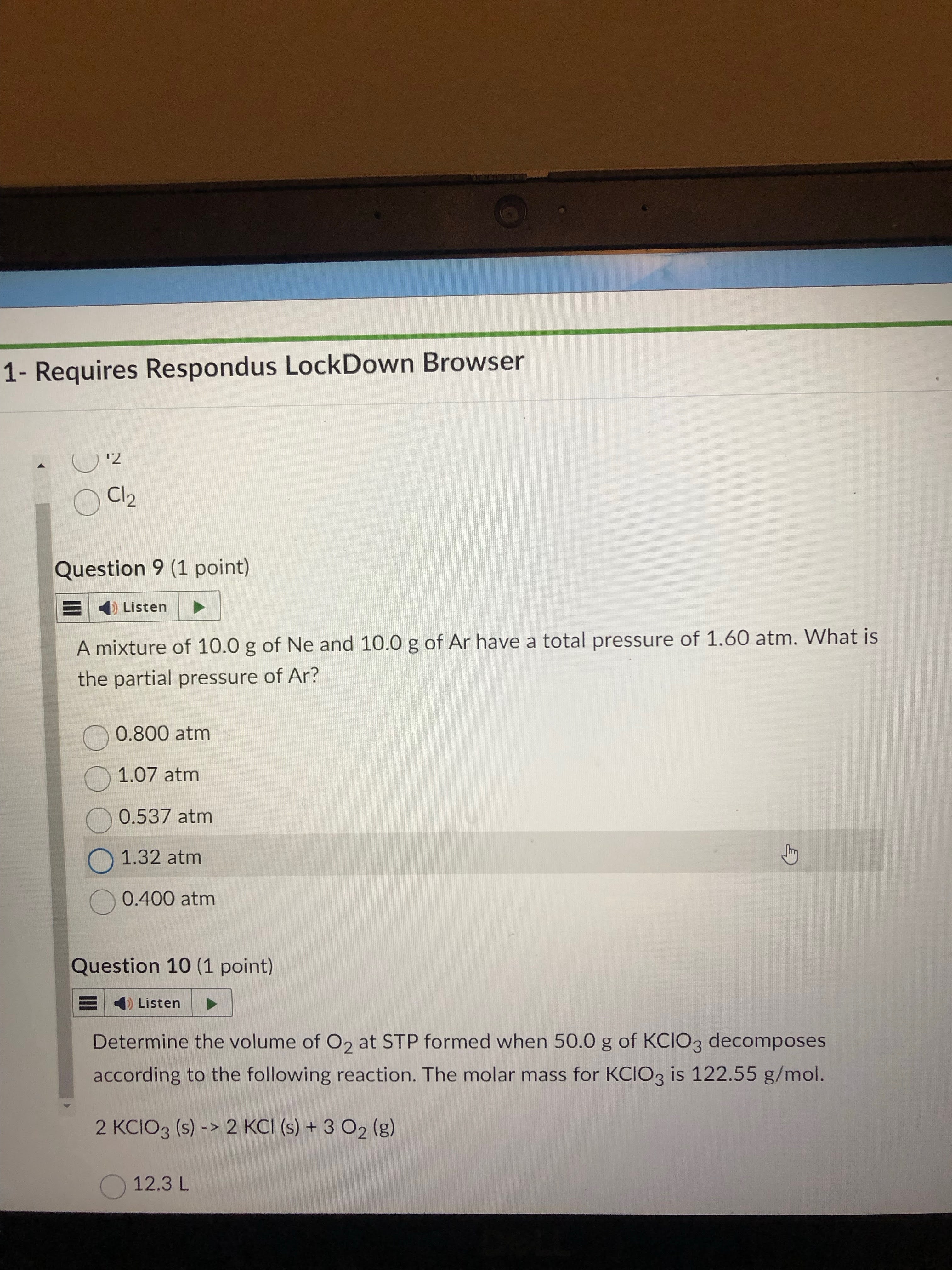
equate each given gram to mols. must turn Ar and Ne to their mol form.
get mol frac of Ar only. then plug it into partial pressure formula that talks about mol frac —→ partial P of gas A= mol frac of gas A times total pressure the gasses combined
answer= 0.537
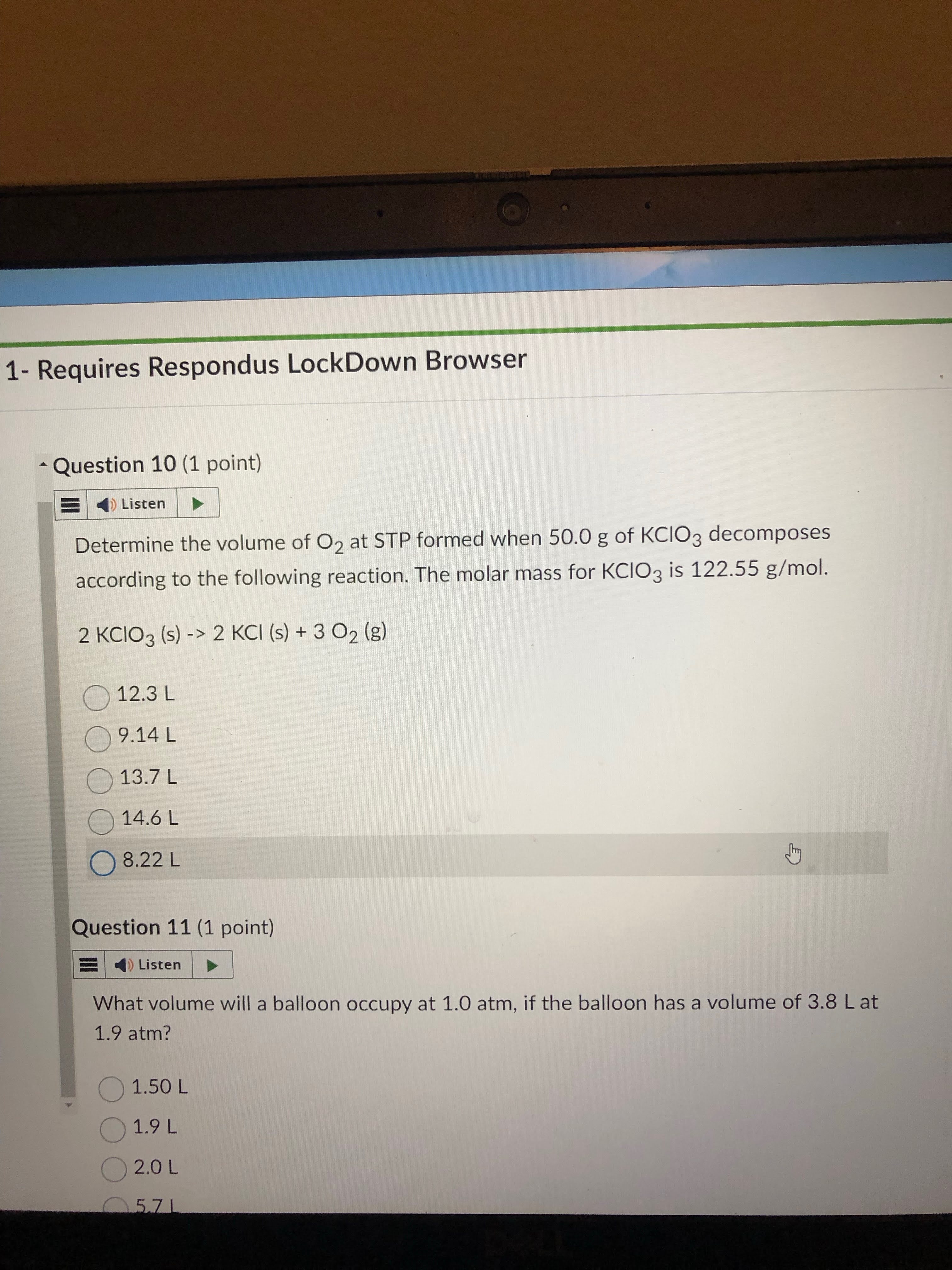
just have to use long conversion to table to jump from given to L at STP of O2.
the path: given grams of kcio3 → mols of kico3 → mols of o2 using stoic → L at STP of o2
answer: 13.7 L
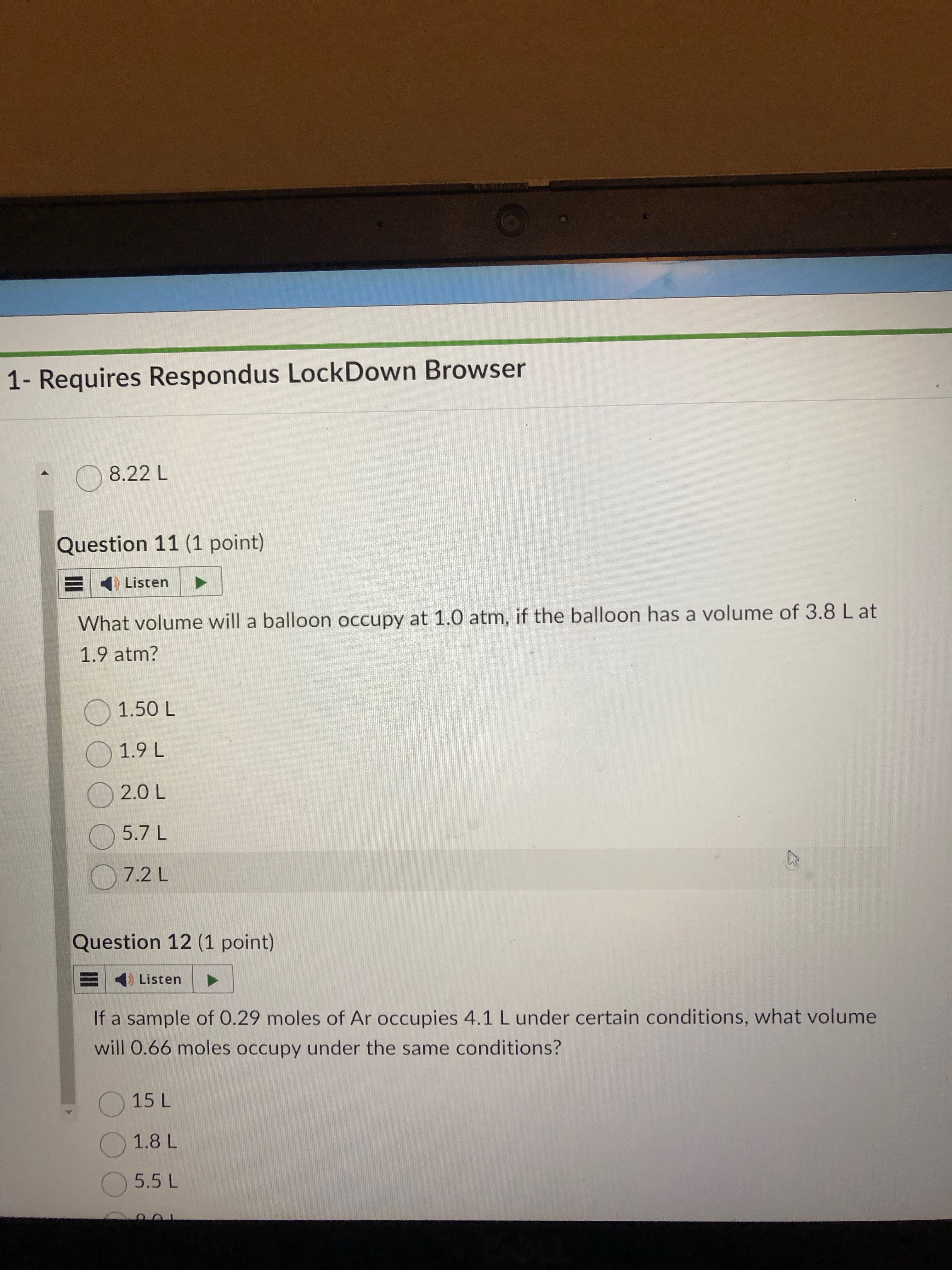
answer: 7.22
boyle law
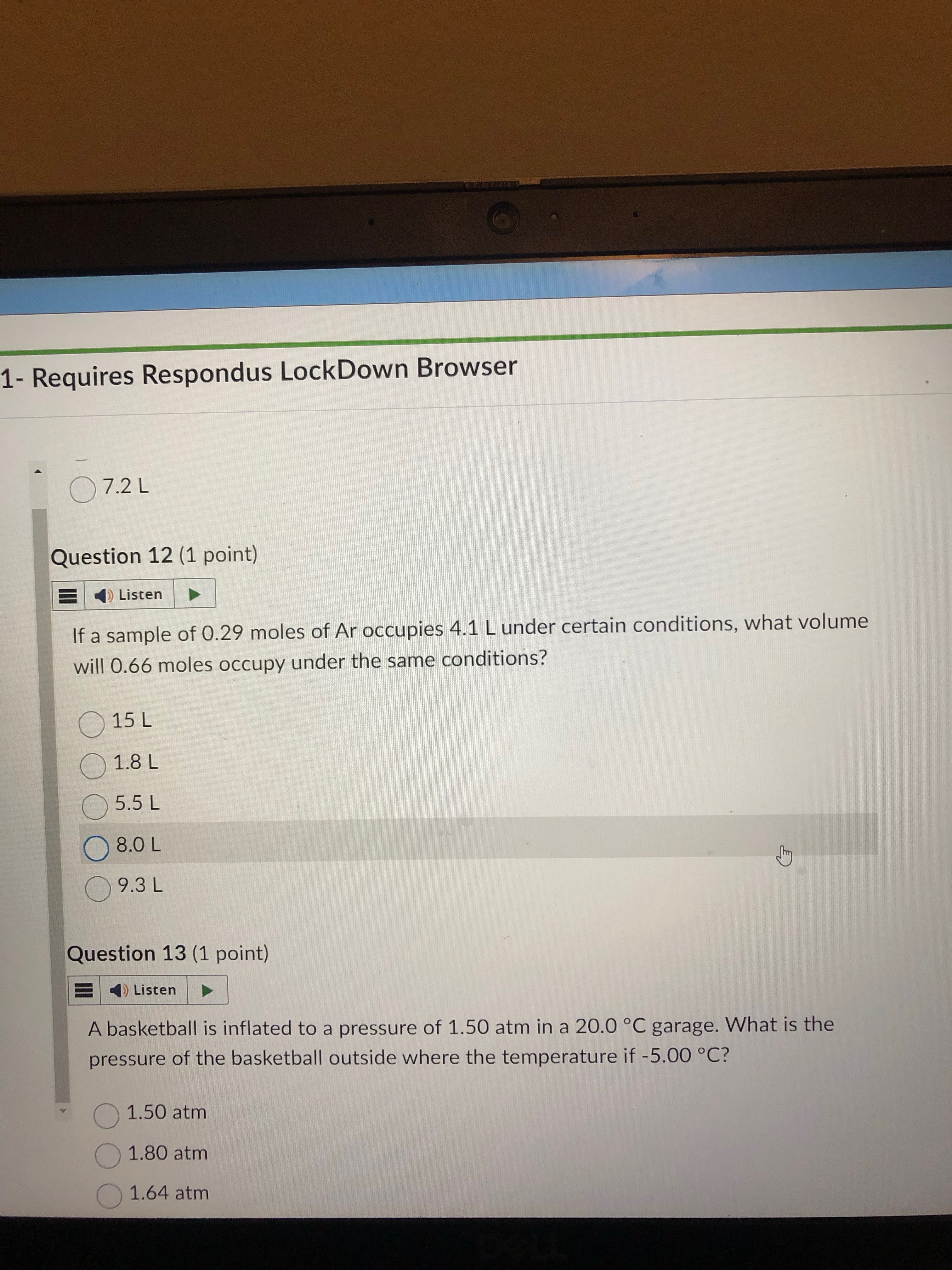
9.3 answer
avo’s law
gay law
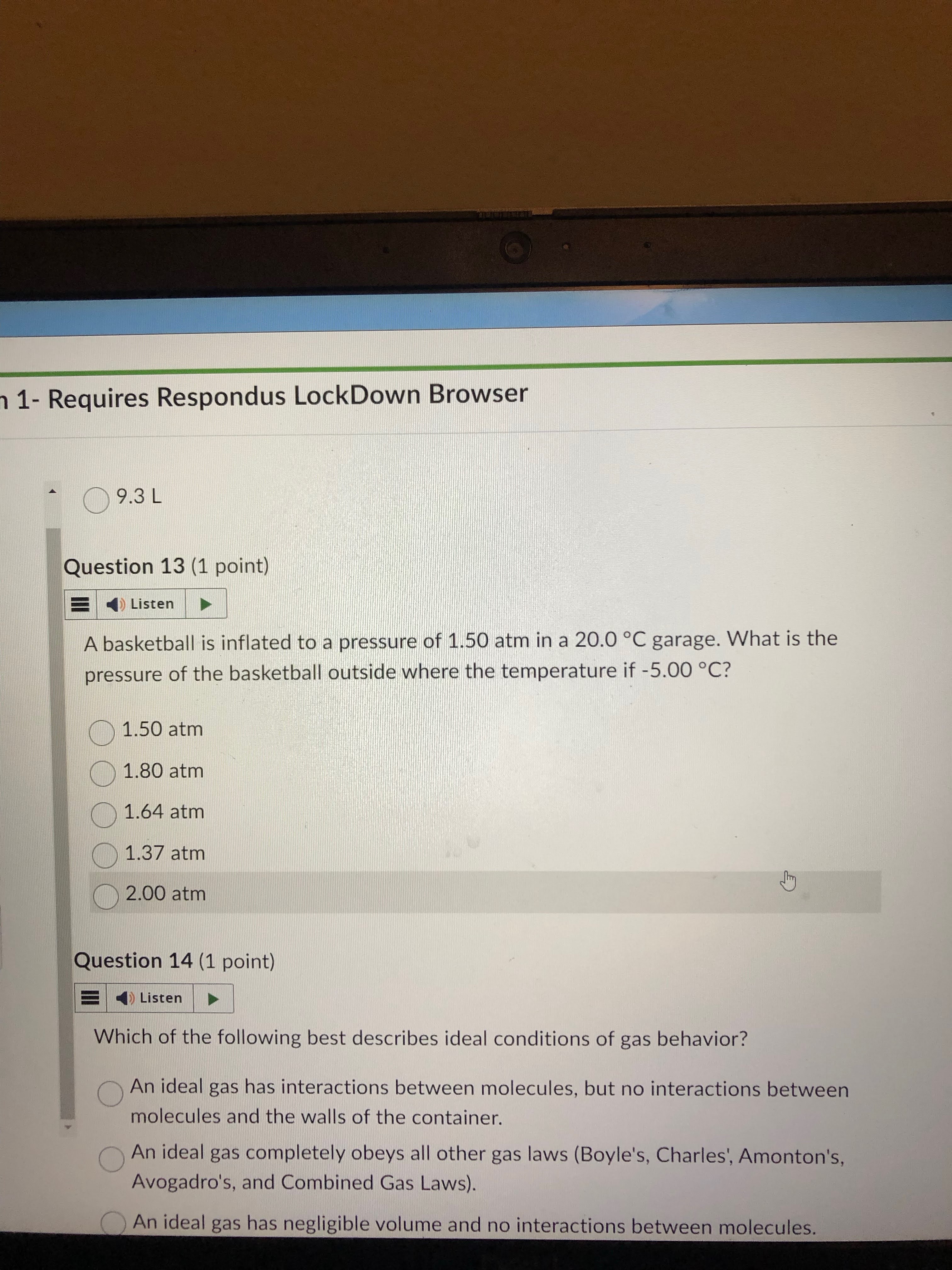
answer= 1.37
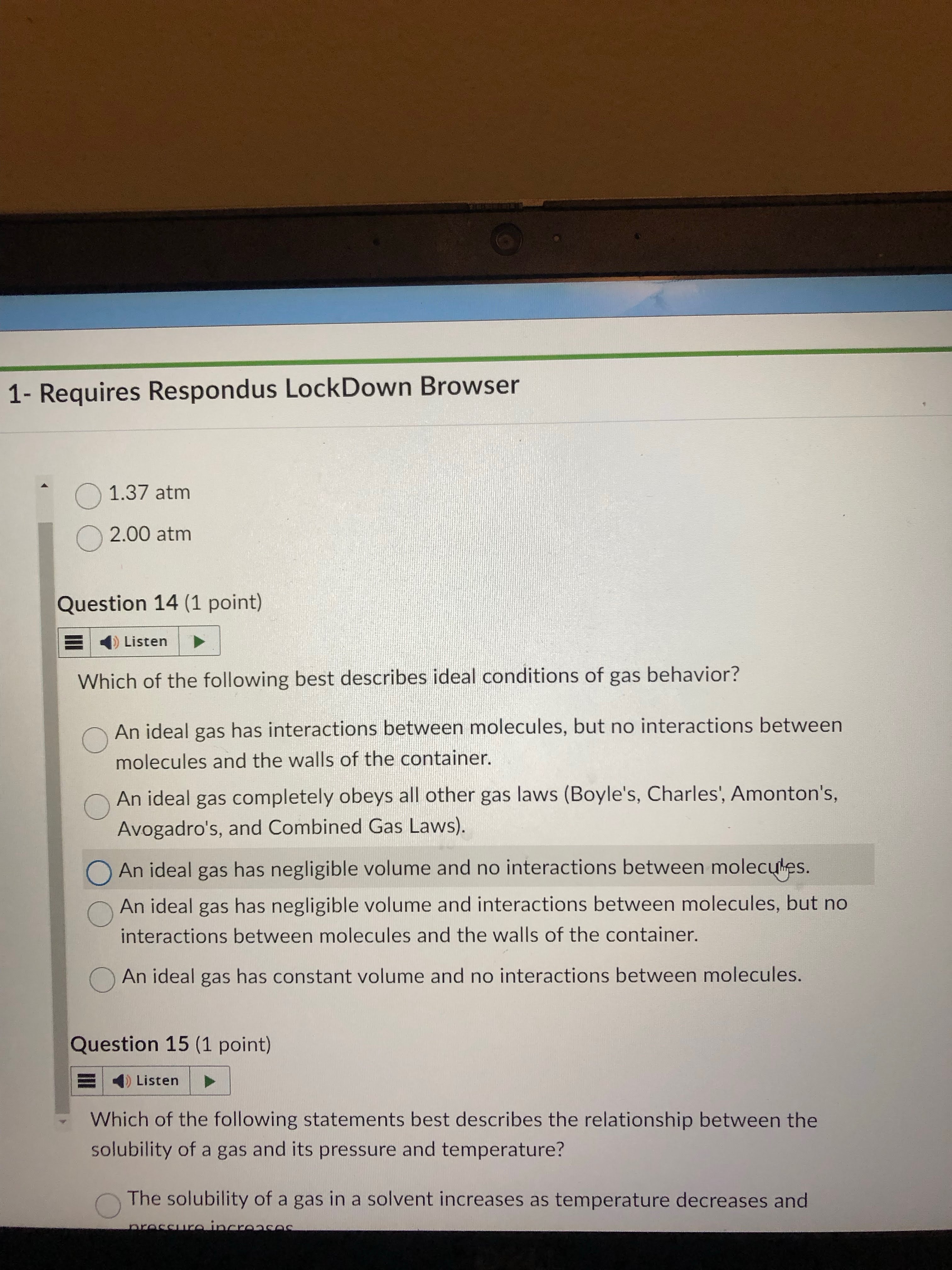
idk
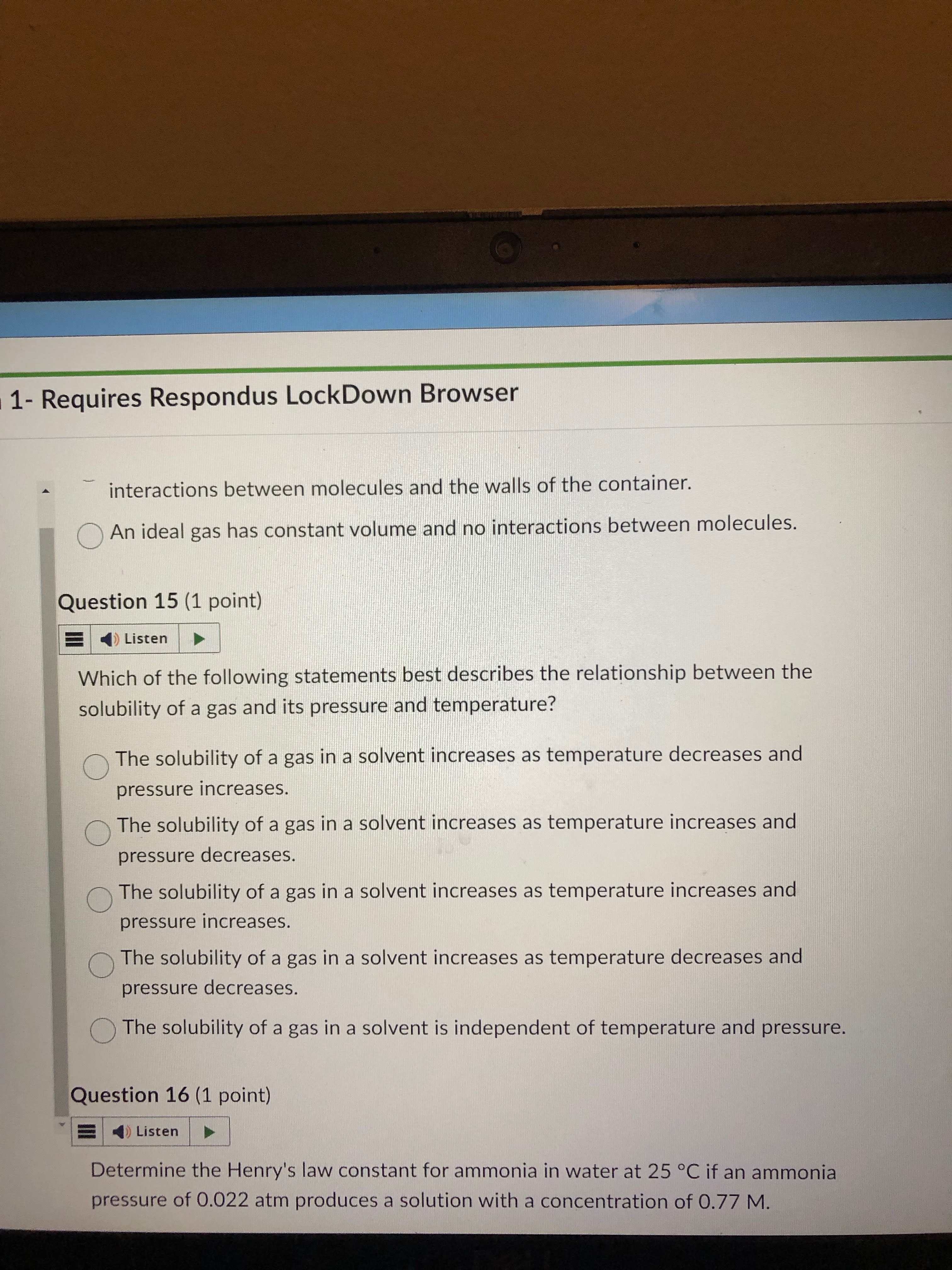
create a table to help answer as well.
first answer
increase of sol means T decrease and P increase
decrease of sol means T increase and P decrease
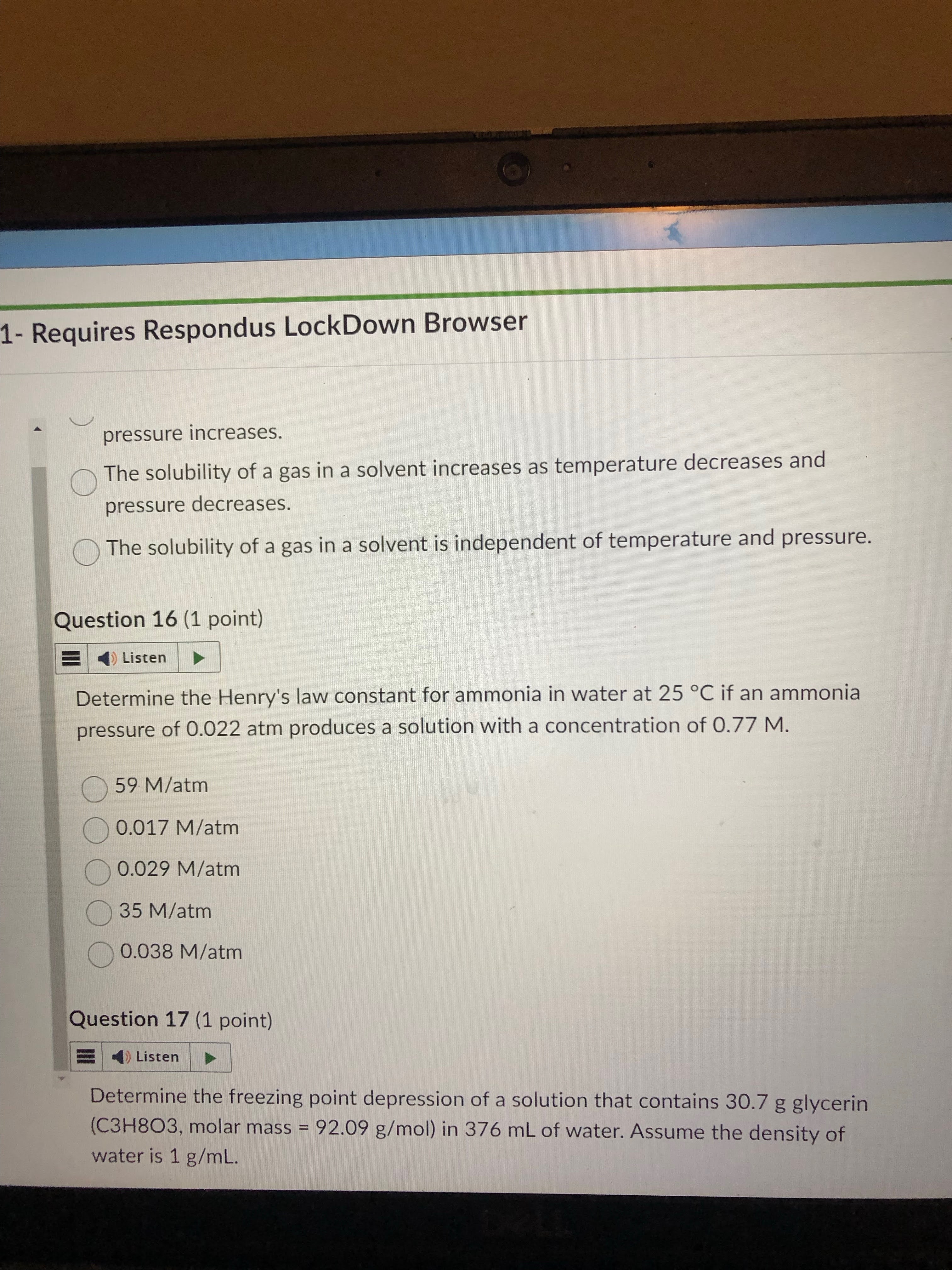
35 M/atm
just remember which one is the henry formula and plug and chug
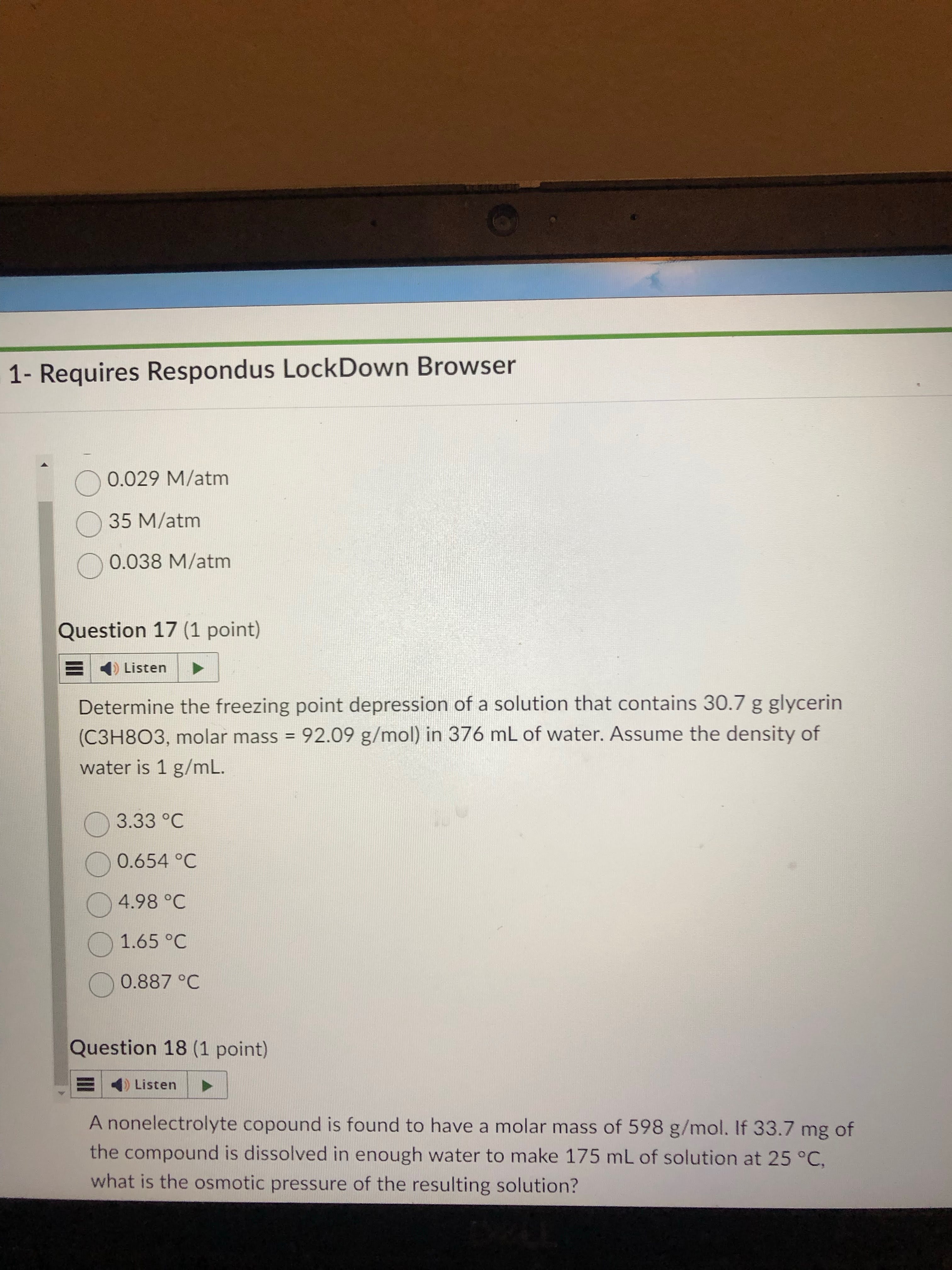
first understand that the “m” part of the formula is asking you to find molality. this means first turn 30.7 g of glycerin to mols.
next, molality means mol per kg of solvent. now that we get mol, find kg by using the given density as a conversion factor. 376 mL of solvent to kg.
THIS IS NONVOLATIVE, VANT HOFF OF 1
finally, plug and chug.
answer: 1.65
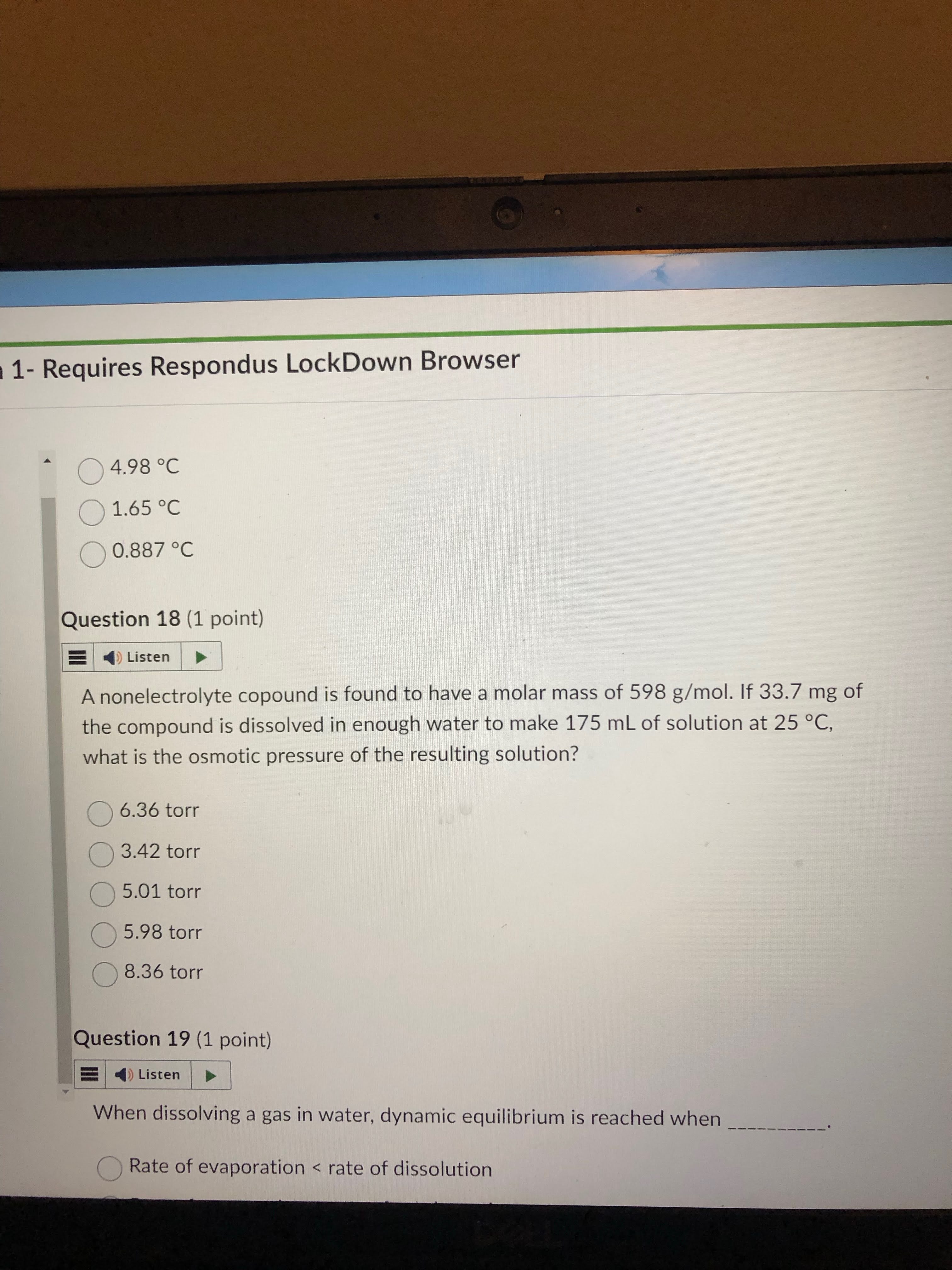
first remember the formula to use. know that it says nonelc to i is one.
second get the M variable by doing 33.7 mg to g to mol. this gives you the numerator of the Molarity formula.
third get the denominator of the Molarity formula by doing 175 ml to L.
finally plug and chug. ITS ASKING FOR AN ANSWER IN TORR. this equation gives you it in atm. remember this unit due to how the constant is in (K mol/ L atm)
answer: 5.98 torr
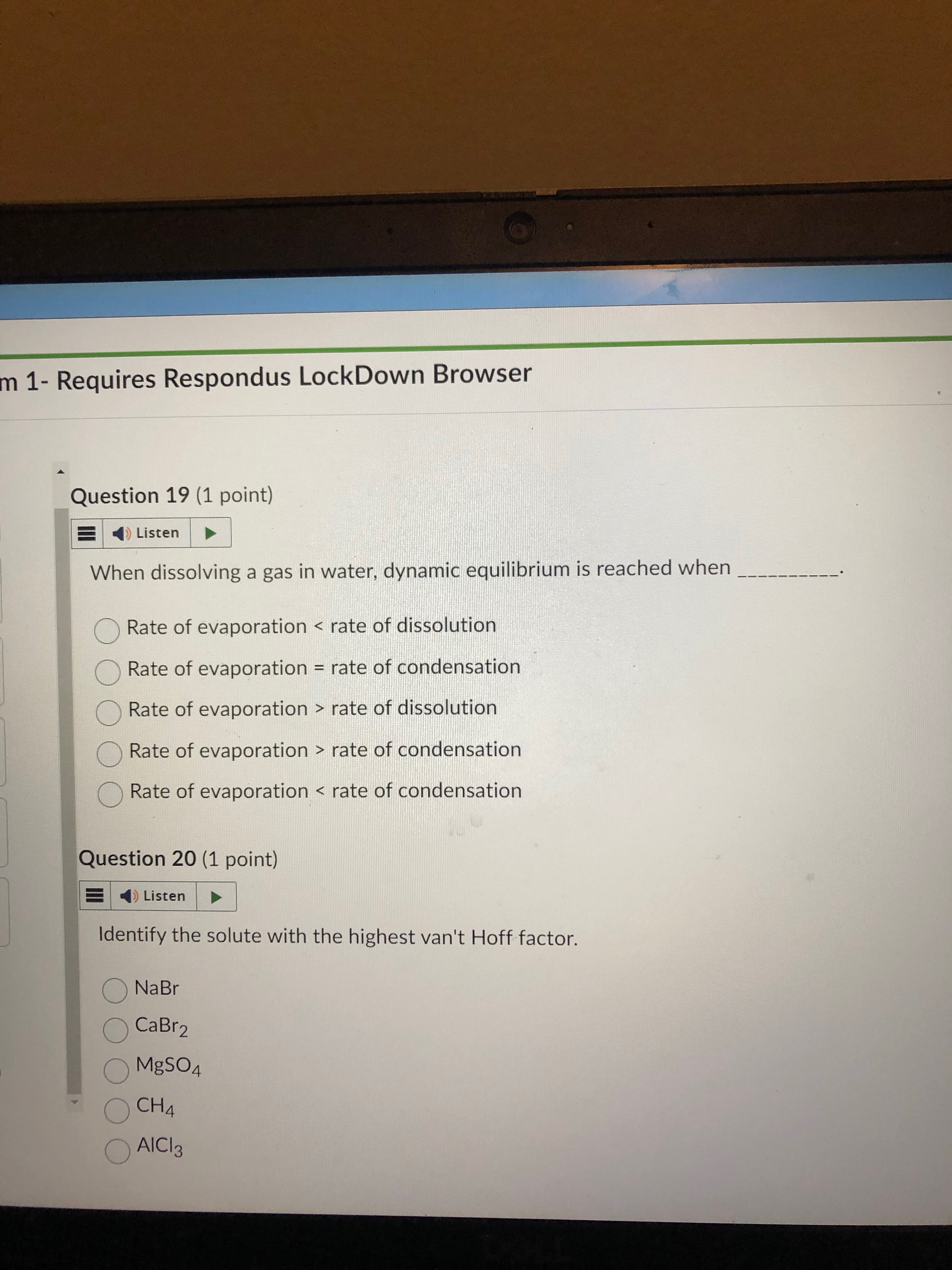
evap rate and condensation rate are equal, get it cuz equil means equal
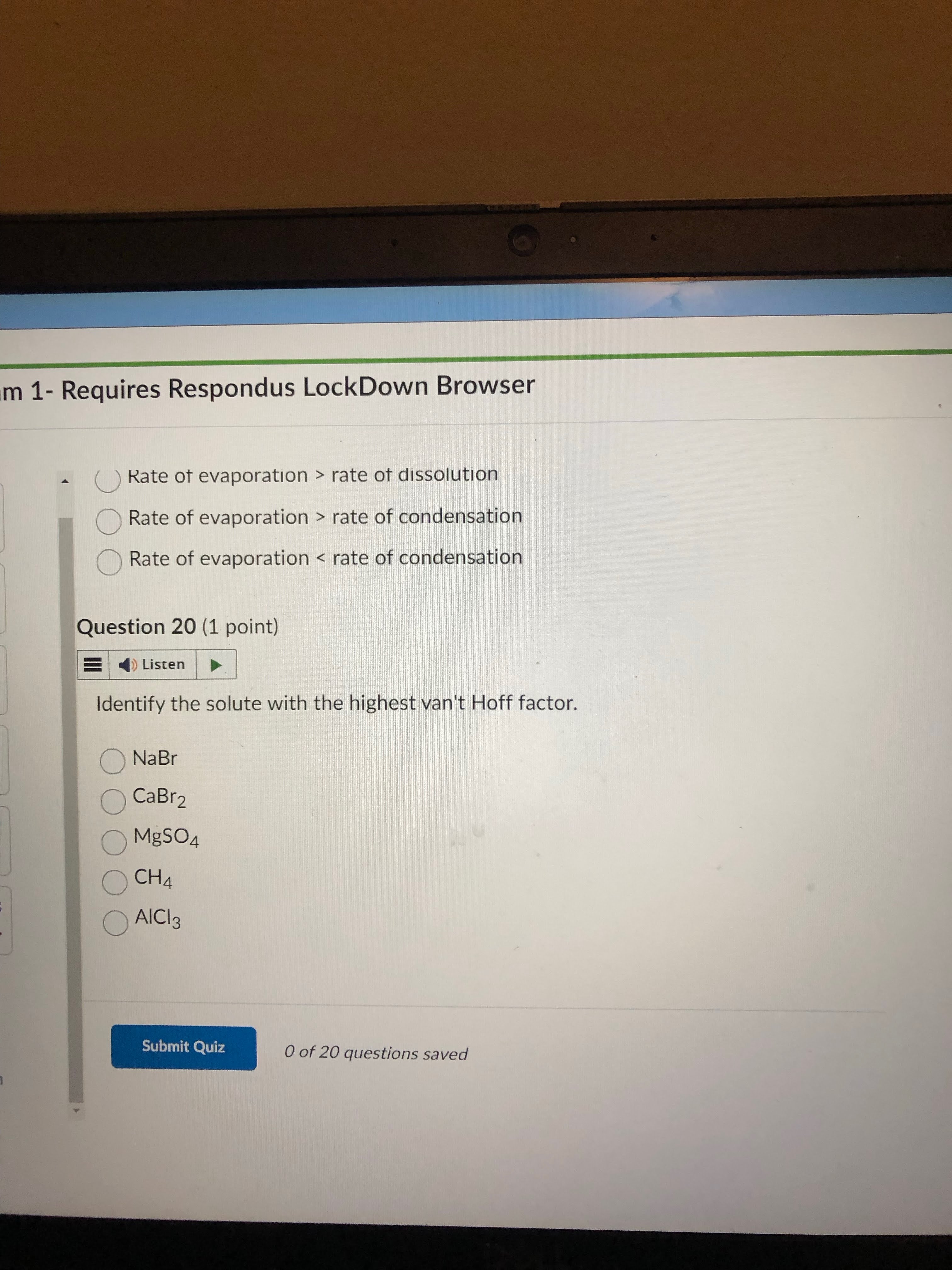
find higest vant off. first ignore the covalent bonds because they just equal 1.
then find ionics by simply writing out a balanced equation for each compound. then add up the coeffs. this will help u see which is the highest added up out of everyone