(CIE A2 Biology) Natural selection effects + the Hardy-Weinberg principle (based on SaveMyExams revision notes)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Allele Frequencies
The relative frequency of an allele (variant of a gene) at a genetic locus in a population.
Genetic Drift
A mechanism of evolution that leads to random changes in allele frequencies due to chance events, more pronounced in small populations.
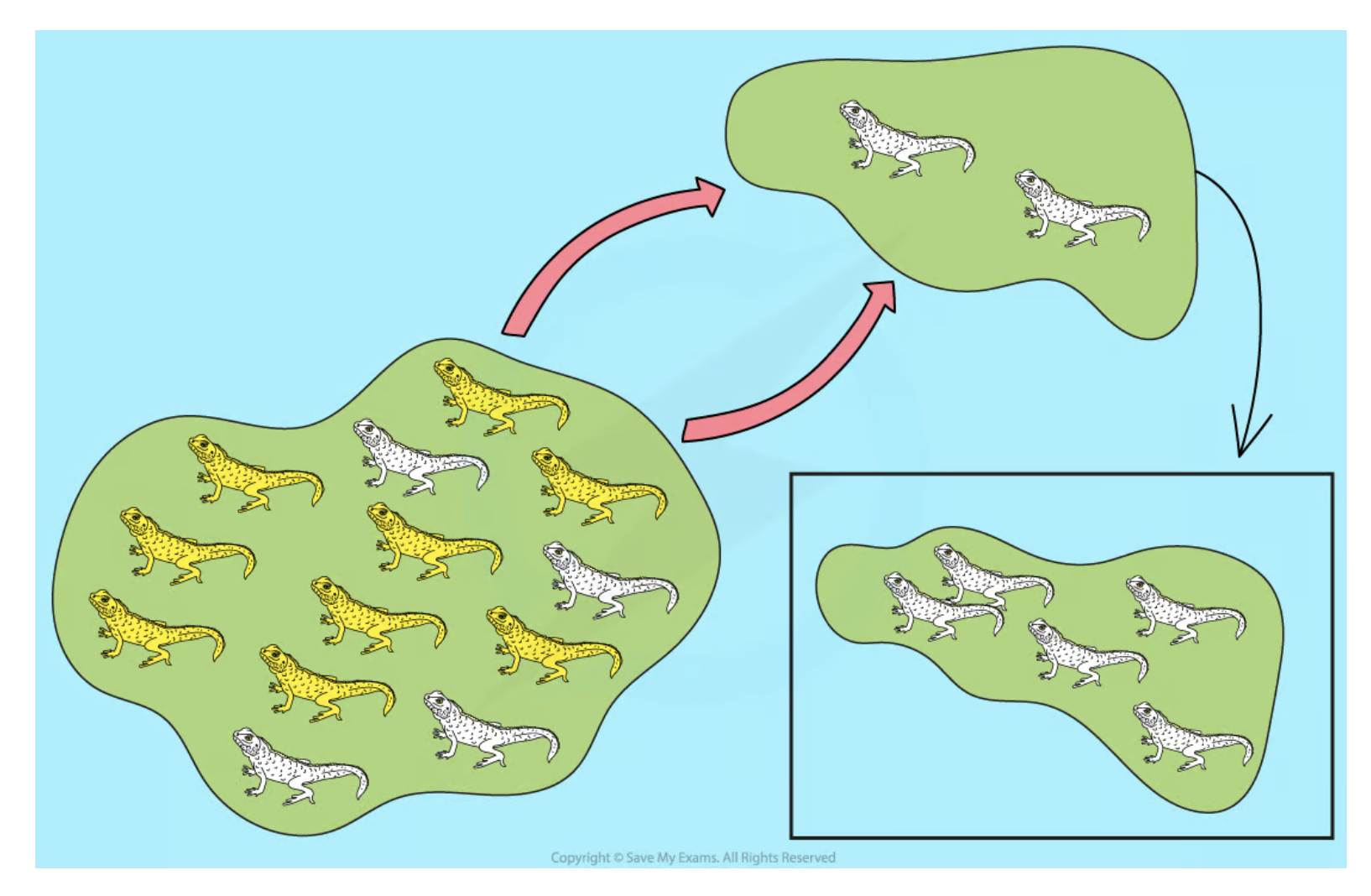
Founder Effect
A form of genetic drift occurring when a small group from a larger population establishes a new population, potentially carrying only a small fraction of the original population's genetic diversity.
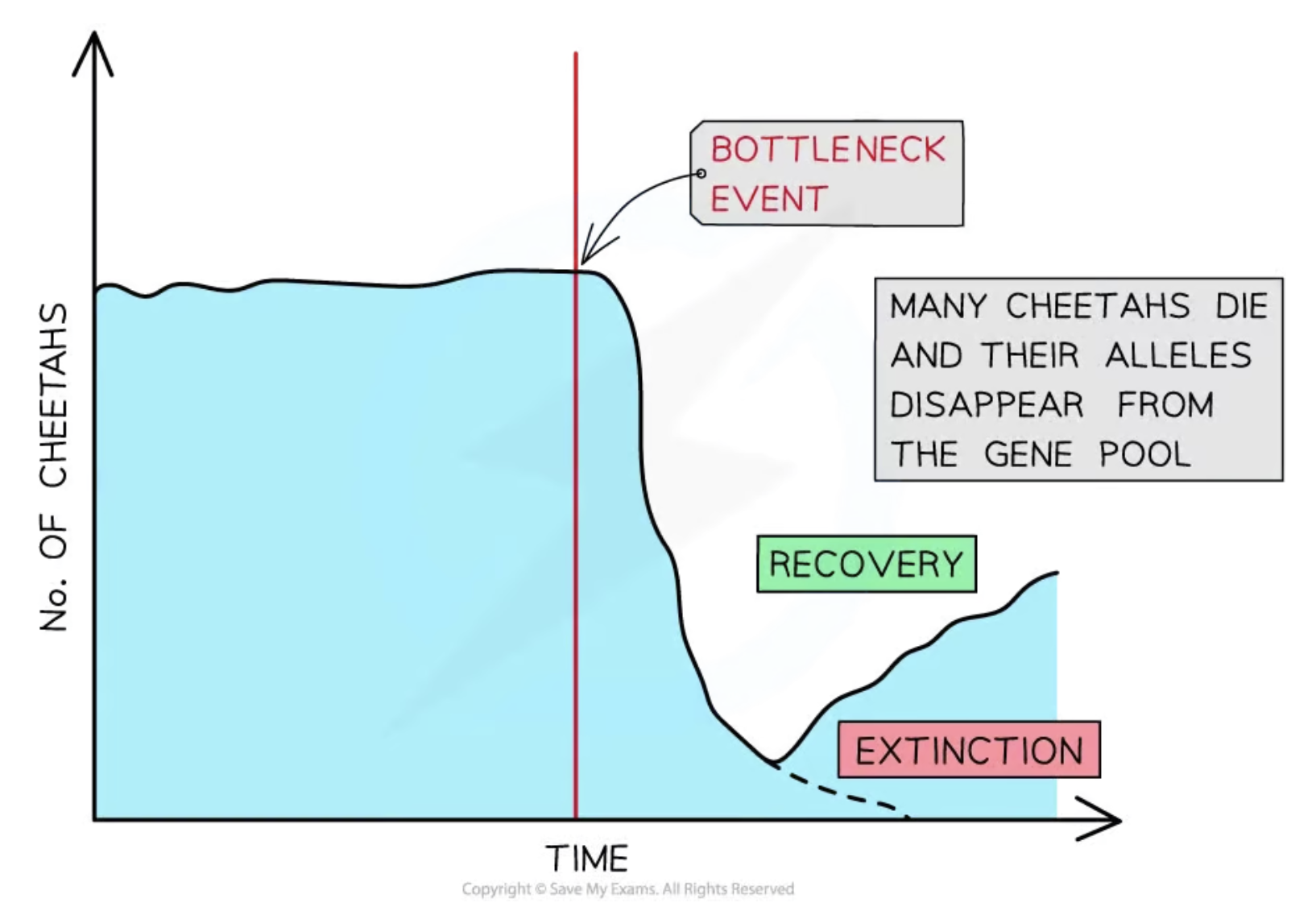
Bottleneck Effect
A dramatic reduction in population size due to environmental events, leading to decreased genetic diversity.
Phenotypic Variation
The observable differences in the physical traits of individuals in a population, which is crucial for natural selection.
Homozygous Dominant
An organism with two identical dominant alleles for a trait, represented as BB.
Homozygous Recessive
An organism with two identical recessive alleles for a trait, represented as bb.
Heterozygous
An organism with one dominant and one recessive allele for a trait, represented as Bb.
Hardy-Weinberg Principle
A mathematical model that describes the genetic variation in a population that is not evolving, stating that allele and genotype frequencies remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary influences.
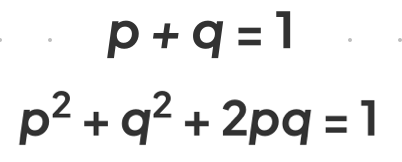
Bactericidal
Antibiotics that kill bacteria.
Bacteriostatic
Antibiotics that inhibit the growth of bacteria.
Antibiotic Resistance
The ability of bacteria to survive and grow despite the presence of antibiotics, often due to the possession of resistance alleles.
Plasmids
Small circular pieces of DNA in bacteria that can carry genes, including those for antibiotic resistance, and can be transferred between bacteria.
Vertical Gene Transfer
The transmission of genetic material from parent to offspring during reproduction.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
The transfer of genetic material between organisms in a manner other than traditional reproduction, often seen in bacteria.