Lab Exam: Exercises 7 - 11 Classifying Organisms
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Cyanobacteria Taxonomy
Domain: Bacteria
Kingdom: NONE
Phylum: Cyanobacteria
Genus: Oscillatoria, Nostoc, Anabaena, Spirulina
Cyanobacteria
Blue green
Gram-negative bacteria with a thick outer membrane
Gliding motility (No flagella)
Ecological producers: Fix carbon - Take in CO2 from the environment and convert it to a carbohydrate; Fix nitrogen - Take N2 gas from the air and convert it into NH3 (Ammonia)
Trichome
Chain of cyanobacteria cells that share resources; Division of labor among them
Heterocyst
Larger cell within a trichome that fixes N2; does not photosynthesize; shares NH3 with the rest of the cells
Akinete
Used for survival; “ Resting spore”; Not tough like an endospore, but can survive a little longer than other cells in the Trichome.
Non-optimal conditions, and it is the last cell standing and then conditions improve —> it can do binary fission to re-create the Trichome.
Anabaena
Domain: Bacteria
Kingdom: NONE
Phylum: Cyanobacteria
Genus: Anabaena

Nostoc
Domain: Bacteria
Kingdom: NONE
Phylum: Cyanobacteria
Genus: Nostoc
More square looking than Anabaena; you will always see a pink glycocalyx; found in swamps
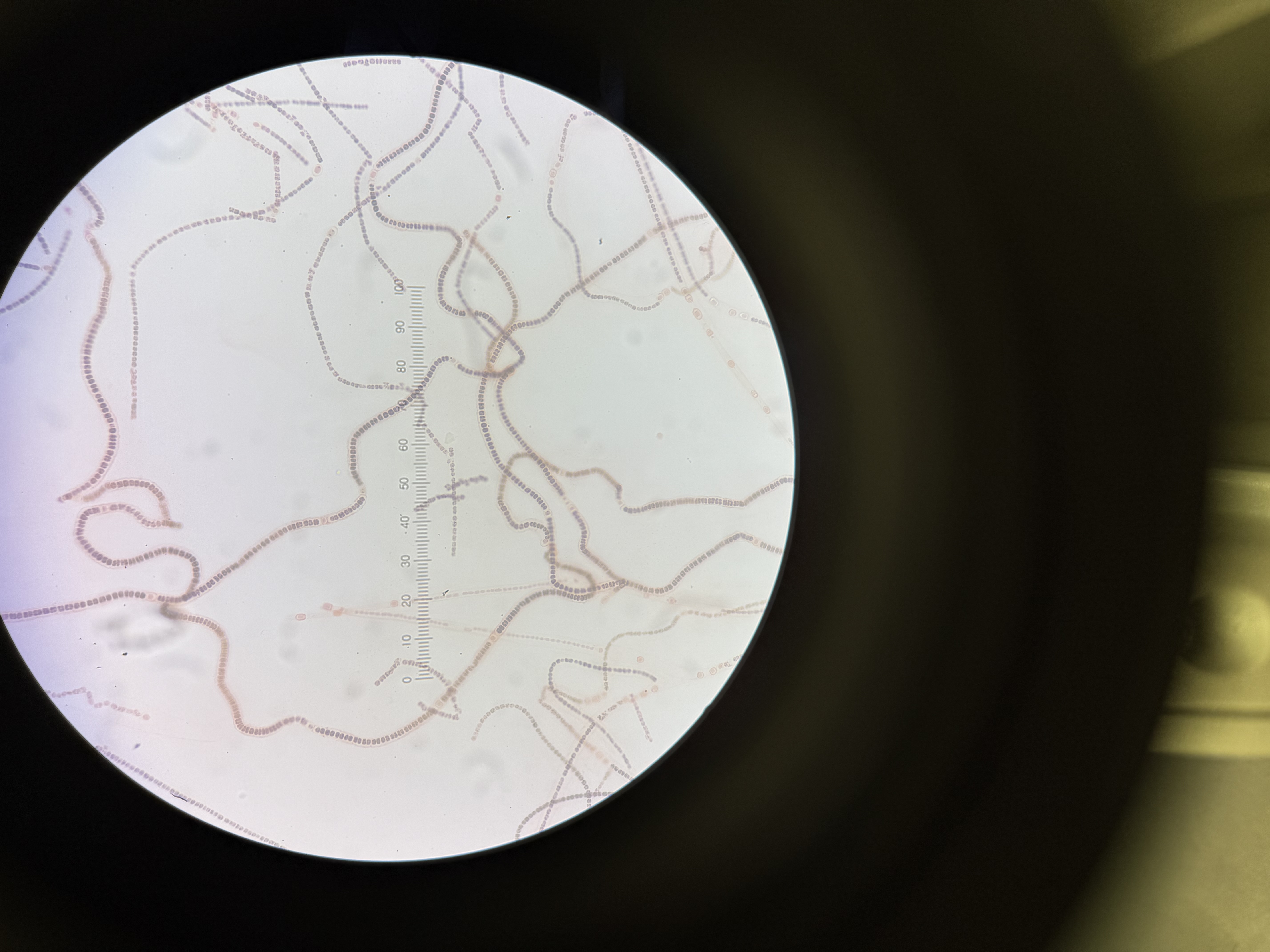
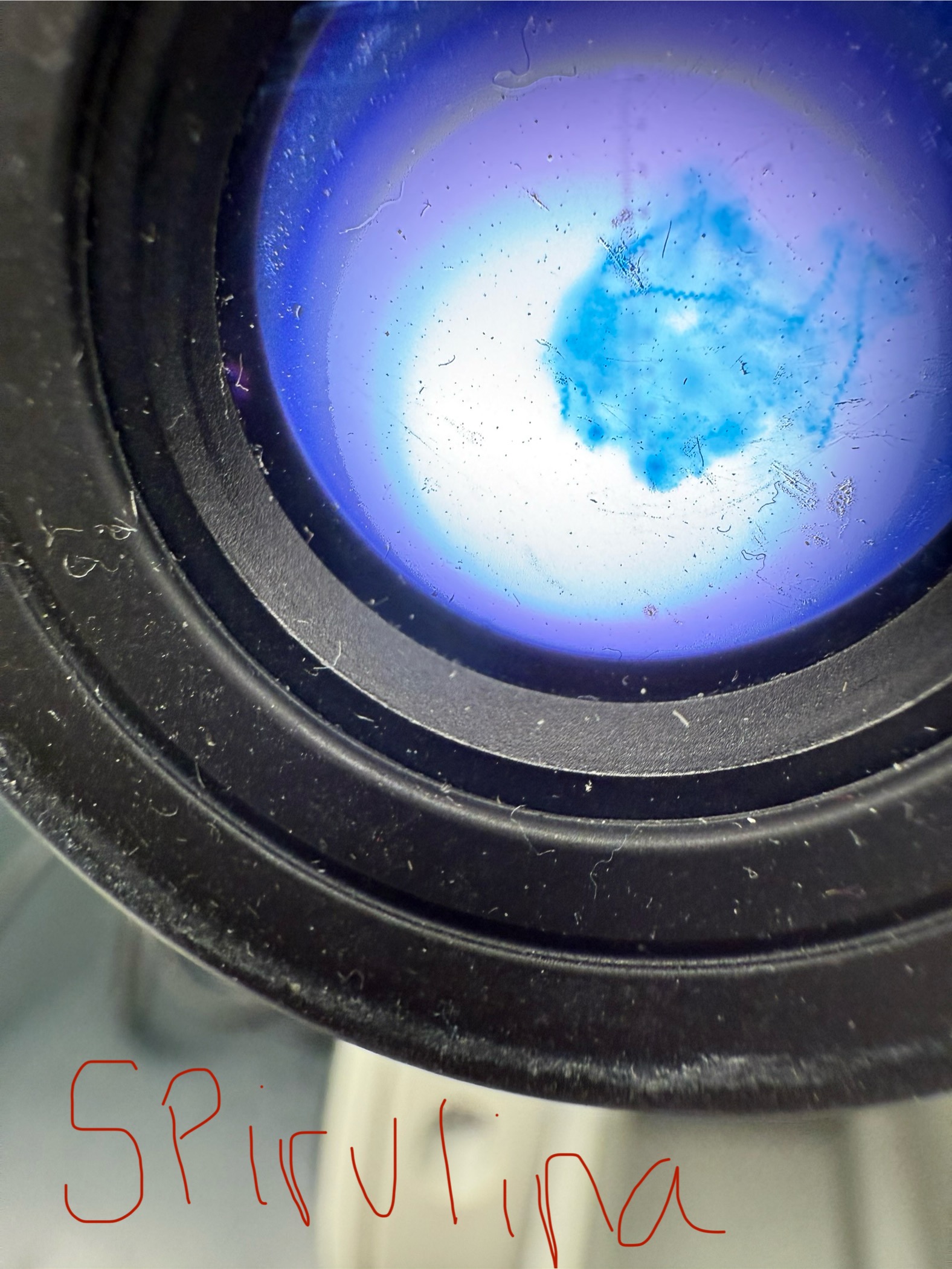
Spirulina
Domain: Bacteria
Kingdom: NONE
Phylum: Cyanobacteria
Genus: Spirulina
Can buy in pills as a supplement; NASA grows it for food and nutrition
Oscillatoria
Domain: Bacteria
Kingdom: NONE
Phylum: Cyanobacteria
Genus: Oscillatoria

Mycology
Study of fungi
Fungi
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Fungi
Characteristics of Fungal Cells
Cell walls made of chitin
Chemoheterotrophs - they get their carbon and energy from organic compounds
Most reproduce sexually and asexually
Most free-living decomposers, but some are pathogens
Mycosis
Disease caused by a fungus living on or in you (fungal infection)
Mycotoxicosis
Disease caused by a toxin produced by a fungus
Fungal “Body Types”
Yeast - single-celled fungi
Filamentous - multi-celled fungi (“fleshy fungi”; mushrooms; molds)
Hyphae
Multi-celled filaments
Septate hyphae vs. aseptate hyphae

Mycelium
Visible mass of hyphae
Dimorphic
Is a yeast in some environments but is filamentous in other environments
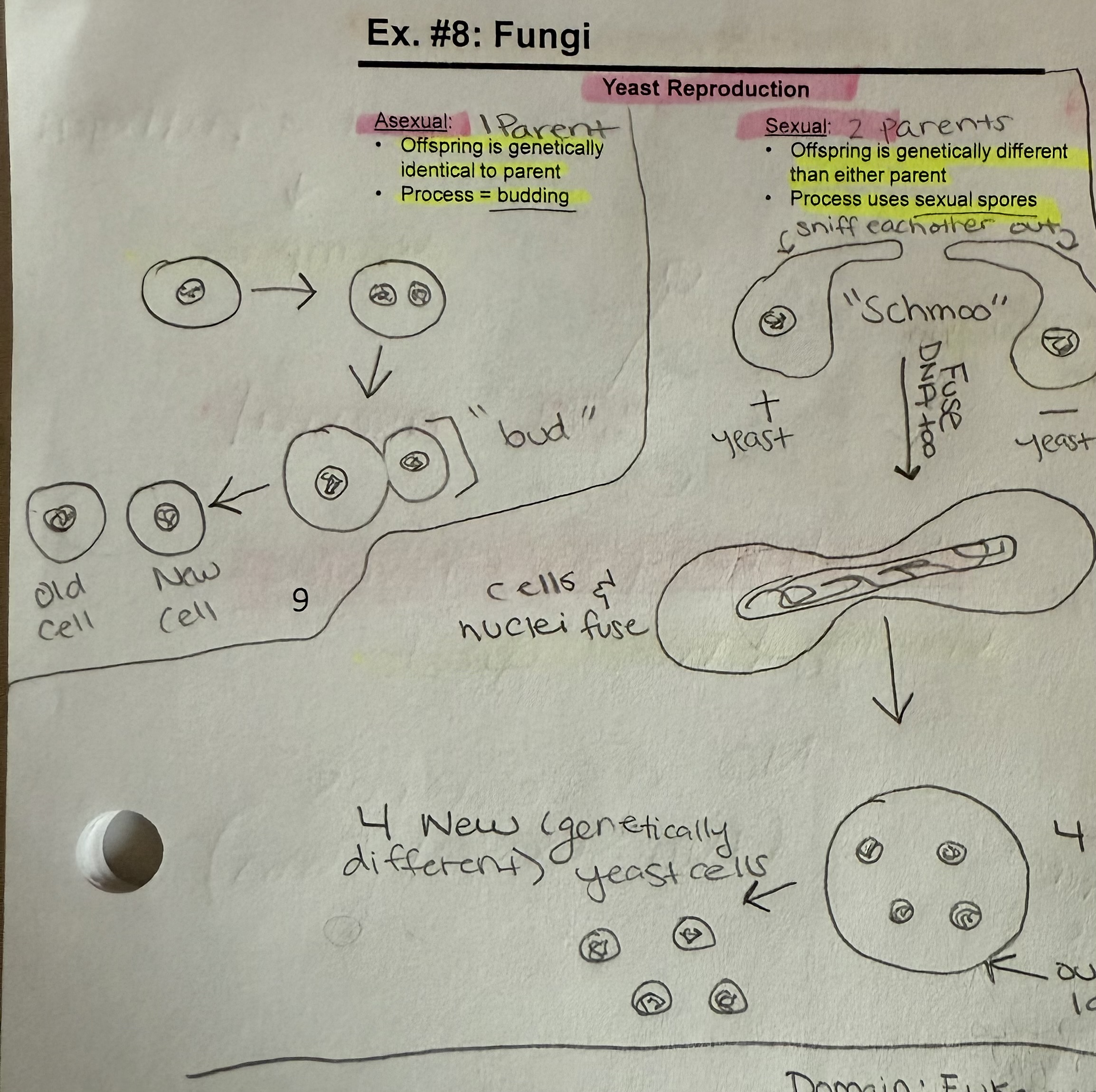
Yeast Reproduction
Asexual (1 parent) - offspring is genetically identical to parent
Process - budding
Sexual (2 parents) - offspring is genetically different than either parent
Process - uses sexual spores
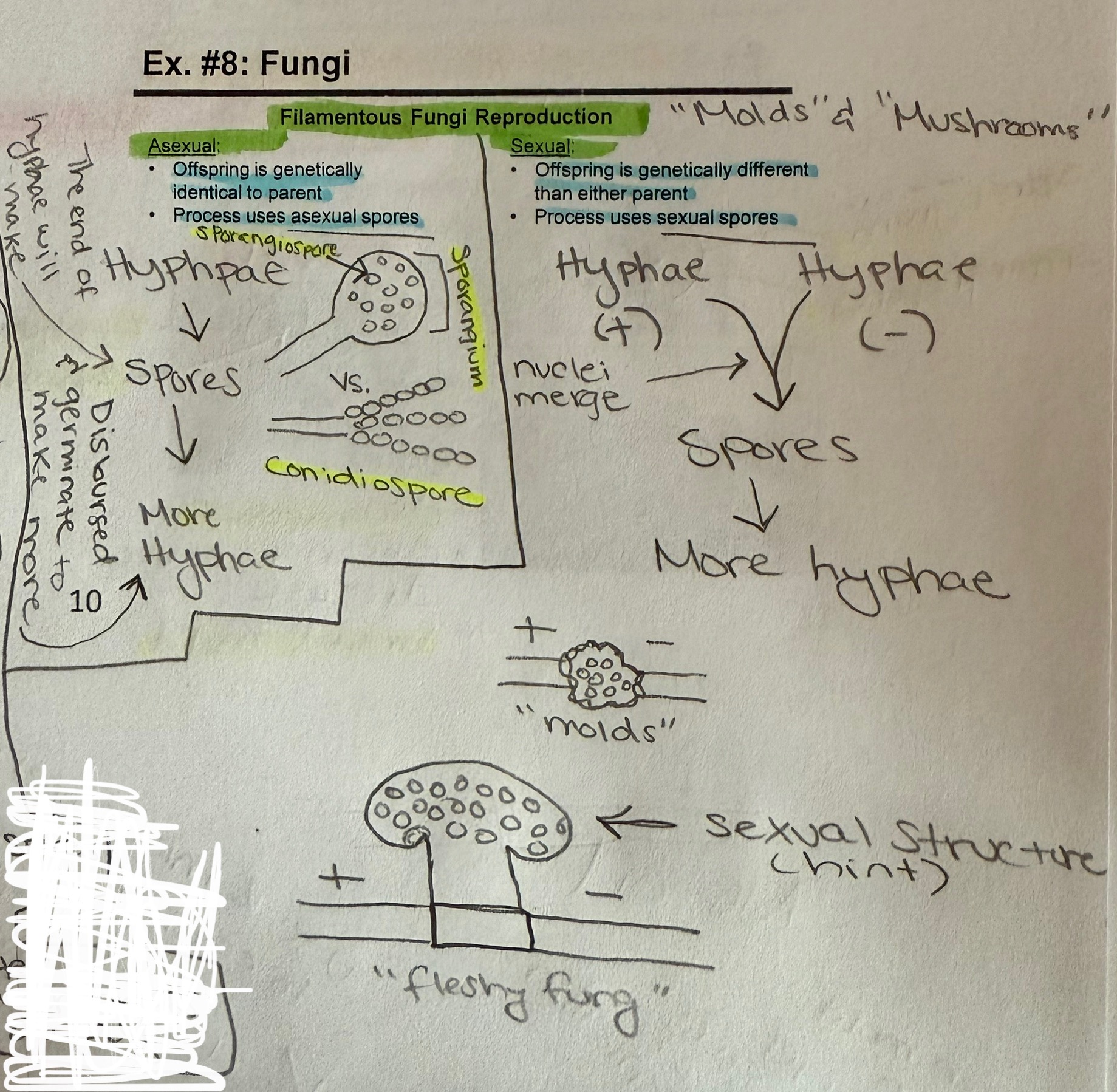
Filamentous Fungi Reproduction
Asexual (1 parent) - offspring is genetically identical to parent
Process - Uses asexual spores
Sexual (2 parents) - Offspring is Genetically different than either parent
Process - Uses sexual spores
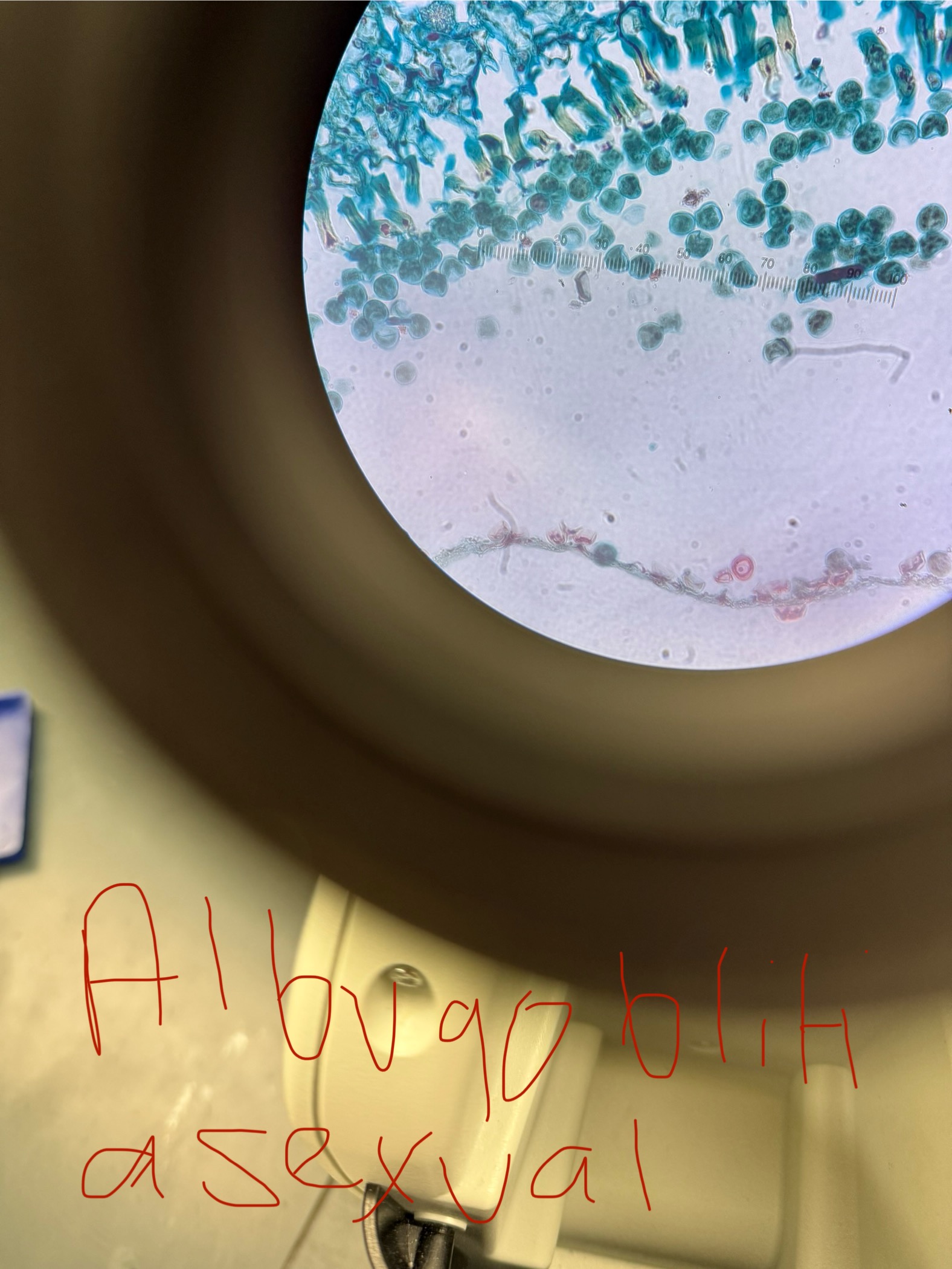
Albugo bliti
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Fungi
Phylum: Oomycota
Genus: Albugo
Species: bliti
Plant pathogen; “white rust”
Asexual spores/spore-containing structure: Sporangiospores/ Sporangium
Sexual spores/spore-containing structure: Oospores/ Oogonium

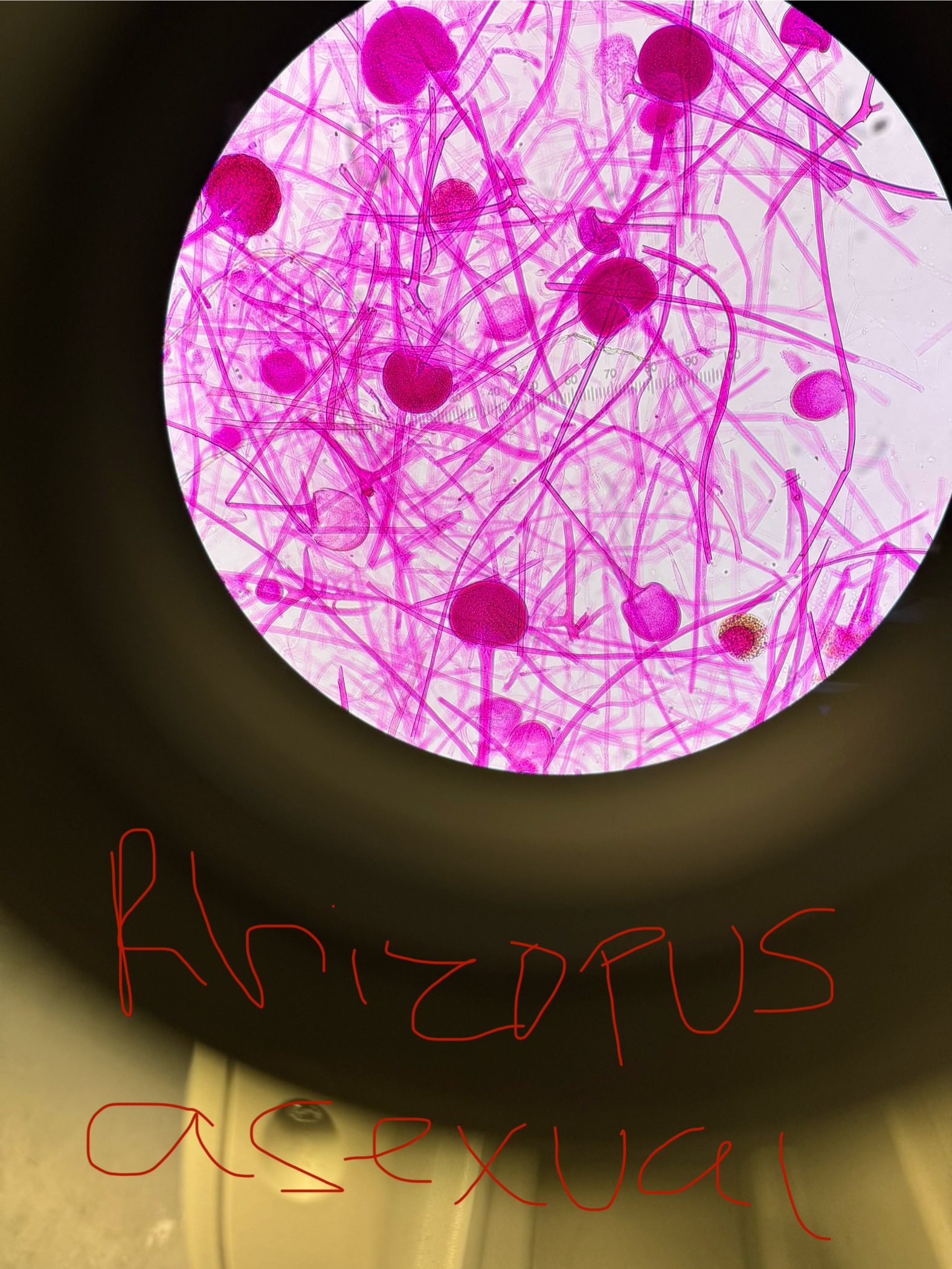
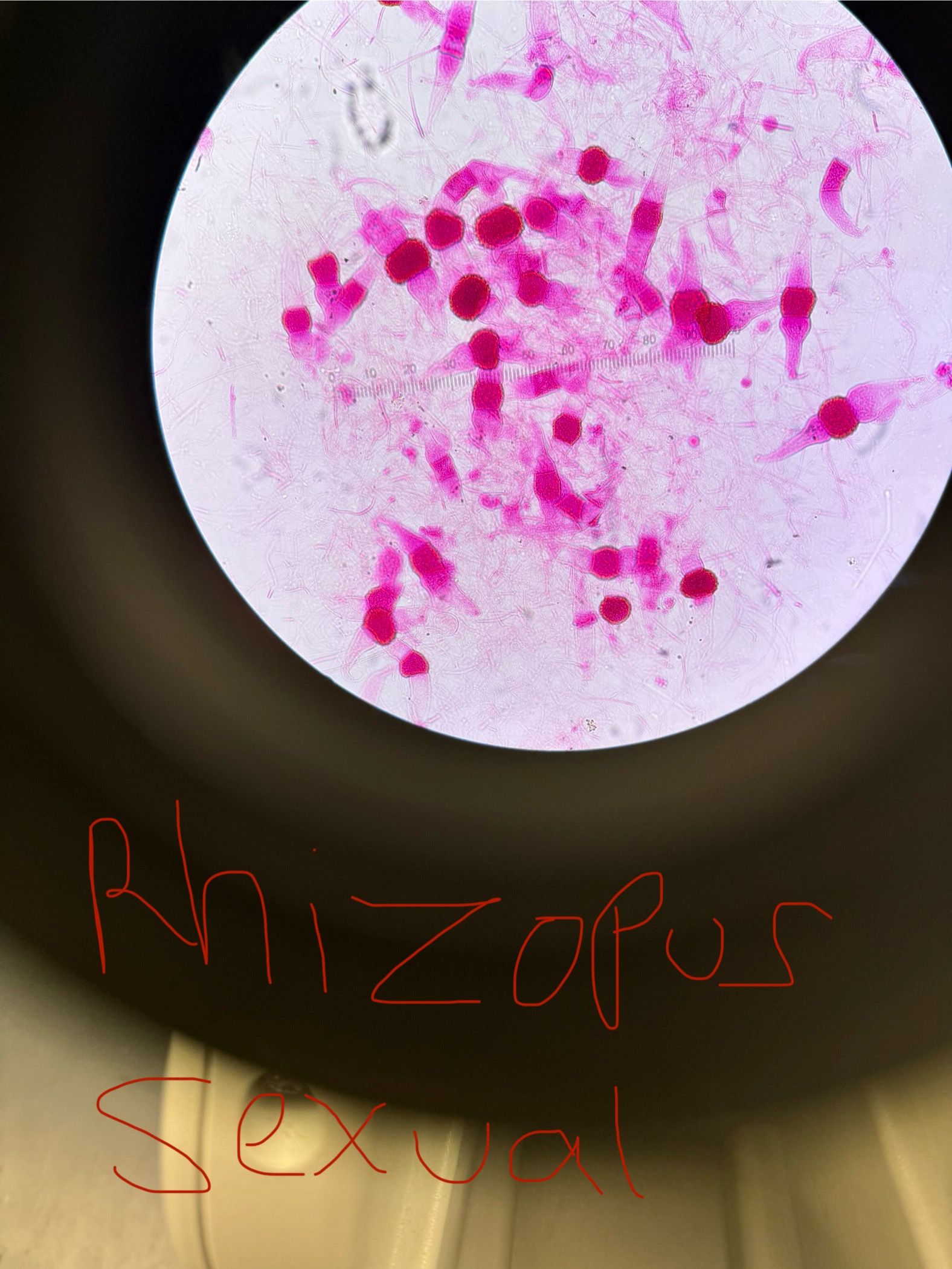
Rhizopus stolonifer
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Fungi
Phylum: Zygomycota
Genus: Rhizopus
Species: stolonifer
Decomposer - doesn’t cause a disease
“Bread mold”
Asexual spores/structure-containing spores: Sporangiospores/ Sporangium
Sexual spores/structure-containing spores: Zygospores/ Zygosporangium
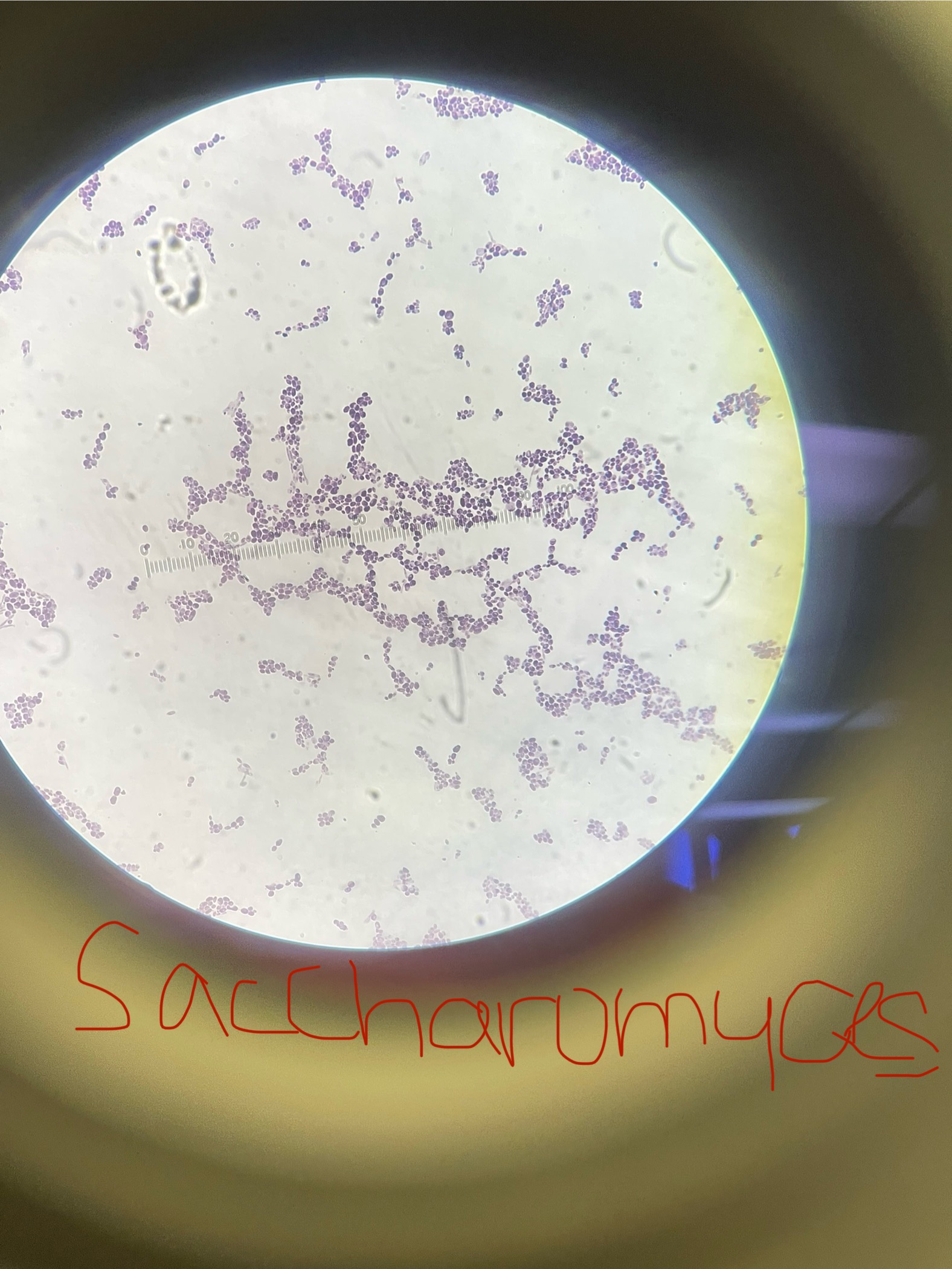
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Fungi
Phylum: Ascomycota
Genus: Saccharomyces
Species: cerevisiae
Decomposer- not a pathogen
No sexual form
Brewing and bread yeast
Asexual - budding
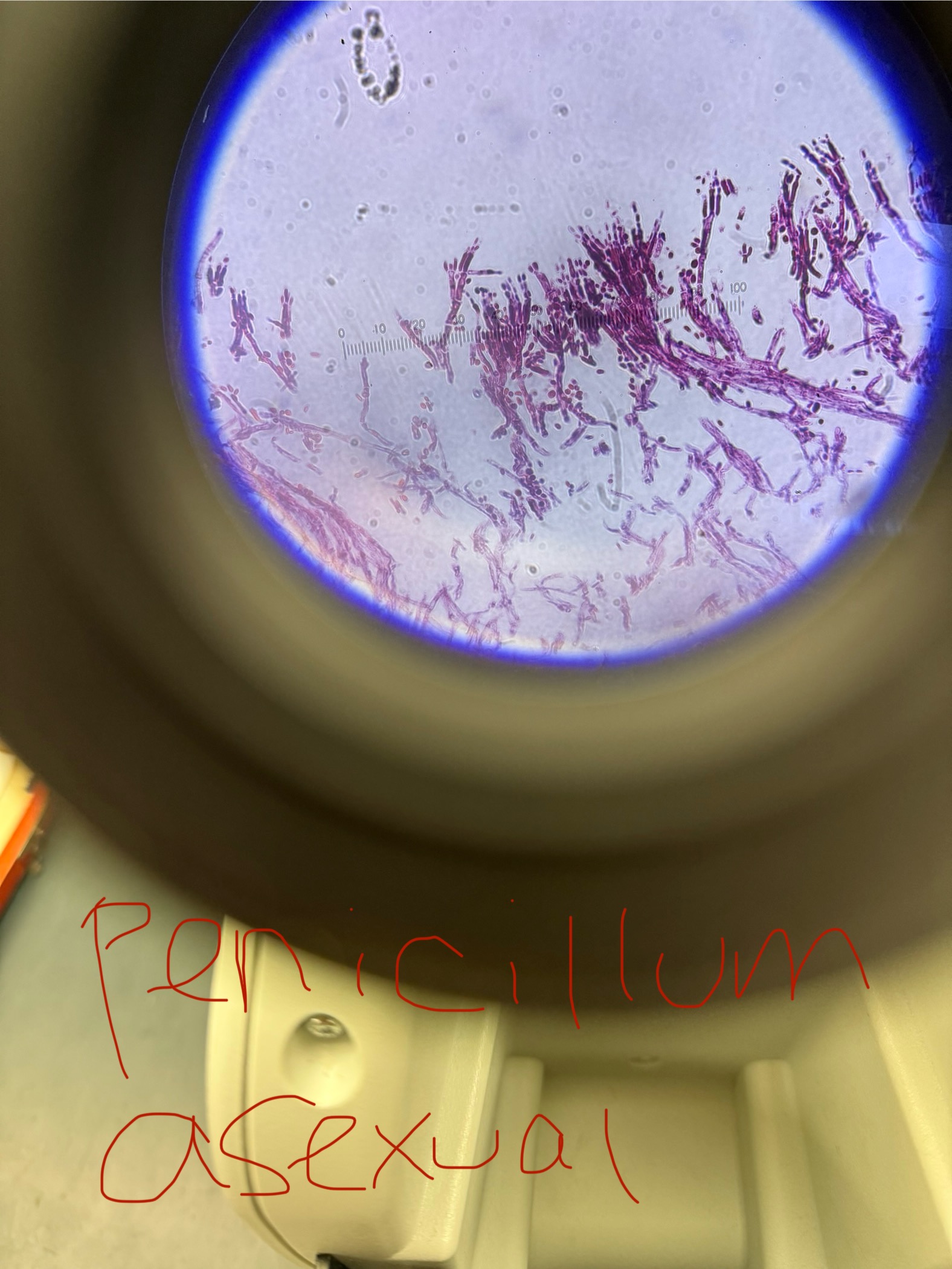
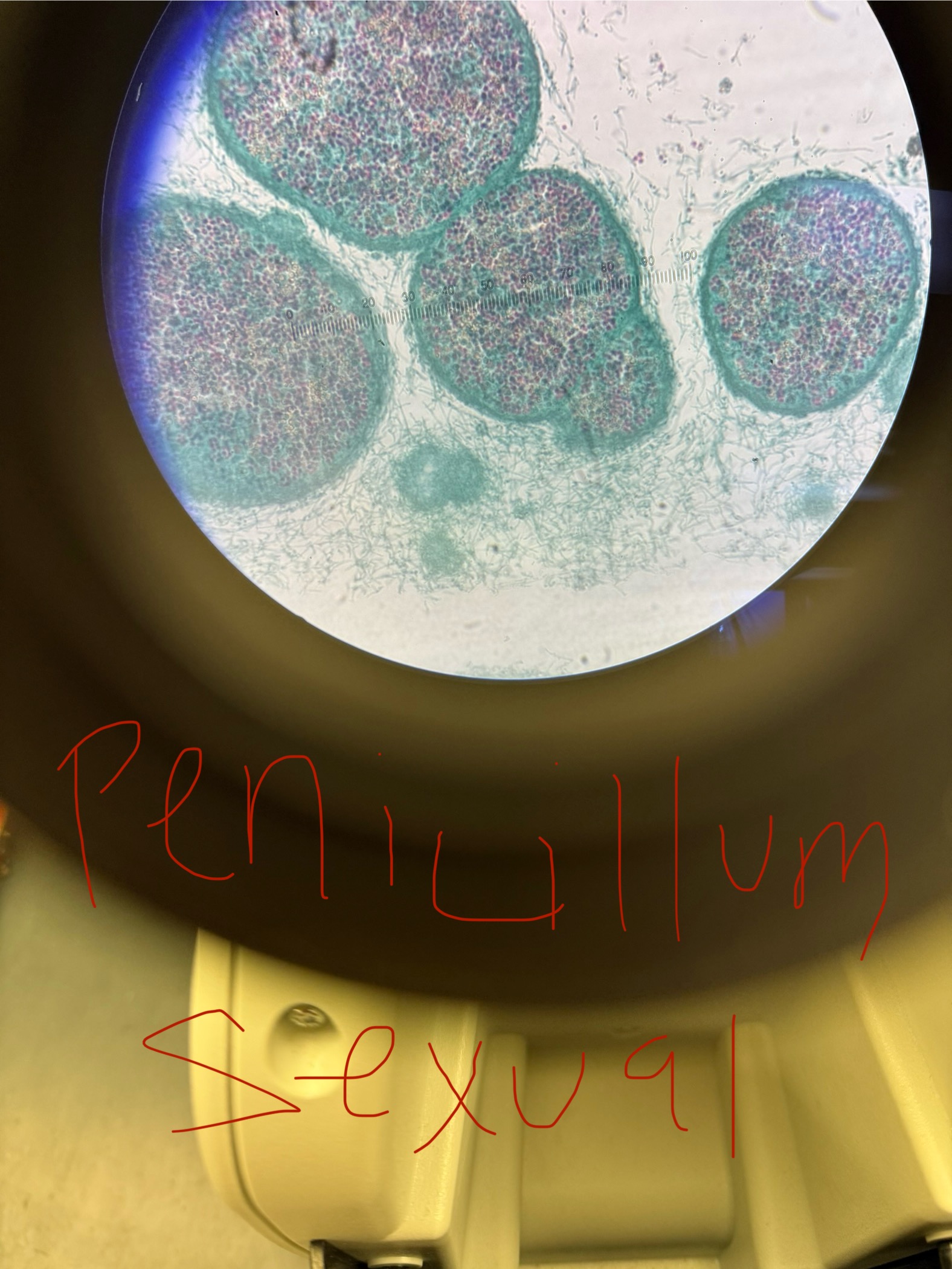
Penicillium chrysogenum
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Fungi
Phylum: Ascomycota
Genus: Penicillium
Species: chrysogenum
Decomposer - not a pathogen
Asexual spores: Conidiospores
Sexual spores/structure-containing spores:
Ascospores/ Ascus
Looks “hairy” in the microscope
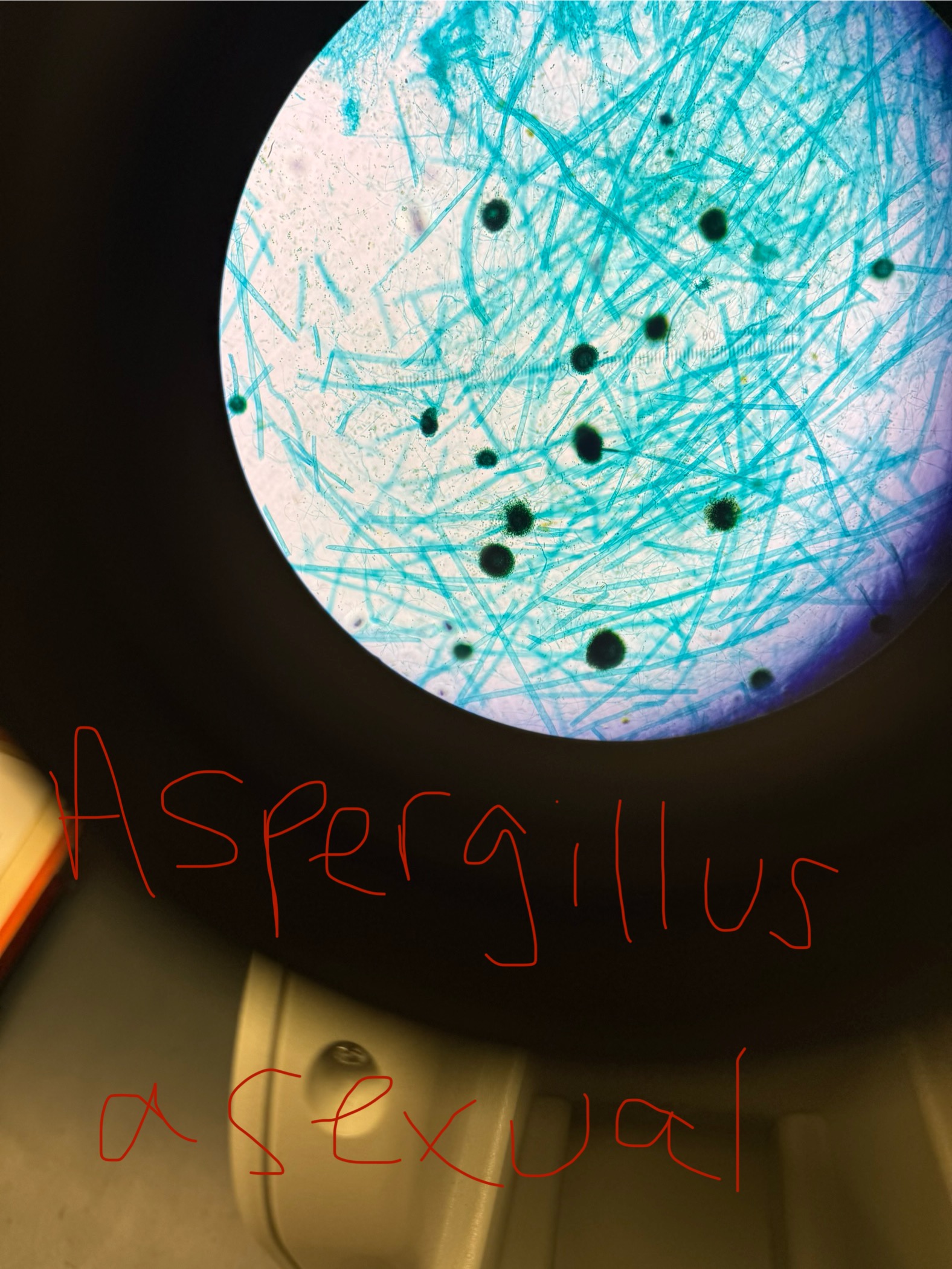
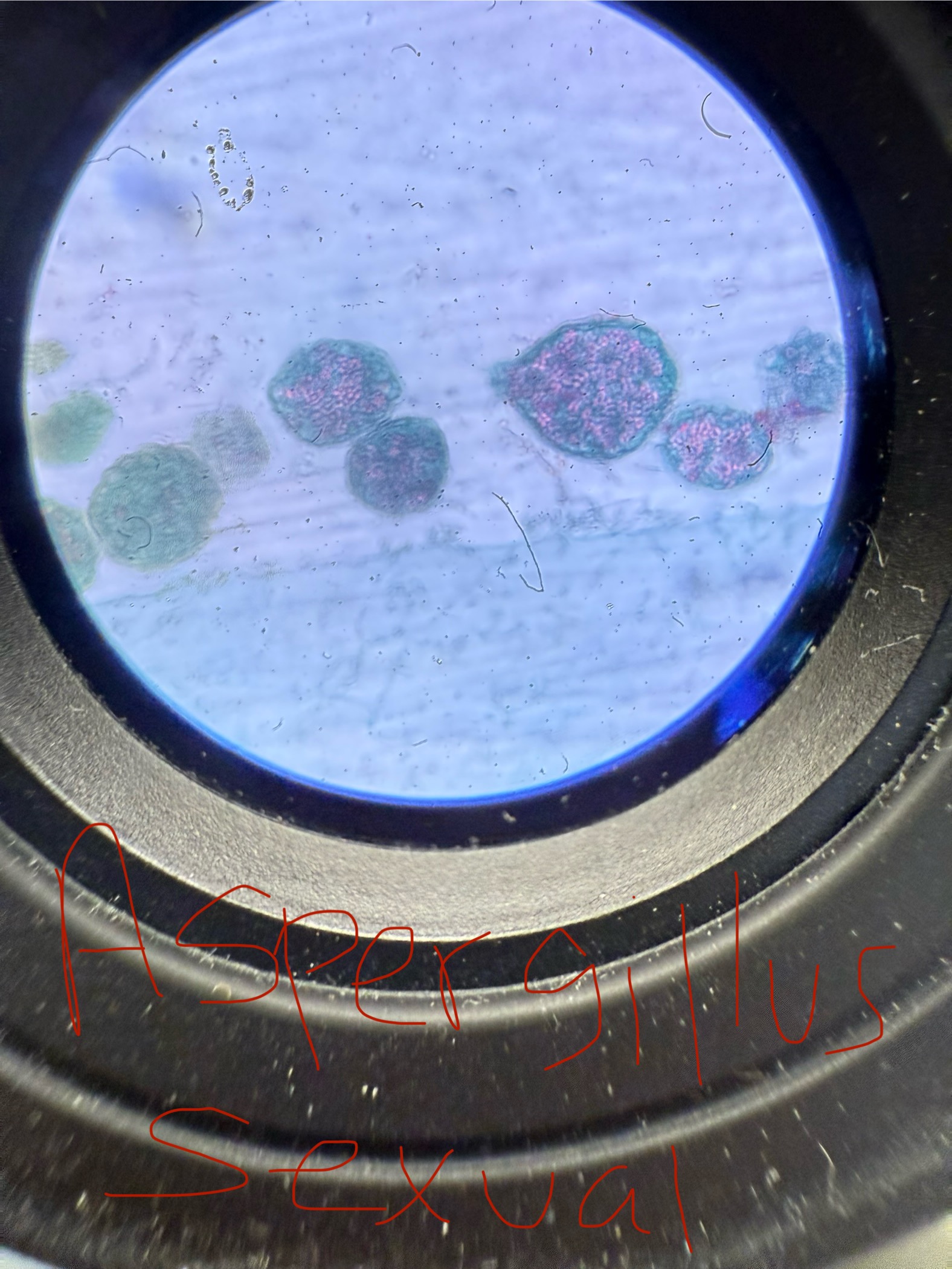
Aspergillus niger
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Fungi
Phylum: Ascomycota
Genus: Aspergillus
Species: niger
Decomposer and pathogen to humans/animals - causes a mycotoxicosis by making Aflatoxin which leads to cancer
“Black mold”
Asexual spores: Conidiospores
Sexual spores/ structure containing spores: Ascospores/ Ascus
Doesn’t look “hairy” under microscope
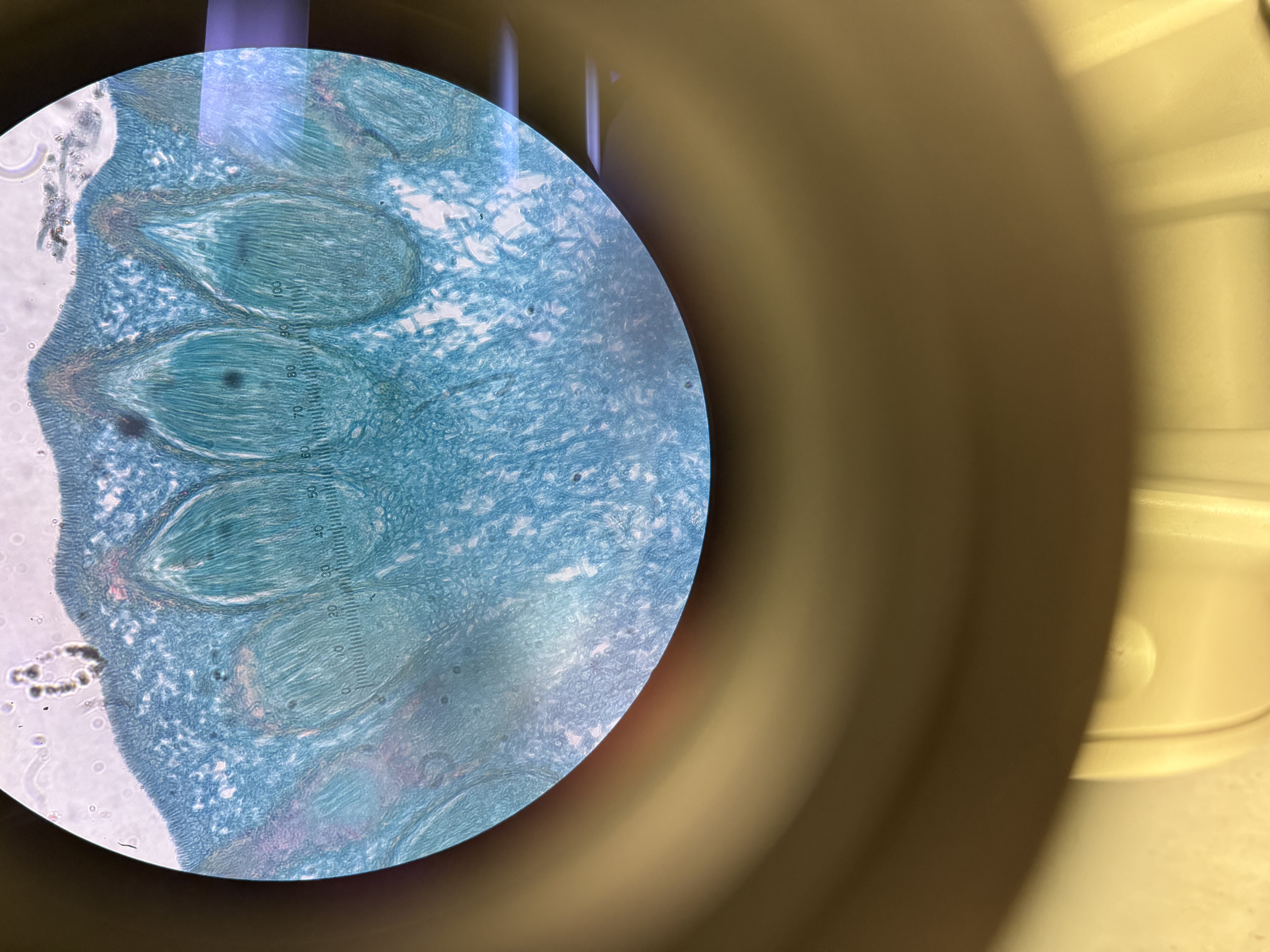
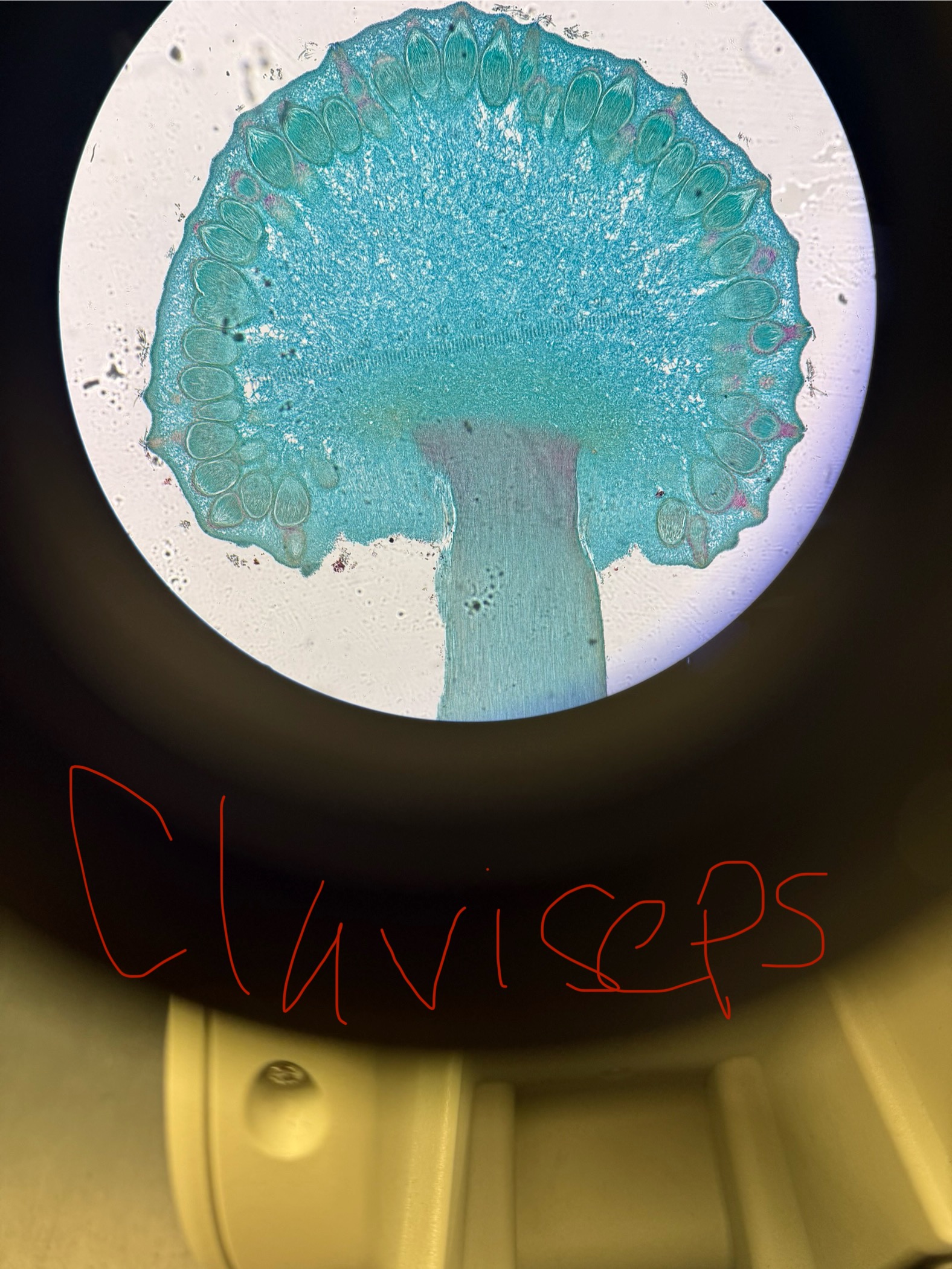
Claviceps purpurea
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Fungi
Phylum: Ascomycota
Genus: Claviceps
Species: purpurea
Pathogen
Mycosis in plants (grains from wheat) - ergot
If animals ingest they get mycotoxicosis - ergotism “St. Anthony’s Fire”
Sexual spores/ structure-containing spores: Ascospores/ Ascus
Algae & Protozoa
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Chlorophyta; Bacillariophyta; Dinophyta; Archaezoa; Amoebozoa; Apicomplexa; Euglenozoa; Ciliophora
Phycology
The study of algae
Characteristics of algae
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Cell walls - composition varies the species (Cellulose, agar, glass, pectin etc.)
Chloroplasts
Photoautotrophs
Some unicellular/ some multicellular
Live in aquatic habitats
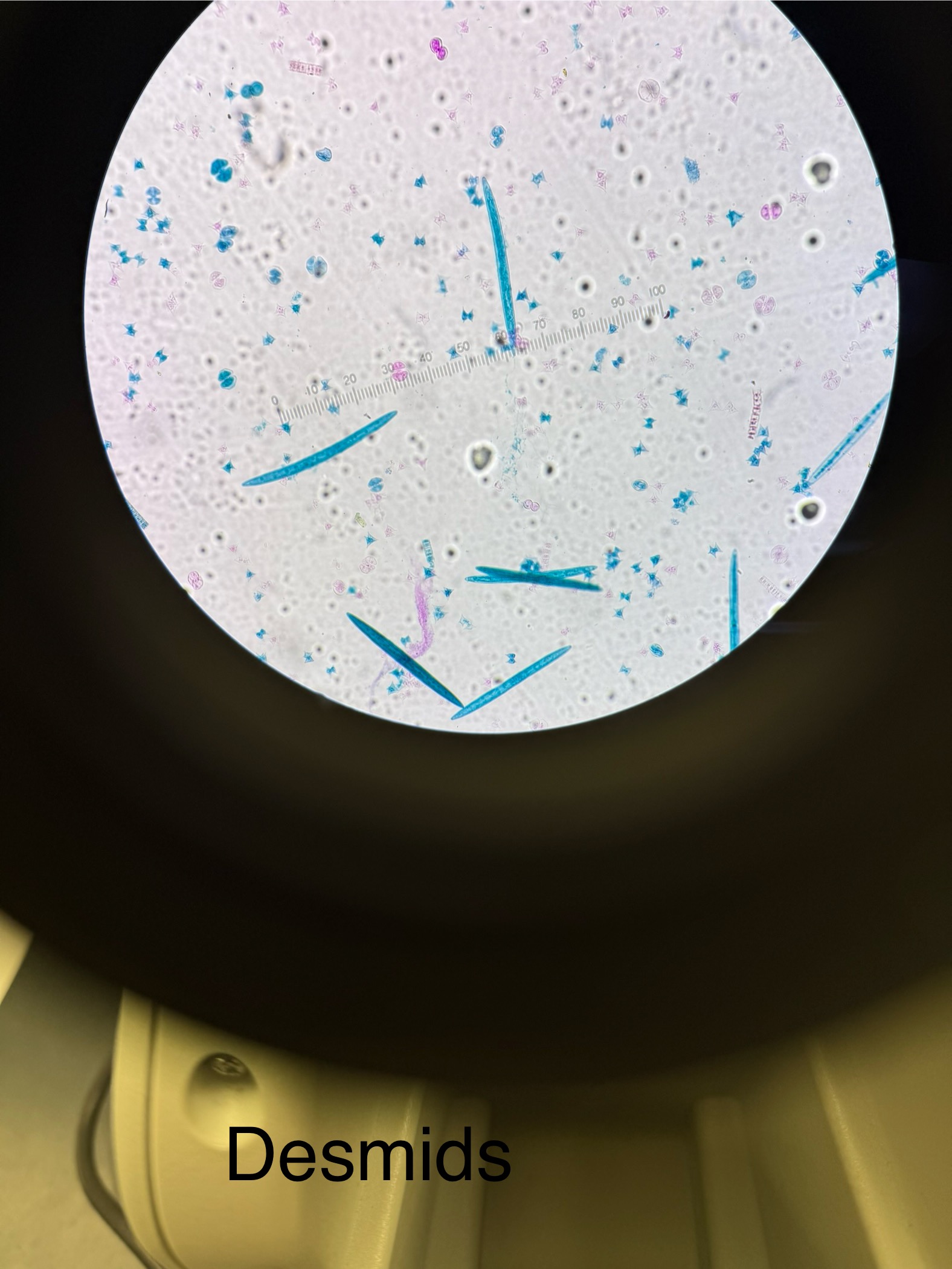
Desmids (common name)
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Chlorophyta
Cell walls made of cellulose & pectin
Aquatic organisms (some freshwater some marine)
Shapes: bow tie; mushroom (2 symmetrical halves); long ones too
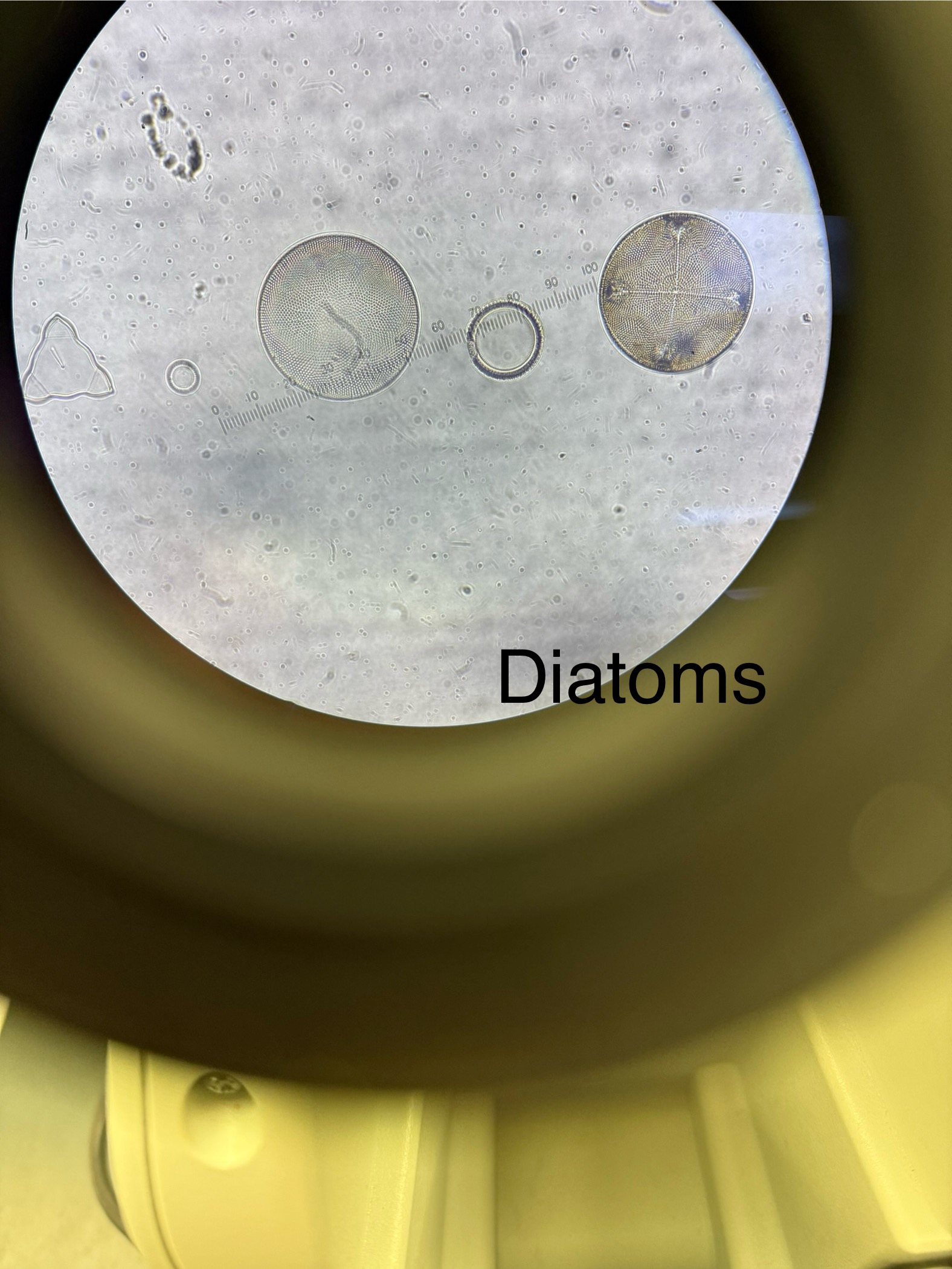
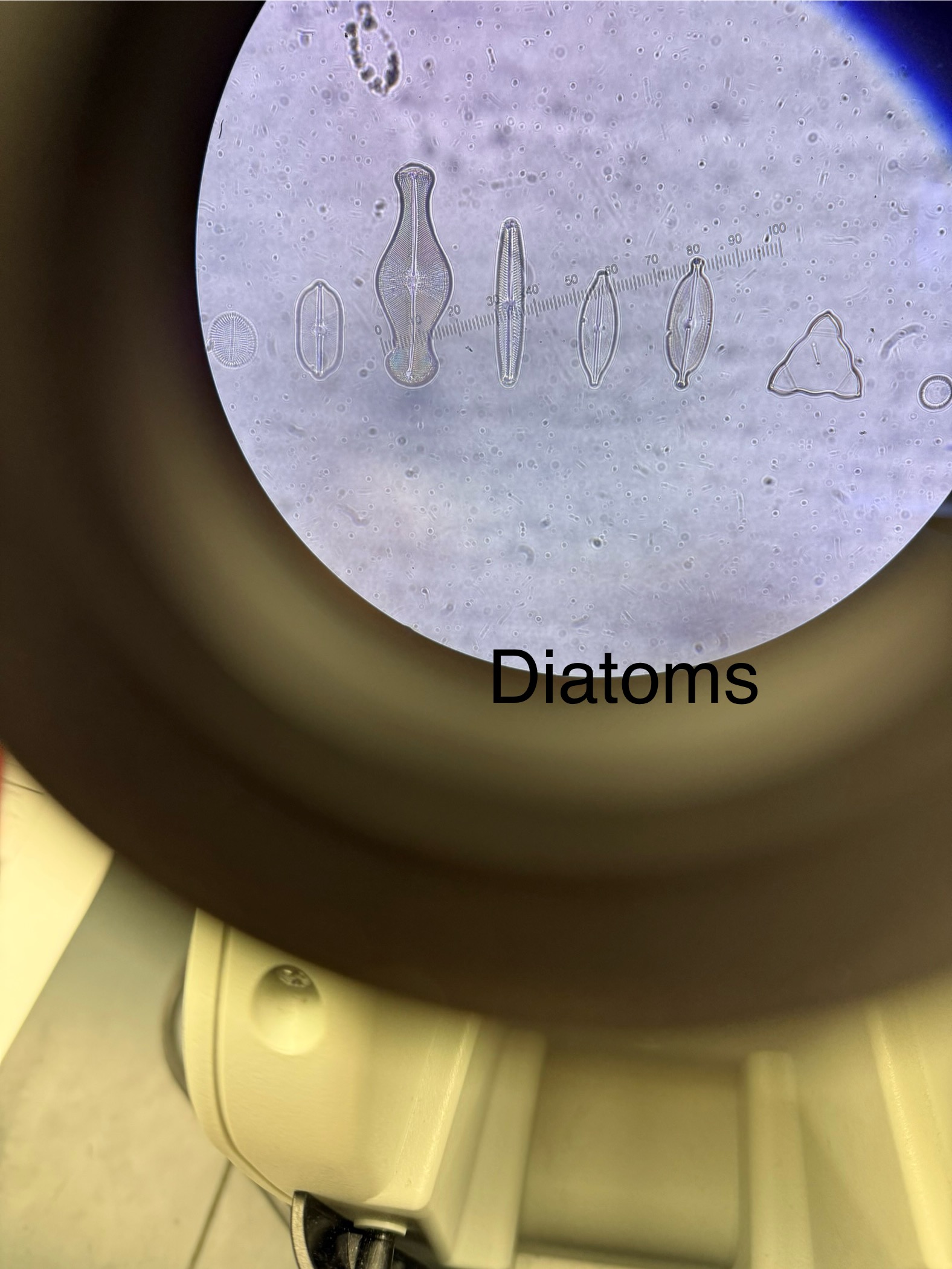
Diatoms ( common name)
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Bacillariophyta
Cell walls made of glass = silica dioxide
Aquatic organisms (Some freshwater, some marine)
Diatomaceous earth: Sedimentary rock formed by dead diatoms
Used as insecticides; abrasive in toothpastes, polish, cleaners; Filtration: water, beer, wine; Dynamite: ingredient used to stabilize nitroglycerin
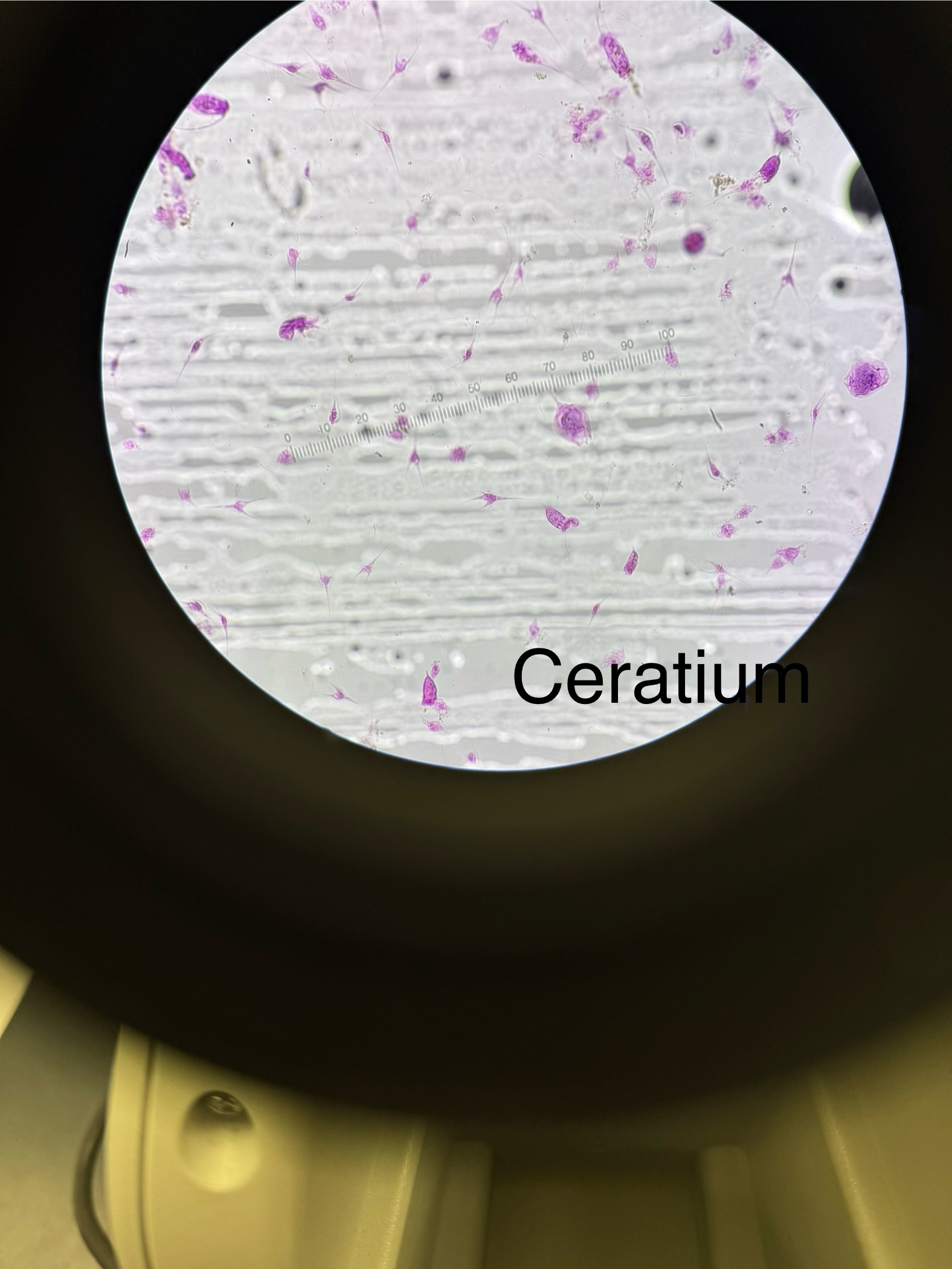
Ceratium
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Dinophyta
Genus: Ceratium
Cell walls made of cellulose
Mostly marine organisms with many being bioluminescent
Common name “dinoflagellates”
Harmless for most however some produce Neurotoxins that cause paralytic shellfish poisoning; Saxitoxin Is the pathogen made by Dinophyta Causing paralysis and death; “ Red tide”
Protozoa
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Single- celled eukaryotes
Chemoautotrophs
Holozoic: eat whole organisms (phagocytosis)
Most free living but some are pathogens
Many use flagella, pseudopodia, or cilia for motility
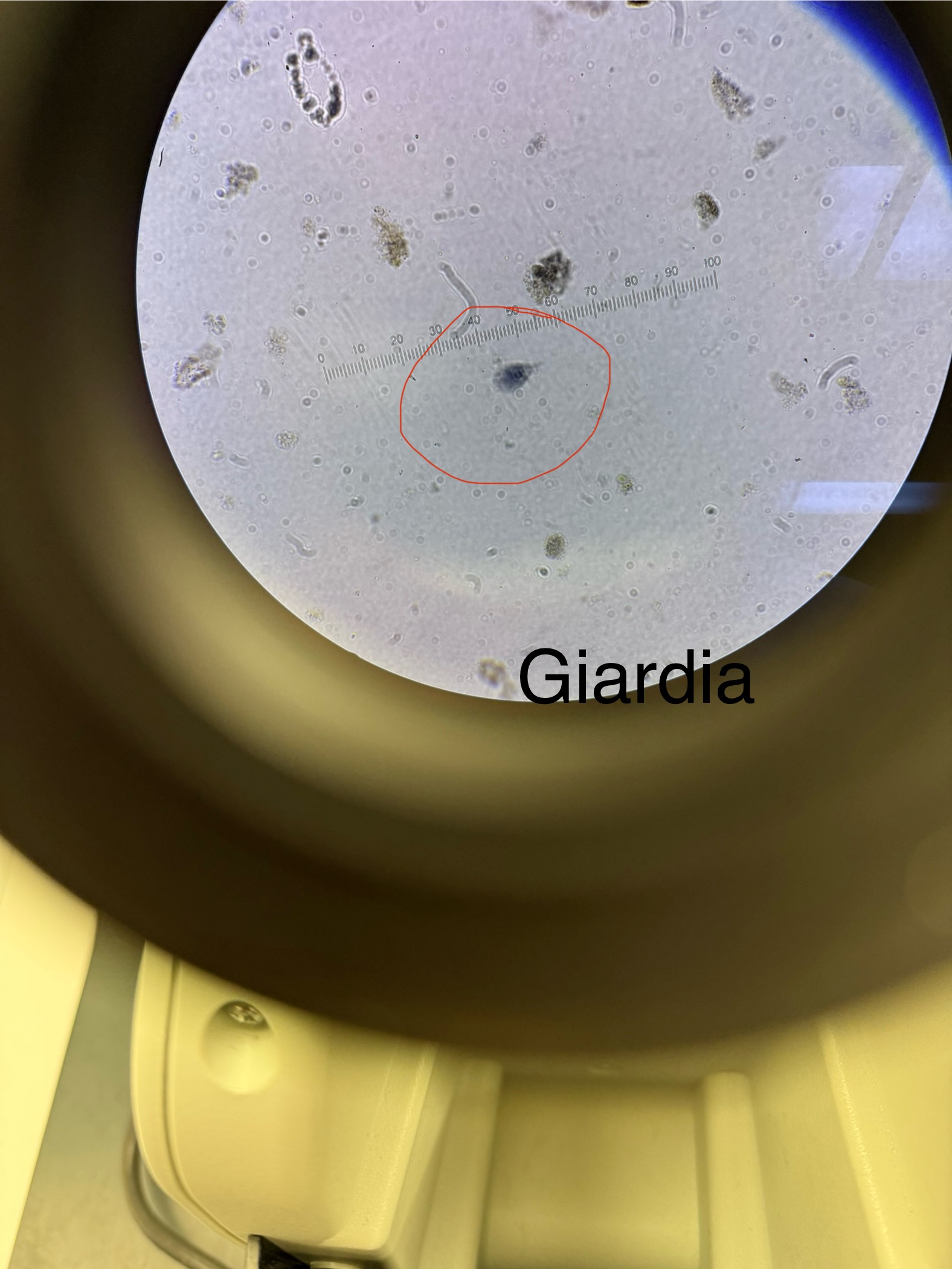
Giardia lamblia
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Archaezoa
Genus: Giardia
Species: lamblia
Causes diarrheal disease
Lack mitochondria and must live in an animal host
Two structural forms:
Trophozoite - active growth and disease “tear drop shape w/ flagella”; dies easier
Cyst - dormant form that survives more
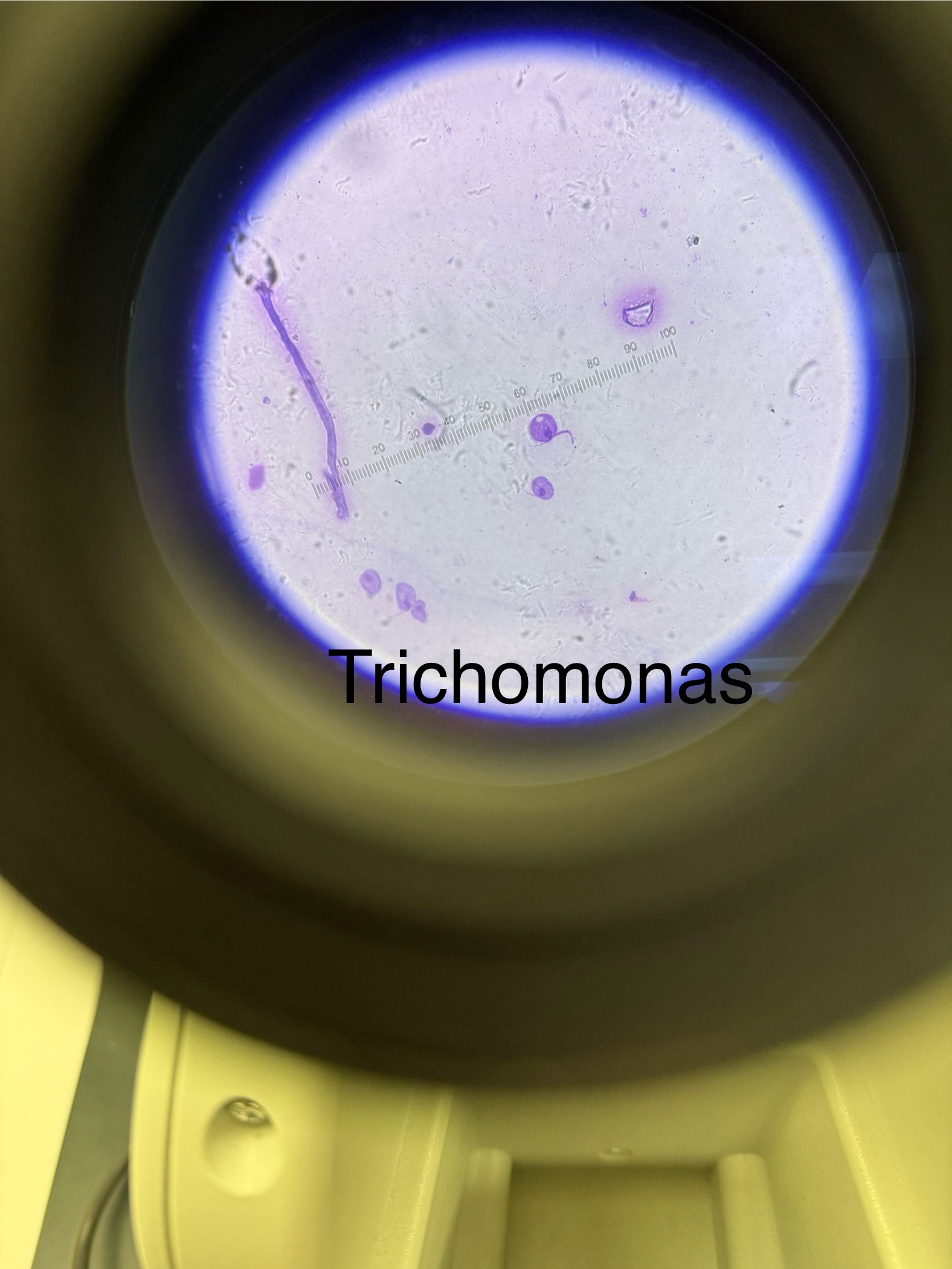
Trichomonas vaginalis
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Archaezoa
Genus: Trichomonas
Species: vaginalis
Causes sexually transmitted disease/infection
Lacks mitochondria and must live in an animal host
Amoeba proteus
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Amoebozoa
Genus: Amoeba
Species: proteus
Aquatic organisms
Harmless
Contains pseudopodia

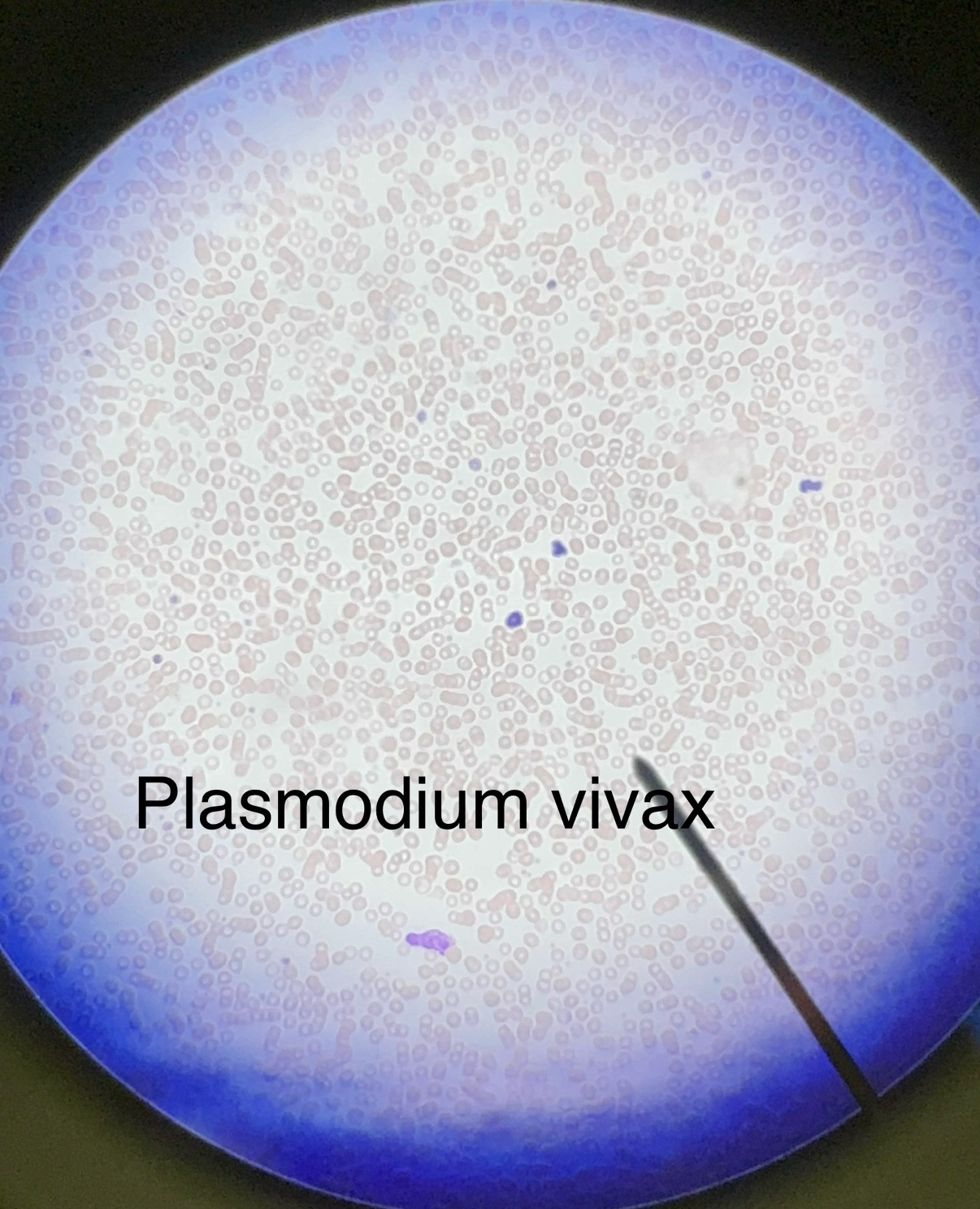
Plasmodium vivax
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Apicomplexa
Genus: Plasmodium
Species: vivax
“Ring form” inside of red blood cells causes malaria
Blood-Bourne pathogen
There are 4 separate species that can cause malaria and are spread by 60 different species of Anopheles mosquito (biological vector)
Malaria is an endemic to more than 90 nations
Anti-malarial drugs are used to treat/ given to travelers
1st malaria vaccine introduced in Africa in 2022
Very effective when used in combo with prophylactic anti-malarial drugs
*Study cycle*
Plasmodium Life Cycle
Infected mosquito bites human depositing plasmodium where it migrates through the bloodstream to the liver of the human
Released into bloodstream from liver may infect new red blood cells
Develops into ring stage in red blood cells
Ring stage grows and divides
*Asexual Reproduction in humans as the Intermediate host*
Plasmodium are released when red blood cell ruptures; Some plasmodium, infects, new red blood cells, and some develop into male and female forms of parasite
Another mosquito bites, the infected human and ingests the male and female forms of the parasite
In mosquitoes, digestive, track, male and female plasmodium unite to form a zygote
*Sexual Reproduction in mosquitoes where they are the definitive host*
Resulting plasmodium that are now genetically different migrate to salivary glands of mosquito
*Cycle is complete when this Infected mosquito bites a human*
Plasmodium → malaria symptoms
Begins with: headache, muscle aches, nausea, vomiting
Recurring Eurythrocytic cycles (every 48 hrs) of high fever, chills, sweating, exhaustion
Cycles can stay mild and eventually stop or progressed to severe attacks, which can be fatal
Additional symptoms, and severity of the disease depend upon which species of Plasmodium is infecting
Plasmodium → malaria treatment
Diagnosis: microscopy
Most traditional treatment is Quinine an extract of tree bark used since the 1600s; glows in the dark; prevents parasite from digesting hemoglobin
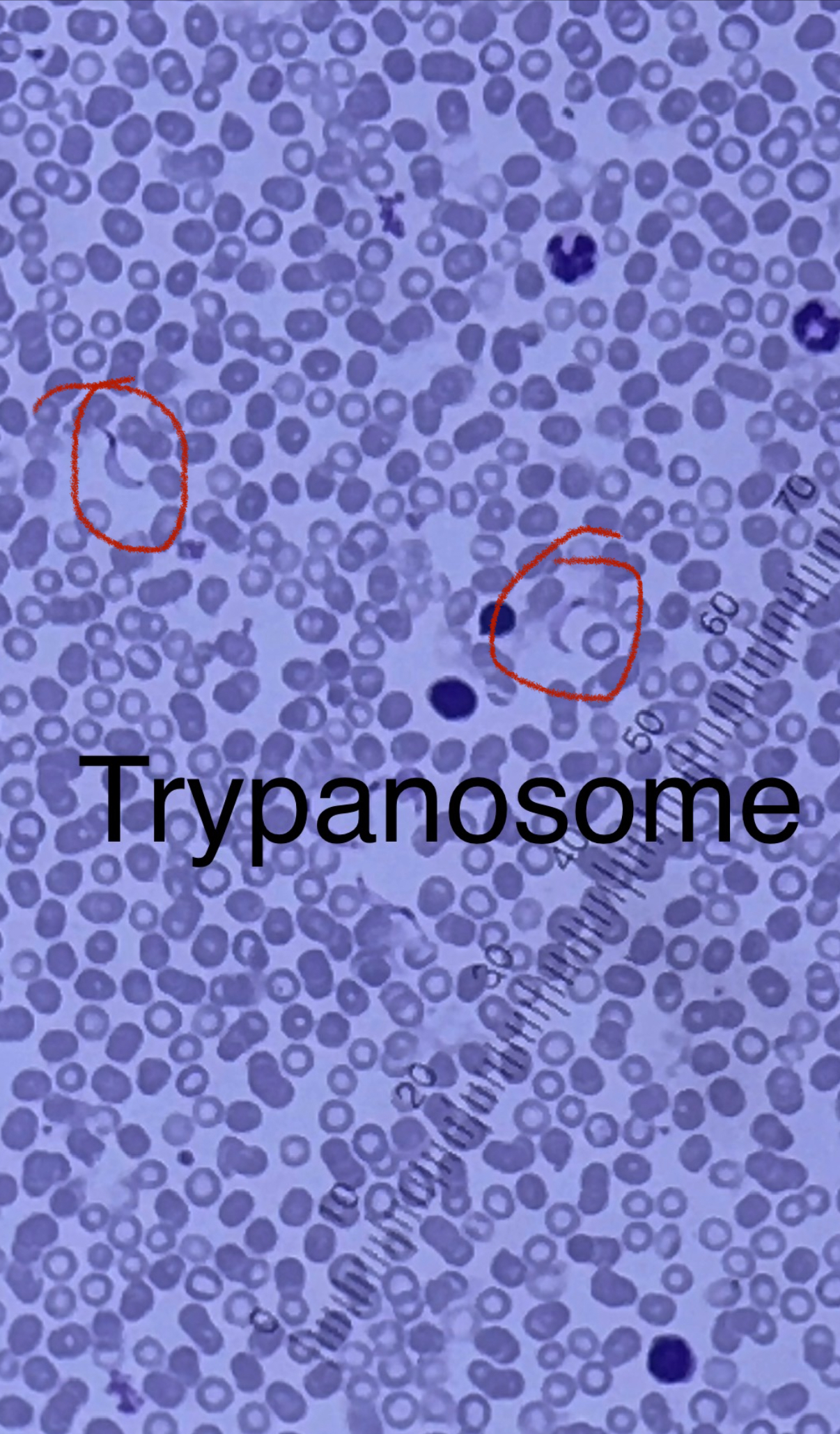
Trypanosoma cruzi/ brucei
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Euglenozoa
Genus: Trypanosoma
Species: cruzi & brucei
Pathogen
Transmitted by biological vectors; Reservoirs: Tigers, elephants, etc.
Seen outside of red blood cells
Purple looking banana parasite about 3 red blood cells long
T. cruzi causes Chaga’s disease (kissing bug) - symptoms- Myocarditis and congestive heart failure
T. brucei causes African sleeping sickness from the (tsetse fly) - symptoms- headache, drowsiness,, and death
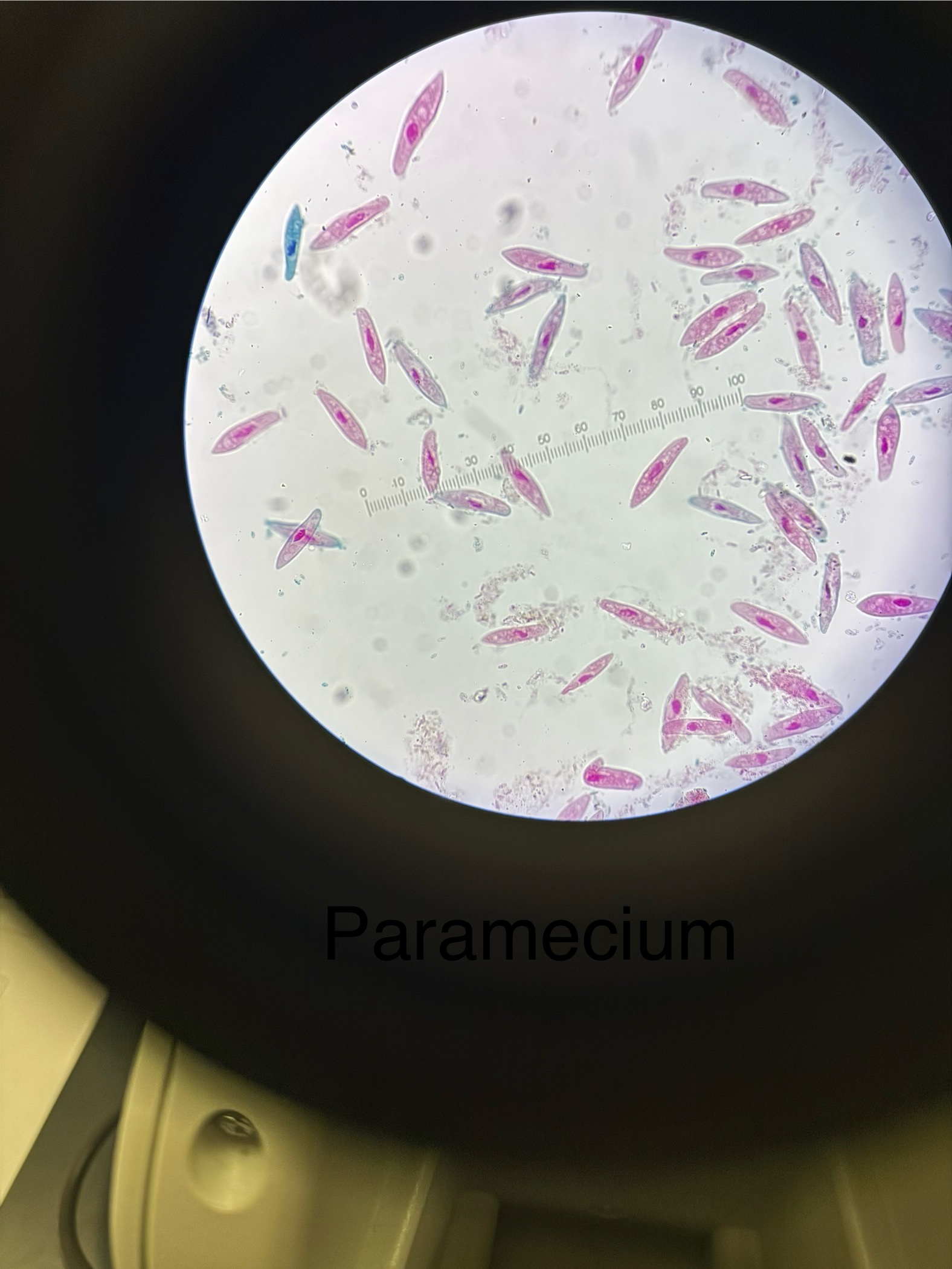
Paramecium caudatum
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Ciliophora
Genus: Paramecium
Species: caudatum
Harmless
For the exam expect purple cells with no visible cilia
Multicellular Parasites
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Trematoda
Class: Cestoda
Phylum: Nematoda
Phylum: Arthropoda
General characteristics of Parasitic Helminths
Chemoheterotrophs
Most found in phyla Platyhelminthes and Nematoda
Highly adapted to life in an animal
Poorly developed digestive system (It lives in a host surrounded by nutrition)
Poorly developed muscular and nervous system systems (Lives in a host no need to hunt for food)
Complex, reproductive system (Offspring must find new host → Numerous offspring, complex life cycle)
General life cycle of Parasitic Helminths
Larvae stage:
developmental stage (asexual reproduction)
Occurs in one or more intermediate hosts
Very numerous (Can be more than one larval stage)
Adult stage:
Mature, sexually reproductive stage
Occurs in the definitive host
Can be monoecious (Male and female sexual structures in one animal) or dioecious (Male animals and female animals)
Produce enormous numbers of offspring (Especially monoecious organisms)
Helmnith Life Cycle - why have 2 or more hosts
Adult and offspring occupied separate habitats
Less competition for resources
Less damage to host
Population dispersed throughout environment → Better chance of species survival
they cause long-term chronic infection
Characteristics of Platyhelminthes
Multi celled eukaryotes, no cell wall
Simple flatworms - Lack nervous system and intestines
Class: Trematoda “Flukes”
Leaf shaped flat worms
Several larval stages
Schistosoma haematobium (blood fluke)
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Trematoda
Genus: Schistosoma
Species: haematobium
Male & female worms
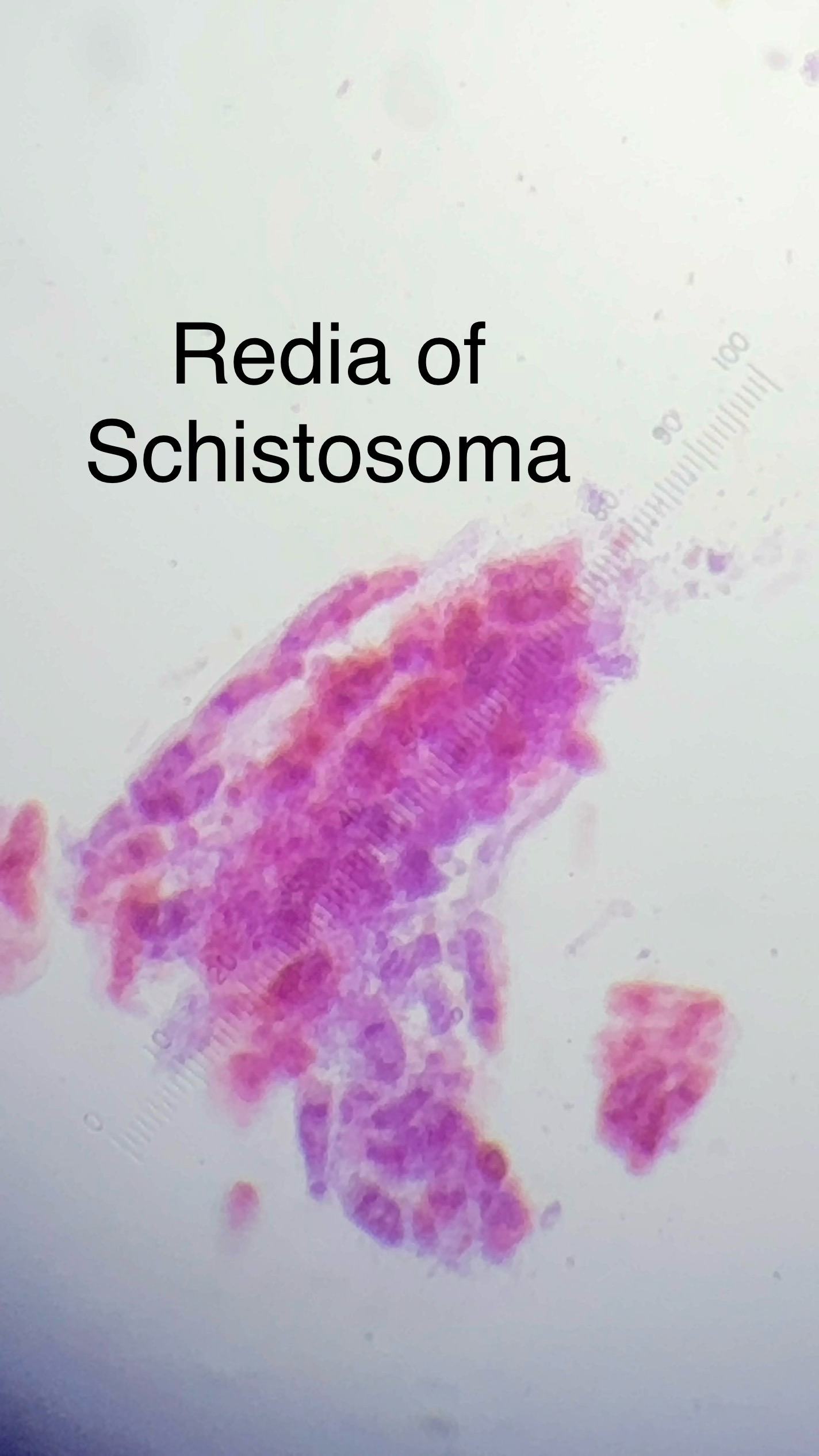
multiple larval stages: miricidium → redia → cercaria → adults
Intermediate and definitive hosts
Chronic infection of blood fluke (causes Shistosomiasis - Bilharzia) → inflammation response to eggs
symptoms: Anemia, fatigue, damage to liver, kidneys, blood vessels, blood in the urine
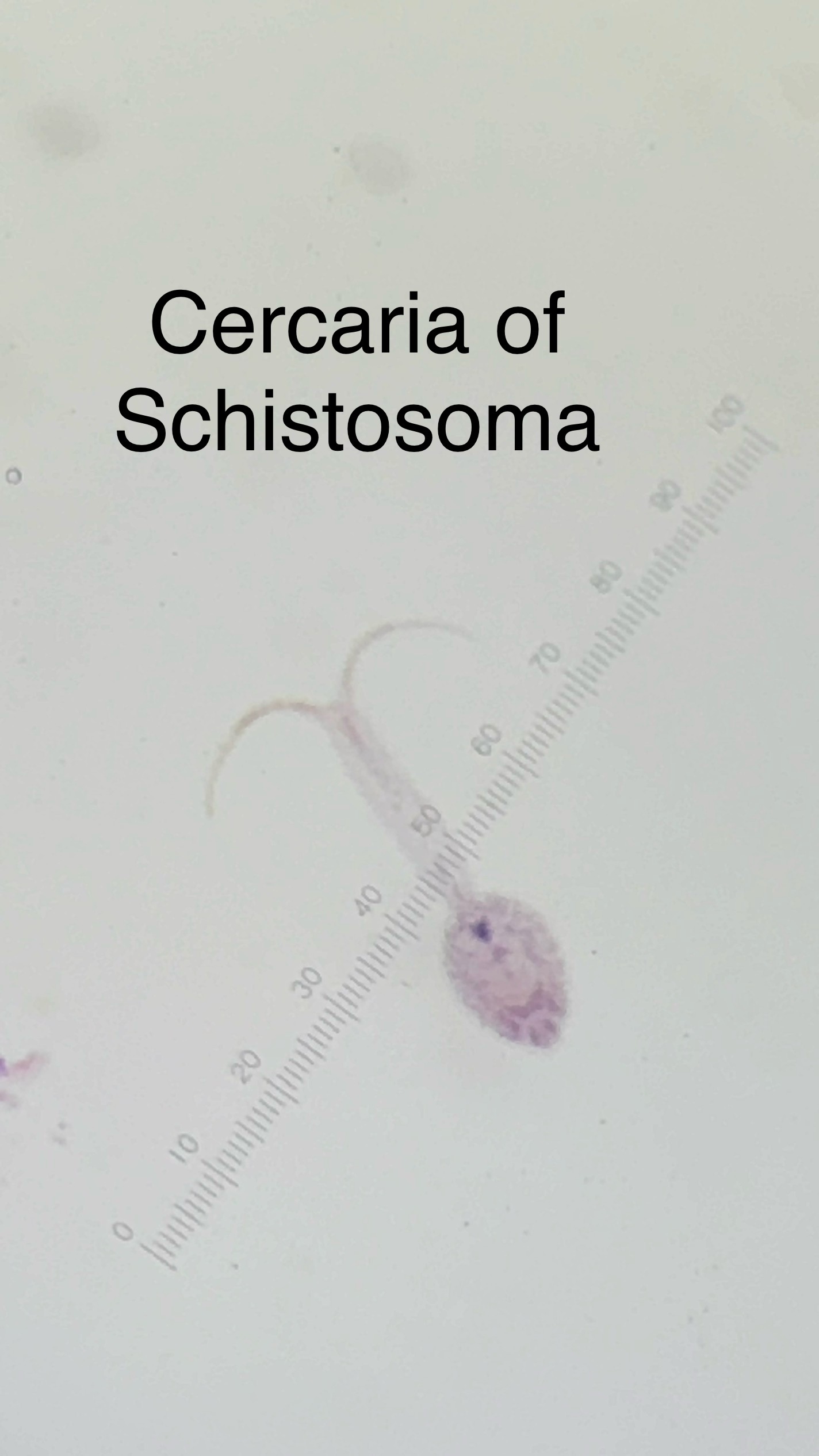
Schistosoma Life Cycle
*Sexual Reproduction in human as difinitive host*
Adult flukes lay eggs inside infected human in the blood vessels around the bladder
Human urinates/deficates in a body of water which releases eggs of this parasite into the water
Eggs hatch into free-swimming larvae (miricidium)
*Miricidium - Young larval form that enters snail and have cilia on them*
Miricidium penetrates a snail
*Asexual Reproduction in the snail that acts as the intermediate host where the miricidium produces redia which is the larval sac stage inside the snail*
The redia matures inside of the snail producing several cercariae which are the larval stage that leaves the snail and burrows into skin
Cercariae are released from the snail
Free-swimming cercariae penetrate human skin, losing its tail
Cercariae Travel through circulatory system to intestinal blood vessels, where they mature into adults where females will lay hundreds of eggs per day
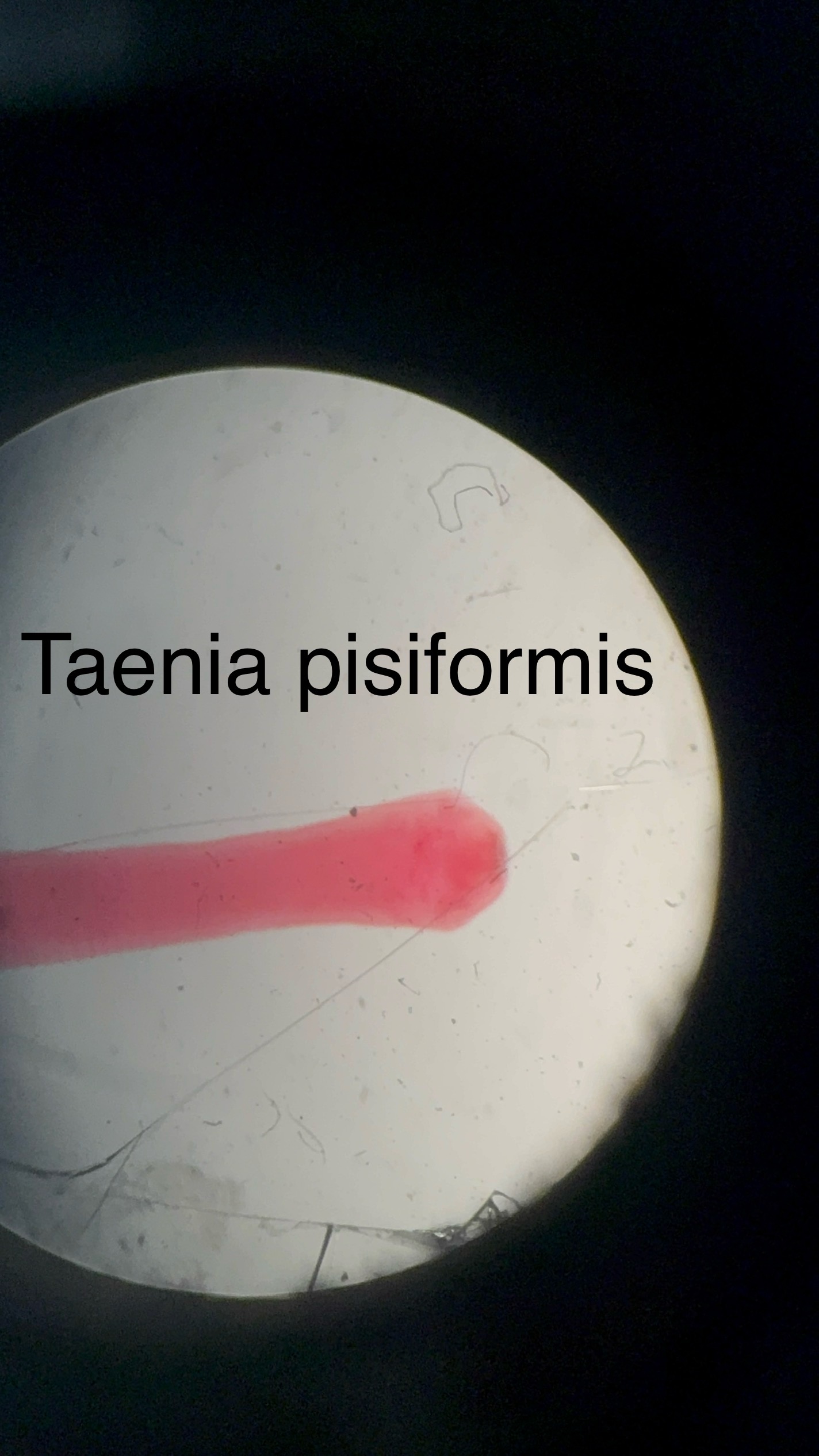
Taenia pisiformis
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Platyhelminthes
Class: Cestoda
Genus: Taenia
Species: pisiformis
Causes Tapeworm disease
Structures:
scolex - attachment or with hooks and suckers
proglattid - Infectious segment of tapeworm (Sexually reproductive)
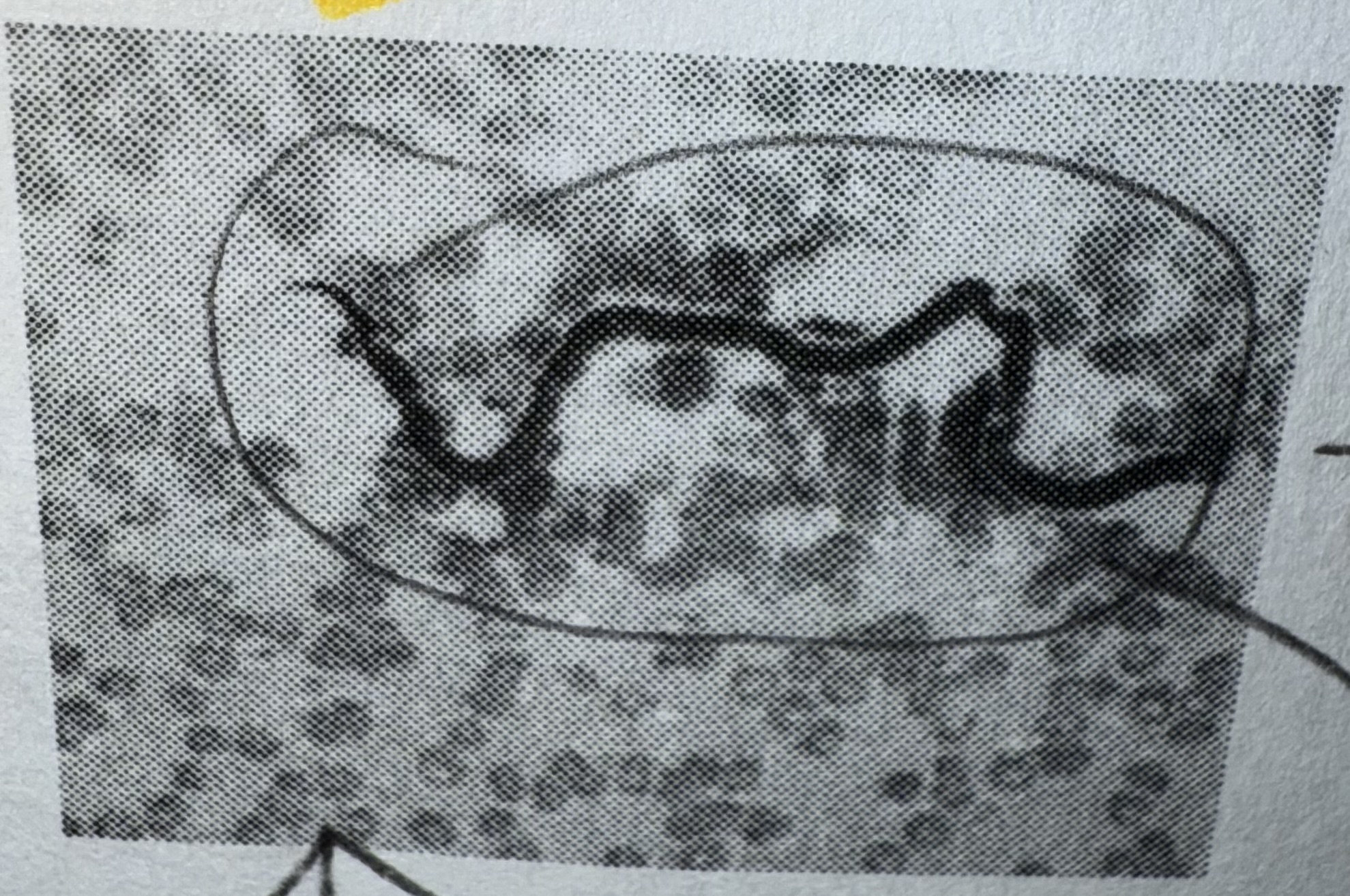
Characteristics of Nematoda
Multi cell eukaryotes, no cell wall
Round worms, with intestines and nervous system; Digestive track, but simple muscle and nervous system
Dirofilaria immitis
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Nematoda
Genus: Dirofilaria
Species: immitis
Spread by mosquitoes
Huge worm seen outside of red blood cells
Disease caused is canine heartworm
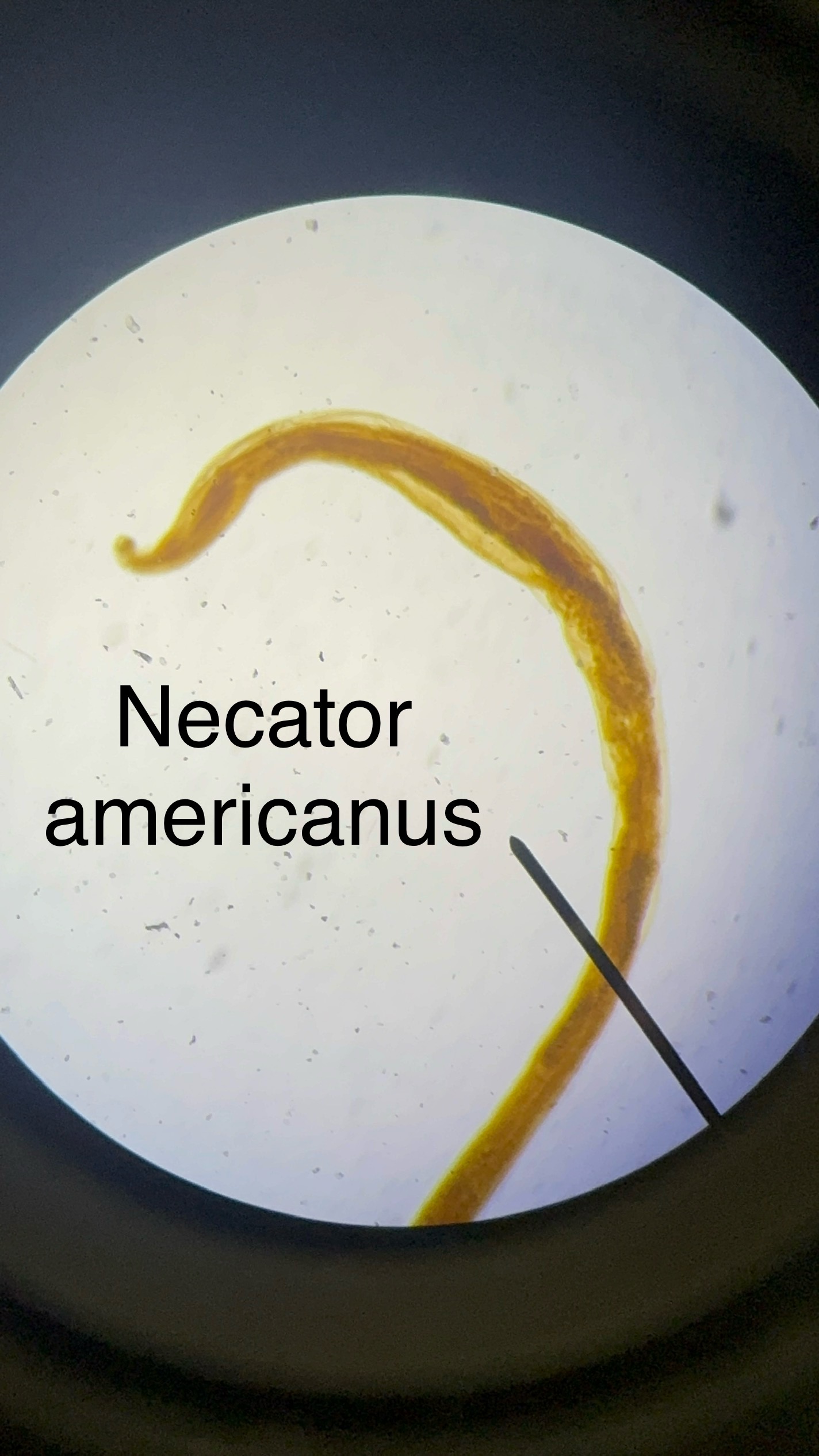
Necator americanus
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Nematoda
Genus: Necator
Species: americanus
Causes “Hookworm” disease
Adult lives in small intestine
Infectious larvae burrows in skin

Characteristics of Arthropoda
Multicellular eukaryotes, no cell wall
Have jointed feet
Dermacentor andersoni
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Genus: Dermacentor
Species: andersoni
Ectoparasite
Dermacentor andersoni Is the vector for bacterial pathogen Rickettsia rickettsii causing the disease “Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever”

Ixodes dammini
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Genus: Ixodes
Species: dammini
Ectoparasite
Ixodes dammini Is the vector for the bacterial pathogen Borrelia burgdorferi which causes Lyme disease

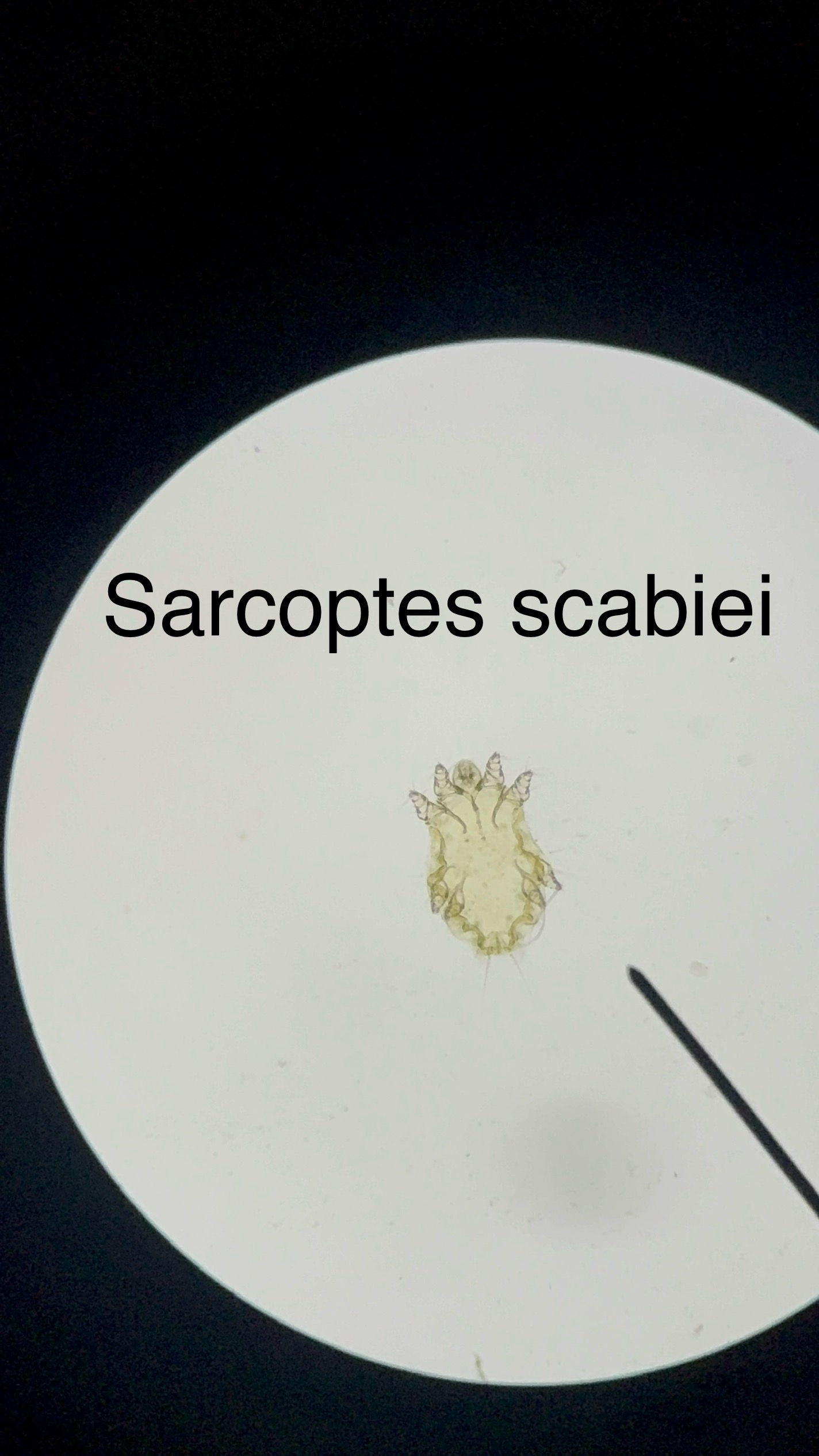
Sarcoptes scabiei
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Genus: Sarcoptes
Species: scabiei
Ectoparasite
Causes Scabies disease
burrows under skin/ itchy
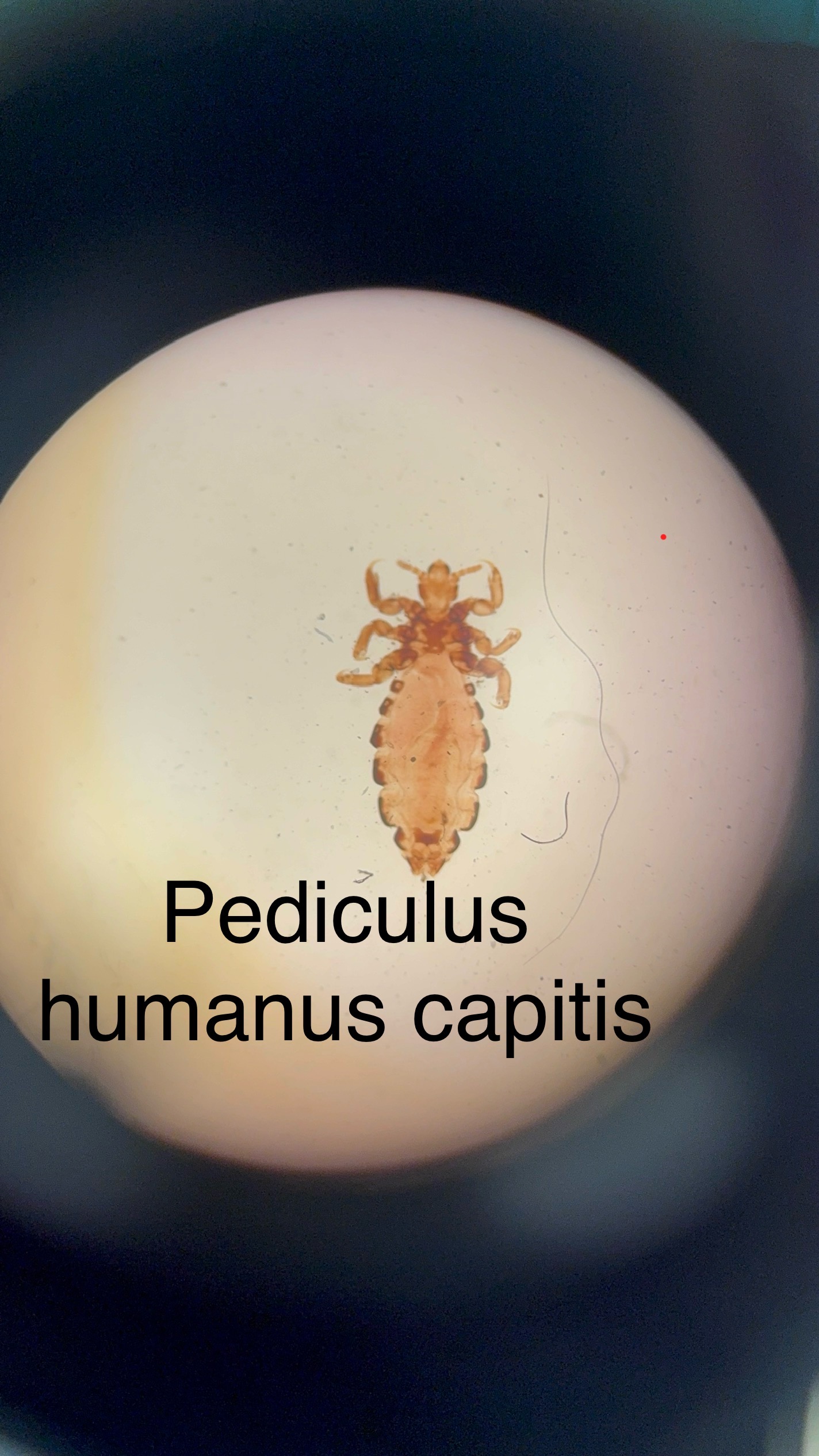
Pediculus humanus capitus
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Arthropoda
Genus: Pediculus
Species: humanus capitus
Ectoparasite
Nits = lice eggs
Causes “head lice” disease
