Path: neuroendocrine tumors
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
chromogranin, synaptophysin
most common markers for neuroendocrine tumors
small cell carcinoma
neuroendocrine neoplasm of the lung that predominantly arises centrally near the hilum and 90% in smokers; associated with paraneoplastic syndromes producing ADH and antibodies; poor prognosis and generally mets by dx
lambert eaton syndrome
paraneoplastic syndrome associated with small cell carcinoma of the lung when the tumor produces antibodies against presynaptic calcium channels
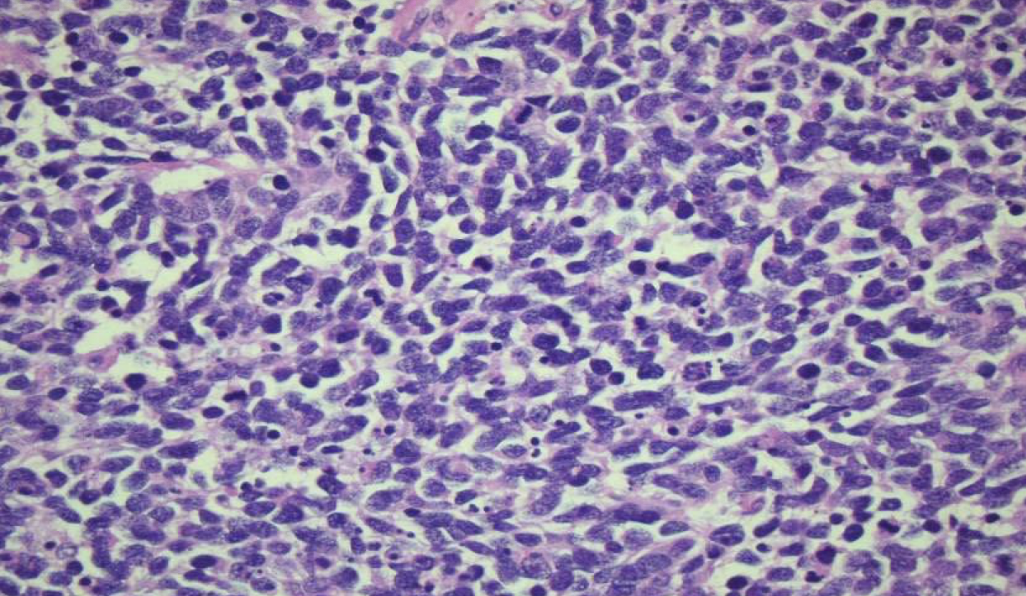
small cell carcinoma of the lung
high grade tumor with scant cytoplasm, ill-defined borders, finely granular nuclear chromatin (“salt and pepper”), absent or inconspicuous nucleoli; extensive necrosis and excessive mitotic activity
MYC
small cell carcinoma of the lung is often associated with amplification of genes in what family?
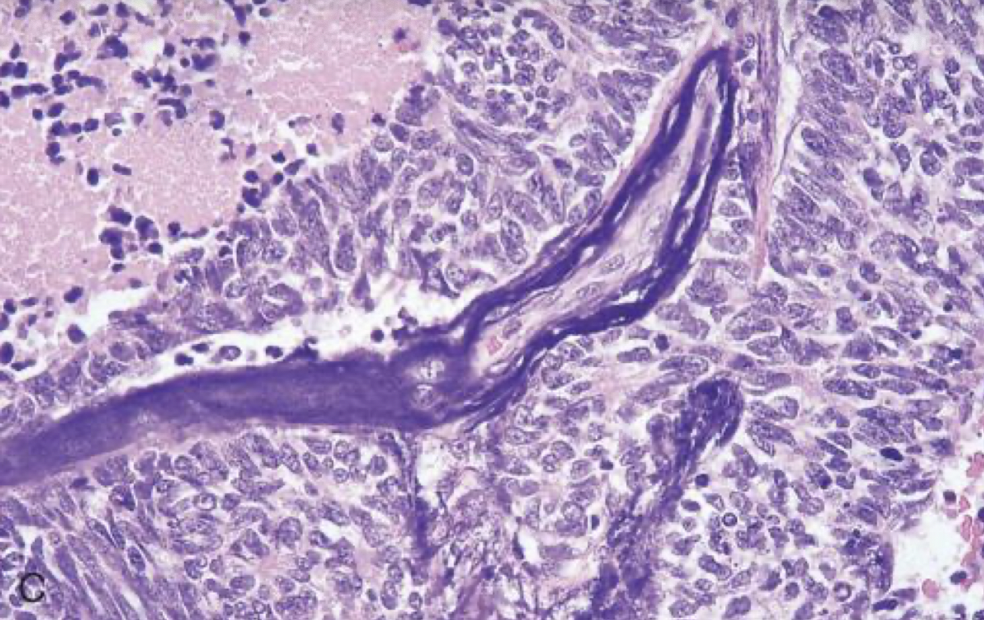
azzopardi effect
as the cells break open, DNA will surround blood vessels in small cell carcinoma of the lung
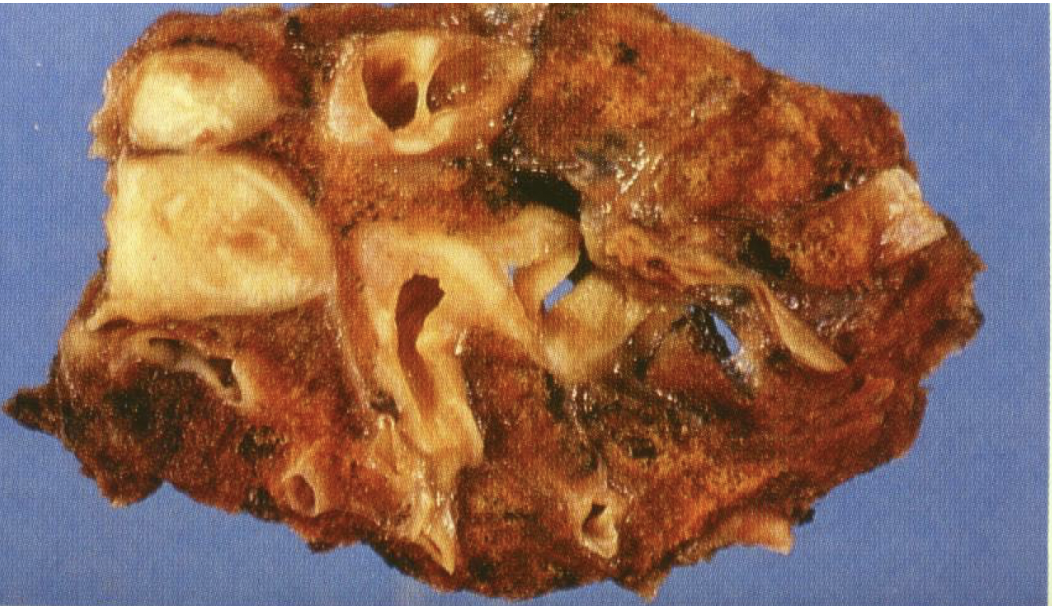
lung carcinoid tumors
low-grade, malignant neuroendocrine neoplasm of the lung; low mitotic activity, no necrosis; peribronchial location of tumor very common; very high 5 year survival rate
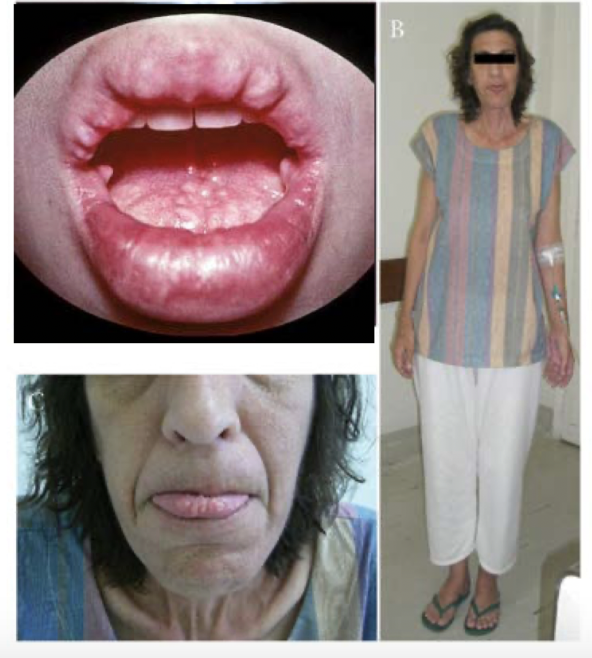
carcinoid syndrome
intermittent diarrhea, flushing, asthmatic wheezing, right-sided valvular heart disease due to lung MAO-A enzymatic breakdown of serotonin; approx 10% of lung carcinoid tumors
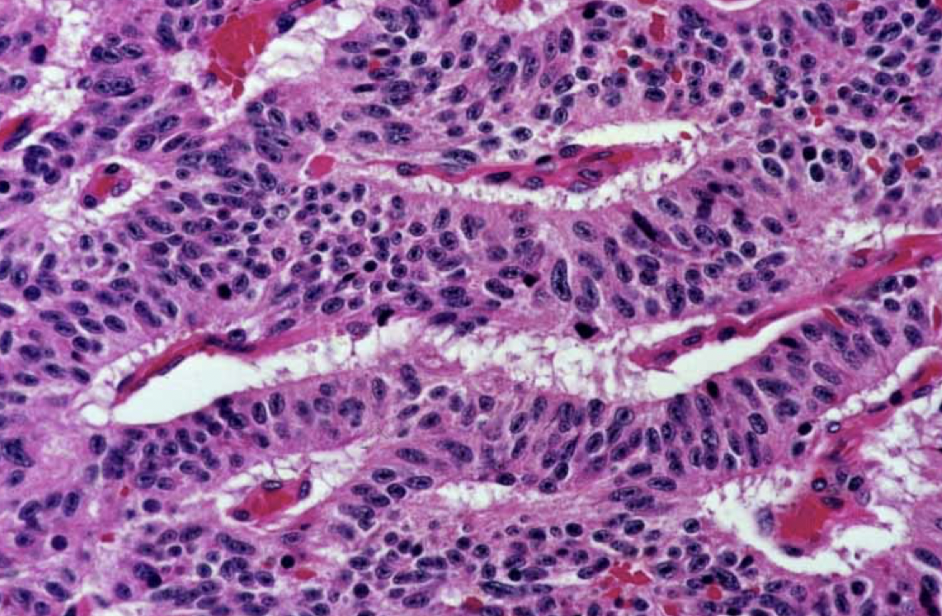
carcinoid tumors (small cell are much darker)
lung small cell or carcinoid tumors are more pink = more cytoplasm?
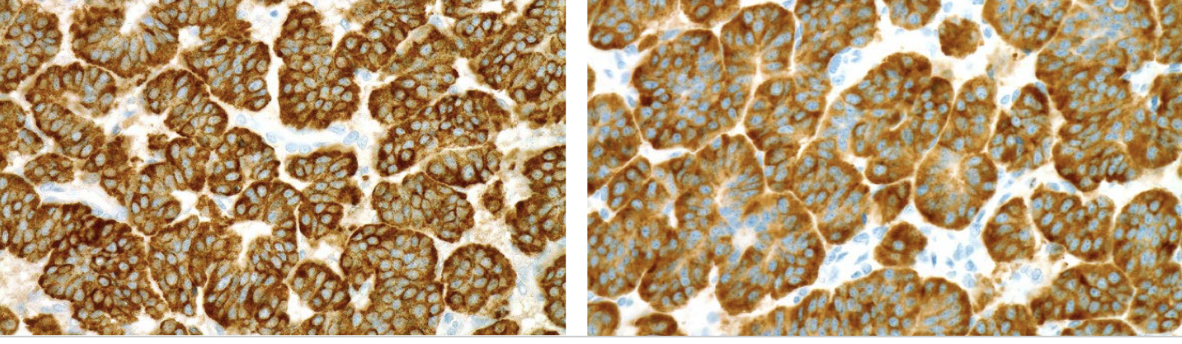
chromogranin, synaptophysin
IHC positive stains for carcinoid lung tumor ?
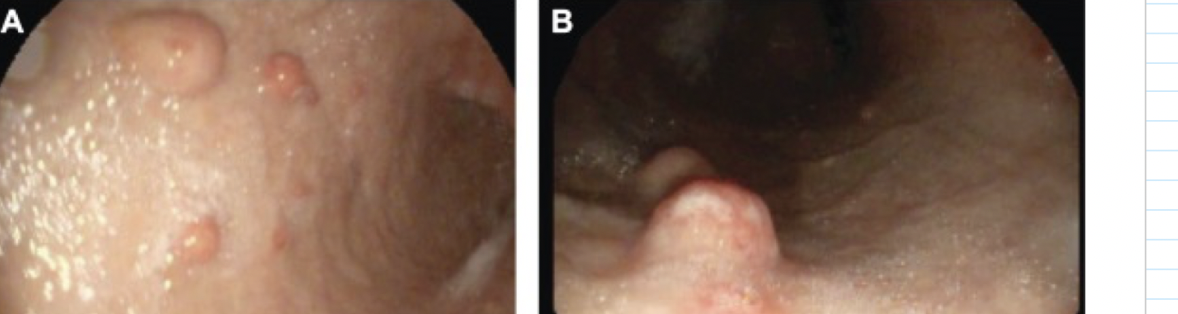
well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors
carcinoid tumors in the GI tract are now referred to as?
1/3 metastasize
1/3 present with secondary malignancy
1/3 are multiple
1/3 rule for carcinoid GI tumors
false (serotonin undergoes first-pass metabolism in the liver)
T/F: carcinoid tumors limited to the GI tract typically cause carcinoid syndrome
foregut NETs (esophagus, stomach, proximal duodenum)
which GI carcinoid tumors most rarely metastasize and are generally cured by resection?
midgut NETs (jejunum and ileum)
which GI carcinoid tumors are often multiple and tend to be very aggressive
hindgut NETs (appendix usually benign, colorectal is variable)
which GI carcinoid tumors typically present with abdominal pain and weight loss when symptomatic?
type 1 ECL-like NET
more gastric NET, often immune with anti-parietal cell or anti-intrinsic factor antibodies leading to low or absent acid secretion; atrophic gastritis
type 2 ECL-like NET
rare gastric NET associated with parietal cell hypertrophy/hyperplasia and hypergastrinemia due to gastrinomas in duodenum or pancreas leading to high acid secretion
histamine
produce by enterochromaffin-like cells in the corpus/fundus of the stomach that promotes acid secretion by parietal cells
zollinger ellison syndrome
caused by gastrinoma (gastrin-secreting) of duodenum or pancreas that can cause type 2 ECL-like NET in the stomach; acid hypersecretion causing recurrent ulcers; positive secretin test
type 3 ECL-like NET
higher grade gastric NET with no hypergastrinemia, normal acid secretion, higher metastatic rate and poorer prognosis; graded from well-differentiated NET to neuroendocrine carcinoma
Ki-67
stain that can be used to differentiate the proliferation rates of different types of gastric NETs
gastrinomas leading to zollinger-ellison syndrome
most duodenal NETs are clinically asymptomatic and found incidental by endoscopy, except?
liver mets are present
small intestinal and ampullary NETs will only cause carcinoid syndrome (diarrhea, bronchospams, and tricuspid valve fibrosis) if?
mitotic activity and Ki-67 IHC
grading of NETs of the digestive system is generally based on?
well-differentiated NET (carcinoid)
most common tumor of the appendix, benign and usually found incidentally after surgery for acute appendicitis
insulin
beta-cells in the islets of langerhans of the pancreas produce?
glucagon
alpha-cells in the islets of langerhans of the pancreas produce?
somatostatin
delta-cells in the islets of langerhans of the pancreas produce?
benign (90%)
most insulinomas of the pancreas are (benign/malignant)?
non-functioning (often found incidentally and symptoms related to mass effect; tend to be larger at dx with more positive lymph nodes)
most pancreatic NETs are?
MEN1 (multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1)
nearly 100% of patients with _______ have pancreatic NET at autopsy
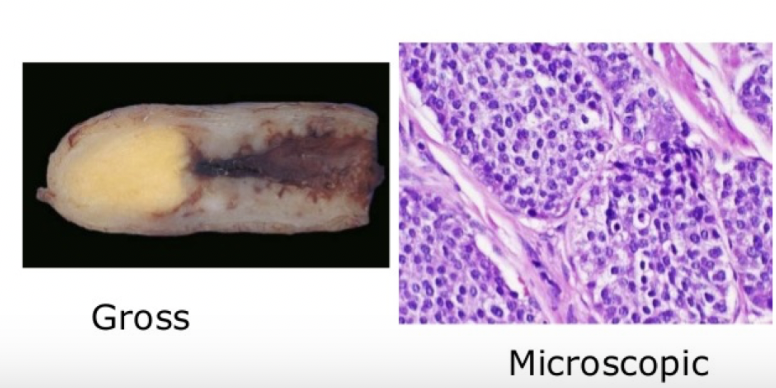
insulinoma
most common functioning pancreatic NET of B cells that is almost always localized to the pancreas and rarely malignant
insulinoma
enlarged islets, without disruption of normal architexture and no evidence of anaplasia (even if malignant); amyloid deposition extracellularly is often seen
low blood glucose
symptoms of hypoglycemia (lethargy, syncope, diplopia)
resolution of symptoms after normalization of glucose
whipple triad
insulinoma
symptomatic patients have low blood glucose (whipple triad) and high C-peptide
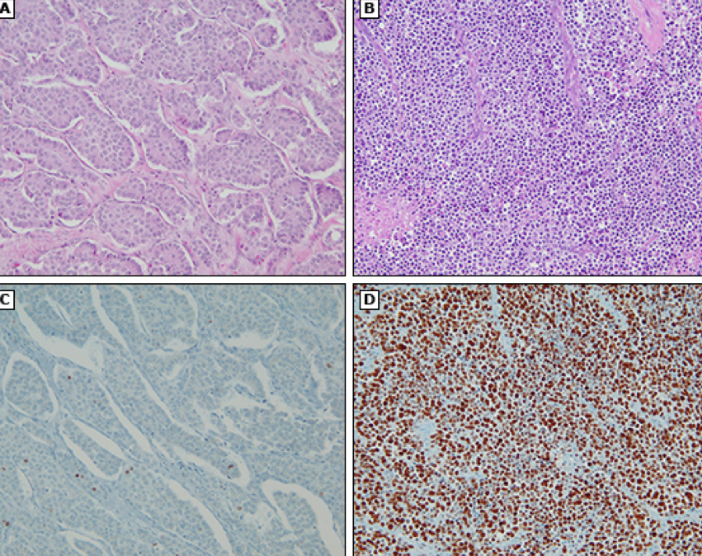
gastrinoma
gastrin secreting pancreatic NET; malignant in 60-90% and spread to LN at time of dx; most sporadic, 1/3 familial
common bile duct
duodenum
pancreatic head
gastrinoma triangle
gastrinoma
associated with MEN1 and zollinger-ellison syndrome; thickened gastric mucosal folds, hypergastrinemia, secretin test positive; most common in duodenum but can also occur in pancreas
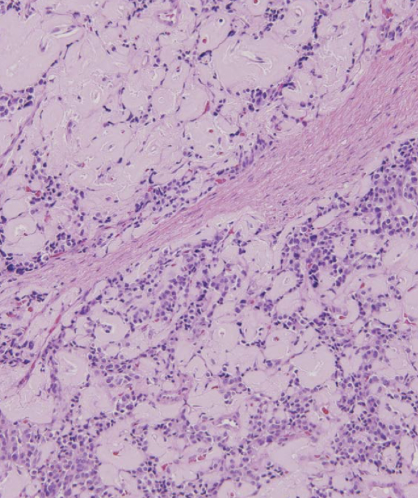
glucagonoma
tumor of pancreatic alpha cells associated with diabetes, dermatitis, deep vein thrombosis, depression, declining weight; large tumors and usually localized or have liver mets
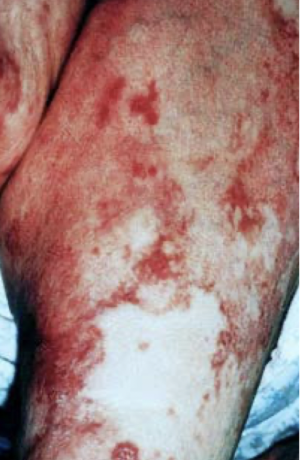
verner-morrison syndrome (pancreatic cholera/WDHA - watery diarrhea, hypokalemia, achlorhydria)
disease caused by uncontrolled secretion of VIP in vipomas; associated with MEN-1
somatostatinoma
very rare tumor of pancreatic D cells causing decreased secretion of secretin, cholecystokinin, glucagon, insulin, gastrin, gastric inhibitory peptide; not associated with NF1 (like ampullary and duodenal)
well-differentiated pancreatic NET
homogenous, well-circumscribed and localized
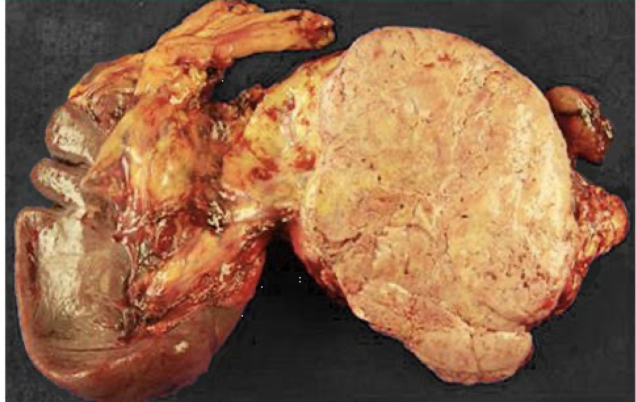
pheochromocytoma
tumor derived from chromaffin cells (arise from neural crest) of the adrenal medulla that results from hyperproduction of catecholamines; most often benign, rule of 10s, surgically correctable hypertension; MEN II or III
paraganglioma
pheochromocytomas derived from extra-adrenal chromaffin in the bladder, organ of zuckerandl, origin of inferior mesenteric artery
pheochromocytoma
von hippel-lindau disease, von recklinghausen disease (neurofibromatosis, schwannomas, gliomas), sturge-weber associated with
pheochromocytoma
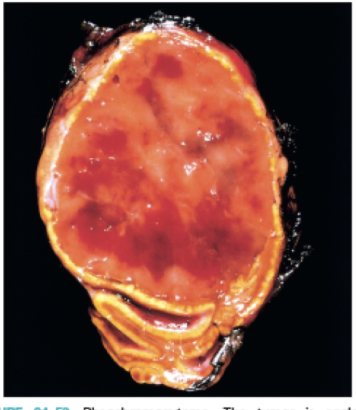
neuroblastoma
highly malignant, catecholamine-producing tumors that occur in early childhood; urinary catecholamines and causes hypertension
neuroblastoma
small round blue cell tumor in the abdomen of a child with homer-wright pseudorosettes
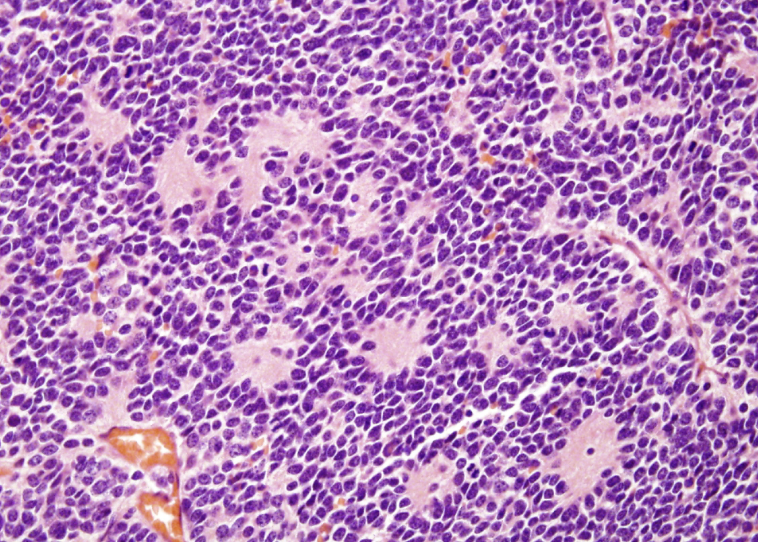
neuroblastoma
amplification of N-myc oncogene to thousands of copies per cell that is related to the aggressiveness of what type of tumor?
pheochromocytoma/neuroblastoma
clonidine suppression test is used for?
multiple endocrine syndromes (MEN)
autosomal dominant conditions characterized by hyperplasia, adenomas, and carcinomas of multiple endocrine organs; younger age, multifocal, aggressive behaviors
wermer syndrome (type 1 MEN)
rare inherited MEN that affects the parathyroid, pituitary, and pancreas from germline mutations in MEN1 tumor supressor; also develop carcinoid tumors, thyroid and adrenocortical adenomas, and lipomas
sipple syndrome (MEN 2A)
multiple endocrine neoplasia associated with medullary thyroid carcinoma (100%), pheochromocytoma, parathyroid hyperplasia; caused by germline mutations in RET proto-oncogene
familial medullary thyroid cancer
variant of MEN 2A that develops at an older age and follow a more indolent course
MEN 2B
multiple endocrine neoplasms with medullary thyroid carcinoma, pheochromocytomas, mucosal neuromas/ganglioneuromas, marfanoid habitus (long axial skeleton); RET gene mutation