Chapter 2 AP Psychology
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
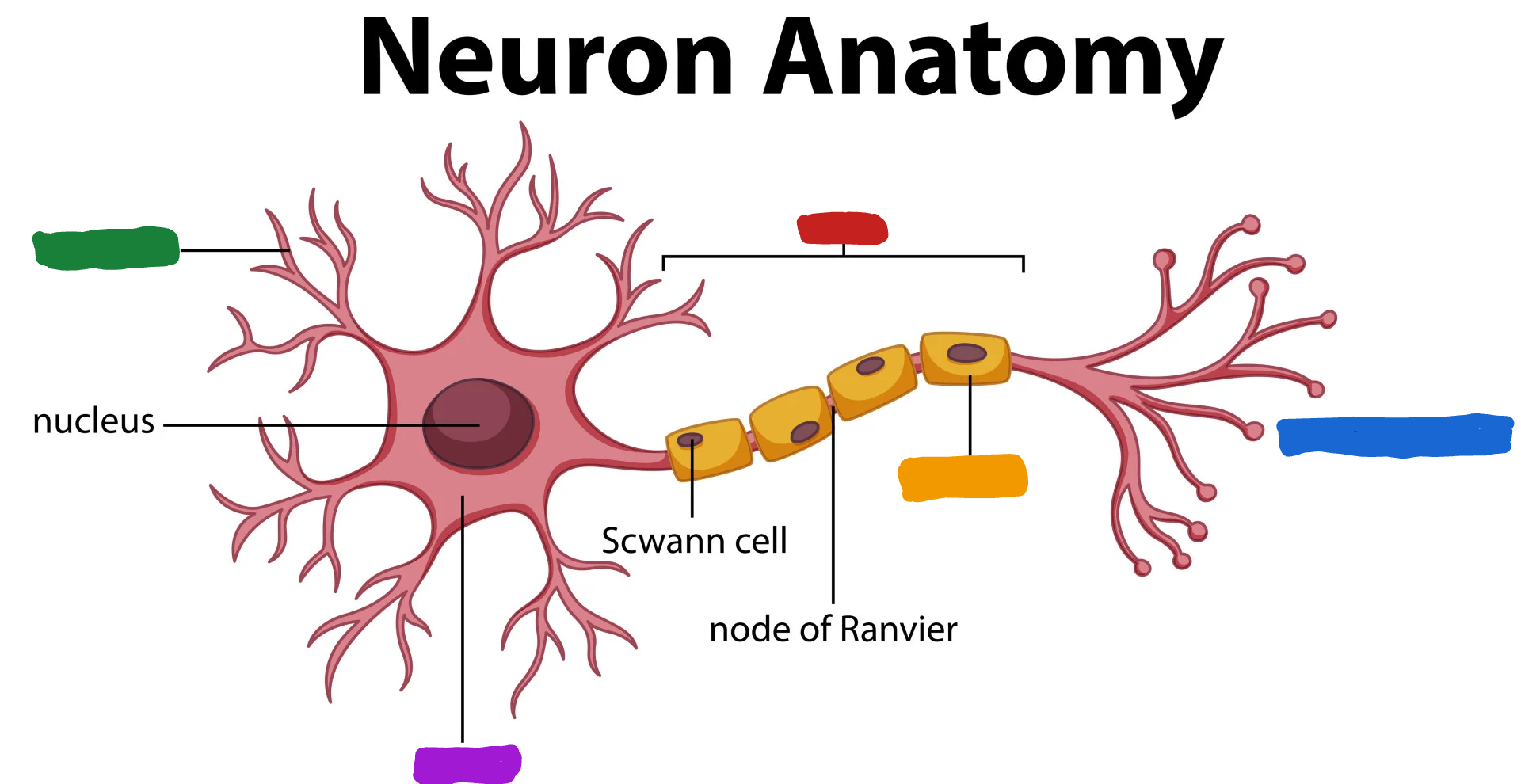
What part of the neuron is the one in red?
Axon
What do the Axon do?
the Axon fibers pass the message to other neurons or to muscle or glans (Axon speak)
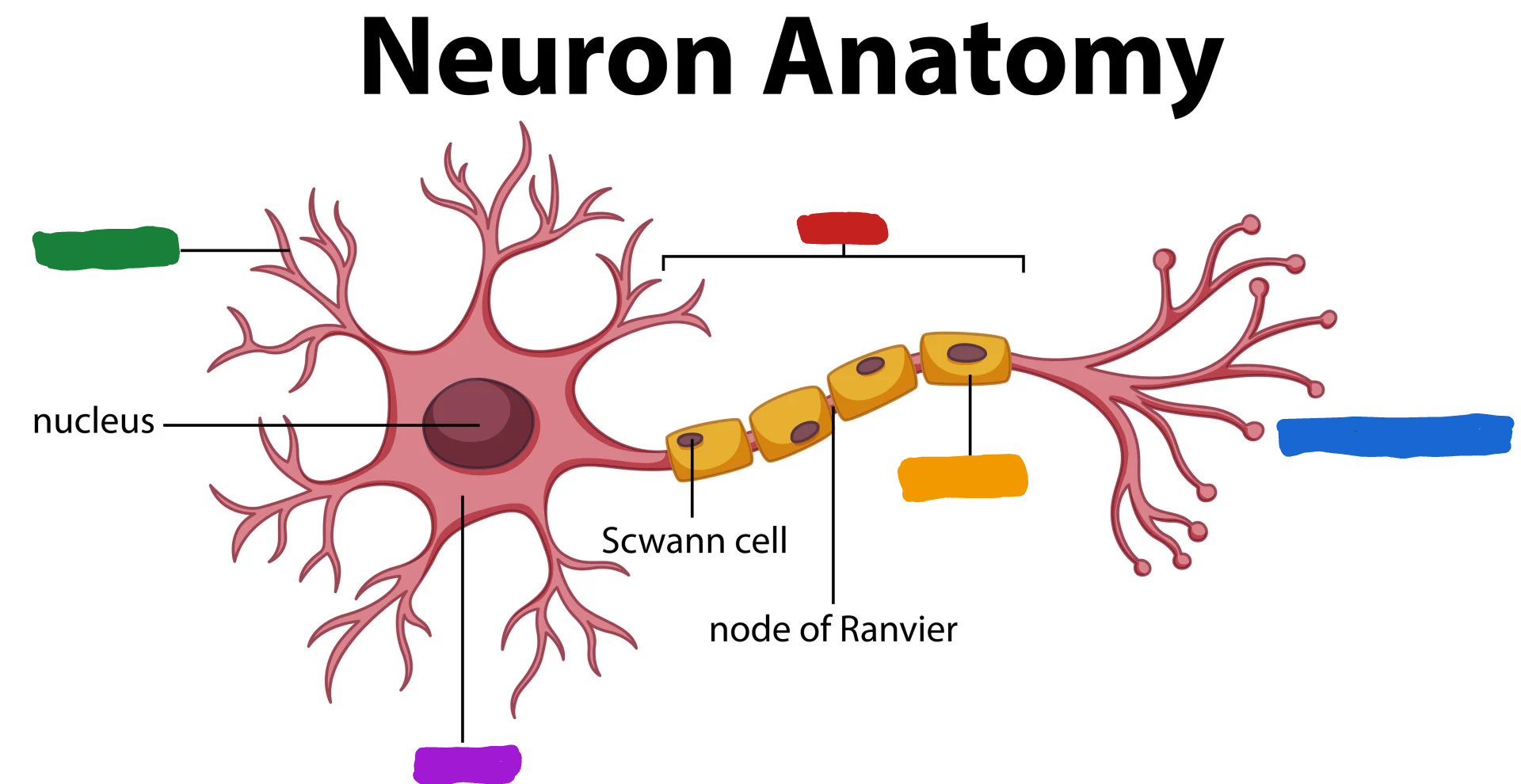
What part of the neuron is the one in green?
Dendrites
What are dendrites?
dendrites fibers receive information and conduct it toward the cell body (Dendrites listen)
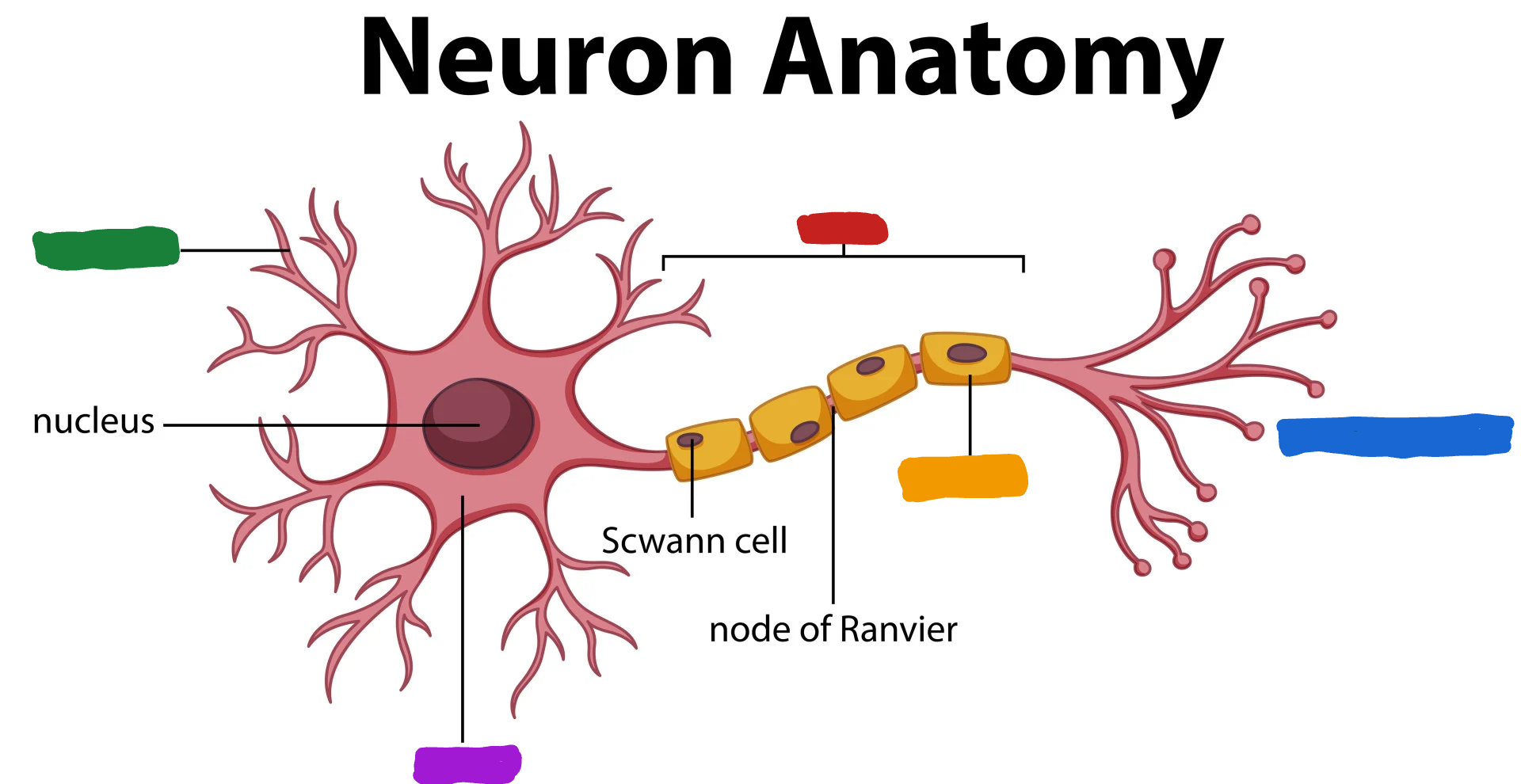
What is the part of the neuron in purple?
Cell body/soma
What is the cell body/ soma?
it is the main structural component of a neuron; cell’s life support center
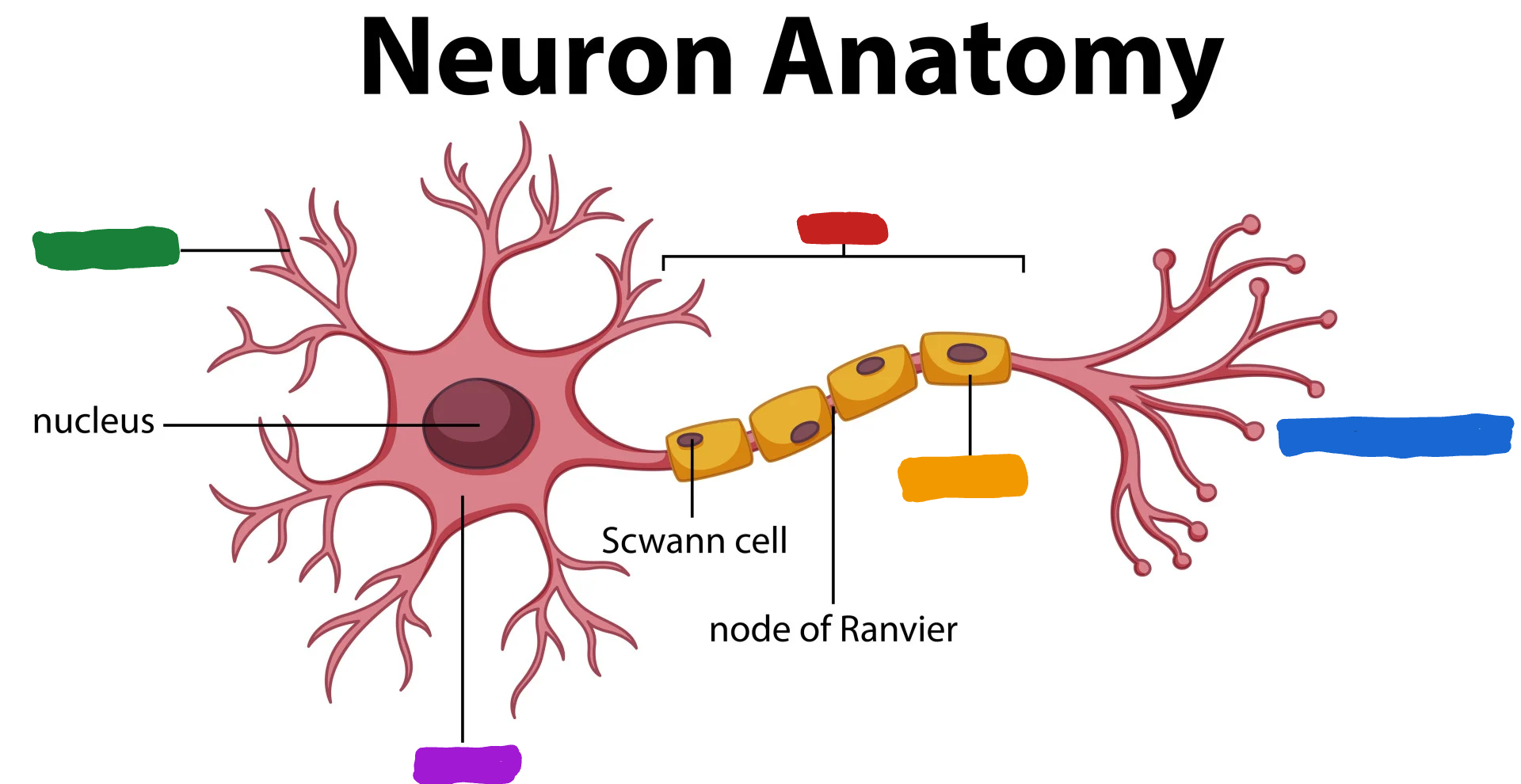
What is the part of the neuron in orange?
Myelin Sheath
What is the myelin sheath?
covers the Axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impluses
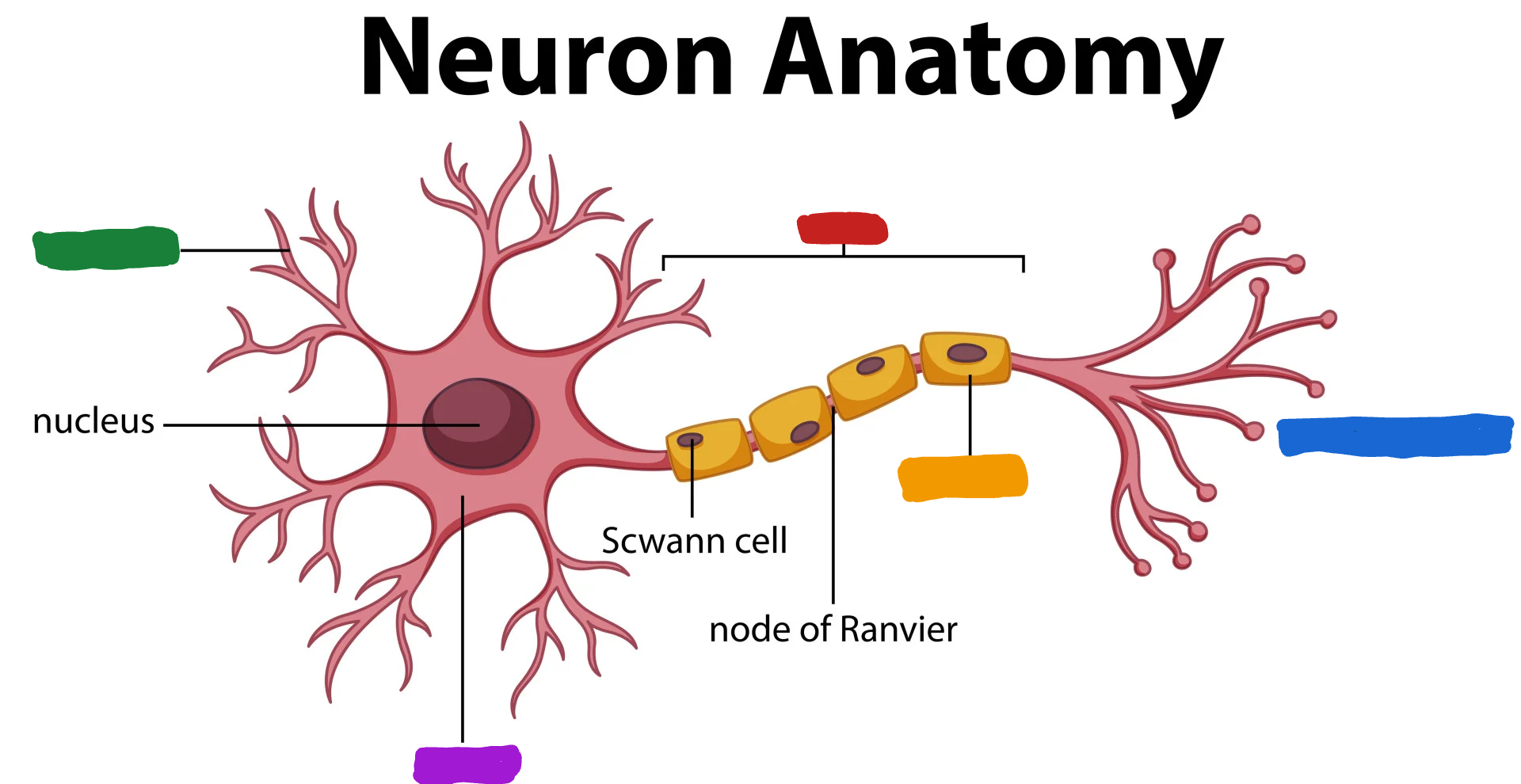
What is the part of the neuron in blue?
Axon terminal
What is the Axon terminal?
forms junctions of other cells
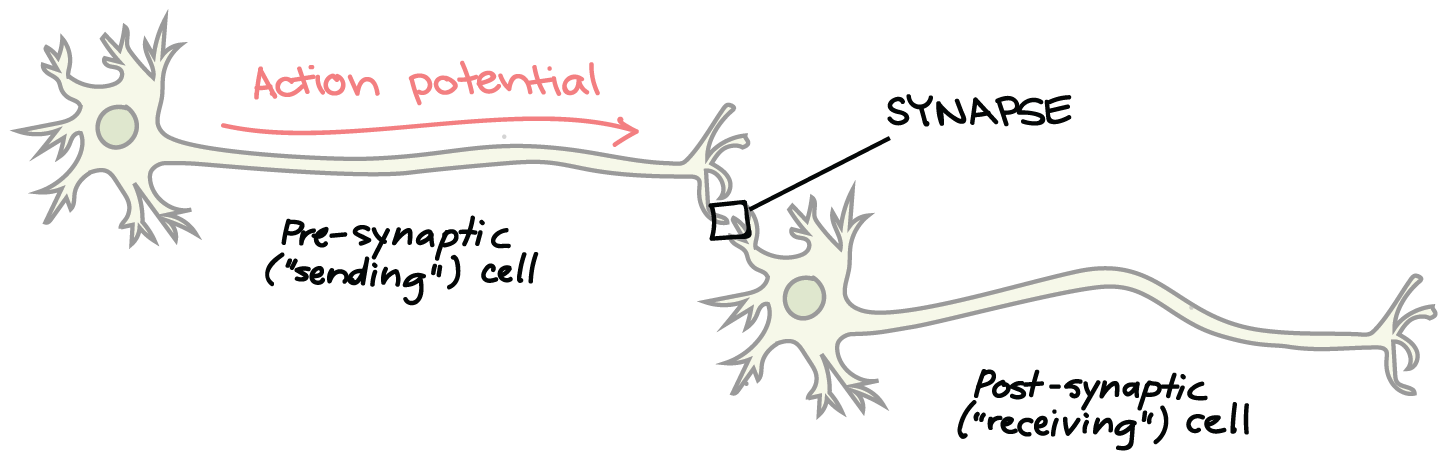
What is the synapse?
is the junction between the Axon of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell-body of the receiving neuron
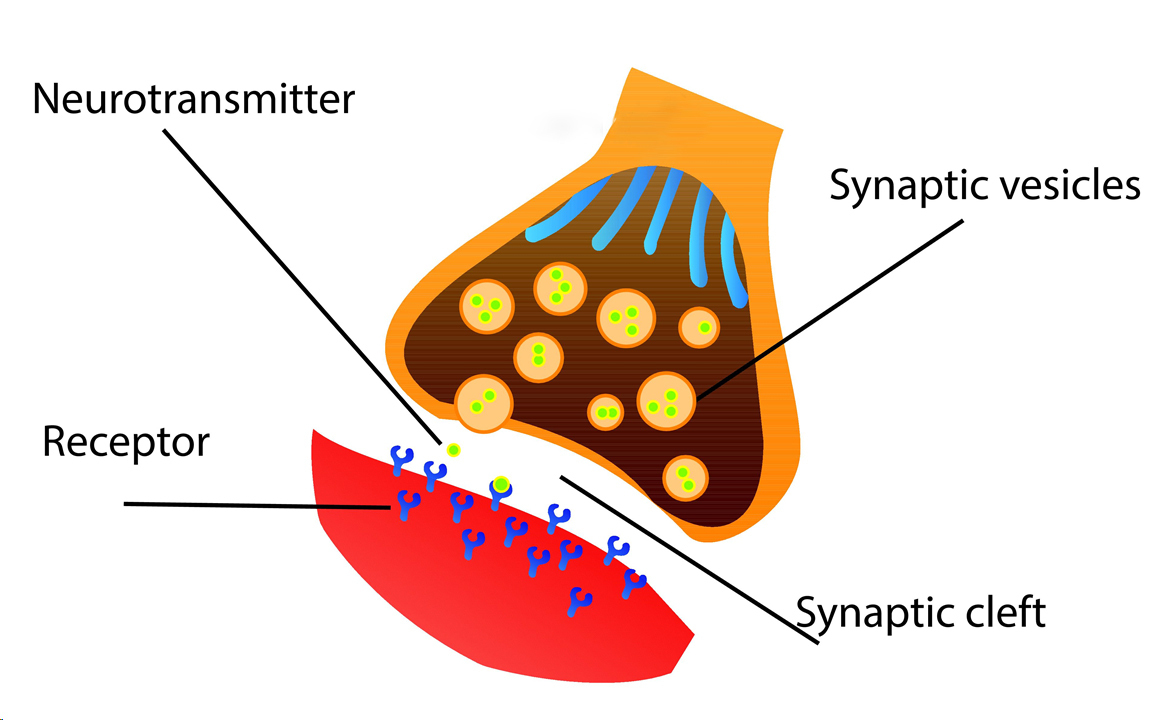
What is the neurotransmitters?
are chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gap of between neurons
What is neutral firing?
the process by which a neuron generates a brief electrical impulse, called an action potential, that travels down its axon to transmit information to other neurons or cells
What are the steps of neutral firing?
Neurotransmitter—>Threshold Met—>Action Potential (“Firing”)—> Depolorization—>
Refractory Period—> Resting Potential (Repolorarized)
What is neural efficiency?
all or none
What are the parts of the Nervous System?
Central (CNS): Brain+Spinal Cord—> Peripheral (PNS)
What are the parts of peripheral (PNS)
Autonomic NS- sweating, breathing, digestion, pupil dilation, blinking, heartbeat (involuntary movement)
Somatic NS- voluntary movement sensory information
What are the parts of Autonomic NS?
Sympathetic NS (Fight or Flight) (UP)
Parasympathetic NS (Rest and Digest) (DOWN)
Neurotransmitters: What is serotonin?
mood states
too little serotonin=depression
Treament: SSRI’s: Selective Serotinin Reuptake Inhibtors—> Prevent Reuptake
Mnemonic for Serotonin
Sir (Serotonin) Sleeps (regulates Sleep) Eats (controls appetite), & Feels Fine (stabilizes mood and happiness)
Neurotransmitters: What is Dopamine?
pleasure
too much pleasure can lead to addiction
also relates to movement; if you have too little it can lead to Parkinson’s
also relates to attention; if you have too much it can lead to Schizophernia
Mnemonic for Dopamine
DOPAMINE: Drive, Openness, Pleasure, Attention, Motivation, Integration, Nurturing, Energy
Neurotransmitters: What are endorphins?
-painkillers in the body that makes you feel physically good
Mnemonic for Endorphins
Endorphins= End Pain (natural painkillers) + Feel Fine (reduce stress)
Neuraltransmitters: What is epinephrine/neuropinphrine?
-adrenaline
-it causes heart rate to go up, pupilsto dilate, breathing to increase, blood flow increases, and neural firing increases
Mnemonic for Epinephrine
Epinephrine= Emergency Energy!
Neuraltransmitters: What is acetylcholine? (ACh)
-movement
-also relates to memory; if it decreases it can cause alzheimer’s
Mnemonic for Acetylcholine (ACh)
ACh= Attention, Contraction, and Harmony
Neuraltransmitters: What is GABA?
an inhibitor (the ability to suppress or restrain thoughts, emotions, or behaviors)
Mnemonic for GABA
GABA= Gone And Be At-ease
Neuraltransmitters: What is Glutamate?
-an excitatory (increase the likelihood that a neuron will "fire" or generate an action potential, leading to increased activity in the brain)
Mnemonic for Glutamate
Glutamate= Go!, like glucose gives u energy
What are afferent/sensory neurons?
neurons that carry incoming information from the body’s tissue and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
What are efferent/motor neurons?
neurons that carry out going information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
What are inter neurons?
neurons within the brain and spinal cord; they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
What is action potential?
a neural impulses; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
What is the resting potential?
the stable electrical charge across a neuron’s membrane when its not sending signals
What is Reuptake?
a neurotransmitter’s re absorption by the sending neuron
What is the threshold?
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
What is the nervous system?
the body’s speedy,electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerves cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
What is the central nervous system?
the brain and the spinal cord
What is the peripheral nervous system?
the sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS)t the rest of the body
What is the somatic nervous system?
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles
What is the autonomic nervous system?
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs
What is the sympathetic nervous system?
the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy
What is the parasymphatic nervous system?
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
What are spinal reflexes?
composed of a single sensory neuron and single motor neuron; a simple autonomic response to a sensory stimulus
What are neurotransmitters? (more specific)
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons; they travel across the synapse and bind to a receptor sites on the receiving neuron
What is the endocrine system?
the body’s “slow” chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream
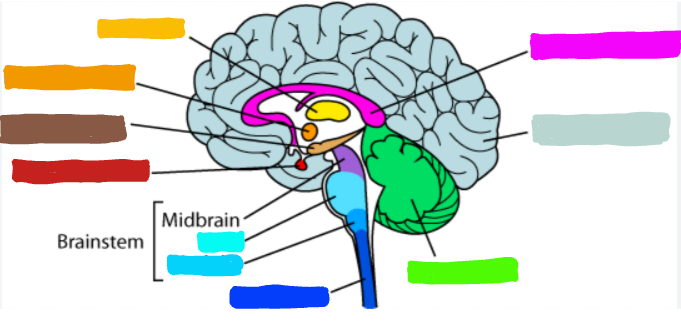
What is the part of the brain in yellow?
Thalamus
What is the thalamus?
a part of the brain that relays messages between lower brain centers and cerebral cortex
What is an example of what the thalamus does?
it acts as an relay station for vision
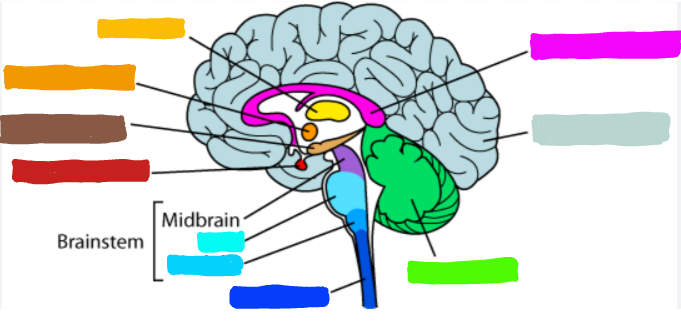
What is the part of the brain in orange?
Hypothalamus
What is the hypothalmus?
a part of the brain that directs several maintenance activities; it helps government the endocrine system, via the pituitary gland and is linked to emotion and reward
What is an example of the hypothalamus?
acts as the body’s thermostate when you get too cold and your muscles begin to shiver to create warmth
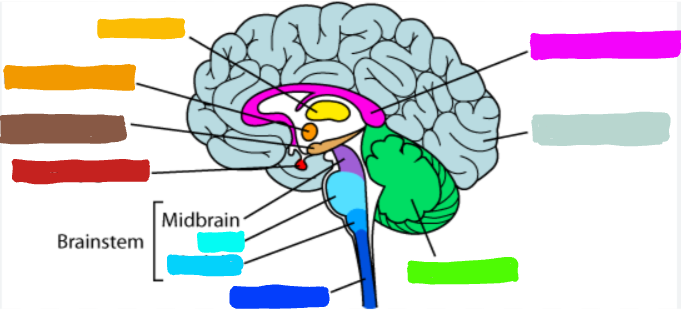
What is the part of the brain in brown?
Hippocampus
What is the hippocampus?
linked to conscious memory
What are examples of the hippocampus?
If affected can result in amnesia
Retrograde Amnesia- can make new memories but can’t remember past ones
Anterograde Amnesia-cannot make new memories bu can remember past ones
Example: meeting a new person at a party
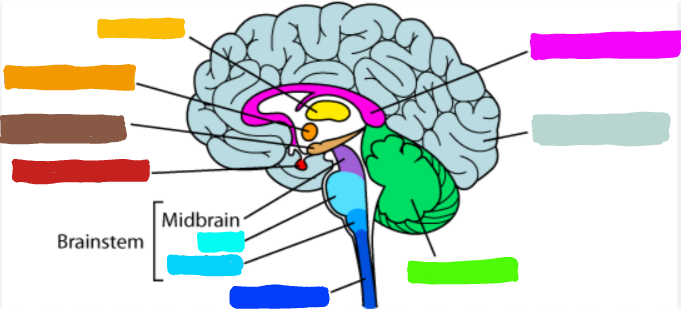
What is the part of the brain in red?
Pituitary Gland
What is the pituitary gland?
the endrocrine’s system most influential gland; regulates the grown and controls other endocrine gland
What is an example of the Pituitary Gland?
it secretes many different hormones. and is influenced under the Hippocampus
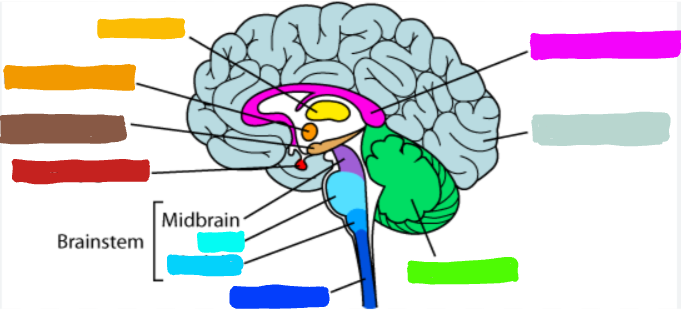
What is the part of the brain in teal?
Pons
What do the Pons do?
helps coordinate movement and control; also essential for vital functions
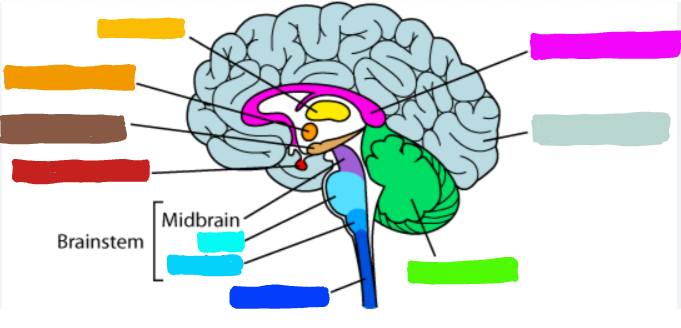
What is the part of the brain in light blue?
Medulla
What is the medulla oblongata?
the part of the brain at the base of the brainstem; controls several essentially bodily functions, like breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, swallowing, etc.
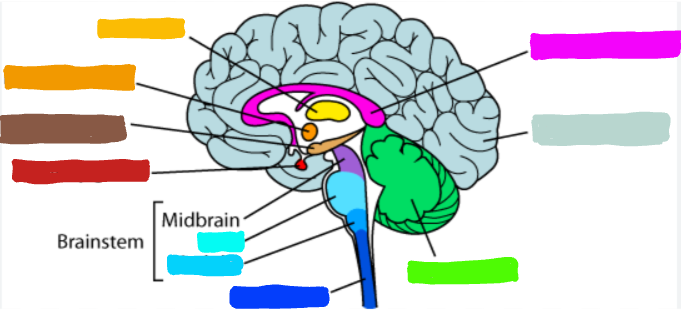
What is the part of the brain in dark blue?
spinal cord
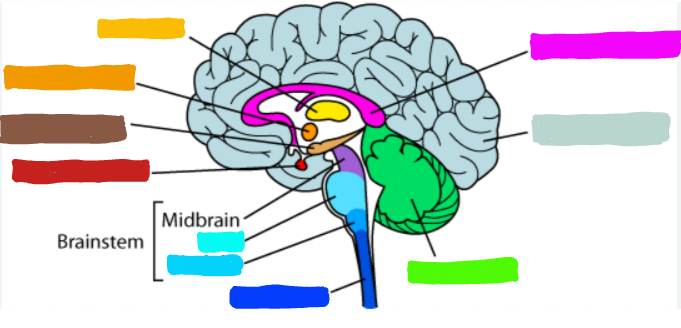
What is the part of the brain in green?
Cerebellum
What is the cerebellum?
the part of the brain that process sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, enables nonoverbal learning and memory
What is the example of what the cerebellum does?
the part of the brain that allows us to learn how to ride a bike
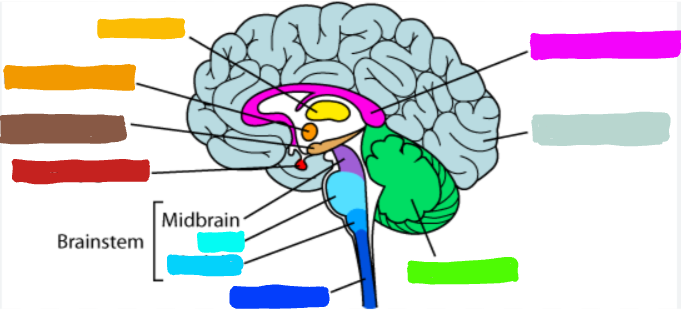
What is the part of the brain in pink?
Corpus Callosum
What is corpus callosum?
the large band of neural fibers connecting two brain hemispheres and carry messages between them
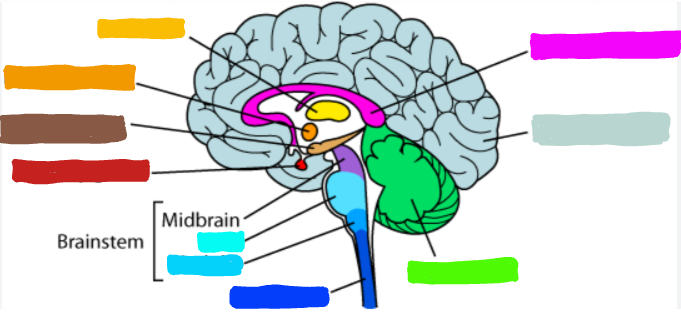
What is the part of the brain in light teal?
Cerebral Cortex
What was the cerebral cortex?
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells converting the cerebral hemispheres, and the body’s ultimate control and information processesing center
What is the cerebrum?
largest part of the brain and is responsible for higher order cognitive function, like thought, reasoning, emotion, etc
What is the example of the cerebrum ?
allows you to form the idea of what you need from a grocery store and to plan accordingly
What is the amygdala?
two Lima bean sized neural clusters in the limbic system that are linked to emotion
What is the example of the amygdala?
when walking down the street and you hear a loud bang, your amygdala gets alerted
What is the Reticular Formation/Activating System ?
a nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus and plays an important role incontrolling arousal
What is an example of the Reticular Activating system?
sleepy-wake cycle: when internal signals activate the RAS to sends signals to the brain cortex to wake up
What is testosterone?
the most important male sex hormone; stimulates the growth of the male sex organs and the development of male characteristics
What are extra details on testosterone?
both men and women have it
however for men it influences their fetal period and puberty
What is estrogen?
sex hormone; contributed to female characteristics
What are extra details on estrogen?
Example: Estradiol
levels peak during ovulation
given off in greater amounts in females than men
What is oxytocin?
is a hormone and neuropeptide that plays a crucial role in various psychological and behavioral proceses
What are extra details on oxytocin?
has a role in promoting prosocial behavior
example: increasing generosity in a study where people are given oxytocin nasal spray gave more money to strangers than placebo group
What are stress hormones?
a hormone that is released in response to stressful situations
What are extra details on stress hormones?
example: cortisol, epinephrine (adrenaline) and nor-epinephrine ( non adrenaline)
What is the Pineal Gland?
a pea size conical mass of tissue behind the third ventricle of the brain secreting a hormone like substance
What are extra details on the Pineal Gland?
plays a crucial role in regulating sleep-wake cycles and producing melatonin
What is the Pancreas?
regulates the level of sugar in the blood
What are extra details on the Pancreas?
plays a crucial role in both digestion and hormone production
What is the Occipital Lobe?
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head
includes areas that receive information from the visual fields
What is the temporal lobe?
The portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears
each receiving information primarily from the opposite ear
What is the parietal lobe?
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear
receives sensory input from touch and body position
somasensory cortex
What is the Frontal Lobe?
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead
involved in speaking, muscle movements, making plans, and judgement
motor and prefrontal cortex
What are association areas?
are areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved primary motor or sensory functions
involved in higher mental functions such as learning,remembering, thinking, and speaking
What is the Broca’s Area?
helps control language expression-an area in the Frontal Lobe, in the left hemisphere that directs the muscle movements
What are extra details on the Broca’s Area?
Broca’s Aphasia: hard time thinking of words and pronouncing; broken speech
What is wernicke’s area?
a brain area involved in language comprehension and exexpression usually in the left temporal lobe
What are extra details on Wernicke’s Area?
Wernicke’s Aphasia: hard time understanding what you say or others say; word salad