AP Psychology Unit 2: cognition
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Perception
the way sensory information is organized, interpreted and consciously experienced
Bottom-Up
purely data-driven and requires no previous knowledge or learning
Top-Down
heavily influenced by our expectations and prior knowledge; your brain applies what it knows to fill in the blanks and anticipate what's next
Perceptual Set
often tend to notice only certain aspects of an object or situation while ignoring other details. This can lead to Perceptual Bias
Schema
concept or mental representation that we use to organize our knowledge
Gestalt principles
the brain forms a perceptual whole that is more than the mere sum of its sensory parts
Closure
makes us see incomplete arrangements as wholes by supplying missing components.
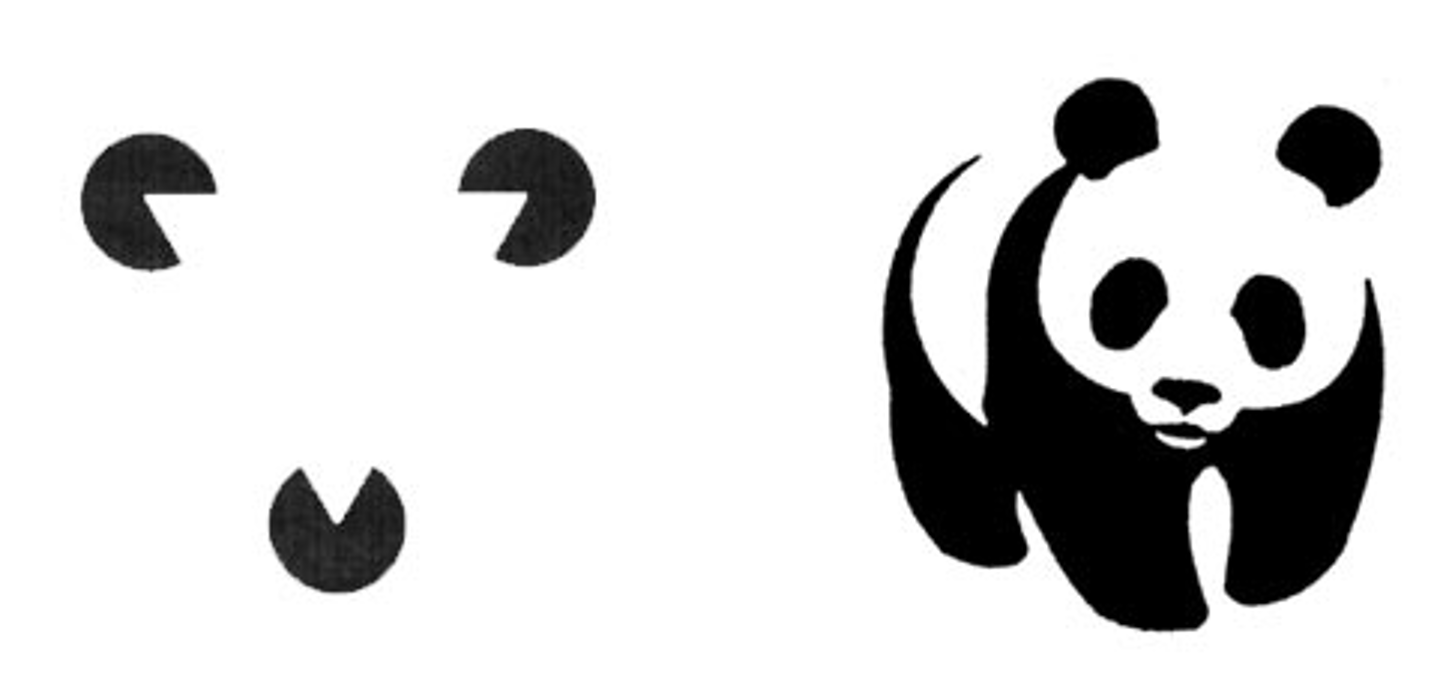
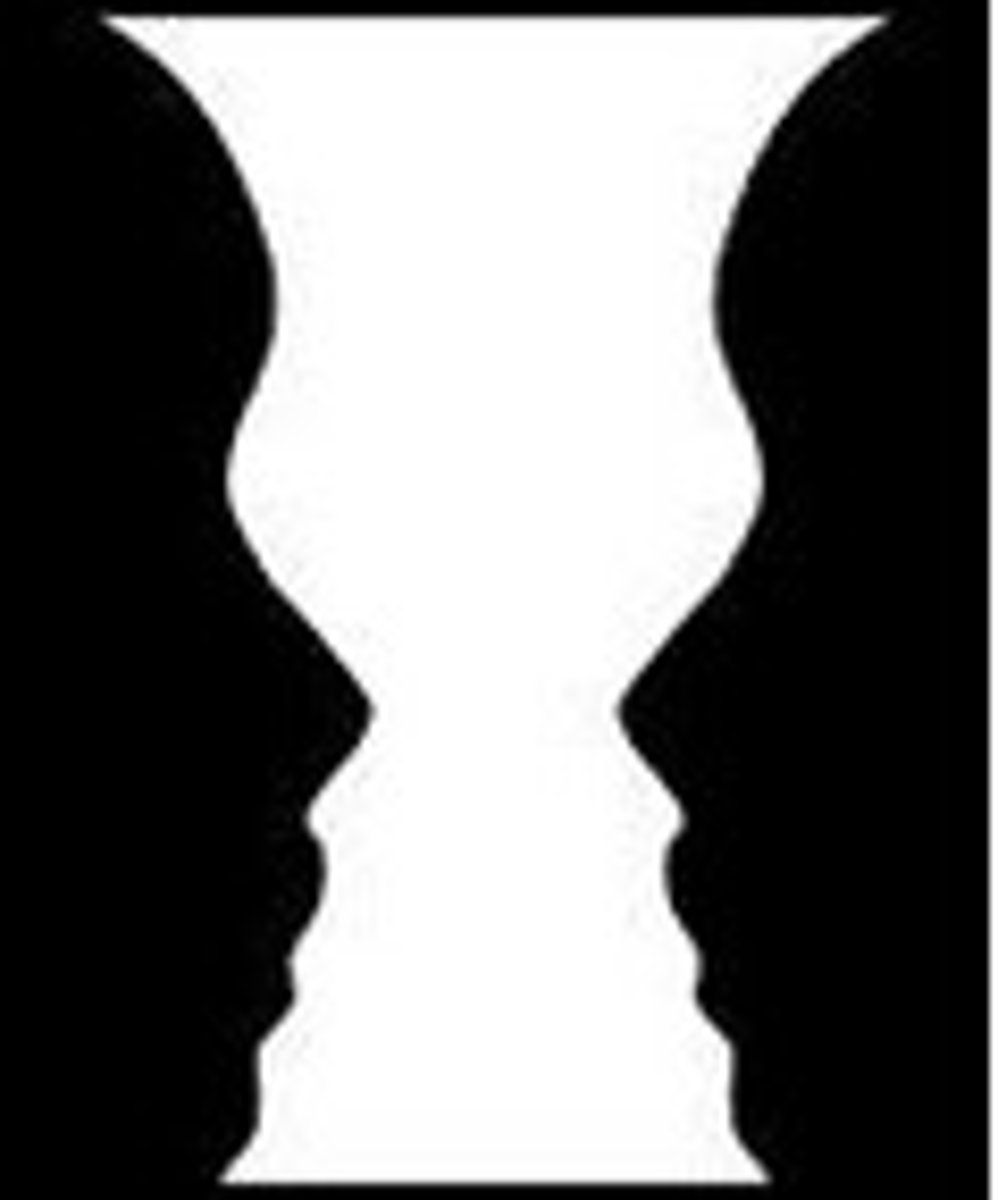
Figure-Ground
Figure: The part of a pattern that commands attention...stands out.
Ground: The part of the pattern that does not command attention...background.

Proximity
We tend to group objects together when they are near each other
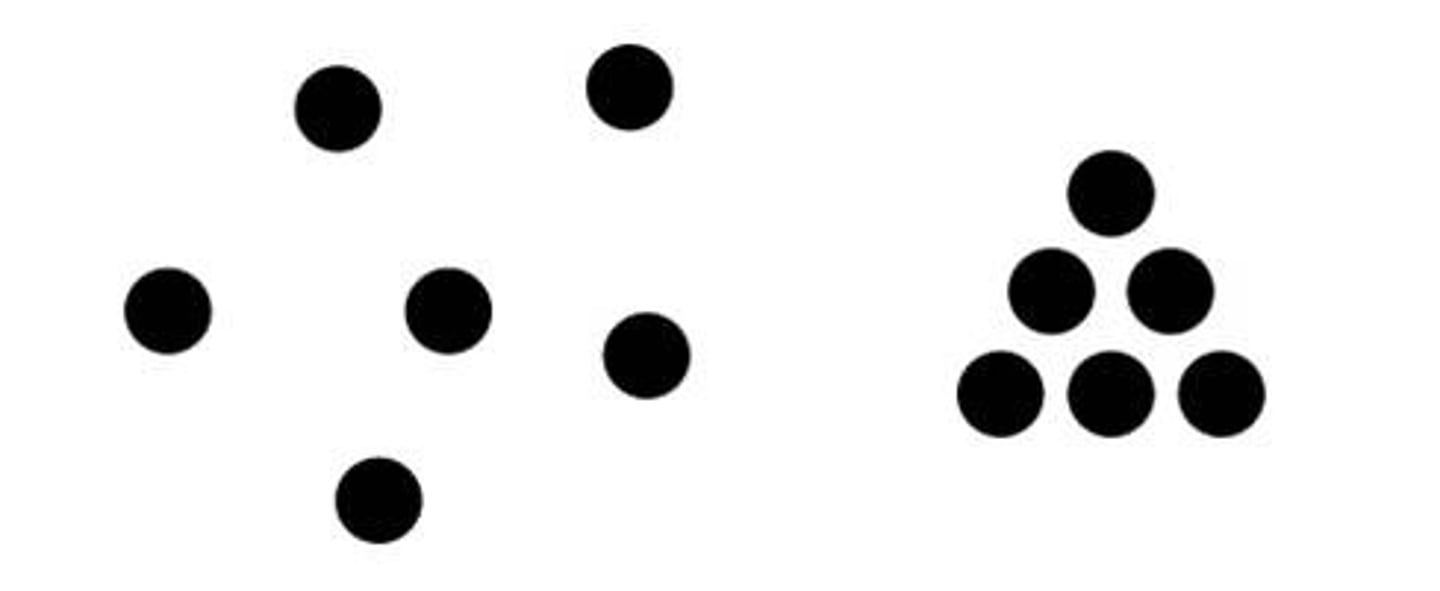
Similarity
We tend to group similar objects together in our perceptions
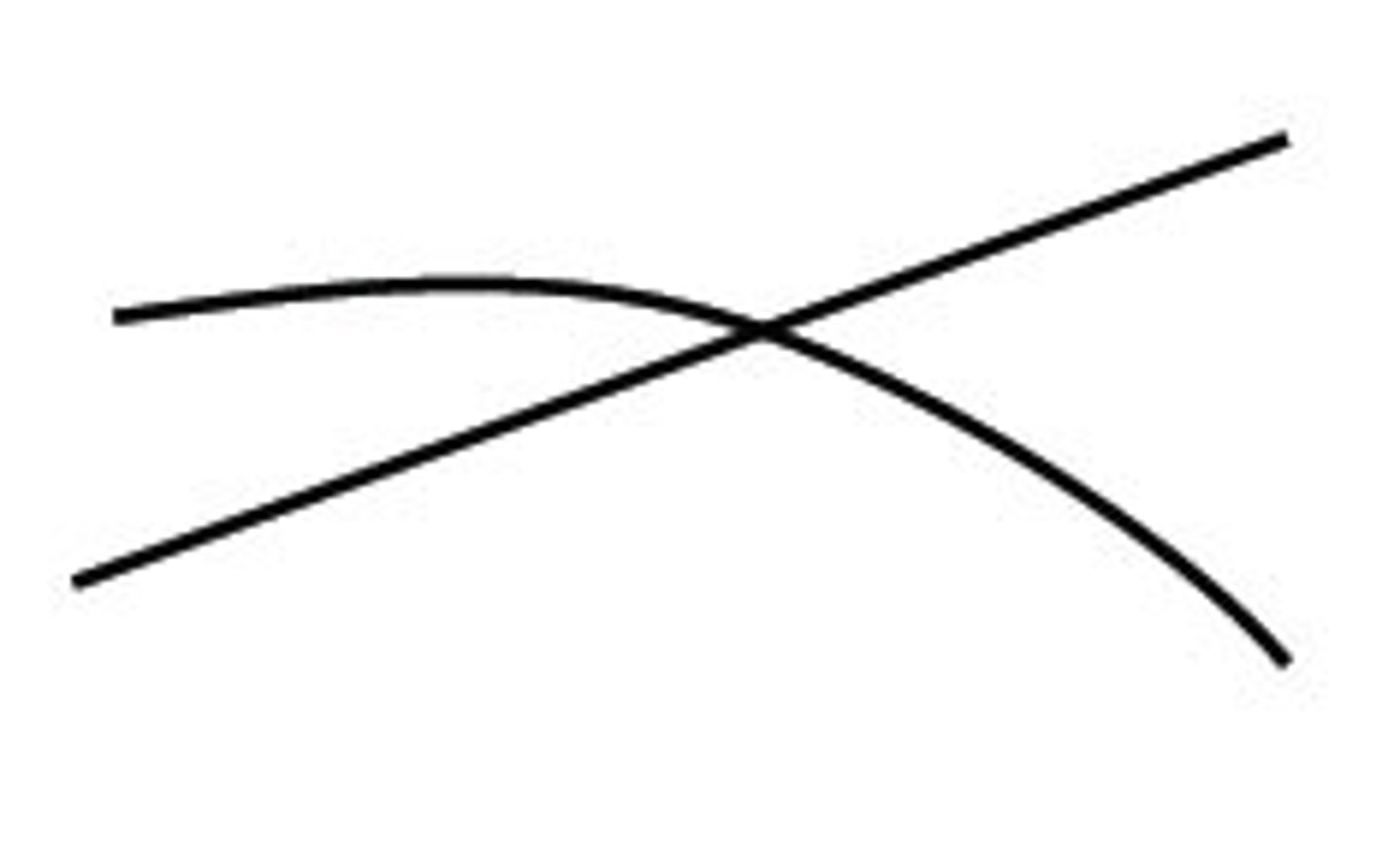
Continuity
Suggests that we are more likely to perceive continuous, smooth flowing lines rather than jagged, broken lines
Attention
the ability to actively process specific information in the environment while tuning out other details
Selective Attention
the ability to focus our attention on some stimuli while ignoring others
Cocktail Party Effect
The ability to tune into one voice from many conversations going on in a noisy environment
Inattentional Blindness
The failure to notice something because your attention is focused on something else. (you get in an accident because you were focused on your phone)
Change Blindness
failure to notice a visible change in the environment
Ebbinghaus Illusion
the tendency of our perceptual systems to adjust our experience of the world to the surrounding context
Ponzo Illusion
if two lines are the same length on my retina, but different distances from me, the more distance line must be longer
depth perception
ability to perceive objects in 3 dimensions and to judge distance (use monocular cues and Binocular cues)
monocular cues
Relative height Relative size
Interposition
Linear Perspective
Texture Gradient
Relative height
objects that are higher to be further away
relative size
if two objects are the same size but are different distances, the one closer will appear larger
Interposition
one object covers another, we perceive is as closer
Linear Perspective
Parallel lines appear to converge in the distance
Texture Gradient
closer objects have a more detailed texture, the texture of objects further away are less distinct
relative clarity
objects near you will appear sharp and in focus, objects further away will appear less detailed and fuzzy
Binocular Cues
Retinal Disparity
Convergence
Retinal Disparity
each eye sees a slightly different image because your eyes are about 6cm apart. You brain combines the 2 images to form our perception
Convergence
when you look at an object that is close to your face your eyes angle inward. The extra effort by your eye muscles is utilized by your brain to help judge distance
Perceptual constancies
our tendency to perceive objects as having standard shapes, sizes, and colors even when the angle we see them at, the distance, or the lighting changes
shape constancy
the tendency to interpret the shape of an object as being constant, even when its shape changes on the retina
Phi Phenomenon
illusion of movement that arises when stationary objects are placed side by side and illuminated rapidly, one after another
concept
mental grouping of similar things, events, and people that is used to remember and understand what things are, what they mean, and what categories or groups they belong to
prototype
a mental image or best example of a category (ideal example)
Accommodation
create new schemas
Assimilation
modify old schemas (aSSimilation - SS = same schema)
diseuquilibrium
unpleasant and therefore serves as motivation to either assimilate or accommodate the new information to make sense of it.
when is equilibrium reached
child has adequately altered their schemas to include the new information
Problem Solving Examples
Trail and error
algorithms
heuristic
insight
algorithm
step-by-step procedure that leads to the correct answer to a problem. By following the instructions correctly, you are guaranteed to arrive at the right solution.
downside of algorithm
time-consuming and may be impractical if action needs to be taken very quickly
heuristic
mental shortcut that allows someone to quickly make judgements and solve problems.
downside of heuristic
really of a rule-of-thumb and don't always guarantee a correct solution
Representativeness Heuristic
decisions are made according to prior expectations or stereotypes
Availability Heuristic
recalling the first or most vivid example that comes to mind
mental set
tendency to only see solutions that have worked in the past (thinking inside the box)
functional fixedness (example of a mental set)
when people are only able to see solutions that involve using objects in their normal or expected manner.
gambler's fallacy
type of bias where we let past event wrongly influence our decisions and predictions about future events.
sunk cost fallacy
type of bias that makes you feel you should continue pouring money, time, or effort into a situation since you've already "sunk" so much into it already
Divergent thinking
ability to generate multiple ideas, possibilities, or solutions to a given problem (thinking outside the box)
Memory
ability to retain knowledge (Encodes -> Stores -> Retrieves)
Multi-Store Model of Memory
The memory model that visualises memory as a system consisting of multiple memory stores through which a stream of data flows for processing.
Sensory Memory
use our sense to take in information from the environment
Working Memory Parts
Visual: iconic memory
Auditory: echoic memory
Tactile
Olfactory
Gustatory
Capacity of sensory memory
Capacity: very large
Duration: very short ( 0.25 sec for iconic memory, longer for echoic)
Short term memory
-very brief
If you do not actively process the information, it will be forgotten in seconds
- limited capacity
Working Memory
the processes we use to make sense of, modify, interpret and store information in short term memory
Phonological Loop
voice inside your head
Visual-Spatial Sketchpad
Mental pictures inside your head (how many windows are there in the front of your house?)
Central Executive
Manages the work of the other components by directing attention to particular tasks
long-term memory
Considered a permanent and limitless memory system
2 main parts of long term memory
Explicit and Implicit
Implicit Memory
Memories for procedures and processes - memories of things you just know how to do; hard to explain to another person
types of implicit memory
procedural, classical conditioning, and priming
Procedural Memory
knowledge of how to perform different actions and skills (doing it without thinking about it; riding a bike)
Priming
Exposure to one stimulus influences the response to another stimulus (after seeing the color yellow, you're asked to name a fruit and you say 'banana')
Explicit Memory
knowledge or experiences that can be consciously remembered. More easily describable to others.
types of explicit memory
Episodic and semantic
Episodic memory
firsthand, autobiographical experiences we have (first kiss; the rainstorm on your 10th birthday party)
semantic memory
knowledge of facts and concepts (knowing the capital of Finland; knowing the boiling point of water)
Prospective memory
involves intention. It is your intention to remember something in the future
Automatic Processing
unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time, and frequency, and of well-learned information, such as word meanings
Effortful Processing
active, conscious encoding and retrieval of information which requires focused attention.
Hippocampus
Involved in moving material into long-term memory in a process called memory consolidation
Consolidation
the act or process of turning short-term memories into more permanent, long-term memories
amygdala
regulating emotions and is best known for its role in the fear response
Cerebellum
role in balance and coordination, the cerebellum is involved in forming implicit memories (procedural memory, motor learning, classical conditioning)
flashbulb memory
seemingly exceptionally clear recollection of an important event
long-term potentiation
activity in the nerve circuits cause changes (increased production of neurotransmitter, increasing the number of receptors) that make those circuits more likely to respond again in the future
Long-term potentiation
if you use it, it will become stronger
Maintenance Rehearsal
process of repeating information mentally (or out loud) for the purpose of keeping it in short-term memory
Chunking
organizing information into groupings (chunks), thereby increasing the number of items that can be held in short-term memory
Elaborative Rehearsal
processing new information in ways that make it more relevant or meaningful
(ex:Making personal connections)
levels of processing
information that is thought of more deeply becomes more meaningful and thus better committed to memory
Shallow Processing
Structural - color, size, shape, or form
Phonemic- sound
Deep Processing
Semantic - processing using meaning
Autobiographical Memory self-reference effect
the memory for events and facts related to one's personal life story
Primacy Effect
better memory for items early in a list
Recency Effect
better memory for items near the end of a list
Context-dependent memory
increase in recall when the environment in which information is learned matches the environment in which it is recalled
State-dependent memory
increase in recall when the individual is in the same physiological or psychological state as during encoding
mood-congruent memory
a person is in a bad mood while learning, they will tend to have better recall if they are in a bad mood when tested than if they are in a good mood when tested
Recognition
involves identifying something as familiar when encountered again
Recall
process of retrieving information from memory without the presence of the original stimuli
Spacing Effect
learning is better when study time is spread out than when it occurs close together
Massed Practice
study all at once (cramming)
Distributed Practice
study is spread out over time
Testing Effect
learning and memory is best accomplished when the information is repeatedly tested during learning (as opposed to merely restudying the material)
Metacognition
the practice of being aware of one's own thinking. Sometimes referred to as 'thinking about thinking"
Mnemonic devices
memory tricks or tools that can help you learn and remember (encode and retrieve) information